Abstract
The talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera L.) is an unconventional source of stem starch, with a 76% starch yield. Talipot starch was cross-linked with epichlorohydrin (EPS) and phosphoric acid (PS), which significantly altered the functional, pasting, rheological, and structural properties. Amylose content of talipot starch was significantly decreased and relative crystallinity was increased by cross-linking. The EPS cross-linked talipot starch has a higher swelling capacity and PS cross-linked talipot starch has a lower swelling capacity. A similar trend was observed in the pasting profile, and EPS has higher peak and final viscosities. The native starch gel has a hardness of 45.54 N, which was increased to 149.69 N in EPS, whereas it decreased to 13.62 N in PS. The paste clarity of all the samples was found to be decreased during cold storage. As compared to the native, both EPS and PS exhibited higher paste clarity. The percent syneresis was considerably decreased in cross-linked starch (CLS). The magnitude of both G′ and G″ was significantly changed by cross-linking. The EPS exhibited increased G′ and G″ values, whereas these decreased in PS.
1. Introduction
The plant kingdom is abundant with starch, one of the most important polysaccharide macronutrients. Starch can be extracted from various sources like cereals, pulses, legumes, etc. [1]. Talipot palm is a tropical monocarpic palm inhabitant in southwestern India, Sri Lanka, etc. [2], and is an unconventional source of starch. According to Navaf et al. [3], the talipot palm’s trunk yields an excellent 76% starch, which is equivalent to other unconventional starch sources such as babassu, breadfruit, etc. [4].
Several industries use starch as a raw material, including textiles, paper, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and food. As industrialization grows at a faster rate, there will be a continuous need for native and modified starches [5]. Physical, chemical, and enzymatic processes can readily modify native starch to offer improved starch functionality, which finds uses in a variety of industries [6]. Starch can be modified chemically to enhance its properties for specific purposes. One of the major classes of modified starches is CLS [7]. Starch cross-linking can be achieved by using chemicals like Epichlorohydrin, phosphoryl chloride, sodium trimetaphosphate, sodium tripolyphosphate, phosphoric acid, etc. [8].
Cross-linking adds intramolecular and intermolecular bonds to the starch molecule, resulting in increased granule stability [9] by forming an ester or ether linkage between the cross-linking reagent and the hydroxyl group of starch. Epichlorohydrin is one of the common cross-linking agents, and it forms distarchglycerols while reacting with starch molecules [10]. Phosphoric acid modification results in three simultaneous effects in starch: viz, esterification, cross-linking, and hydrolysis [5].
Talipot flour is one of the new and underutilized starch sources that have to be explored to meet the rising demand for starch in both food and non-food applications. This study aimed to explore the effect of cross-linking agents, viz., epichlorohydrin and phosphoric acid on the functional, pasting, textural, rheological, and structural characteristics of unconventional talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera L.) starch.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starch Isolation
The stem pith flour of the fully grown talipot palm was used to isolate starch using 0.5 M NaOH by the method followed by Navaf et al. [3]. The yield of talipot starch was 76%, and the isolated native starch was labeled as CNS.
2.2. Modification with Epichlorohydrin
Talipot starch was modified with epichlorohydrin by employing the procedure described by Siroha & Sandhu [11] with minor modifications. A 75 mL solution of 0.5% NaOH was added to 50 g of starch. It was then mixed with 0.5% v/w of epichlorohydrin with continuous mixing for 5 h at room temperature using a magnetic stirrer. The pH was then adjusted to 5 using 1M HCl. It was then centrifuged and washed with distilled water many times. Finally, the starch slurry was neutralized using 1 M NaOH and centrifuged. The starch samples were dried in an air oven at 40 °C. The starch sample cross-linked with epichlorohydrin was designated as EPS.
2.3. Modification with Phosphoric Acid
The method reported by Ogunmolasuyi et al. [5] was used to modify talipot starch with phosphoric acid, with minor modifications. A 40% starch suspension was prepared using a 5% phosphoric acid solution. It was then stirred for 1 h using a magnetic stirrer at 50 °C. The cooled slurry was then centrifuged for 5 min at 2000 rpm. The collected starch was hot air dried at 40 °C and designated as PS.
2.4. Amylose Content
The calorimetric method suggested by Williams et al. [12] was used to quantify the amylose content in native and CLSs.
2.5. Swelling Power (SP)
The method adapted by Navaf, Sunooj, Aaliya, et al. [2] was used to investigate the swelling power of native and CLSs. The swelling power was determined using the following equation after taking note of the residue’s final weight.
2.6. Pasting Profile
A Rapid Visco-Analyzer (RVA starch master 2, Newport Scientific, Warriewood, NSW, Australia) was used to determine the pasting properties of native and CLSs. The pasting characteristics, such as peak viscosity (PV), trough viscosity (TV), breakdown viscosity (BV), setback viscosity (SV), and final viscosity (FV) were recorded.
2.7. Gel Textural Properties
A texture profile analyzer (TA-HD plus, 5197, Stable Microsystems Ltd., Godalming, Surrey, GU71YL, UK) was used to determine the textural parameters of native and CLSs by using the method followed by Navaf, Sunooj, Krishna, et al. [13].
2.8. Light Transmittance
The percentage light transmittance of the native and CLS gel was investigated by following the method used by Aaliya et al. [14].
2.9. Rheological Properties
The rheological parameters of native and CLS were analyzed by using a rotational rheometer (Anton Paar instrument, Graz, Austria), by following the procedure described in Navaf et al. [3].
2.10. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
The crystalline characteristic and relative crystallinity of native and CLSs were studied using XRD (BRUKER AXS, D2 PHASER, Karlsruhe, Germany). The relative crystallinity was calculated using the following equation.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Using SPSS software (IBM SPSS statistics 23. IBM Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA), the one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple range test were conducted at a significant difference level of p ≤ 0.05.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Amylose Content
The CNS exhibited a high amylose content of 26.13 ± 0.71%, and it decreased in both EPS and PS to 19.15 ± 0.34 and 21.84 ± 0.51, respectively (Table 1). The formation of ester linkages between starch chains in CLSs causes a decrease in the amylose content. It prevents the iodine amylose complex formation [14]. In general, acid treatment increases amylose content by the hydrolysis of amylopectin to amylose. However, the production of dextrin and the addition of a phosphate functional group may be the reason for the decline in amylose content in phosphoric acid-treated starch [5]. Sharma et al. [15] also observed a reduction in amylose content of faba bean starch cross-linked with sodium trimetaphosphate. They have also stated that the intra- and intermolecular bonds forming between amylose and amylopectins might cause the decline in amylose content in CLS.

Table 1.
Amylose content and relative crystallinity of untreated and CLSs.
3.2. Swelling Power (SP)
Figure 1 displays the swelling power (SP) of CNS and CLSs. The cross-linking with epichlorohydrin improved the swelling capacity of talipot starch. However, it decreased with phosphoric acid cross-linking. The SP of CNS and CLSs increased with the increase in temperature. This could be due to the temperature-induced degradation of starch granules that facilitates an increased amount of water migration into granules. The swelling power of CNSs and EPS ranged from 2.33–8.36 g/g and 2.41–8.97 g/g, respectively. The increased SP of EPS was due to the low degree of cross-linking, which may retain granule integrity and increase the amount of water entrapped in granules. Similar observations were made in low-degree cross-linked tapioca starch [7,16]. PS exhibited decreased SP, and it ranged from 1.77–2.91 g/g. The hydrogen bonds that stabilize the structure of double helices in starch granules will be broken down when they are heated in excess water and replace hydrogen bonds formed by water molecules, and this increases the volume of the starch granules [17]. The decreased SP of PS is perhaps due to the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds during phosphoric acid treatment. A similar observation was made in phosphoric acid-treated yam starch [5].
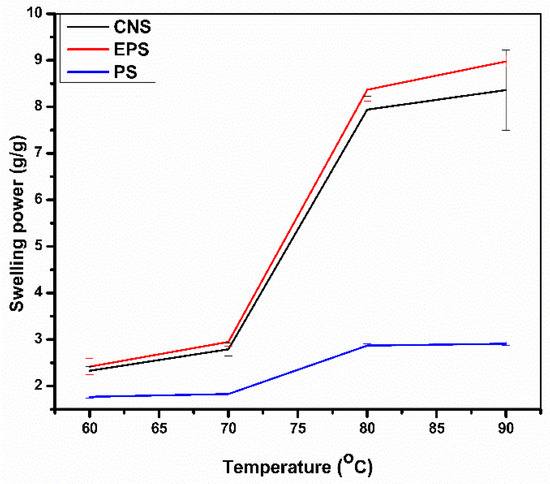
Figure 1.
Swelling power of untreated and CLSs.
3.3. Pasting Profile
The pasting profiles of CNS, EPS, and PS are given in Figure 2. The pasting characteristics such as PV, TV, BV, SV, and FV of CNS are 3646 cP, 1765 cP, 1881 cP, 797 cP, and 2562 cP, respectively. EPS exhibited an improved pasting profile, whereas the pasting profile of PS showed a decreasing trend. The PV, TV, BV, SV, FV of EPS and PS are 5408 cP, 4417 cP, 991 cP, 3019, 7436 cP, and 2773 cP, 892 cP, 1881 cP, 797 cP,1689 cP, respectively. The breakdown viscosity measures the resistance to deformation and is the indication of the stability of the starch gel during heating and shearing [18]. It was observed that EPS exhibited lower setback viscosity and, thereby, higher stability. However, CNS and PS did not show any significant (p ≤ 0.05) difference in breakdown viscosity. The setback viscosity is the measure of the ability to reassociate the starch molecules during cooling, and it indicates short-term retrogradation [19]. It was observed that EPS exhibited a higher setback viscosity and thus had a strong gel.
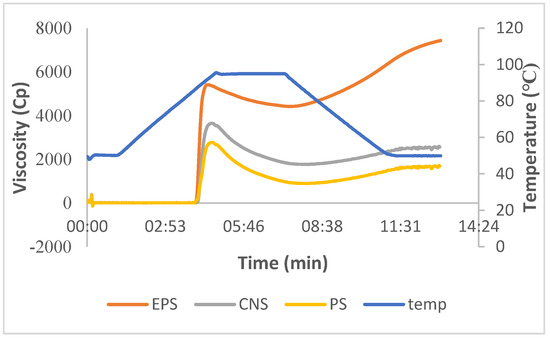
Figure 2.
Pasting profile of untreated and CLSs.
The increased pasting profile of EPS is due to the lower degree of cross-linking. Jyothi et al. [7] reported that epichlorohydrin cross-linked cassava starch exhibited high swelling power and improved pasting profile. Kurakake et al. [20] stated that cross-linking depresses the granule disintegration and thus results in an enhanced peak and final viscosity. The decreased peak viscosity of PS may be due to lower swelling power caused by the hydrolysis of glycosidic linkages. Similarly, cross-linking with the phosphate group restricted the re-orientation of amylose and amylopectin, leading to decreased setback and final viscosities [11].
3.4. Gel Texture
Gel textural properties such as hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess, and chewiness of CNS, EPS, and PS are presented in Table 2. The gel texture properties were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) changed in EPS and PS. EPS starch exhibited an improved textural property over CNS. However, it decreased in PS. The hardness of CNS was 45.54 N, and EPS exhibited a 3.2-fold increase in gel hardness. This finding is inconsistent with those regarding cross-linked rice starch as reported by Liu et al. [21]. In contrast, the hardness value of PS was decreased to 0.3 times the hardness of CNS value. The increased hardness of EPS may be due to the higher setback viscosity, resulting in higher re-orientation of starch molecules which form a strong gel. The lower gelation capacity and setback viscosity of PS limits the rate at which leached starch molecules reoriented, ending in the development of the weak gel during cold storage [22].

Table 2.
Textural properties of native and CLSs.
The springiness measures the elastic characteristic of a gel [13] and was significantly (p ≤ 0.050) changed after treatments. CNS exhibited a springiness value of 0.91 ± 0.02 mm, and it was increased to 0.97 ± 0.01 mm in EPS. However, it decreased to 0.87 ± 0.01 mm in PS. Chewiness measures the energy required for mastication. A higher gumminess and chewiness were also noticed in EPS, whereas it decreased in PS. The gumminess and chewiness values of EPS were 66.75 ± 0.63 Nmm and 63.73 ± 0.46 Nmm, respectively. Cohesiveness indicates the internal bond strength of the gel, and CNS exhibited a higher Cohesiveness value of 0.52 ± 0.01. The cross-linking of starch significantly (p ≤ 0.05) decreased the cohesiveness.
3.5. Light Transmittance
Figure 3 illustrates how cold storage affects the light transmittance in CNS, EPS, and PS. The paste clarity of all the samples was found to decrease during cold storage. CNS exhibited a decrease in light transmittance from 30.47 ± 0.99 to 7.87 ± 0.91 during a storage period of 168 h. Similarly, the light transmittance of EPS decreased from 32.43 ± 0.50 to 1.96 ± 0.91, and that of PS decreased from 35.89 ± 0.71 to 15.67 ± 0.82%. The retrogradation rate, aggregate synthesis, and leaching of starch components, which causes turbidity to occur, are only a few of the variables that affect the light transmittance and paste clarity of starch gel [23]. The retrogradation or re-orientation of the starch molecule leads to the creation of junction zones that impart opacity and impede light transmission, causing the reduction in light transmittance of talipot starches during storage.
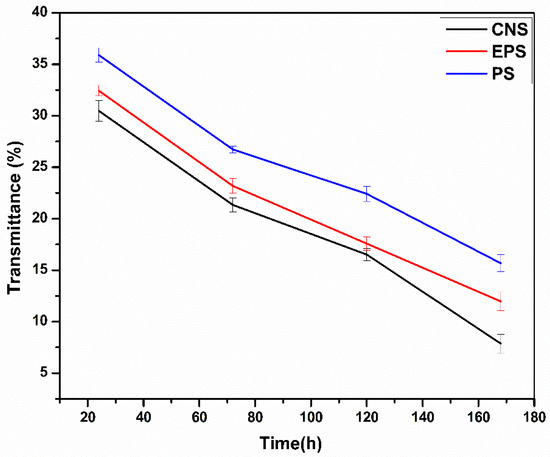
Figure 3.
Light transmittance of untreated and CLSs.
Compared to the CNS, both EPS and PS exhibited high paste clarity. The increased light transmittance of EPS is due to high swelling power. Navaf et al. [2] stated that the light transmittance of the starch granule is linearly related to the swelling power. The swollen granules exhibited high light transmittance. Contrary to our observation, Jyothi et al. [7] reported a decrease in light transmittance of epichlorohydrin-treated starches. They claimed that the increased production of dense granules following cross-linking, which reflects light, may cause reduced light transmittance. The smaller, highly light-transparent molecules created by the hydrolysis of starch molecules may be the cause of improved light transmittance and paste clarity of PS. Researchers previously noticed an improvement in the paste clarity of phosphoric acid-treated yam starch [5].
3.6. Rheological Properties
The dynamic rheological properties measure the flow and deformation behavior of starch gel under stress. Figure 4 shows how the storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli of CNS, EPS, and PS change as a function of angular frequency. The magnitudes of G′ and G″ were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) changed by cross-linking. EPS exhibited increased magnitudes of G′ and G″, whereas PS shows a decreasing trend. However, all the samples exhibited a high G′ than G″ (G′ > G″) value, which indicates a solid-like behavior of gel. The increased G′ and G″ values of EPS is perhaps due to the formation of rigid gel with high molecular integrity. Similarly, an increase in the G′ and G″ values of epichlorohydrin-treated sorghum starch was previously noticed by Sandhu et al. [10]. Wongsagonsup et al. [16] stated that low deformability and high granular rigidity result in increased gel G′ value. The decreased G′ and G″ values of PS starch are due to the restricted rate of retrogradation, which leads to the development of a weak gel.
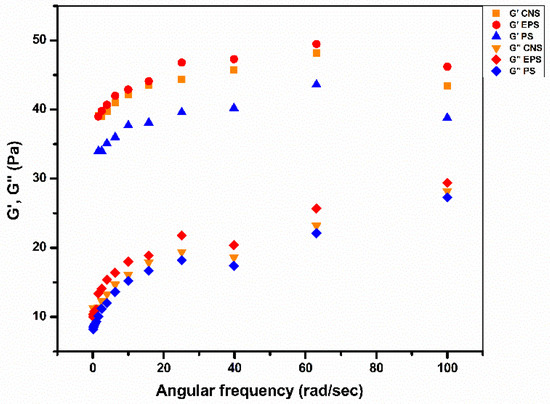
Figure 4.
Rheological behavior of untreated and CLSs.
3.7. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
Figure 5 displays the diffractograms of the CNS, EPS, and PS. It demonstrated that the crystalline pattern was not significantly affected by the cross-linking of talipot starch with epichlorohydrin or phosphoric acid. All the diffractograms exhibited similar pattern characteristics of type-A crystalline patterns with diffraction peaks at an angle of 15.1°, 17.2°, 18.1°, and 23.2°. A similar observation was reported in cross-linked corn starch [24]. The branch points of type-A starch are clustered in both amorphous and crystalline regions, which help to weaken the structure of type-A starch and make enzymatic digestion easier [1].
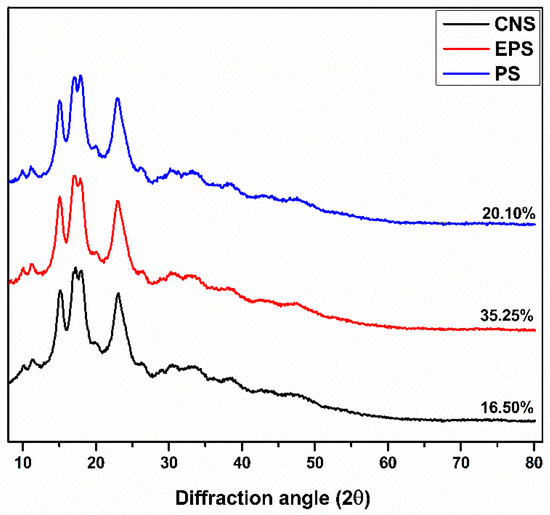
Figure 5.
X-ray diffractogram of untreated and CLSs.
The relative crystallinity of CNS was 16.5% and was increased to 35.25% and 20.10% in EPS and PS, respectively (Table 1). The creation of a more ordered structure through cross-linking may be the cause of the enhanced RC value of EPS. Similarly, the increased RC value of PS could be ascribed to the hydrolysis of the amorphous region and the formation of phosphate dieter bond, giving increased integrity. These observations are inconsistent with the result noticed in cross-linked pulse starches [25] and sorghum starch [10].
4. Conclusions
Treatment of talipot starch with epichlorohydrin and phosphoric acid significantly changed the functional, pasting, textural, rheological, and structural properties. Amylose content of talipot starch was considerably decreased, whereas the relative crystallinity was increased. Treatment with epichlorohydrin improved the talipot starch’s ability to swell and its pasting characteristics. However, it decreased in phosphoric acid-treated starch. EPS has lower breakdown viscosity, indicating higher stability during agitation. Starch treated with epichlorohydrin showed higher gel hardness than native. At the same time, phosphoric acid-treated starch showed a lower hardness value. Paste clarity of talipot starch was significantly improved in both EPS and PS. Treatment with EPS profoundly increased the G′ and G″ of talipot starch. CLSs can be utilized for various food products like canned food, dairy products, etc.
Supplementary Materials
The presentation material of this work is available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/IECBM2022-13391/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N.; methodology, M.N.; software, M.N.; validation, M.N., and K.V.S.; formal analysis, M.N.; data curation, M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.; writing—review and editing, K.V.S.; supervision, K.V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Shijin A., Department of Food Science and Technology and Central Instrumentation Facility, Pondicherry University for providing laboratory and instrumental facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chi, C.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Miao, S. Basic principles in starch multi-scale structuration to mitigate digestibility: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaf, M.; Sunooj, K.V.; Aaliya, B.; Sudheesh, C.; Akhila, P.P.; Sabu, S.; Sasidharan, A.; George, J. Talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera L.) a nonconventional source of starch: Effect of citric acid on structural, rheological, thermal properties and in vitro digestibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaf, M.; Sunooj, K.V.; Aaliya, B.; Sudheesh, C.; George, J. Physico-chemical, functional, morphological, thermal properties and digestibility of Talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera L.) flour and starch grown in Malabar region of South India. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, Á.L.; Angela, A.; Meireles, M. New Starches are the Trend for Industry Applications: A Review. Food Public Health 2014, 4, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmolasuyi, A.M.; Egwim, E.C.; Adewoyin, M.A.; Nkop, J.E. Effect of phosphoric acid treatment on physicochemical, functional, and structural properties of starch extracted from yam (Dioscorea rotundata). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheesh, C.; Sunooj, K.V.; Navaf, M.; Bhasha, S.A.; George, J.; Mounir, S.; Kumar, S.; Sajeevkumar, V.A. Hydrothermal modifications of nonconventional kithul (Caryota urens) starch: Physico-chemical, rheological properties and in vitro digestibility. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2916–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, A.N.; Moorthy, S.N.; Rajasekharan, K.N. Effect of cross-linking with epichlorohydrin on the properties of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) starch. Starch/Staerke 2006, 58, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Chang, Y.H. Rheological, pasting, and structural properties of potato starch by cross-linking. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, L.; Singh, J.; Singh, N. Effect of cross-linking on some properties of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) starches. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.S.; Siroha, A.K.; Punia, S.; Sangwan, L.; Nehra, M.; Purewal, S.S. Effect of degree of cross linking on physicochemical, rheological and morphological properties of Sorghum starch. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroha, A.K.; Sandhu, K.S. Physicochemical, rheological, morphological, and in vitro digestibility properties of cross-linked starch from pearl millet cultivars. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.C.; Kuzina, F.D.; Hlynka, I. A Rapid colorimetric procedure for estimating the Amylose content of starches and flours. Cereal Chem. 1970, 47, 411–421. [Google Scholar]
- Navaf, M.; Sunooj, K.V.; Krishna, N.U.; Aaliya, B.; Sudheesh, C.; Akhila, P.P.; Sabu, S.; Sasidharan, A.; Mir, S.A.; George, J. Effect of Different Hydrothermal Treatments on Pasting, Textural, and Rheological Properties of Single and Dual Modified Corypha Umbraculifera L. Starch. Starch/Starke 2021, 74, 2100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaliya, B.; Sunooj, K.V.; Babu, C.; Rajkumar, S.; Navaf, M.; Akhila, P.P.; Sudheesh, C.; George, J.; Lackner, M. Effect of Thermal Pretreatments on Phosphorylation of Corypha umbraculifera L. Stem Pith Starch: A Comparative Study Using Dry-Heat, Heat-Moisture and Autoclave Treatments. Polymers 2021, 13, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Kaur, M.; Sandhu, K.S.; Godara, S.K. Effect of cross-linking on physico-chemical, thermal, pasting, in vitro digestibility and film forming properties of Faba bean (Vicia faba L.) starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsagonsup, R.; Pujchakarn, T.; Jitrakbumrung, S.; Chaiwat, W.; Fuongfuchat, A.; Varavinit, S.; Dangtip, S.; Suphantharika, M. Effect of cross-linking on physicochemical properties of tapioca starch and its application in soup product. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.M.; Hasnain, A. Physicochemical, morphological, thermal, pasting, and textural properties of starch acetates. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 32, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheesh, C.; Sunooj, K.V.; George, J.; Kumar, S.; Appukuttan, V. Physico-chemical, morphological, pasting and thermal properties of stem flour and starch isolated from kithul palm (Caryota urens) grown in valley of Western Ghats of India. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braşoveanu, M.; Nemţanu, M.R. Pasting properties modeling and comparative analysis of starch exposed to ionizing radiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 168, 108492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakake, M.; Akiyama, Y.; Hagiwara, H.; Komaki, T. Effects of cross-linking and low molecular amylose on pasting characteristics of waxy corn starch. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ramsden, L.; Corke, H. Physical properties of cross-linked and acetylated normal and waxy rice starch. Starch/Staerke 1999, 51, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaf, M.; Sunooj, K.V.; Aaliya, B.; Sudheesh, C.; Akhila, P.P.; Sabu, S.; Sasidharan, A.; George, J. Impact of gamma irradiation on structural, thermal, and rheological properties of talipot palm (Corypha umbraculifera L.) starch: A stem starch. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 201, 110459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Jabeen, M.; Geelani, H.; Masoodi, F.A.; Saba, I.; Muzaffar, S. Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of Indian Horse Chestnut (Aesculus indica Colebr.) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Effect of cross-linking on the physicochemical and physiological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Vasanthan, T. Effect of phosphorylation techniques on structural, thermal, and pasting properties of pulse starches in comparison with corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).