Rational Solutions to the Fourth Equation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Hierarchy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rational Solutions to Order 1 of the NLS4 Equation
3. Rational Solutions to Order 2 of the NLS4 Equation Depending on Two Real Parameters
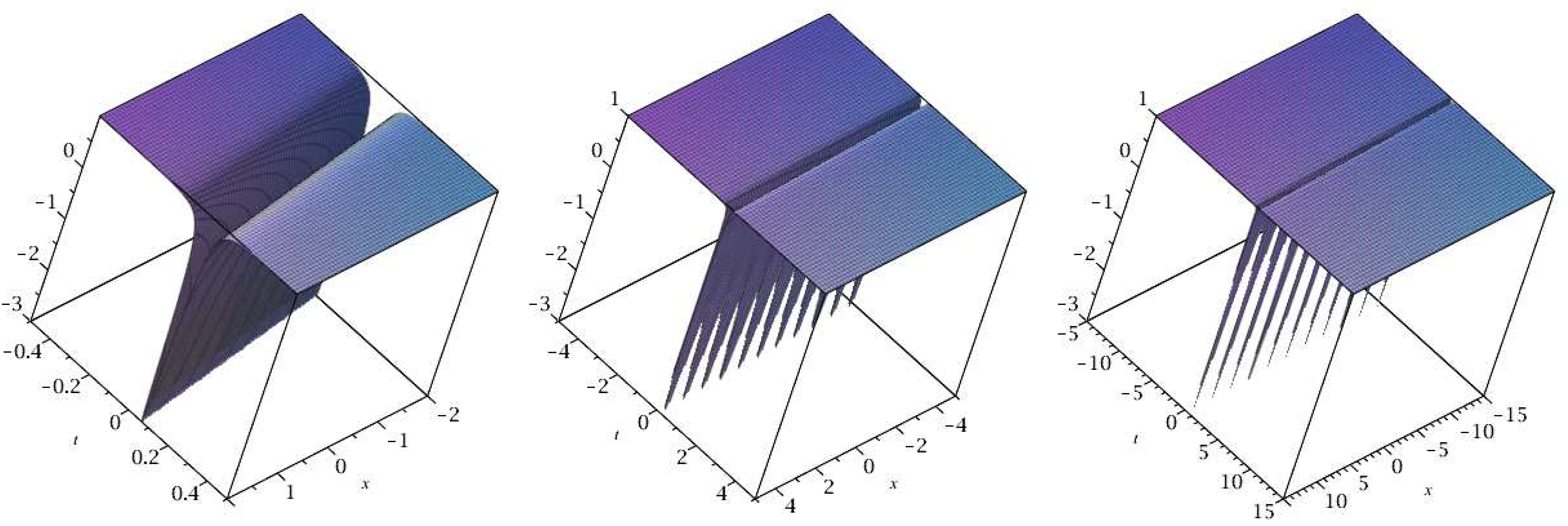
4. Rational Solutions to Order 3 of the NLS4 Equation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Zakharov, V.E. Stability of periodic waves of finite amplitude on a surface of a deep fluid. J. Appl. Tech. Phys. 1968, 9, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmediev, N.; Eleonski, V.; Kulagin, N. Generation of periodic trains of picosecond pulses in an optical fiber: Exact solutions. Sov. Phys. JETP 1985, 62, 894–899. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmediev, N.; Ankiewicz, A.; Soto-Crespo, J.M. Rogues waves and rational solutions of nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 026601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmediev, N.; Ankiewicz, A. First-order exact solutions of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation in the normal-dispersion regime. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 47, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankiewicz, A.; Kedziora, D.J.; Akhmediev, N. Rogue wave triplets. Phys Lett. A 2011, 375, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubard, P.; Gaillard, P.; Klein, C.; Matveev, V.B. On multi-rogue wave solutions of the NLS equation and positon solutions of the KdV equation. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2010, 185, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleonskii, V.; Krichever, I.; Kulagin, N. Rational multisoliton solutions of nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Dokl. Math. Phy. 1986, 287, 606–610. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard, P. Families of quasi-rational solutions of the NLS equation and multi-rogue waves. J. Phys. A Meth. Theor. 2011, 44, 435204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, P. Degenerate determinant representation of solution of the NLS equation, higher Peregrine breathers and multi-rogue waves. J. Math. Phys. 2013, 54, 013504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, P. Other 2N-2 parameters solutions to the NLS equation and 2N+1 highest amplitude of the modulus of the N-th order AP breather. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2015, 48, 145203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S. Modified Korteweg. de Vries equation and scattering theory. Proc. Jpn. Acad. 1972, 48, 466–469. [Google Scholar]
- Wadati, M. The exact solution of the modified Korteweg-de Vries equation. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 32, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y. Algebraic soliton of the modified Korteweg-de Vries equation. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1976, 41, 1817–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdury, A.; Ankiewicz, A.; Akhmediev, N. Periodic and rational solutions of modified Korteweg-de Vries equation. Eur. Phys. J. D 2016, 70, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, M.; Porsezian, K.; Daniel, M. Effect of discreteness on the continuum limit of the Heisenberg spin chain. Phys. Lett. A 1998, 133, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, M.; Daniel, M.; Porsezian, K. On the integrability aspects of the one-dimensional classical continuum isotropic biquadratic Heisenberg spin chain. J. Math. Phys. 1992, 33, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, M.; Porsezian, K.; Lakshmanan, M. On the integrable models of the higher order water wave equation. Phys. Lett. A 1993, 174, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, G.; Sadaf, M.; Dawood, M.; Baleanu, D. Optical solitons for Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel equation with Kerr law non-linearity using improved tan expansion technique. Res. Phys. 2021, 29, 104758. [Google Scholar]
- AlQarni, A.A.; Ebaid, A.; Alshaery, A.A.; Bakodah, H.O.; Biswas, A.; Khan, S.; Ekici, M.; Zhou, Q.; Moshokoa, S.P.; Belic, M.R. Optical solitons for Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel model by Riccati equation approach. Optik 2019, 182, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, R.T.; Babatin, M.M.; Biswas, A. Bright optical solitons for Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel model by semi-inverse variational principle. Optik 2018, 154, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshed, S.; Biswas, A.; Majid, F.B.; Zhou, Q.; Moshokoa, S.P.; Belic, M. Optical solitons in birefringent fibers for Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel model using exp(-iϕ)-expansion method. Optik 2018, 172, 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X. The global solutions for a fourth order NLS equation. Act. Math. Sci. 1995, 15, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Chen, F. Rogue waves for the fourth-order nonlinear Schrdinger equation on the periodic background. Chaos 2021, 31, 023129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakharov, V.E.; Shabat, A.B. Exact theory of two dimensional self focusing and one dimensinal self modulation of waves in nonlinear media. Sov. Phys. JETP 1972, 34, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Its, A.R.; Kotlyarov, V.P. Explicit expressions for the solutions of nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Dockl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Its, A.R.; Rybin, A.V.; Salle, M.A. Exact integration of nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Teore. Mat. Fiz. 1988, 74, 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard, P. Towards a classification of the quasi rational solutions to the NLS equation. Theor. Math. Phys. 2016, 189, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, H.; Grelu, P.; Mihalache, D. Models for supercontinuum generation beyond the slowly-varying-envelope approximation. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 053816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, H.; Mihalache, D. Few-optical-cycle solitons: Modified Korteweg-de Vries sine-Gordon equation versus other non-slowly-varying-envelope-approximation models. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 063835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, R. Exact envelope-soliton solutions of a nonlinear wave equation. J. Math. Phys. 1973, 14, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, P. Rational solutions to the mKdV equation associated to particular polynomials. Wave Motion 2021, 107, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Guzman, J.; Alqahtani, R.T.; Zhou, Q.; Mahmood, M.F.; Moshokoa, S.P.; Ullah, M.Z.; Biswas, A.; Belic, M. Optical solitons for Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel model with spatiotemporal dispersion using the method of undetermined coefficients. Optik 2017, 144, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.; Wani, S.A.; Ramirez, W.; Gandara, F.F. Properties and applications of Bell polynomials of two variables. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2024, 35, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, P. Rogue Waves of the Lakshmanan Porsezian Daniel Equation Depending on Multi-parameters. As. J. Adv. Res. Rep. 2022, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaillard, P. Rational Solutions to the Fourth Equation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Hierarchy. AppliedMath 2024, 4, 1418-1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath4040075
Gaillard P. Rational Solutions to the Fourth Equation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Hierarchy. AppliedMath. 2024; 4(4):1418-1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath4040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaillard, Pierre. 2024. "Rational Solutions to the Fourth Equation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Hierarchy" AppliedMath 4, no. 4: 1418-1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath4040075
APA StyleGaillard, P. (2024). Rational Solutions to the Fourth Equation of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Hierarchy. AppliedMath, 4(4), 1418-1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath4040075




