Abstract
The coastal region of the Caribbean is notable for the chemical diversity found in its sponge products, resulting in the biosynthesis of a range of natural marine products, including polyketides. The objective of this manuscript is to summarize the isolated polyketides from sponges of the genus Plakortis located around the Caribbean coasts. This review provides a comprehensive overview of specimen location, isolation procedures, characterization methods, and biological assay studies of about 95 polyketides isolated from 1978 to 2024 in the Caribbean coasts of The Bahamas, Cayman Islands, Belize, Dominica, Jamaica, Martinique, Panamá, Puerto Rico, and Tobago. The Caribbean polyketides have been isolated from different types of Plakortis sp., such as P. simplex, P. halichondroides, P. zyggompha, and P. angulospiculatus, which have demonstrated antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic, and antiviral activities. A variety of linear polyketides with different functionalities have been reported, including endoperoxides (1,2-dioxane), lactones, indane-type bicyclics (spiculane and zyggomphic), alcohols, alkenes, styryl groups, α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids, and ketones, as well as related natural products of biosynthetic origin. The aim is to encourage further exploration by researchers in the Caribbean’s coastal marine environments, promoting the discovery and investigation of novel polyketide cyclic peroxides and related secondary metabolites to identify additional bioactive medicinal natural products.
1. Introduction
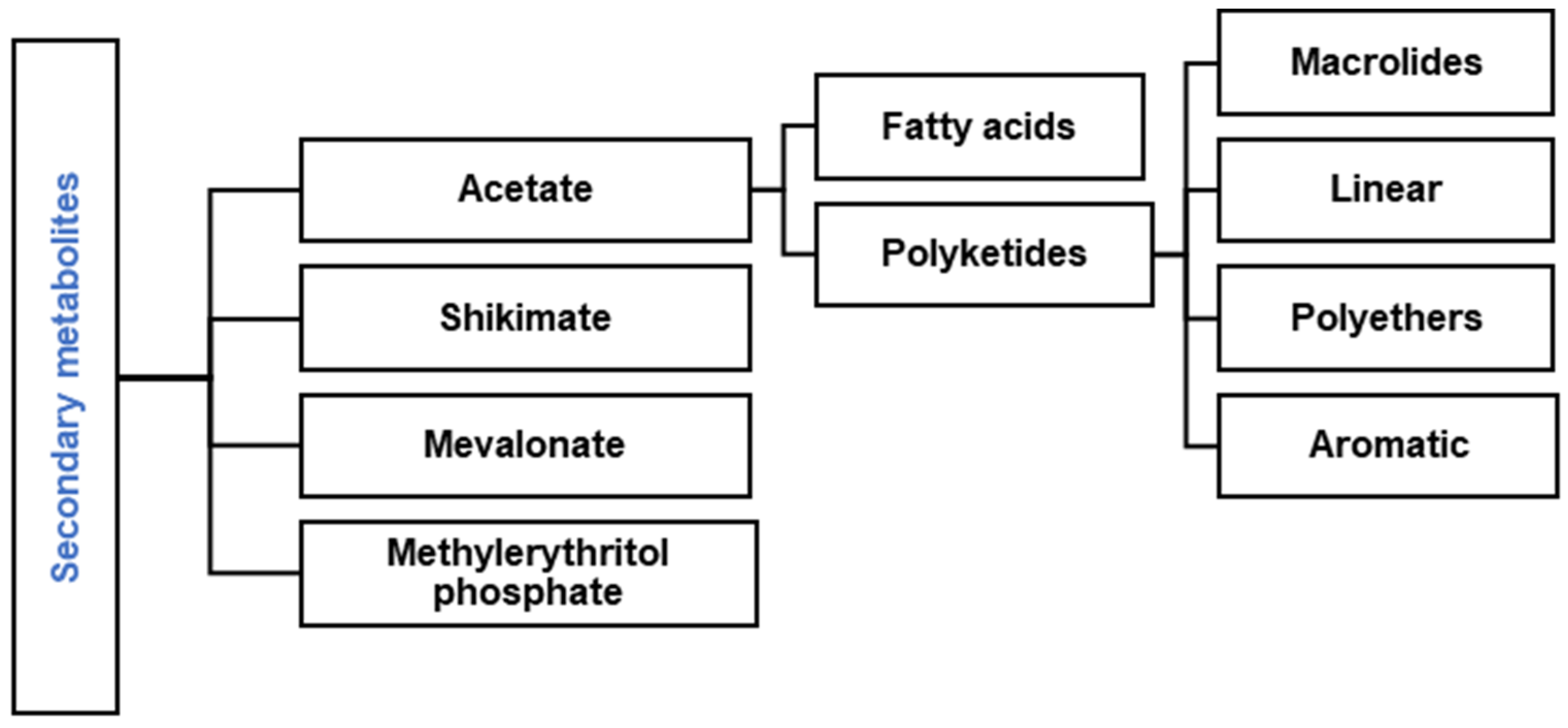
Animals, plants, bacteria, fungi, and marine organisms produce secondary metabolites or natural products [1,2,3,4,5]. Secondary metabolites can be classified based on their biosynthesis and building blocks in four pathways: acetate, shikimate, mevalonate, and methylerythritol phosphate (Figure 1). One essential and extensive group of natural products is polyketides (PKs), divided into four large subgroups: macrolide, linear, polyether, and aromatic compounds (Figure 1) [3,6,7]. The biosynthesis of polyketides is derived from the acetate pathway (Figure 1) through the Claisen condensation of acetyl-CoA (C2-units), propionyl-CoA (C3-units), and methylmalonyl-CoA (C4-units) catalyzed by the multifunctional enzyme polyketide synthases (PKSs) [8,9,10,11,12]. Linear polyketides are another subgroup of metabolites produced by PKS enzymes in some fungal strains [13] and marine organisms like microalgae and sponges [1,14].
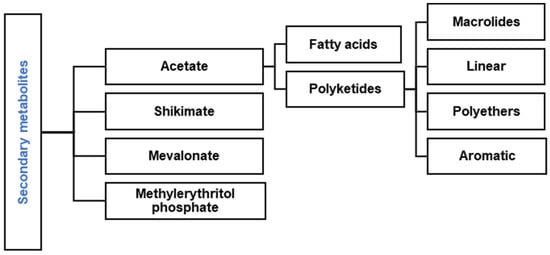
Figure 1.
Classification of polyketides in natural products.
Natural polyketide products have approximately five times more bioactivity than the average of other natural product families. Moreover, around 20% of top-selling small-molecule drugs are polyketides [15,16]. They possess broad biological activities such as antibiotic, anticancer, antifungal, antiparasitic, immunomodulatory, and cholesterol-lowering action [6,8,15]. A category of polyketides composed of propionate units is known as polypropionate natural products. This category of metabolites can be found in polyether antibiotics, polyene antifungals, macrolides antibiotics, and spiroketals [8,17,18,19,20,21]. Different efforts have been made to report the structure and bioactivity of polypropionates isolated from marine organisms around the globe [8,22,23,24,25]. For example, in 1998, 168 marine polypropionates were isolated from mollusks and then reported. Also, another review described the structural features and biological activities of 165 polypropionates isolated mainly from marine organisms, which were reported from 1999 to 2020 [8]. The Caribbean coastal region stretches along the Southern United States, Eastern Central America, and Northern South America [26]. It has a rich marine biodiversity that produces different types of bioactive secondary metabolites. Particularly, in 2020, a small selection of different types of secondary metabolites originating from the Caribbean region was reported, including polyketides, peptides, alkaloids, terpenes, and glucolipids, which possess antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, and antipathogenic properties [27].
In 2022, various compounds were reported, including polyketides, nonribosomal peptides, hybrid polyketide–nonribosomal peptides, terpenes, and alkaloids produced by microorganisms such as fungi and bacteria [28]. The research summarized their roles in insect infections, the distribution of genes among microbial species, and their potential in developing novel bio-insecticides [28]. In the same year, 243 marine natural products were summarized, mainly alkaloids, polyketides, and terpenoids, reported from 2012 to 2021, providing important chemical and biological insights for future marine drug development and presenting general rules about the source organisms, structure–specialty, and organism–bioactivity relationships of these compounds [29]. Recently, in 2023, we reported a summary of a group of polypropionates with bioactive properties (antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral), which include macrolides, linear and polycyclic ethers, and related polypropionates isolated from Caribbean microorganisms, including marine sponges, corals, cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates, mollusks, and certain types of algae [6]. In 2016, a summary of the chemical synthesis, biosynthetic interrelationships, therapeutic potential, and biological activity of a particular group of linear polyketides known as peroxide and peroxide-derived polyketide metabolites was reported from marine sponges studied for 35 years, from 1981 to 2016 [30].
Based on our knowledge, marine cyclic endoperoxides, indane-type polyketides, and other linear bio-related polyketides isolated from the sponges of the genus Plakortis collected along the coasts of the Caribbean region have not been summarized until now (2024). This review summarized 95 polyketides based on the locations where the marine sponges were collected along the Caribbean coast. We then described the methodology for their extraction, isolation, physical and structural characterization methods, and reported bioactivities. This work aims to highlight novel and bioactive marine polyketide endoperoxides and related linear metabolites identified around the Caribbean coasts that possess potential anticancer, antimalarial, antifungal, and antibacterial activities.
2. Collection, Extraction, Isolation, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivity
2.1. Coasts of the Bahamas
The Bahamas are southeast of Florida in the United States and north of Cuba and the Caribbean Sea [31]. The archipelagic nation is composed of over 700 islands and 2400 cays. The main islands include New Providence, Grand Bahama, and Andros, each offering unique coastal features. Other notable islands in The Bahamas archipelago include Exuma, Abaco, and Eleuthera.
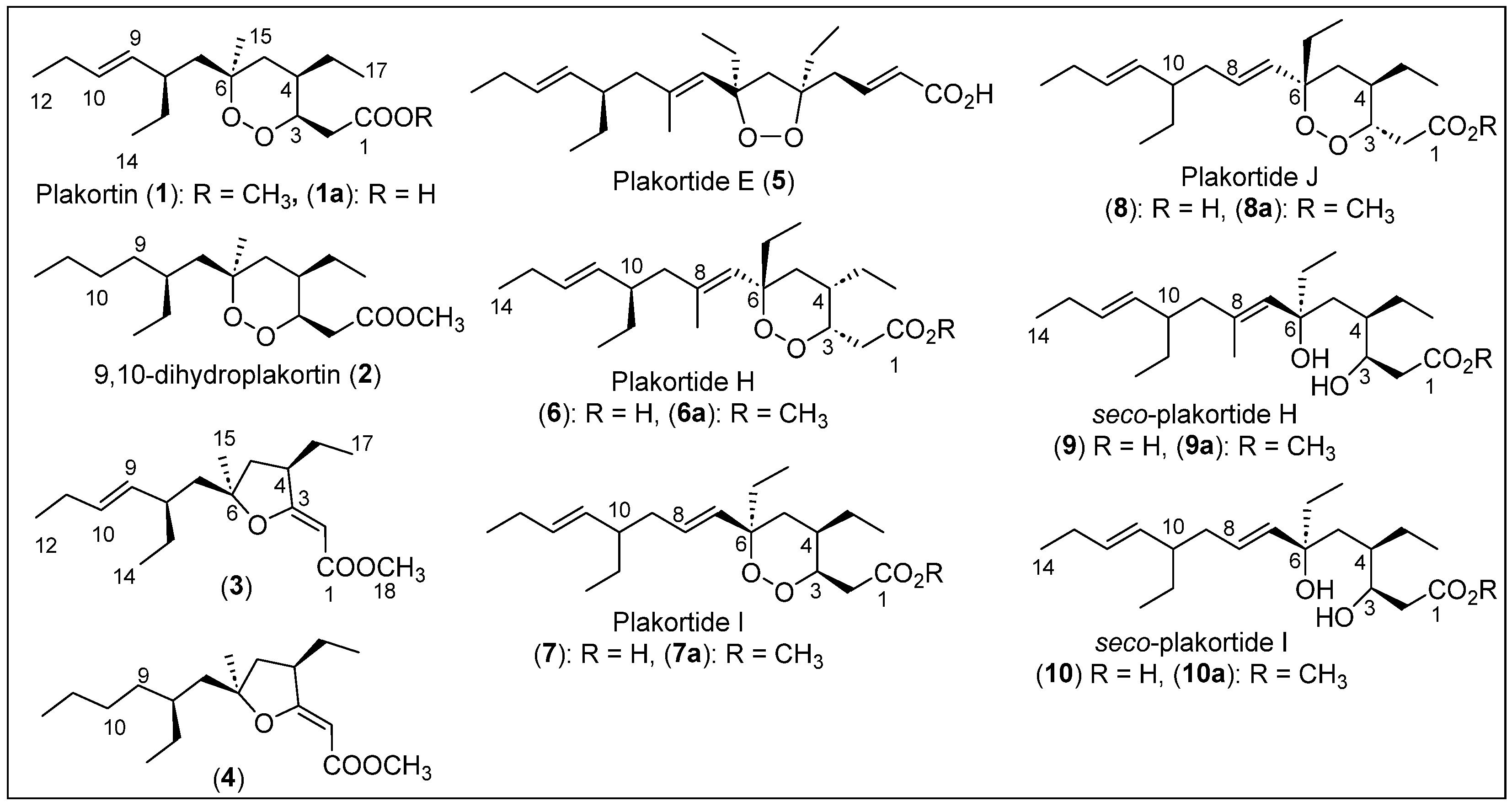
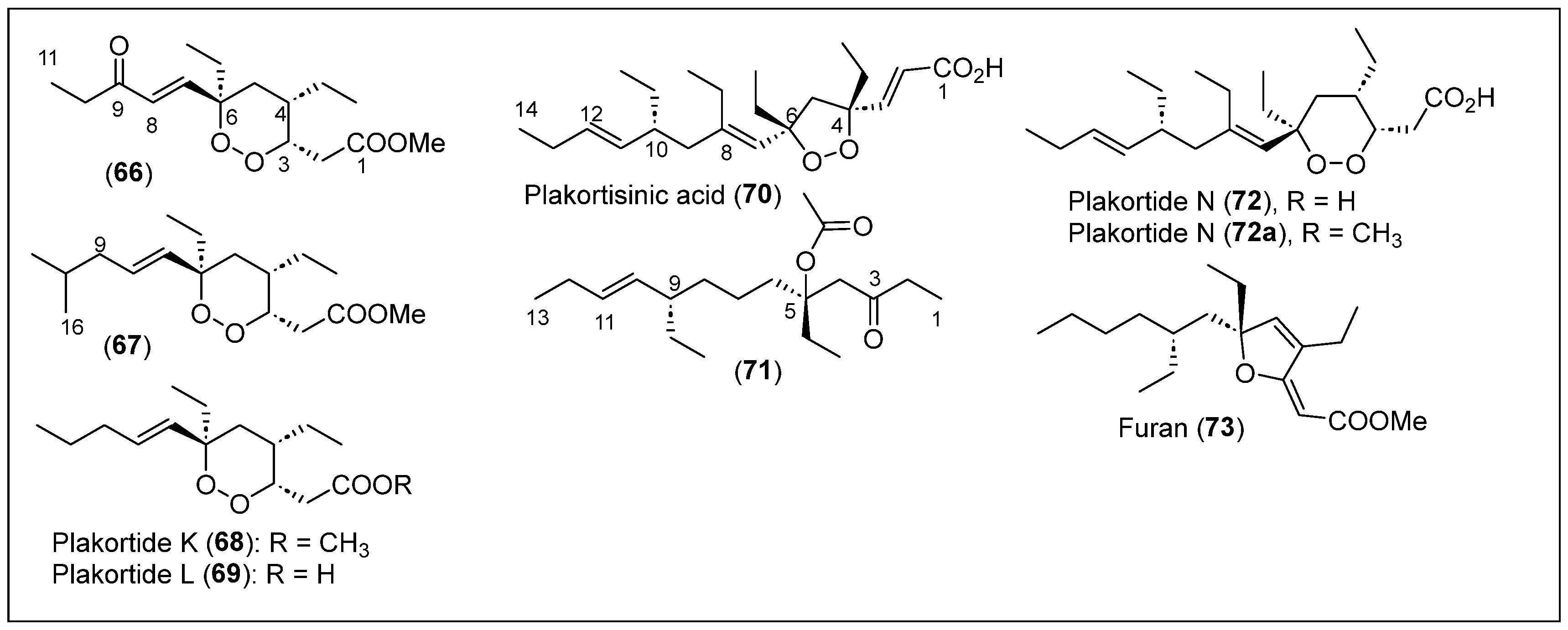
Cafieri et al. collected a specimen of the Caribbean sponge Plakortis simplex on the coasts of Little San Salvador Island in The Bahamas [32]. Then, the organism was homogenized and consecutively extracted with methanol and chloroform. The methanol extract was extracted with butanol and water, and the organic phase was subjected to reverse-phase (RP) silica gel chromatography and eluted with a gradient of a low-polarity solvent mixture. After purification by medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC) over silica gel and various high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) purifications, the known peroxide polyketide plakortin (1) was obtained as a major product [33], along with three new related metabolites, dihydroplakortin or 9,10-dihydroplakortide (2) and furan derivatives 3 and 4, as pure colorless oils (Figure 2). Higgs and Faulkner reported the relative configuration of cyclic peroxide 1 in 1978 [33], but Cafieri and collaborators elucidated the absolute stereochemistry of the four stereogenic centers of compound 1 employing Mosher’s method [32]. Indeed, compound 2 has a six-membered ring cycloperoxide (1,2-dioxane) with the same absolute configuration for its chiral centers as compound 1 (Figure 2). Mosher’s method was also employed to determine the absolute configuration of compounds 3 and 4, characterized by the presence of a tetrahydrofuran moiety. High-resolution electron impact mass spectrometry (HREIMS) was used to deduce the molecular formulas for compounds 2, 3, and 4. Their full structural characterization was achieved using 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data and two-dimensional NMR characterizations, such as homonuclear correlation spectroscopy (COSY), homonuclear Hartmann–Hahn spectroscopy (HOHAHA), heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence (HMQC), heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC), and rotating-frame nuclear Overhauser effect correlation spectroscopy (ROESY).
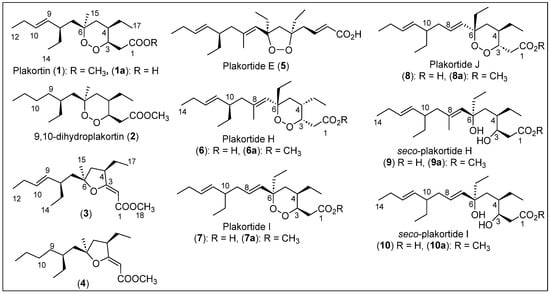
Figure 2.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 1–10.
Compounds 1 and 3 have a double bond at C-9,10 with E geometry, while compounds 2 and 4 lack the olefins at C-9,10. The double bond at C-2,3 of the tetrahydrofuran ring for compounds 3 and 4 has a Z configuration (Figure 2). Plakortin (1) has an IC50 cytotoxic activity of 7.0 μg/mL, and its 9,10-dihydro derivative (2) is much less active (IC50 > 20 μg/mL) against the WEHI 164 murine fibrosarcoma cell line after 72 h. Compounds 3 and 4 are moderately cytotoxic (IC50 of 10.0 and 15.5 μg/mL, respectively) against the WEHI 164 cell line.
E. Fattorusso et al. in 2002 reported the isolation of three antimalarial cyclic endoperoxides, plakortin (1), 9,10-dihydroplakortide (2), and plakortide E (5) (Figure 2), from the sponge P. simplex, collected on the coast of Berry Islands in The Bahamas [34]. The homogenized specimen was extracted with methanol and chloroform four times (Figure 2). Then, the methanol extract was partitioned (water–butanol) and concentrated in vacuo. The organic crude was purified sequentially by column chromatography (CC), MPLC, and HPLC to recover compounds 1 and 2 and plakortide E (5). In 1996, A. D. Patil et al. reported the isolation and characterization of plakortide E (5) from the same sponge (P. simplex) collected on Jamaica’s coast [35]. The six-membered peroxides 1 and 2 exhibit in vitro antimalarial activity against CQ-R and CQ-S Plasmodium falciparum clones. Compound 1 showed IC50 values of 1263.52 nM against D10 and 735.54 nM against W2. On the other hand, compound 2 showed IC50 values of 1117.38 nM against D10 and 760.44 nM against W2. Compound 5 (plakortide E), with a five-membered peroxide, was inactive against P. falciparum. Additional studies will be needed to determine the mechanism of action of plakortin (1) and its derivatives.
In 2000, E. Fattorusso et al. reported the isolation and structural characterization of plakortides H (6), I (7), and J (8), as well as the seco-plakortide H (9) and seco-plakortide I (10) (Figure 2) from the sponge P. simplex collected from the coast of Berry Islands [36]. The sponge was also homogenized and extracted sequentially with methanol and chloroform. The methanol extract was then partitioned with butanol and water. After the organic phase was concentrated in vacuo, it was purified by RP chromatography and normal-phase chromatography, and an inseparable mixture of the carboxylic acids 6 to 10 was obtained. Then, the mixture of carboxylic acids was converted into the corresponding methyl esters (6a-10a) with CH2N2 and then purified by direct-phase HPLC. In 1996, Patil et al. reported the isolation of plakortide H (6) and the corresponding methyl ester 6a from the sponge Plakortis halichondrioides collected on the coast of Jamaica [37].
The structural characterization of plakortide acids (6), I (7), and J (8), as well as seco-plakortides H (9) and I (10) has been performed by analyzing the structures of their corresponding methyl esters 6a–10a (Figure 2). High-resolution electron ionization mass spectrometry (HREIMS) and the structures determined the molecular formulas that were elucidated with 1H and 13C NMR and COSY, HMQC, and HMBC two-dimensional NMR characterizations. The combination of nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) couplings and ROESY correlations allows for the determination of the relative stereochemistry and the absolute stereochemistry of the chiral centers of these compounds, except for C-10, which was established with the application of Mosher’s method (Figure 2). The cytotoxic studies’ activity against WEHI 164, a murine fibrosarcoma cell line, showed an IC50 (μg/mL) of 7.1 for 6a; 9.5 for 7a; 8.2 for 8a; 14.1 for 9a; 19.2 for 10a; 2.5 μg/mL for the mixture of acids 6, 7, and 8; and 4.0 μg/mL for the mixture of seco-acids 9 and 10. Carboxylic acids 6 to 8 are generally more active than the corresponding methyl esters 6a–8a, and the seco-plakortides 9 and 10 are less active than cycloperoxides 6–8.
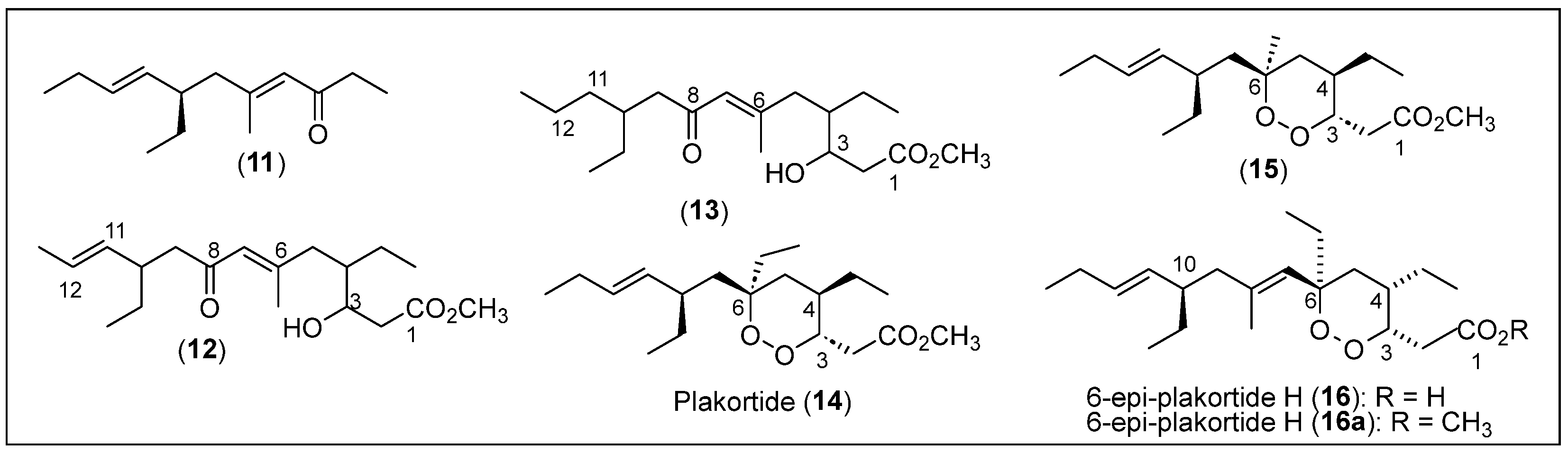
Five polyketide cycloendoperoxides, compounds 11 to 15 (Figure 3), were isolated from the sponge P. simplex in the study by Campagnuolo et al. [38], in which polyketide ketones 12 and 13 and the cyclic peroxide 14 (named with the trivial name of plakortide Q) were reported for the first time. Compounds 11 and 15 were previously isolated from P. halichondrioides from the coasts of Belize and Jamaica, respectively [33,39]. In the isolation procedure, the sponge P. simplex collected along the coasts of the Bahamas was extracted using a mixture of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)/methanol (MeOH) solvents. Then, the MeOH layer was partitioned between n-butanol and water. The organic phase was purified and separated using reverse-phased liquid chromatography (RP-LC) with silica. Using MPLC and HPLC, an inseparable mixture of the new compounds 12, 13, and 14 was obtained along with the known compounds plakortide (1) and dehydroplakortide (2) (Figure 2) [32,33].
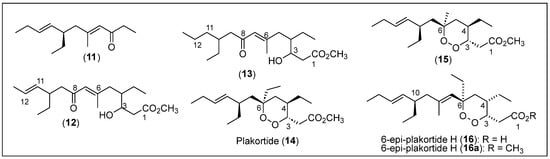
Figure 3.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 11–16.
Then, compounds 12 and 13 were successfully isolated and purified by HPLC. High-resolution fast atom bombardment mass spectroscopy (HRFABMS) determined the molecular formulas of compounds 11 to 14, and the corresponding structures were elucidated by employing one-dimensional and two-dimensional (HMBC, COSY, and ROESY) spectral analyses (Figure 3). The absolute configurations of the chiral centers at C-3, C-4, and C-6 belonging to the cyclic peroxide rings of 14 and 15 were established using Mosher’s modified method [40]. Among these polyketide derivatives, compounds 11–13 are non-cycloperoxide polyketides, while compounds 14 and 15 are polyketide cycloperoxides (Figure 3). In their structures, compounds 14 and 15 contain a 1,2-dioxane ring; compounds 11, 12, and 13 have an α,β-unsaturated ketone functionality confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and ultraviolet (UV) analyses; and compounds 12 and 13 have an alcohol functional group. When analyzing the non-cycloperoxides 12 and 13, they are closely related structures, whereas 11 is an 11,12-dihydro derivative. Compound 13 is also a diastereomer of plakortin (1) with a different configuration at C-3 and a close analog of plakortide 14. Still, it has an ethyl group at C-6 instead of a methyl group (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
The relative and absolute configurations at the three chiral centers (C-3, C-4, and C-10) of compounds 12 and 13 were not determined due to the limited material available. The bioassays performed with plakortin (1), plakortide Q (14), and compound 15 showed in vitro antimalarial activity. They were studied using a plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase assay (pLDH). Compounds 1, 14, and 15 presented activities against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of P. falciparum, which are the protozoans responsible for malaria. The efficacy is higher for the chloroquine-resistant strain. Among these products, plakortin (1) presents a higher activity than that of compounds 14 and 15, indicating that changing the C-3 configuration can lower the antimalarial activity.
S. Oli and collaborators, for the first time, isolated an endoperoxide polyketide named plakortide E (5) from the sponge P. halichondroides in 2014, which was collected at a depth of 30 m on the coast of The Bahamas (Figure 3) [41]. To isolate plakortide E (5) (Figure 2), the collected sponge was freeze-dried and sequentially extracted with cyclohexane, methylene dichloride, and MeOH. The crude cyclohexane phase was separated under CC utilizing a mixture of cyclohexane, methylene dichloride, methanol, and formic acid (2:1:1:0.05). After elution, several fractions were collected and purified using preparative HPLC to yield pure compound 5 (Figure 2). The obtained polyketide plakortide E (5) was characterized by employing mass spectrometry (MS) and one-dimensional NMR spectral data analyses. Product 5 was tested for its in vitro antiparasitic activity against Trypanosoma brucei and showed an IC50 value of 5 μM.
In addition, compound 5 was identified as a new protease inhibitor against the parasite cathepsin-L-like protease falciparum-2 from P. falciparum and against the mammalian serine proteases chymotrypsin and the serine protease from Dengue virus (NS2B/NS3 protease). These results demonstrated that plakortide E (5) would be a non-competitive, reversible inhibitor of cysteine proteases. Interestingly, plakortide E (5) did not show activity against Leishmania donovani and Candida albicans, and no cytotoxic effects against J774.1 macrophages at a 100 μM concentration were observed.
T. Schirmeister et al. in 2017 reported the isolation of various endoperoxides, including compound 16, plakortide E (5), plakortin (1), and dihydroplakortin (2) (Figure 2 and Figure 3) from a sample of the sponge P. halichondrioides collected at a depth of 30 m from the coast of Inagua Island, The Bahamas, in 2013 [42]. For isolation, extraction, and purification, the frozen samples of the sponge were cut into small pieces, and the tissue was lyophilized and then sequentially extracted with cyclohexane, methylene chloride, and methanol solvents. After CC guided by a thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis and preparative RP-HPLC of the dichloromethane extract, a fraction with a mixture of several acidic compounds was identified and converted into an ester mixture using the Steglich esterification [43]. The esterification employs methanol, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) as a coupling reagent and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) as a catalyst. The 6-epimer of plakortide ester 16a was obtained and then hydrolyzed with lithium hydroxide (LiOH) in tetrahydrofuran and water (THF/H2O) to yield pure acid 16 after purification by RP-HPLC.
The structure of acid 16 was identified as a diastereomer of plakortide H acid (6) after the spectroscopic analysis by 1H, 13C, and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy (i.e., COSY and NOESY) and MS (Figure 3). The absolute configurations of 16 and 16a were elucidated in this work, including the C-10 configuration, which has not been previously reported, and compared with the literature to confirm a novel isolation of compound 16 (Figure 3) [44,45]. The crude cyclohexane extract was purified by chromatography on silica gel and followed by a TLC analysis, and preparative RP-HPLC was used to purify the selected eluted fractions to obtain first the known plakortide E (5), then plakortin (1), and lastly, dihydroplakortin (2). The structure of 5 was confirmed by the NMR (1H, 13C-NMR, and two-dimensional NMR) and MS data, and the optical rotation agreed with those reported previously [41]. The structure of plakortin (1), the compound, was analyzed by NMR spectroscopy and MS and was identified according to the literature data (Figure 2) [39,46,47]. Plakortin (1) was converted into its known acid, plakortic acid (1a) [48], via hydrolysis with LiOH, and the crude product was purified via preparative RP-HPLC. A biological activity study against the drug-sensitive leukemia CCRF-CEM cell line and its multi-drug-resistant subline CEM/ADR5000 was performed with endoperoxides acids (16, 1a, and 6) and esters 1 and 2 to determine their cytotoxic effects. Compounds 16 and 1a have lower IC50 values of 0.18 μM and 0.19 μM for the CCRF-CEM cell line, respectively. For the CEM/ADR5000 cell line, compounds 16 and 1a showed IC50 values of 0.36 μM and 0.24 μM, respectively. Based on the IC50 values, acid compound 16 exhibited the highest potent cytotoxicity towards both cell lines, and the endocyclic peroxide esters 1 and 2 showed weaker activities.
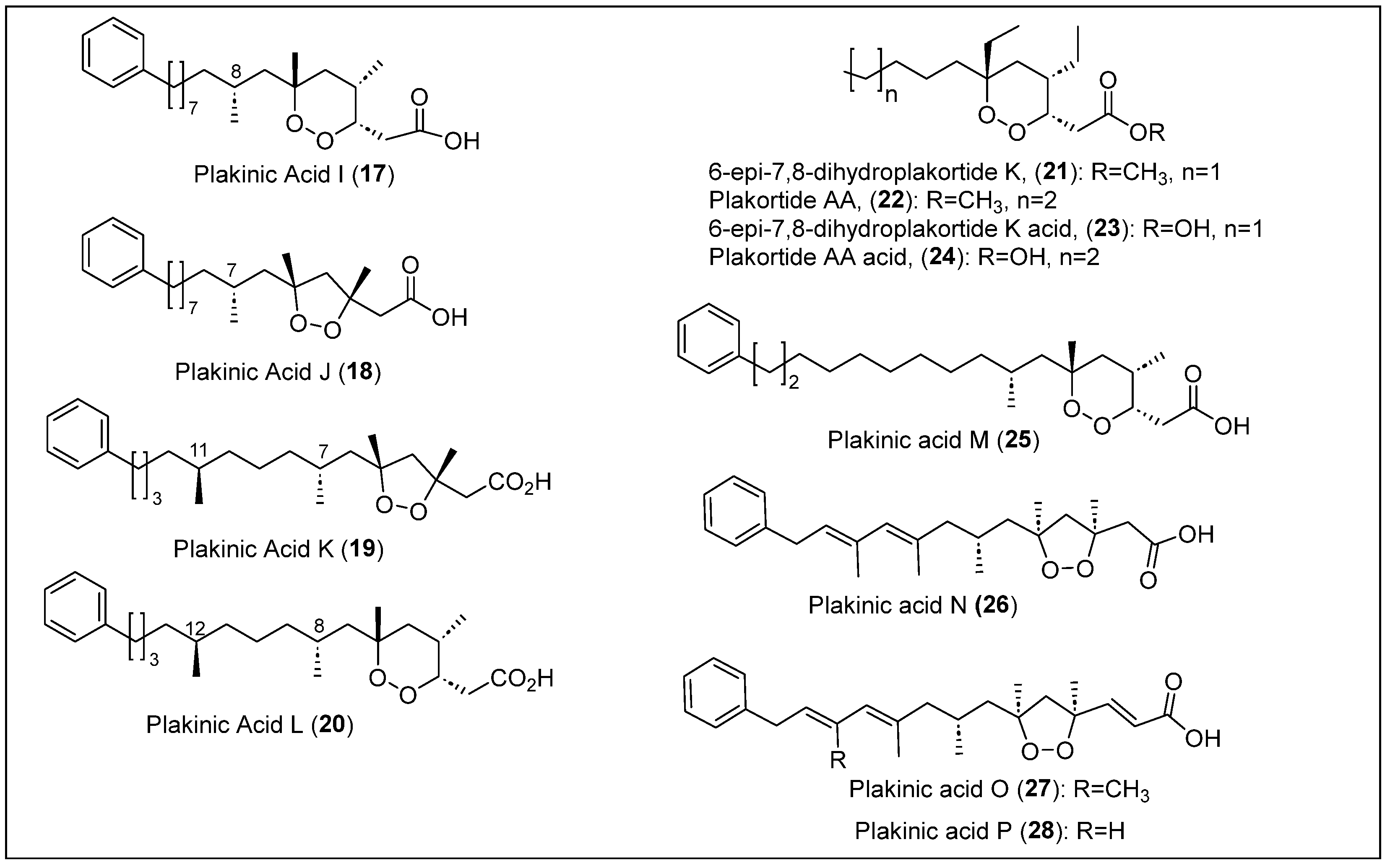
Dalisay et al. isolated two new endoperoxides, plakinic acid I (17) and plakinic acid J (18), from the sponge P. halichondrioides collected in The Bahamas (Figure 4) [49]. This article determined the absolute stereochemistry of plakinic acid I (17) and J (18) using the liposomal circular dichroism (CD) technique. The complete configuration of the stereocenters corresponding to the 1,2-dioxane rings of compounds 17 and 18 (Figure 4) was determined using 1H-NMR and NOESY correlations, chemical degradations, and Mosher’s ester method. Other techniques used to characterize these compounds were UV-Vis, FT-IR, 13C-NMR, and MS. Ultimately, it was determined that the chemical formula for plakinic acid I (17) is C25H40O4 and for plakinic acid J (18) is C24H38O4 (Figure 4). Compounds 17 and 18 have demonstrated the inhibition of haplodeficient paired lag1D/LAG1 strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This causes the yeast phosphoinositide pathway to not occur efficiently, causing protein impairment (misfolding). Later, the same research group collected the marine sponge P. halichondrioides-Xestospongia deweerdtae from the genera Plakortis and Xestospongia, respectively, on the coast of The Bahamas [50,51]. This two-sponge association organism was extracted with equal parts methanol and dichloromethane that yielded a dark-brown residue, which consequently was extracted with n-hexane, chloroform, n-butanol, and water. An antifungal bioassay-guided fractionation showed that the extract soluble in chloroform exhibited potent activity against the S. cerevisiae lag1∆/LAG1 strain. This fraction was later subjected to flash chromatography (FC), and after this, HPLC was used to further purify the active portion to yield plakinic acid K (19) and plakinic acid L (20).
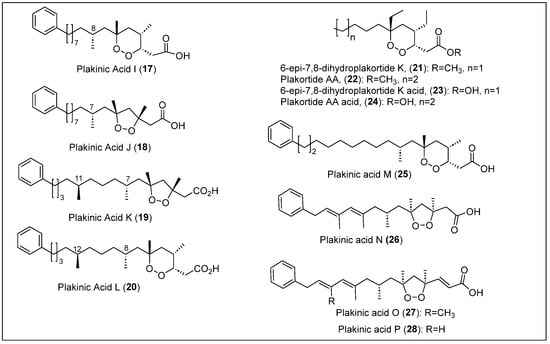
Figure 4.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 17–28.
The molecular formula for both 19 and 20 was determined by HREIMS, UV, IR, 1H, and 13C NMR spectra, which gave a formula of C26H44O4 and C25H40O4, respectively (Figure 4). Compared to known plakinic acids I (17) and J (18), the difference between 19 and 20 is a methyl group at C-12 and C-11, respectively. CD was performed to determine the configuration of the C-8/C-7 and C-12/C-11 of 19 and 20, respectively. Combining 1H-NMR and specific rotation analyses allowed for the determination of the absolute configuration of the 1,2-dioxolane ring of 19 and 20 (Figure 4). The compounds assayed demonstrated exceedingly antifungal activity (MICs ≤ 0.5 µg/mL) against strains of C. albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida krusei, and Cryptococcus neoformans, among others that were mentioned.
M. T. Jaminson and collaborators reported the discovery of five new natural endoperoxides, which are 6-epi-7,8-dihydroplakortide K (21), plakortide AA (22), and plakinic acids N-P (27–28), in addition to plakinic acid M 26, which was already known (Figure 4) [52]. These polyketides were isolated from the sponges P. halichondrioides-X. deweerdtae and Plakortis zyggompha collected at Plana Cays, The Bahamas, at a depth of 34 m. Metabolites 21 and 22 were obtained from a methanol–dichloromethane extract of P. zyggompha that was partitioned, and the resulting hexane fraction was separated through silica gel FC guided by an antifungal bioassay. The resulting methyl ester fraction was purified through RP-HPLC to yield pure ester compounds 21 and 22 (Figure 4). High-resolution electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HRESITOFMS) was used to determine the molecular formula of each compound, and the structures were characterized by NMR spectroscopy. The relative configuration of 21 was determined by an ROESY analysis, and the absolute configuration was established using modified Mosher’s method [53]. Compound 22 has an additional methylene group in the alkyl chain, and the 1H-NMR spectrum is almost identical to that of homolog 21. The antifungal sponge P. halichondrioides−X. deweerdtae was extracted with dichloromethane, followed by the same solvent partition and chromatography purification process employed for P. zyggompha. The RP-HPLC yielded the known compound plakinic acid M (25) [51], and the subsequent gel filtration (Sephadex LH-20) produced trace amounts of compounds of plakinic acids N-P (26–28).
Carboxylic acids 26 to 28 (Figure 4) were characterized employing the same spectroscopic techniques as 21 and 22. Compounds 27 and 28 were consistent with an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid like plakortide E (5) [16], and the relative configuration was determined by an ROESY analysis. Unfortunately, due to the lability of compounds N-P (26–28), their absolute configuration could not be determined after chemical manipulations. Still, using the density functional theory (DFT) calculation of 13C-NMR chemical shifts, the absolute configuration of 26 was determined. The antifungal properties of compounds 21, 22, and 25–28 (Figure 4) against a panel of pathogenic fungi, including C. albicans, Cryptococcus gattii, Cryptococcus grubii, and C. krusei, were evaluated. Compounds 21 and 22 were inactive against all strains of Candida and Cryptococcus, but their corresponding carboxylic acids 23 and 24 were very active (MIC90 = 2.7−36 μM). The most active of all endoperoxides against fluconazole-resistant C. krusei was plakinic acid M (25), which was already known (MIC90 = 2.7 μM). Plakinic acids N-P (26–28) did not show any activity against fungi, possibly due to their decomposition during the assay (Figure 4).
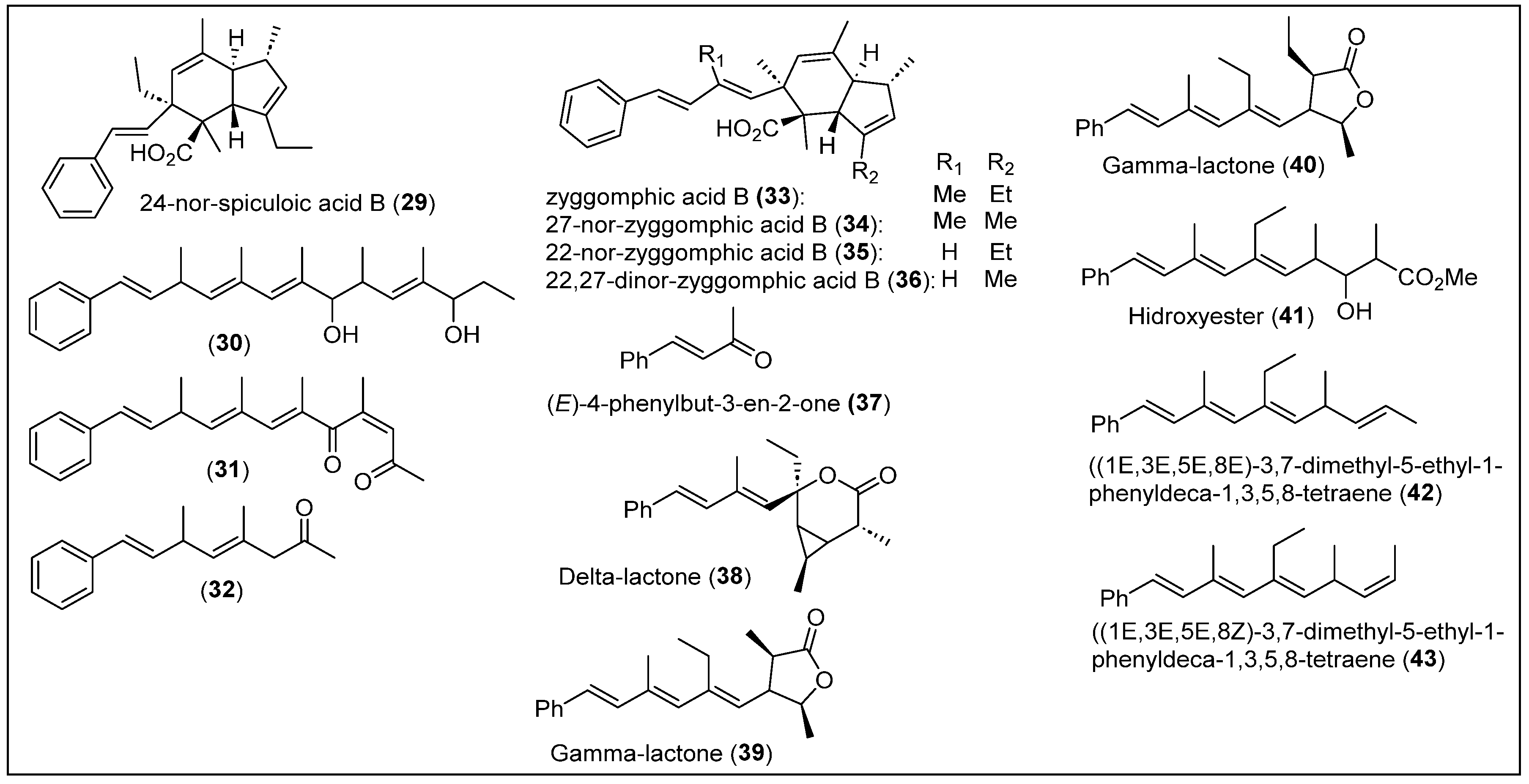
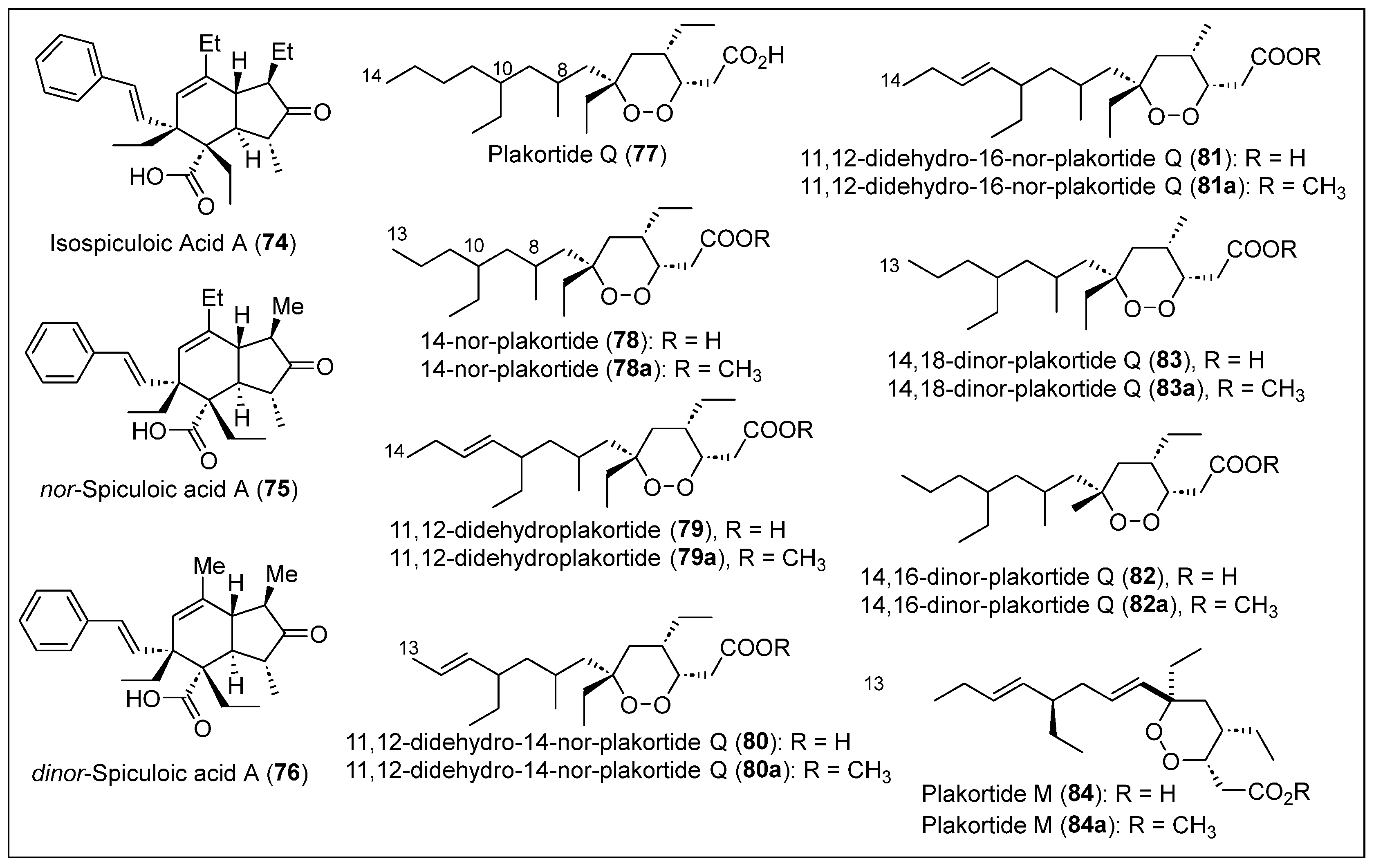
In 2010, S. Ankisetty et al. reported the isolation of the new compound 24-nor-spiculoic acid B (29) (Figure 5) and the known compound spiculoic acid B (57) from a deep reef sponge Plakortis angulospiculatus collected from a depth of 61.6 m at Bock Wall, The Bahamas [54]. Additionally, linear polyketides 30–32 (Figure 5) were isolated from a different marine sponge, P. halichondrioides, harvested at Bock Wall at a depth of 91.4 m. The freeze-dried individual sponges, P. angulospiculatus and P. halichondrioides, underwent CH2Cl2-MeOH extraction. Subsequently, the extract from each sponge was subjected to C-18 FC, followed by RP-HPLC to isolate the compound (29) and compounds 30–32, respectively. Compound (29) is classified as a spiculoic-derived class of polyketide; this skeleton can be identified by the four butyrate units found in spiculoic acids A (54) and B (55) [55]. The butyrate and propionate units in each structure determine that these compounds are closely related to synthetic processes. Compounds 30–32 only have one aromatic ring, which is part of the styryl group, and are differentiated by the length of the side chain and its substituents; 30 has two hydroxy moieties, 31 has two ketone functionalities, and 32 has one ketone group (Figure 5). The respective molecular formulas are C25H32O2 for compound 29, C25H36O2 for compound 30, C22H26O2 for compound 31, and C16H20O for compound 32, which were determined by HRESIMS (Figure 5). The structures of compounds 29–32 were analyzed and characterized by one-dimensional and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy, and compound 55 was confirmed by comparing its spectroscopic data with those in the literature [55]. The relative configuration of compounds 29 and 55 and the configuration for the double bonds of compounds 30–32 were established by NOESY correlations (Figure 5).
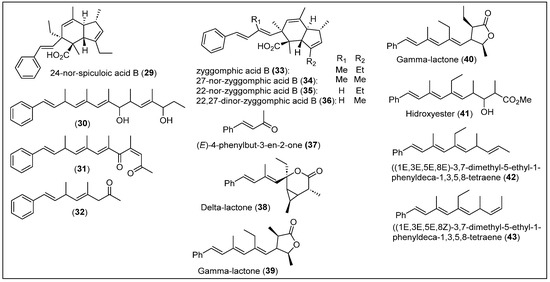
Figure 5.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 29–43.
In summary, 32 compounds were collected along the coasts of The Bahamas. These compounds originate from the sponges P. simplex, P. halichondrioides, P. halichondrioides-X. deweerdtae, and P. zyggompha. These polyketides were completely isolated and purified. Generally, these compounds exhibited various biological activities, such as antiparasitic, antifungal, anti-leukemia, anti-WEHI 164, and cytotoxic activity against the NFkB factor. However, the absolute configuration of compounds 7–10, 12–13, and 30–32 (and their respective derivatives) is still being determined, leaving their chiral centers with unresolved stereochemistry.
2.2. Coast of Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands are in the Western Caribbean Sea, south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica [56]. The research group of S. Ankisetty reported the isolation of another new group of cyclic compounds, zyggomphic acid B (33), 27-nor-zyggomphic acid B (34), 22-nor-zyggomphic acid B (35), and 22,27-dinor-zyggomphic acid B (36) (Figure 5) from another sample of P. angulospiculatus collected at a depth of 57.9 m off Little Cayman [54]. This sponge was subjected to a series of RP-HPLC studies to yield novel compounds 33–36. The molecular formula of C27H34O2 for compound 33, C26H32O2 for compounds 34 and 35, and C25H30O2 for compound 36 were determined by HRESIMS. The structure of the polyketides 33–36 was fully characterized by 1H, 13C, and two-dimensional (i.e., COSY, HMBC, HSQC, and distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer (DEPT-135)) NMR analyses (Figure 5). The relative configurations of compounds 33 to 36 were established by NOESY and HMBC correlations.
Compounds 33–36 are classified as indane-type polyketides, and they have three rings: cyclopentene and cyclohexene, which are fused, and one benzene, which is part of a styryl group (Figure 5). The difference between them lies in the substituents R1 and R2, and compounds 33–36 have an additional unsaturation in the styryl group concerning compounds 29 and 55 (Figure 5). The isolated compounds 29, 30, and 33–36 were tested for their anti-inflammatory activity using in vitro assays for the inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) activity, as well as the inhibition of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation via oxidative stress. Compounds 29 and 34 had a potent inhibition of NFκB’s activity. The cytotoxicity of these compounds was also evaluated to determine the selectivity index of their bioactivity concerning cytotoxicity. No inhibition of ROS generation and cytotoxicity was observed.
2.3. Coast of Belize
The coasts of Belize are situated along the Caribbean Sea in Central America [57]. These coastal waters host rich marine life, including vibrant coral reefs, many fish species, and other unique marine organisms, contributing to the ecological richness of the region. In 1979, Ravi, Armstrong, and Faulkner reported polyketide metabolites 37 to 43 from the sponge P. halichondrioides collected at the Lighthouse Reef (Figure 5) [58]. The sponge was homogenized in methanol, concentrated in vacuo, and extracted with hexane. The organic phase was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to obtain a paste. The crude product was placed in a Florisil column, increasing the polarity gradient. The hexane-soluble fraction was separated into several secondary metabolites from ethanol. After repurification via chromatography, three main compounds were isolated: trans-4-phenyl-3-buten-2-one (37) and two lactones (delta and gamma) (38–39).
Another gamma lactone (40), a hydroxy ester (41), and two tetraenes (E/Z isomers) (42–43) were extracted as minor metabolites (Figure 5). Delta lactone 38, which falls within the main compounds, has a formula of C21H26O2, and FT-IR and NMR were performed to detect the ester and confirm the skeleton of 21 carbons. UV-Vis was also performed to study the absorption of the conjugated benzene functionality. Gamma (39) lactone has a formula of C21H26O2, and the same spectroscopic techniques were applied (Figure 5). The UV-Vis analysis determined a third conjugation between the alkenes and phenyl groups in this case. The minor gamma lactone (40) has a formula of C22H28O2, showing the same stereochemistry as lactone 39. The hydroxyester (41) has a formula of C22H30O3. After performing 1H-NMR, its structure was confirmed, ruling out the possibility of being a methyl ester formed by adding methanol to lactone 39 (Figure 5). Finally, isomers 42–43 are hydrocarbons with the formula C20H26; their only difference is the E/Z configuration of C-8. It is essential to highlight that the spectroscopic techniques used to determine the structure of all the previously mentioned compounds were FT-IR, UV-Vis, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR (Figure 5).
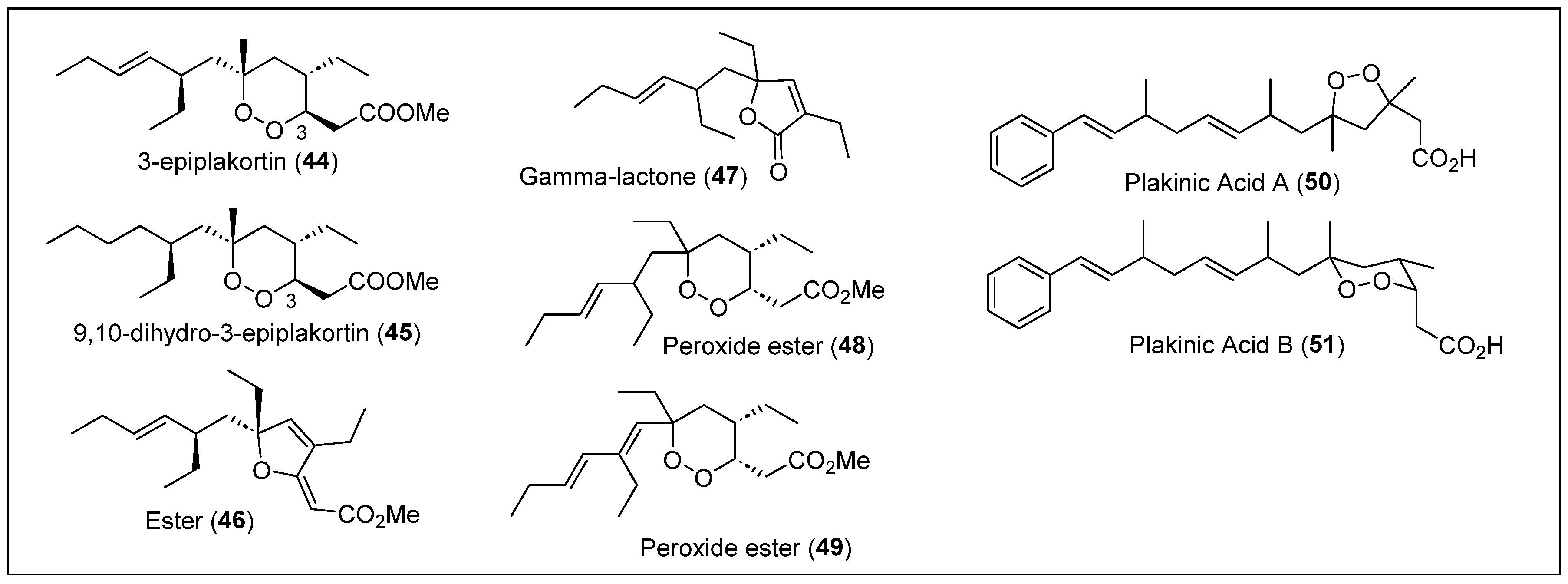
In 1980, Stierle and Faulkner reported the isolation and characterization of polyketides from three Plakortis sponges collected at the Lighthouse and Glover Reefs [39]. The first sample of P. halichondrioides was extracted and stored at −20 °C to be homogenized and extracted with ethanol. This sponge gave new compounds: 3-epiplakortin (44) and 9,10-dihydro-3-plakortin (45) (Figure 6). Compound 44 has a formula of C18H32O4 and is an isomer of plakortin (1). Compound 45 has a formula of C18H34O4, with an 1H-NMR spectrum identical to 44, except for the olefin signals. The 1H-NMR spectra for the epimeric compounds 1 and 45 only differ for the signals for the protons at C-2 and C-3 (Figure 6).
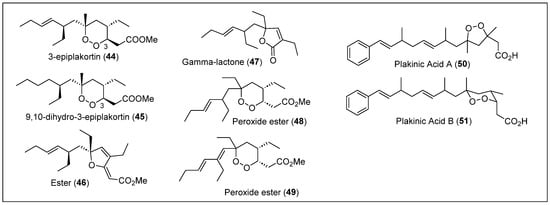
Figure 6.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 44–51.
The second P. halichondrioides sample was extracted similarly to the previous one and showed the presence of an ester (46) with the formula C19H30O3 (Figure 6). The characterization techniques used for this compound are FT-IR, UV-Vis, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR. In 1996, Schmidt and Faulkner reported elucidating the relative and absolute configuration of ester 46 employing chemical degradation methods and Mosher’s method [59]. The third Plakortis sample was extracted with dichloromethane and gave three new compounds: one lactone (47) and two peroxide esters (48 and 49) (Figure 6). LC was performed to obtain these compounds in a pure state. Gamma lactone 47 has a formula of C16H26O2. Compounds 48 and 49 only differ in the number of double bonds or instaurations, confirmed by 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR, because compound 48 has a formula of C23H40O4 and 49 has a formula of C23H43O4. The relative and absolute stereochemistry of compounds 46–49 and the biological activity of compounds 44–49 were not reported in this study (Figure 6).
In 1983, D. Phillipson and K. Rinehart reported the isolation of two new endoperoxide acids, plakinic acids A (50) and B (51) (Figure 6), with antifungal properties from the sponge P. zyggompha [48]. The major compounds were extracted with toluene and methanol (1:3). RP-HPLC was performed until the new bioactive compounds were obtained. Plakinic acid A (50) has a formula of C22H32O4, and B (51) has a formula of C24H34O4; both formulas were identified with HRFABMS (Figure 6). The FT-IR spectrum characterized the carboxylic acid functionality for both compounds. Then, compounds 50 and 51 were converted to the corresponding methyl esters to easily separate them by FC on silica gel followed by HLPC on a semipreparative silica gel column. The structure of the methyl esters of 50 and 51 and the relative stereochemistry of the six-membered ring in 50 were determined by an NMR analysis (Figure 6). These two new acid compounds, 50 and 51, showed fungal activity against S. cerevisiae (yeast) and Penicillium atrovenetum (filamentous fungus), while the methyl esters 50 and 51 were inactive. Furthermore, acids 50 and 51 inhibited L1210, a leukemia cell line, and presented an ID50 of 0.14 μg/mL.
2.4. Coasts of Dominica
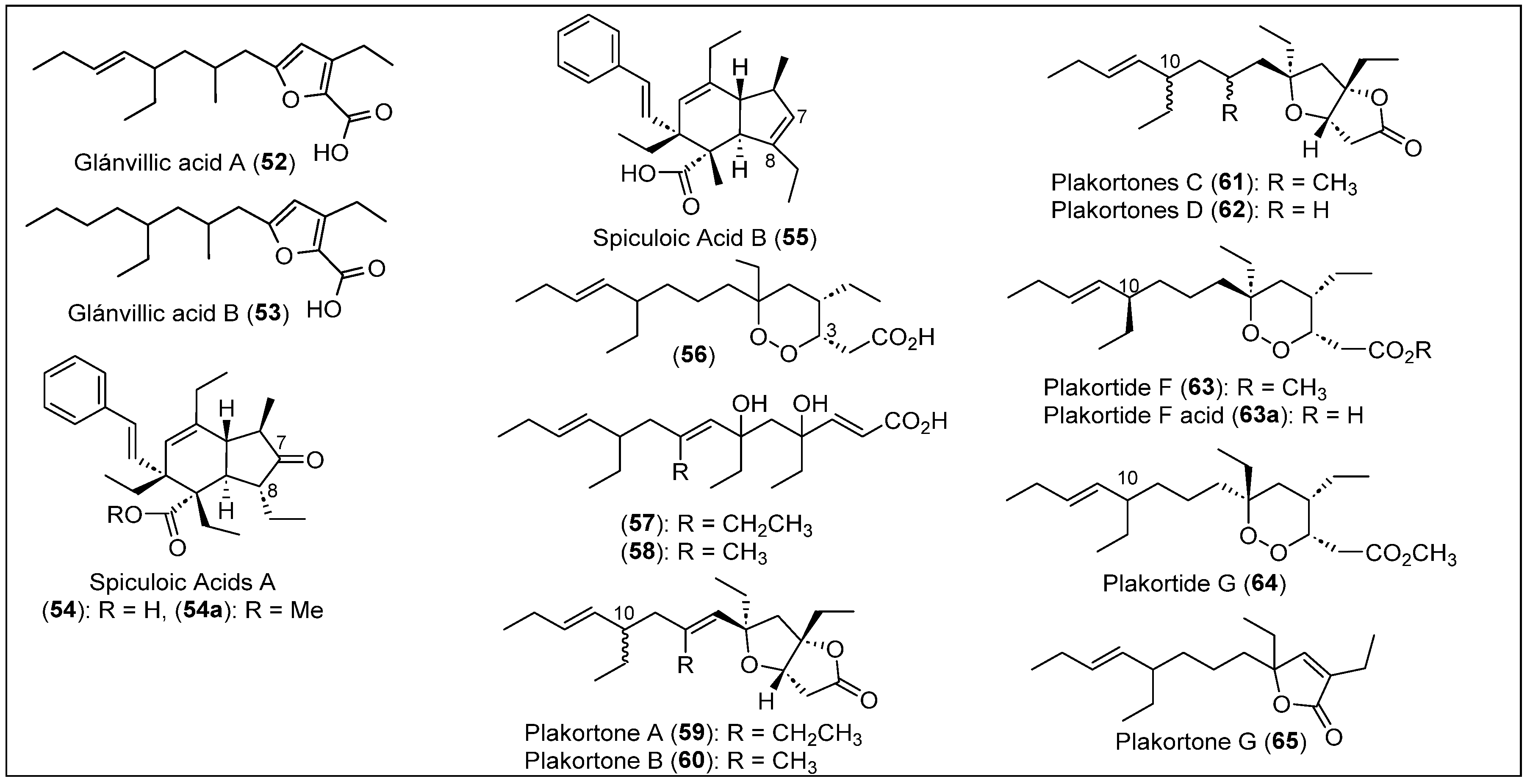
Dominica is located in the Eastern Caribbean Sea, between Guadeloupe to the north and Martinique to the south [60]. Two secondary metabolites, glánvillic acids A (52) and B (53), were obtained from the sponge P. halichondrioides found near Prince Rupert Bay [61]. The glánvillic acids 52 and 53 are the first polyketides in that family that contain an aromatic furan ring. The sponge P. halichondrioides was extracted several times with ethanol. The extracts were combined, concentrated in vacuo, and partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The organic phase was purified through bioassay-guided chromatography employing Sephadex LH-20, flash silica gel, and RP-CC followed by RP-HPLC to provide an inseparable mixture of glánvillic acids A (52) and B (53). Then, the mixture of acids was reacted with diazomethane to produce the methyl esters 52a and 53b, which were successfully separated using normal-phase HPLC. Methyl glánvillate A (52a) and B (53b) were analyzed by HRFABMS to determine their molecular formula (Figure 8). However, this study did not determine the relative and absolute stereochemistry of 52 and 53. Furans 52 and 53 showed significant in vitro cytotoxicity against murine leukemia P388 (IC50′s > 20 g/mL).
Spiculoic acids A (54) and B (55) (Figure 8) are polyketides that were recently discovered and isolated from the sponge P. angulospiculatus collected on the coast of Dominica [55]. Their isolation consisted of consecutive extractions with methanol, concentration in vacuo, and then partitioning with ethyl acetate and water. The resulting bioactive organic phase was fractionated with silica gel chromatography with a gradient elution to obtain spiculoic acids (54) and B (55) (Figure 8). The structures of the corresponding polyketide-derived spiculane carbon skeleton of 54 and 55 were analyzed by one-dimensional and two-dimensional NMR data, and the NOESY examination confirmed that the relative stereochemistry for both compounds was identical except for the presence of a C-7,8 olefin in 55 in place of the C-7 ketone/C-8 methine in 56. Only the spiculoic acid A (55) isomer shows cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells MCF-7 with an IC50 of 8 μg/mL, making it an excellent candidate for antitumoral activity. Furthermore, spiculoic acid B (55) was shown to be inactive.
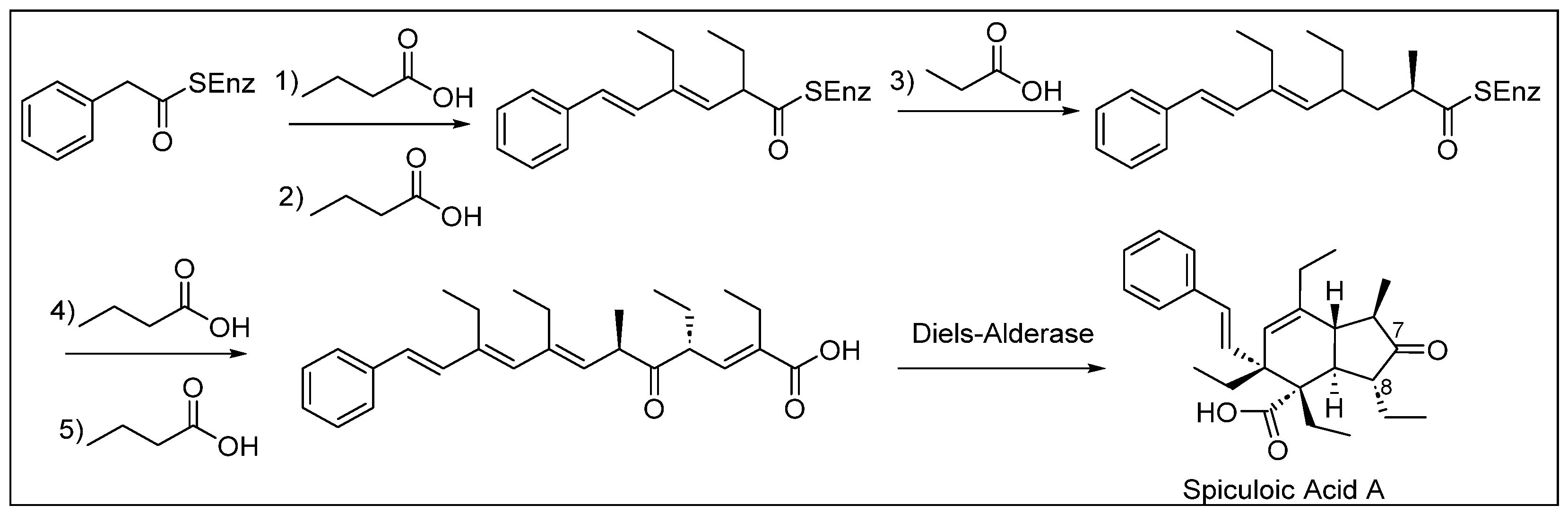
Most polyketides are synthesized from acetate and propionate building blocks, but the use of butanoate (C4) units was proposed to synthesize spiculoic acid A (54) (Figure 7). For biosynthesis, a phenyl acetic acid starter unit and five extension units, four of butyrate and one of propionate, are needed to construct the spiculane skeleton of spiculoic acid A (54). The first three condensation–dehydration reactions create a conjugation in the molecule. The fourth addition of butyrate breaks the conjugation pattern, and a final condensation reaction occurs to form a conjugated double bond with the carbonyl bond. Finally, a possible intramolecular cycloaddition occurs with the enzyme Diels–Alderase, which generates the chiral centers of the bicyclic skeleton [55].
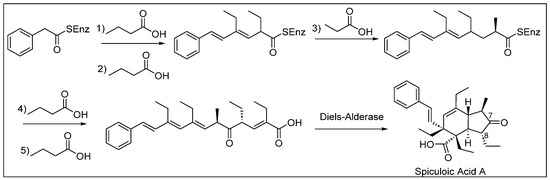
Figure 7.
Proposed biosynthesis of spiculoic acid A (54).
2.5. Coasts of Jamaica
Jamaica is an island south of Cuba and west of Hispaniola and additionally includes smaller islands and cays along its coastlines [62]. In 1983, A. Rudi and Kashman reported the isolation and characterization of three polyketides from the sponge P. halichondrioides, which was collected off the coast of Jamaica [63]. For the extraction and purification of the cyclic peroxide acid (55) and two alkylated dihydroxy α,β-unsaturated acids (57 and 58) (Figure 8), the sponge was extracted with ethyl acetate. The resulting crude material was chromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 and then purified by silica gel chromatography. Seven polyketide metabolites were obtained; four are known compounds, namely, the furane α,β-unsaturated methyl ester (46), plakortin (1), 3-epi-plakortin (44), and plakortic acid (1a) [39,59]. The structures of new compounds 56–58 (Figure 8) were determined by MS, 1H, 13C, and two-dimensional (COSY, HMQC, and HMBC) NMR correlations. The relative configuration of compounds 56-58 (Figure 8) remains to be established. The cytotoxicity against P-388 murine leukemia of compounds 56-58 showed IC50 values of 0.5 and 10 μg/mL, respectively.
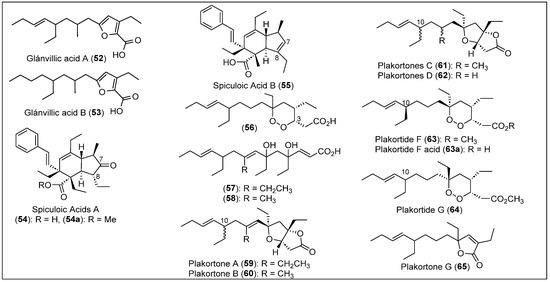
Figure 8.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 52–65.
In 1996, A. D. Patil et al. reported for the first time the isolation of plakortones A-D (59–62) (Figure 8) and a novel acid, plakortide E (5) (Figure 2), from the sponge P. halichondrioides collected in Jamaica [35]. The freeze-dried sponge was extracted sequentially with ethyl acetate and methanol to isolate polyketide. The less polar extract showed an ability to stimulate SR-Ca2+ ATPase activity. It was purified by CC using silica gel to obtain various active fractions that preparative TLC and HPLC purified to yield plakortones A-D (59–62) (Figure 8) and plakortide E (5) (Figure 2). Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESIMS) was used to deduce the molecular formula, and the structure of bicyclic lactones 60 to 63 (Figure 8) and five-membered peroxide five were determined by MS and by employing one-dimensional and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy, FT-IR, and UV spectroscopic analyses. The relative stereochemistry of the bicyclic lactone in plakortone A (59) (Figure 8) was established by NOE data, except for the relative configuration at C-10. They found that the relative configuration of plakortones B-D (60–62) is identical to plakortone A (59) (Figure 8). The NOE data determined the relative stereochemistry of the five-membered peroxide (1,2-dioxalane) moiety in plakortide E (5) (Figure 2). This work did not determine the absolute stereochemistry of plakortones A-D (60–63) (Figure 8) or E (5) (Figure 2). Compounds 59 to 62 resulted in a novel class of activators of cardiac SR-Ca2+-pumping ATPase active at micromolar concentrations. Plakortone D (62) showed the highest potency with EC50 = 2.8 ± 0.4 μM, in contrast to plakortone A (59), which showed a lower activity with EC50 = 14.5 ± 4.6 μM. Due to the limited solubility of compounds 59–62 in aqueous media, it was impossible to determine the in vitro cardiac relaxation.
The sponge P. halichondrioides was collected by hand at a depth of 30 m on the West Fore Reef at Discovery Bay in 1996 by A.D. Patil and coworkers. They isolated new plakortides F (63), G (64), and H (6) (Figure 2 and Figure 8) [37]. The sponge was extracted with ethyl acetate and then with methanol. The ethyl acetate extract was separated by CC with silica gel to collect several bioactive fractions. The extract was tested for SR-Ca2+ ATPase activity, and only the fractions that showed activity were used to determine the identities of the compounds. A preparative TLC and HPLC technique demonstrated the presence of three new cyclic peroxides, plakortides F (63), G (64) (Figure 8), and H (6) (Figure 2), including the known 3-epiplakortide (44) and the α,β-unsaturated ester (46) reported by Stierle and Faulkner in 1980 from the coast of Belize (Figure 8) [39]. Plakortide F (64) has a formula of C21H38O4 determined by high-resolution desorption chemical ionization mass spectrometry (HRDCIMS). The structure was elucidated by FT-IR, 13C, and 1H, and two-dimensional (COSY, HMBC, NOE, and HMQC) NMR was performed to study the stereochemistry.
The structure of Plakortide G (64) (Figure 8) was studied by HRDCIMS, UV-Vis, FT-IR, and NMR spectroscopic techniques. Diastereomeric compounds 63 and 64 have the same molecular formula of C21H38O4 but have an inverted stereochemistry at C-6 (Figure 8). Plakortide H (6) has a formula of C22H38O4, and the same spectroscopic characterization techniques for the two previous compounds, 63 and 64, were used to elucidate its structure. The relative stereochemistry of the six-membered peroxide moiety of plakortides F (63), G (64), and H (6) was analyzed and determined by NOE experiments, and only plakortides G (64) and H (6) have the same relative stereochemistry around the peroxide ring (Figure 8). However, the relative configuration at C-10 and the absolute configuration of the plakortides (63, 64, and 6) were not determined. Plakortides F (63), G (64), and H (6) demonstrated the ability to enhance SR-Ca2+ uptake in the same concentration range (10-100 µM). 3-epiplakortin (44) reached the highest level of stimulation in comparison with plakortides F (63), G (64), and H (6). Interestingly, the new diastereomers, plakortides F (63) and G (64), showed the same activity (Figure 8).
In 2001, J. Gochfeld and M.T. Hamann reported the isolation and biological evaluation of three secondary metabolites, in which only two of them are polyketide-derived compounds: plakortide F (63) and plakortone G (65) (Figure 8) from Plakortis sp. [64]. Samples of this sponge were collected at a depth of approximately 40 m at Discovery Bay in Jamaica. Among the three main secondary metabolites in this sponge, polyketide lactone plakortone G (66) had not been reported in the literature. Plakortide F (63) is a known peroxide reported by Patil et al. [35,37]. The proposed structure for plakortone G (65) is shown in Figure 8. To obtain the new polyketide plakortone G (65), the first step was to remove all the water from the sponge via lyophilization. Then, an extraction utilizing 1:1 isopropyl-ethyl acetate was performed extensively, with the crude extract being further separated by silica gel vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) utilizing a mobile phase of a mixture of 9:1 hexane to ethyl acetate. The obtained phase was purified using normal-phase and RP-HPLC, and plakortone G (65) was successfully isolated (Figure 8).
The structural characterization of polyketide 65 was achieved using high-resolution electrospray ionization Fourier transform mass spectrometry (HRESI-FTMS), 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR combined with DEPT, HMBC, and NOESY spectra. Compounds 63 and 65 possess a shared carbon backbone, with the primary distinction being that compound 63 is a cyclic endoperoxide, while compound 65 is an α,β-unsaturated lactone. This observation suggests the plausible derivation of lactone 65 from the peroxide structure of compound 63 (Figure 8). After confirming the identity of plakortone G (65) and plakortide F (63), an analysis of their biological activity was performed as part of the investigation.
In general, plakortone G (65) is less active than plakortide F (63) and does not exhibit antifungal or antimicrobial activity against C. albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, C. neoformans, Mycobacterium intracellulare, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, or methicillin-resistant S. aureus. However, plakortone G (65) reduces malarial activity in the D6 and W2 clones of P. falciparum, indicating that the new compound has great potential to become an effective antimalarial agent. Plakortone G (65) and plakortide F (63) are active against several cancer lines, but they are not selective toward any cell line (Figure 8). Plakortide F (63) showed moderate activity against Toxoplasma gondii and HIV-1. Further studies should be performed to evaluate its effectiveness as an antimalarial drug and to study other applications for which the compound may be helpful (Figure 8).
In summary, 33 compounds (33–65) were collected in the Cayman Islands, Belize, Dominica, and Jamaica. These compounds originate from the sponges P. halichondrioides, P. angulospiculatus, and P. zyggompha. These polyketides were completely isolated and purified. Generally, these compounds exhibited various biological activities, such as antifungal, anti-leukemia, anti-human breast cancer, and cytotoxic activity against the NFkB factor. However, the absolute configuration of compounds 41–43, 47–53, 56–62, and 64–65 (and their respective derivatives) still needs to be determined, leaving their chiral centers with unresolved stereochemistry.
Four cyclic peroxides, compounds 66, 67, plakortide K (68), and plakortide L (69) (Figure 9), were isolated from an undescribed species of the sponge Plakortis sp. collected at a depth of 45.5 m in Discovery Bay [65]. The sponge was extracted with CH2Cl2-acetone (1:1) in a blender, filtered, concentrated, and dried to obtain a brownish paste. The crude product was purified by column chromatography and preparative TLC to obtain compounds 66, 67, K (68) (Figure 9), and compound L (69) after purification by gel permeation chromatography on Sephadex LH20. HRESI-FTMS was used to determine the molecular formula of compounds 66 to 69 (Figure 9), and FT-IR, one-dimensional, and two-dimensional NMR analyses elucidated their structures. The coupling constants, NOESY correlations, and molecular modeling were analyzed to determine the relative stereochemistry of 66, 67, 68, and 69 (Figure 9). Compound 66 has an α,β-unsaturated ketone confirmed by UV analysis, compounds 66–68 are methyl esters, and 69 is the corresponding carboxylic acid of ester 68. Compound 66 showed an in vitro antimalarial activity of IC50 = 570 ng/mL against a W2 clone of P. falciparum. Compounds 66–69 (Figure 9) did not show antifungal or antimalarial activity.
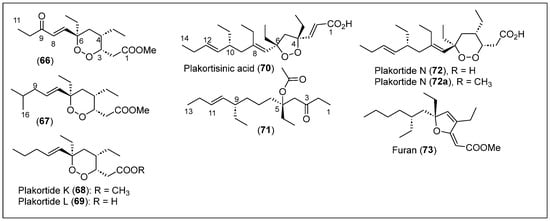
Figure 9.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 66–73.
R. Mohammed et al. (2010) reported a bioassay-guided isolation of Plakortis species collected at a 18–20 m depth at Discovery Bay [66]. After isolation, two new secondary metabolites were discovered: plakortisinic acid (70) (Figure 9), which is a five-membered ring containing endoperoxide, and a new ketone derivative (71) (Figure 9). The sponge also produced other previously reported compounds like the α,β-unsaturated ester (46) [39,59], plakortide N (72) [37], plakortide F (63) [37,63], the free acid (63a) [63], plakortone D (62) (Figure 8) [35], and a furan-containing molecule (73) [67]. The sponge was exhaustively extracted with ethanol, dried, and separated into several fractions using VLC using a gradient of n-hexane to ethyl acetate and MeOH to extract and isolate these metabolites. The bioactive fractions were screened using PharmaMar cytotoxic assay screening against HT29, A549, and SK-MEL-28 cell lines. All fractions were repurified via chromatography on VLC, screened by TLC, and purified with HPLC and Sephadex LH-20 to produce compounds 70,71, 46, 63, 63a, 62, 72, and 73 (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
The structures of the new compounds 70 and 71 (Figure 9) were characterized by MS and NMR (one- and two-dimensional) analyses; specifically, their relative configurations were established by NOESY correlations, and the absolute configurations were assigned using ab initio calculations comparing the calculated and experimental optical rotations. Only the cyclic endoperoxides plakortide N (72) and the plakortide F free acid (63a) (Figure 8) exhibited activity against AIDS opportunistic infections with C. albicans, C. galabrata, C. krusei, and C. neoformans. At the same time, the new compounds 71 and 72 and the known compounds 46, 63, 63a, and 65 did not show any antimicrobial activity.
In vitro anti-M. tuberculosis (Mtb) and antiprotozoal activities against malaria and Leishmania parasites in bioactive studies were determined for compounds 70, 71, 46, 63, 63a, 62, 72, and 73 (Figure 8 and Figure 9). The results demonstrated that compounds 70 and 71 were the most active against L. donovani, with IC50 values of 3.1 and 2.8 μg/mL, respectively, while compounds 72 and 73 were inactive. Plakortide F ester (63) exhibited moderate activity, compound 70 showed low activity, and compound 70 was inactive against P. falciparum (Figure 9). Plakortide F acid (63a), plakortisinic acid (70), and plakortide N (72) were moderately active against Mtb inhibition at 64 μg/mL. Compounds 70, 46, 63, and 63a were subject to an in vitro anti-HIV-1 activity study in human PBM cells, and plakortide N (72) exhibited the highest anti-HIV-1 activity in human PBM cells with an EC50 of 7.8 μM and an EC90 of 22.1 μM, but it is highly cytotoxic to CEM and Vero cells. Plakortide N (72) and plakortide F acid (63a) (Figure 8 and Figure 9) showed moderate cytotoxicity against the NCI tumor cell lines and showed promising activity against colon cancer (KM12 cell line) and melanoma (LOX IMVI cell line). Unfortunately, plakortisinic acid (70) was completely inactive against all tumor cell lines.
2.6. Coasts of Martinique
Martinique is in the Eastern Caribbean Sea, north of Saint Lucia and south of Dominica [68]. Three complex bicyclic polyketides: iso-, nor-, and dinor-, spiculoic acids A (74–76) (Figure 10) were extracted and isolated from the organism P. zyggompha by F. Berrué et al. [69]. This sponge belongs to the order Homosclerophorida, family group Plakinidae, and genus Plakortis. A sample of this species was obtained from 20 m below the surface near “Rocher du Diamant” from the waters south of Martinique Island. The three mentioned polyketides, isospiculoic acid A (74), nor-spiculoic acid A (75), and dinor-spiculoic acid A (76), are classified as/known for having a spiculane skeleton (Figure 10) [55]. The frozen P. zyggompha sample was extracted with a 1:1 solution of methanol and dichloromethane. The resulting product evaporated to produce a brown paste-like substance, partitioned with water and CH2Cl2. The organic CH2Cl2 phase was purified with silica gel CC. Using a gradient of hexane–methanol, several fractions were obtained, and the most bioactive fraction was purified via an HPLC C18 semipreparative column to isolate the compounds isospiculoic acid A (74), nor-spiculoic acid A (75) and dinor-spiculoic acid A (76) (Figure 10). The structures and relative stereochemistry of spiculoic acids A 74–76 (Figure 10) were determined by MS and one- and two-dimensional NMR (COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY) analyses. The bioactivity of compounds 74–76 was studied employing a colorimetric analysis performed using the sulforhodamine B method [45] to see their in vitro cytotoxic against three tumor cell lines, including lung A549, colon HT29, and breast MDA-MB-231 carcinomas. Only compounds 74 and 76 (Figure 10) showed moderate cytotoxic activity against A549 and HT29 tumor cell lines. Compounds 74, 75, and 76 (Figure 10) were all inactive against MDA-MB-231.
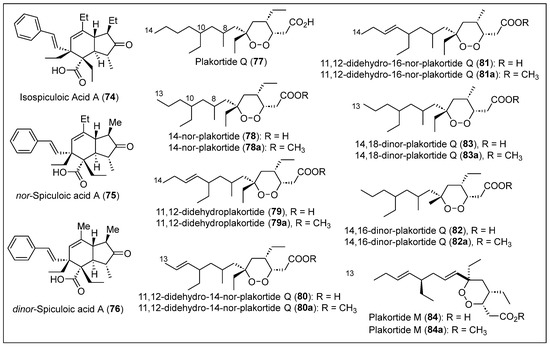
Figure 10.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 74–84.
Later, F. Berrué et al. reported the extraction and isolation of seven additional bioactive cyclic peroxides from the same sponge P. zyggompha obtained on the island [70]. The seven isolated endoperoxide natural products were plakortide Q (77) (Figure 10), 14-nor-plakortide Q (78), 11,12-didehydroplakortide Q (79), 11,12-didehydro-14-nor-plakortide Q (80), 11,12-didehydro-16-nor-plakortide Q (81), 14,16-dinor-plakortide Q (82), and 14,18-dinor-plakortide Q (83), which are classified as endoperoxide polyketides (Figure 10). These natural products are biosynthesized via specific enzyme-aided reactions, as suggested by the same stereochemistry between all the compounds [55]. Plakortide Q acid (77) and inseparable mixtures of acid compounds 78–79 and 80–83 (Figure 10) were obtained following the previously reported isolation protocol for spiculoic acid A derivatives 74–78 [69]. The inseparable mixtures of carboxylic acids 78–79 and 80–83 were esterified separately and purified by HPLC with a modified phenyl-hexyl column stationary phase. The methyl esters 79a–83a were separated from their corresponding mixtures, even though an inseparable mixture of 80a/81a and 82a/83a was obtained (Figure 10).
The structure of compounds 77, 78a, 79a, a mixture of 80a/81a, and a mixture 82a/83a were fully characterized by MS and NMR analyses. The NOESY correlations confirmed that the relative stereochemistry of the 1,2-dioxane ring is the same for all of cyclic peroxides 77 to 83 (Figure 10). The relative configurations at the C-8 and C-10 chiral centers of the aliphatic chain and the absolute configuration of 77-83 remain undetermined. Plakortides Q (77), 79, and 81 have an additional methylene unit in their corresponding aliphatic chains compared to compounds 78, 80, 82, and 83. Compounds 77, 78, 82, and 83 have saturated aliphatic chains, and compounds 79, 80, and 82 (Figure 10) have unsaturated aliphatic chains. The bioactivity of the seven endoperoxide polyketides (78–83) was studied using cell lung carcinoma A549, colon carcinoma HT29, and breast MDA-MB-231 cell samples. The results indicated that plakortide Q (78) and the mixture of 80a/81a (Figure 10) are the most active compounds for all cell lines. In general, the carboxylic acid plakortide Q (78) is more active than the methyl esters 78a–83a, presenting valuable cytotoxic properties against the tumor cells A549 and HT29 (IC50 values of 3.6 and 3.9 mM, respectively).
2.7. Coast of Panamá
Panama’s Caribbean coast stretches along the eastern part of the country [71]. In 1978, M. D. Higgs and D. J. Faulkner reported for the first time the isolation of plakortin (1) and polyketide ketone 9 (Figure 2) from the sponge P. Halichondrides collected at a depth of 10 m at Hookers Reef [33]. The sponge was extracted with ethanol several times in a Soxhlet extractor, and then the extract was concentrated. The resulting crude paste was extracted between water and ether. Then, the organic crude extract was purified by Florisil and liquid chromatography (LC) to obtain plakortin (1) and compound 9 (minor component) (Figure 2). MS was used to determine the molecular formula C18H32O4 of 1, and the structure was elucidated using FT-IR, 1H-, and 13C-NMR spectra and employing a chemical degradation method to confirm the presence of the six-membered peroxide. The optically active plakortin 1 methyl ester has two ethyl groups at C-4 and C-8 and an alkene with a trans geometry. This pioneering report excludes biological assays for compounds 1 and 9 (Figure 2).
2.8. Coast of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico is an island located in the Northeastern Caribbean Sea, east of the Dominican Republic [72]. Puerto Rico’s archipelago includes the Vieques and Culebra Islands. In addition, there are islets such as Mona, Monito, Desecheo, and various others that contribute to the territorial diversity of Puerto Rico. In 2003, del Sol Jiménez et al. reported the isolation, structure, stereochemistry, and biological properties of two new cycloperoxides, plakortide M (84) and N (72) (Figure 9 and Figure 10), from the sponge P. halichondrioides collected by diving off of Mona Island [44]. The homogenized and dry sponge was extracted with a mixture of 1:1 of MeOH-chloroform and then partitioned between hexane and water. The resulting organic phase was purified by silica gel CC to obtain non-polar fractions composed of the known polyketide ester 46 [39,59] and plakortide F (63) (Figure 6 and Figure 8) [35,37,63], and the more polar fractions yielded the new cyclic endoperoxide compounds 84 and 72 (Figure 9 and Figure 10).
Compound 46 and plakortide F (63) (Figure 6 and Figure 8) were confirmed by a comparison of the 1H and 13C-NMR and HREIMS data with the previously reported literature [35,37,39,63]. Plakortide M (84) has a molecular formula of C20H34O4, and plakortide N (72) has a formula of C22H38O4. The structure of compounds 84 and 72 (Figure 9 and Figure 10) was elucidated by one- and two-dimensional (COSY, HMQC, and HMBC) NMR analyses. Compound 84 was converted into methyl ester 84a (Figure 10) to determine the relative stereochemistry based on the NOESY correlations, and the hydrogenation of ester 84a achieved the absolute configuration and was then converted into a Mosher’s derivative. The comparison and analysis of the 1H-NMR spectrum of the endoperoxy ring in 84 and 72 (Figure 9 and Figure 10) and their optical rotations suggest that they have the same relative and absolute stereochemistry. Plakortides M (84) and N (72) exhibited potent cytotoxic activity against several cancer cell lines but were not selective. Methyl esters 84a and 72a showed no significant inhibitory activity against M. tuberculosis H37Rv. Compound 84a showed the highest cytotoxicity against P. falciparum with an IC50 of 8 µg/mL.
In summary, 19 compounds (66-84) were collected in Jamaica, Martinique, and Puerto Rico. These compounds originate from the sponges P. halichondrioides and P. zyggompha. These polyketides were completely isolated and purified. Generally, these compounds exhibited various biological activities, such as antifungal, anti-cancer, anti-malaria, anti-HIV, and anti-Mtb. However, the absolute configuration of compounds 77-83 (and their respective derivatives) still needs to be determined, leaving their chiral centers with unresolved stereochemistry.
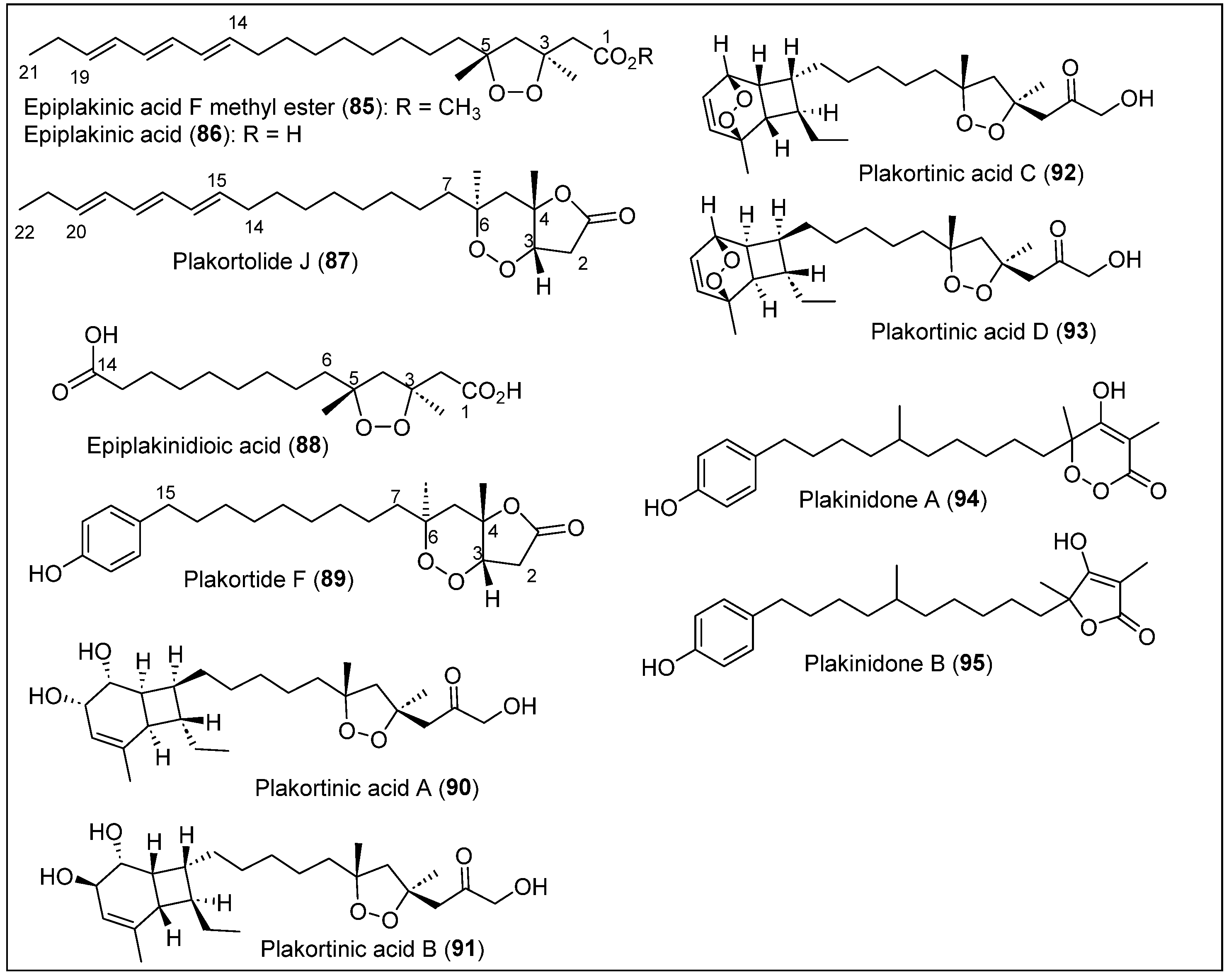
The isolation of new polyketides, epiplakinic acid F methyl ester (85), plakortolide J (86), and epiplakinidioic acid (87), along with the known compounds epiplakinic acid F (88) and plakortolide F (89) (Figure 11), were reported by Jiménez-Romero et al. in 2010 from the sponge P. halichondrioides collected at depths of 30 m off of Mona Island [73]. The three new compounds are classified as cycloperoxides. Epiplakinic acid F methyl ester (85) and epiplakinidioic acid (87) (Figure 11) are five-membered-ring polyketide endoperoxides, and plakortolide J (86) is a peroxide–lactone. The organism was first frozen and lyophilized for isolation and purification before extraction. The dry specimens were cut into small pieces and blended in a mixture of chloroform-MeOH. After filtration, the crude extract was concentrated and stored to yield a dark paste suspended in water and extracted with n-hexane. The concentration of the organic phase under a reduced pressure yielded a dark-brown oil, a portion of which was chromatographed over silica gel. Several fractions were analyzed by TLC and 1H-NMR analyses and repurified via silica gel CC to obtain subfractions that yielded pure epiplakinic acid F methyl ester (85), plakortolide J (86), and epiplakinidioic acid (87).
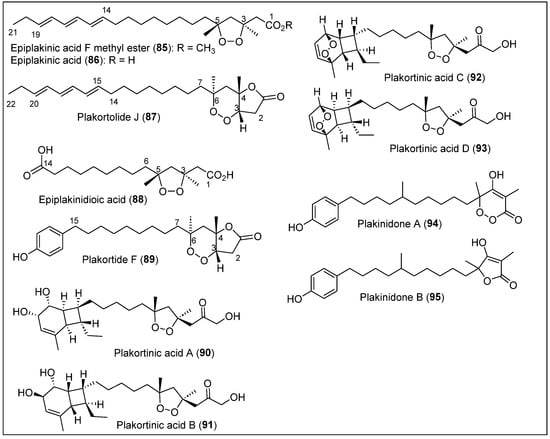
Figure 11.
Structures of Caribbean polyketides 86–95.
In addition, the known epiplakinic acid F (88) and plakortolide F (89) were obtained (Figure 11) [74,75]. The molecular formulas for epiplakinic acid F methyl ester (85), plakortolide J (86), and epiplakinidioic acid (87) are C24H40O4, C24H38O4, and C16H28O6, respectively, and were established by HREIS. The UV, FT-IR, and NMR spectroscopic data and chemical analyses determined the structures of these metabolites (Figure 11). The absolute configuration for polyketides 85 and 86 was determined by degradation reactions followed by applying Kishi’s method. Epiplakinic acid F methyl ester (85) and epiplakinidioic acid (87) have a 1,2-dioxolane ring (with trans-oriented methyl substituents at the C-3 and C-5 positions) (Figure 11). Plakortolide J (86) has a unique peroxide–lactone moiety; compounds 85 and 86 have a conjugated triene in their alkyl chains compared with two carboxylic acids at both ends of compound 87 (Figure 11). The cytotoxic activity of the natural cycloperoxides 85–89 against DU-145 prostate cancer and A2058 melanoma cell lines was evaluated. Compounds 87 and 88 (Figure 11) were very active against melanoma cells. Plakortide F (89) showed in vitro potent cytotoxicity against LOX IMVI melanoma, IGROV1 ovarian cancer, and UO-30 renal cancer. Compound 88 showed in vitro strong antimalarial activity (with an IC50 of 0.3 μg/mL) against Plasmodium falciparum, and compounds 85 and 88 showed good activity with IC50 values of 4 μg/mL and 3 μg/mL, respectively. Compounds 85, 86, 87, and 89 (Figure 11) showed moderate-to-weak in vitro activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv.
Plakortinic acids A (90) and B (91) (Figure 11) were isolated from a two-sponge symbiotic association of P. halichondrioides-X. deweerdtae collected on Mona Island by Jiménez-Romero et al. [76]. Recently, they reported the isolation and characterization of plakortinic acids C (92) and D (93) as a continuation of their previous work [77]. Plakortinic acid (90) and B (91) (Figure 11) are new cyclic peroxide-containing natural products that have novel bicyclo [4.2.0]octadiene motifs, and plakortinic acids C (92) and D (93) have unprecedented peroxide-polyketides with a 7,8-dioxatricyclo [4.2.2.0]dec-9-ene scaffold.
For the isolation and purification of plakortinic acids A (90), B (91), C (92), and D (93) (Figure 11) from the sponge specimens, the biomass was extracted with methanol–chloroform, filtrated, and concentrated to yield a paste that was suspended in water and extracted with n-hexane. The organic phase was concentrated to obtain an oil that was chromatographed to obtain various fractions. The resulting bioactive fraction was purified by chromatography to obtain an inseparable 1:1 mixture of A (90) and B (91) (Figure 11) [76], along with the previously reported epiplakinic acid F (88) [73]. Plakortinic acid C (92) and plakortinic acid D (93) were isolated as a 3:1 mixture of diastereomers from the less polar fraction eluted over silica gel [77]. Each mixture of 90/91 and 92/93 (Figure 11) was converted into the corresponding methyl esters. After successive CC and HPLC (normal- and reversed-phase), an inseparable mixture of methyl esters 90a/91a and 92a/93a was obtained. Nevertheless, polarimetry, HREIS, FT-IR, one-dimensional, and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy characterized each inseparable mixture of esters. The NOESY correlations were used to determine the relative configurations of the stereocenters. The absolute configuration of 92 and 93 was analyzed by comparisons with the optical rotation of plakortinic acids A (90) and B (91). The mixture of 90/91 (Figure 11) displayed IC50 values of 0.3 and 0.5 μM for the A2058 melanoma and DU-145 prostate cancer cell lines, respectively [76]. The mixture of compounds 92/93 (Figure 11) showed a lower level of in vitro toxicity against a panel of 60 tumor cell lines [77].
Recently, in 2024, Amador et al. reported that plakortinic acid C (92) and plakortinic acid D (93) are inseparable endoperoxides, which were also isolated from the sponges P. symbiotica-X. deweerdtae on Mona Island (west of Puerto Rico) [78]. This differs from a previous study [76], in which they were isolated from the symbiotic relationship between P. halichondrioides-X. deweerdtae. The study reveals for the first time that compounds 92/93 possess antiplasmodial properties, making them effective against malaria. Additionally, their toxicity was evaluated against erythrocytes, and they showed no toxicity. Polyketides 92 and 93 demonstrated an EC50 of 5.3 µM against the organism. Both compounds are the first marine natural products to show activity against malaria, and their structure (Figure 11) contains the motif 7,8-dioxatricyclo [4.2.2.02,5]decen-9-ene.
2.9. Coast of Tobago Island
Tobago Island is situated in the Southern Caribbean Sea, northeast of the island of Trinidad and Venezuela [79]. Kushlan and Faulkner isolated plakinidone A (94) and B (95) from the sponge P. angulospiculatus collected at the Tobago Cays at a depth of 17 m in Horse Shoe Reef (Figure 11) [80]. Plakinidone A (94) and B (95) only differ in their ring systems, as shown in Figure 11. Plakortidone A (94) has an α,β-unsaturated six-membered peroxide, and plakortidone B (95) has an α,β-unsaturated five-membered lactone (Figure 11). To obtain these compounds, the dry P. angulospiculatus was kept in methanol for several months and then decanted to obtain a crude extract. Afterward, the methanol was evaporated, and the aqueous remaining solution was diluted and extracted with hexane, CH2Cl2, and ethyl acetate. The CH2Cl2 phase was then separated with CC, and the more polar of the fractions was further purified by preparative HPLC using a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate in a ratio of 2:3, which yielded plakinidone in small amounts. 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, FT-IR, DEPT spectra, and MS were used to characterize the obtained polyketide. The relative and absolute stereochemistry of plakortidones 94 and 95 (Figure 11) has yet to be determined. The investigators demonstrated that the mixture of plakinidone A (94) and B (95) (Figure 11) showed mild antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and Bacillus subtilis but was inactive against C. albicans. It is expected that plakinidone A (94) and B (95) (Figure 11) could have great potential as antimicrobial and antifungal agents. Still, only some tests were performed during the investigation, which necessitates further studies.
In summary, 11 compounds (85–95) were collected in Puerto Rico and on Tobago Island. These compounds originate from the sponges P. halichondrioides and P. halichondrioides-X. deweerdtae, P. angulospiculatus, and P. zyggompha. These polyketides were completely isolated and purified. Generally, these compounds exhibited various biological activities, such as antibacterial, anti-cancer, anti-malaria, and anti-Mtb. However, the absolute configuration of compounds 94–95 still needs to be determined, leaving their chiral centers with unresolved stereochemistry.
Along the coasts of The Bahamas, P. simplex and P. halichondroides were the most abundant sponges; P. zyggompha, and P. angulospiculatus were also identified (Table 1). The coasts of Belize, Dominica, Jamaica, Panamá, and Puerto Rico also exhibited the presence of P. halichondroides. Notably, P. angulospiculatus (collected from The Bahamas and Martinique) and P. zyggompha (collected from Dominica) produced polyketides with a bicyclic indane-type skeleton. Interestingly, A. D. Rodríguez and coworkers collected a sample of two-sponge association of P. halichondrioides-AX. deweerdtae in Mona, Puerto Rico (Table 1), which produced a new class of cyclic peroxides that have bicyclo [4.2.0]octadiene 7,8-dioxatricyclo [4.2.2.0]dec-9-ene motifs (Figure 11). Finally, Table 1 summarizes the compounds discussed in this review. The table includes the location of the isolation, the species, their biological activity, and references.

Table 1.
Summary of polyketides 1–95.
3. Conclusions
We have summarized the collection, extraction, isolation, structural characterization, and biological activity of 95 Caribbean polyketides (including congeners) that were isolated from different types of Plakortis sponges, such as P. simplex, P. halichondroides, P. zyggompha, and P. angulospiculatus, located around the coasts of The Bahamas, Cayman Islands, Belize, Dominica, Jamaica, Martinique, Panamá, Puerto Rico, and Tobago. Plakortis sp. produced bio-related metabolites with different functional groups, like cyclic endoperoxides (i.e., 1,2-dioxolane and 1,2-dioxane rings), bicyclic compounds (i.e., spiculane, indane-type), furan, lactone, α,β-unsaturated ketone, diols, conjugates alkenes, carboxylic acid, methyl esters, and phenyl, phenol, and styryl groups (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11). The biological activities presented in some of these compounds and congeners are antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic, and antiviral (Table 1).
This review aims to inspire researchers to continue exploring these Caribbean coasts, encouraging them to rediscover, uncover, and investigate novel polyketide natural products in the coming years. Due to their distinctive chemical structures and bioactivities, these secondary metabolites hold significant potential for drug discovery. Some compounds still require comprehensive reviews of their structural elucidation and biological activity. By researching and connecting the potential of these compounds, scientists aim to develop new therapeutic agents and expand our understanding of the ecological impact of polyketides in marine ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R.R.-B.; methodology, R.R.R.-B.; validation, R.R.R.-B.; formal analysis, R.R.R.-B. and J.A.R.-V.; data curation, R.R.R.-B., J.A.R.-V., F.C.-C., U.M.-S., Y.W.O.-C., A.E.-C., A.C.-G. and K.Y.Á.-D.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R.R.-B.; writing—review and editing, R.R.R.-B. and J.A.R.-V.; visualization, R.R.R.-B.; supervision, R.R.R.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Authors thanks to the different funding bodies that support this work. J.A.R.-V. was supported by UPR-RP DEGI and received funds through the FIPI Fellowship, UPRAA and Evertec scholarships. R.R.R.-B. was supported by the Sloan Scholars Mentoring Network (SSMN) of the Social Science Research Council (SSRC) in partnership with the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
All authors would like to thank the Chemistry Department of the University of Puerto Rico, Río Piedras Campus (Puerto Rico, USA) for their support of this work and the opportunity to offer the special topics course (QUIM 5995/8994) of Medicinal Natural Product Chemistry as part of Raúl R. Rodríguez-Berríos’s Chemical Educational Teaching and Research Projects. This project assesses and evaluates students’ learning processes and experiences to prepare a review article. We especially would like to thank the following Chemistry Educational Research in Organic Chemistry (CEROC) Laboratory members: Cristtian Rivera-Torres, Mia A. Padilla-Garcia, Giuliana I. Cabrera-Guevarez, Fabiola J. Hernández-Morales, and Daliana M. Agosto-Disdier for helping us with their suggestions and discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.S. The Role of Natural Product Chemistry in Drug Discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.R. Natural Products: The Secondary Metabolites; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 17, ISBN 0-85404-490-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.J. Natural Products Chemistry: Sources, Separations and Structures; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-138-45357-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gutzeit, H.O.; Ludwig-Müller, J. Plant Natural Products: Synthesis, Biological Functions and Practical Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; ISBN 3-527-68200-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Berríos, R.R.; Ríos-Delgado, A.M.; Perdomo-Lizardo, A.P.; Cardona-Rivera, A.E.; Vidal-Rosado, Á.G.; Narváez-Lozano, G.A.; Nieves-Quiñones, I.A.; Rodríguez-Vargas, J.A.; Álamo-Diverse, K.Y.; Lebrón-Acosta, N. Extraction, Isolation, Characterization, and Bioactivity of Polypropionates and Related Polyketide Metabolites from the Caribbean Region. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, C. Structures and Mechanisms of Polyketide Synthases. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6416–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W. Natural Polypropionates in 1999–2020: An Overview of Chemical and Biological Diversity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, A.J. Biosynthesis of Polyketides and Related Compounds. Science 1967, 156, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertweck, C. The Biosynthetic Logic of Polyketide Diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, B.J. Biosynthesis of Polyketides. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1997, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risdian, C.; Mozef, T.; Wink, J. Biosynthesis of Polyketides in Streptomyces. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Lin, T.; Hu, P.; Shen, Y. Seven Novel Linear Polyketides from Xylaria Sp. NCY2. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2010, 93, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B. Polyketide Biosynthesis beyond the Type I, II and III Polyketide Synthase Paradigms. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, J. A New Role for Polyketides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, K.J. Chapter 1 Introduction to Polyketide Biosynthesis. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 459, pp. 3–16. ISBN 978-0-12-374591-0. [Google Scholar]
- Koskinen, A.M.; Karisalmi, K. Polyketide Stereotetrads in Natural Products. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfeld, W.; Kirst, H.A. Macrolide Antibiotics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; ISBN 3-7643-6186-7. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, A.W.; Robinson, J.A. Polyethers. In Genetics and Biochemistry of Antibiotic Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 443–476. ISBN 978-0-7506-9095-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zotchev, S. Polyene Macrolide Antibiotics and Their Applications in Human Therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, F.; Albizati, K.F. Chemistry of Spiroketals. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1617–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.-N.; Hong, L.-L.; Gu, B.-B.; Sun, Y.-T.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.-T.; Lin, H.-W. Natural Products from Sponges. In Symbiotic Microbiomes of Coral Reefs Sponges and Corals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 329–463. [Google Scholar]
- Mbaoji, F.N.; Nweze, J.A.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, S.; Onwuka, A.M.; Peter, I.E.; Mbaoji, C.C.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y. Novel Marine Secondary Metabolites Worthy of Development as Anticancer Agents: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenical, W. Marine Microbial Natural Products: The Evolution of a New Field of Science. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.-L.; Ding, Y.-F.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.-W. Chemical and Biological Diversity of New Natural Products from Marine Sponges: A Review (2009–2018). Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintz, S.W. The Caribbean Region. Daedalus 1974, 103, 45–71. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20024204 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Demeritte, A.; Wuest, W.M. A Look around the West Indies: The Spices of Life Are Secondary Metabolites. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toopaang, W.; Bunnak, W.; Srisuksam, C.; Wattananukit, W.; Tanticharoen, M.; Yang, Y.-L.; Amnuaykanjanasin, A. Microbial Polyketides and Their Roles in Insect Virulence: From Genomics to Biological Functions. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 2008–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. Structural and Biological Insights into the Hot-Spot Marine Natural Products Reported from 2012 to 2021. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1867–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.D.; Perkins, M.V. Structural Diversity and Chemical Synthesis of Peroxide and Peroxide-Derived Polyketide Metabolites from Marine Sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, K.C. The Bahamas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Ianaro, A. Metabolites from the Sponge Plakortis Simplex. Determination of Absolute Stereochemistry of Plakortin. Isolation and Stereostructure of Three Plakortin Related Compounds. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 7045–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, M.D.; Faulkner, D.J. Plakortin, an Antibiotic from Plakortis Halichondrioides. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 3454–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Parapini, S.; Campagnuolo, C.; Basilico, N.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Taramelli, D. Activity against Plasmodium Falciparum of Cycloperoxide Compounds Obtained from the Sponge Plakortis Simplex. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.D.; Freyer, A.J.; Bean, M.F.; Carte, B.K.; Westley, J.W.; Johnson, R.K.; Lahouratate, P. The Plakortones, Novel Bicyclic Lactones from the Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides: Activators of Cardiac SR-Ca2+-Pumping ATPase. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Di Rosa, M.; Ianaro, A. Metabolites from the Sponge Plakortis Simplex. Part 3: Isolation and Stereostructure of Novel Bioactive Cycloperoxides and Diol Analogues. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 7959–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.D.; Freyer, A.J.; Carte, B.; Johnson, R.K.; Lahouratate, P. Plakortides, Novel Cyclic Peroxides from the Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides: Activators of Cardiac SR-Ca2+-Pumping ATPase. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnuolo, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D. Antimalarial Polyketide Cycloperoxides from the Marine SpongePlakortis Simplex. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, D.B.; Faulkner, D.J. Metabolites of Three Marine Sponges of the Genus Plakortis. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 3396–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kashman, Y.; Kakisawa, H. High-Field FT NMR Application of Mosher’s Method. The Absolute Configurations of Marine Terpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 4092–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oli, S.; Abdelmohsen, U.; Hentschel, U.; Schirmeister, T. Identification of Plakortide E from the Caribbean Sponge Plakortis Halichondroides as a Trypanocidal Protease Inhibitor Using Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmeister, T.; Oli, S.; Wu, H.; Della Sala, G.; Costantino, V.; Seo, E.-J.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of Endoperoxides from the Caribbean Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides towards Sensitive and Multidrug-Resistant Leukemia Cells: Acids vs. Esters Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, S.; Zahoor, A.F.; Hussain, S.M.; Ahmad, S.; Mansha, A.; Parveen, B.; Ali, K.G.; Irfan, A. Steglich Esterification: A Versatile Synthetic Approach toward the Synthesis of Natural Products, Their Analogues/Derivatives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Sol Jiménez, M.; Garzón, S.P.; Rodríguez, A.D. Plakortides M and N, Bioactive Polyketide Endoperoxides from the Caribbean Marine Sponge Plakortis h Alichondrioides. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, E.A.; Quintela, A.L.; Ferreira, E.G.; Sousa, T.S.; Pinto, F.d.C.L.; Hajdu, E.; Carvalho, M.S.; Salani, S.; Rocha, D.D.; Wilke, D.V.; et al. Cytotoxic Plakortides from the Brazilian Marine Sponge Plakortis Angulospiculatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoye, T.R.; Alarif, W.M.; Basaif, S.S.; Abo-Elkarm, M.; Hamann, M.T.; Wahba, A.E.; Ayyad, S.-E.N. New Cytotoxic Cyclic Peroxide Acids from Plakortis Sp. Marine Sponge. ARKIVOC Free. Online J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Persico, M.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W.; Guo, Y.-W.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fattorusso, C. Endoperoxide Polyketides from a Chinese Plakortis Simplex: Further Evidence of the Impact of Stereochemistry on Antimalarial Activity of Simple 1, 2-Dioxanes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4572–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, D.W.; Rinehart, K.L., Jr. Antifungal Peroxide-Containing Acids from Two Caribbean Sponges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 7735–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Quach, T.; Nicholas, G.N.; Molinski, T.F. Amplification of the Cotton Effect of a Single Chromophore through Liposomal Ordering—Stereochemical Assignment of Plakinic Acids I and J. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4431–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Quach, T.; Molinski, T.F. Liposomal Circular Dichroism. Assignment of Remote Stereocenters in Plakinic Acids K and L from a Plakortis− Xestospongia Sponge Association. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Quach, T.; Molinski, T.F. Liposomal Circular Dichroism. Assignment of Remote Stereocenters in Plakinic Acids K and L from a Plakortis-Xestospongia Sponge Association. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jamison, M.T.; Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Peroxide Natural Products from Plakortis Zyggompha and the Sponge Association Plakortis Halichondrioides–Xestospongia Deweerdtae: Antifungal Activity against Cryptococcus Gattii. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, J.A.; Mosher, H.S. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Enantiomer Regents. Configurational Correlations via Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Chemical Shifts of Diastereomeric Mandelate, O-Methylmandelate, and. Alpha.-Methoxy-. Alpha.-Trifluoromethylphenylacetate (MTPA) Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankisetty, S.; Gochfeld, D.J.; Diaz, M.C.; Khan, S.I.; Slattery, M. Chemical Constituents of the Deep Reef Caribbean Sponges Plakortis Angulospiculatus and Plakortis Halichondrioides and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-H.; van Soest, R.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R.J. Spiculoic Acids A and B, New Polyketides Isolated from the Caribbean Marine Sponge Plakortis Angulospiculatus. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, M.A.; Davies, J.E. The Cayman Islands: Natural History and Biogeography; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 978-94-011-0904-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bolland, O.N. Belize: A New Nation in Central America, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-429-03508-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, B.N.; Armstrong, R.W.; Faulkner, D.J. Some Aromatic Compounds from the Marine Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 3109–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Faulkner, D.J. Absolute Configuration of Methyl (2Z, 6R, 8R, 9E)-3, 6-Epoxy-4, 6, 8-Triethyl-2, 4, 9-Dodecatrienoate from the Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 6681–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slinger-Friedman, V. Dominica. In Landscapes and Landforms of the Lesser Antilles; Allen, C.D., Ed.; World Geomorphological Landscapes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 153–171. ISBN 978-3-319-55785-4. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.E.; Allen, T.M.; Van Soest, R.; Behrisch, H.W.; Andersen, R.J. Glánvillic Acids A and B and Methyl Capucinoate A, New Metabolites Isolated from the Caribbean Sponges Plakortis h Alichondrioides and Plakinastrella o Nkodes. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, G.C. Geochemical Mapping in Jamaica. Environ. Geochem. Health 1996, 18, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y. Three New Cytotoxic Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gochfeld, D.J.; Hamann, M.T. Isolation and Biological Evaluation of Filiformin, Plakortide F, and Plakortone G from the Caribbean Sponge Plakortis Sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-F.; Gao, H.-F.; Kelly, M.; Hamann, M.T. Plakortides I–L, Four New Cyclic Peroxides from an Undescribed Jamaican Sponge Plakortis Sp. (Homosclerophorida, Plakinidae). Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9379–9383, Corrigendum in Tetrahedron 2002, 6, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R.; Peng, J.; Kelly, M.; Yousaf, M.; Winn, E.; Odde, S.; Bie, Z.; Xie, A.; Doerksen, R.J.; Hamann, M.T. Polyketide-Peroxides from a Species of Jamaican Plakortis (Porifera: Demospongiae). Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, R.S.; Piña, I.C.; Rangel, H.R.; Dagger, F.; Suárez, A.I.; Reddy, M.V.R.; Faulkner, D.J. Antileishmanial cyclic peroxides from the Palauan sponge Plakortis aff. angulospiculatus. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 3057–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlin, E.A.; Allen, C.D. Martinique. In Landscapes and Landforms of the Lesser Antilles; Allen, C.D., Ed.; World Geomorphological Landscapes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 173–189. ISBN 978-3-319-55785-4. [Google Scholar]
- Berrué, F.; Thomas, O.P.; Fernández, R.; Amade, P. Iso-, nor-, and Dinor-Spiculoic Acids A, Polyketides from the Marine Sponge Plakortis Zyggompha. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrué, F.; Thomas, O.P.; Bon, C.F.-L.; Reyes, F.; Amade, P. New Bioactive Cyclic Peroxides from the Caribbean Marine Sponge Plakortis Zyggompha. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11843–11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, E.J. A Geographic Overview of Panama. In The Río Chagres, Panama; Harmon, R.S., Ed.; Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 52, pp. 3–18. ISBN 978-1-4020-3298-1. [Google Scholar]
- Appeldoorn, R.S.; Alfaro, M.; Ballantine, D.L.; Bejarano, I.; Ruíz, H.J.; Schizas, N.V.; Schmidt, W.E.; Sherman, C.E.; Weil, E. Puerto Rico. In Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems; Loya, Y., Puglise, K.A., Bridge, T.C.L., Eds.; Coral Reefs of the World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 12, pp. 111–129. ISBN 978-3-319-92734-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Romero, C.; Ortiz, I.; Vicente, J.; Vera, B.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Nam, S.; Jove, R. Bioactive Cycloperoxides Isolated from the Puerto Rican Sponge Plakortis Halichondrioides. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.L.; Dickerson, A.; Khan, A.A.; Kondru, R.K.; Beratan, D.N.; Wipf, P.; Kelly, M.; Hamann, M.T. New Peroxylactones from the Jamaican Sponge Plakinastrella Onkodes, with Inhibitory Activity against the AIDS Opportunistic Parasitic Infection Toxoplasma Gondii. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Killday, K.B.; McCarthy, P.J.; Schimoler, R.; Chilson, K.; Selitrennikoff, C.; Pomponi, S.A.; Wright, A.E. Three New Peroxides from the Sponge Plakinastrella Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Romero, C.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Nam, S. Plakortinic Acids A and B: Cytotoxic Cycloperoxides with a Bicyclo[4.2.0]Octene Unit from Sponges of the Genera Plakortis and Xestospongia. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Romero, C.; Amador, L.A.; Rodríguez, A.D. Plakortinic Acids C and D: A Pair of Peroxide-Polyketides Possessing a Rare 7,8-Dioxatricyclo[4.2.2.02,5]Dec-9-Ene Core from a Two-Sponge Association of Plakortis Symbiotica–Xestospongia Deweerdtae. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 66, 152833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, L.A.; Colón-Lorenzo, E.E.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Serrano, A.E. Probing the Antiplasmodial Properties of Plakortinic Acids C and D: An Uncommon Pair of Marine Peroxide-Polyketides Isolated from a Two-Sponge Association of Plakortis Symbiotica and Xetospongia Deweerdtae Collected near Puerto Rico. Life 2024, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, J.C. Geology of Tobago, British West Indies. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1948, 59, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushlan, D.M.; Faulkner, D.J. A Novel Perlactone from the Caribbean Sponge Plakortis Angulospiculatus. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).