Abstract
Lung cancer presents a global health challenge, demanding exploration of its molecular intricacies for treatment targets. The goal is to delay progression and intervene early, reducing patient burden. Novel biomarkers are urgently needed for early diagnosis. We analysed RNA sequencing on lung cancer samples from NCBI’s SRA database. Using Bioconductor in R, we identified key genes, including hub genes TOP2A and TMEM100, crucial for cellular processes. Additionally, FDA-approved drugs are repurposed as multitargeted inhibitors against upregulated genes, validated through simulations. This approach aims to inhibit the function of crucial genes, potentially offering effective treatment for lung cancer within a comprehensive strategy.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer stands as a global health challenge, causing the highest number of cancer-related deaths worldwide. According to recent statistics, lung cancer accounts for more fatalities than breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers combined, making it a critical area of focus in oncology [1]. Lung cancer is particularly dangerous because it often does not show symptoms until it has progressed to an advanced stage, making early detection difficult and reducing the likelihood of effective treatment [2]. Amidst this alarming situation, there arises an imperative need to address this disease comprehensively. Effective management of lung cancer depends on the ability to diagnose the disease at an early stage, where therapeutic interventions are most effective. Early diagnosis is crucial because it opens the door to a wider array of treatment options, including surgical resection, which is often curative for early-stage lung cancer. However, the current diagnostic methods, primarily relying on imaging and histopathological analysis, often fall short in identifying early-stage lung cancer, highlighting the necessity for more sensitive and specific biomarkers. There is a pressing demand for innovative biomarkers and targeted interventions that can facilitate timely detection and intervention. The molecular underpinnings of lung cancer are complex, involving a myriad of genetic and epigenetic alterations that drive tumorigenesis and progression. Understanding these molecular changes is key to developing novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. This study endeavours to delve into the intricate molecular landscape of lung cancer, focusing particularly on the identification of crucial genes that play a pivotal role in early diagnosis and prognosis [3]. Addressing the global burden of lung cancer requires a multifaceted approach that prioritises early diagnosis through the identification of reliable biomarkers and the development of targeted therapies. This study’s focus on the molecular complexities of lung cancer seeks to contribute to this goal by uncovering key genetic biomarkers that can serve as both diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets. Through these efforts, we hope to improve survival rates and quality of life for lung cancer patients worldwide, ultimately alleviating the burden of this devastating disease.
2. Material and Methods
To understand the nature and molecular intricacies of lung cancer, a simple and sequential pipeline was followed, as shown in Figure 1. This pipeline is crucial for uncovering the important genes responsible. With the aim of comprehensively understanding the genetics of this disease, our methodology was meticulously designed to ensure the robustness, reliability, and reproducibility of results.
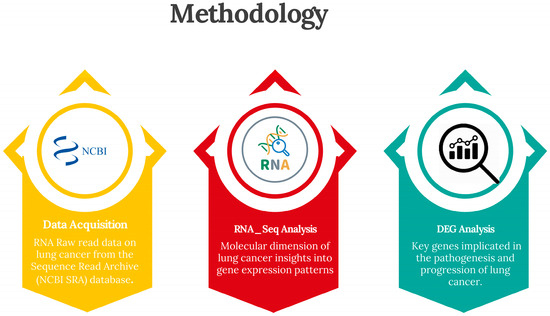
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the study.
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
In this study, lung cancer RNA sequencing data were acquired from the National Center for Biotechnology Information’s Sequence Read Archive (NCBI SRA) database. Rigorous selection criteria were applied to ensure the quality and relevance of the samples to the study objectives [4]. The raw sequencing reads underwent comprehensive preprocessing steps to prepare them for downstream analysis. This included adapter trimming, quality filtering, and removal of low-quality reads using state-of-the-art bioinformatics tools. Quality control measures were implemented to evaluate the integrity and reliability of the sequencing data, ensuring that subsequent analyses were based on high-quality data [5]. These measures aimed to mitigate potential biases and artefacts that could affect the accuracy and robustness of the results. By adhering to strict preprocessing and quality control protocols, this study maintained a rigorous standard of data integrity, enabling confident interpretation of the findings [6]. This methodological approach laid a solid foundation for subsequent analyses, providing assurance that the results were based on reliable and representative data.
2.2. Analysis of Key Genes
Differential gene expression analysis was conducted to identify genes that are differentially expressed between lung cancer samples and healthy controls. This analysis was performed using Bioconductor packages in the R programming environment (Deseq2), employing state-of-the-art statistical methods to ensure robustness and accuracy [7]. Key genes implicated in lung cancer pathogenesis and early diagnosis were identified based on differential expression patterns and biological significance. Candidate genes were prioritised for further analysis based on their known roles in cellular functions and relevance to lung cancer biology [8].
3. Results
3.1. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
In our investigation, differential gene expression analysis revealed a complex interpretation of genetic activity between lung cancer samples and their healthy counterparts. A total of 2000 genes exhibited significant differences in expression levels, underscored by an adjusted p-value of less than 0.05. Within this cohort, 1483 genes were found to be upregulated, while 131 genes displayed downregulation in lung cancer specimens compared to healthy tissue controls [9]. Notably, among the genes showing the most pronounced differences in expression were well-known oncogenes such as TOP2A, TMEM100, and MIR96, indicating their heightened activity in the tumorigenic process. Conversely, tumour suppressor genes such as TP53 and CDKN2A exhibited downregulation, hinting at their potential role in the loss of regulatory control observed in lung cancer development. This comprehensive analysis not only illuminates the breadth of genetic dysregulation characterising lung cancer but also highlights specific genes that may serve as pivotal targets for therapeutic intervention and diagnostic stratification [10].
3.2. Identification of Key Genes
Further exploration of the differentially expressed gene set led to the identification of a select group of key genes integral to the pathogenesis and early detection of lung cancer. Among these, TOP2A and TMEM100 emerged as particularly promising candidates, boasting multifaceted roles in critical cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and cytoskeletal dynamics. The functional significance of these genes was underscored by their enrichment in pathways intricately linked to cancer biology, including cell cycle regulation, DNA repair mechanisms, and signalling cascades pivotal in disease progression [11,12].
4. Discussion
Lung cancer, usually caused by uncontrolled cell growth in lung tissues, represents a significant global health burden. It is characterised by high mortality rates and limited treatment options, making it a priority area for medical research and intervention. Our study contributes to the understanding of this complex disease by elucidating key genes involved in its pathogenesis and progression. Through differential gene expression analysis, we identified a multitude of genes that were significantly dysregulated between lung cancer samples and healthy controls [13,14]. This dysregulation reflects the intricate interplay of genetic factors underlying the development and progression of lung cancer [15]. Notably, our analysis revealed the upregulation of several oncogenes, such as CTPS1, AKR1C2, and IGHG3. The elevated expression of these genes underscores their pivotal role in driving tumorigenesis, contributing to the uncontrolled proliferation and survival of cancer cells [16]. On the other hand, we observed the downregulation of crucial tumour suppressor genes such as FZD4 and SHE, suggesting a loss of regulatory control mechanisms that normally inhibit cancer development [16,17]. This imbalance between oncogene activation and tumour suppressor gene inhibition is a hallmark of cancer progression. Further, our study identified key genes, such as TOP2A and TMEM100, which play critical roles in cellular processes, including proliferation and apoptosis. TOP2A (Topoisomerase II Alpha) is involved in DNA replication and repair, and its overexpression is often associated with increased cell proliferation and poor prognosis in cancer patients [18]. TMEM100 (Transmembrane Protein 100) has been implicated in various cellular signalling pathways and is thought to act as a tumour suppressor. The dysregulation of these genes points to their significant functional roles in lung cancer biology. These genes are enriched in pathways related to cell cycle regulation and DNA repair, highlighting their importance in maintaining genomic integrity and controlling cell division. The disruption of these pathways is a critical factor in the development and progression of lung cancer, as it leads to uncontrolled cell growth and resistance to apoptosis (programmed cell death) [18,19]. The identification of these key genes provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms driving lung cancer progression. These findings offer potential targets for therapeutic intervention, as targeting these dysregulated genes could inhibit cancer growth and improve treatment efficacy. Additionally, these genes may serve as biomarkers for early diagnosis, enabling the detection of lung cancer at a more treatable stage. Our study advances the understanding of the molecular basis of lung cancer and identifies potential avenues for personalised treatment and precision medicine approaches. The detailed characterisation of these genes and their associated pathways offers a roadmap for developing new therapeutic strategies and diagnostic tools. However, further research is needed to validate these findings and translate them into clinical practise. Future studies should focus on functional assays to confirm the roles of these genes in lung cancer, as well as clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of targeted therapies based on these molecular insights. Ultimately, these efforts aim to improve patient outcomes and reduce the global burden of lung cancer [20].
5. Conclusions
Our study provides a comprehensive understanding of the molecular complexity underlying lung cancer, revealing significant dysregulation of key genes crucial to disease pathogenesis and progression. Through rigorous analysis, we identified TOP2A and TMEM100 as central players, shedding light on their involvement in vital cellular processes such as proliferation and apoptosis and their enrichment in pathways pivotal to cancer development. These findings not only offer potential targets for therapeutic intervention but also hold promise for improved diagnostic strategies. Our exploration into drug repurposing unveils novel opportunities for treatment, leveraging FDA-approved drugs as multitargeted inhibitors against dysregulated genes. The clinical implications of our research are substantial, paving the way for personalised treatment approaches and advancing precision medicine in lung cancer management. Further validation and translation of these findings into clinical practise hold the potential to revolutionise the treatment paradigm and ultimately enhance patient outcomes in lung cancer. Moreover, the integration of these molecular insights with emerging technologies such as liquid biopsy and genomic editing could further refine diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy. Collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies will be crucial in bringing these innovations from the bench to the bedside. Such advancements are essential to tackling the global burden of lung cancer effectively, offering hope for better survival rates and quality of life for patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, S.N.A.S.; methodology, S.N.A.S.; implementation and coding, S.N.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.N.A.S.; writing—review, S.N.A.S.; visualisation, S.N.A.S.; supervision, R.P.; editing and improvements, R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study is available in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) repository, accessible at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rami-Porta, R.; Wittekind, C.; Goldstraw, P.; International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) Staging Committee. Complete resection in lung cancer surgery: Proposed definition. Lung Cancer 2005, 49, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooreldeen, R.; Bach, H. Current and future development in lung cancer diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dama, E.; Melocchi, V.; Colangelo, T.; Cuttano, R.; Bianchi, F. Deciphering the molecular profile of lung cancer: New strategies for the early detection and prognostic stratification. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Campbell, K.R.; Lun, A.T.; Wills, Q.F. Scater: Pre-processing, quality control, normalization and visualization of single-cell RNA-seq data in R. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, W. RSeQC: Quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2184–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. A pipeline for RNA-seq based eQTL analysis with automated quality control procedures. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.I.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Tian, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Meng, Z.; Wang, K.; Duan, X.; et al. Identification of candidate biomarkers correlated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer via integrated bioinformatics analysis. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yi, J.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; et al. An integrated epigenomic-transcriptomic landscape of lung cancer reveals novel methylation driver genes of diagnostic and therapeutic relevance. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemira, M.; Collin, F.; Szalkowska, A.; Bielska, A.; Chwialkowska, K.; Reszec, J.; Niklinski, J.; Kwasniewski, M.; Kretowski, A. Molecular signature of subtypes of non-small-cell lung cancer by large-scale transcriptional profiling: Identification of key modules and genes by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Cancers 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Horvath, S. Understanding network concepts in modules. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otálora-Otálora, B.A.; Florez, M.; López-Kleine, L.; Canas Arboleda, A.; Grajales Urrego, D.M.; Rojas, A. Joint transcriptomic analysis of lung cancer and other lung diseases. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 491390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beane, J.; Vick, J.; Schembri, F.; Anderlind, C.; Gower, A.; Campbell, J.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.H.; Xiao, J.; Alekseyev, Y.O.; et al. Characterizing the impact of smoking and lung cancer on the airway transcriptome using RNA-Seq. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.A.; Relan, V.; Wright, C.M.; Davidson, M.R.; Sriram, K.B.; Savarimuthu Francis, S.M.; Clarke, B.E.; Duhig, E.E.; Bowman, R.V.; Fong, K.M. Common pathogenic mechanisms and pathways in the development of COPD and lung cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Girard, N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collisson, E.; Campbell, J.; Brooks, A.; Berger, A.; Lee, W.; Chmielecki, J.; Beer, D.; Cope, L.; Creighton, C.; Danilova, L.; et al. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma: The cancer genome atlas research network. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, C.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of young Chinese patients with lung adenocarcinoma identified a distinctive genetic profile. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Masciale, V.; Aramini, B.; Coló, G.P.; Tonelli, R.; Marchioni, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Gozzi, F.; Andrisani, D.; Castaniere, I.; et al. Molecular mechanisms and cellular contribution from lung fibrosis to lung cancer development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).