Impact of Surface Modification on Performance of Solar Concentrators
Abstract
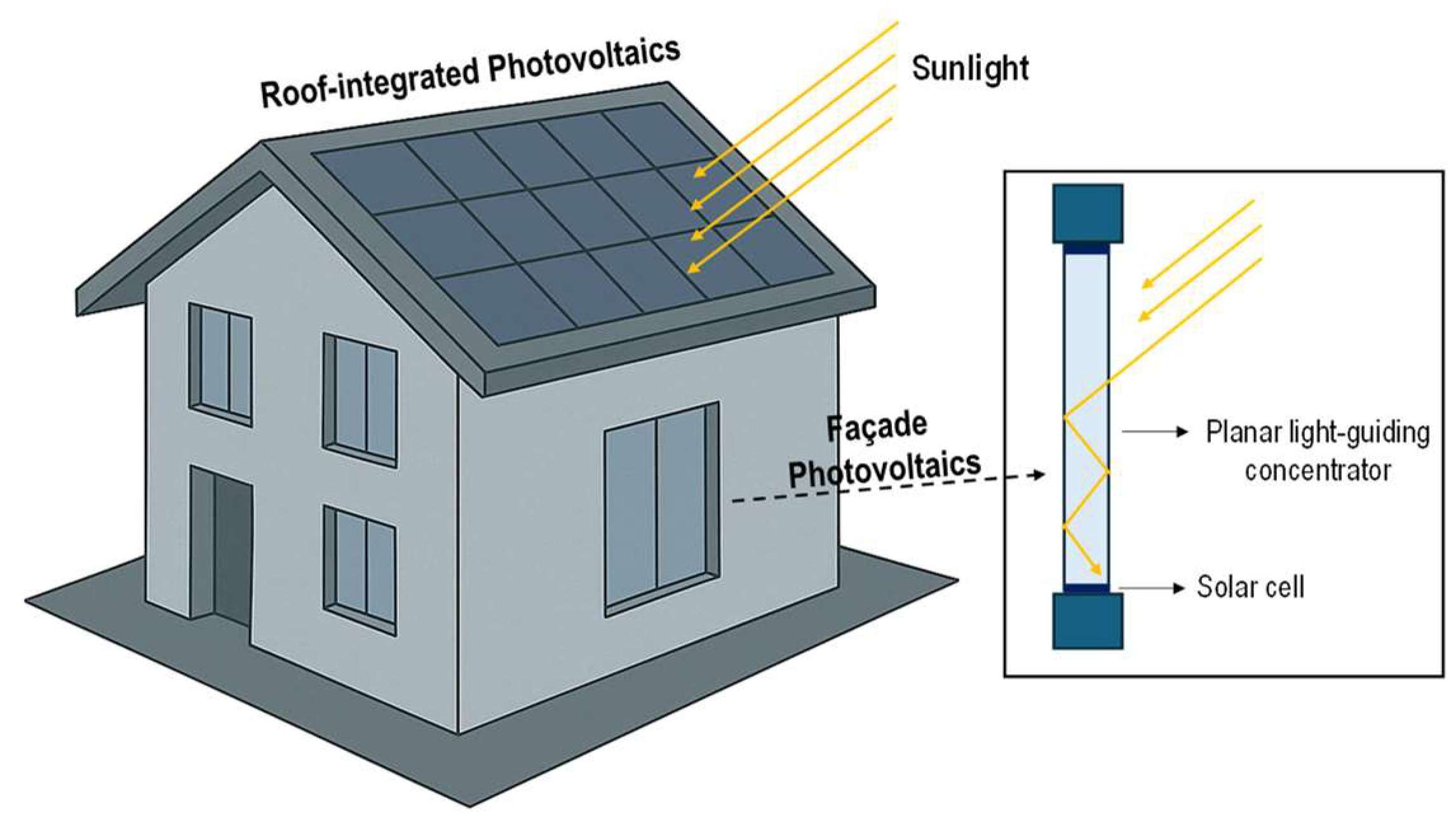
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Contributions
- -
- To investigate how powder-blasted surface modifications on PMMA influence light scattering and total internal reflection.
- -
- To characterize the optical (transmission and angular scattering) and electrical (photovoltaic output) performance of the concentrators using laboratory measurements.
- -
- To compare the experimental results with ray-tracing simulations conducted in OptisWorks, assessing the software’s ability to model non-imaging concentrators accurately.
- -
- To determine the optimal concentrator size for maximizing efficiency while minimizing optical losses.
2. Materials and Methods
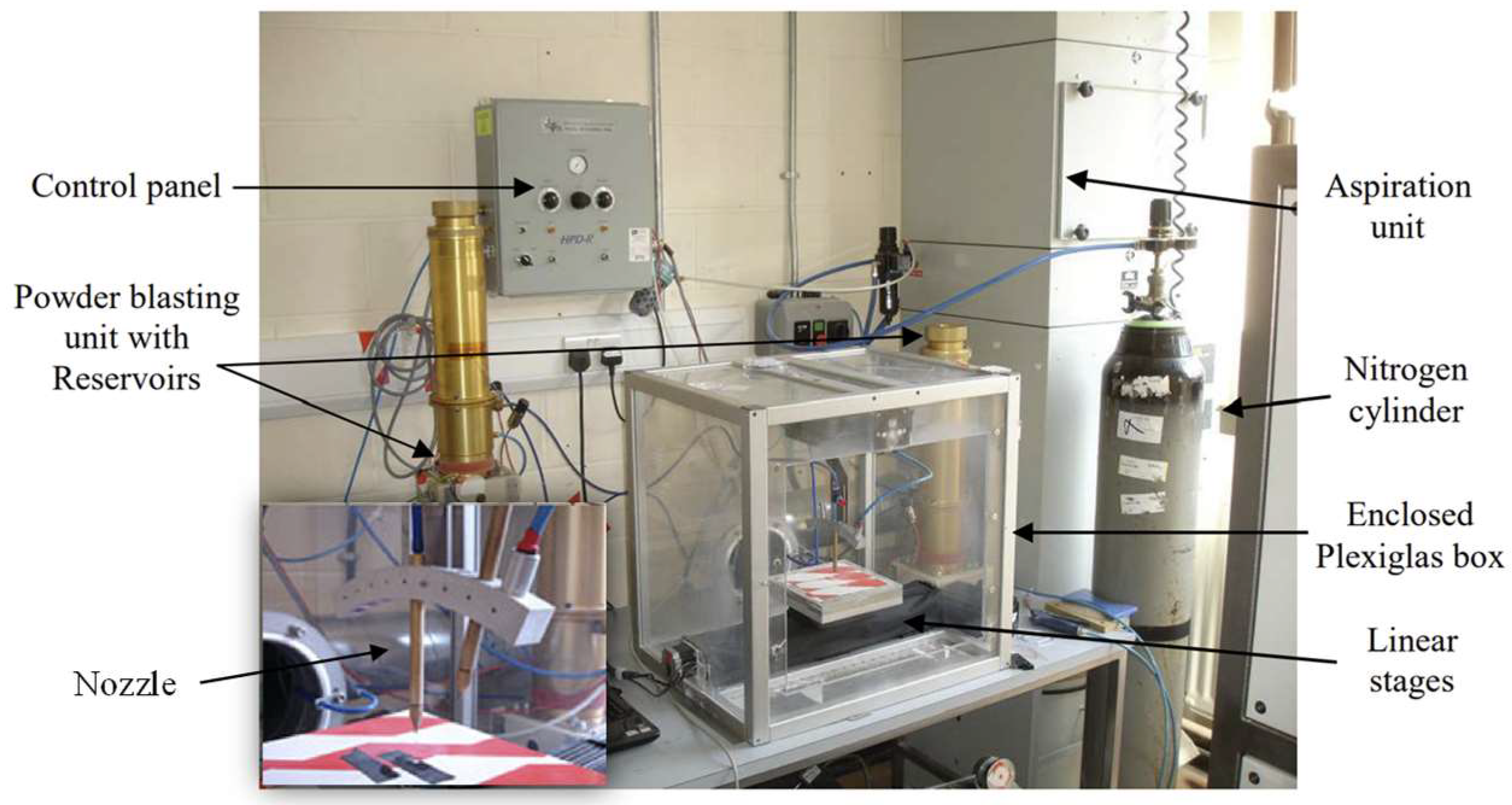
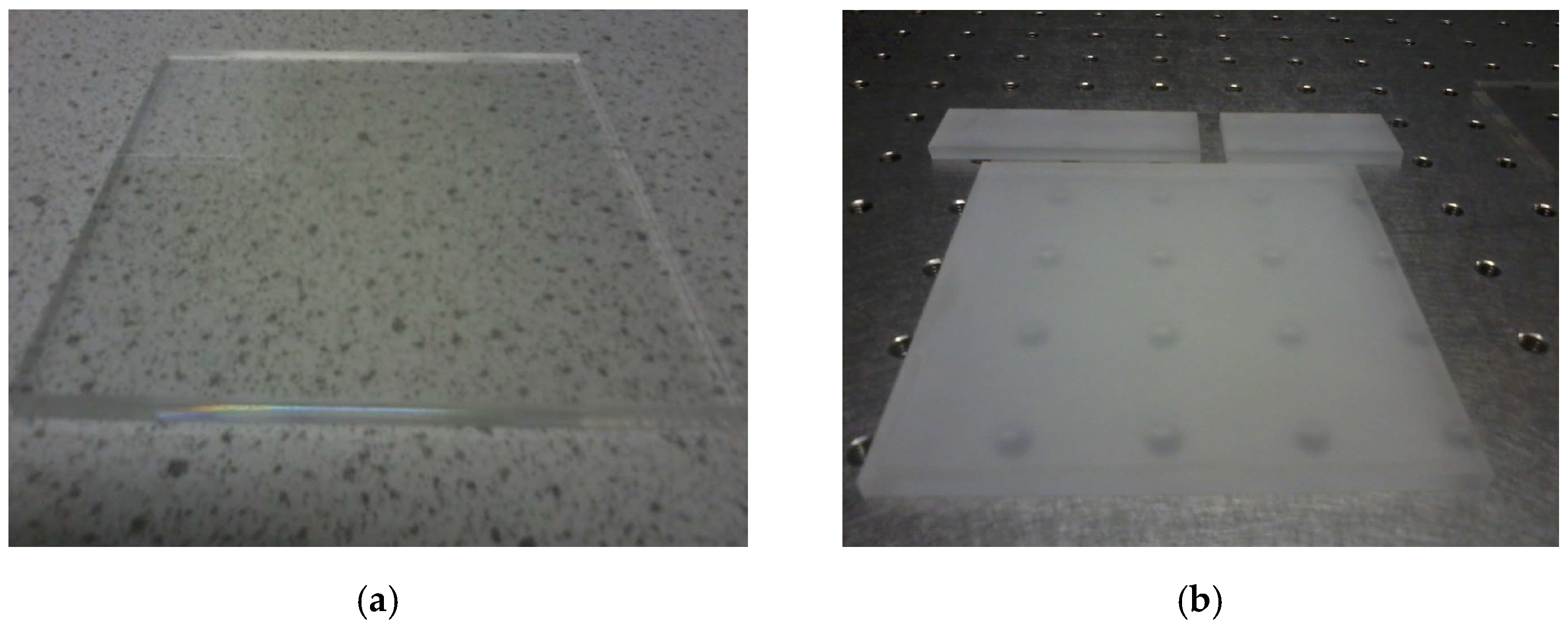
2.1. Sample Preparation
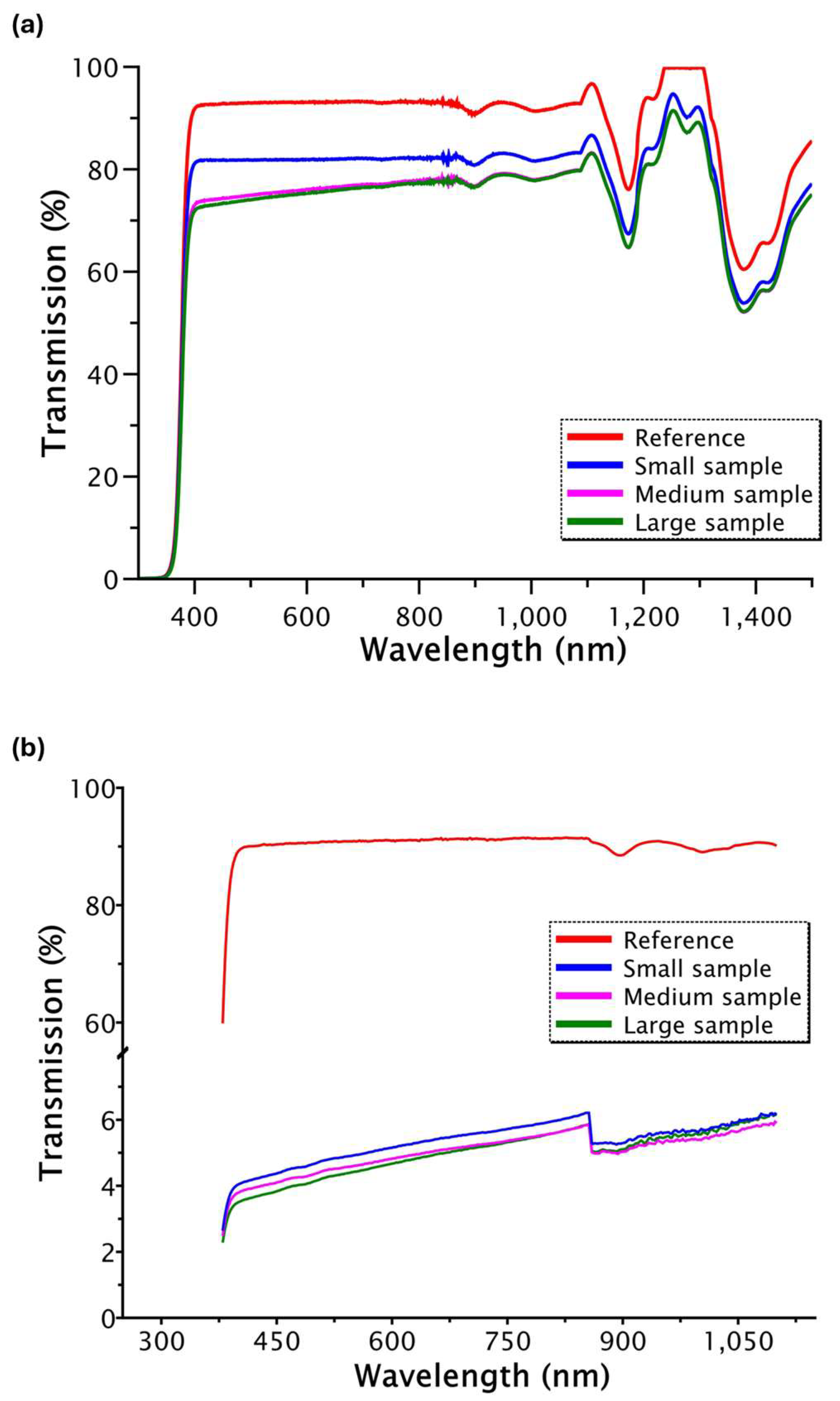
2.2. Transmission Measurements
- Direct (collimated) geometry: The sample was placed perpendicular to the incident beam and aligned along the same optical axis as the detector, allowing for the measurement of specular (zero-angle) transmission.
- Integrating sphere geometry: To account for scattered light at non-zero angles, the sample was positioned in front of an integrating sphere, capturing the total transmitted light over all angles within the acceptance range of the sphere.
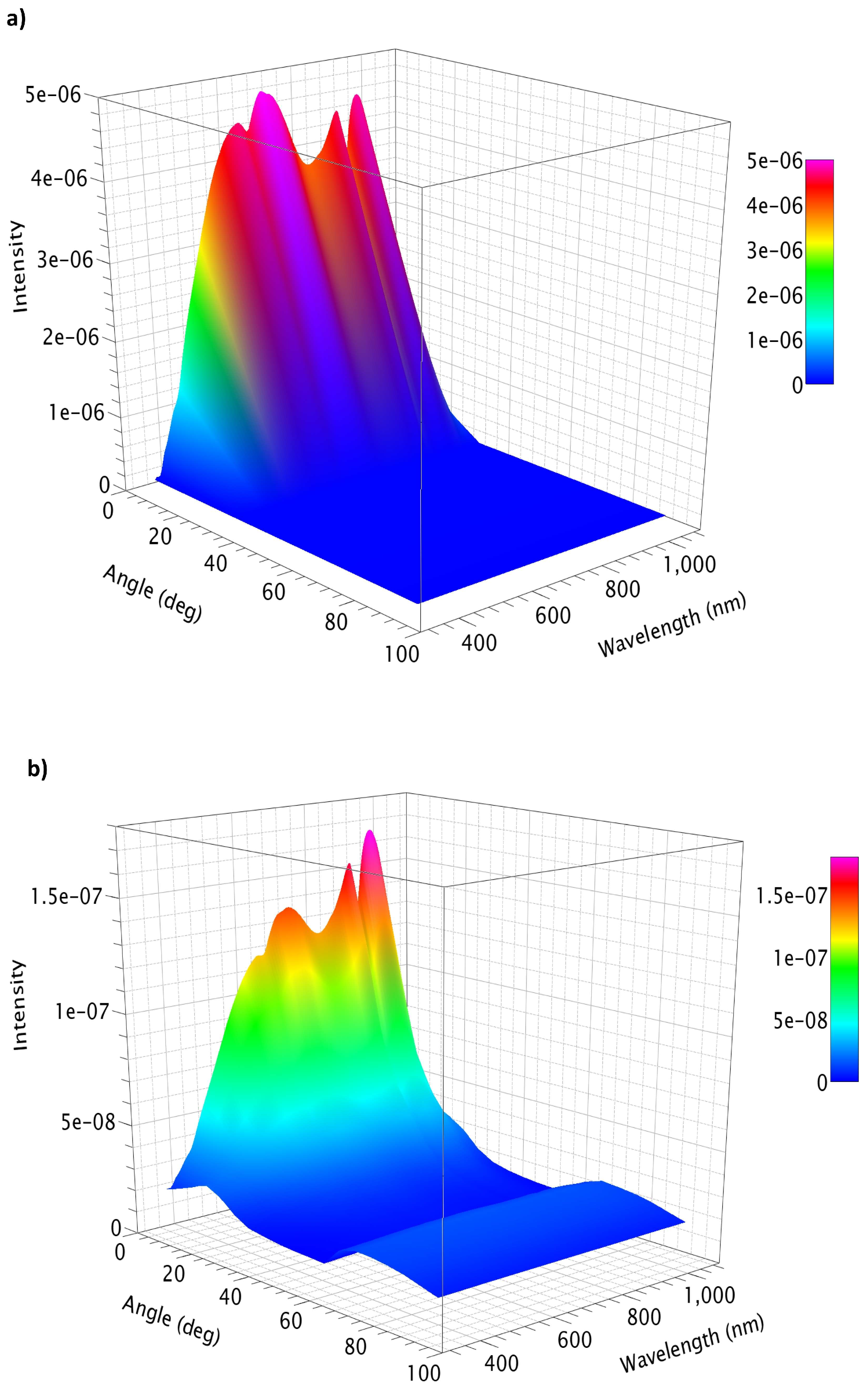
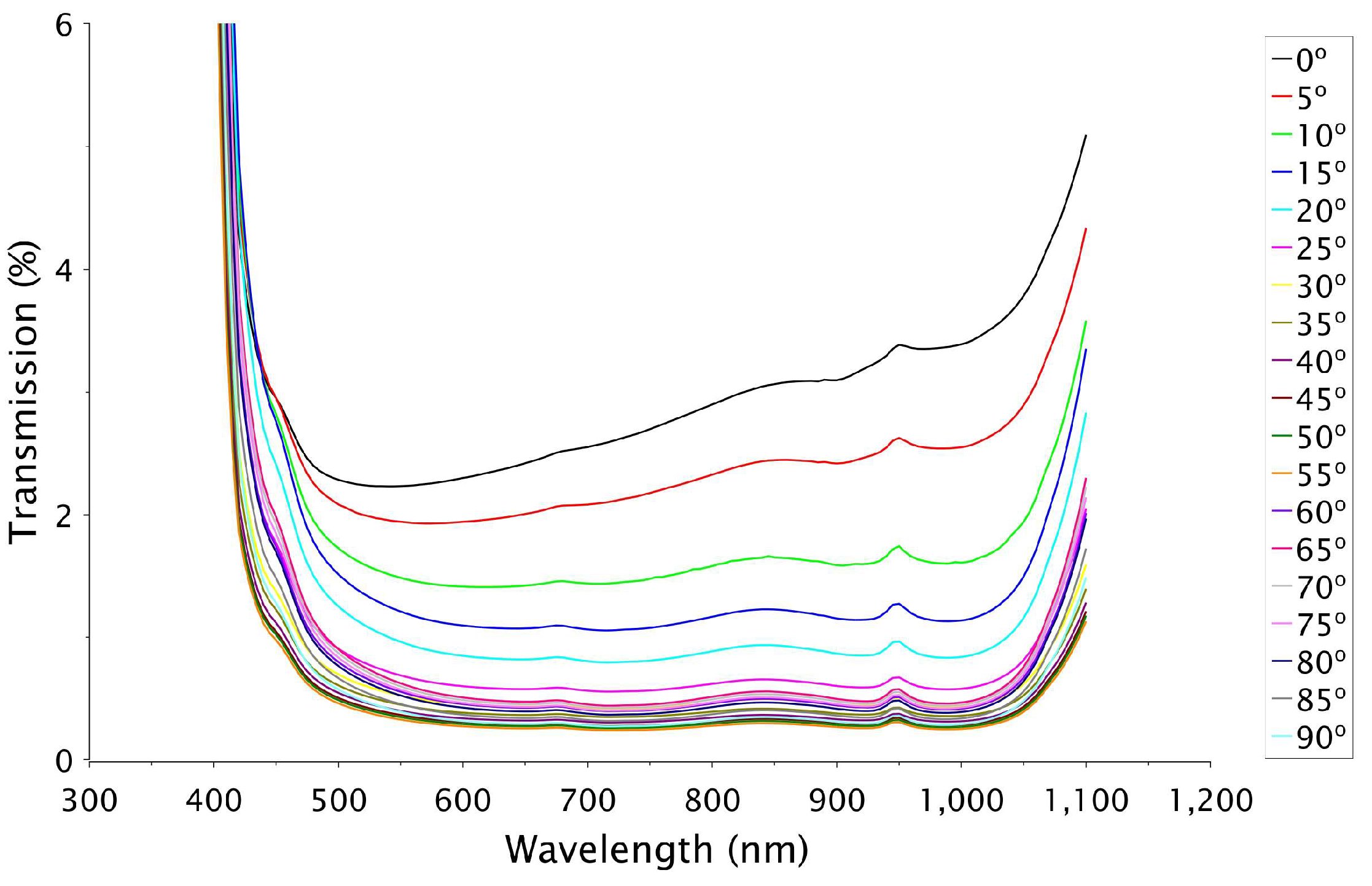
2.3. Scattering Measurements
2.4. Solar Cell Characterization
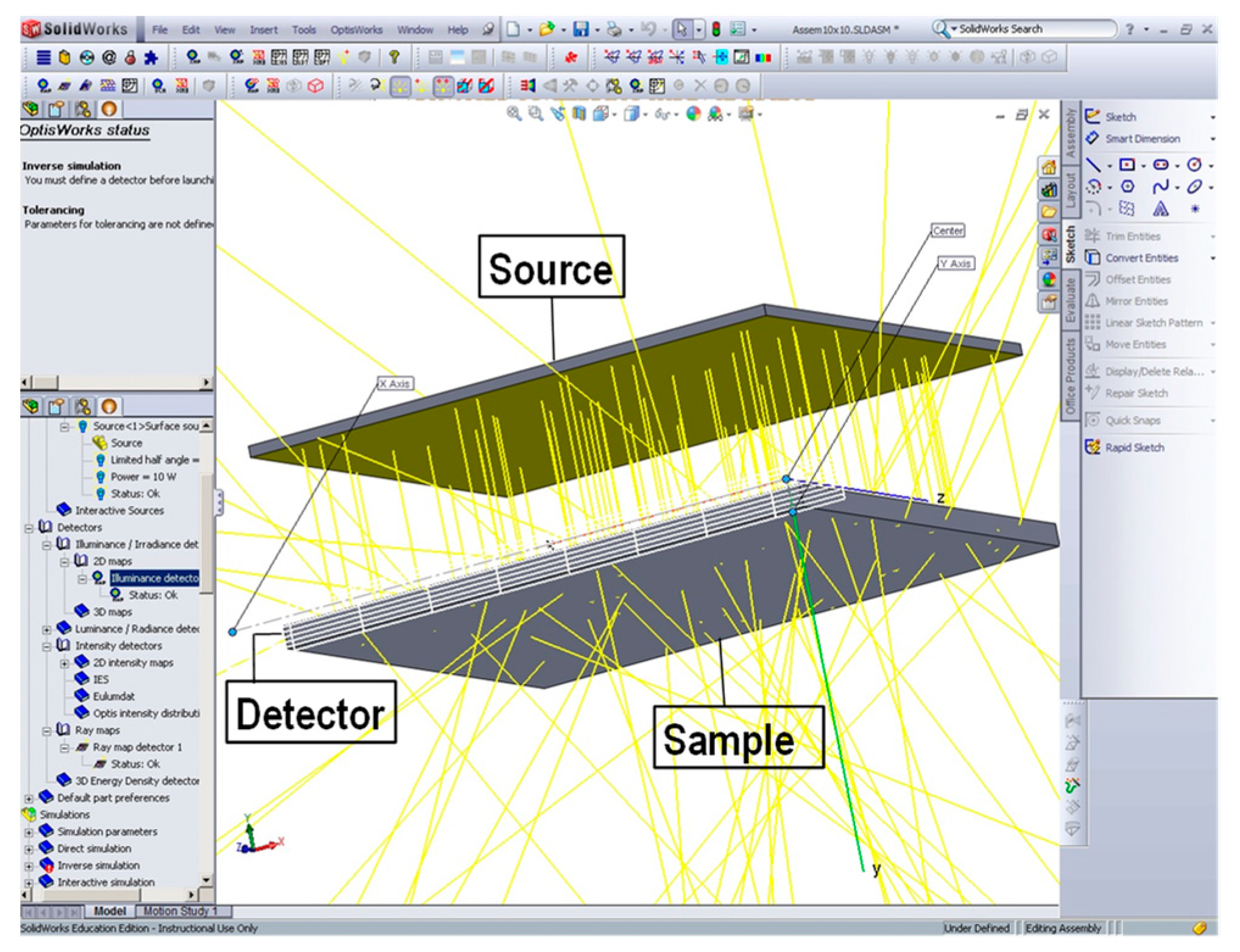
2.5. Simulations in OptisWorks Software
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Transmission
3.2. Angular Scattering Characterization
3.3. Photovoltaic Performance
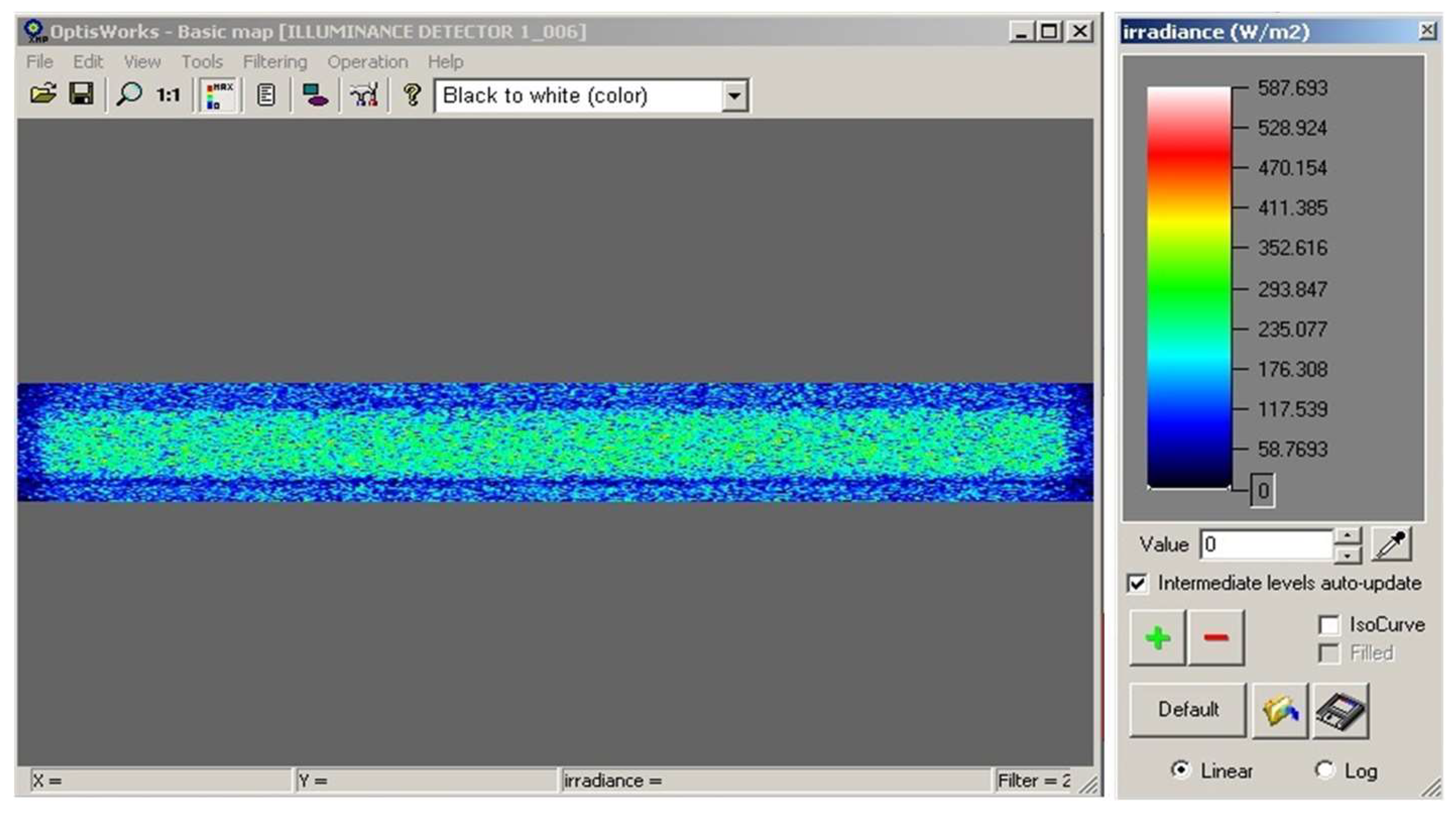
3.4. Ray-Tracing Simulation Results and Comparison with Experimental Data
- -
- Surface model simplification: The powder-blasted surface was modeled as a perfect Lambertian scatterer with 100% diffuse transmission. Although this approach captures the general angular dependence, it does not fully account for the complex, random microstructure of the actual surface.
- -
- Scattering anisotropy: While the surface was modeled as an ideal Lambertian scatterer, real powder-blasted textures may exhibit non-uniform angular distributions. Slight directional biases—e.g., toward forward or backward scattering—can reduce the fraction of light confined by TIR, especially in small waveguides where path length is limited. This may partly explain the higher simulation–experiment discrepancy (23%) observed in the smallest sample.
- -
- Material and environmental variability: Small fluctuations in PMMA properties, solar simulator alignment, and environmental conditions (e.g., slight variations in temperature or air gap) may also affect the experimental outcomes.
- -
- Solar cell efficiency assumptions: The conversion from optical to electrical power assumes a constant 15% cell efficiency, which may not accurately reflect the true behavior under low-flux edge illumination conditions.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PV | Photovoltaics |
| BIPV | Building-integrated photovoltaics |
| PMMA | Poly(methyl methacrylate) |
| CPC | Compound parabolic concentrator |
| LSC | Luminescent solar concentrator |
| PPC | Planar photonic concentrator |
| TIR | Total internal reflection |
| I–V | Current–voltage |
| Isc | Short-circuit current |
| Voc | Open-circuit voltage |
| FF | Fill factor |
| η | Efficiency |
| AM1.5 | Air Mass 1.5 (solar spectrum standard) |
| LCOE | Levelized cost of electricity |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| UV/VIS/NIR | Ultraviolet–visible–near-infrared |
References
- IRENA. Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2023; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2024; Available online: https://www.irena.org/Publications (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Skandalos, N.; Kapsalis, V.; Ma, T.; Karamanis, D. Towards 2030 of Eco-Designed Building Integrated Photovoltaics. Solar 2023, 3, 434–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q.; He, F.; et al. Annual research review of perovskite solar cells in 2023. Mater. Futures 2024, 3, 022102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Zuo, C.; Odunmbaku, G.O.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; et al. Major strategies for improving the performance of perovskite solar cells. iEnergy 2023, 2, 172–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Dunlop, E.D.; Yoshita, M.; Kopidakis, N.; Bothe, K.; Siefer, G.; Hao, X. Solar cell efficiency tables (version 62). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2023, 31, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandalos, N.; Wang, M.; Kapsalis, V.; D’Agostino, D.; Parker, D.; Bhuvad, S.S.; Udayraj; Peng, J.; Karamanis, D. Building PV integration according to regional climate conditions: BIPV regional adaptability extending Köppen-Geiger climate classification against urban and climate-related temperature increases. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, P.; Bonomo, P.; Frontini, F.; Mace, P.; Bosch, E. BIPV Status Report 2020. In Building Integrated Photovoltaics: A Practical Handbook for Solar Buildings’ Stakeholders; SUPSI—Swiss BIPV Competence Centre and Becquerel Institute: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo, P.; Frontini, F.; Loonen, R.; Reinders, A.H.M.E. Comprehensive review and state of play in the use of photovoltaics in buildings. Energy Build. 2024, 323, 114737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Mapping the Surface Heat of Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Optics 2021, 2, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madala, S.; Boehm, R.F. A review of nonimaging solar concentrators for stationary and passive tracking applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R. Principles of solar concentrators of a novel design. Sol. Energy 1974, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablonovitch, E.; Cody, G.D. Intensity enhancement in textured optical sheets for solar cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1982, 29, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.D.; Gillett, A.R. Rapid, Chemical-Free Generation of Optically Scattering Structures in Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Using a CO2 Laser for Lightweight and Flexible Photovoltaic Applications. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 1308381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.H.; Ruby, D.S.; Gee, J.M. Characterization of random reactive ion etched-textured silicon solar cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2001, 48, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.; Paetzold, U.W.; Ghosh, M.; Zhang, W.; Merdzhanova, T.; Jost, G.; Sommer, N.; Michard, S.; Gordijn, A. Fabrication of Light-Scattering Multiscale Textures by Nanoimprinting for the Application to Thin-Film Silicon Solar Cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2014, 4, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.R.; Bueno, B.; Eisenlohr, J.; Kuhn, T.E. Evaluating BIPV Modules with Respect to Textural Appearance, Glare, Colour and Electricity Yield. In Symposium Photovoltaische Solarenergie (PV) 2021. 2021. Available online: https://publica-rest.fraunhofer.de/server/api/core/bitstreams/c03aee12-2c77-48ca-8e7d-405cec5fe492/content (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Mallick, T.K.; Eames, P.C. Electrical performance evaluation of low-concentrating non-imaging photovoltaic concentrator. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2008, 16, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, M.J.; Mapel, J.K.; Heidel, T.D.; Goffri, S.; Baldo, M.A. High-efficiency organic solar concentrators for photovoltaics. Science 2008, 321, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher-Oberlehner, G.; Bardosova, M.; Pemble, M.; Richards, B.S. Planar photonic solar concentrators for building-integrated photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 104, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavinia, H.; Singh, H. Modelling and experimental analysis of low concentrating solar panels for use in building integrated and applied photovoltaic (BIPV/BAPV) systems. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzberger, A.; Wittwer, V. Fluorescent planar collector-concentrators for solar energy conversion. In Festkörperprobleme 19: Plenary Lectures of the Divisions “Semiconductor Physics” “Metal Physics” “Low Temperature Physics” “Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics” “Thin Films” “Surface Physics” “Surface Physics” “Magnetism” of the German Physical Society (DPG) Freudenstadt, March 21–25, 1983; Treusch, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 427–451. [Google Scholar]
- Shurcliff, W.; Jones, R.C. The trapping of fluorescent light produced within objects of high geometrical symmetry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1949, 39, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelder, J.; Zewai, A.; Cole, T. Luminescent solar concentrators. 1: Theory of operation and techniques for performance evaluation. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 3090–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debije, M.G.; Verbunt, P.P. Thirty years of luminescent solar concentrator research: Solar energy for the built environment. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinardi, F.; Colombo, A.; Velizhanin, K.A.; Simonutti, R.; Lorenzon, M.; Beverina, L.; Viswanatha, R.; Klimov, V.I.; Brovelli, S. Large-area luminescent solar concentrators based on ‘Stokes-shift-engineered’ nanocrystals in a mass-polymerized PMMA matrix. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Sanchez, J.-M. Luminescent solar concentrators: Photo-stability analysis and long-term perspectives. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 202, 110134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Pillai, S.R. Effect of Texture Thickness and Angles on Performance Output of a Solar Cell. Eng. Proc. 2024, 61, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polché, M.; Miguel, B.F.J.; González, C.A.G.; Contreras, G.G.; Arellano, V.H.R. Study of the Scattering Effect by SiO(2) Nanoparticles, in a Luminescent Solar Concentrator Sensitized with Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-M.; Fu, H.-Y.; Ying, S.-P.; Hsu, T.-W. Performance of Luminescent Solar Concentrators Integrated with Negative Replica Layers of Leaf Surface Microstructures. Materials 2022, 15, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wu, R.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhen, H. Numerical analysis of the angular insensitive photovoltaic light harvesting with the biomimetic scattering film inspired by the rose petal epidermal topography. Sol. Energy 2018, 170, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Huang, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, R.; Dong, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, H. Design of random microlens arrays with large scattering angles. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-P.; Lin, J.-S.; Lin, T.-C.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Kuo, C.-W.; Chung, M.-H.; Hsieh, T.-E.; Liu, L.-C.; Juang, F.-S.; Chen, N.-P. Using high haze (>90%) light-trapping film to enhance the efficiency of a-Si:H solar cells. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 3325–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Sugawara, H.; Taniguchi, J. Large-Scale Moth-Eye-Structured Roll Mold Fabrication Using Sputtered Glassy Carbon Layer and Transferred Moth-Eye Film Characterization. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, N.; Jacobo-Martín, A.; Vallerotto, G.; Hernández, J.J.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.; Domínguez, C.; Rodríguez, I.; Antón, I. Fabrication of high-performance lens arrays for micro-concentrator photovoltaics using ultraviolet imprinting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensink, H.; Schlautmann, S.; Goedbloed, M.H.; El Wenspoek, M.C. Fine Tuning the Surface Roughness of Powder Blasted Glass Surfaces. In Sensor Technology 2001; Elwenspoek, M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Min, C.H.; Kang, Y.S.; Kim, T.S. Modeling and Recipe Optimization of Anti-Glare Process Using Sandblasting for Electronic Display Glass. Electronics 2020, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daabo, A.M.; Bellos, E.; Pavlovic, S.; Bashir, M.A.; Mahmoud, S.; Al-Dadah, R.K. Characterization of a micro thermal cavity receiver—Experimental and analytical investigation. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 18, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, S.; Daabo, A.M.; Bellos, E.; Stefanovic, V.; Mahmoud, S.; Al-Dadah, R.K. Experimental and numerical investigation on the optical and thermal performance of solar parabolic dish and corrugated spiral cavity receiver. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 150, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrouche, A.; Hardy, D.A.; Ross, D.; Richards, B.S. Luminescent solar concentrators: From experimental validation of 3D ray-tracing simulations to coloured stained-glass windows for BIPV. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 122, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, N.; Richards, B.S.; Mallick, T.K. Evaluation and optimization of the optical performance of low-concentrating dielectric compound parabolic concentrator using ray-tracing methods. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacrotte, Y. Novel Patterning Technology for the LTCC Based Packaging of an Optical Encoder, Microsystems Engineering Centre; School of Engineering & Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University: Edinburgh, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, R.C.; Gray, A.K.; Coleman, T.A. Material Supply System and Method. U.S. Patent US20110211920A1, 1 September 2011. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20110211920A1/en (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Lacrotte, Y.; Carr, J.P.; Kay, R.W.; Desmulliez, M.P. Fabrication of a low temperature co-fired ceramic package using powder blasting technology. Microsyst. Technol. 2013, 19, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticconi, F.; Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Zhurbenko, V. Models for scattering from rough surfaces. Electromagn. Waves 2011, 10, 203–226. [Google Scholar]
- Meinardi, F.; Ehrenberg, S.; Dhamo, L.; Carulli, F.; Mauri, M.; Bruni, F.; Simonutti, R.; Kortshagen, U.; Brovelli, S. Highly efficient luminescent solar concentrators based on earth-abundant indirect-bandgap silicon quantum dots. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X. Achieving High-Efficiency Large-Area Luminescent Solar Concentrators. JACS Au 2023, 3, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenham, S.R.; Green, M.A.; Watt, M.E.; Corkish, R.; Sproul, A. Applied Photovoltaics; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]




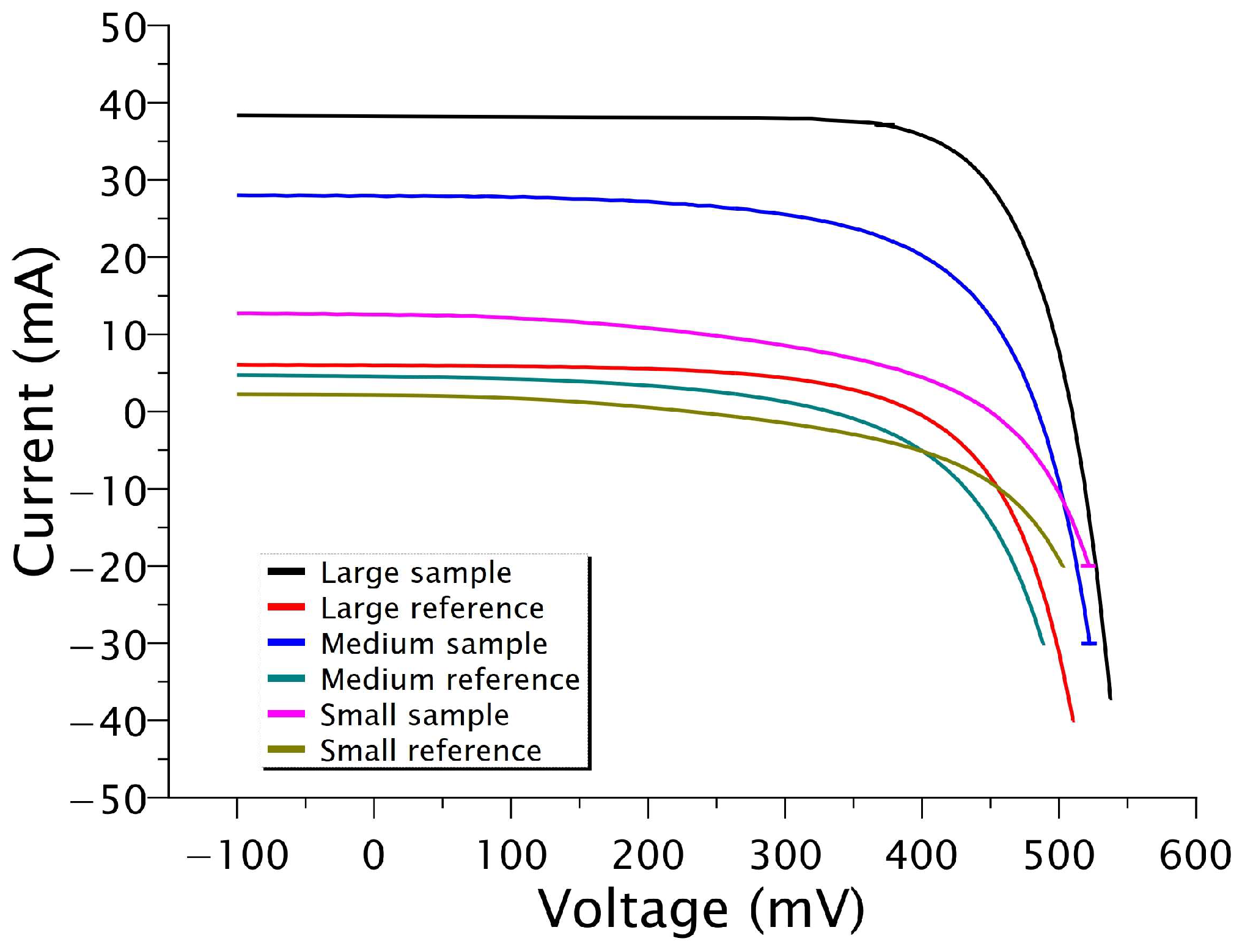
| Sample | Vmpp (mV) | Impp (mA) | Isc (mA) | Voc (mV) | FF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 cm | 391 | 34.8 | 41.2 | 500 | 66.1 |
| Reference | 282 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 391 | 56.9 |
| 25 × 75 mm | 364 | 23 | 27.9 | 482 | 62.4 |
| Reference | 218 | 3.1 | 4.5 | 327 | 45.6 |
| 25 × 50 mm | 291 | 8.8 | 12.6 | 445 | 45.8 |
| Reference | 136 | 1.4 | 2.1 | 227 | 39.6 |
| Sample | Max Power (mW) | Increased Power Ratio | Active Area (cm2) | Active Area Efficiency (%) | Increased Efficiency Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 cm | 14.64 | 11 | 100 | 0.15 | 5 |
| Reference | 1.32 | 0.03 | |||
| 25 × 75 mm | 8.38 | 12.3 | 18.75 | 0.44 | 11 |
| Reference | 0.68 | 0.04 | |||
| 25 × 50 mm | 2.56 | 13.5 | 12.5 | 0.21 | 10.5 |
| Reference | 0.19 | 0.02 |
| Sample | Average Irradiance (W/m2) | Total Flux—OptisWorks (W) | Total Flux—Experimental (W) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 × 10 cm | 289.1 | 0.11 | 0.098 | 10 |
| 25 × 75 mm | 196.3 | 0.059 | 0.056 | 5 |
| 25 × 50 mm | 222.1 | 0.022 | 0.017 | 23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skandalos, N.; Kocher-Oberlehner, G. Impact of Surface Modification on Performance of Solar Concentrators. Solar 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/solar5020017
Skandalos N, Kocher-Oberlehner G. Impact of Surface Modification on Performance of Solar Concentrators. Solar. 2025; 5(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/solar5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkandalos, Nikolaos, and Gudrun Kocher-Oberlehner. 2025. "Impact of Surface Modification on Performance of Solar Concentrators" Solar 5, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/solar5020017
APA StyleSkandalos, N., & Kocher-Oberlehner, G. (2025). Impact of Surface Modification on Performance of Solar Concentrators. Solar, 5(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/solar5020017






