Abstract
Musculoskeletal fitness (MF) is a multidimensional construct that combines muscle strength, endurance, and power to allow for the performance of tasks against one’s own body weight or an external resistance. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of school-based programs on promoting MF in children aged 6 to 10. PubMed and Web of Science databases were used as searching tools. A total of 16 studies were included in a systematic review with primary school-based program interventions measuring at least one variable related to musculoskeletal fitness. Parameters for measuring explosive power, especially standing broad jump (SBJ), have a large potential for development throughout school-based programs. Long-lasting interventions did not necessarily improve MF; however, there were shorter interventions that caused the improvement in a larger number of parameters. Our findings imply that increased physical activity during a school week, together with improved lesson content, is crucial for MF development in this age group.
1. Introduction
Musculoskeletal fitness (MF) is a multidimensional construct that combines muscle strength, endurance, and power to allow for the performance of tasks against one’s own body weight or an external resistance [1]. In recent years, MF has received a lot of research attention. Several studies have investigated that in youth, MF is negatively associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, metabolic diseases [2,3,4], and obesity [5]. Additionally, poor fitness in children is increasing global health concerns. This was confirmed by a big Dutch study, which indicated that the performance in children aged from 9 to 12 is declining [6]. Thankfully, Emaljanovas et al. [7] tested kids aged from 6 to 10, and the results showed that MF increased over time (better results in older kids). However, there is a great potential for children to improve their MF [8]. Moreover, children should learn about MF because many health advantages are related to that field, including lower cardiovascular risk factors, enhanced bone mineral density (lower chance of osteoporosis), better flexibility, and improved glucose tolerance [9].
The facts mentioned above suggest that children have the potential to develop a healthier lifestyle with the right guidance. One of the most influential places that can significantly contribute is the school environment. School-based fitness and exercise programs have the ability to give useful evidence of children′s physical fitness levels at various ages [10]. School has a very important role, since children spend a significant part of their day in class [11]. In addition, children can acquire the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for lifetime physical activity habits such as MF in physical education (PE) lessons. Moreover, the World Health Organization says that with the schools’ support, all kids should be physically active, through games, sports, physical education, and planned physical activities [12]. The role of school-based exercise programs has been viewed as an important procedure that needs the structuring of all time spent in school, beginning with planning the kids’ activities as they arrive at school [13]. Unfortunately, few findings have been reported specifically about school-based exercise programs in the last two decades promoting MF, to the authors’ knowledge and as of the time this review is written. On the other hand, some studies concluded that no significant development is observed when the variables are obesity, sedentary behavior, and physical activity [14,15]. Moreover, most studies have mainly focused on older children, and thus there is limited research investigating school-based exercise programs in children aged 6 to 10. Therefore, it is important to understand the mechanisms underlying MF, since muscle improvements come either with training intervention or the biological maturity of the child.
The aims, designs, and methodological quality are given and critically analyzed. The objective of this review was to summarize recent intervention studies with the aim of promoting MF in children aged 6 to 10, carry out a systematic review where the research gap is fulfilled in this area, and show the importance of MF in this age group. To the best of our knowledge, no study has focused particularly on the age span of 6 to 10 years. Moreover, we emphasized the importance of activities that strengthen only muscles. In the last twenty years, new, modernized programs were introduced for developing MF in children. Therefore, this study was carried out to investigate this unknown field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Identification
A systematic review was conducted using a PRISMA [16]. Academic databases PubMed and Web of Science were searched from 2003 until May 2022 to identify original research studies in English that investigated school-based exercise programs for promoting musculoskeletal fitness in children aged 6 to 10 years.
The studies were identified by searching the key terms shown in Table 1. All search levels 1–3 were connected to Boolean operators “AND”. Search terms within each search level were merged with “OR”. Age limit was set to between 6 and 10 years in the search field as well as the filter option for age limitation “Child: 6-12 years” in “PubMed”. Additional filter options for age limits were not available in the Web of Science academic database. All data were extracted and imported into the “Rayyan” web-based reference manager.

Table 1.
Search strategy to identify articles.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
Articles examining school-based musculoskeletal fitness published in English between 2003 and May 2022 were included. Any type of review, narrative, systematic, or meta-analysis was excluded. Studies that were conducted with participants below or over 6 to 10 years were also removed. Lastly, articles about children who have any type of health problem were discarded. Furthermore, 16 studies were analyzed, as shown in Figure 1.
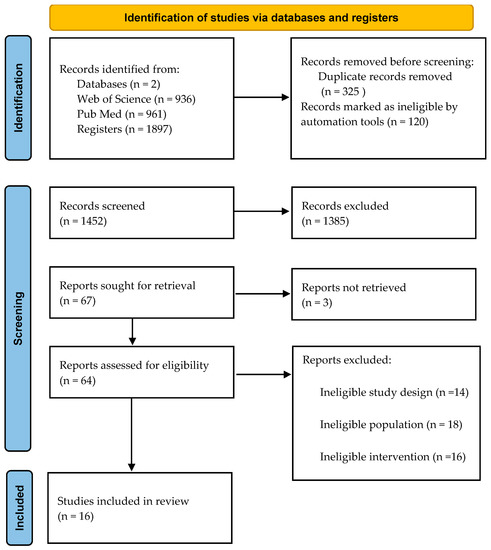
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
Checklist was used to assess the quality and risk of bias by two independent authors (M.A. and D.S). To examine the complete text and determine relativity and bias risk, k-statistics data were used to estimate reviewer concordance. Blind ON option was enabled in the “Rayyan” web tool while reviewing all articles. The received data were examined by the third reviewer (S.P.), who also participated in the final judgment of the selection.
3. Results
3.1. Quality of the Studies
The study assessment scores were calculated using the total number of studies included in the quantitative synthesis and the points each research received on the PEDro scale [17] (Table 2).

Table 2.
PEDro scale results.
3.2. Selection and Characteristics of Studies
There were 1894 studies found after searching electronic resources and reading reference lists. A total of 1449 studies were examined after duplicates were removed. A total of 64 studies were evaluated and selected for eligibility after 1385 research studies were rejected due to inclusion requirements. Two articles were without retrieved reports; 62 were assessed for eligibility. The remaining articles were additionally screened with a full-text read; after that, 16 articles were included in the final analysis, which are shown in Table 3. The criterion for the analysis was to include all the found variables that relate to MF. The used variables that included MF were explosive strength, isometric strength, balance, flexibility, speed, and agility.

Table 3.
Participants, variables, interventions, and results of included studies.
Fourteen studies from nine different countries (Romania, Sweden, Italy, France, Germany, England, Denmark, Spain, Brazil) met the eligibility criteria. The sample of total participants included in this review was 7887. The highest number of participants was 4500 [18], whereas the lowest number of participants was 70 [19]. All of the studies included only male participants, except for the four studies [8,18,20,21], which included both male and female participants, and one study which included only female participants [22]. The longest intervention (36 months) was by [8] and [20], while the shortest (5 months) was by [23]. In each study, there was a significant improvement in at least one tested outcome. Moreover, only one study [24] included high-intensity interval training as a promotion of the MS system in elementary schools. Most interventions were based only on improving MF through modified PE lessons. However, one study included additional nutrition lessons [19], and one study included teacher education related to nutrition [25].
Measured variables were assessed either with the complete Eurofit, Fitnessgram, or Prefit battery test or partly divided as independent or alternative tests. Explosive power of lower limbs was assessed with standing broad jump (SBJ) [18,19,20,21,24,26,27,28,29], with an improvement in seven studies [18,19,21,24,26,28,29], and vertical jump [22,23,30], with an increase in two studies [22,30]. Isometric strength was assessed with the dynamometry of hand grip [20,23,24,26,29,30], with an improvement in four studies [23,26,29,30], knee flexion/extension, with an improvement in two studies [8,30], and bent-arm hang [20,21], with an improvement only in the study by Serbescu et al. (2006) [21]; balance was measured with the flamingo balance test [21,28,31], with an improvement only in the study by Larsen et al. (2018) [28]; the ability of speed was determined with a 20 m [26,27,28] sprint test, with an improvement only in the study by Larsen et al. (2017) [31], and a 10m [19] sprint test without improvement; body composition parameters were evaluated with the body mass index [18,20,23,24,32], waist circumference [24,33], fat mass [8,22,24], fat-free mass [32], and lean mass [8,22,30]; flexibility was assessed with sit-and-reach tests [19,21,24,26,29], with an improvement in three studies [19,21,26].
There were four studies [8,22,27,29] that had daily intervention PE lessons from 12 to 60 min in a range of 10 months to 36 months. Six studies [20,24,26,28,32,33] had no daily or additional intervention but had modified PE lessons, with the span of their intervention during the normal PE curriculum being 6 min to 45 min (min = 1, max = 4 per week) from 9 to 36 months. In intervention studies [19,21,23,25,32] in which experimental groups had additional PE lessons (min = 1 − max = 2 per week), the frequency range of the lessons was from 45 min to 60 min and 5 months to 12 months.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to examine the effectiveness of school-based exercise programs promoting muscle fitness in children aged from 6 to 10. The school environment has long been considered the optimal location for MF promotion since children spend most of their time in school. Primary schools should be the fundamental base for promoting and developing musculoskeletal fitness among children. Overall, there were 16 intervention studies that examined how school-based programs improve MF fitness after both short and long interventions. The major findings of this systematic review show that most of the studies that included explosive power of lower limbs in children were enhanced after physical exercise programs in schools. These findings have significant clinical and public health implications providing evidence-based data supporting the advantages of school-based physical exercise as an effective strategy for improving musculoskeletal fitness in children aged 6 to 10. Moreover, according to recent research, exercise enhances muscle function [19,29,32,33,34], and certain intervention programs have been shown to have excellent impacts on MF [24,26,27]. Furthermore, school-based programs promoting MF are crucial in the childhood period since it is a sensitive period for physical development and for establishing healthy habits, which can have an impact on later maturation, adolescence, and adulthood.
Children with higher weight status have better performance in isometric strength outcomes such as in handgrip tests [34]. As it is difficult to involve such a young schooler in more complex exercises, tests for measuring isometric strength in elementary schools are limited to handgrip and bent-arm hang (BAH) tests. Estimating repetitive strength is also commonly used in elementary schools. Exercises such as sit-ups and push-ups are frequent options when assessing repetitive strength. Our review focused on children aged 6 to 10, and therefore, push-ups are unfeasible to perform at that age. On the other hand, Nobre et al. [26] showed that plyometric training has a small-to-moderate effect size in improving sit-ups (d = 0.39). The same authors assessed the impact of plyometric training on handgrip strength with near-to-small improvement (d = 0.23). In the study by Sollerhed et al. [20], bent-arm hang performance did not improve with expanded physical education lessons. In contrast to that, Serbescu et al. [21] showed that an intervention of extracurricular training involving moderate-intensity-impact exercises achieved progress in BAH performance. In one study [26], plyometric training proved to be an excellent tool for enhancing the number of repetitions and overall strength in sit-ups. Therefore, while there are numerous methods to gain strength, the ideal for kids this age are activities that are simple for them to perform and do not put them at risk for injury. Although these exercises for improving strength in children are basic and easy to perform, they are beneficial for overall health and especially in MF development in children aged 6 to 10.
Explosive strength can be enhanced with the implementation of resistance training [35]. Serbescu et al. [21] showed earlier that various plyometric exercises can improve explosive strength in boys and girls in primary schools. More recently, the results obtained by Weber et al. [19] show that explosive power can also progress with the utilization of soccer training sessions and aquafitness. On the other hand, they show no improvement in the explosive strength of upper extremities when additional PE lessons are incorporated. Furthermore, M N Larsen et al. [27] analyzed the positive effect of small-sided games on standing broad jump, as well as circuit strength training. In contrast to the previous studies, Sollerhed and Ejlertsson [20] found that expanded PE lessons do not have statistically significant improvement in SBJ. Expanded PE lessons reveal plenty of benefits in MF; despite that, there is a lack of evidence for progress in explosive power. On the other hand, Martinez-Vizcaino et al. [24] conducted research with a focus on HIIT training effects in schoolchildren, and concluded that there were no significant improvements in upper body strength but only in lower extremities such as in SBJ. It can be affirmed that HIIT is a new, modernized program. With HIIT, children can have positive outcomes in MF, and as [24] suggested, it can be embedded in PE classes and can be incorporated into lots of interesting games. The reason for poor MF in children could be a deficiency in resistance exercises with external load or bodyweight exercises applied in elementary schools. In addition, the PE curriculum needs important changes, not just to expand the duration of PE lessons but also to modify exercise sets for developing muscle fitness. Therefore, different sports that include games and interesting PE lessons can be a great addition for children to show better results in explosive power. Furthermore, HIIT training is a new and modern program that can contribute to children’s performance as additional training for the lower extremities.
The studies [19,21,26] revealed that with additional PE lessons, plyometric training and moderate-intensity-impact exercises can improve MF in children, such as flexibility. Moreover, expanded PE lessons improve BMI status, balance, and plate tapping [20]. Intervention that was conducted by [31] showed that small-sided football plus other ball games had positive effects on running speed. Furthermore, Siegrist et al. [25] discovered that with additional PE lessons, the average waist circumference of all children in the intervention group decreased significantly, with the impact being stronger in overweight and obese children. Therefore, more than half (54%) of the intervention group of overweight children lowered their waist circumference. Children should be encouraged to exercise, especially between the ages of 6 and 10 when they need to establish a routine and begin exercising. Furthermore, awareness about physical exercise and its advantages should be raised on a higher level in elementary schools as well as involving school-based programs as a successful strategy for developing MF.
The main limitation of this review was dissimilar tests presented in articles for evaluating MF. Furthermore, the participants of the analyzed studies were not homogeneous considering the BMI of the tested children. On the other hand, the key strength of this systematic review was that differences in biological maturity are not manifested in this specific age group (6 to 10 years), which allows clearly determining which school-based programs are most efficient for developing MF.
5. Conclusions
The observed results of this systematic review show that SBJ parameters developed in the majority of studies with interventions that promote MF. Long-lasting interventions did not necessarily improve MF; however, there were shorter interventions that caused the improvement in a larger number of parameters. Our findings suggest that the improved content of the lessons is important for a better development of MF in this age category, as well as an increased volume of physical activities during one school week.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.S. and N.T.; methodology, M.A. and D.S.; software, S.P.; validation, N.T.; formal analysis, D.P.; investigation, M.A. and S.P.; resources, D.S. and M.A.; data curation, D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S. and S.P.; writing—review and editing, N.T.; visualization, N.T. and D.P.; supervision, N.T.; project administration, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Committee on Fitness Measures and Health Outcomes in Youth; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine. Fitness Measures and Health Outcomes in Youth; Pate, R., Oria, M., Pillsbury, L., Youth, C., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grontved, A.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Moller, N.C.; Kristensen, P.L.; Froberg, K.; Brage, S.; Andersen, L.B. Muscle strength in youth and cardiovascular risk in young adulthood (the European Youth Heart Study). Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steene-Johannessen, J.; Anderssen, S.A.; Kolle, E.; Andersen, L.B. Low muscle fitness is associated with metabolic risk in youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelishadi, R.; Gheiratmand, R.; Ardalan, G.; Adeli, K.; Mehdi Gouya, M.; Mohammad Razaghi, E.; Majdzadeh, R.; Delavari, A.; Shariatinejad, K.; Motaghian, M.; et al. Association of anthropometric indices with cardiovascular disease risk factors among children and adolescents: CASPIAN Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 117, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runhaar, J.; Collard, D.C.M.; Singh, A.S.; Kemper, H.C.G.; van Mechelen, W.; Chinapaw, M. Motor fitness in Dutch youth: Differences over a 26-year period (1980–2006). J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeljanovas, A.; Mieziene, B.; Cesnaitiene, V.J.; Fjortoft, I.; Kjønniksen, L. Physical Fitness and Anthropometric Values Among Lithuanian Primary School Children: Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detter, F.; Nilsson, J.A.; Karlsson, C.; Dencker, M.; Rosengren, B.E.; Karlsson, M.K. A 3-year school-based exercise intervention improves muscle strength—A prospective controlled population-based study in 223 children. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B.J.; Rollo, S.; Sampson, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Lang, J.J.; Tremblay, M.S.; Tomkinson, G.R. Health-Related Criterion-Referenced Cut-Points for Musculoskeletal Fitness Among Youth: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 2629–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krochmal, P.; Cooper, D.M.; Radom-Aizik, S.; Lu, K.D. US School-Based Physical Fitness Assessments and Data Dissemination. J. Sch. Health 2021, 91, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriemler, S.; Meyer, U.; Martin, E.; van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Andersen, L.B.; Martin, B.W. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: A review of reviews and systematic update. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.P.; Willumsen, J.; Bull, F.; Chou, R.; Ekelund, U.; Firth, J.; Jago, R.; Ortega, F.B.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. 2020 WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour for children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: Summary of the evidence. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, H.S.; Şahin, F.N.; Maksimovic, N.; Drid, P.; Bianco, A. School-based intervention programs for preventing obesity and promoting physical activity and fitness: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynynen, S.T.; Van Stralen, M.M.; Sniehotta, F.F.; Araújo-Soares, V.; Hardeman, W.; Chinapaw, M.J.M.; Vasankari, T.; Hankonen, N. A systematic review of school-based interventions targeting physical activity and sedentary behaviour among older adolescents. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2016, 9, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.S.; Tidwell, D.K.; Hall, M.E.; Lee, M.L.; Briley, C.A.; Hunt, B.P. A meta-analysis of school-based obesity prevention programs demonstrates limited efficacy of decreasing childhood obesity. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodera, P.; Volta, E.; Gobbi, G.; Milioli, M.A.; Mirandola, P.; Bonetti, A.; Delsignore, R.; Bernasconi, S.; Anedda, A.; Vitale, M. Specifically designed physical exercise programs improve children’s motor abilities. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.S.; Spörkel, O.; Mertens, M.; Freese, A.; Strassburger, K.; Kemper, B.; Bachmann, C.; Diehlmann, K.; Stemper, T.; Buyken, A.E.; et al. Positive Effects of Promoting Physical Activity and Balanced Diets in a Primary School Setting with a High Proportion of Migrant School Children. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollerhed, A.C.; Ejlertsson, G. Physical benefits of expanded physical education in primary school: Findings from a 3-year intervention study in Sweden. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbescu, C.; Flora, D.; Hantiu, I.; Greene, D.; Benhamou, C.L.; Courteix, D. Effect of a six-month training programme on the physical capacities of Romanian schoolchildren. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2006, 95, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenevi-Lundgren, S.; Daly, R.M.; Linden, C.; Gardsell, P.; Karlsson, M.K. Effects of a daily school based physical activity intervention program on muscle development in prepubertal girls. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sandercock, G.R.H.; Cohen, D.D.; Griffin, M. Evaluation of a multicomponent intervention to improve weight status and fitness in children: Upstarts. Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Soriano-Cano, A.; Garrido-Miguel, M.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; de Medio, E.P.; Madrid, V.M.; Martínez-Hortelano, J.A.; Berlanga-Macías, C.; Sánchez-López, M.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V.; et al. The effectiveness of a high-intensity interval games intervention in schoolchildren: A cluster-randomized trial. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M.; Lammel, C.; Haller, B.; Christle, J.; Halle, M. Effects of a physical education program on physical activity, fitness, and health in children: The JuvenTUM project. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, G.G.; De Almeida, M.B.; Nobre, I.G.; Dos Santos, F.K.; Brinco, R.A.; Arruda-Lima, T.R.; De-Vasconcelos, K.L.; De-Lima, J.G.; Borba-Neto, M.E.; Damasceno-Rodrigues, E.M.; et al. Twelve weeks of plyometric training improves motor performance of 7- to 9-year-old boys who were overweight/obese: A randomized controlled intervention. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.N.; Nielsen, C.M.; Orntoft, C.; Randers, M.B.; Helge, E.W.; Madsen, M.; Manniche, V.; Hansen, L.; Hansen, P.R.; Bangsbo, J.; et al. Fitness Effects of 10-Month Frequent Low-Volume Ball Game Training or Interval Running for 8–10-Year-Old School Children. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2719752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.N.; Nielsen, C.M.; Helge, E.W.; Madsen, M.; Manniche, V.; Hansen, L.; Hansen, P.R.; Bangsbo, J.; Krustrup, P. Positive effects on bone mineralisation and muscular fitness after 10 months of intense school-based physical training for children aged 8-10 years: The FIT FIRST randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mačak, D.; Popović, B.; Babić, N.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Madić, D.M.; Trajković, N. The effects of daily physical activity intervention on physical fitness in preschool children. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 40, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeras-Chueca, C.; Villalba-Heredia, L.; Perez-Lasierra, J.L.; Marín-Puyalto, J.; Lozano-Berges, G.; Matute-Llorente, Á.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Gonzalez-Aguero, A.; Casajús, J.A. Active Video Games Improve Muscular Fitness and Motor Skills in Children with Overweight or Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivel, D.; Isacco, L.; Lazaar, N.; Aucouturier, J.; Ratel, S.; Doré, E.; Meyer, M.; Duché, P. Effect of a 6-month school-based physical activity program on body composition and physical fitness in lean and obese schoolchildren. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M.; Hanssen, H.; Lammel, C.; Haller, B.; Halle, M. A cluster randomised school-based lifestyle intervention programme for the prevention of childhood obesity and related early cardiovascular disease (JuvenTUM 3). BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmeyer, A.; Kehne, M.; Herrmann, C. Effects of an intervention for promoting basic motor competencies in middle childhood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervin, R.B.; Fryar, C.D.; Wang, C.Y.; Miller, I.M.; Ogden, C.L. Strength and Body Weight in US Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e782–e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, C.; Marinho, D.A.; Barbosa, T.M.; Izquierdo, M.; Marques, M.C. Effects of concurrent training on explosive strength and VO2max in prepubescent children. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).