Abstract
A functional product obtained from beet molasses vinasse (V) was supplemented to hypertensive rats (SHR) to assess its preventive effects against high blood pressure and endothelial dysfunction. Fifteen potential bioactive compounds (including phenolic acids, flavonoids and terpenoids, and glycosylated compounds) were identified and quantified in V by HPLC-MS. The most notable finding of the study was that the blood pressure values remained similar to those at the beginning of the study in the SHR+V group. At the same time, they increased progressively in the SHR control group, reaching a significant difference of 16% (p < 0.05) after 5 weeks of supplementation. Quantitative PCR and Western blot analyses of the aorta demonstrated that V ingestion by hypertensive rats led to decreased ACE mRNA levels and higher SOD2 and eNOS gene expression via promotion of Nrf2 transcriptional activity and down-regulation of the NF-κB pathway. These results are associated with an increased antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vasodilatory response. In conclusion, the intake of vinasse-derived products could mitigate hypertension and associated endothelial dysfunction.
1. Introduction
The relationship between arterial hypertension and oxidative stress has been extensively studied, both factors being involved in endothelial dysfunction [1]. Endothelial dysfunction is responsible for key processes in the vasculature. These include vasoconstriction, leukocyte infiltration, increased vascular permeability, and smooth muscle proliferation in the vascular wall. Such events have been implicated in developing hypertension and cardiovascular disorders [2]. Several redox signaling mechanisms are involved in developing oxidative stress and hypertension. In this regard, oxidative stress modulates the expression of antioxidant and pro-oxidant enzymes through Nrf2/NF-κB transcription factors and decreases NO bioavailability [3].
According to various studies, foods with a high polyphenol content can improve vascular function and reduce arterial pressure [4]. Polyphenols can act through several antioxidant and antihypertensive mechanisms, such as regulation of Nrf2/NF-κB pathways and radical scavenging. Vinasse is a liquid by-product of the sugar and ethanol industry. The vinasses of beet molasses are obtained after distilling the alcohol and concentrating the solution. They contain large amounts of inorganic salts, amino acids, humic acids, betaine, and other organic compounds. Phenolic, terpenoids, alkaloids, and melanoidins have been described as important bioactive compounds present in molasses [5,6] and, from the perspective of the circular economy, those compounds that remain in vinasse may favor its valorization as a functional food and feed ingredient.
This study aimed to evaluate the preventive effect against endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive rats (SHR) of the daily intake for 5 weeks of a functional product obtained from beet molasses vinasse with antioxidant properties.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Functional Product Obtained from Beet Molasses Vinasse (V)
The vinasse was produced in the Azucarera del Guadalfeo S.A (Lobres, Granada, Spain) from beet molasses. It was submitted to a pasteurization treatment (100 °C for 10 min) to generate a safe and stable functional product (V). The proximal composition (p/p wet matter) of V was 87% water, 4.6% protein, 7.1% total carbohydrates, <0.9% fat, 0.4% soluble fiber, 0.3% insoluble fiber, and 1,6% ashes (0.9% K, 0.3% Na).
2.2. HPLC-MS Analysis of Polar Bioactive Compounds
Diluted samples of the V product were analyzed using an Agilent RRLC 1200 series liquid chromatograph (Agilent Technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with a diode array detector and an Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 1.8 µm particle size) (Agilent Technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). The mobile phases used were water with 0.1% formic acid as phase A and acetonitrile as phase B, with the following optimized gradient: 5% phase B, 20 min 45% B, 30 min 95% phase B, 2 min 5% B. The flow was 0.8 mL/min, and the column temperature was maintained at 40 °C. Compounds were detected with a Bruker Daltonics microTOF II time-of-flight mass detector (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with an ESI interface from Agilent Technologies (positive ionization mode, mass range of 50–1000 m/z) Bruker Daltonics microTOF II. Ultrapure nitrogen was used as ionization and drying gas (2 bar and 9 L/min flow, 190 °C, 4500 V capillary voltage, and −500 V end plate offset). To perform the quantification, 9 calibration levels were prepared from commercial standards (gallic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, schaftoside, and an acetylneuramic acid derivative, Sigma-Aldrich Co., St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.3. Animals, Experimental Groups, and General Procedures
All procedures with animals followed the Spanish and European laws and were approved by the Ethics Committee for Experimental Animal Care at the University of Burgos. In this study, 12-week-old male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) and Wistar–Kyoto (C) control rats were assigned to 4 groups: normotensive (C, n = 4), normotensive supplemented (C+V, n = 4), hypertensive (SHR, n = 6), or hypertensive supplemented (SHR+V, n = 6). The animals were maintained at 21 ± 2 °C and humidity at 40 ± 10%, with a 12:12 h light:dark cycle and free access to food (LASQCdiet® Rod14-H, Sodispan, Madrid, Spain) and water. Rats were supplemented daily with V product (0.5 mL = 62.5 mg solid product dissolved in 2 g of yogurt) or a salt-equivalent yogurt with 3.87 mg of salt for 5 weeks.
2.4. Blood Pressure Measurement
Blood pressure was recorded every week before supplementation in conscious, pre-warmed, restrained rats by the tail-cuff plethysmographic method using a LE 5001 Pressure Meter (Panlab, Barcelona, Spain) and a pulse transducer for rat model LE160R (Panlab).
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
Total RNA was isolated from aortic tissue using TRI Reagent solution (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), treated with DNase I and reverse-transcribed (1 μg of total RNA; First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and amplified using SG qPCR Master Mix (EURx) and qPCR conditions: 95 °C, 3 min; 45 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. The sequences of primer sets (forward and reverse) were: Nrf2, 5′-AGAAGTACCTGTGAGTCC-3′ and 5′-CTCTCCTGCGTATATCTC-3′; NF-κB, 5′-ACGATCTGTTTCCCCTCATCT-3′ and 5′-TGCTTCTCTCCCCAGGAATA-3′; eNOS, 5′-TATTTGATGCTCGGGACTGC-3′ and 5′-AACGAAGATTGCCTCGGTTT-3′; SOD2, 5′-AAGGTCGCTTACAGATTGCC-3′ and 5′-CTCCCACACATCAATCCCC-3′; ACE, 5′-TGGAGCATCTCTACCACCAA-3′ and 5′-TGTATTTGTCCCCATAGCGG-3′; GAPDH, 5′-ACTCCCTCAAGATTGTCAGC-3′ and 5′-CTTCCACGATGCCAAAGTTG-3′. Results were obtained using the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Relative gene expression was expressed as folds of change compared to the control group (C).
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
A Western blot was performed to analyze the expression of phosphorylated forms of Nrf2 and NF-κB. Briefly, aortic tissue was homogenized and total protein was extracted using Laemmli buffer (100 °C, 5 min) and then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and incubated overnight with rabbit-specific primary antibodies (1:1000) against Nrf2 [EP1809Y], phospho-Nrf2 (S40) [EP1809Y], NF-κB-p65, phos-phor-NF-κB-p65 (Cell Signaling Technology), and β-actin (Sigma-Aldrich). Then, the membranes were incubated with a horseradish-peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody anti-rabbit (1:3000, Anti-rabbit IgG-HRP-linked). Immunodetection was performed with an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Clarity Western ECL substrate, Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA) and developed using autoradiography. Using Fiji ImageJ 1.52b software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), protein bands were quantified by densitometry, and their relative amounts were normalized to the housekeeping protein β-actin.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using the Statgraphics Centurion 19 software (Statgraphics Technologies Inc., Warrenton, VA, USA). Results were reported as the mean ± standard deviation. Results were subjected to an analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey post hoc test to establish statistical differences among mean values. The statistical significance level was set up at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Polar Bioactive Compounds in V Functional Product
Table 1 shows the main compounds identified in the V product by HPLC-TOF-MS analysis proposed for each chromatographic peak along with their retention time, m/z, error, molecular formula, description, and concentration in the liquid product. Eleven different phenolic compounds (both phenolic acids and flavonoids, several of them glycosylated), an amino acidic derivative of sialic acid, an iridoid terpene, and two fatty acids (or an auxin derivative) were found, with feruloyl-methyldopamine and the three derivatives of gallic acid being the most abundant.

Table 1.
Identification and quantification of polar compounds in the V product by HPLC-TOF-MS.
3.2. Systolic Blood Pressure Levels in SHR during the 5-Week V Supplementation
Figure 1 shows the effects on systolic blood pressure (SBP) of supplementing the diet of hypertensive (SHR) and control (C) rats for 5 weeks with the functional product derived from vinasses (V) or an equivalent amount of salt as a control of supplementation. Blood pressure at the beginning of the study was significantly 1.3 times higher in the hypertensive rat groups than in the controls. The control groups remained unchanged throughout the study, with no effect of the functional ingredient observed. In contrast, blood pressure in the hypertensive control rats (SHR) group increased significantly from 171 to 199 mmHg. At the same time, it remained stable in the SHR+V group throughout the 5 weeks of supplementation, being 16% significantly lower compared to the SHR control group at the end of the study. Other authors observed reduced SBP in SHR rats supplemented with polyphenol-rich dietary by-products [7,8].
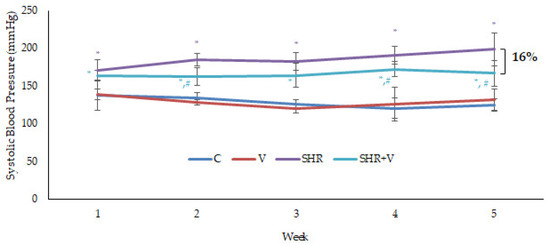
Figure 1.
Blood pressure of hypertensive (SHR) and control (C) rats supplemented daily with salt or with the vinasse-derived product (V). Results are mean ± SD of n = 4 (control groups) and n = 6 (hypertensive groups). The asterisk indicates statistical differences between hypertensive groups and control. The number sign (#) indicates the statistical difference between SHR and SHR+V groups.
3.3. Gene and Protein Expression of Transcription Factors and Enzymes Implicated in Endothelial Dysfunction and the Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Response
There is a close relationship between hypertension and oxidative stress. The main mechanism of endothelial dysfunction is an imbalance between the production of nitric oxide (NO) by vascular endothelial cells and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), resulting in a decrease in NO bioavailability and an excessive accumulation of ROS, leading to oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and DNA. In this context, the transcription factor Nrf2 is an important regulator of the gene expression of antioxidant enzymes (SOD2, CAT, HO), whereas the factor NF-κB modulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation [1].
Another important factor in the development of oxidative stress in hypertension is the over-activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS). Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays an important role in the RAS, converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which is responsible for the increase in blood pressure through its vasoconstrictive effect and stimulating the production of ROS by endothelial cells via several pathways; one of the most important being the enzyme NADPH oxidase, which generates the superoxide radical. In both humans and experimental animals, hypertension has been associated with increased oxidative stress mediated by NADPH oxidase and activation and/or overexpression of ACE [9].
Therefore, in this study, we evaluated by q-PCR the effect of supplementation with a vinasse product (V) in thoracic aortas of the control (C) and hypertensive (SHR) rats on gene expression of the transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB and the enzymes SOD2, eNOS, and ACE. In addition, the activation of the transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB was assessed by Western blot by evaluating the ratio of the protein concentration of their active (phosphorylated) and total forms.
The gene expression results (Figure 2) indicated that consumption of product V in the control animals did not alter the expression of the NF-κB factor. In contrast, it significantly increased the expression of Nrf2 mRNA. An increase in NF-κB gene expression and a decrease in Nrf2 expression were also observed in the SHR group compared with their C control. In contrast, ingesting the vinasse-derived product in hypertensive rats modulated the expression of both transcription factors by significantly reducing NF-κB and increasing Nrf2. Therefore, the results indicate that consuming the functional vinasse-derived product for 5 weeks induces changes in transcription factors of aortic cells that induce an antioxidant (control and hypertensive groups) and anti-inflammatory response (only in the hypertensive group).
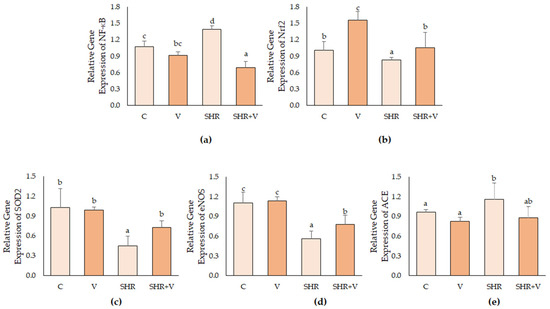
Figure 2.
Gene expression (qPCR) of NF-κB (a), Nrf2 (b), SOD2 (c), eNOS (d), and ACE (e) in thoracic aorta of hypertensive (SHR) and control (C) rats supplemented daily with salt or with the vinasse-derived product (V). Results were represented as relative fold-change concerning the normotensive non-supplemented (C) rats. Results are mean ± SD of n = 4 (control groups) and n = 6 (hypertensive groups). Different letters indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences between groups.
The gene expression of the three enzymes analyzed is also shown in Figure 2. As mentioned above, these three enzymes play an important role in the regulation of oxidative stress and hypertension: superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) is involved in the modulation of superoxide levels, exerting an antioxidant effect; the enzyme eNOS acts as a regulator of endothelial nitric oxide levels, the main vasodilator; and the enzyme ACE, whose product angiotensine II is a potent vasoconstrictor and inducer of free radical generation in endothelial cells. No effect of V supplementation was observed in the control rats. However, hypertensive rats had significantly reduced levels of SOD2 and eNOS gene expression and overexpression of ACE. In contrast, V supplementation modulated the changes associated with oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and hypertension, and the mRNA levels of these enzymes in the SHR+V group were more similar to those in the control groups. These results agree with other authors who observed the antioxidant effect of sugarcane molasses vinasse in vitro [10].
Lastly, Figure 3 shows the effect of V supplementation on NF-κB and Nrf2 transcription factor protein activation in the control and hypertensive rat aortas by Western blot. V intake did not alter the expression of any transcription factors in the control rats. Hypertension significantly increased the expression of NF-κB, a regulator of pro-inflammatory processes, and decreased the levels of Nrf2, a regulator of antioxidant mechanisms, compared to the control group. In hypertensive rats, it was observed that the supplementation with V modulated the pro-inflammatory factor NF-κB, reducing its activation levels to the same level as in the control group. However, the activity of the phosphorylated active form (p-Nrf2) was modulated but remained lower than in controls. Other authors observed these antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects for some polyphenols such as ferulic acid [11,12], a phenolic acid that derives some of the major potential bioactive compounds in the V product.
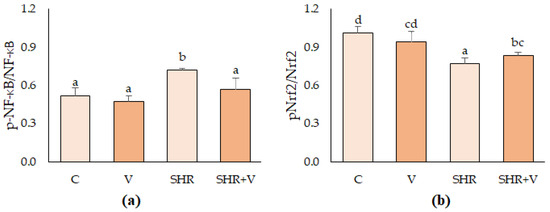
Figure 3.
Activation of NF-κB (a) and Nrf2 (b) transcription factors in thoracic aorta of hypertensive (SHR) and control (C) rats supplemented with salt or with the vinasse-derived product (V). The graphs represent the densitometry results of the phosphorylated factors concerning the total. Results are mean ± SD of n = 4 (control groups) and n = 6 (hypertensive groups). Different letters indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences between groups.
Therefore, 5 weeks of vinasse-derived functional product (V) intake could modulate aortic cell transcription factor gene expression and protein activation, inducing an antioxidant (in both the control and hypertensive groups, by increased/normalized Nrf2 mRNA levels) and anti-inflammatory response (observed only in hypertensive rats, by reduced NF-κB gene expression and protein activation in the supplemented groups).
4. Conclusions
The ingestion of a functional product extracted from beet molasses vinasse for a 5-week period led to a reduction in blood pressure in hypertensive rats. This improvement was accompanied by notable changes in the redox state with modifications in the expression of enzymes associated with an increased in antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vasodilatory response in the rats’ aortas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.P.-G. and P.M.; methodology, G.G., M.C.-S., G.L.-G. and M.A.L.-B.; investigation, G.G., M.C.-S., P.M. and R.D.P.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, G.G. and R.D.P.-G.; writing—review and editing, M.C.-S. and P.M.; supervision, R.D.P.-G. and P.M.; project administration, R.D.P.-G.; funding acquisition, R.D.P.-G. and P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Junta de Andalucía and the European Union (FEDER), grant number PY18-CO-0047 (AZUBIOACT project), with the collaboration of the Azucarera del Guadalfeo S.A. M.A. López-Bascón is grateful to “Consejería de Transformación Económica, Industria, Conocimiento y Universidades de la Junta de Andalucía” for a postdoctoral researcher contract (POSTDOC_21_00031). G.L.G.’s postdoctoral contract is with the Juan de la Cierva Formación-2021 (FJC2021-047564-I) and is funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and the European Union “NextGenerationEU/PRTR”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The company that supplied the vinasses co-financed the AZUBIOACT project, since collaboration with the business was required to obtain the regional public aid granted.
References
- Wang, L.; Cheng, C.K.; Yi, M.; Lui, K.O.; Huang, Y. Targeting Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2022, 168, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ilyas, I.; Little, P.J.; Li, H.; Kamato, D.; Zheng, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, J.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases and beyond: From Mechanism to Pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 924–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casper, E. The Crosstalk between Nrf2 and NF-NF-ΚB Pathways in Coronary Artery Disease: Can It Be Regulated by SIRT6? SSRN J. 2022, 330, 122007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K.; Yamori, Y. Inhibition of Endothelial Dysfunction by Dietary Flavonoids and Preventive Effects against Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, V.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Di Nunzio, M.; Danesi, F.; Caboni, M.F.; Bordoni, A. Sugar Cane and Sugar Beet Molasses, Antioxidant-Rich Alternatives to Refined Sugar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12508–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Meng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, S. Antioxidant and In Vitro Anticancer Activities of Phenolics Isolated from Sugar Beet Molasses. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, G.; Cavia-Saiz, M.; Rivero-Pérez, M.D.; González-SanJosé, M.L.; Muñiz, P. Wine Pomace Product Modulates Oxidative Stress and Microbiota in Obesity High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández-Sobrino, R.L.; Soliz-Rueda, J.R.; Suárez, M.; Mulero, M.; Arola, L.; Bravo, F.I.; Muguerza, B. Study, Effect of Dealcoholization and Possible Mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siti, H.N.; Kamisah, Y.; Kamsiah, J. The Role of Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Vascular Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease (a Review). Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, R.; Zhao, Z. Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Recovered Phenolics with Antioxidant and Antihyperglycemic Potential from Sugarcane Molasses Vinasse. Foods 2022, 11, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A. Anti-Hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, S.; Zheng, J.; Gong, X.; Xiao, B. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Alveolar Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway and Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).