Abstract
Managing soil fertility is vital for agriculture. However, modern farming excessively relies on mineral fertilizers, which lessens profit and endangers ecosystem health. Grasslands made up of Poaceae and Fabaceae, including woody species, offer feed for livestock, lowers farmers’ economic risks, and conserve resources. Grassland crops can enhance soil fertility in a more sustainable way than mineral fertilization. To counter fertilizer-driven soil decline, permanent grasslands or crop rotations are effective. Also, grassland soils generally contain more nitrogen, potassium and organic matter and less phosphorus than cropland soils. They additionally enhance soil’s physical and biological parameters, limiting erosion while elevating biodiversity. This work focuses on the benefits of grasslands towards crop production, reviewing their influence on soil fertility parameters that boost soil health.
1. Introduction
Modern agriculture faces several challenges in producing food to support an increasing world population, while also requiring rapidly adapting to climate change. Soil fertility is one of the key aspects of agricultural management. Nevertheless, enhancing crop yield has driven farmers to excessive utilization of inorganic fertilizers, with heavy damage to biodiversity and posing environmental and human health risks [1].
Agro-ecological practices can increase the sustainability of modern agriculture by adapting ecological principles and traditional practices, which minimizes the impact on the environment, boosts soil fertility, and contributes to the management of crop protection [2,3].
Soil fertility emerges from the interaction of biological, chemical, and physical processes [4]. Soil microbial and mesofauna communities are extremely relevant for plant nutrition and defense [5]. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), and beneficial nematodes are examples of important contributors to the enhancement of soil biological fertility [6,7,8]. Soil chemical fertility influences and is influenced by the other components and is related to the concentration of inorganic elements and their bioavailability. Key parameters in this context include the cation exchange capacity (CEC), soil organic matter (SOM) or content (SOC), ratios of macro- and micronutrients, and the pH that can influence their availability to plants [9]. Lastly, soil physical fertility relates to porosity, structure, and drainage that influence water availability and aeration [10].
Grasslands, encompassing both natural expanses and cultivated areas, predominantly comprise members of the Poaceae and Fabaceae families. These ecosystems stand as primary sources of sustenance for numerous livestock, underpinning global food security [11]. The use of pastures and forages has been associated with several ecosystem services that enhance the farm’s long-term sustainability. These benefits include the promotion of soil fertility, carbon storage, water regulation, biodiversity, pollination, and pest control [12,13]. Hence, the use of these crops can be considered an agroecological measure that ensures sustainable food production.
In this study, a review of the beneficial role of grasslands on soil chemical fertility is presented comparing the effects of implementing croplands versus grasslands.
2. Bibliographic Sources
The research was performed using the Web of Science search engine (https://www.webofknowledge.com, last accessed on 1 July 2023), in all available databases, on published works from 2018 to 2023, using the topics “grassland crops” and “soil fertility”. A total of 17 works were retrieved concerning soil chemical fertility parameters measured in croplands in comparison to grasslands (Figure 1). Works were mainly published in journals specialized in agriculture, environmental sciences, biodiversity conservation, plant sciences, and chemistry. These selected articles were cited 108 times; thus, the average number of citations per article is approximately 6.35.
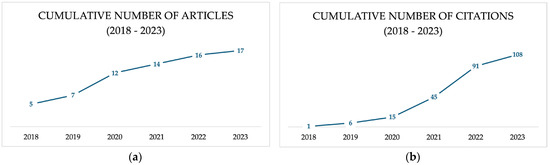
Figure 1.
The cumulative number of published articles (a) and respective cumulative number of citations (b) between January 2018 and July 2023.
To assess the beneficial influence of grassland crops, when compared to croplands, on soil chemical fertility, a total of 10 parameters were considered. For this purpose, percentual relative differences of mean values were calculated following this formula:
where GL is the grassland mean value and CL is the cropland mean value.
Relative Differences (%) = [(GL-CL)/GL] × 100
3. The Influence of Grasslands on Soil Chemical Fertility
Differences between conventional crop fields and grasslands were reported for the selected soil chemical parameters. Several reports suggest a tendency for increased levels of soil organic carbon (SOC) or soil organic matter (SOM) through forage or pasture cultivation. Likewise, grassland soils frequently exhibited elevated nitrogen and potassium content, indicating improved nutrient conditions. Similarly, the C/N ratio tended to be slightly higher in pastures and forage soils, contributing to a slower and more sustained organic matter mineralization.
In contrast, cropland soils frequently showed elevated phosphorus concentrations, most likely due to the overuse of mineral-based fertilizers. This underscores the significance of careful phosphorus management to mitigate potential ecological implications.
Soils influenced by pastures and forages reportedly maintained pH values closer to neutrality when compared to croplands. This tendency can be partly explained by the pH buffering characteristics of soils with higher SOM. The complex interplay of organic compounds in the soil acts as a buffering system, stabilizing pH levels and mitigating abrupt fluctuations that could disrupt plant nutrient uptake (Table 1).

Table 1.
Relative mean differences (%) of soil chemical fertility parameters reported for grassland and cropland species measured at specific soil depths.
The beneficial role of grasslands in soil fertility is strongly connected to the agricultural practices used and the crops grown. In fact, the precise net impact of grasslands on the overall improvement of soil fertility may be undervalued due to the difficulty in adequately implementing control plots for diverse land uses with varying levels of mineral fertilizer application.
Generally, great focus has been given to the topsoil layer, given its crucial role in plant nutrition [9]. This soil layer is the most bioactive part of agricultural soils since beneficial microbial communities that can fix atmospheric N2 and solubilize phosphorus are deeply dependent on the proximity to the plant’s roots [31,32]. Furthermore, the impact of land use is prone to diminish with the increase in soil depth, putatively related to the volume explored by the root system of the crops. On the other hand, root architecture can substantially alter the depth of the soil layers that can be influenced [33]. Therefore, the traditional combination of grasses and legumes is a proficient approach for more comprehensive soil volume exploration, with the added benefit of enhancing rhizosphere microbial activity [34].
4. Conclusions
The study of the beneficial role of grasslands for soil fertility can reveal novel means to improve food sustainably. Several fertility parameters were found to be greater in pastures and forages than in croplands. Switching to an eco-friendlier crop production system supported by the integration of grasslands into sustainable agricultural practices may improve crop yields, soil health, and biodiversity and provide other benefits in the long term.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.C., M.O.T. and J.M.S.F.; methodology, T.C. and J.M.S.F.; formal analysis, T.C.; investigation, T.C.; data curation, T.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.C.; writing—review and editing, T.C., M.O.T. and J.M.S.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The Story of Phosphorus: Global Food Security and Food for Thought. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, G.; Licciardo, F.; Verrascina, M.; Zanetti, B. The Agroecological Approach as a Model for Multifunctional Agriculture and Farming towards the European Green Deal 2030—Some Evidence from the Italian Experience. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.H.; Verweij, S.E.; Janssen, S.J.C.; De Haan, J.; Fujita, Y. An Open Soil Health Assessment Framework Facilitating Sustainable Soil Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17375–17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, L.K.; Murphy, D.V. What Is Soil Biological Fertility? In Soil Biological Fertility: A Key to Sustainable Land Use in Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, R.P. Soil Health Paradigms and Implications for Disease Management. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Barrulas, P.; Pinto, A.P.; Brito, I.; Teixeira, D.M. Mycorrhizal Colonization of Wheat by Intact Extraradical Mycelium of Mn-Tolerant Native Plants Induces Different Biochemical Mechanisms of Protection. Plants 2023, 12, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, C.K.; Saraf, M. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): A Review. J. Agric. Res. Dev. 2015, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, D.; Orlando, V.; Collett, R.L.; Moreira, D.; Costa, S.R.; Inácio, M.L. Linking Nematode Communities and Soil Health under Climate Change. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Pearson: Columbus, OH, USA, 2016; Volume 910. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, R.; Kukal, S.S.; Hira, G.S. Soil Physical Fertility and Crop Performance as Affected by Long Term Application of FYM and Inorganic Fertilizers in Rice–Wheat System. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, F.P. The Role of Grasslands in Food Security and Climate Change. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, G.; Aguilera, G.; Öckinger, E. Grasslands Enhance Ecosystem Service Multifunctionality above and Below-Ground in Agricultural Landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondini, M.; Martin, M.; De Camillis, C.; Uwizeye, A.; Soussana, J.-F.; Robinson, T.; Steinfeld, H. Global Assessment of Soil Carbon in Grasslands. In From Current Stock Estimates to Sequestration Potential; FAO Animal Production and Health Paper, 187; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cantú Silva, I.; Yáñez Díaz, M.I. Effect of the Change of Land Use on the Contents of Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2018, 9, 122–151. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Yu, P.; Zhu, X.; Sun, T.; Jia, H. Relationships between soil physiochemical properties and soil respiration under different land uses in an alpine grassland during freeze-thaw period. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 7364–7373. [Google Scholar]
- Kharal, S.; Khanal, B.R.; Panday, D. Assessment of Soil Fertility under Different Land-Use Systems in Dhading District of Nepal. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolando, J.L.; Dubeux, J.C.B.; Ramirez, D.A.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.; Turin, C.; Mares, V.; Sollenberger, L.E.; Quiroz, R. Land Use Effects on Soil Fertility and Nutrient Cycling in the Peruvian High-Andean Puna Grasslands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shao, M. Soil Fertility Increases Rapidly during the 6-10 Yr Following Conversion of Cropland to Grassland in China’s Loess Plateau Region. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 98, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Olesen, J.E.; Jensen, M.L.; Sørensen, P.; Christensen, B.T. Converting Temperate Long-Term Arable Land into Semi-Natural Grassland: Decadal-Scale Changes in Topsoil C, N, 13 C and 15 N Contents. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja, J.C.M.; Campos, M.C.C.; de Lima, A.F.L.; da Cunha, J.M.; Simões, E.L.; de Oliveira, I.A.; Silva, L.S. Multivariate Analysis in the Evaluation of Soil Attributes in Areas under Different Uses in the Region of Humaitá, AM. Rev. Ambiente Água 2019, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damene, S.; Bahir, A.; Villamor, G.B. The Role of Chomo Grass (Brachiaria humidicola) and Exclosures in Restoring Soil Organic Matter, Total Nitrogen, and Associated Functions in Degraded Lands in Ethiopia. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Ezequiel Furch, N.; Bissolino, M.; Frasier, I.; Daniel Scherger, E.; Raul Quiroga, A. Effect of perennial pastures in physical and biological fertility in Mollisols of the semiarid Pampas region. Cienc. Del Suelo 2020, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, A.; Poeplau, C.; Weiser, C.; Fahrion-Nitschke, A.; Don, A. Exports and Inputs of Organic Carbon on Agricultural Soils in Germany. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2020, 118, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyameasem, J.K.; Reinsch, T.; Taube, F.; Yaw Fosu Domozoro, C.; Marfo-Ahenkora, E.; Emadodin, I.; Malisch, C.S. Nitrogen Availability Determines the Long-Term Impact of Land Use Change on Soil Carbon Stocks in Grasslands of Southern Ghana. SOIL 2020, 6, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatokhin, A.A.; Chamurliev, O.G.; Zelenev, A.V.; Chamurliev, G.O.; Vorontsova, E.S. Field Crop Rotations in Organic Agriculture of the Volgograd Region. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 27, 00152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankó, L.; Tóth, G.; Marton, C.L.; Hoffmann, S. Hot-Water Extractable C and N as Indicators for 4p1000 Goals in a Temperate-Climate Long-Term Field Experiment: A Case Study from Hungary. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Das, M.; Sarkar, A. Distinct Nature of Soil Organic Carbon Pools and Indices under Nineteen Years of Rice Based Crop Diversification Switched over from Uncultivated Land in Eastern Plateau Region of India. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.S.; Dechow, R.; Flessa, H. Inventory and Assessment of PH in Cropland and Grassland Soils in Germany. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2022, 185, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrip, H.; Schwartz, R.C.; He, Z.; Todd, R.W.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Zhang, M.; Parker, D.; Brauer, D.; Min, B.R. Soil Water Extractable Organic Matter under Long-Term Dryland Cropping Systems on the Texas High Plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraka, T.; Elias, E.; Lelago, A. Effects of Land-Use-Cover-Changes on Selected Soil Physicochemical Properties along Slope Position, Coka Watershed, Southern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaz, A.; Elhaissoufi, W.; Khourchi, S.; Benmrid, B.; Borden, K.A.; Rchiad, Z. Benefits of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria on Belowground Crop Performance for Improved Crop Acquisition of Phosphorus. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.M.; Teixeira, K.R. dos S. Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria in the Family Acetobacteraceae and Their Role in Agriculture. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villordon, A.Q.; Ginzberg, I.; Firon, N. Root Architecture and Root and Tuber Crop Productivity. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, S.T.; Beniston, J.; Glover, J.D.; Hodson, A.; Culman, S.W.; Lal, R.; Ferris, H. Root Traits and Soil Properties in Harvested Perennial Grassland, Annual Wheat, and Never-Tilled Annual Wheat. Plant Soil 2014, 381, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).