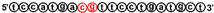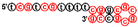Abstract
Synthetic CpG oligonucleotides are promising components of immunomodulatory drugs for the treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases, cancers, and allergies. Phosphorothioate modification stabilizes these compounds, contributing to the achievement of a clinical effect, but at the same time changes their immunomodulatory properties. We used the diffusible fluorescent dye dihydroethidium and the non-diffusible 6-carboxy-2′,7′dihydrochlorofluorescein diacetate and cytochrome c probes to demonstrate that it is the phosphorothioate backbones that determine the pronounced nonspecific pro-oxidant effect of CpG ODN on neutrophils. At the same time, as was shown using diaminofluorescein diacetate, the potentiation of nitric oxide synthesis in these leucocytes by CpG ODN class A strictly depends on the presence of CpG motifs and a palindromic “hairpin”. The results obtained will contribute to a more complete understanding of the physiological action of therapeutic agents based on synthetic CpG oligonucleotides.
1. Introduction
Synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) with non-methylated CpG motifs mimic bacterial DNA fragments and have a range of immunomodulatory properties [1]. A significant disadvantage of native phosphodiester (PO) oligonucleotide constructs is their sensitivity to endonuclease degradation. Phosphorothioate (PS) modifications increase resistance to the nucleases, thus providing ODNs half-life sufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect. Depending on the structural features and activity on peripheral blood mononuclear cells, synthetic CpG ODNs are usually divided into three main classes. Class A ODNs have PS-modified poly-guanosine ends and a phosphodiester palindromic central fragment forming a “hairpin”. Yamamoto et al. were the first to discover oligonucleotides with unique palindromic sequences containing CpG but not GpC motifs to augment NK cells activity in mice [2]. Later, CpG ODNs with PO palindromic core sequences such as 5′ -purine-purine-C-G-purine-pyrimidine-C-G-pyrimidine-pyrimidine-3′, such as ODN 2216 [3] and ODN 2336 [4], have been characterized as major contributors to strong IFN-α production in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Class B ODN are completely phosphoroathioate-substituted linear molecules stimulating B lymphocytes and NK cells [5]. Class C ODNs contain a completely PS backbone and CpG-containing palindromic motif. They stimulate B cells as well as type I IFN secretion of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells [6]. Immune cells responsiveness to CpG motifs containing ODNs is provided by TLR9 receptor [7]. Pronounced immunoregulatory properties determine CpG ODNs attractiveness as vaccine adjuvants, immunoprotective agents in cancer therapy and anti-allergens [8]. However, clinical trials of preparations based on PS ODNs have revealed a number of inherent disadvantages that prevent their widespread implementation. Serious side effects, namely thrombocytopenia, fatigue, fever, rashes, leukopenia, and complement activation [9], are most likely associated with the non-selectivity of the oligonucleotides action. In addition to peripheral blood mononuclear cells, other cells of the immune system, in particular, neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes, PMNLs), can also be targets of PS CpG ODNs.
Neutrophils are the most abundant phagocytic immune cells. Their main role is to kill invading microorganisms launching a wide range of effector responses among which the generation of large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is central. The bulk of ROS is derived from superoxide (O2•−) produced by NADPH oxidase (Nox). Patients with chronic granulomatous disease, which is a disorder etiologically associated with loss of Nox functionality, suffer from recurrent bacterial and fungal infections [10,11]. Being a powerful antimicrobial weapon, neutrophils-derived ROS also play an important role in the progression of inflammatory disorders. Disturbances in the regulation of ROS formation causes endothelial dysfunction and tissue injury [12,13].
Neutrophils have a rich receptor arsenal for recognizing pathogen- and damage-associated molecular patterns [14] as well as proinflammatory cytokines. These cells are the first to respond to the appearance of pro-inflammatory stimuli and rush from the bloodstream to the tissues, finding themselves in the foci of damage or pathogen penetration much earlier than other leukocytes. High reactogenicity, which provides neutrophils with the ability to timely and effectively implement the microbicidal function, at the same time, is the Achilles’ heel of these cells, making them sensitive to any drug effect.
Previously, we have shown the ability of PS CpG ODN to potentiate leukotriene synthesis in neutrophils, revealed their pro-apoptogenic activity, and noticed their pro-oxidant effect [15,16]. This study was conducted to differentiate non-selective and sequence-determined specific effects of class A CpG ODNs on the oxidative status of neutrophilic granulocytes.
2. Materials and Methods
Oligodeoxyribonucleotides were synthesized and purified by DNA-synthesis (Moscow, Russia). Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS), Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fibrinogen from human plasma, cytochrome c from equine heart (Cyto C), Iron containing superoxide-dismutase (Fe-SOD) from E. coli and 4,5-Diaminofluorescein diacetate (DAF-2 DA) were purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). 6-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (Carboxy-H2DCF-DA) and Dihydroethidium (DHE) were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA).
2.1. Neutrophils Isolation
Human peripheral neutrophils were isolated from the citrate-anticoagulated blood of healthy volunteers by previously described standard technique [17]. Briefly, after dextran sedimentation allowing the removal of erythrocytes, neutrophils were isolated from leukocyte-rich plasma by centrifugation through Ficoll-Paque (1.077 g/mL), followed by hypotonic lysis of the remaining erythrocytes and double washing with PBS. Neutrophils (96–97% purity, 98–99% viability as established by trypan blue staining) were then suspended at 2 × 107 cells/mL D-PBS containing 1 mg/mL glucose and stored at room temperature.
2.2. ROS Detection
Cytoplasmic ROS production was monitored by measuring green fluorescence of H2DCF oxidation product according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, human neutrophils were incubated with 5 μM Carboxy-H2DCF-DA for 60 min, at room temperature, followed by a PBS wash. PMNLs were then resuspended in HBSS supplemented with 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4 (HBSS/HEPES), divided into fibrinogen-coated wells of a 96-well plate (4 × 105 cells/well) and incubated, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 in the presence of agents added according to experimental protocol. Fluorescence intensity was monitored every 10 min for at least 30 min using a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany) with excitation and emission wavelengths of 488 and 525 nm, respectively.
Total superoxide anion production was detected by measuring of hydroxyethidium (EOH) fluorescence [18]. PMNLs were suspended in HBSS/HEPES supplemented with 10 µg/mL DHE and divided into fibrinogen-coated wells of 96-well plate (4 × 105 cells/well) followed by incubation, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 in the presence of agents added according to the experimental protocol. Fluorescence intensity was monitored every 5 min for at least 30 min using a CLARIOstar microplate reader with excitation and emission wavelengths of 480 and 567 nm, respectively.
Semi-quantitative determination of extracellular superoxide was carried out using spectrophotometric detection of SOD-inhibitable reduction of Cyto C. The method originally proposed by Babior et al. [19] was adapted to continuous assay in a microtiter plate format [20,21]. Reaction mixtures (HBSS/HEPES containing 30 µM Cyto C with or without ODNs or identical samples with Fe-SOD (100 U/mL)) were pre-warmed in fibrinogen-coated wells of 96-well plate. Added PMNLs (4 × 105 cells/probe) were then incubated for at least 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2, while absorption spectra were measured every 5 min in the range of 500–600 nm using a CLARIOstar microplate reader. PMNLs samples in HBSS/HEPES were used as blanks to cut off the light scattering of cell suspension. The rate of Cyto C reduction (ferrocytochrome c formation) was estimated as the difference between the absorption values at 550 and 531 nm (absorption peaks inherent in ferri- and ferrocytochrome c, respectively).
2.3. Quantification of Neutrophils Adhesion
PMNLs suspended in HBSS/HEPES were divided into fibrinogen-coated wells of 96-well plate (2 × 105 cells/well). After 30 min incubation, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 in the presence of agents added according to the experimental protocol weakly attached cells were carefully removed by washing with warm PBS. The percent of adhered neutrophils was determined by the method based on the measurement of absorption of 2,3-diaminophenazine, a colored product of MPO-catalyzed oxidation of o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD) by H2O2 [22]. H2O2 (4 mM final concentration) with 5.5 mM OPD in permeabilizing buffer (67 mM Na2HPO4, 35 mM citric acid, and 0.1% Triton X-100) was added to wells with attached PMNLs for 5 min. The reaction was stopped by adding of 1 M H2SO4. The absorption was measured at a wavelength of 490 nm and compared with the calibration values.
2.4. Study of PMNLs Morphology by Scanning Electron Microscopy
Morphological changes in neutrophils under the ODNs action were detected using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). PMNLs (1.5 × 106 cells/mL HBSS/HEPES) were seeded on fibrinogen-coated coverslips placed into the cultural dishes with pre-warmed HBSS/HEPES. Samples were incubated, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 with or without additives for 20 min. Cells attached to the substrate were then fixed by 2.5% glutaraldehyde in HBSS/HEPES containing 5 mM EDTA and 0.5 mM PMSF followed by post-fixing with 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate, 0.1 M sucrose, pH 7.3. Subsequent dehydration was carried out in a series of acetones (10–100%) with drying in a Balzer apparatus at the critical point with liquid CO2 as the transition liquid. The dried samples were sputtered with gold/palladium and visualized on a CamScan S-2 scanning electron microscope at a voltage of 15 kV. ImageJ-win64 software was used to quantify the area occupied by neutrophils on the substrate.
2.5. NO Detection
Nitrogen oxide (NO) production was monitored by measuring green fluorescence of triazolofluorescein (DAF-2T), the reaction product of DAF-2 with NO. PMNLs were incubated with 5 μM DAF-2 DA for 60 min, at room temperature, followed by a PBS wash. Loaded PMNLs were then resuspended in HBSS/HEPES, divided into fibrinogen-coated wells of a 96-well plate (4 × 105 cells/well) and incubated, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 in the presence of agents added according to experimental protocol. Fluorescence intensity was monitored every 10 min for at least 30 min using a CLARIOstar microplate reader.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
To quantify ROS generation and adhesion RM one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s or Tukey’s multiple comparison test was performed. Two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used for NO synthesis quantification. Statistical calculation and plotting are performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.2.0 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
A comparative study of prooxidative properties was carried out for CpG-containing oligonucleotides belonging to three major classes: class A (ODNs 2216 and 2336), class B (ODNs 2006 and 1668) and class C (ODN 2395) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Oligodeoxyribonucleotides used in the study.
To evaluate the effect of oligonucleotides on cytoplasmic ROS accumulation by human neutrophils in vitro, we used Carboxy-H2DCF-DA. This cell permeant probe is known to predominantly retain in the cytosol. Being non-selective, this indicator is convenient for the total assessment of cytoplasmic accumulation of, primarily, hydrogen peroxide, as well as other reactive oxygen species. We also used the approach described by Peshavariya [18] for predominant detection of total superoxide, both extra- and intracellular. Briefly, the method is based on the measurement of the yellow fluorescence of 2-hydroxyethidium (EOH), formed by the interaction of DHE with superoxide and, unlike ethidium, does not intercalate into DNA. The spectrophotometric measurement of SOD-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction made it possible to assess CpG ODNs effect on the formation of the extracellular superoxide.
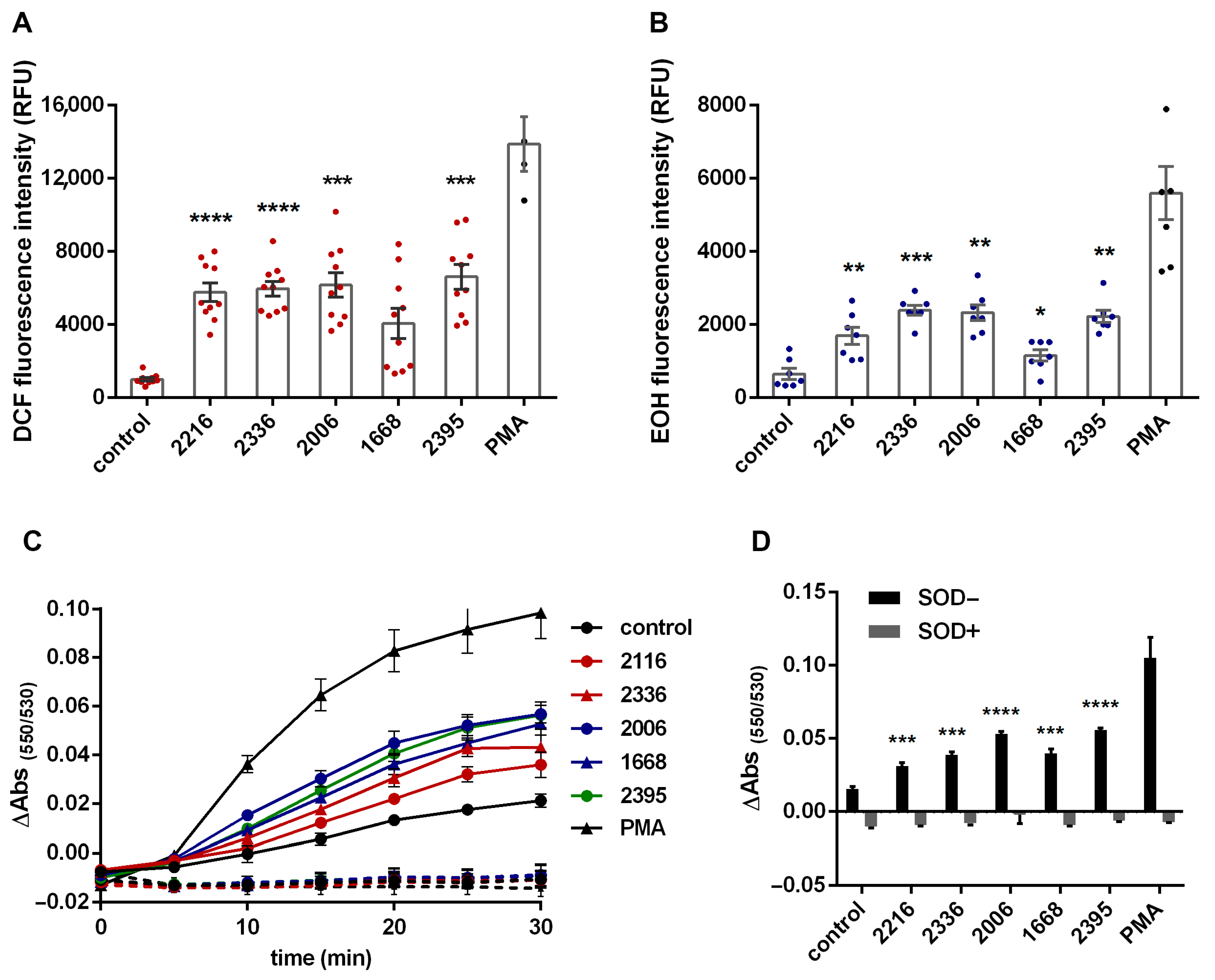
It turned out that oligonucleotides of all three classes, including class B ODN 1668, which is a murine TLR9 ligand, have powerful prooxidant properties, causing both hydrogen peroxide accumulation in PMNLs cytoplasm (Figure 1A) and the formation of intra- and extracellular pools of superoxide (Figure 1B–D). The cytochrome c reduction under the treatment with ODNs was completely eliminated by the addition of SOD, which indicates the absence of other reducing agents, except for superoxide anion.
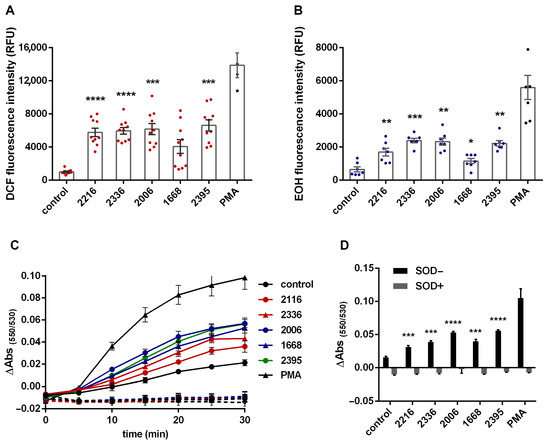
Figure 1.
CpG oligonucleotides classes A, B and C have a pronounced prooxidant effect on neutrophils. H2DCF-DA-loaded (A) or DHE-stained (B) PMNLs were treated with 1 µM ODNs, except control samples, and cultured in HBSS/HEPES medium for at least 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2, and 5 nM PMA was used as positive control in several experiments (not included in the statistical analysis). DCF (A) or EOH (B) fluorescence (excitation/emission 488/525 or 480/567 nm, respectively) was measured every 10 min for DCF and every 5 min for EOH. Data are represented as scatter plots with bars indicating means ± SEM of fluorescence intensity values at 30 min after addition of stimuli (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 compared with controls, RM one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (C,D). PMNLs were incubated for 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2 in the presence of 30 µM Cyto C without additives (control) or with 1 µM ODNs (solid lines (C), black bars (D)). Fe-SOD (100 U/mL) was added for reference probes (dotted lines (C), grey bars (D)). Absorbance spectra were recorded every 5 min to assume the rate of Cyto C reduction. Presented are changes in differences between absorption values at 550 and 531 nm (ΔAbs(550/531)) as typical blank corrected curves obtained for triplets of single experiment (C) or summary data plots (means ± SEM, n = 3) for ΔAbs(550/531) after 30 min incubation (D) (*** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 compared with control, RM one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
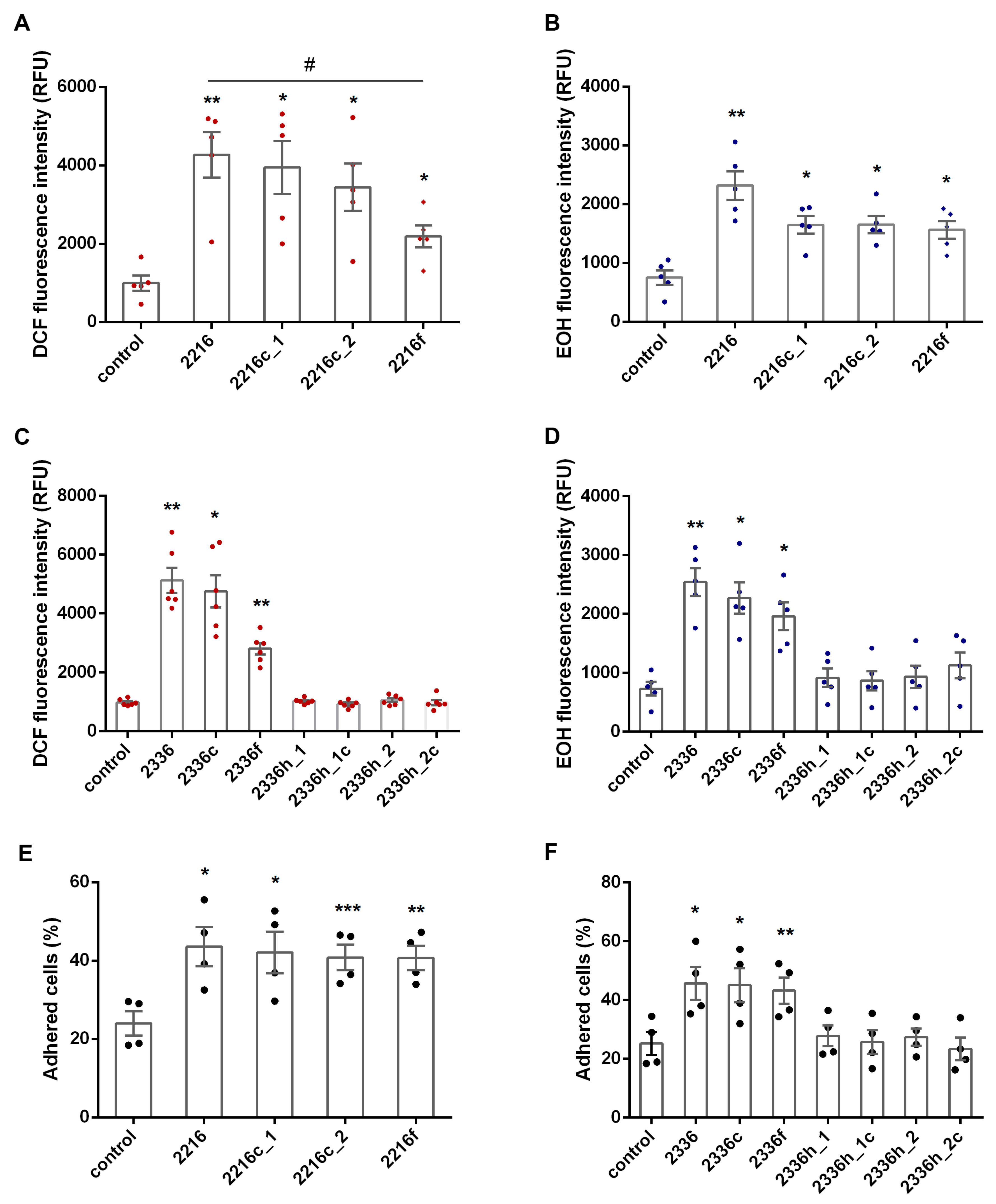
Trying to find out whether the identified effect on ROS formation is specific, in particular, whether it depends on the presence of CpG fragments, considered to be precisely responsible for the formation of the target immunomodulatory effect, we focused on class A ODNs 2216 and 2336. The prooxidant potential of analogs of these compounds, in which fragments CpG were replaced by GpC, namely, ODN 2216c_1 and 2336c, were evaluated. For ODN 2216 this substitution violates the palindromicity of the central fragment, so another control sequence, 2216c_2, was synthesized. We also used fragments of both A class ODNs containing CpG, but not capable of forming a “hairpin”, representing regions from the center of the palindrome to the 3′ end of the original backbone (2216f and 2336f). All oligonucleotide structures used in the work are presented in Table 1.
It turned out that the inversion of CpG to GpC, as well as the central region palindromicity disturbance, do not eliminate the prooxidant effect of class A ODNs, only slightly restraining it (Figure 2A–D). Structures 2216f and 2336f, lacking both palindromic regions and 5′ terminal poly-guanosine sequences, demonstrated the weakest effect on cytoplasmic ROS accumulation compared to the initial oligonucleotides (Figure 2A,C). Similarly, the substitution of CpG for GpC in class B ODN 1668 also did not interfere with its prooxidant effect manifestation (Supplementary Figure S1).
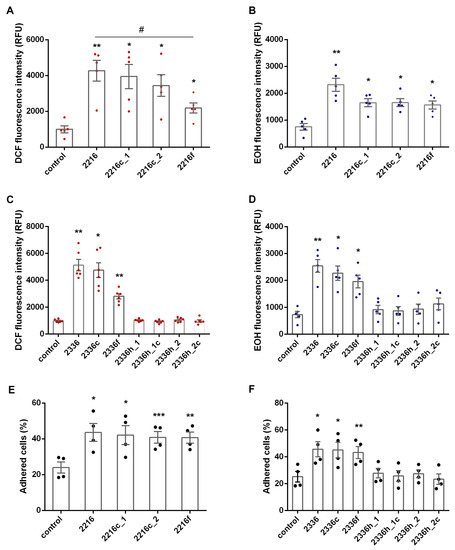
Figure 2.
Both ROS overproduction and adhesion of neutrophils provoked by class A ODNs are not dependent on CpG or palindromicity but mainly depend on the presence of phosphorothioate regions. H2DCF-DA-loaded (A,C) or DHE-stained (B,D) PMNLs (4 × 105 cells/mL HBSS/HEPES medium) were treated with 1 µM ODNs, except control samples, and cultured in 96-well plates for at least 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2. DCF (A,C) or EOH (B,D) fluorescence (excitation/emission 488/525 or 480/567 nm, respectively) was measured every 10 min for DCF and every 5 min for EOH. Data are represented as scatter plots with bars indicating means ± SEM of fluorescence intensity values at 30 min after addition of stimuli (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with controls, # p < 0.05 for indicated pair of data, RM one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test). (E,F) PMNLs (2 × 105 cells/mL HBSS/HEPES medium) were treated with 1 µM ODNs, except control samples, and cultured in 96-well plates for 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2. The number of attached neutrophils was determined by chromogenic assay of myeloperoxidase-coupled ortho-Phenylenediamine dihydrochloride oxidation. Data are represented as scatter plots with bars indicating means ± SEM of adhered PMNLs percentages (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared with controls, RM one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test).
To evaluate the dependence of the prooxidant effect on the presence of PS substitutions, short phosphodiester palindromes 2336h_1 and 2336h_2 were synthesized, essentially representing the “hairpin” of oligonucleotide 2336 (Table 1). The sequence 2336h_2 is a full copy of the phosphodiester region 2336, and 2336h_1 repeats its palindromic region. Each of these structures was evaluated in parallel with appropriate GpC control, namely, 2336h_1c and 2336h_2c. It turned out that the presence of phosphorothioate poly-guanosine fragments in the structure of stimulating ODNs is of decisive importance for the potentiation of ROS production by neutrophils: neither 2336h_1 nor 2336h_2 caused detectable accumulation of ROS (Figure 2C,D). Taking into account the vulnerability of PO oligonucleotides to endonuclease degradation, we carried out similar measurements in the concentration range of 2336h_1 and 2336h_2 from 1 to 20 μM, without revealing any noticeable effect (data not shown).
Considering that integrin-mediated cell attachment can promote Nox activation, we tested the effect of ODNs 2216, 2336 and their derivatives on neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen-coated substrate. Class A ODNs potentiated adhesion of neutrophils to the immobilized fibrinogen, with doubling the number of adhered cells. Like the prooxidant activity, this effect did not depend on the presence of CpG repeats and “hairpins” and was completely absent in structures without phosphorothioate regions (Figure 2E,F).
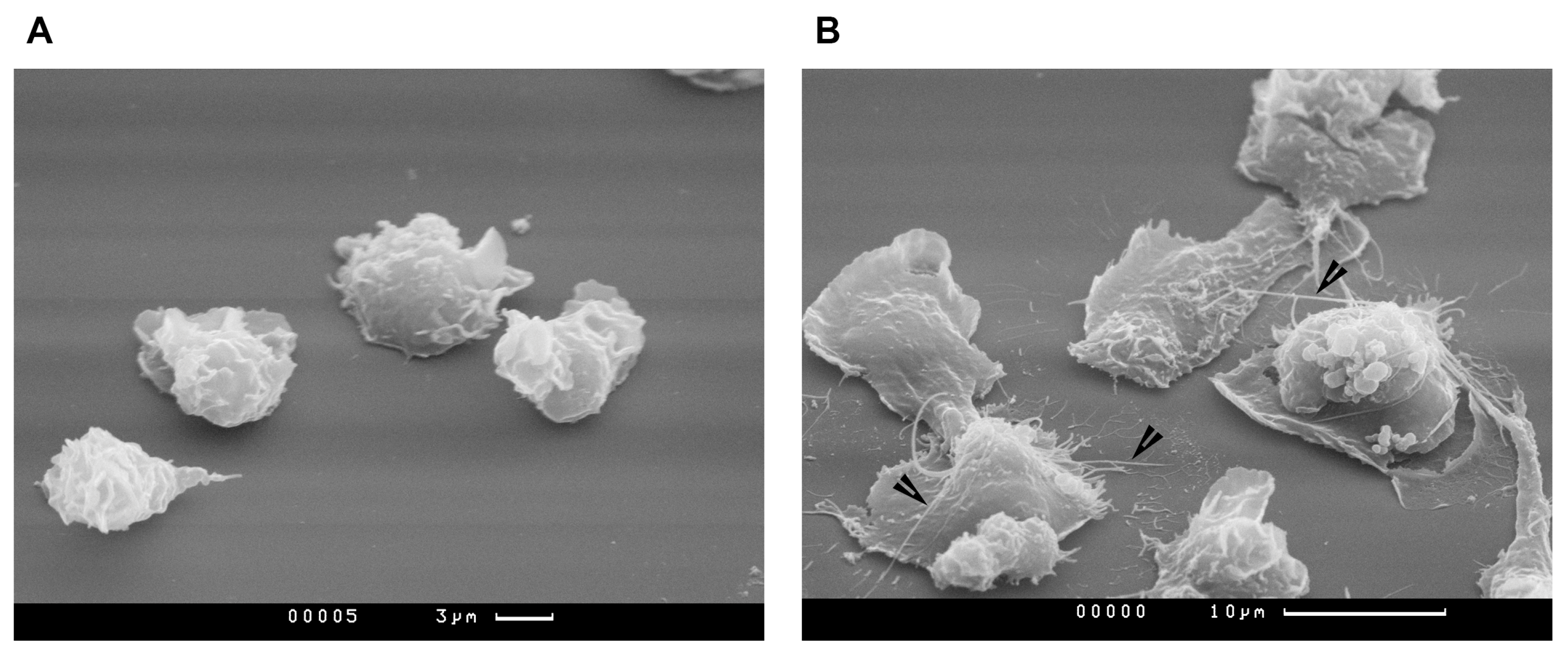
While studying the effect of synthetic oligonucleotide sequences on neutrophils, we also analyzed their effect on the morphology of these cells. Scanning electron microcopy of the samples showed, in particular, that the cultivation of neutrophils in the presence of CpG ODNs, especially class A structures, leads to the formation of cytonemes (Figure 3). It is known for such structures formation to be caused, among other things, by NO, an endogenous gasotransmitter and the reactive nitrogen species precursor [24]. It was decided to check whether CpG ODNs are direct or indirect inducers of neutrophil NO synthase.
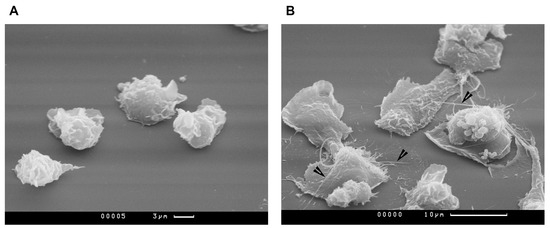
Figure 3.
Class A CpG ODNs affect neutrophils morphology, causing binding of cytonemes. Presented are scanning electron microscopy images of neutrophils attached to fibrinogen-coated substrata in control conditions (A) or the presence of 1 µM CpG ODN 2216 (B). The cytonemes are depicted by arrows. PMNLs suspended in HBSS/HEPES (1.5 × 106 cells/mL) were was applied to fibrinogen-coated slides placed in culture dishes and incubated for 25 min, at 37 °C, under 5% CO2 without additives or in the presence of CpG ODN. Adhered cells were then sequentially fixed by (1) 2.5% glutaraldehyde in HBSS/HEPES supplemented with 5 mM EDTA and 0.5 mM PMSF; (2) 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate containing 0.1 M sucrose, pH 7.3. After this, acetone dehydration samples were dried in a Balzer apparatus at the critical point with liquid CO2 as the transition liquid. Prepared samples were sputtered with gold/palladium and examined on a CamScan S-2 scanning electron microscope at a voltage of 15 kV.
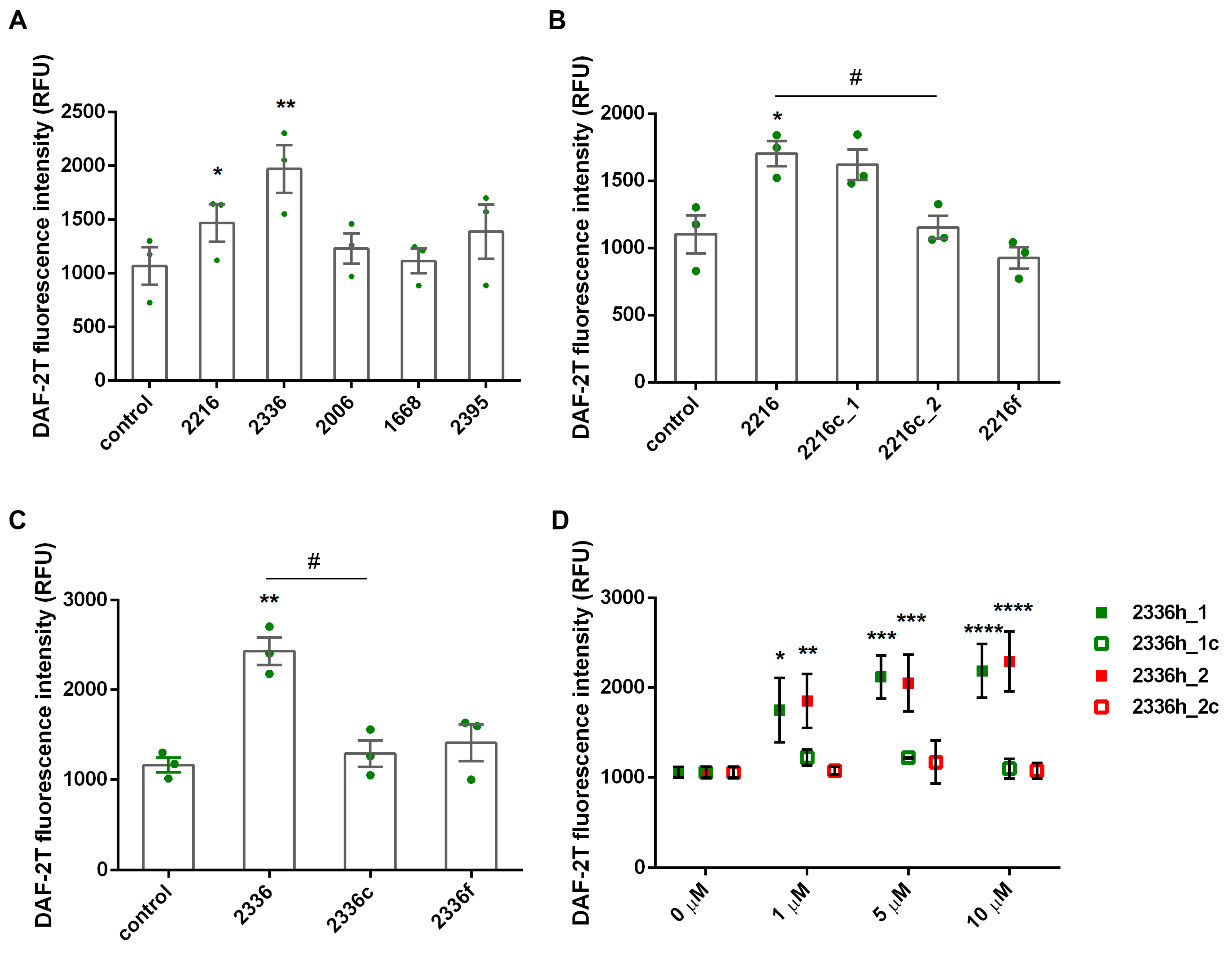
Of all CpG oligonucleotides used in this study, only class A ODNs had a significant stimulating effect on the production of endogenous nitric oxide by neutrophils (Figure 4A). At the same time, in contrast to the essentially nonspecific potentiation of ROS production, this effect turned out to be very sensitive to the presence of CpG containing a palindromic hairpin (Figure 4C,D). Moreover, phosphodiester structures that mimic the palindromic region of ODN 2336 (2336h_ and 2336h_2) also induced NO synthesis in a dose-dependent manner and lost this ability when CpG was replaced by GpC.
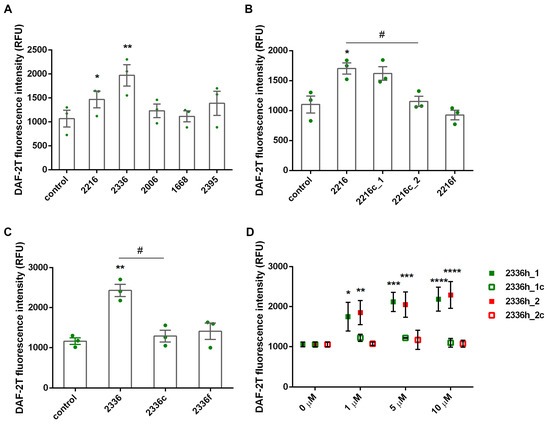
Figure 4.
Class A ODNs induce NO synthesis by neutrophilic granulocytes. This effect is only sensitive to the presence of CpG containing palindromic regions. DAF-2-loaded PMNLs (4 × 105 cells/mL HBSS/HEPES medium) were treated with 1 µM ODNs (A–C) or with ODNs at indicated concentrations (D), except control samples, and cultured in 96-well plates for at least 30 min, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2. DAF-2T fluorescence (excitation/emission 488/525) was measured every 5 min. Presented are scatter plots with bars indicating means ± SEM of fluorescence intensity values at 30 min after addition of stimuli (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with controls, # p < 0.05 for indicated pair of data, RM one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test) (A–C) or scatters indicating means ± SEM (n = 3) of fluorescence intensity values at 30 min after addition of stimuli (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 compared with controls, two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test) (D).
4. Discussion
The prooxidant component of the effect of CpG-containing oligonucleotides on neutrophilic granulocytes was noted in a few works of both ours [16,25] and other research groups [26,27]. On the one hand, this is one of the manifestations of the immunostimulatory activity of these compounds, which may be useful, in particular, in facilitating the overcoming of excessive bacteria-associated inhibition of apoptosis [16]. At the same time, it may underlie undesirable side effects when using CpG ODNs in therapy, since uncontrolled potentiation of neutrophils for ROS production can lead to undesirable effects, for example, vascular endothelium damage or tissue necrosis in inflammation loci.
The results of this work not only additionally confirmed the ability of phosphorothioate-containing CpG oligonucleotides of different classes to stimulate the production of ROS by neutrophilic granulocytes (Figure 1), including potentially the most dangerous for surrounding tissues extracellular superoxide (Figure 1C,D). We also revealed the non-specificity of this effect for at least ODNs of class A (Figure 2A–D) and B (Supplementary Figure S1). As it turned out, prooxidant activity is not mediated by the main characteristic feature of these compounds, namely, the presence in their structure unmethylated CpG inserts. The presence of a palindrome that forms the central “hairpin”, that being the specialty of class A ODNs, also turned out to be insignificant from the point of view of ROS formation by ODN-treated neutrophils. Prooxidant activity was completely absent only in sequences identical to the central part of ODN 2336, but lacking phosphorothioate-substituted terminal fragments, even at high concentrations. One might assume that such a difference in properties would be associated with the insecurity of phosphodiester structures from the endonuclease cleavage; however, these short sequences almost completely retained the ability to stimulate NO production by neutrophils (Figure 4).
Our results are consistent with the data obtained by Zhang et al. for B class CpG ODN 1826, a murine TLR9 agonist [28]. They showed the CpG-independent character of the uptake of phosphorothioate-substituted ODNs by microglial cells line. TLR9 is traditionally considered to be the main receptor that recognizes CpG oligonucleotides and mediates their immunomodulatory properties [29]. However, phosphorothioate modification, which protects synthetic oligonucleotide structures from endonuclease degradation, although it increases the efficiency of ODN uptake by cells, but due to non-specific affinity for cell surface proteins [30]. These proteins have so far been only partially identified. Separately, it is worth mentioning the scavenger receptor, which has a high affinity for polyanionic ligands, such as phosphorothioate-substituted ODN structures. Class A scavenger receptors (SRA) stimulation can lead to selective ERK phosphorylation, which upregulated cytosol ROS levels in neutrophils [31]. It is also known for SRA to potentiate macrophage adhesion [32]. Thus, an additional enhancement of the pro-oxidant effect can be achieved by the inclusion of integrin-dependent mechanisms. This assumption is confirmed by the fact that the ability to enhance neutrophil adhesion was also sensitive only to the presence of phosphorothioate regions in ODNs structure (Figure 2E,F). All studies described were carried out under conditions of cell interaction with a fibrinogen-coated substrate. Neutrophils interaction with immobilized fibrinogen, mediated by β2 integrins, can induce Nox activation and translocation of the enzyme complex cytosolic subunits at the plasma membrane [33].
The stimulating effect of phosphorothioate CpG oligonucleotides on ROS production by neutrophils is nonspecific and is inherent in all three ODN classes. The ability to induce the NO synthesis in neutrophils, on the contrary, was revealed only for class A ODNs 2216 and 2336. It can be assumed that the mechanism of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), the main source for the production of NO in mammalian cells, stimulation is associated precisely with the specific interaction of the central “hairpin” of these oligonucleotides with the TLR9 receptor, since this effect was completely eliminated in violation of palindromicity or inversion of CpG regions and was preserved in fully phosphodiester sequences mimicking the central palindrome fragment of class A ODN 2336. The confirmation of this hypothesis requires additional direct experimental evidence and will be the subject of further research. Several studies have shown that NOS activation in a macrophage cell line occurs when exposed to class B CpG ODN and is TLR9 mediated [34,35]. According to our results, class B ODNs 2006 and 1668, as well as class C ODN 2395, do not have a significant effect on NO synthesis by neutrophils. NO plays an important role in the regulation of functional responses of neutrophilic granulocytes and mediates their interaction with surrounding cells [36,37,38]. At the same time, toxicity of this intermediate is greatly enhanced by reacting with superoxide to form peroxynitrite [39]. NOS stimulation may exacerbate the detrimental effects of nonspecific activation of ROS production by phosphorothioate-substituted CpG oligonucleotides.
A limitation of this study is that the in vitro results are extremely simplistic and cannot be directly extrapolated to in vivo systems. In particular, we found that the supplementing of incubation medium by close to physiological concentrations of human serum albumin (HSA) significantly reduced ROS accumulation under the action of phosphorothioate ODNs, and the pH balance in the cellular environment is also a strong limiting factor: in the absence of artificial buffering with HEPES, ROS production and accumulation also significantly decreased (Supplementary Figure S2). Nonetheless, the results presented may be useful in finding a balance between the targeted and non-specific effects of synthetic CpG oligonucleotides potentially suitable for therapeutic purposes.
5. Conclusions
An in vitro study has shown that synthetic CpG ODNs have a pronounced effect on the prooxidant activity of neutrophilic granulocytes. This effect is complex and includes:
(a) non-specific stimulation of both cytoplasmic and extracellular ROS generation caused by phosphorothioate modification of oligonucleotides backbone;
(b) potentiation of nitric oxide synthesis, which, in the case of class A ODN 2336, is triggered precisely by the CpG-containing palindromic “hairpin”.
The revealed phenomenon should be taken into account in the development and testing of drugs based on synthetic oligonucleotides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/oxygen3010002/s1, Figure S1: Inversion of the CpG motif to GpC does not affect the prooxidant effect of class B ODN 1668; Figure S2: Class A CpG ODNs affect neutrophils morphology, causing the binding of cytonemes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A.G. and G.F.S.; methodology, E.A.G.; software, G.M.V.; formal analysis, G.M.V.; investigation, E.A.G. and S.I.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A.G.; writing—review and editing, G.F.S.; funding acquisition, G.F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant number 20-04-00816.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Experimental and the subject consent procedures were approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Lomonosov Moscow State University, Application # 6-h, version 3, Bioethics Commission meeting # 131-d held on 31 May 2021.
Informed Consent Statement
The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Data Availability Statement
All of the data is contained within the article and the supplementary materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wagner, H. Bacterial CpG DNA Activates Immune Cells to Signal Infectious Danger. Adv. Immunol. 1999, 73, 329–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kataoka, T.; Kuramoto, E.; Yano, O.; Tokunaga, T. Unique palindromic sequences in synthetic oligonucleotides are required to induce IFN [correction of INF] and augment IFN-mediated [correction of INF] natural killer activity. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 4072–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, A.; Rothenfusser, S.; Hornung, V.; Jahrsdörfer, B.; Blackwell, S.; Ballas, Z.K.; Endres, S.; Krieg, A.M.; Hartmann, G. Identification of CpG oligonucleotide sequences with high induction of IFN-α/β in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, J. CpG Motifs to Modulate Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 25, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Heeg, K.; Wagner, H.; Lipford, G.B. DNA activates human immune cells through a CpG sequence-dependent manner. Immunology 1999, 97, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, J.; Weeratna, R.; Payette, P.; Jurk, M.; Schetter, C.; Laucht, M.; Wader, T.; Tluk, S.; Liu, M.; Davis, H.L.; et al. Characterization of three CpG oligodeoxynucleotide classes with distinct immunostimulatory activities. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; Häcker, H.; Redecke, V.; Hausmann, S.; Akira, S.; Wagner, H.; Lipford, G.B. Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9237–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinman, D.M. Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.R.; Sikic, B.I. Clinical studies of antisense therapy in cancer. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D588–D593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, F.; Allen, L.-A.; Apicella, M.; Nauseef, W. NADPH oxidase activation and assembly during phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6732–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, D. Chronic granulomatous disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2016, 118, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, K.P. Evidence of direct toxic effects of free radicals on the myocardium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1988, 4, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, J.; Fabregat, I.; Frapart, Y.M.; Ghezzi, P.; Görlach, A.; Kietzmann, T.; Kubaichuk, K.; Knaus, U.G.; Lopez, M.G.; Olaso-Gonzalez, G.; et al. European contribution to the study of ROS: A summary of the findings and prospects for the future from the COST action BM1203 (EU-ROS). Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 94–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.E. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: All we need to know about danger. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viryasova, G.; Golenkina, E.; Hianik, T.; Soshnikova, N.; Dolinnaya, N.; Gaponova, T.; Romanova, Y.; Sud’Ina, G. Magic Peptide: Unique Properties of the LRR11 Peptide in the Activation of Leukotriene Synthesis in Human Neutrophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golenkina, E.A.; Viryasova, G.; Galkina, S.I.; Arifulin, E.A.; Gaponova, T.V.; Romanova, Y.M.; Sud’Ina, G.F. Synthetic CpG oligonucleotides as potential modulators of neutrophil survival in PAMP-associated inhibition of apoptosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, D.A.; Zagryagskaya, A.N.; Pushkareva, M.A.; Bachschmid, M.; Peters-Golden, M.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Sud’Ina, G.F. Cholesterol and its anionic derivatives inhibit 5-lipoxygenase activation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and MonoMac6 cells. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshavariya, H.M.; Dusting, G.J.; Selemidis, S. Analysis of dihydroethidium fluorescence for the detection of intracellular and extracellular superoxide produced by NADPH oxidase. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babior, B.M.; Kipnes, R.S.; Curnutte, J.T. Biological Defense Mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud’Ina, G.F.; Brock, T.G.; Pushkareva, M.A.; Galkina, S.I.; Turutin, D.V.; Peters-Golden, M.; Ullrich, V. Sulphatides trigger polymorphonuclear granulocyte spreading on collagen-coated surfaces and inhibit subsequent activation of 5-lipoxygenase. Biochem. J. 2001, 359, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffstein, S.T.; Gennaro, D.E.; Manzi, R.M. Neutrophils may directly synthesize both H2O2 and O2? since surface stimuli induce their release in stimulus-specific ratios. Inflammation 1985, 9, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.; Lenhoff, H.M. A sensitive and versatile chromogenic assay for peroxidase and peroxidase-coupled reactions. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 105, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Roman, M.; Tighe, H.; Lee, D.; Corr, M.; Nguyen, M.-D.; Silverman, G.J.; Lotz, M.; Carson, D.A.; Raz, E. Immunostimulatory DNA Sequences Necessary for Effective Intradermal Gene Immunization. Science 1996, 273, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, S.I.; Fedorova, N.V.; Golenkina, E.A.; Stadnichuk, V.I.; Sud’Ina, G.F. Cytonemes Versus Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Fight of Neutrophils with Microbes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viryasova, G.M.; Golenkina, E.A.; Galkina, S.I.; Gaponova, T.V.; Romanova, Y.M.; Sud’Ina, G.F. Effects of phosphodiester and phosphorothioate ODN2216 on leukotriene synthesis in human neutrophils and neutrophil apoptosis. Biochimie 2016, 125, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonegio, R.G.; Lin, J.D.; Beaudette-Zlatanova, B.; York, M.R.; Menn-Josephy, H.; Yasuda, K. Lupus-Associated Immune Complexes Activate Human Neutrophils in an FcγRIIA-Dependent but TLR-Independent Response. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Adcock, I.M.; Ito, K.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Folkerts, G. Cigarette smoke induces CXCL8 production by human neutrophils via activation of TLR9 receptor. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 36, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weinschenk, T.; Schluesener, H.J. Uptake, intracellular distribution, and novel binding proteins of immunostimulatory CpG oligodeoxynucleotides in microglial cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 160, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, U.; Shibata, T.; Tanji, H.; Ishida, H.; Krayukhina, E.; Uchiyama, S.; Miyake, K.; Shimizu, T. Structural basis of CpG and inhibitory DNA recognition by Toll-like receptor 9. Nature 2015, 520, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltinger, C.; Saragovi, H.U.; Smith, R.M.; LeSauteur, L.; Shah, N.; DeDionisio, L.; Christensen, L.; Raible, A.; Jarett, L.; Gewirtz, A.M. Binding, uptake, and intracellular trafficking of phosphorothioate-modified oligodeoxynucleotides. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Fan, S.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xia, L.; Tang, J.; et al. Stimulation of the class-A scavenger receptor induces neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) by ERK dependent NOX2 and ROMO1 activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, I.; Hughes, D.; Gordon, S. Divalent cation-independent macrophage adhesion inhibited by monoclonal antibody to murine scavenger receptor. Nature 1993, 364, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Hudik, E.; Le Bars, R.; Roux, B.; Dang, P.M.-C.; El Benna, J.; Nüsse, O.; Dupré-Crochet, S. Class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases control sustained NADPH oxidase activation in adherent neutrophils. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 178, 114088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-G.; Kim, J.-R.; Baek, S.-H. Toll-like receptor 9-mediated cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation regulates expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudla, M.; Srisatjaluk, R.; Utaisincharoen, P. Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS-treated mouse macrophage cell line (RAW264.7) requires Toll-like receptor 9. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y.; Billiar, T.R. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Inflammatory Diseases. Mol. Med. 2000, 6, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denninger, J.W.; Marletta, M.A. Guanylate cyclase and the NO/cGMP signaling pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1411, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, S.I.; Golenkina, E.A.; Viryasova, G.; Romanova, Y.M.; Sud’Ina, G.F. Nitric Oxide in Life and Death of Neutrophils. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5764–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, J.S.; Koppenol, W.H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad, and ugly. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1996, 271, C1424–C1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).