Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substances and Experimental Groups
2.1.1. Bio-AgNP Synthesis
2.1.2. Bio-AgNP Characterization
2.1.3. Bio-AgNP and Simvastatin Antimicrobial Activity
2.1.4. Bacteria and Growing Conditions
2.1.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
2.1.6. Antimicrobial Combination Assay
2.1.7. Biofilm Formation Inhibition Assay
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Bio-AgNP Characterization
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Antimicrobial Combination (FICI) Assays
3.3. Biofilm-Formation-Inhibition Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| Bio-AgNP | Biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles |
| AgNP | Silver nanoparticles |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| SIM | Simvastatin |
| FICI | Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PBP2a | Penicillin-binding protein 2a |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| HMG-CoA | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoenzymeA reductase |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| TSA | Tryptone Soy Agar |
| TSB | Tryptic Soy Broth |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| MHB | Mueller Hinton Broth |
| OD | Optical density |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy |
| ATCC | American-Type Culture Collection |
References
- Hassoun, A.; Linden, P.K.; Friedman, B. Incidence, Prevalence, and Management of MRSA Bacteremia across Patient Populations—A Review of Recent Developments in MRSA Management and Treatment. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Report on Infection Prevention and Control; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9789240051164. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.S.; de Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishovitz, J.; Hermoso, J.A.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. Penicillin-Binding Protein 2a of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.-F.; Schneper, L.; Mathee, K. Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: From Antibiosis to Resistance and Bacteriology. APMIS 2010, 118, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; El-Naenaeey, E.-S.Y.; Kandeel, T.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Mosbah, R.A.; Nassar, M.S.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bendary, M.M. Promising Antibiofilm Agents: Recent Breakthrough against Biofilm Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Carbone, D.; Parrino, B.; Pecoraro, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P. Therapeutic Strategies To Counteract Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA Biofilm-Associated Infections. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, L.; Gaio, V.; Cerca, N.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Biofilm Formation of Multidrug-Resistant MRSA Strains Isolated from Different Types of Human Infections. Pathogens 2021, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaux, D.; Chauhan, A.; Rendueles, O.; Beloin, C. From in Vitro to in Vivo Models of Bacterial Biofilm-Related Infections. Pathogens 2013, 2, 288–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Gillings, M.; Paulsen, I. Antibiotic Discovery: Combatting Bacterial Resistance in Cells and in Biofilm Communities. Molecules 2015, 20, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Balaji, K.; Girilal, M.; Yadav, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venketesan, R. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Synergistic Effect with Antibiotics: A Study against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Baek, K.-H. Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Antibacterial Potential of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles against Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria along with Its Anticandidal and Antioxidant Effects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimenez, I.F.; Anazetti, M.C.; Melo, P.S.; Haun, M.; De Azevedo, M.M.M.; Durán, N.; Alves, O.L. Cytotoxicity on V79 and HL60 Cell Lines by Thiolated-β-Cyclodextrin-Au/Violacein Nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A Review on Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Biocidal Properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; De Souza, G.I.; Esposito, E. Mechanistic Aspects of Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Several Fusarium Oxysporum Strains. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, E.; Ribeiro, J.; Nishio, E.; Scandorieiro, S.; Costa, A.; Cardozo, V.; de Oliveira, A.; Durán, N.; Panagio, L.; Kobayashi, R.; et al. New Approach For Simvastatin As An Antibacterial: Synergistic Effect With Bio-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7975–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foletto, V.S.; da Rosa, T.F.; Serafin, M.B.; Bottega, A.; Hörner, R. Repositioning of Non-Antibiotic Drugs as an Alternative to Microbial Resistance: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 58, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annamanedi, M.; Varma, G.Y.N.; Anuradha, K.; Kalle, A.M. Celecoxib Enhances the Efficacy of Low-Dose Antibiotic Treatment against Polymicrobial Sepsis in Mice and Clinical Isolates of ESKAPE Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 00805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.d.S.; da Rosa, T.F.; Serafin, M.B.; Bottega, A.; Coelho, S.S.; Foletto, V.S.; Rampelotto, R.F.; Lorenzoni, V.V.; Marion, S.d.L.; Hörner, R. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Amitriptyline and Its Synergistic Effect with Ciprofloxacin, Sulfamethoxazole–Trimethoprim, and Colistin as an Alternative in Drug Repositioning. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Thangamalai, R.; Padmanaban, S.; Kannan, P.; Srinivasan, M.R.; Arunaman, C.S. In-Vitro Synergistic Antibacterial Effect of Atorvastatin and Ampicillin against Resistant Staphylococcus spp. and E. coli Isolated from Bovine Mastitis. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.H.T.; Lareu, R.R.; Dix, B.R.; Hughes, J.D. Statins: Antimicrobial Resistance Breakers or Makers? PeerJ 2017, 5, e3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.B.; Preiss, D.; Tobert, J.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Page, R.L.; Goldstein, L.B.; Chin, C.; Tannock, L.R.; Miller, M.; Raghuveer, G.; et al. Statin Safety and Associated Adverse Events A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, E38–E81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Maki, K.C.; Ito, M.K.; Cohen, J.D.; Sponseller, C.A.; Bell, M.; Brinton, E.A.; Jacobson, T.A. Statin Associated Muscle Symptoms: Characteristics of Patients and Recommendations by Providers. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schech, S.; Graham, D.; Staffa, J.; Andrade, S.E.; La Grenade, L.; Burgess, M.; Blough, D.; Stergachis, A.; Chan, K.A.; Platt, R.; et al. Risk Factors for Statin-Associated Rhabdomyolysis. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2007, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, L.L.; McCormick, M.L.; Denning, G.M.; Weintraub, N.L. Antioxidant Effects of Statins. Drugs Today 2004, 40, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, M.; Fujiwara, D.; Takeda, T.; Kino, T.; Tomonari, Y.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Satou, T.; Sakaguchi, K.; Nishida, S. The Sensitivity of Head and Neck Carcinoma Cells to Statins Is Related to the Expression of Their Ras Expression Status, and Statin-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated via Suppression of the Ras/ERK and Ras/MTOR Pathways. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.; Brahmandam, A.; Brownson, K.E.; Huynh, N.; Reynolds, J.; Lee, A.I.; Fares, W.H.; Ochoa Chaar, C.I. Statin Therapy Associated with Improved Thrombus Resolution in Patients with Deep Vein Thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2019, 7, 169–175.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, J. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Statins on Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of 15 Randomized Controlled Trials. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, A.; Wheeler-Jones, C.P.D.; Gage, M.C. The Immunomodulatory Effects of Statins on Macrophages. Immuno 2022, 2, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerwood, S.; Cohen, J. Unexpected Antimicrobial Effect of Statins. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 61, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, T.S.; Cuzzullin, M.C.; Franco, G.C.; Schwartz-Filho, H.O.; de Andrade, E.D.; Groppo, F.C.; Cogo-Müller, K. Statins and Antimicrobial Effects: Simvastatin as a Potential Drug against Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, R.D.P.; Casarin, R.C.V.; de Lima, P.O.; Cogo-Müller, K. Statins with Potential to Control Periodontitis: From Biological Mechanisms to Clinical Studies. J. Oral. Biosci. 2021, 63, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolina de Carvalho, R.D.; de Andrade Moreno, J.; Roque, S.M.; Chan, D.C.H.; Torrez, W.B.; Stipp, R.N.; Bueno-Silva, B.; de Lima, P.O.; Cogo-Müller, K. Statins and Oral Biofilm: Simvastatin as a Promising Drug to Control Periodontal Dysbiosis. Oral. Dis. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Leng, H.; Yuan, W.; Song, C. Simvastatin-Hydroxyapatite Coatings Prevent Biofilm Formation and Improve Bone Formation in Implant-Associated Infections. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.; Khan, H.; Khan, A.; Cameotra, S.; Alzohairy, M. Anti-Biofilm Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles against MRSA and MRSE Isolated from Wounds in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 33, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarusha, L.; Paoletti, S.; Travan, A.; Marsich, E. Alginate Membranes Loaded with Hyaluronic Acid and Silver Nanoparticles to Foster Tissue Healing and to Control Bacterial Contamination of Non-Healing Wounds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.-M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-Related Infections: Bridging the Gap between Clinical Management and Fundamental Aspects of Recalcitrance toward Antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cluzet, V.C.; Gerber, J.S.; Nachamkin, I.; Metlay, J.P.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Davis, M.F.; Julian, K.G.; Royer, D.; Linkin, D.R.; Coffin, S.E.; et al. Duration of Colonization and Determinants of Earlier Clearance of Colonization with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Durán, N.; Alves, O.L.; Esposito, E.; de Souza, G.I.; Marcato, P.D. Processo de Produção de Nanopartículas de Prata Estabilizadas por Proteínas na Produção de Produtos Têxteis Antibacterianos e o Tratamento dos Efluentes Produzidos. Braz. patent PI 0605681-4 A, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.A.; Ansary, A.A.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I. Extracellular Biosynthesis of CdSe Quantum Dots by the Fungus, Fusarium Oxysporum. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Odds, F.C. Synergy, Antagonism, and What the Chequerboard Puts between Them. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doern, C.D. When Does 2 Plus 2 Equal 5? A Review of Antimicrobial Synergy Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Su, B.-A.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Hsu, H.-J.; Ko, W.-C.; Tang, H.-J. Efficacy of Combination Oral Antimicrobial Agents against Biofilm-Embedded Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Gharaei-Fathabad, E.; Naghibi, F. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Induced by the Fungus Penicillium Citrinum. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birla, S.S.; Tiwari, V.V.; Gade, A.K.; Ingle, A.P.; Yadav, A.P.; Rai, M.K. Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata and Its Combined Effect against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, N.; Prakash, S. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by the Fungus Aspergillus Niger and Its Efficacy against Mosquito Larvae. Rep. Parasitol. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vala, A.K.; Shah, S.; Patel, R.N. Biogenesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Marine- Derived Fungus Aspergillus Flavus from Bhavnagar Coast, Gulf of Khambhat, India. J. Mar. Biol. Oceanogr. 2014, 3, 1000122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Chand Mali, S.; Trivedi, R. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Enicostemma Axillare (Lam.) Leaf Extract. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2814–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharara, J.; Ramezani, T.; Hosseini, N.; Mousavi, M. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Coating with Zataria Multiflora Leaves Extract Induced Apoptosis in HeLa Cells Through P53 Activation. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 627–639. [Google Scholar]
- Noronha, V.T.; Paula, A.J.; Durán, G.; Galembeck, A.; Cogo-Müller, K.; Franz-Montan, M.; Durán, N. Silver Nanoparticles in Dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 1110–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandorieiro, S.; de Camargo, L.C.; Lancheros, C.A.C.; Yamada-Ogatta, S.F.; Nakamura, C.V.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Duran, N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Synergistic and Additive Effect of Oregano Essential Oil and Biological Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 00760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, E.K.; Yamada, A.Y.; de Araujo, L.A.; Anversa, L.; Garcia, D.d.O.; de Souza, R.L.B.; Martins, H.M.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Affect Motility and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 656984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisignano, C.; Ginestra, G.; Smeriglio, A.; La Camera, E.; Crisafi, G.; Franchina, F.A.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Alibrandi, A.; Trombetta, D.; Mondello, L.; et al. Study of the Lipid Profile of ATCC and Clinical Strains of Staphylococcus Aureus in Relation to Their Antibiotic Resistance. Molecules 2019, 24, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habash, M.B.; Goodyear, M.C.; Park, A.J.; Surette, M.D.; Vis, E.C.; Harris, R.J.; Khursigara, C.M. Potentiation of Tobramycin by Silver Nanoparticles against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00415-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Remelli, W.; Forlani, F.; Gambino, M.; Landini, P.; Cappitelli, F. Effects of Chronic Sub-Lethal Oxidative Stress on Biofilm Formation by Azotobacter vinelandii. Biofouling 2012, 28, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles: Present Situation and Prospects for the Future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.-Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIckey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Different Drugs for Bad Bugs: Antivirulence Strategies in the Age of Antibiotic Resistance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Yang, P.W.; Yang, S.F.; Hsieh, K.P.; Tseng, S.P.; Lin, Y.C. Topical Simvastatin Promotes Healing of Staphylococcus Aureus-Contaminated Cutaneous Wounds. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz; Özcengiz, G. Antibiotics: Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity, Resistance and Multidrug Efflux Pumps. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smelser, L.K.; Walker, C.; Burns, E.M.; Curry, M.; Black, N.; Metzler, J.A.; McDowell, S.A.; Bruns, H.A. Short Term, Low Dose Simvastatin Pretreatment Alters Memory Immune Function Following Secondary Staphylococcus Aureus Infection. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Smékalová, M.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Röderová, M.; Dyčka, F.; Šebela, M.; Prucek, R.; Tomanec, O.; et al. Bacterial Resistance to Silver Nanoparticles and How to Overcome It. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocate, K.P.; Reis, G.F.; de Souza, P.C.; Oliveira Junior, A.G.; Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Furlaneto, M.C.; de Almeida, R.S.; Panagio, L.A. Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin against Toxigenic Species of Aspergillus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, J.; Sarkhel, S.; Mukherjee, N.; Jaiswal, A. Nanomaterial-Based Antimicrobial Coating for Biomedical Implants: New Age Solution for Biofilm-Associated Infections. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45962–45980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Immobilized Silver Nanoparticles Enhance Contact Killing and Show Highest Efficacy: Elucidation of the Mechanism of Bactericidal Action of Silver. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.; Karandikar, B.; Bonn-Savage, N.; Gibbins, B.; Roullet, J.-B. Antimicrobial Surface Functionalization of Plastic Catheters by Silver Nanoparticles. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, C. Audit of Catheter-Associated UTI Using Silver Alloy-Coated Foley Catheters. Br. J. Nurs. 2006, 15, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Catalano, M.; Taurino, A.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A.; Sannino, A. Antibacterial Coatings on Haemodialysis Catheters by Photochemical Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussin, J.; Robles-Botero, V.; Casañas-Pimentel, R.; Rojas, F.; Angiolella, L.; San Martín-Martínez, E.; Giusiano, G. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles Targeting Skin and Soft Tissue Infectious Agents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orta-García, S.T.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Ochoa-Martínez, A.C.; Ruiz-Vera, T.; Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; Velázquez-Salazar, J.J.; Yacamán, M.J.; Navarro-Contreras, H.R.; Pérez-Maldonado, I.N. Analysis of Cytotoxic Effects of Silver Nanoclusters on Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells ‘ in Vitro’. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.F.; Paschoal, A.C.C.; Klimeck, T.D.F.; Kuligovski, C.; Marcon, B.H.; de Aguiar, A.M.; Murray, P.G. Biological Synthesis of Low Cytotoxicity Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) by the Fungus Chaetomium Thermophilum—Sustainable Nanotechnology. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, H.; Kopecki, Z.; Bright, R.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S.; Goswami, N.; Vasilev, K. Ultrasmall AgNP-Impregnated Biocompatible Hydrogel with Highly Effective Biofilm Elimination Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41011–41025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.T.; Chen, Y.T.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Girsang, S.P.; Wang, R.S.; Chang, Y.C.; Shen, S.H.; Shen, C.R.; Lin, T.P.; Wan, D.; et al. Dual-Functional Antibiofilm Polymer Composite for Biodegradable Medical Devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehregan, D.R.; Mehregan, D.A.; Pakideh, S. Cheilitis Due to Treatment with Simvastatin. Cutis 1998, 62, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, O.M.; Campbell, W.W. Dermatomyositis-like Syndrome and HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor (Statin) Intake. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, B. Lupus Erythematosus and Other Autoimmune Diseases Related to Statin Therapy: A Systematic Review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadir, R.; Liebmann, J. Clinical Oncology Case Report Radiation Reaction Recall Following Simvastatin Therapy: A New Observation. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 7, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, S.; Bourke, B.; Hazelwood, E.; Bourke, J.F. Simvastatin-Occupational Contact Dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 2007, 57, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peramiquel, L.; Serra, E.; Dalmau, J.; Vila, A.T.; Mascaró, J.M.; Alomar, A. Occupational Contact Dermatitis from Simvastatin. Contact Dermat. 2005, 52, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, S.A.; Pearse, A.D.; Anstey, A.V. Chronic Actinic Dermatitis Secondary to Simvastatin. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2002, 18, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskay, T.; Kutluay, L. Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by Simvastatin. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 28, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoebner, P.-E.; Michot, C.; Ligeron, C.; Durand, L.; Meynadier, J.; Meunier, L. Simvastatin-Induced Lichen Planus Pemphigoides. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2003, 130, 187–190. [Google Scholar]

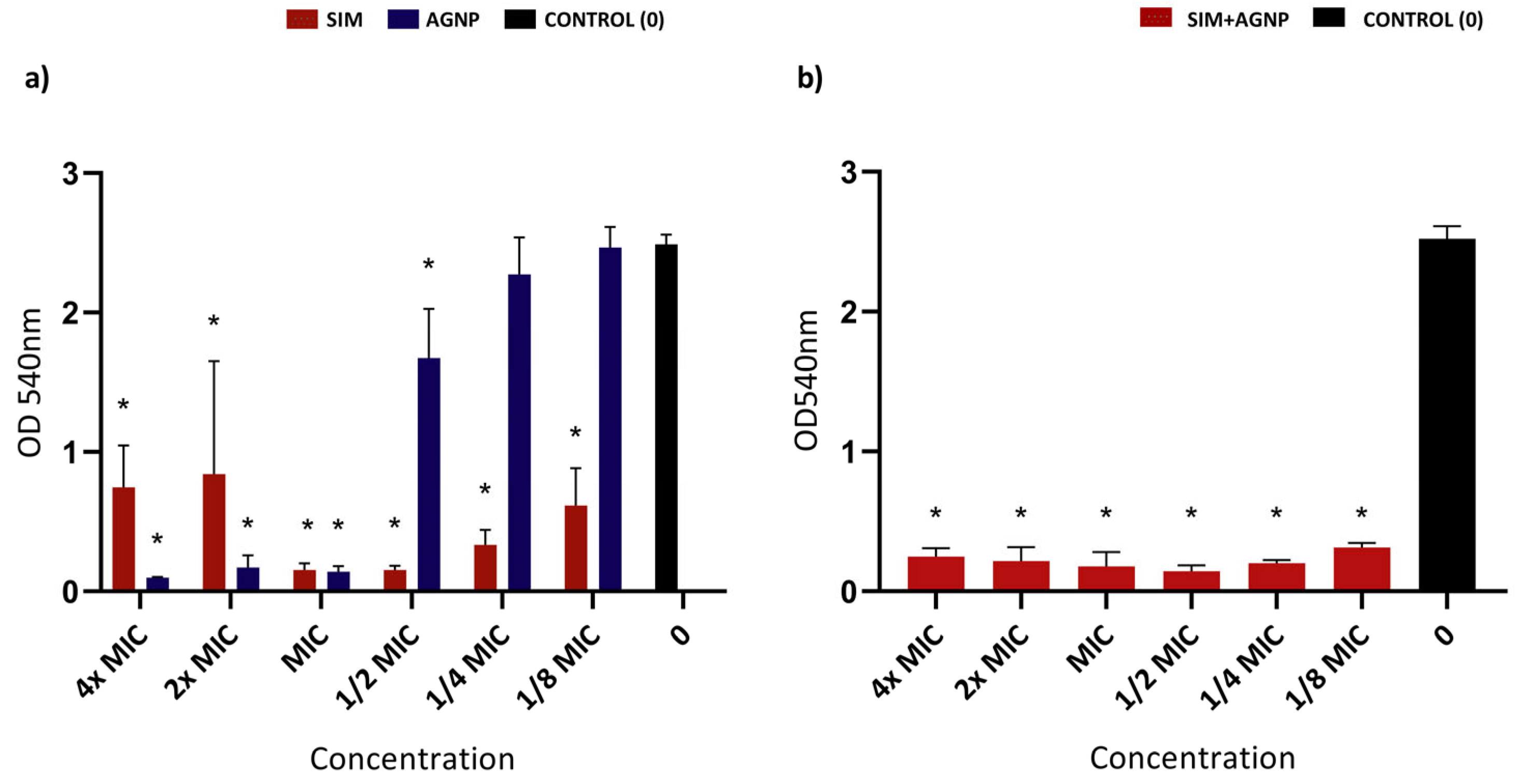

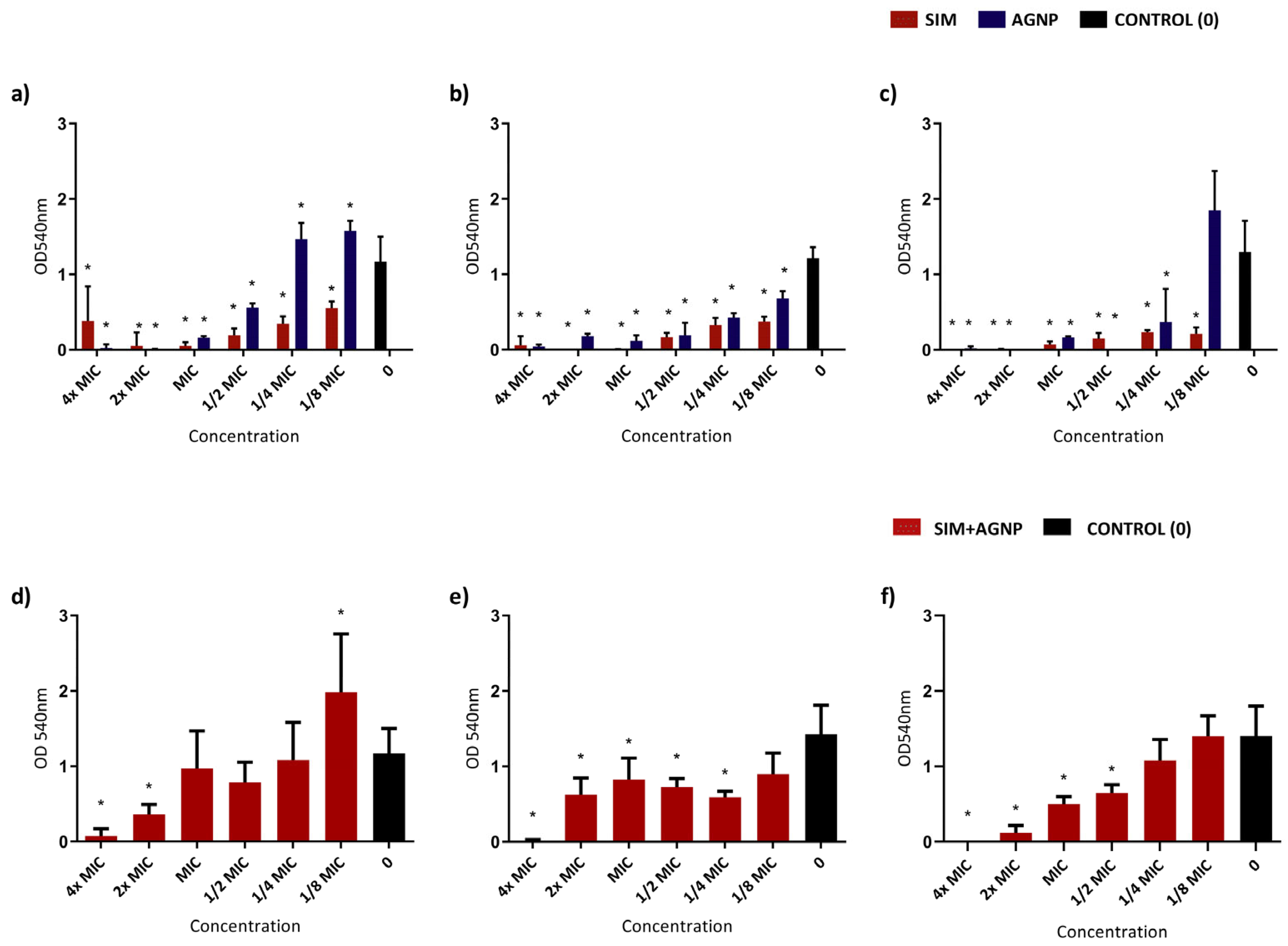
| Strains | MIC | Association MIC | FICI Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIM (μM) | Bio-AgNP (μM) | SIM + Bio-AgNP | ||
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 74.66 | 31.88 | 74.66 + 31.88 | 0.32 |
| S. aureus ATCC 43300 | 149.32 | 63.75 | 149.32 + 63.75 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus ATCC 33591 | 149.32 | 31.88 | 149.32 + 31.88 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus ATCC 6538 | 74.66 | 31.88 | 74.66 + 31.88 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus HC 3817719 (MRSA) | 74.66 | 187.5 | 74.66 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus HC 10106876 (MRSA) | 74.66 | 187.5 | 74.66 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus HC 9120358 (MRSA) | 74.66 | 187.5 | 74.66 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus HC 12092392 (MSSA) | 74.66 | 93.75 | 74.66 + 93.7 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus HC 985444 (MSSA) | 74.66 | 93.75 | 74.66 + 93.75 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus 909 (MSSA) | 149.32 | 187.5 | 149.32 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus 1734 (MSSA) | 74.66 | 93.75 | 74.66 + 93.75 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus 1744 (MSSA) | 74.66 | 187.5 | 74.66 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
| S. aureus 1641 (MSSA) | 74.66 | 187.5 | 74.66 + 187.5 | 2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, A.C.F.; Roque, S.M.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Nakazato, G.; Durán, N.; Cogo-Müller, K. Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin. Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4, 3-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010002
da Silva ACF, Roque SM, Duarte MCT, Nakazato G, Durán N, Cogo-Müller K. Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin. Future Pharmacology. 2024; 4(1):3-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010002
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Ana Carolina Furian, Sindy Magri Roque, Marta Cristina Teixeira Duarte, Gerson Nakazato, Nelson Durán, and Karina Cogo-Müller. 2024. "Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin" Future Pharmacology 4, no. 1: 3-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010002
APA Styleda Silva, A. C. F., Roque, S. M., Duarte, M. C. T., Nakazato, G., Durán, N., & Cogo-Müller, K. (2024). Modulation of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation through Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin. Future Pharmacology, 4(1), 3-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol4010002






