Abstract
Meloidogyne graminicola (Mg), commonly referred to as rice root-knot nematodes (RKNs), is one of the most prevalent plant parasitic nematodes in rice agroecosystems, and sustainable agricultural practices are still limited. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of soil microbiotas extracted from different agricultural practices in reducing RKN damage to rice plants. We used conservation agriculture (CA), cover crops with machine tillage (CA), conservation agriculture without tillage (CAU), and conventional agriculture practices (CT). All types of soil microbiotas were isolated from soil samples collected from each rice agricultural practice in the Preah Vihear and Kampong Thom provinces of Cambodia in order to test the effectiveness of the microbiotas against Mg on rice plants (Variety IR64). The experiment was conducted in test tubes, using sterilized sand to grow rice. Then, 250 juveniles (J2) were used to infect each tube and were classified into three treatments: (1) infected 25 mL of microbiota suspensions from non-sterilized soil (M); (2) infected 25 mL of microbiota from sterilized soil (ST); and (3) a control with only J2 (CT). After 3 weeks of infection, rice plants were examined under microscopes to measure the number of nematodes (J2 and eggs). The results showed that the number of nematodes was significantly different under treatment (ST) 230 ± 100.132 compared to treatment (M) 159 ± 64.41, respectively. The data demonstrated that soil microbiotas in CA were effective in reducing Mg damage to rice roots, a method which can be used as a biological control to lower RKN in rice plants. However, further research is required to conduct the assessment of the effects of microbiotas on rice development and yield and determine the taxa of beneficial microbiomes with the most benefit to rice growth.
1. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa) is a crucial staple food crop for the bulk of the human population and may be a model organism for monocotyledon plants. It is a widely cultivated crop within the world, being grown in over 100 countries, primarily in Asian countries [1]. However, due to changes in farming practices to reduce water use, the number of soil-borne infections (including nematodes) is rising globally, and these pathogens could pose a threat to rice production. The root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola (Mg), the rice root nematode Hirschmanniella oryzae, and the cyst nematode Heterodera spp. are the three most destructive nematodes attacking the crop [2]. One of the most damaging worms to rice is M. graminicola, which causes a gall to form on the rice roots. After passing through the root elongation zone, RKNs enter the vascular cylinder and proceed along the apoplectic route toward the root tip. They use their style to breach the cell wall and inject secretions from their pharyngeal glands into the plant cells, resulting in large cells that serve as long-term feeding sites [3].
M. graminicola, which may significantly slow down rice seedling growth and can reduce rice yield by about 80%, is common in the world’s main rice-producing nations. In southeast Asia and other places, deep-water and lowland rice are very common. For the control of M. graminicola in fields, chemical nematicides (carbofuran, phorate, and chlorpyriphos) have been used as seed treatments or soil applications and have significantly reduced the gall, egg mass production, and soil populations of these pests [4]. However, the potential negative impact of chemical nematicides on the environment and humans has led to a total ban on or restricted use of these chemicals. Dicot-based crop rotation with a follow-up period may lower nematode numbers and boost rice productivity. Numerous bacteria and fungi in the microbiota, such as Pseudomonas fluorescens and Paecilomyce lilacinus, have been shown to support plant development and create chemicals that prevent nematode egg hatching or kill nematodes [5].
Cambodia is an agrarian country, with one-third of the total land area allocated to agricultural production. Rice is the main agricultural product and the country’s staple food, contributing approximately 26% of GDP [6,7]. However, rice cultivation has faced many problems, including pests and diseases. Plant parasitic nematode (PPN) is one of the major pests in rice production in Southeast Asia, reducing rice yield from 16 to 80% of the total crop production [8]. The use of pesticides to suppress pests can cause effects on plants such as perturbation in the development of the reproductive organs, growth reduction, and alteration of carbon and nitrogen metabolism, leading to lower nutrient availability for plant growth and also contaminating environments such as soil, water, turf, and other vegetation. Moreover, farmers mainly produce organic rice through traditional practices, including land preparation using a power tiller, manual transplanting, and harvesting. The rice yield in this area has been decreasing from year to year for long periods spanning more than 40 years due to monoculture-based rice practices and the low return of organic amendments to rice fields, conditions which result in soil fertility decline and compacted soil layers.
This study focused on evaluating the potency of microbiotas in terms of controlling Mg damage to rice when these microbiotas are extracted from different types of rice farming soil, including three different agriculture practices: conservation agriculture (CA) with machine tillage in Rovieng district, Preah Vihear province; conservation agriculture without tillage (CAU) from the field experiments in Stung Chinith, Santuk district, Kampong Thom province; and conventional agriculture (CT) from both sites. The experiment on the effectiveness of microbiotas at controlling nematodes was conducted over a 3-week period in order to observe the number of root galls and the number of nematodes J2 after extraction.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Test Effectiveness of Microbiome on Rice Root-Knot Nematode
2.1.1. Sampling Method
Five soil sampling points containing microbiotas were collected from a rice field where different agriculture practices were applied: CA (conservation agriculture using cover crop with machine tillage), CAU (conservation agricultural practice using cover crop without tillage), and CT (conventional agricultural practice) at 0–20 cm depth. The samples were then mixed to create a composite sample. The rationale behind choosing certain agricultural practices like CA, CAU, and CT for microbiome extraction is to identify the beneficial microbiota from each agricultural practice’s ability to suppress the nematodes. The samples were stored at room temperature until further experiments were conducted with microbiomes.
2.1.2. Microbiome Extraction
Three hundred grams of each soil sample were placed into an Erlenmeyer flask, and 150 mL of distillation water was added and then mixed well. Soil suspensions were shaken for 1 h at 120 rpm in an incubated shaker to release microorganisms from the soil particles. After shaking, large soil particles were allowed to settle for 10 min, and the suspensions were sieved through a series of sieves at 100, 50, and 25 µm, respectively. Microbiomes were collected on the third sieve (25 µm), rinsed several times with distilled water, and collected in a suspension of around 50 mL. Then, we filtered the collection through the coffee filter, collected at least 50 mL of filtrated suspensions, and put them back into a clean 50 mL Falcon tube. Then, we transferred the suspensions into the hatching column and kept them in a dark place for 2 days. After 2 days, we collected the suspensions of around 30–40 mL into a falcon tube, rested them for 1 h, and then removed the surface suspensions and kept 25 mL for infection with nematode suspensions.
2.1.3. Nematode Extraction
Nematodes were recovered from infected roots following the Baermann funnel method outlined by Bellafiore et al. in 2008 [9]. The rice roots containing root galls were collected and washed using tap water to remove soil and foreign substances. After washing, the roots were cut into 2 cm segments using scissors. They were soaked in sodium hypochlorite solution (concentration 0.6%) for 3 min, mixed one time for 5 s, placed for 2 s in a blender three times, and soaked in bleach for an additional 3 min. After soaking, the mixture was filtered through a series of sieves (upper to lower) of 100, 50, and 25 µm, respectively. Nematodes were recovered on a 25 µm sieve and then rinsed several times with tape-distilled water. Nematodes were collected into 25 mL of filtrate and placed into a 50 mL beaker. The volume was measured before counting under the microscope for exact quantification.
2.1.4. Experimental Design
Firstly, rice seeds were germinated in a petri dish by putting the seed on wet tissue, using tap water, covering it with a petri dish, and transferring it into a growth chamber (model KBW 240/Growth Chambers with Light) by setting up a weekly program with a temperature of 29 °C, 80% humidity, 50% fan, 50% UV, 12 h of daylight, and 12 h of darkness. Three days later, rice plants were planted in three conditions. In the first condition, sand was sterilized and two germinated rice plants were planted in the tube. Then, 25 mL of soil microbiome suspension from non-sterilized soil and 1000 µL of nematode suspensions containing 250 J2 were added (M). In the second condition, sand was sterilized with 25 mL of soil microbiome suspension from sterilized soil and infected with 250 J2 (ST). In the third condition, sand was sterilized and infected with 250 J2 without microbiome suspension as a control (CTL). Infected rice plants were placed into a growth chamber that was set up as a weekly program. Six days later, 0.7 g or 4 seeds of rice nutrient were added to the rice in each tube. We then placed back into the growth chamber. Next, rice germination was planted in the growth chamber for 3 weeks. After 3 weeks, rice plants were used to observe the number of nematodes (for nematode extraction, repeat the method in point Section 2.1.3 nematode extraction before counting the number of nematodes).
2.1.5. Assessment the Suppressive of Nematode on Rice Plants Using Microbiome
After 3 weeks of growing, 33 variables of rice plants were used to measure the parameter number of Mg. Root-knot nematodes were counted after extraction from rice root using the method described in Section 2.1.3. After being extracted, RKNs were counted under a microscope.
2.1.6. Statistical Analysis
The descriptive statistics were conducted using the 2016 Excel version. Other statistical analyses were carried out using R Studio version 4.2.0. Before choosing the corresponding statistical tests, the normality distribution was performed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Due to the non-normal distribution of the data sets, non-parametric tests, such as the Kruskal–Wallis test at a confidence interval of 95%, were used to test the effectiveness of microbiomes versus different agricultural practices in terms of suppressing nematodes and their effects on plant growth. The same test was used to compare the significant differences between rice plants infected with microbiomes from non-sterilized soil and nematodes (M) from CA, CAU, and CT versus those infected with microbiota from sterilized soil and infected nematodes (ST). The Dunn test was performed in order to compare the different subsets of all possible pairs.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Microbiome from Different Agriculture Practices
3.1.1. Root-Knot Nematode Suppression Using Microbiomes
The effects of beneficial microbiotas versus non-microbiotas on the total number of nematodes extracted from rice plants were compared. There was a significant difference (p = 0.0299) in the number of nematodes. The rice plants infected by microbiotas from non-sterilized soil (M) contained fewer nematodes compared to the plant’s inoculation of microbiotas from sterilized soil (ST), with 159 vs. 230 nematodes, as shown in Figure 1. On the other hand, the number of galls had no significant difference suitable for discussion in this study. The variety of soil microbes is a great indicator of soil health. Plant defense, soil-borne disease suppression, and plant growth promotion are all impacted by the high microbial variety and activity [10]. Bacillus spp., from the firmicutes family of bacteria, of which many produce a variety of lytic enzymes and antibiotic chemicals, is frequently mentioned as a biocontrol agent against soil-borne diseases and nematodes [11]. According to Padgham and Sikora (2007) [12], the galling of M. graminicola on rice was decreased by up to 40% when rice seeds were treated with endophytic bacterial antagonists. Additionally, it was shown that certain endophytes greatly reduced the number of root-knot nematode progeny, most likely via indirect mechanisms based on interactions between endophytes and plants rather than through nematicidal activity.
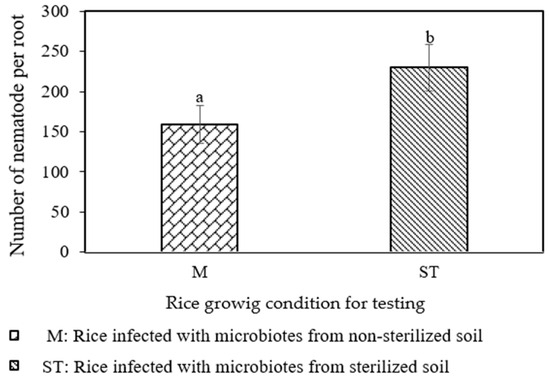
Figure 1.
The number of nematodes in rice root as affected by (M) and non-affected by microbiotas (ST). Error bars represent standard error. The latter a,b on bar showed the significant difference in number of nematodes in rice root with (p = 0.0299).
3.1.2. Effect of Microbiote from Various Agricultural Practices to Control Nematode
After demonstrating how well the microbiotas can decrease nematodes, the microbiotas in different agricultural practices in Rovieng district, Preah Vihear province, were compared. The outcome indicated that there was no clear differentiation in the quantity of nematodes in the agricultural practices CA and CT (p = 0.1469). However, the average number of nematodes in rice inoculum, as assessed via microbiota extraction from CA, was less than the number of nematodes in rice inoculum as assessed via microbiota extraction from CT (93 vs. 105), as shown in Figure 2. Although there was no discernible difference in the number of nematodes in the two agricultural practices, the microbiotas from the CA system, which used the cover crops Stylosanthes, Crotalaria juncea, and Crotalaria ochroleuca, had a greater impact on nematode suppression than the CT system, which used traditional practices for rice growing. Masson et al. (2022) [13] reported that CA agricultural practices with cover crops Stylosanthes guianensis and Crotalaria juncea have the capacity to enhance soil quality, promote biodiversity, and decrease the abundance of PPNs in the rhizosphere (−64% of Meloidogyne spp. in roots and −92% of Hirschanniella spp.). Additionally, cultivation of Crotalaria ochroleuca has significantly enhanced the mycorrhizal soil potential by encouraging the development of the mycelial network, which is regarded as a key element in the functioning of the AM symbiosis and is involved in a variety of soil biological processes, including nutrient transformations, plant growth promotion, and the suppression of disease [14].
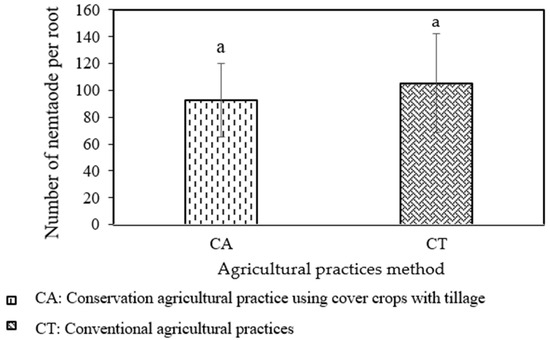
Figure 2.
Effect of microbiotas from various agricultural practices to control nematode. Error bars represent standard error. The letter a on bar showed significant different of number of nematodes in rice root that inoculated with microbiomes with (p > 0.05).
In Stung Chinith, Santuk district, Kampong Thom province, the three agricultural techniques were compared for the number of nematodes in rice that had microbiome infections, as shown in Figure 3 below. The number of infected nematodes among the various had a significant difference of p = 0.01486. Agricultural methods have a lower amount of nematode 146 in comparison to other systems, as shown in rice inoculated with CA microbiota. The highest number of nematodes (264) was from rice inoculum and the microbiota from CT practices. On the other hand, according to the findings of this investigation, the microbiome that was isolated from the CA agricultural system following the growth of cover crops had a greater potential to inhibit nematodes compared to the CAU with the same cover crop but no tilling. However, in CAU agricultural practice with the same cover crop (Stylosanthes guianensis and Crotalaria juncea) as CA, the trilling technique was not applied after planting the cover crop, which had an effect on microbiome diversity in the soil. Tillage practices alter the physical and chemical conditions of the soil, which has a variety of effects on soil organisms [15]. According to Benkhoua et al. (2017) [14], the total quantities of bacteria and fungi decreased in no-tillage systems by 25.5–22.7%. The uniform distribution of residues in the arable layer and increased oxygen supply to soil microsites in the CA with a tillage system may, it may be argued, have stimulating effects on microbial development [16].
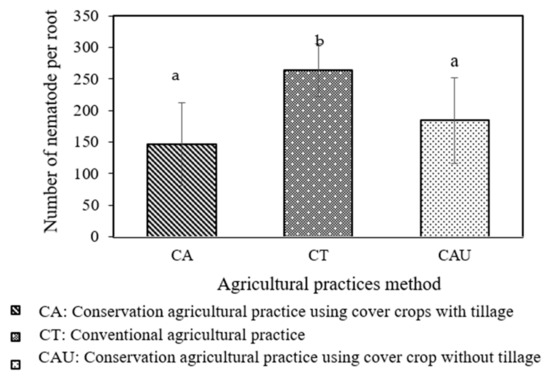
Figure 3.
Effect of microbiotas from various agricultural practices on controlling nematodes. Error bars represent standard error. The letter a,b on bar showed a significantly different of number of nematodes in rice root that inoculated with microbiotas with (p = 0.01486).
4. Conclusions and Recommendation
In conclusion, after testing the effect of the microbiome of rice root-knot nematode for 3 weeks in the growth chamber, the result illustrated that the microbiotas extracted from CA (conservation agricultural practices using cover crop with tillage) had potential as a biological control for suppressing Mg. However, the characteristics of the microbiota were not clearly understood in this study. On the other hand, no significant differences were observed in the effect of the microbiotas from different agricultural practices on rice development (plant length, number of leaves, and root length) because of the short period of rice planting in a small bottle in the growth chamber, and so we could not evaluate the effect of microbiotas and Mg on rice plant development. Moreover, the biodiversity of the microbiotas, species identification of the microbiotas, and the use of beneficial chemicals to control nematodes that are released by the microbiotas should be the focus of the next investigation in order to identify the specific microbiome with the ability to suppress Mg. Last but not least, further studies should be conducted in greenhouses containing growing rice until it is harvested to evaluate the potential effect of microbiotas in terms of controlling nematodes, rice development, and yield in a suitable duration for 3 months, assess the taxa of beneficial microbiomes with the most benefit to rice growth, and identify the specific bacterial strains that have benefits as nematode biocontrols such as Pasteuria, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Streptomyces, Arthrobacter, and Variovorax, or fungal isolates of Pochonia, Dactylella, Nematophthora, Purpureocillium, Trichoderma, Hirsutella, Arthrobotrys, and Mortierella.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S. and M.S.; methodology, B.S.; validation, B.S. and M.S.; formal analysis, K.U. and S.S.; investigation, K.U.; resources, M.S.; data curation, B.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.U.; writing—review and editing, B.S.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, M.S.; project administration, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Higher Education Improvement Project (HEIP), IDA Credit No.6221-KH; and by Sustainable Rice Production within an Agroecology Framework—JEAI-HEALTHYRICE project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The Higher Education Improvement Project (HEIP), IDA Credit No.6221-KH; and by Sustainable Rice Production within an Agroecology Framework—JEAI-HEALTHYRICE project. Bellafiore Stephane and Malyna Suong for help in collecting data, designing the experiment, reviewing data and this proceeding paper, and Sourkea Sorn for help in the lab experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Depar, N.; Rajpar, I.; Memon, M.Y.; Imtiaz, M. Mineral Nutrient Densities in Some Domestic and Exotic Rice Genotypes. Pak. J. Agric. Agric. Eng. Vet. Sci. 2011, 27, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.; Luc, M.; Plowrighti, R.A. Chapter 3 Nematode Parasites of Rice. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture; C.A.B International Institute of Parasitology: Wallingford, UK, 1990; pp. 69–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen, g.; Mitchum, M.G. Mitchum and Abstract, Molecular Insights in the Susceptible Plant Response to Nematode Infection. In Plant Cell Monographs Volume 15; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.R.; Zaidi, B.; Haque, Z. Nematicides control rice root-knot, caused by Meloidogyne graminicola. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2012, 51, 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, Z.A. PGPR: Prospective biocontrol agents of plant pathogens. In PGPR Biocontrol Biofertilization; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 111–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophea, K. Technical Assistance Consultant’s Report: The Rice Situation in Cambodia; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2012; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- MAFF. “BUSINESS OPERATION PLAN FOR: Two Rice Seed Centers In Battambang and Prey Veng Provinces”. 2021. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/linked-documents/44321-014-ld-03.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- De Waele, D.; Elsen, A. Challenges in tropical plant nematology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 45, 457–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellafiore, S.; Shen, Z.; Rosso, M.N.; Abad, P.; Shih, P.; Briggs, S.P. Direct identification of the Meloidogyne incognita secretome reveals proteins with host cell reprogramming potential. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reasoner, D.J.; Geldreich, E. A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinheya, C.C.; Yobo, K.S.; Laing, M.D. Biological control of the rootknot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica (Chitwood) using Bacillus isolates, on soybean. Biol. Control 2017, 109, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgham, J.L.; Sikora, R.A. Biological control potential and modes of action of Bacillus megaterium against Meloidogyne graminicola on rice. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massona, A.-S.; Vermeireb, M.-L.; Leng, V.; Simonine, M.; Tivet, F.; Thi, H.N.; Brunela, C.; Suong, M.; Kuokd, F.; Moulin, L.; et al. Enrichment in Biodiversity Maturation of the soil food web under Conservation Agriculture is Associated with Suppression of rice-parasitic nematodes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 331, 107913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhoua, N.; Hafidi, M.; Badri, W.; Baudoin, E.; Thioulouse, J.; Prin, Y.; Galiana, A.; Ouahmane, L.; Ouhammou, A.; Sanguin, H.; et al. Management of the mycorrhizal soil infectivity with Crotalaria ochroleuca, an indigenous wild legume in the tropics: Impacts on microbial functional diversity involved in phosphorus mobilization processes in a sahelian soil. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladivko, E.J. Tillage systems and soil ecology. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 61, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Garcıa, J.R.; de Velázquez-García, J.; Gallardo-Valdez, M.; Dıaz-Mederos, P.; Caballero-Hernández, F.; Tapia-Vargas, L.M.; Rosales-Robles, E. Tillage effects on microbial biomass and nutrient distribution in soils under rain-fed corn production in central-western Mexico. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).