Abstract
Regulatory potential of microRNAs in growth, metabolism, and stress adaptation is well known. In total, 15 common oat genotypes were performed by miRNA-based markers. Markers involved in MiRNAs sequences provide an effective type of putative functional markers. Markers involved to photosynthesis regulation, growth, and biomass production (miR408, miR156) generated 40% of all amplified loci. Those associated with nutrition accumulation and homeostasis (miR827 and miR399) generated 29% and stress-responsive markers (miR398 and miR858) 31%. Proteomics approaches (SDS and A-PAGE electrophoresis) detected sufficient diversity between the analyzed samples and genetic-related dendrograms were constructed based on the electrophoretic profiles.
1. Introduction
Due to the significantly changing climatic conditions, it is necessary to apply approaches to identify the genomic potential of plant genetic resources for adaptation to abiotic stress and thus provide a platform for successful genotype selection. The plant organism must cope with environmental stresses in natural and agricultural conditions. A genetic background allows plants to adapt to the environment by various mechanisms at the molecular level. From this point of view, genome screening by functional markers may provide knowledge for identifying added value of plant genetic resources.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified to be involved in regulation of plant stress responses [1,2,3]. The high conservation of miRNA sequences allowed us to develop an effective type of putative functional markers [4,5,6,7]. The fundamental potential of miRNA-based markers relies on the primer design based on the consensus sequences of mature miRNAs which are part of the step-loop structures. The advantages of this marker system include high polymorphism, reproducibility, and inter-species transferability [4,5]. The abundance of mature miRNAs, which is linked to the expression of MIRNA genes, varies greatly among miRNAs, tissue types or developmental stages, indicating the spatially and temporally regulated expression patterns of plant miRNAs [8,9]. Polymorphism amplified by the application of miRNA markers indicates changes in miRNA loci sequences, which may result in changes in target gene regulation [4,10].
Plant seed storage proteins are characterized by a polymorphism due to the existence of several discrete forms because of heterozygosity. The polymorphism results from the in vivo hybridization of protein subunits, controlled by independent genes of different chromosome loci that are expressed at different times. Polymorphism can also be induced by post-translational changes in proteins, such as acylation, glycosylation, phosphorylation, deamination, decarboxylation, methylation, etc. [11].
The aim of our study was to detect the polymorphism of miRNA-based markers to characterize the oat genotypes. Proteomics approaches detected diversity between the analyzed samples.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
Grains of oat varieties (Avena sativa L.) Vaclav, Valentin, Vendelin, Viliam, Vit, Flamingsgarand, Flamingsregent, Fuchs, Arne, Magne, Calibre, Cascade, Lord, Senator, and Marloo were analyzed. Samples were obtained from the Gene Bank of Seed Species of the Slovak Republic NPPC VÚRV in Piešťany.
2.2. Selection of Markers and Primers Design
The suitable microRNA markers were selected based on their functional involvement in the Poaceae family (wheat, barley, maize, rice) [12,13,14,15]. Database miRBase (https://www.mirbase.org (accessed on 16 March 2021)) (release 22.1) [16] was used to search and browse microRNA sequences. Sequences-based homology search was carried out by BLASTn (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast (accessed on 16 March 2021)) and CLUSTAL OMEGA (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/ (accessed on 16 March 2021)) algorithms. The primers were designed according to the methodologies [4,5].
2.3. MicroRNA-Based Marker Assay
Plants were grown in pot experiments under controlled growth chamber conditions (23 °C, 16/8 h photoperiod, 50% humidity). After 15 days of growth, bulk leaf samples (10 plants) were taken for DNA extraction. Total genomic DNA was extracted using the NucleoSpin™ Plant II (Macherey-Nagel™, GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany) and quantified by the Implen NanoPhotometer®. The miRNA-based marker assays were performed based on protocols [4,5], modified by [17]. MiRNA-based PCR amplicons were separated on 15% TBE-UREA PAGE gels and scored for their length and gel migration characteristics by GeneTool™ gel analysis software version 4.3.10.0 (Syngene, Synoptics Ltd., Cambridge, UK).
2.4. SDS-PAGE
Electrophoretic analysis of oat seed stock protein polymorphism was performed on SDS-PAGE according to [18]. Electrophoretic profiles of individual varieties were scanned with a GS-800 Calibrated Densitometer (BioRad, BioRad Laboratories Inc., Berkeley, CA, USA) and evaluated using Doc-It LS Image analysis and GelAnalyzer. A dendrogram using the Jaccard similarity coefficient and the UPGMA algorithm for statistical interpretation of electropherograms was constructed in the DendroUPGMA program, which is available online (http://genomes.urv.cat/UPGMA/ (accessed on 26 August 2021)).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MiRNA-Based Assay
For genomic screening of 15 oat genotypes originating from six countries (Austria-AUS-1, Australia-AUT-2, Canada-CAN-2, Deutschland DEU-3, Slovakia SVK-5, and Sweden SWE-2), six different miRNA-based markers (miR156, miR398, miR399, miR408, miR827 and miR858) were used. In total, 849 miRNA-based loci were amplified, which represents an average of 57 fragments per genotype. Balanced amplification was also observed depending on the origin of the genotype. The range of amplified fragments varied from 46 (Flamingsregent, DEU) to 67 (Senator, AUT). The representation of individual types of miRNA loci was marker specific.
A predominance of the miR398 (22% of the total number of amplified fragments) marker was observed in the genome of the analyzed oat samples. MiRNA398 (miR398) is considered a stress-responsive miRNA involved in the plant stress regulation mechanism [1,12]. MiR398 has been reported to be associated with various stress conditions such as oxidative stress [19], water deficit [20], salt stress, and abscisic acid stress [21]. Due to optimal and controlled growth conditions, it is not possible to predict the influence of any of the above stress factors, considering the short time interval (15 days) of growth. The predominant presence of miR398 loci may indicate the genomic potential of the analyzed genotypes in terms of their tolerance to abiotic stress, whereas miR398 represents a highly conserved miRNA in diverse monocots and dicots, and it can be assumed that it is important for plants stress tolerance [1,12]. The highest number of loci (16) was recorded in genotype Vaclav and the lowest in genotype Valentine (9) both originating from Slovakia.
The second most represented type of miRNA-based marker was miR408 (21% of the total number of amplified fragments) (Figure 1). The highest number of loci (14) was recorded in genotypes Cascade (CAN) and Magne (SWE) and the lowest in genotypes Vendelin and Vit (9) both from Slovakia. Studies have shown that miR408 is involved in the development, light signaling pathway, and biotic stress reactions as well as biomass production [2,3]. Constitutive expression of miR408 affects various stages of development and promotes intense plant growth and seed yield by increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. Therefore, miR408 is likely to have a pleiotropic effect on plant growth and development [22].
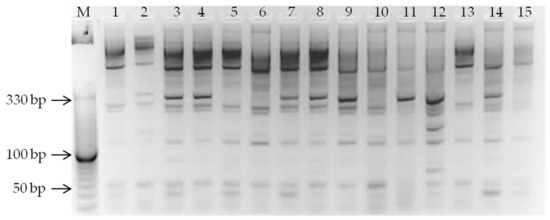
Figure 1.
A representative genome fingerprinting of oat samples based on electrophoretic separation of “touch-down” PCR products amplified by miR408-based primers. Genotypes: 1—Arne; 2—Calibre; 3—Cascade; 4—Flamingsgarand; 5—Flamingsregent; 6—Fuchs; 7—Lord; 8—Magne; 9—Marlov; 10—Senator; 11—Vaclav; 12—Valentin; 13—Vendelin; 14—Viliam; 15—Vit.
Similar to marker miR408, the marker miR156 having 19% representation within amplified loci is also considered as the most conserved miRNAs indicating that its role is essential for the development and existence of plants [23,24]. The highest number of loci (4) was recorded in genotype Calibre (CAN) and the lowest (9) in genotypes Lord and Senator (AUT), Marloo (AUS), and Vendelin (SVK).
The representation of the marker miR827 was recorded at the level of 16% of the total number of amplified fragments. MiR827 plays an important role in regulatory mechanisms related to nutrient homeostasis, especially phosphorus. It is characterized by increased activity in conditions of phosphorus deficiency [25,26]. The highest number of amplified miR827 loci (15) was recorded in genotype Senator (AUT) and the lowest (4) in Vendelin (SVK) and Flamingsregent (DEU).
Several studies confirmed the roles of miR399 in the regulation of phosphate accumulation and homeostasis [27]. However, its responsiveness may be species- and tissues/organ-specific [28]. Genotype Vit (SVK) recorded the highest number (15) of miR399 loci and the lowest (3) was recorded in Calibre from Canada. Total representation of the marker miR399 was 13% of the total number of amplified fragments.
Finally, the least represented type of markers was miR858 (9%), with the highest number of loci (9) in genotype Magne (SWE). Amplification was not recorded for multiple genotypes (Calibre, Flaminsgarand, Flamingsregent, and Vaclav). The role of miR858 was described in the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are known for their antifungal activity and miR858 functions as negative regulator of plant immunity by controlling biosynthesis of flavonoids [29]. We can therefore assume that the activity of this type of marker was below the level of detection.
3.2. SDS-PAGE Analyses
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) is one of the most common methods suitable for the identification and differentiation of plant genotypes based on their electrophoretic profiles. SDS-PAGE has also been shown to be suitable for the detection of oat genetic diversity (Figure 2). By the action of a constant electric current, the grain storage proteins of individual genotypes were divided into three groups based on different molecular weights, namely HMW-GS (high molecular weight glutelin subunits), LMW-GS (low molecular weight glutelin subunits), and prolamins, as well as residual albumins and globulins, which have the lowest weight [11,30].
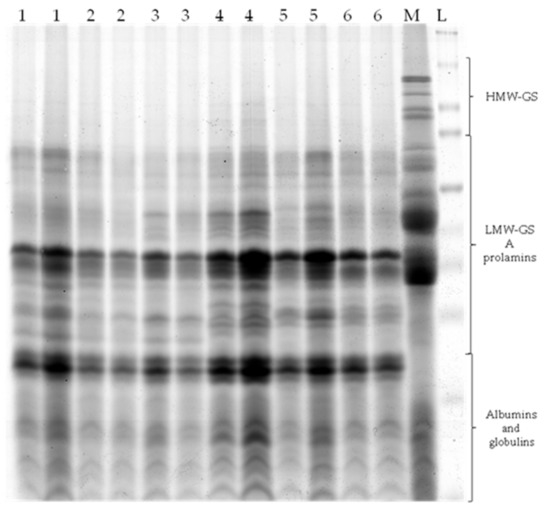
Figure 2.
A representative PAGE gel. 1 Flamingsregent; 2 Fuchs; 3 Arne; 4 Magne; 5 Calibre; 6 Cascade; M—Triticum aestivum L.; L—Spectra Multicolor Broad Range Protein Ladder.
Electropherograms show that the molecular weight of HMW-GS oats was 85 kDa to 80 kDa, LMW-GS ranged from 65 kDa to 30 kDa, and residual albumins and globulins ranged from 28 kDa to 4 kDa. The results further show that on average in the samples there were 3.77% HMW-GS (range 2.71–5.58%), 42.55% LMW-GS and prolamins (range 40.21–44.64%), and 53.69% of residual albumins and globulins (49.89–55.47%) (Figure 3). These results correspond to the findings of other authors [11,30,31,32,33].
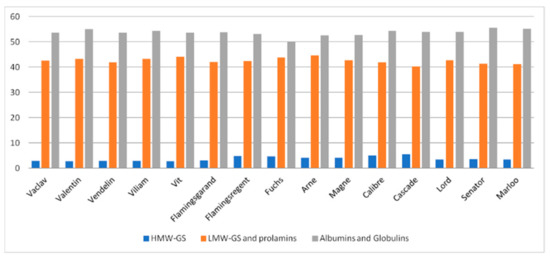
Figure 3.
Percentage of protein fraction in genotypes of oat analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
The dendrogram (SDS-PAGE) divided the analyzed varieties into two main clusters, while the FUCHS variety was separated from the other varieties, which means that it is genetically the most distant from the other varieties. In the second cluster, the remaining fourteen varieties were separated into two further sub-clusters.
There were four varieties in the first sub-cluster and the remaining ten were in the second sub-cluster. The most genetically similar in terms of glutelin polymorphism was Senator and Marloo, then Ame and Cascade. Similar dendrograms because of research were achieved in their work [30,31,32,33].
4. Conclusions
Because of the functionality of miRNA-based markers, their application is appropriate in terms of characterizing the added value of plant genetic resources. The genome screening points out that all tested genotypes should have sufficient genetic background in order the provide biomass while having the potential for adaptability to environmental conditions. From this point of view, we can assume that genotypes Magne (SWE) and Vaclav (SVK) have available higher stress adaptation potential as the number of amplified loci of the stress-sensitive markers miR398, miR858, and miR408 was the highest. On the other hand, the lowest amplification of miR156-, miR408-, and miR827-based markers associated with plant growth and nutrition homeostasis was observed in genotype Vendelin (SVK). SDS -PAGE analysis allows us to detect the genetic diversity of tested oat genotypes based on glutelin polymorphism.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/IECPS2021-11917/s1, The poster presentation. Figure S1: MicroRNA-Based and Proteomics Fingerprinting of Avena sativa L. Genotypes.
Author Contributions
K.R., Z.G. and Ľ.H., methodology and investigation of miRNA-based markers assay; M.C., Ľ.H., Z.G. and Ž.B., methodology and investigation of proteome; K.R. and Z.G., writing and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication was supported by the project VEGA No. 1/0291/21, KEGA No. 026SPU-4/2021, KEGA No. 027SPU-4/2021 and by the Operational Program Integrated Infrastructure within the project: Demand-driven research for the sustainable and innovative food, Drive4SIFood 313011V336, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, C.; Ding, Y.; Liu, H. MiR398 and plant stress responses. Physiol. Plant. 2011, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bej, S.; Basak, J. MicroRNAs: The potential biomarkers in plant stress response. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barciszewska-Pacak, M.; Milanowska, K.; Knop, K.; Bielewicz, D.; Nuc, P.; Plewka, P.; Pacak, A.M.; Vazquez, F.; Karlowski, W.; Jarmolowski, A.; et al. Arabidopsis microRNA expression regulation in a wide range of abiotic stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Ma, B.I.; Mason, A.S.; Xiao, M.; Wei, L.; An, Z. MicroRNA-based molecular markers: A novel PCR-based genotyping technique in Brassica species. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, C.B.Y.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Pandey, G.; Khan, Y.; Prasad, M. Development of novel microRNA-based genetic markers in foxtail millet for genotyping applications in related grass species. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.K.; Ganie, S.A. Identification and characterization of salt responsive miRNA-SSR. Gene 2014, 535, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganie, S.A.; Mondal, T.K. Genome-wide development of novel miRNA-based microsatellite markers of rice (Oryza sativa) for genotyping applications. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegler, J.L.; Grof, C.P.L.; Eamens, A.L. Profiling of the Differential Abundance of Drought and Salt Stress-Responsive MicroRNAs Across Grass Crop and Genetic Model Plant Species. Agronomy 2018, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Gu, J.; Guo, C.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, K. Expression pattern of wheat miRNAs under salinity stress and prediction of salt-inducible miRNAs targets. Front. Agric. China 2011, 5, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, M.; Unver, T.; Budak, H. Regulation of barley miRNAs upon dehydration stress correlated with target gene expression. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 10, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálová, Z.; Palenčárová, E.; Chňapek, M.; Balážová, Ž. Využitie Obilnín, Pseudoobilnín a Strukovín v Bezlepkovej Diéte, 1st ed.; [Use of Cereals, Pseudo-Cereals and Legumes in a Gluten-Free Diet]; Slovenská Poľnohospodárska Unierzita: Nitra, Slovakia, 2012; 182p, ISBN 978-80-552-0826-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sunkar, R.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.K. Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrera-Figueroa, B.E.; Gao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, J.; Jin, H.; Liu, R.; Zhu, J. High throughput sequencing reveals novel and abiotic stress-regulated microRNAs in the inflorescences of rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehr, L. Systemic regulation of mineral homeostasis by microRNA. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akdogan, G.; Tufekci, E.D.; Uranbey, S.; Unver, T. MiRNA-based drought regulation in wheat. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S. The microRNA Registry. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D109–D111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ražná, K.; Hlavačková, L. The applicability of genetic markers based on molecules microRNA in agriculturel research. Open Access J. Agri. Res. 2017, 2, 000125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, C. Identification of cereal varieties by gel electrophoresis of the grain proteins. In Seed Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 17–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sunkar, R.; Kapoor, A.; Zhu, J.K. Posttranscriptional Induction of Two Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Genes in Arabidopsis Is Mediated by Downregulation of miR398 and Important for Oxidative Stress Tolerance. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trindade, I.; Capitão, C.; Dalmay, T.; Fevereiro, M.P.; Dos Santos, D.M. miR398 and miR408 are up-regulated in response to water deficit in Medicago truncatula. Planta 2010, 231, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, W.X.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.J.; Mendu, V.; Willcut, B.; Dinkins, R.; Tang, X.; Tang, G. Differential and dynamic regulation of miR398 in response to ABA and salt stress in Populus tremula and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Huang, D.; Guo, Z.; Kuang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Ma, Z.; Gao, S.; Lerdau, M.T.; Chu, C.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA408 enhances photosynthesis, growth, and seed yield in diverse plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barvkar, V.T.; Pardeshi, V.C.; Kale, S.M.; Qiu, S.; Rollins, M.; Datla, R.; Gupta, V.S.; Kadoo, N.Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of microRNA genes and their targets in flax (Linum usitatissimum): Characterization of flax miRNA genes. Planta 2013, 237, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Shen, J.; Hou, X.; Yao, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. Gradual increase of miR156 Regulates Temporal Expression Changes of Numerous Genes during Leaf Development in Rice. ASPB 2012, 158, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, L.C.; Lin, S.; Shih, A.C.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Tseng, C.; Li, W.; Chiou, T. Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, A.W.; Shi, B.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Langridge, P.; Baumann, U. Discovery of barley miRNAs through deep sequencing of short reads. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, G.; Ai, Q.; Yu, D. Uncovering miRNAs involved in crosstalk between nutrient deficiencies in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajwanshi, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Jayanandi, K.; Deb, B.; Lightfoot, D.A. Orthologous plant microRNAs: Microregulators with great potential for improving stress tolerance in plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2525–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Tiwari, M.; Pandey, A.; Bhatia, C.; Sharma, A.; Trivedi, P.K. MicroRNA858 Is a Potential Regulator of Phenylpropanoid Pathway and Plant Development. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregova, E.; Šliková, S.; Hozlár, P. Seed protein electrophoresis for identification of oat registered cultivars. Potravinarstvo 2015, 9, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, O.D. The Spectrum of Major Seed Storage Genes and Proteins in Oats (Avena sativa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mickowska, B.; Litwinek, D.; Gambuś, H. Oat raw materials and bakery products–amino acid composition and celiac immunoreactivity. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment 2016, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajnincová, D.; Gálová, Z.; Chňapek, M. Comparison of selected wheat, oat and buckwheat genotypes on proteomic level. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2019, 20, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).