Abstract
This study evaluated the probiotic and safety potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from undisturbed soil in Mount Karadzica, North Macedonia. Seven isolates demonstrated strong antimicrobial activity against Salmonella enterica ATCC 10708, tolerance to 0.3–2% bile salts, and survival at pH 3.0, indicating resilience under gastrointestinal conditions. They grew across 25–44 °C, tolerated 6.5% NaCl, and exhibited no β-hemolytic activity. Six isolates were susceptible to all antibiotics tested, except one resistant to ampicillin. The findings highlight the novelty of isolating Bacillus spp. from soil as potential probiotics, offering promising applications in improving dietary nutrition and functional food safety.
1. Introduction
Bacillus species are widely distributed, rod-shaped bacteria that are Gram-positive and produce catalase. They are commonly present in soil, plant materials, and fermented foods, as well as in the gastrointestinal tracts of both humans and animals [1]. Bacillus subtillis, among the most extensively researched Gram-positive bacteria, is an aerobic or facultatively anaerobic organism that serves as a paradigm for understanding cellular differentiation and exploring industrial applications [2]. This microorganism synthesizes multiple small antimicrobial peptides and bacteriocins such as surfactin, bacilysin, and subtilin, which hold significant value in biomedical engineering, food production, and agriculture. These peptides exhibit wide-ranging antimicrobial effects and rapid pathogen eradication, positioning them as promising therapeutic options in light of increasing concerns regarding microbial resistance to traditional antibiotics. Moreover, they offer advantages in terms of safety and environmental compatibility [3]. Spore-forming bacteria like Bacillus spp. are utilized as probiotic supplements for humans and animals, offering transient presence in the digestive tract without causing harm, and they are characterized by the formation of heat- and cold-resistant spores that maintain stability in dietary conditions [4].
The probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. lies in their ability to withstand harsh gastrointestinal conditions, including low pH and high bile concentrations, and their capability to produce bioactive compounds such as antimicrobial peptides. These attributes enable Bacillus strains to suppress pathogens, enhance gut microbiota balance, and improve host health. Recent studies have explored their applications in promoting growth in livestock, improving immune responses, and developing functional foods and dietary supplements. For instance, Bacillus strains are known to enhance nutrient absorption and produce enzymes that aid in digestion [5]. Furthermore, their spore-forming ability ensures prolonged shelf life and stability, making them ideal for incorporation into commercial probiotic formulations. The safety of Bacillus spp. as probiotics is another critical consideration. While many strains exhibit beneficial properties, it is essential to evaluate their antibiotic resistance profiles, hemolytic activity, and ability to avoid transferring resistance genes. Recent publications have focused on addressing these safety concerns, highlighting strains with minimal risks and significant benefits [6]. This study aims to build upon these findings by isolating Bacillus strains from undisturbed soil and assessing their probiotic potential and safety attributes.
Increasing consumer demand for premium, chemical-free, and antibiotic-free food products has stimulated research into natural alternatives, specifically involving beneficial microorganisms or their derivatives. Recent studies have concentrated on antimicrobial peptides or proteins synthesized by food-grade bacteria, which effectively suppress the growth of pathogens individually or in combinations, are susceptible to enzymatic degradation, and do not present pathogenic risks to humans. Despite the wide variety of bacterial species capable of producing antimicrobials, only a limited number are employed as natural preservatives in food contexts [2,7,8]. It is crucial to evaluate the safety of each strain thoroughly before proceeding with clinical trials and ensuring its safe incorporation into dietary supplements, food, and beverages. Prior research has demonstrated the efficacy of incorporating Bacillus-based probiotics in poultry diets to promote growth, with corresponding products also accessible for human consumption [9]. Due to the promising characteristics of Bacillus species as potential probiotic candidates and the limited availability of Bacillus probiotics in commercial markets, this study aimed to isolate preferred Bacillus strains from undisturbed soil from Mount Karadzica in North Macedonia. Following isolation, these strains were characterized morphologically and physiologically, and their probiotic properties were examined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Bacterial Isolation, and Identification
Soil samples were collected aseptically from Mount Karadzica in North Macedonia, 34 km from Skopje, the capital city. The samples were placed in sterile bags and stored at 4 °C for subsequent analysis. Isolation involved diluting the soil sample in a 0.9% saline solution and heating it to 70 °C for 30 min to enhance the growth of spore-forming bacteria. Serial dilutions of the sample were subsequently plated on nutrient agar (NA) plates and incubated at 37 °C overnight [8]. Qualitative analyses were conducted based on the morphological characteristics of Bacillus spp. [10,11].
2.2. In Vitro Assessment of Probiotic Properties
2.2.1. Survival Under Gastric Juice Conditions and Bile Salts
The method described by Nguyen et al. [11] was utilized to assess the resistance of the tested isolates to acidic pH levels. To assess bile salt tolerance, modifications were made to the method originally described by Gilliland et al [12]. Nutrient broth (NB) supplemented with varying concentrations of bile salts (0%, 0.3%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, and 2%) was inoculated with each probiotic strain and incubated at 37 °C for 24 and 48 h. Growth in both control (no bile salts) and test cultures was measured at 24 and 48 h by assessing turbidity (FAU).
2.2.2. Optimum Temperature and Growth Tolerance in Presence of Sodium Chloride
The temperature tolerance test involved inoculating isolate cultures into broth-filled tubes and then incubating them at temperatures of 25 °C, 30 °C, 37 °C, and 44 °C for durations of 24 and 48 h. Bacterial growth was monitored to assess temperature tolerance. Testing was conducted on the isolates to see how sensitive they were to a nutrient broth containing 6.5% NaCl. The tubes were incubated at 37 °C and the turbidity of the tubes was assessed [13].
2.2.3. Arginine Hydrolysis and Catalase Tests
For the arginine hydrolysis test, a basal MRS broth medium supplemented with 0.2% ammonium citrate, with and without 0.3% arginine, was prepared. Colonies that had grown in the basal medium were then inoculated into the prepared media and incubated at the optimal temperature for 24 h. On the 2nd and 7th day of incubation, a drop of the cultures was transferred to a glass slide, followed by the addition of three drops of Nessler’s reagent (K2HgI4), and the observation of a color change from yellow to brown. The catalase activity was determined by adding 3% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to the cultivated colonies on a glass slide.
2.3. Safety Assessment
2.3.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility
The isolates were inoculated on nutrient agar, and antibiotic discs were applied using sterile tweezers to assess their antibiotic sensitivity via the Kirby–Bauer method. After incubation, the presence of a zone of inhibition was observed [13].
2.3.2. Hemolysis Test
For the hemolysis test, the isolates were cultured in broth at their optimal temperature for 15 h and subsequently streaked onto blood agar supplemented with 5% sheep blood. The plates were then incubated at the optimal temperature for 24 h. Hemolytic activity was evaluated by observing partial hydrolysis resulting in a green zone (α-hemolysis), complete hydrolysis resulting in a clear zone around the colony (β-hemolysis), or no reaction (γ-hemolysis) against red blood cells.
3. Results
3.1. Sampling, Bacterial Isolation, and Identification
The bacteria isolates from the soil sample from Mount Karadzica were isolated and sampled on nutrient agar plates. A total of 46 isolates exhibiting diverse morphological characteristics were chosen and initially identified as Bacillus species through morphological analysis. Seven isolates were selected based on their capacity to inhibit Salmonella enterica ATCC 10708 [14]. The selected colonies appeared to be circular and white. Microscopic characterization proved that 100% of them were Gram-positive and rod-shaped or also known as Bacillus (Figure 1).
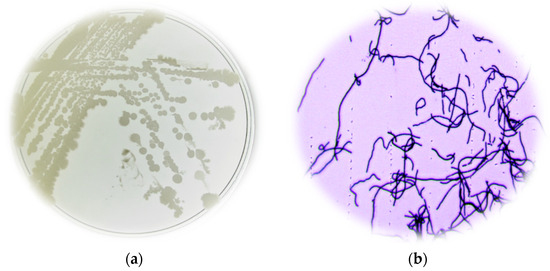
Figure 1.
(a) Macroscopic characteristics of Bacillus spp. (isolate B27) isolated from soil; (b) microscopic characteristics of Bacillus spp. (isolate B27) isolated from soil.
3.2. In Vitro Assessment of Probiotic Properties
3.2.1. Survival Under Gastric Juice Conditions and Bile Salts
Probiotics need to withstand the acidic conditions of the stomach and effectively colonize the gastrointestinal tract [14]. After exposure to acidic conditions (pH 3.0), growth was observed for all seven selected isolates, indicating that the isolates have the capacity to grow at pH 3, i.e., tolerance to low pH values after the incubation period of 24 and 48 h. In addition, all seven isolates exhibited significantly high survival rates in 0.3–2% bile salt solutions (Figure 2).
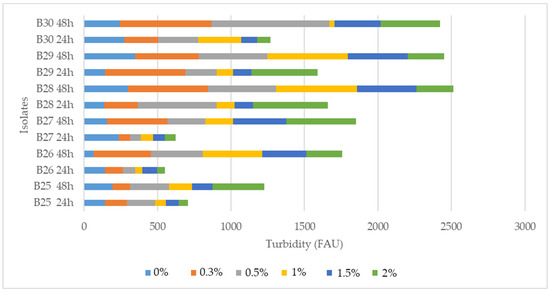
Figure 2.
The survival of selected probiotic Bacillus isolates in 0.3–2% bile salts solutions.
3.2.2. Optimum Temperature and Growth Tolerance in Presence of Sodium Chloride
In this study, the results indicated that the seven selected strains grow at 25 °C to 44 °C and tolerate 6.5% sodium chloride. The optimal temperature for four of the isolates was 30 °C, and 37 °C for one selected isolate, while the other two had optimal temperature growth at 44 °C (Table 1).

Table 1.
Temperature growth conditions and tolerance to sodium chloride of the isolates.
3.2.3. Arginine Hydrolysis and Catalase Tests
Five mL of MRS broth containing 0.3% arginine and 0.2% ammonium citrate was inoculated with active cultures at 37 °C for 24 h. After incubation, 100 µL of inoculated culture was transferred onto glass slides and an equal volume of Nessler’s reagent was pipetted on the cultures. All the isolates showed a bright orange color, which indicated positive reactions. Six out of seven isolates were catalase-positive; only isolate B27 was catalase-negative.
3.3. Safety Assessment
3.3.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility
The antibiotic susceptibility of the seven probiotic Bacillus strains was tested using two groups of antibiotics. The first was cell wall inhibitors including ampicillin and streptomycin. The protein synthesis inhibitors included were chloramphenicol and tetracycline. Antibiotics that could perform both mechanisms of action depending on the concentration and susceptibility of the bacteria like rifampicin were also included [15]. Six of the isolates were susceptible to all antibiotics with different mechanisms of action, while isolate B28 was observed to be resistant to ampicillin.
3.3.2. Hemolysis Test
To characterize any potential hemolytic activity, the strains were streaked onto sheep blood agar plates and incubated overnight. The agar displayed a greenish hue surrounding the streaks where the colonies grew, indicating that the strains exhibit α-hemolysis (Figure 3).
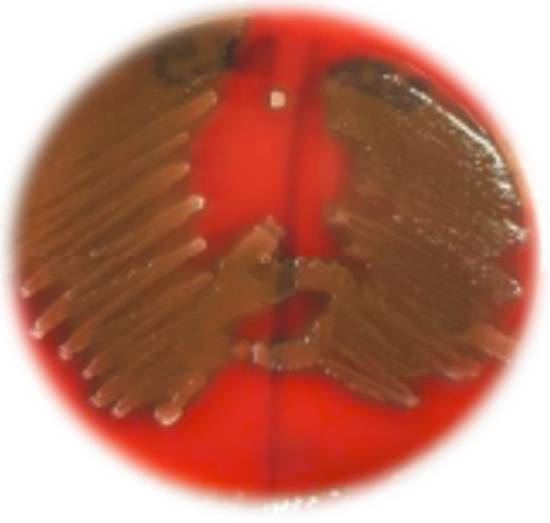

Figure 3.
Blood hemolysis assay of the isolates indicating α-hemolysis.
4. Discussion
The significance of a healthy commensal microbiota for mammalian hosts is evident, leading to the widespread use of probiotics for preventing and treating various health issues in both humans and animals. However, optimizing the survival of probiotic cells throughout their formulation and delivery poses a significant challenge. Probiotic bacteria must navigate a lengthy journey, from processing and shelf life to passage through the gastrointestinal tract, where they encounter extreme conditions [8]. Spore-forming bacteria, especially various strains of Bacillaceae, are becoming more prevalent in dietary supplements, food, and beverages. This is attributed to their ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain stability throughout manufacturing, storage, and transportation processes [10]. Based on the results obtained from this study, the seven selected isolates have high survival rates at pH 3.00. A similar study indicates the same rates for strains isolated from contaminated soil [13]. Certain studies have noted that certain Bacillus species exhibit varying degrees of tolerance or sensitivity to concentrations of bile salts [16]; however, the present results showed the capacity of these isolates to grow at 0.3–2% of bile salt solution. In another study, B. amyloliquefaciens LN demonstrated survival after being incubated for 3 h at pH 2.0 or 3.0 and in LB broth with 0.3% oxgall for 12 h. These findings suggest that B. amyloliquefaciens LN has the potential to withstand the acidic conditions of the stomach and may persist in the intestinal environment, where it could perform its probiotic functions effectively [17]. Temperature plays a crucial role in influencing the growth and survival of microorganisms, with variations observed across genera that align with the optimal temperature ranges found in their natural habitats [2]. The obtained results in this study show that the seven selected strains grow at 25 °C to 44 °C and tolerate 6.5% sodium chloride. Previous analysis for different Bacillus strains shows less tolerance at high temperatures and different concentrations of sodium chloride [18]. The seven selected isolates were streaked on sheep blood agar plates to evaluate their hemolytic potential, revealing incomplete hemolysis, a trait found in various Bacillus strains in commercial probiotics [19], posing a safety concern if these strains contact the bloodstream; however, oral probiotics rarely breach the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream, with few reported cases mainly in hospitalized patients [20]. Confirming the antibiotic susceptibility of bacterial strains intended for probiotic use is crucial for safety assurance, as their tolerance can aid in restoring gut microflora post-antibiotic treatment; however, the main concern with Bacillus spp. as probiotics lies in their potential to transfer antibiotic-resistant genes despite not being part of the commensal gut microbiota, although various strains of this genus are incorporated into food sources [2]. In this study, only strain B28 showed resistance to ampicillin. Building on the promising results of this study, future research will focus on further characterizing the Bacillus strains isolated from Mount Karadzica to better understand their genetic makeup and confirm their species identity through genomic sequencing. Additionally, in vivo studies will be conducted to evaluate their safety and efficacy as probiotics, including their potential to modulate the gut microbiota and support gastrointestinal health. We also aim to explore the broader applications of these strains in the food industry, particularly as natural preservatives, due to their antimicrobial properties. Furthermore, investigating the synergistic effects of these strains in combination with other probiotics could provide valuable insights into their potential as multi-strain formulations for enhanced therapeutic effects. Ultimately, these future studies will help to establish the strains’ practical applications and contribute to the development of safe, effective probiotic products.
5. Conclusions
The focus on biodiversity within soil ecosystems has markedly intensified over the past two decades. Numerous studies have been conducted to isolate probiotic bacteria from various sources. The results of the present research demonstrated that undisturbed soil from Mount Karadzica in North Macedonia can be considered a reservoir of bacteria with antimicrobial activities, with the potential for use as probiotic cultures. The selected isolates exhibited strong probiotic characteristics, including high survival rates in harsh gastrointestinal conditions, resistance to bile salts, and growth tolerance at varying temperatures. Their broad antimicrobial activity against Salmonella enterica ATCC 10708 and favorable safety profile, as shown by antibiotic susceptibility and non-hemolytic activity, further support their potential for use in functional foods. While the results are preliminary, they indicate that these strains could play a significant role in enhancing the nutritional quality of diets and contribute to the development of natural, safe probiotic supplements. Nevertheless, additional in vitro or in vivo experiments should be performed to ascertain whether they can be approved for application.
Author Contributions
S.K., D.K. and N.A.-P. contributed to the design and implementation of the research, to the analysis of the results, and to the writing of this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Macedonian Ecological Society, whose support is gratefully acknowledged. Their contribution made it possible to carry out the research and achieve the findings presented in this study.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Thi Lan Anh, H.; Thi Thanh Hue, L.; Hai Linh, B.N.; Tuan Dung, N.H.; Duong Minh, D.; Thi Le Quyen, T.; Trung, T.T. In vitro safety evaluation of Bacillus subtilis species complex isolated from Vietnam and their additional beneficial properties. Vietnam J. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenea, G.N.; Gonzalez, G.L.; Moreno, J.L. Probiotic Characteristics and Antimicrobial Potential of a Native Bacillus subtilis Strain Fa17.2 Rescued from Wild Bromelia sp. Flowers. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, H.; Zhang, D. Bacillus subtilis: A universal cell factory for industry, agriculture, biomaterials and medicine. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, V.L.; Lopes, N.M.; Zacaroni, O.F.; Silveira, V.A.; Pereira, R.A.N.; Freitas, J.A.; Almeida, R.; Salvati, G.G.S.; Pereira, M.N. Lactation performance and diet digestibility of dairy cows in response to the supplementation of Bacillus subtilis spores. Livest. Sci. 2017, 200, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golnari, M.; Bahrami, N.; Milanian, Z. Isolation and characterization of novel Bacillus strains with superior probiotic potential: Comparative analysis and safety evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciurescu, G.; Dumitru, M.; Gheorghe, A.; Untea, A.E.; Drăghici, R. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, bone mineralization, and bacterial population of broilers fed with different protein sources. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5960–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.M.; Yoon, S.-G.; Choi, T.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.J.; Koo, M. The Bactericidal Effect of a Combination of Food-Grade Compounds and their Application as Alternative Antibacterial Agents for Food Contact Surfaces. Foods 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimelman, H.; Shemesh, M. Probiotic Bifunctionality of Bacillus subtilis—Rescuing Lactic Acid Bacteria from Desiccation and Antagonizing Pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brutscher, L.M.; Borgmeier, C.; Garvey, S.M.; Spears, J.L. Preclinical Safety Assessment of Bacillus subtilis BS50 for Probiotic and Food Applications. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasova-Pancevska, N.; Kungulovski, D.; Petrova, E.U.; Radmanovik, N.; Boskovski, O.; Frcovski, E.; Premcevski, H.; Kostandinovska, S. The Influence of Different Climatic Types on the Number of Bacillus spp. Isolated from Soil in North Macedonia. J. Agric. Plant Sci. 2023, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum PH04, a Potential Probiotic Bacterium with Cholesterol-lowering Effects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliand, S.E.; Staley, T.E.; Bush, L.J. Importance of bile tolerance of Lactobacillus acidophilus used as a dietary adjunct. J. Dairy Sci. 1984, 67, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostandinovska, S.; Kungulovski, D.; Atanasova-Pancevska, N. Potential Probiotic Bacillus Strains Isolated from Contaminated Soil in North Macedonia: Salmonella Growth Inhibition. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2024, 31, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-K.; Han, K.J.; Son, S.-H.; Eom, S.J.; Lee, S.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Multifunctional Effect of Probiotic Lactococcus lactis KC24 Isolated from Kimchi. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkhairi Amin, F.A.; Sabri, S.; Ismail, M.; Chan, K.W.; Ismail, N.; Mohd Esa, N.; Mohd Lila, M.A.; Zawawi, N. Probiotic Properties of Bacillus Strains Isolated from Stingless Bee (Heterotrigona itama) Honey Collected across Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, T. In vitro Assessment of Probiotic Properties of Bacillus Isolated from Naturally Fermented Congee from Inner Mongolia of China. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Cheng, K.-C.; Liu, J.-R. Isolation and Characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain with Zearalenone Removal Ability and its Probiotic Potential. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.-L.; Lee, N.-K.; Yang, S.-J.; Kim, W.-S.; Paik, H.-D. Probiotic Characterization of Bacillus subtilis P223 Isolated from Kimchi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, T.; Wu, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Wen, J. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Characteristics and Genotypes of Bacillus spp. from Probiotic Products of Diverse Origins. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelin, I.; Flett, K.B.; Merakou, C.; Mehrotra, P.; Stam, J.; Snesrud, E.; Hinkle, M.; Lesho, E.; McGann, P.; McAdam, A.J.; et al. Genomic and Epidemiological Evidence of Bacterial Transmission from Probiotic Capsule to Blood in ICU Patients. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).