Abstract
Selenium was discovered in the first quarter of the 19th century and classified as a chalcogen belonging to the 16th group, along with oxygen, sulfur, tellurium, and polonium. Selenium plays a crucial role in the activation of antioxidant enzymes in the body and helps to reduce oxidative stress by preventing cell damage. It is believed to have cancer-protective effects, including mechanisms such as reducing DNA damage, regulating cell growth, supporting the immune system, and engaging in epigenetic interactions. These are attributed to the antioxidant properties of selenium. The purpose of this paper was to elucidate the effects of selenium exposure on the incidence and mortality of various cancer types using the meta-meta-analysis method.
1. Introduction
Selenium, a chemical element, made its debut in the scientific realm during the early 19th century and was subsequently categorized as a chalcogen, being grouped within the 16th column of the periodic table alongside oxygen, sulfur, tellurium, and polonium. It assumes a pivotal role in orchestrating the activation of various antioxidant enzymes within the human body, effectively contributing to the intricate balance of oxidative and antioxidative processes [1,2,3]. By harnessing its antioxidative prowess, selenium works diligently to thwart the deleterious impacts of oxidative stress, preventing cellular damage that can otherwise culminate in a cascade of adverse health outcomes [1,2,3,4].
As science delves deeper into selenium’s intricacies, an expanding body of research has underscored its potential cancer-protective properties. These protective effects are conjectured to stem from a multifaceted interplay of factors. Notably, selenium is speculated to function as a guardian against carcinogenesis through a spectrum of mechanisms. Firstly, its capacity to curtail DNA damage has garnered significant attention, contributing to the preservation of genomic stability and averting potential mutations that could catalyze the cancerous transformation of cells [2,3,4,5,6]. Moreover, selenium’s role in regulating cell growth has emerged as another critical facet, wherein it exercises control over the delicate balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis, preventing uncontrolled growth that is emblematic of malignancies. Additionally, selenium’s engagement in epigenetic interactions, wherein it influences gene expression without altering DNA sequences, has emerged as a promising avenue. These interactions, often mediated by the modification of histones and DNA methylation, further contribute to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and guard against the onset of carcinogenic processes [1,2,3,4,5,6,7].
The purpose of this paper was to elucidate the effects of selenium exposure on the incidence and mortality of cancer using the meta-meta-analysis method.
2. Methods
To ensure a rigorous and exhaustive exploration of the subject matter, a comprehensive and systematic literature search was meticulously conducted across related databases, including PubMed/Medline, Web of Science (WoS), and Scopus. This methodical approach aimed to capture an extensive collection of relevant studies, employing a well-defined set of predetermined keywords tailored to the research objectives.
The research methodology encompassed both primary and secondary meta-meta-analyses, involving the amalgamation of odds ratios (OR) and relative risks (RR) for outcomes documented in the chosen meta-analyses. A comprehensive analysis was conducted to synthesize all available data, culminating in a unified pooled estimate. This analytical framework enabled a comprehensive assessment of the multifaceted interplay between selenium and cancer-related outcomes, fostering a nuanced understanding of the subject matter.
The variability in outcomes across various studies was assessed through the χ2-based Cochran’s Q test (with a significance level set at p < 0.05) as well as I2 statistics. These analytical tools were employed to measure the importance of heterogeneity among the collected data. The meta-meta-analyses were conducted using both random effects and fixed effects models, with the appropriate method selected based on the level of heterogeneity present in the data. The potential publication bias was identified based on the outcome indicated by Egger’s linear regression asymmetry test [8] and Begg and Mazumdar’s rank correlation test [9]. The statistical significance across all meta-meta-analyses was assessed at the conventional two-tailed p-value threshold of <0.05. The statistical computations for the meta-meta-analyses were conducted using Prometa3® [10], in conjunction with the R statistical software version 4.2.0 [11]. These analyses were carried out in accordance with well-established guidelines for meta-analytic methodologies, ensuring a rigorous and systematic approach to the data evaluation process.
3. Results and Discussion
A comprehensive analysis was conducted on a total of 22 reports containing 16 eligible meta-analyses [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27] that adhered to the inclusion criteria, aiming to evaluate the association between selenium exposure and cancer incidence as well as mortality. Through a pooled analysis encompassing 18 reports originating from 16 separate meta-analyses that examined the link between selenium exposure and cancer risk, a remarkable finding occurred.
In the pooled analysis of 18 reports from a total of 16 meta-analyses [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27] evaluating selenium exposure and cancer risk, higher selenium exposure was associated with a 22% lower risk of cancer (OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.72–0.85, p < 0.001) (Figure 1a). Considerable and remarkable heterogeneity was detected across the studies incorporated in the analysis (Q = 105.5, df = 17, I2 = 83.8%, p < 0.001). As a result, this meta-meta-analysis was executed utilizing a random effects model. According to Begg and Mazumdar’s rank correlation test (z = −0.49, p = 0.622), there was no evidence of publication bias in the study reports (Figure 1b).
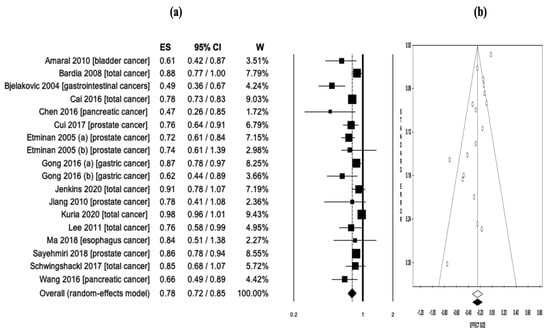
Figure 1.
(a) The pooled effect size (ES) associated with selenium exposure (low and high exposure) and cancer risk, and (b) the funnel plot depicting the relationship between selenium exposure and cancer risk [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Similarly, a parallel pooled analysis involving four meta-analyses [12,15,21,22] that investigated selenium exposure and cancer-related mortality confirmed this trend. The outcome highlighted a significant correlation between increased selenium exposure and reduced mortality rates (RR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.83–0.94, p < 0.001) (Figure 2a). No significant heterogeneity was observed among the studies enclosed in this analysis (Q = 2.02, df = 3, I2 = 0.00%, p = 0.568). Therefore, this meta-meta-analysis was carried out using a fixed effects model. The results of Egger’s linear regression asymmetry test (Intercept = −0.59, t = −0.87, p = 0.476) and Begg and Mazumdar’s rank correlation test (z = −0.68, p = 0.497) indicated no publication bias in the study reports (Figure 2b).
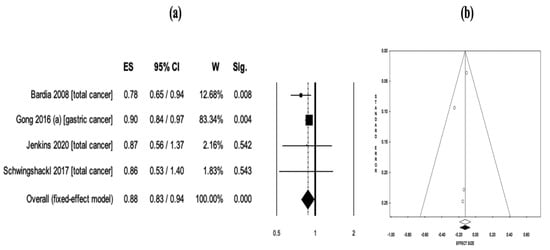
Figure 2.
(a) The pooled effect size (ES) associated with selenium exposure (low and high exposure) and cancer mortality, and (b) the funnel plot depicting the relationship between selenium exposure and cancer mortality [12,15,21,22].
In a recent meta-analysis conducted by Kuria et al. [23], which incorporated 37 primary studies, it was reported that selenium at recommended daily levels of 55 µg/day demonstrated a reduced risk of cancer (RR = 0.94, 95% CI: 0.90–0.98, p < 0.05). Moreover, various meta-analyses evaluating selenium exposure and the risk of pancreatic cancer [27], prostate cancer [26], gastric cancer [21], and bladder cancers [17] have emphasized the protective effects of selenium against cancer. In this paper, high selenium exposure was associated with a 22% lower risk of cancer (OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.72–0.85, p < 0.001), and concurrently, higher selenium exposure was found to be linked with reduced mortality (RR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.83–0.94, p < 0.001). These findings notably highlight the significance of selenium’s protective effects against cancer.
4. Conclusions
Taken together, the findings of this paper highlight the potential efficacy of selenium in reducing the risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Furthermore, this investigation posits that elevated levels of selenium exposure may serve as a reasonable strategy for not only preempting but also managing cancer. The findings also support the potential role of selenium in cancer prevention and highlight its importance as a possible intervention for improving health outcomes in individuals at a risk of cancer. Furthermore, considering the cancer types and dose–response relationships, it is crucial and critical to plan more comprehensive and well-designed prospective studies and randomized controlled trials.
Author Contributions
M.E.A.: conceptualization, methodology, software, data analysis, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and critical review; Y.B.: visualization, investigation, validation, writing—original draft preparation, and critical review; H.E.: conceptualization, methodology, software, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and critical Review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
For accessing the datasets used in this study, individuals interested should establish direct contact with the corresponding author (MEA) and submit a formal request outlining their intention to obtain the data. Subsequently, the corresponding author (MEA) will furnish additional details and instructions pertaining to the process of accessing the datasets.
Conflicts of Interest
The entirety of the authors involved in the execution of this study announces that they have no conflicts of interest to declare. No financial, personal, or professional affiliations exist that may exert any potential influence or bias upon the outcomes and conclusions presented within this research. This unequivocal declaration is made with the purpose of upholding transparency and safeguarding the credibility and objectivity of this study.
References
- Garbo, S.; Di Giacomo, S.; Łażewska, D.; Honkisz-Orzechowska, E.; Di Sotto, A.; Fioravanti, R.; Zwergel, C.; Battistelli, C. Selenium-Containing Agents Acting on Cancer—A New Hope? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, W.; Benedetti, R.; Handzlik, J.; Zwergel, C.; Battistelli, C. The innovative potential of selenium-containing agents for fighting cancer and viral infections. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Méplan, C.; Hesketh, J. Selenium and cancer: A story that should not be forgotten-insights from genomics. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whanger, P.D. Selenium and its relationship to cancer: An update. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 91, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedirko, V.; Jenab, M.; Méplan, C.; Jones, J.S.; Zhu, W.; Schomburg, L.; Siddiq, A.; Hybsier, S.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. Association of Selenoprotein and Selenium Pathway Genotypes with Risk of Colorectal Cancer and Interaction with Selenium Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Cilloni, S.; Crespi, C.M. The Epidemiology of Selenium and Human Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 136, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProMeta-3 Professional Statistical Software for Conducting Meta-Analysis. It Is Based on ProMeta 2.1 Deployed by Internovi in 2015. Available online: https://idostatistics.com/prometa3/ (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Cerhan, J.R.; Sood, A.K.; Limburg, P.J.; Erwin, P.J.; Montori, V.M. Efficacy of antioxidant supplementation in reducing primary cancer incidence and mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, W.; Shao, L.; Zhong, D.; Wu, Y.; Cai, J. Association between intake of antioxidants and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, K.H.; Tian, J.H.; Guan, Q.L.; Yao, N.; Cao, N.; Mi, D.; Wu, J.; Ma, B.; Yang, S. Efficacy of antioxidant vitamins and selenium supplement in prostate cancer prevention: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Boeing, H.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Gottschald, M.; Dietrich, S.; Hoffmann, G.; Chaimani, A. Dietary Supplements and risk of cause-specific death, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of primary prevention trials. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2004, 364, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.F.; Cantor, K.P.; Silverman, D.T.; Malats, N. Selenium and bladder cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Selenium Exposure and Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-analysis and Meta-regression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Serum selenium levels and prostate cancer risk: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, M.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Gleave, M.; Chambers, K. Intake of selenium in the prevention of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2005, 16, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Y.; He, J.G.; Li, B.S. Meta-analysis of the association between selenium and gastric cancer risk. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15600–15605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kitts, D.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Sahye-Pudaruth, S.; Paquette, M.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Patel, D.; Kavanagh, M.; Tsirakis, T.; Kendall, C.W.C.; et al. Selenium, antioxidants, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuria, A.; Fang, X.; Li, M.; Han, H.; He, J.; Aaseth, J.O.; Cao, Y. Does dietary intake of selenium protect against cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Myung, S.K.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Ju, W.; Seo, H.G.; Huh, B.Y. Effects of selenium supplements on cancer prevention: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Q.; Fang, X.; Chen, L.; Qiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Min, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, F. Increased total iron and zinc intake and lower heme iron intake reduce the risk of esophageal cancer: A dose-response meta-analysis. Nutr. Res. 2018, 59, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayehmiri, K.; Azami, M.; Mohammadi, Y.; Soleymani, A.; Tardeh, Z. The association between selenium and prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liang, L. Association between selenium intake and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).