Abstract
The use of the flowers (blossoms) of the coffee plant (genus Coffea) has been neglected over the years, as the focus has primarily been on the cost-efficient production of coffee beans. Because of societal changes and economic pressures, there is an increasing demand for sustainability, so the focus has also widened towards the various by-products of the coffee production. The coffee flower is a by-product because it can be harvested following pollination without any risk to the bean production. The coffee flower can be used as a whole or as floral water in some food and cosmetic products. The flower can also be prepared as a tea-like beverage with hot water infusion. Another side-chain product in coffee plantations is the so-called coffee flower honey, which is rarely monofloral due to the short flowering period. To date, there have been few studies on coffee flowers and their sensory characterization. In this work, various compounds in Coffea arabica, C. canephora, and C. liberica flowers were identified and quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with diode array detection (DAD), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), and near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Caffeine, chlorogenic acids, organic acids, trigonelline, and sugars were quantified. Additionally, the sensory testing of coffee flower infusions according to the German norm DIN 10 809 was performed. With the acquired data, a principal component analysis (PCA) was performed in which hay, hops, sage, dried apricot, and honey were identified as major flavor descriptors in addition to the floral coffee flower flavors. The coffee flower is judged as a promising ingredient, which needs to be further assessed regarding its possible approval within the novel food regulations of the European Union.
Keywords:
coffee by-products; coffee flower; coffee blossom; tea; infusion; analysis; HPLC; NMR; NIR; novel food 1. Introduction
In 1713, the first botanical description of the coffee tree was known as Jasminum arabicum. This classification arose because of the flower aroma, which was very reminiscent of jasmine, and therefore, the coffee flower (blossom) was often confused with jasmine. It was not until 1737 that Linnaeus classified the coffee tree in its own genus Coffea, with the only known species at that time being C. arabica []. The coffee flower (Figure 1) is a by-product because it can be harvested following pollination without any risk to the bean production []. The flower can be used as a whole or as floral water in some food and cosmetic products [,,], or it can be prepared as a tea-like beverage with hot water infusion [,]. Another side-chain product in coffee plantations is the so-called coffee flower honey, which is rarely monofloral due to the short flowering period [,]. Despite the known possibilities of using the coffee flower as food, there have been few studies on coffee flowers and their sensory characterization to date. It is known that they contain bioactive components such as caffeine, trigonelline, chlorogenic acid (5-caffeoylquinic acid), protocatechuic acid, gallic acid, melanoidins, and sugars [,]. This study investigates coffee flower compounds, aiming toward food uses and a possible approval according to the novel food regulations of the European Union in the future.

Figure 1.
Coffee flowers (a) on the tree during the short flowering period, and (b) in the air-dried state similar to the samples analyzed in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
In this work, various compounds in 35 different Coffea arabica, C. canephora, and C. liberica flowers from El Salvador, Malaysia, India, and Thailand were identified and quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with diode array detection (DAD), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), and near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Additionally, the sensory testing of coffee flower infusions according to the German norm DIN 10809 was performed. With the acquired data, a principal component analysis (PCA) was performed. All samples were analyzed in the air-dried state. Additionally, a roasted coffee flower tea of C. arabica from the trade was analyzed. To ensure the homogeneity of the samples, each of them was finely ground and stored in air- and light-impermeable bags until use. In general, established analytical methods for coffee or tea were applied, and the specific sample preparation for coffee flowers is as follows.
2.1. Sample Preparation
An aliquot was taken from each coffee flower. Before processing for analysis, they were ground and homogenized using an analytical mill and then stored in an airtight plastic container.
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
For HPLC analysis, ISO 14502-2:2007-12 was used []. For this purpose, 200 mg of the sample material was weighed into a 10 mL extraction tube with a screw cap. The samples were then mixed with 5 mL of a 70% methanol extraction solution, which had previously been temperated at 70 °C in a water bath, and then sealed. This was followed by mixing the extraction tube with the sample solution using a vortex mixer and bathing in 70 °C water for 5 min. After extraction was complete, the extraction mixture was cooled to room temperature (T = 20 °C) and centrifuged (rcf = 3500× g for 10 min). The supernatant was then decanted into a 10 mL volumetric flask and the procedure was repeated with the sample remaining in the extraction tube.
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.3.1. Extraction of Water-Soluble Compounds for 1H-NMR
A total of 150 mg of the ground coffee flower was weighed into a 15 mL Falcon tube as a triplicate. Then, 8 mL of distilled water was added to the coffee flower sample, and the tube was capped and extracted for 20 min using a vertical shaker. The mixture was then filtered through a syringe-attached membrane filter. Then, 70 µL of TSP and 100 µL of buffer were pipetted with 600 µL of the extract into a 4 mL screw-top glass tube. The tube was sealed and the contents were mixed using a vortex mixer. After mixing the diluted extract, 600 µL was removed and pipetted into a 5 mm NMR tube.
2.3.2. Extraction of Fat-Soluble Compounds for 1H-NMR
A total of 150 mg of coffee flower was weighed as a triplicate in 4 mL screw-top glass vial. Then, 1500 µL of chloroform solvent was added, which was spiked with tetramethylsilane (TMS). After sealing the sample, it was extracted on a shaker for 20 min. Then, the mixture was filtered using a membrane filter. Finally, 600 µL of the diluted coffee flower extract was taken and transferred to a 5 mm NMR tube.
2.4. Near Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy
The homogenized coffee flower was distributed in a layer of about 1 cm into a round glass Petri dish so that the entire bottom was covered. After filling, the sample was pressed firmly with a metal stamp and placed on the Petri dish holder above the measuring beam. In the spectrometer, the sample cell was measured in diffuse reflectance mode over the entire wavelength range of λ = 800–2500 nm.
2.5. Sensory Analysis
To achieve comparable conditions between the individual flower samples, the coffee flower tea was prepared according to DIN 10809 in infusion vessels and bowls []. After 5 min, the tea was poured into a bowl and could be tasted after a short cooling period. Tasting was conducted using cupping spoons. The flavor profile of each flower was evaluated using a test panel with intensities ranging from 0 to 4 (0 = very weak intensity; 4 = very strong intensity). The result of the tasting of each flower sample was documented as a summarized overall result by agreement between the test group. Two of the coffee flowers were excluded from the evaluation because they were not suitable for consumption due to off-flavors. The remaining samples were evaluated after final assessment by Excel statistical software (Xlstat, Addinsoft, Paris, France) and a principal component analysis was generated from the data obtained.
3. Results
The full raw results of all methods included in this paper are provided as Supplementary Materials.
3.1. HPLC/NMR Analysis
Compounds, such as caffeine, 5-chlorogenic acid, 3,4-Dicaffeoylquinic acid, and 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid, were detected and quantified using HPLC and NMR (Table 1). Caffeine and chlorogenic acid were analyzed with both methods. The NMR analysis allowed the quantification of several water-soluble compounds, such as organic acids and sugars.

Table 1.
Determination of the organic compounds in the coffee flower samples (n = 35).
The fat-soluble compounds were only qualitatively detected during NMR analysis. However, several fatty acids were identifiable. These include saturated, mono-, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
3.2. NIR Analysis
The results of the NIR analysis are shown in Table 2. The analyzed compounds were water, ash, and protein content. Additionally, the concentration of essential oils within four of the samples was measured.

Table 2.
Determination of water, ash, and protein in the coffee flowers (n = 15).
3.3. Sensory Analysis
With the acquired data from the sensory analysis, a principal component analysis (PCA) was performed in which hay, hops, sage, dried apricot, and honey were identified as major flavor descriptors in addition to the floral coffee flower flavors. The scores plot shows a trend for differentiation according to the color of the coffee cherry that is formed following flowering. The upper two quadrants contain mainly coffee plants that produce red coffee cherries. The lower right quadrant, on the other hand, contains coffee plants that tend to form yellow coffee cherries. The samples shown in the lower left quadrant indicate both types of coffee cherry, which are mainly due to hybrids of both coffee plants. The results of this analysis are shown in Figure 2.
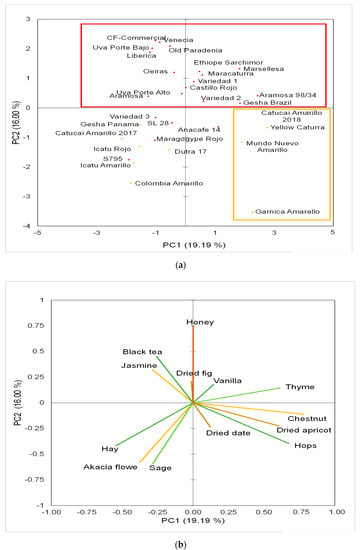
Figure 2.
Principal component analysis of the sensory analysis results of the 33 coffee flower samples; (a) scores plot; (b) loadings plot.
4. Conclusions
This work quantified compounds such as caffeine, chlorogenic acids, organic acids, trigonelline, and sugars within coffee flowers. Furthermore, several fatty acids could be identified. With the acquired data from the sensory analysis, a principal component analysis (PCA) was performed in which hay, hops, sage, dried apricot, and honey were identified as major flavor descriptors in addition to the floral coffee flower flavors.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/Foods2022-12967/s1, raw results (Microsoft Excel format).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.W.L. and S.S.; methodology, D.W.L.; software, K.W.; validation, K.W.; formal analysis, K.W.; investigation, K.W.; resources, D.W.L.; data curation, K.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W.; writing—review and editing, D.W.L., S.S., E.R. and S.G.W.; visualization, K.W.; supervision, D.W.L. and E.R.; project administration, D.W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The teams of the plant-based food and NMR laboratories at CVUA Karlsruhe are warmly thanked for their excellent technical assistance. The coffee farmers and pickers are thanked for providing the samples. Special thanks are owed to Andres Quintanilla (El Salvador) for his special commitment providing single-variety coffee flowers.
Conflicts of Interest
S.S. is owner of Coffee Consulate, Mannheim, Germany. Coffee Consulate is an independent training and research center. Coffee Consulate is currently researching the potential of coffee by-products. However, S.S. reports no conflicts of interest related to the work under consideration. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bi, X.; Huang, J.; Hu, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; et al. Preparation method of coffee flower tea. Patent CN110959719A, 16 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Rajcic de Rezende, T.; Schwarz, S. An update on sustainable valorization of coffee by-products as novel foods within the European Union. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.; Schwarz, S.; Rieke-Zapp, J.; Cantergiani, E.; Rawel, H.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Martuscelli, M.; Gottstein, V.; Angeloni, S. Coffee by-products as sustainable novel foods: Report of the 2nd international electronic conference on foods—Future foods and food technologies for a sustainable world. Foods 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrillaga, N.G. A new perfume oil from coffee flowers. Rev. Agric. Puerto Rico 1942, 34, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Berry-Caillet, V.; Husson, J.; Barro, L. Floral Water from Coffee Flowers. Patent WO2022053 605A1, 10 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Charrier, A.; Berthaud, J. Botanical classification of coffee. In Coffee: Botany, Biochemistry and Production of Beans and Beverage; Clifford, M.N., Willson, K.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Buawangpong, N.; Burgett, M. Honey bees and coffee. Bee World 2015, 92, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiassi, M.; de Souza, V.; Lago, A.; Carvalho, G.; Curi, P.; Guimarães, A.; Queiroz, F. Quality of honeys from different botanical origins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 4167–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.T.; Cho, E.J.; Song, Y.; Oh, C.H.; Funada, R.; Bae, H.-J. Use of coffee flower as a novel resource for the production of bioactive compounds, melanoidins, and bio-sugars. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu Pinheiro, F.; Ferreira Elias, L.; De Jesus Filho, M.; Uliana Modolo, M.; Gomes Rocha, J.D.C.; Fumiere Lemos, M.; Scherer, R.; Soares Cardoso, W. Arabica and conilon coffee flowers: Bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity under different processes. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN ISO 14502-2:2007-12; Determination of Substances Characteristic of Green and Black Tea–Part 2: Content of Catechins in Green Tea–Method Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (ISO 14502-2:2005 + Corrigendum 1:2006). Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [CrossRef]
- DIN 10809:1988-08; Analysis of Tea; Preparation of Liquor for Use in Sensory Tests. Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).