Production of Exopolysaccharides Through Fermentation of Secondary Whey with Kefir Grains †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Kefir Grains and Maintenance
2.2. Secondary Whey Production
2.3. Fermentation
2.4. Extraction of EPS
2.5. Secondary Whey and Freeze-Dried Solid Characterization
2.6. Statical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
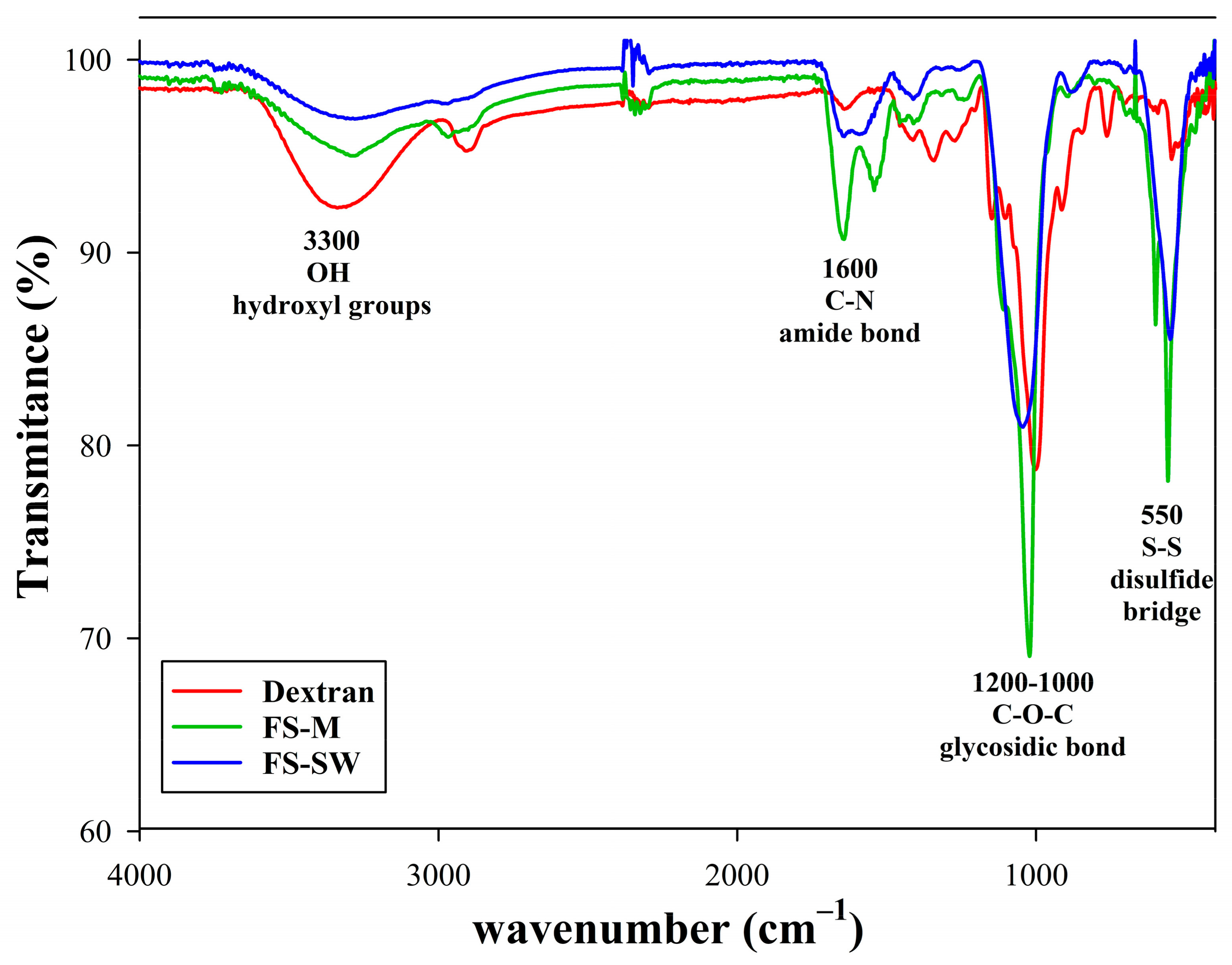
Freeze-Dried Solid Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cirrincione, S.; Breuer, Y.; Mangiapane, E.; Mazzoli, R.; Pessione, E. ’Ropy’ phenotype, exopolysaccharides and metabolism: Study on food isolated potential probiotics LAB. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 214, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, T.T.; Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances of bacteria and their potential environmental applications. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Feng, W.; Li, C.; Song, S. Physicochemical Properties of Exopolysaccharide Produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens ZW3 Isolated from Tibet Kefir. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimada, P.; Abraham, A. Kefiran improves rheological properties of glucono-lactone induced skim milk gels. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Nan, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Chemical and physical characteristics and antioxidant activities of the exopolysaccharide produced by Tibetan kefir grains during milk fermentation. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 43, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.; Gaudino Caputo, L.; Tavares Carvalho, J.; Evangelista, J.; Schneedorf, J. Antimicrobial and healing activity of kefir and kefiran extract. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Zhu, X.; Omura, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kitamura, S. Effects of an exopolysaccharide (kefiran) on lipids, blood pressure, blood glucose, and constipation. BioFactors 2004, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskard, C.A.; El-Nezami, H.S.; Kankaanpää, P.E.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J.T. Surface binding of aflatoxin B1 by lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Bui, D.C.; Hong, P.T.; Hoang, Q.K.; Nguyen, H.T. Exopolysaccharide production by lactic acid bacteria: The manipulation of environmental stresses for industrial applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Pérez, C.; Roldán-Hernández, L.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.; Trant, J.F.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S. Insights on the interaction between kefiran and whey proteins using computational analyses. Chem. Proc. 2023, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, D.; Martindale, W.; Romeih, E.; Hebishy, E. Recent advances in whey processing and valorisation: Technological and environmental perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, N.; Rao, P.S.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, M. Waste to nutrition: The evolution of whey, a byproduct to galactooligosaccharides production. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. Bacterial exopolysaccharides. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1972, 8, 143–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’hir, S.; Rtibi, K.; Mejri, A.; Ziadi, M.; Aloui, H.; Hamdi, M.; Ayed, L. Development of a novel whey date beverage fermented with kefir grains using response surface methodology. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1218058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londero, A.; Hamet, M.F.; De Antoni, G.L.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir grains as a starter for whey fermentation at different temperatures: Chemical and microbiological characterization. J. Dairy Res. 2012, 79, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Polysaccharide production by kefir grains during whey fermentation. J. Dairy Res. 2001, 68, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlan-Velázquez, L.F.; González-Olivares, L.G.; García-Garibay, M.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S.; Gómez-Ruiz, L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Cruz-Guerrero, A. Effect of biogenic exopolysaccharides in characteristics and stability of a novel Requeson-type cheese. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F.G. A Colorimetric method for the determintion of sugars. Nature 1951, 4265, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitating microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimada, P.S.; Abraham, A.G. Comparative study of different methodologies to determine the exopolysaccharide produced by kefir grains in milk and whey. Le Lait 2003, 83, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FS-SW | FS-M | |
|---|---|---|
| Freeze-dried solid yield (mg) | 632.6 ± 30.8 | 6138.1 ± 493.2 |
| Total sugars (mgeq glucose/L) | 75.33 ± 0.38 | 73.66 ± 1.68 |
| Total soluble proteins (mgeq BSA/L) | 26.04 ± 2.63 | 86.18 ± 3.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Martínez, A.; Jiménez-Pérez, C.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.; Trant, J.F.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S. Production of Exopolysaccharides Through Fermentation of Secondary Whey with Kefir Grains. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2024, 40, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2024040044
Hernández-Martínez A, Jiménez-Pérez C, Cruz-Guerrero A, Trant JF, Alatorre-Santamaría S. Production of Exopolysaccharides Through Fermentation of Secondary Whey with Kefir Grains. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2024; 40(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2024040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Martínez, Aidalú, Carlos Jiménez-Pérez, Alma Cruz-Guerrero, John F. Trant, and Sergio Alatorre-Santamaría. 2024. "Production of Exopolysaccharides Through Fermentation of Secondary Whey with Kefir Grains" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 40, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2024040044
APA StyleHernández-Martínez, A., Jiménez-Pérez, C., Cruz-Guerrero, A., Trant, J. F., & Alatorre-Santamaría, S. (2024). Production of Exopolysaccharides Through Fermentation of Secondary Whey with Kefir Grains. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 40(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/blsf2024040044







