Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration in a Caribbean Reef Lagoon Indicate an Ecosystem Shift After Repeated Disturbances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sargassum Brown Tides (SBTs)
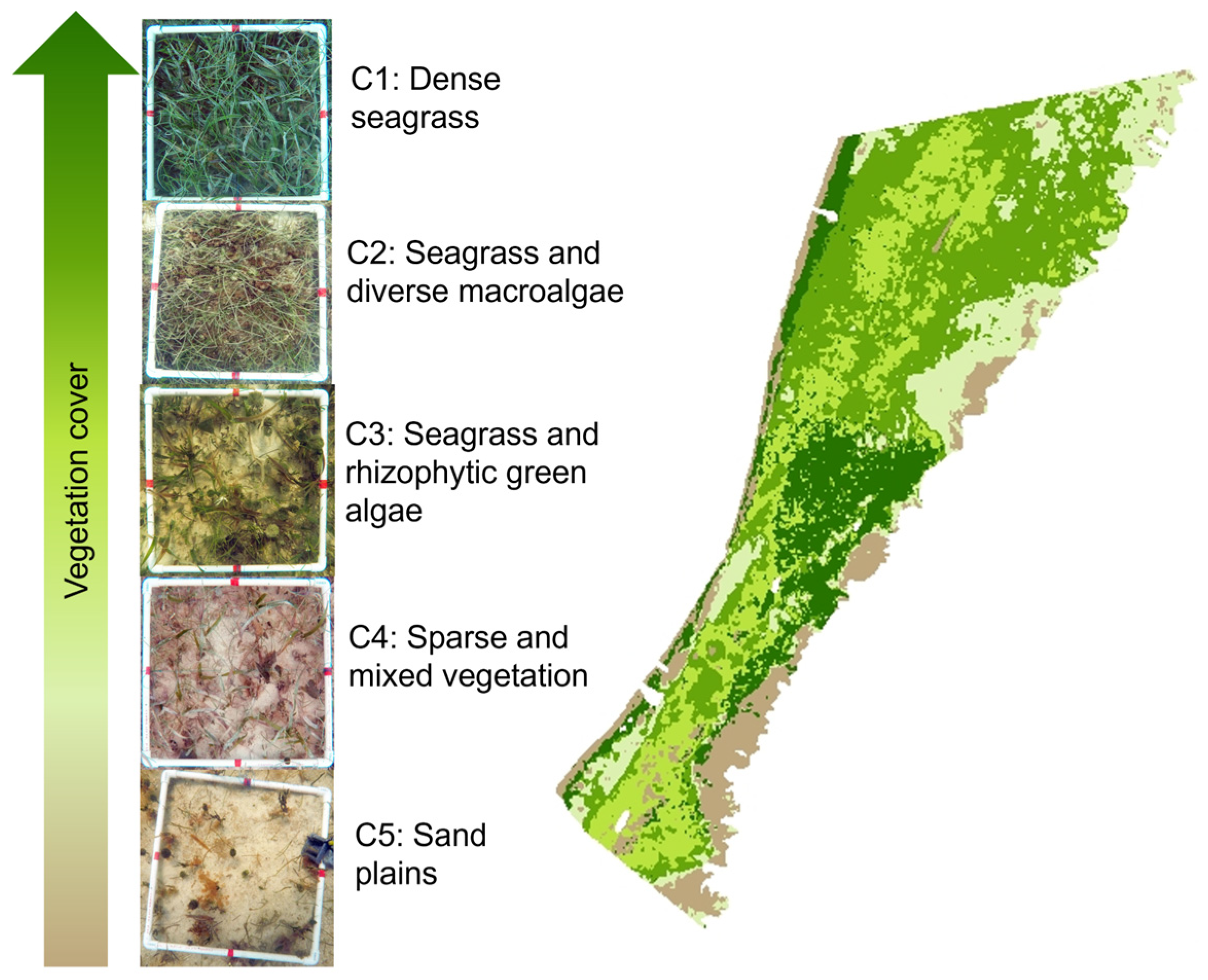
2.3. Thematic Maps of Seagrass Meadows
2.4. Near-Shore Seagrass Meadows
2.5. Landscape Analysis
3. Results
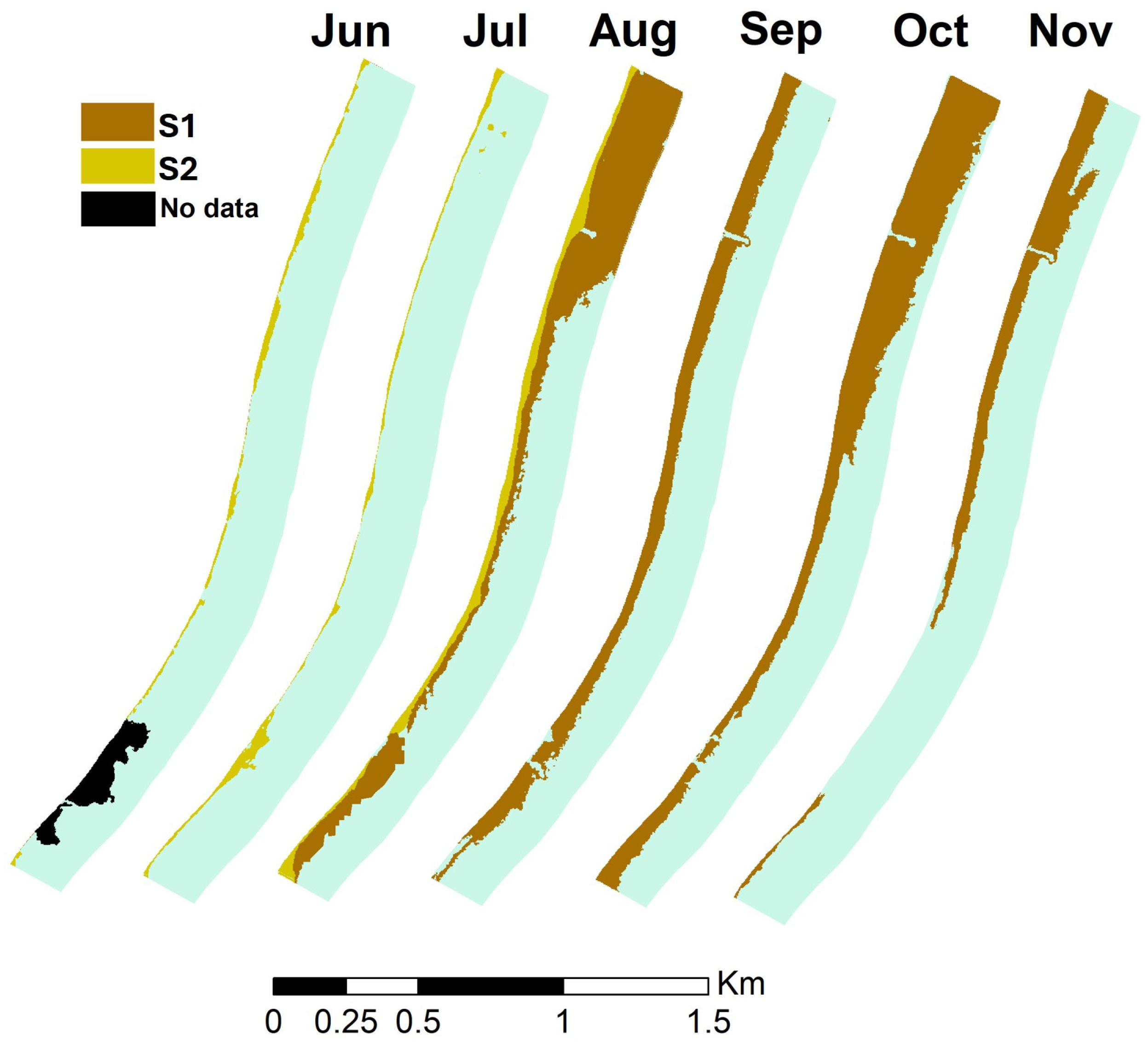
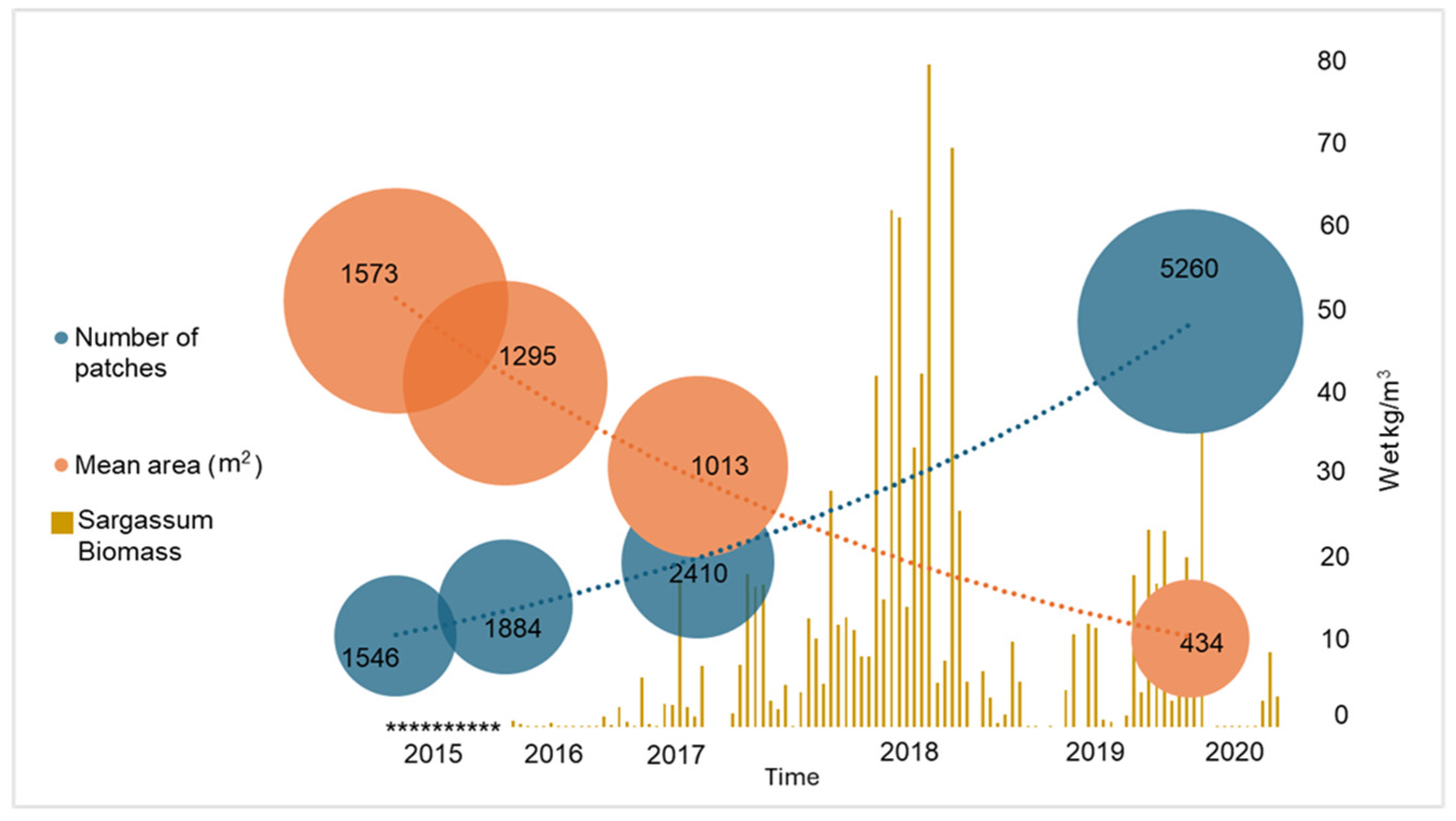
3.1. Detection of Sargassum Brown Tides (SBTs)
3.2. Accuracy of Thematic Maps for Seagrass Meadows
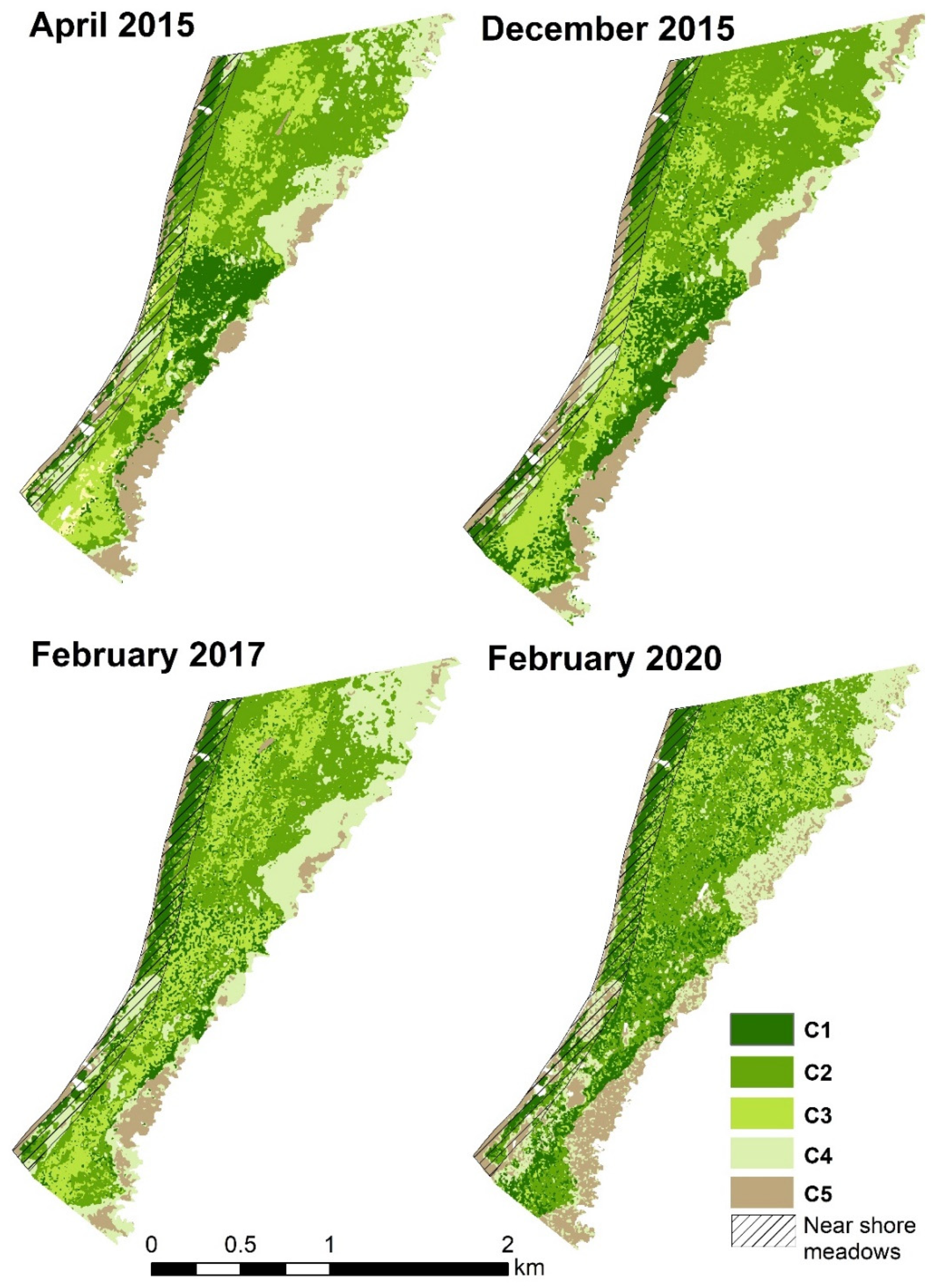
3.3. Near-Shore Seagrass Meadow Change Analysis
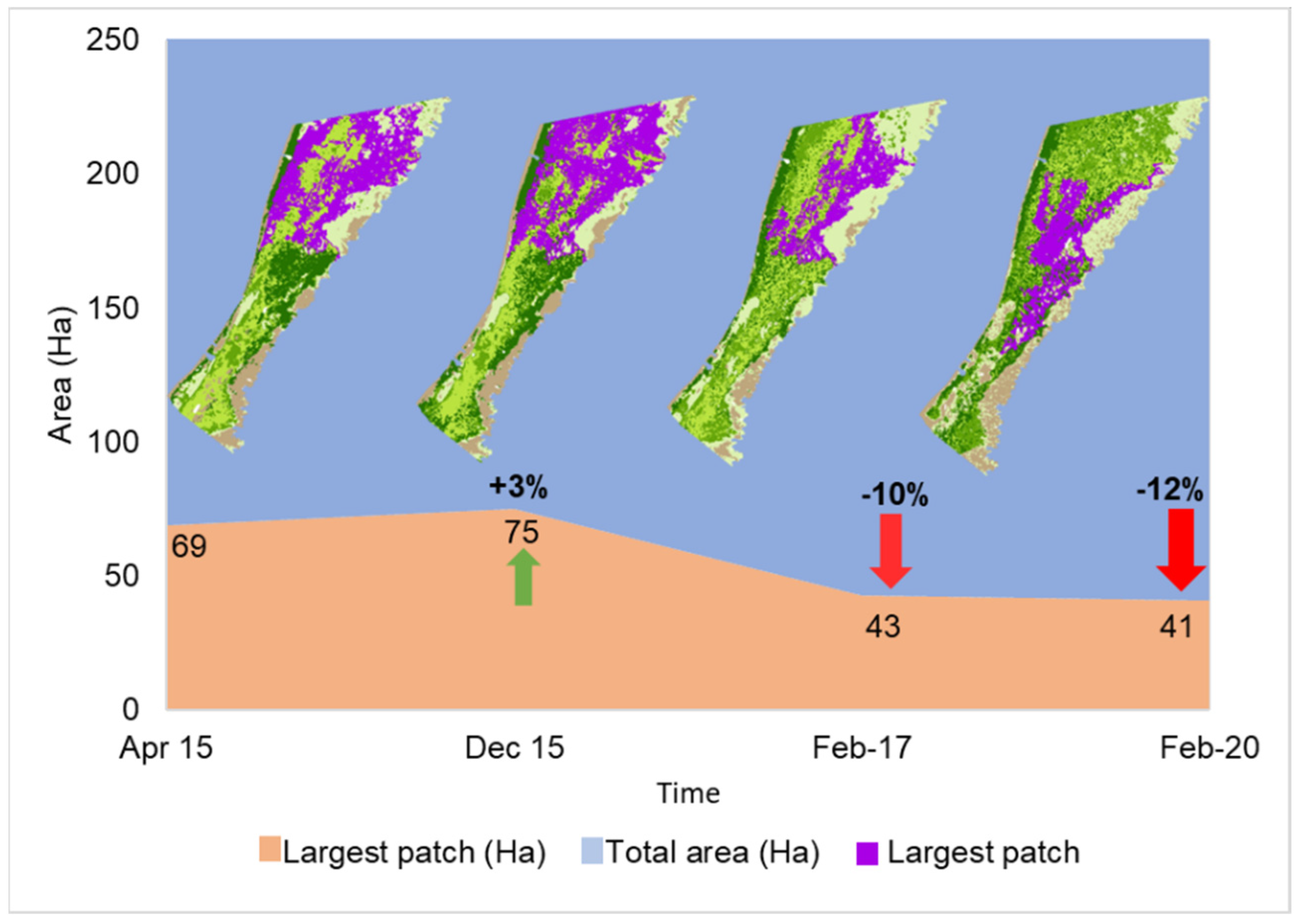
3.4. Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration and Fragmentation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Sargassum Brown Tides
4.2. Remote Sensing of the Seagrass Meadows
4.3. Changes in the Spatial Configuration of the Seagrass Meadows
4.4. Ecosystem Shift
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Serrano, O. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hays, G.; Orth, R.J. Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 253, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.W.; Ackerman, J.D.; Verduin, J.; Keulen, V.M. Fluid dynamics in seagrass ecology—From molecules to ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 193–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Cortés, J.; Collin, R.; Fonseca, A.C.; Gayle, P.M.; Guzmán, H.M.; Weil, E. Caribbean-wide, long-term study of seagrass beds reveals local variations, shifts in community structure and occasional collapse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Borum, J.; Short, F.T.; Walker, D.I. Seagrass ecosystems: Their global status and prospects. In Aquatic Ecosystems: Trends and Global Prospects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, A.; Chartrand-Miller, K.; Erftemeijer, P.; Fonseca, M.; McKenzie, L.; Rasheed, M.; Coles, R. A comparison of threats, vulnerabilities and management approaches in global seagrass bioregions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Arana, H.A.H.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Espinoza-Avalos, J.; Canizales-Flores, H.M.; González-Godoy, C.E.; Collado-Vides, L. Severe impacts of brown tides caused by Sargassum spp. on near-shore Caribbean seagrass communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Elizondo, R.M.; Vázquez-Delfín, E. Muerte y destrucción del sargazo: Escenarios naturales de degradación. Av. Perspect. 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Medina-Valmaseda, A.E.; Blanchon, P.; Monroy-Velázquez, L.V.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Delgado-Pech, B.; Vásquez-Yeomans, L.; Francisco, V.; García-Rivas, M.C. Faunal mortality associated with massive beaching and decomposition of pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Ochoa, R.; Enríquez, S. Environmental degradation of the Mexican Caribbean reef lagoons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, L.; Hardy, R.F.; Hochberg, E.J. Spectral and Spatial Requirements of Remote Measurements of Pelagic Sargassum Macroalgae. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Mapping and Quantifying Sargassum Distribution and Coverage in the Central West Atlantic Using MODIS Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 350–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Predicting Sargassum Blooms in the Caribbean Sea from MODIS Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3265–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; McGillicuddy, D.J.; Barnes, B.B.; Liu, Y.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Zhang, S.; Hernandez, F.J. Pelagic sargassum in the Gulf of Mexico Driven by Ocean Currents and Eddies. Harmful Algae 2024, 132, 102566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Hernández, J.; Enriquez, C.; Zavala-Hidalgo, J.; Cuevas, E.; van Tussenbroek, B.; Uribe-Martínez, A. Sargassum Transport Towards Mexican Caribbean Shores: Numerical Modeling for Research and Forecasting. J. Mar. Syst. 2024, 241, 103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Barreda-Bautista, B.; Metcalfe, S.E.; Smith, G.; Sjögersten, S.; Boyd, D.S.; Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; López-Ramírez, P.; Magaldi, A.; Ressl, R.; Perera-Valderrama, S.; et al. Monitoring Holopelagic Sargassum spp. Along the Mexican Caribbean Coast: Understanding and Addressing User Requirements for Satellite Remote Sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1166000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Pérez, M.C.; Reisinger, A.S.; Gibeaut, J.C. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Decaying Stages of Pelagic Sargassum spp. Along Shorelines in Puerto Rico Using Google Earth Engine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, R.; Muñiz-Castillo, A.I.; Euán-Avila, J.I.; Hernández-Núñez, H.; Valdés-Lozano, D.S.; Collí-Dulá, R.C.; Arias-González, J.E. Assessing temporal dynamics on pelagic Sargassum influx and its relationship with water quality parameters in the Mexican Caribbean. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 48, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Heege, T.; Kolb, M.; Ohlendorf, S.; Uribe, A.; Muller, A.; Garza, R.; Ressl, R.; Aguirre, R.; Marino, I.; et al. Benthic Habitat and Bathymetry Mapping of Shallow Waters in Puerto Morelos Reefs Using Remote Sensing with Physics-Based Data Processing. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 4383–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Ramírez, P.A.; Blanchon, P.; Olioso, A.; Hernandez-Nuñez, H.; Sobrino, J.A. Accuracy of IKONOS for mapping benthic coral-reef habitats: A case study from the Puerto Morelos Reef National Park, Mexico. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3671–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P.; Lazuardi, W. Random Forest Classification Scenarios for Benthic Habitat Mapping Using PlanetScope Image. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, A.; Pertiwi, A.P.; Lee, C.B.; Traganos, D. Bahamian seagrass extent and blue carbon accounting using Earth observation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1058460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.D.; Velázquez-Ochoa, R.; Enríquez, S. Seagrass depth distribution mirrors coastal development in the Mexican Caribbean—An automated analysis of 800 satellite images. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 733169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursanidis, D.; Topouzelis, K.; Chrysoulakis, N. Mapping Coastal Marine Habitats and Delineating the Deep Limits of Neptune’s Seagrass Meadows Using Very High Resolution Earth Observation Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 8670–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veettil, B.K.; Ward, R.D.; Lima, M.D.A.C.; Stankovic, M.; Hoai, P.N.; Quang, N.X. Opportunities for Seagrass Research Derived from Remote Sensing: A Review of Current Methods. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Bujang, J.S.; Zakaria, M.H.; Hashim, M. The application of remote sensing to seagrass ecosystems: An overview and future research prospects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 61–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, M.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Holmer, M.; Laursen, J.S. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Eelgrass (Zostera marina) Landscapes: Influence of Physical Setting. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 78, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizcano-Sandoval, L.; Anastasiou, C.; Montes, E.; Raulerson, G.; Sherwood, E.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Seagrass distribution, areal cover, and changes (1990–2021) in coastal waters off West-Central Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 279, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P.; Fauzan, M.A.; Kumara, I.S.W.; Yogyantoro, R.N.; Lazuardi, W.; Zhafarina, Z. Analysis of Reflectance Spectra of Tropical Seagrass Species and Their Value for Mapping Using Multispectral Satellite Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8955–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietkerk, M.; Dekker, S.; De Ruiter, P.C.; van de Koppel, J. Self-organized patchiness and catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Science 2004, 305, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M. Implications of spatial heterogeneity for catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems. Ecology 2005, 86, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kéfi, S.; Guttal, V.; Brock, W.A.; Carpenter, S.R.; Ellison, A.M.; Livina, V.N.; Seekell, D.A.; Scheffer, M.; Van Nes, E.H.; Dakos, V. Early warning signals of ecological transitions: Methods for spatial patterns. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzow, M.A.; Hunsicker, M.E. Early warning signals, nonlinearity, and signs of hysteresis in real ecosystems. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianen, M.J.; Herman, P.M.; Bouma, T.J.; Lamers, L.P.; van Katwijk, M.M.; van der Heide, T.; van de Koppel, J. Habitat collapse due to overgrazing threatens turtle conservation in marine protected areas. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.S.; Eklöf, J.S.; van Katwijk, M.M.; O’Brien, K.R.; de la Torre-Castro, M.; Boström, C.; van der Heide, T. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms for the adaptive management of seagrass ecosystems—A review. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.I. Dynamics of seagrasses and associated algae in coral reef lagoons. Hidrobiológica 2011, 21, 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- Coronado, C.; Candela, J.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; Sheinbaum, J.; López, M.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J. On the circulation in the Puerto Morelos fringing reef lagoon. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Afluencia masiva de sargazo pelágico a la costa del Caribe mexicano (2014–2015). In Florecimientos Algales Nocivos en México; García-Mendoza, E., Quijano-Scheggia, S.I., Olivos-Ortiz, A., Núñez-Vázquez, E.J., Eds.; CICESE: Ensenada, Mexico, 2016; pp. 352–365. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, V.; Uribe-Martínez, A.; Cuevas, E.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Francisco, V.; Silva, R. Massive influx of pelagic Sargassum spp. on the coasts of the Mexican Caribbean 2014–2020: Challenges and opportunities. Water 2020, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, J.; Arriaga, J.; Montoya, L.D.; Mariño-Tapia, I.J.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Mendoza, E.T.; Appendini, C.M. Beaching and natural removal dynamics of pelagic Sargassum in a fringing-reef lagoon. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Vera, E.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Álvarez-Filip, L.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Temporal changes in the composition and biomass of beached pelagic Sargassum species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 167, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.J.; Ávila-Mosqueda, S.V.; Salas-Acosta, E.R.; Magaña-Gallegos, E.; Mancera, E.E.; Reali, M.A.G.; de la Barreda-Bautista, B.; Boyd, D.S.; Metcalfe, S.E.; Sjogersten, S.; et al. Spectral characteristics of beached Sargassum in response to drying and decay over time. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; p. 853. [Google Scholar]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.; Barba-Santos, M.G.; Wong, G.R.; van Dijk, J.K. A Guide to the Tropical Seagrasses of the Western Atlantic, 1st ed.; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Instituto de Biología: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Littler, D.S.; Littler, M.M. Caribbean Reef Plants, 1st ed.; Offshore Graphics, Inc.: Deerfield Beach, FL, 2000; p. 542. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v7: User Manual/Tutorial, 1st ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2015; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.C. A filter-based post-processing technique for improving homogeneity of pixel-wise classification data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps; Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors. Available online: https://www.fragstats.org (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Sánchez, A.; Gonzalez-Jones, P.; Camacho-Cruz, K.A.; Anguas-Cabrera, D.; Ortiz-Hernández, M.C.; Rey-Villiers, N. Influence of pelagic sargassum influxes on the δ15N in Thalassia testudinum of the Mexican Caribbean coastal ecosystem. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Lyons, M.; Kovacs, E.M.; Maxwell, P.; Saunders, M.I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Phinn, S.R. Multi-temporal mapping of seagrass cover, species and biomass: A semi-automated object-based image analysis approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Hawthorne, T.L.; Hessing-Lewis, M.; Duffy, E.J.; Reshitnyk, L.Y.; Feinman, M.; Searson, H. Developing an Introductory UAV/Drone Mapping Training Program for Seagrass Monitoring and Research. Drones 2020, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, L.R.; Ávila-Mosqueda, S.V.; Silva, R.; Mendoza, E.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Mapping the structure of mixed seagrass meadows in the Mexican Caribbean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1063007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréfouët, S.; Kramer, P.; Torres-Pulliza, D.; Joyce, K.E.; Hochberg, E.J.; Garza-Pérez, R.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Multi-site evaluation of IKONOS data for classification of tropical coral reef environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkum, A.W.; Orth, R.J.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 691. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heide, T.; Bouma, T.J.; van Nes, E.H.; van de Koppel, J.; Scheffer, M.; Roelofs, J.G.; Smolders, A.J. Spatial self-organized patterning in seagrasses along a depth gradient of an intertidal ecosystem. Ecology 2010, 91, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.A.; D’Odorico, P.; McGlathery, K.J.; Wiberg, P.L. Spatially explicit feedbacks between seagrass meadow structure, sediment, and light: Habitat suitability for seagrass growth. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Rentería, F.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Puerto Morelos, Quintana Roo, Mexico; CARICOMP: Caribbean Coral Reef, Seagrass, and Mangrove Sites; Special Report UNESCO: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Ruíz-Rentería, F.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Barba-Santos, G.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Jordán-Garza, G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Environmental state and tendencies of the Puerto Morelos CARICOMP site, Mexico. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2010, 58, 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Null, K.A.; Knee, K.L.; Crook, E.D.; de Sieyes, N.R.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Hernández-Terrones, L.; Paytan, A. Composition and fluxes of submarine groundwater along the Caribbean coast of the Yucatan Peninsula. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 77, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mendoza, P.G.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Cuellar-Martinez, T.; Pérez-Bernal, L.H. Temporal trends of organic carbon accumulation in seagrass meadows from the northern Mexican Caribbean. Catena 2020, 194, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J.; Oxenford, H.A.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E.; Cróquer, A.; Bastidas, C.; Ogden, J.C. The CARICOMP Network of Caribbean Marine Laboratories (1985–2007): History, key findings, and lessons learned. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, C.; Jackson, E.L.; Simenstad, C.A. Seagrass landscapes and their effects on associated fauna: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, S.D.; Fernandes, M.; Burnell, O.W.; Doubleday, Z.A.; Griffin, K.J.; Irving, A.D.; Falkenberg, L.J. Testing for thresholds of ecosystem collapse in seagrass meadows. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, P.S.; Möllmann, C. Marine ecosystem regime shifts: Challenges and opportunities for ecosystem-based management. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20130275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, W.C. Effects of light on seagrass photosynthesis, growth and depth distribution. Aquat. Bot. 1987, 27, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Boyer, J.N.; Durako, M.J.; Hefty, L.N.; Peterson, B.J. Forecasting responses of seagrass distributions to changing water quality using monitoring data. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, C.; Oxenford, H.; Cumberbatch, J.; Fardin, F.; Doyle, E.; Cashman, A. Golden Tides: Management Best Practices for Influxes of Sargassum in the Caribbean with a Focus on Clean-Up; Centre for Resource Management and Environmental Studies (CERMES), The University of the West Indies, Cave Hill Campus: Kingston, Jamaica, 2016; 17p. [Google Scholar]


| Metric | Scale | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number of patches | Patch/Landscape | Total amount of individual patches inside the landscape |
| Mean patch size | Patch | Mean area of the patches (m2) |
| Patch number per class | Class | How many patches compose each class |
| Largest patch | Class | Size of the largest patch around the study of a determinate class |
| Largest Patch Index (LPI) | Landscape | Percent of the landscape that the largest patch comprises: Area (m2) of the largest patch (100) Landscape area (m2) |
| 2018 | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. |
| Covered area (m2) | No data | 0 | 0 | 221,198 | 142,246 | 264,986 | 106,875 |
| Mean length (m) | No data | 0 | 0 | 67 | 48.8 | 82 | 41.7 |
| Max length (m) | No data | 0 | 0 | 189 | 69.7 | 201 | 124 |
| 2019 | |||||||
| Covered area (m2) | 22,923 | 0 | 0 | 84,664 | 390,339 | 245,709 | No data |
| Mean length (m) | 32 | 0 | 0 | 37 | 131 | 79 | No data |
| Max length (m) | 13 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 200 | 126 | No data |
| Class | Description | April 2015 | December 2015 | February 2017 | February 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Dense seagrass | 19.4 | 10.1 | 18.1 | 16.9 |
| C2 | Seagrass and diverse algae (red/brown and green) | 1.5 | 9.5 | 12.6 | 10.1 |
| C3 | Seagrass and rhizophytic green algae | 4.3 | 13.2 | 6.4 | 5.6 |
| C4 | Sparse vegetation (seagrass and algae) | 21.6 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 7.6 |
| C5 | Sand plains, (with sparse or solitary seagrass or algae) | 2.6 | 9.6 | 5.2 | 10.2 |
| Class | April 2015 | December 2015 | February 2017 | February 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 35.2 | 42.8 | 36.2 | 51.3 |
| C2 | 86.8 | 88.4 | 74.7 | 76.5 |
| C3 | 52.5 | 50.8 | 55.6 | 36.5 |
| C4 | 39 | 30.1 | 60.2 | 46.2 |
| C5 | 26 | 31.8 | 17.7 | 33.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ávila-Mosqueda, S.V.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Garza-Pérez, J.R. Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration in a Caribbean Reef Lagoon Indicate an Ecosystem Shift After Repeated Disturbances. Coasts 2025, 5, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5010008
Ávila-Mosqueda SV, van Tussenbroek BI, Garza-Pérez JR. Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration in a Caribbean Reef Lagoon Indicate an Ecosystem Shift After Repeated Disturbances. Coasts. 2025; 5(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁvila-Mosqueda, S. Valery, Brigitta I. van Tussenbroek, and Joaquín Rodrigo Garza-Pérez. 2025. "Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration in a Caribbean Reef Lagoon Indicate an Ecosystem Shift After Repeated Disturbances" Coasts 5, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5010008
APA StyleÁvila-Mosqueda, S. V., van Tussenbroek, B. I., & Garza-Pérez, J. R. (2025). Changes in Seagrass Landscape Configuration in a Caribbean Reef Lagoon Indicate an Ecosystem Shift After Repeated Disturbances. Coasts, 5(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5010008








