Abstract
In Portugal, there are four venomous species, the horned viper (Vipera latastei), seoane (Vipera seoanei), rat snake (Malpolon monspessulanus), and the hooded snake (Macroprotodon brevis ibericus), and in the UK, there is one: the common European adder (Vipera berus). Snake venom is a complex mixture of toxins whose composition varies depending on the family, genera, species, and even subspecies. In Europe, particularly Portugal, there are no published data on the frequency of these types of incidents, but it is estimated to be high, mainly in dogs. Thus, to characterize the injuries caused by the bite of venomous snakes in domestic animals, the authors describe cases in dogs, cats, and goats with a suspected snakebite. Animals presented wounds compatible with snakebites, with two points 1 to 1.8 cm apart that could be noted on the head or limbs. The main clinical signs observed included pain, oedema, and necrosis. From the animals that died, a post-mortem examination revealed subcutaneous and muscular necrosis and hemorrhages of surrounding tissues, including muscles and organic hemorrhages. The severity of envenomation depends on the quantity of inoculated venom; the species, age, size, and previous state of health of the bitten animal; the bite location; and post-bite excitability. With this study, the authors hope to help improve the knowledge regarding snakebites in Europe.
1. Introduction
There are 3000 snake species worldwide, but only 15% are considered venomous [1]. Venomous snake species can be broadly grouped into three families: Colubridae, Elapidae, and Viperidae. In Europe, 11 species are venomous [2]. In Portugal, there are four venomous species, the horned viper (Vipera latastei), seoane (Vipera seoanei), rat snake (Malpolon monspessulanus), and the hooded snake (Macroprotodon brevis ibericus), and in the UK there is one: the common European adder (Vipera berus) [3,4] (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
(A) Vipera latastei; (B) Vipera seoanei; (C) Malpolon monspessulanus; (D) Macroprotodon brevis ibericus; (E) Vipera berus (Creative commons License Wikipedia).
They possess canaliculated venom devices, that is, hollow fangs located anteriorly in the maxilla, associated with a venom gland, whose content is inoculated at high pressure by gland compression by skeletal muscle fibers [5]. Snake venom is a complex mixture of toxins, the composition of which varies depending on the family, genera, and species [6]. In this mixture, it is possible to find enzymes (serine proteases, zinc metalloproteases, phospholipase A2 (PLA2), fibrinogenases, factor X, and prothrombin, among others) L-amino acid oxidases, and proteins without enzymatic activity (natriuretic peptides, disintegrins, Kunitz-type protease inhibitor, cysteine, type C lecithin, neuronal, vascular and endothelial growth factors, and protein secretions rich in cysteine (CRISP)). Different types of PLA2 isoenzymes are responsible for hemolysis, myotoxicity, presynaptic and postsynaptic neurotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, oedema, and pro- or anti-coagulant effects [7]. The factors responsible for the severity of envenomation are the amount and dangerousness of the inoculated venom; the species, age, size, and previous state of health of the bitten animal; bite location; and post-bite excitability [8].
The main manifestations caused by the venom of ophidians are pain of varying intensity, oedema, hemorrhages, changes in the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea), neurological signs (ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, ptyalism, dysphagia, lethargy), respiratory changes, leukocytosis, anemia, and thrombocytopenia [7,8].
Snakebite envenoming is an acute and potentially life-threatening disease affecting humans and domestic animals. It is a major issue in rural communities [9]. It is estimated that 150,000 animals (mainly dogs and cats) are bitten by snakes in the United States annually, with reported canine mortality frequencies ranging from 1 to 30% [1]. The annual incidence of poisoning of humans in Europe varies between 4000 and 20,000 cases; the incidence in animals is believed to be 30 times higher and with a higher mortality rate of 3.5–14% [10]. The data on snakebites in domestic animals are dispersed and still scarce in various regions. Therefore, the real number of animals affected every year in Europe is unknown at the moment [11]. With the cases presented, the authors hope to help improve the knowledge regarding snakebites in Europe.
2. Material and Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of domestic animals admitted with snakebites to the Veterinary Hospital of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro (Vila Real, Portugal), Santa Marinha Veterinary Clinic (Avanca, Portugal), and Calweton Veterinary Group (Callington, UK) from 2020 to 2023. This study included animals where two fang marks were observed at the wound site or the owners were witnesses of the attack.
3. Results
This study involved eight animals from Portugal and the United Kingdom, including one feline, two goats, and six canids. The dogs were from four breeds, including Labrador Retriever (one), Whippet (one), Springer Spaniel English (two), and Collie (one). The cat was of mixed breed. Overall, 20% (one) of dogs were males and 80% (four) were females. The cat was a male (one). Both goats were females (two). The age of the animals was between 3 and 12 years.
The bite wounds were localized on the face (62.5%, 5/8), neck (12.5%, 1/8), and limbs (12.5%, 1/8). The clinical signs observed on presentation in all cases were oedema and erythema. All the dogs survived. The cat and the goats did not survive. Antivenom was administrated only in two animals; the remaining animals were treated with support treatment.
Next, we present three cases in detail, one from a dog and the other from a cat.
3.1. Feline, Neutered Male, Three Years Old
According to the owners, the animal disappeared for one day and when it returned, it was staggering, was very exhausted, and had anorexia. Regarding the region where this animal lived, the most probable species responsible for the bite was Malpolon monspessulanus or Vipera latastei.
On physical examination, the temperature was 41.7 °C and the right hind limb was edematous, especially in the tarsal area, painful to the touch, and without support. The animal was hospitalized and treated with IV fluids, and antibiotic therapy (enrofloxacin and amoxicillin + clavulanic acid) was started. Twelve hours after admission, it presented a generalized tonic–clonic seizure treated with IV diazepam. Radiography of the limb was performed (Figure 2) and blood was taken for analysis, where leukopenia with neutropenia and increased ALT, creatinine, and urea were observed (Table 1).
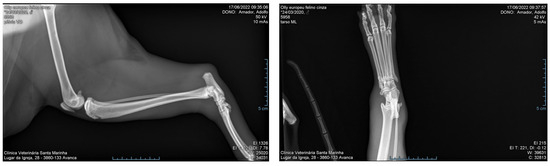
Figure 2.
Radiography of the right hind limb of a male cat 12 h after a snakebite.

Table 1.
Values of biochemical parameters in a snakebite in a cat.
After 24 h, a hematoma began to form on the inner thigh, with a small area of skin in the center starting to necrose. In the following days, the limb became more edematous, the area of necrotic skin increased, and the animal remained prostrate. However, its temperature was within normal values. An ultrasound was performed (Figure 3), where a slightly hypoechoic pancreas and a slight generalized peritoneal reaction were observed.
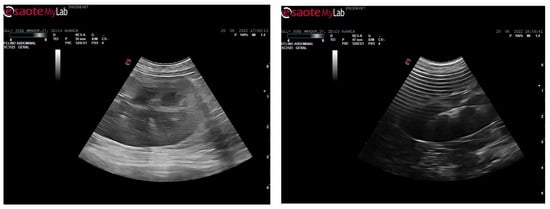
Figure 3.
Abdominal echography with hypoechoic pancreas and slight generalized peritoneal reaction in a cat bitten by a venomous snake.
On the third day of hospitalization, the animal had a fever, and the antibiotic therapy was changed to enrofloxacin, metronidazole, and ceftriaxone. After three days, its temperature returned to normal values, but the necrotic lesion continued progressing, and generalized edema throughout the body was observed. Transfusion of fresh frozen plasma was performed on the sixth day of hospitalization, as he had hypoalbuminemia, but he did not show improvement and died after two days. Necropsy was not performed.
3.2. Canine, Whippet, Neutered Female, Four Years
The owners did not see the viper (Vipera berus) but there are plenty in the surrounding area. After the animal had been sniffing the grass, the animal became lethargic, with its head down, and started swelling around the mouth/face (Figure 4).
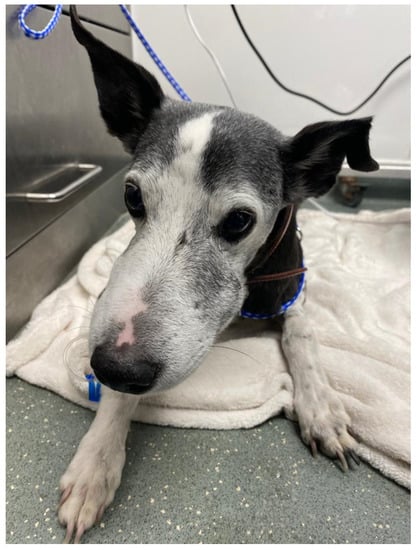
Figure 4.
Oedema of the face and mouth in a female dog bitten by a venomous snake.
On physical examination, it was panting, had a temperature of 38.3 °C, and had swelling around the mouth that went towards the ventral head which was painful to the touch and did not allow head manipulation. The animal was admitted and placed on IV fluids, with meloxicam, chlorpheniramine, and buprenorphine; a fan was also set to help to cool it down. The owners declined antivenom. Blood tests were performed (Table 2).

Table 2.
Values of the biochemical parameters 24 h after snakebite.
During the night, the animals breathing stabilized, although its face became more swollen. Swelling progressed to the axilla region and paracetamol was added to the treatment. The animal was comfortable on the second day of treatment, so it was sent home with Synulox, Metacam, Mirtazapine, Prevomax, Omeprazole, and Hills A/D. At home, she continued to not eat, and oedema spread down to the front legs. The animal was readmitted again and treated with IV fluids, Piriton, Dexadreson, Synulox, Prevomax, and omeprazole. A small cut was noticed on the left side of the neck with some necrotic skin that was removed (Figure 5). The animal fully recovered.
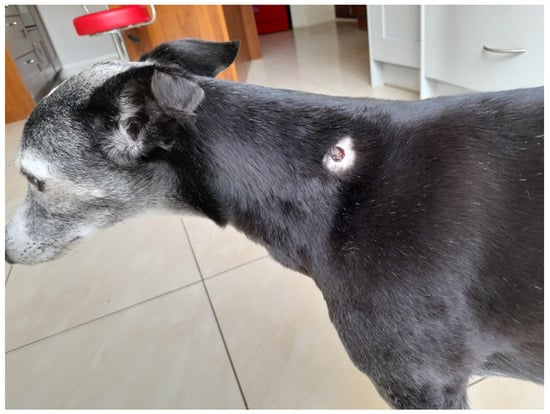
Figure 5.
Possible snakebite wound in a dog.
3.3. Small Ruminant, Autochthonous Bravia Goats, Female, Adult
Two animals presented lethargy, bowed heads, and oedema of the face. In addition, bite marks were observed on the face and neck. In the region where this animal lived, the most probable responsible species for the bite was Malpolon monspessulanus, Macroprotodon brevis, or Vipera latastei. Unfortunately, both animals died before initiating treatment due to oedema of the glottis (Figure 6).
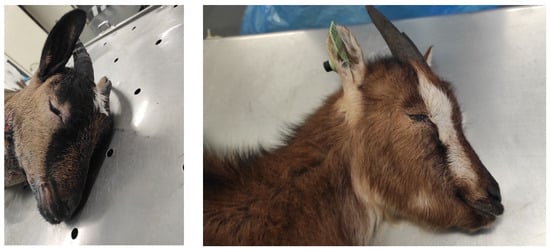
Figure 6.
Oedema of the face and mouth in two goats bitten by a venomous snake.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
In the present study, snakebites were mostly observed in the head region or on the limbs, findings that are consistent with other studies [1,12]. These results might suggest that dogs are prone to intentional contact with vipers when playing in the fields or when they are guard animals [13]. Additionally, due to these behavioral characteristics in dogs, most snakebites occur in the distal parts of the limbs or head region [1]. One study reported that young, mature dogs of medium to large breeds are most commonly bitten by snakes [12]. This was also observed in this study.
Most animals had oedema and erythema, and only a small number presented cyanosis and tissue necrosis. These findings may be of non-venomous snakebites or “dry” bites, which induce insufficient envenomation [1].
The standard treatment protocol for snake envenomation needs to be improved for domestic animals; at the moment, the only accepted treatment is the administration of antivenom and supportive care (intravenous crystalloid fluid therapy and pain control) [14]. Antivenom limits clinical signs and reverses coagulopathy; unfortunately, due to the high price, many owners cannot afford this treatment.
The present study has several limitations owing to its retrospective design. Medical records were occasionally incomplete because data from three different animal hospitals were collected for analysis due to the low incidence of snakebites in animals in Portugal. The majority of cases occurred in the UK. Although snakebites in small animals in some regions of Europe are an uncommon medical problem, they should be considered as they can eventually lead to death, as observed in one case. In the future, more studies are necessary to help improve triage and treatment of animal victims of snakebites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.; methodology, A.G., C.P., M.I.S., J.P. and I.P. software, A.G. and I.P.; validation A.G., J.P., F.S. and I.P.; formal analysis, A.G. and I.P.; investigation, A.G. and I.P.; resources, A.G. and I.P.; data curation, A.G. and I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.; writing—review and editing, A.G., J.P., F.S., C.P., M.I.S. and I.P.; visualization, A.G. and I.P.; supervision, A.G. and I.P.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, I.P., J.P. and F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The participation of Pires I, Prada J., Silva F. was supported by the projects UIDB/CVT/00772/2020 and LA/P/0059/2020, funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). (Project UIDB/CVT/0772/2020). The participation of Garcês A. was supported by National Funds from FCT Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the project UIDB/04033/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.-K.; Lim, J.H.; Choi, G.; Bae, S.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Jang, M. Clinical Features and Management of Snake Bites in 70 Dogs in Korea. J. Veter Sci. 2022, 23, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paro, B. The 11 VENOMOUS SNAKES Found in Europe! (ID Guide). Bird Watching HQ. Available online: https://birdwatchinghq.com/venomous-snakes-of-europe/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Cabral, M.; Almeida, J.; Almeida, P.; Dellinger, T.; Ferrand de Almeida, M.; Oliveira, M.; Palmeirim, J.; Queirós, A.; Rogado, L.; Santos-Reis, M. Livro Vermelho Dos Vertebrados de Protugal; Instituto da Conservação da Natureza: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/es (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Palci, A.; LeBlanc, A.R.H.; Panagiotopoulou, O.; Cleuren, S.G.C.; Mehari Abraha, H.; Hutchinson, M.N.; Evans, A.R.; Caldwell, M.W.; Lee, M.S.Y. Plicidentine and the Repeated Origins of Snake Venom Fangs. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20211391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. (Ed.) Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-0-429-05420-4. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, C.; Nogué, S. Changes in viper bite poisonings. Med. Clin. 2015, 144, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliam, L.L.; Brunker, J. North American Snake Envenomation in the Dog and Cat. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 1239–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolon, I.; Babo Martins, S.; Ochoa, C.; Alcoba, G.; Herrera, M.; Bofia Boyogueno, H.M.; Sharma, B.K.; Subedi, M.; Shah, B.; Wanda, F.; et al. What Is the Impact of Snakebite Envenoming on Domestic Animals? A Nation-Wide Community-Based Study in Nepal and Cameroon. Toxicon X 2021, 9–10, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, F.M.S.; Casewell, N.R.; Al-Abdulla, I.; Landon, J. Production and Assessment of Ovine Antisera for the Manufacture of a Veterinary Adder Antivenom. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolon, I.; Finat, M.; Herrera, M.; Nickerson, A.; Grace, D.; Schütte, S.; Babo Martins, S.; Ruiz de Castañeda, R. Snakebite in Domestic Animals: First Global Scoping Review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 170, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroch, I.; Harrus, S. Retrospective Study of the Epidemiological, Clinical, Haematological and Biochemical Findings in 109 Dogs Poisoned by Vipera Xanthina Palestinae. Vet. Rec. 1999, 144, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segev, G.; Shipov, A.; Klement, E.; Harrus, S.; Kass, P.; Aroch, I. Vipera Palaestinae Envenomation in 327 Dogs: A Retrospective Cohort Study and Analysis of Risk Factors for Mortality. Toxicon 2004, 43, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armentano, R.A.; Schaer, M. Overview and Controversies in the Medical Management of Pit Viper Envenomation in the Dog. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2011, 21, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).