Evaluation of an Ion-Associate Phase Formed In Situ from the Aqueous Phase by Adding Benzethonium Chloride and Sodium Ethylbenzenesulfonate for Microextraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
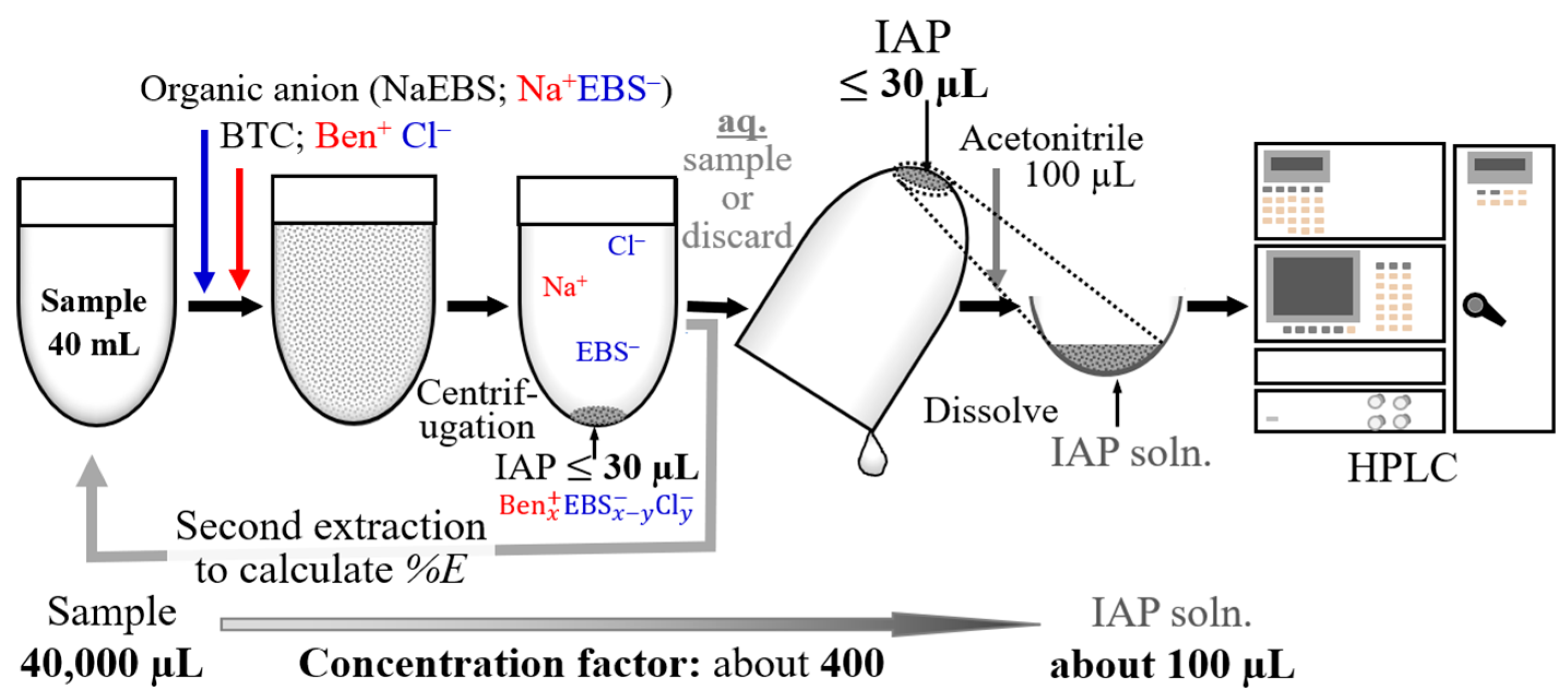
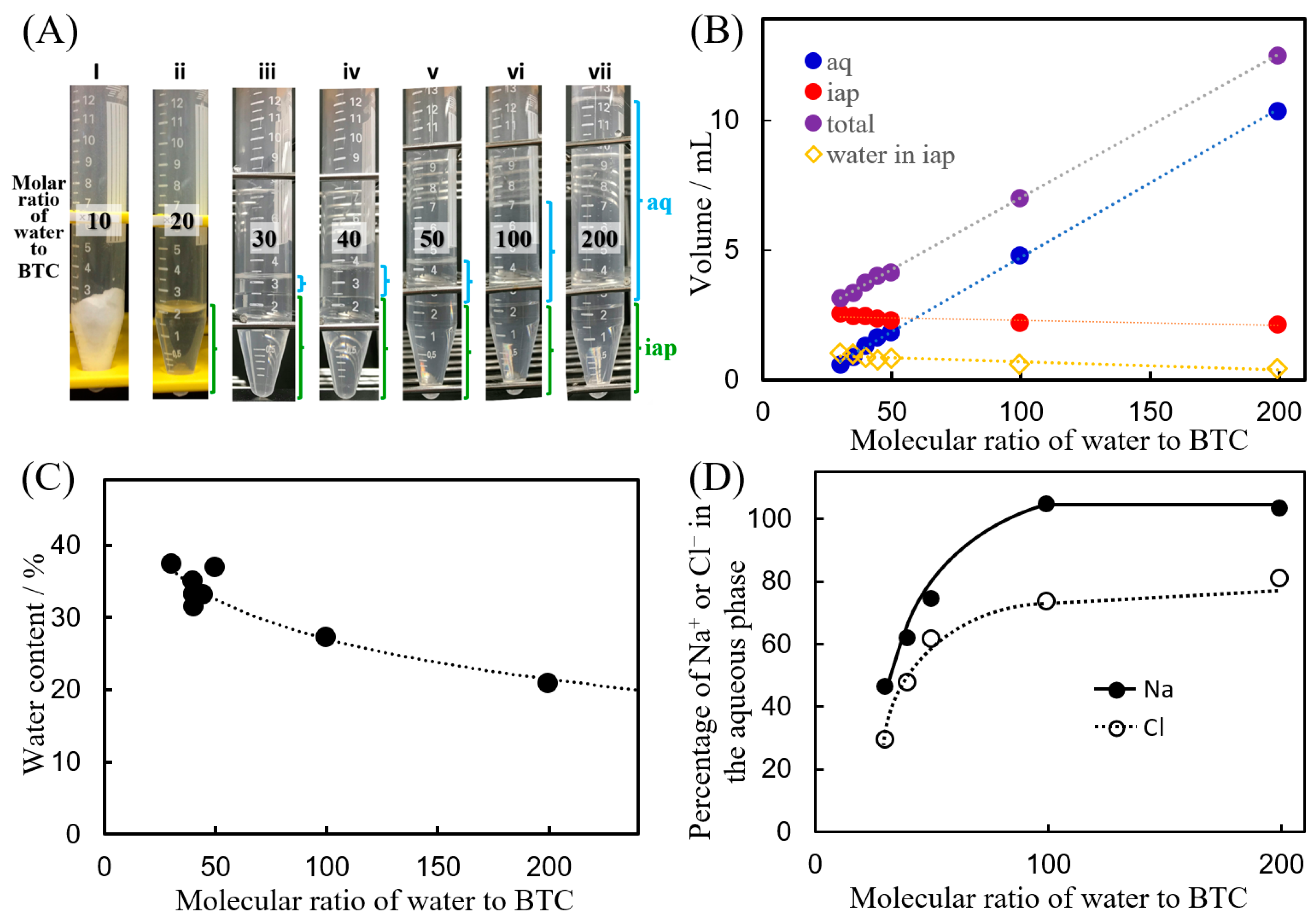
2.3. Determination of the Volume of IAP
2.4. Determination of Percent Extraction (% E) of PAHs, Estrogen, and Pesticides in an IAP Consisting of Ben and EBS
3. Results and Discussion
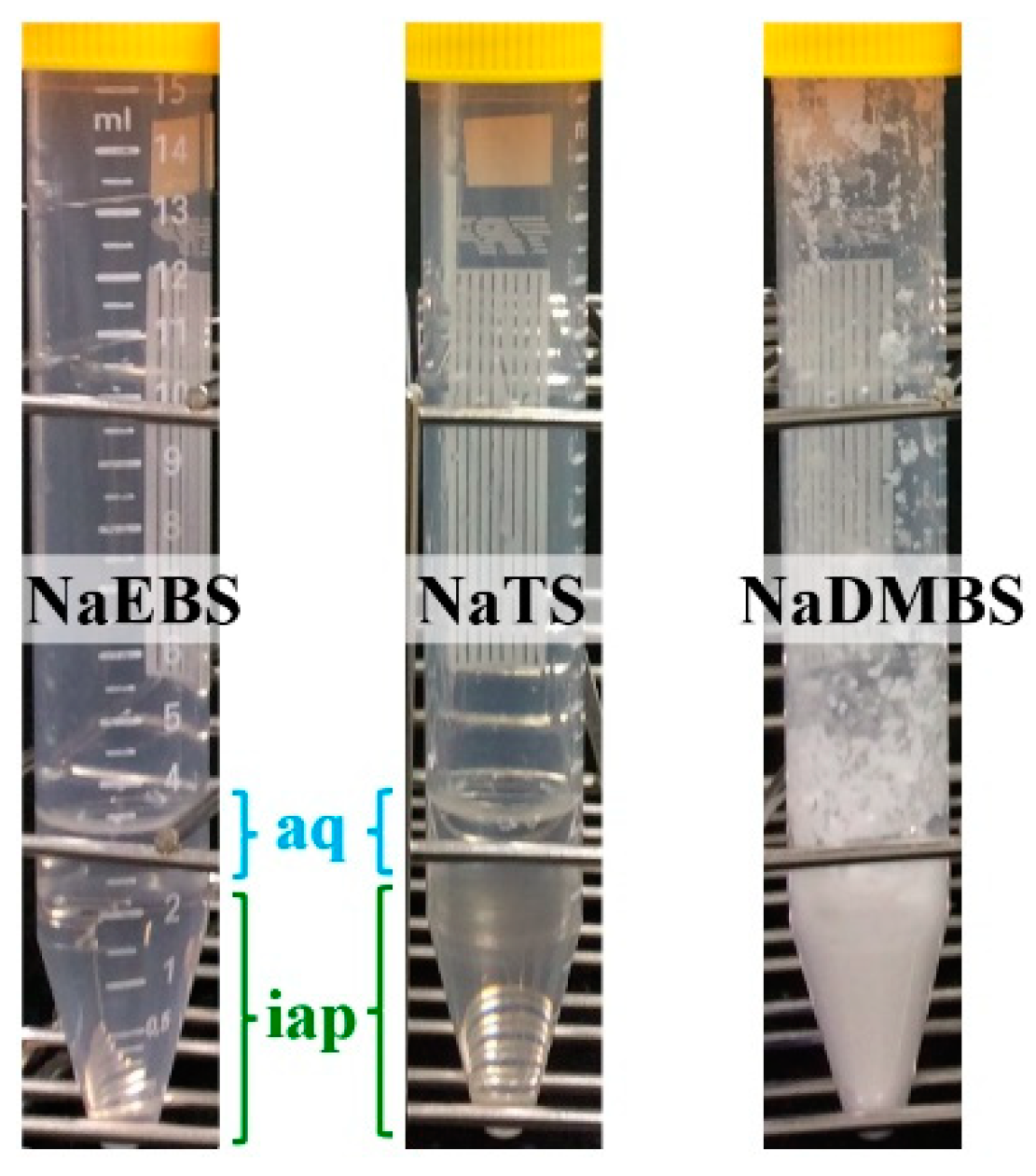
3.1. Analysis of IAP Combinations That Did Not Require pH Adjustment
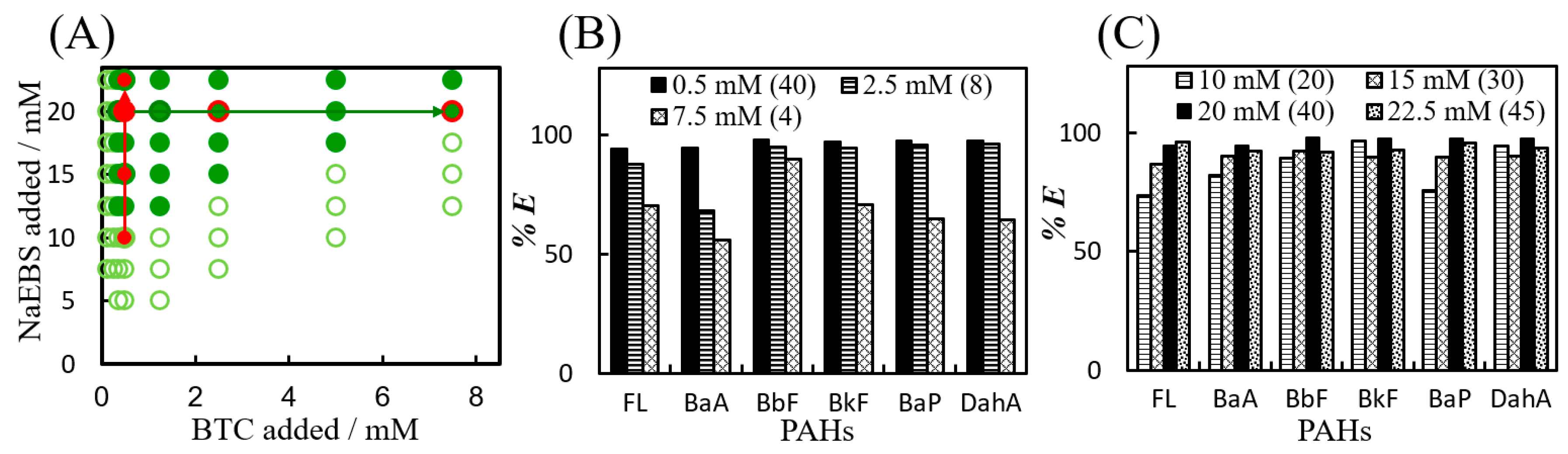
3.2. Effect of BTC and NaEBS Concentrations on PAH Extraction into IAPs
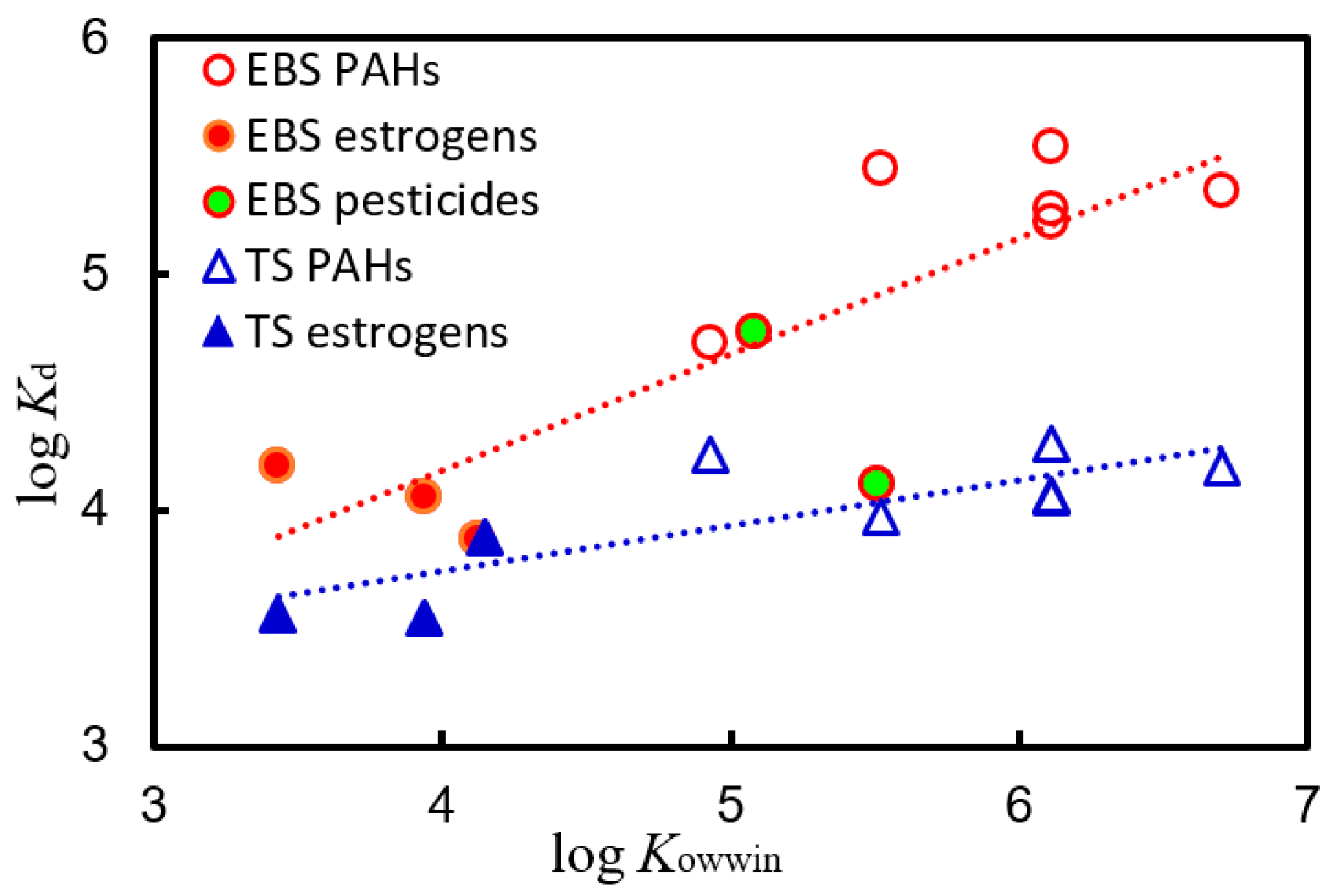
3.3. Distribution Coefficients for PAHs, Estrogens, and Pesticides
3.4. Composition of the IAP: Water Content, Chloride Ion Concentration, and Sodium Ion Concentration
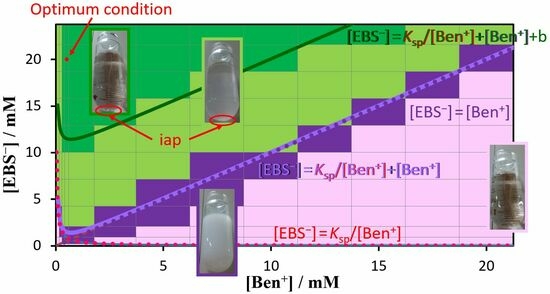
3.5. Regions of Ion Associate and Solvent Formation
0.19 0.19 0.81 0.81 mole ratio
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beshana, S.; Hussen, A.; Seyoum Leta, S.; Kaneta, T. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with microfuidic paper-based analytical device for the determination of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides in the water sample. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattahi, N.; Shamsipur, M.; Nematifar, Z.; Babajani, N.; Moradi, M.; Soltani, S.; Akbari, S. Novel deep eutectic solvent-based liquid phase microextraction for the extraction of estrogenic compounds from environmental samples. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 14467–14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohama, N.; Matsuhira, K.; Okazaki, T.; Sazawa, K.; Hata, N.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguchi, S. Colorimetric analysis based on solid-phase extraction with sedimentable dispersed particulates: Demonstration of concept and application for on-site environmental water analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 8389–8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.L.; Li, J.H.; Xu, S.F.; Ying, R.J.; Ma, J.P.; Liao, C.Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Yu, J.B.; Chen, L.X. Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seawater using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 99, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, N.; Kasahara, I.; Taguchi, S. Micro-phase sorbent extraction for trace analysis via in situ sorbent formation: Application to the preconcentration and the spectrophotometric determination of trace ammonia. Anal. Sci. 2002, 18, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, N.; Kawashima, M.; Kasahara, I.; Taguchi, S. Micro-phase sorbent extraction for trace analysis via in situ sorbent formation: Application to the spectrophotometric determination of nitrite in environmental waters. Anal. Sci. 2003, 19, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuna, K.; Murashima, R.; Okazaki, T.; Sazawa, K.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguchi, S.; Nakayama, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Takamura, Y.; Hata, N. Organic Ion-associate Phase Extraction/Back-microextraction for the Preconcentration and Determination of Lithium Using 2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-3,5-heptanedione by Liquid Electrode Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry and GF-AAS in Environmental Water. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, M.; Mizuna, K.; Sazawa, K.; Okazaki, T.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguchi, S.; Hata, N. Organic Ion-Associate Phase Microextraction/Back-Microextraction for Preconcentration: Determination of Nickel in Environmental Water Using 2-Thenoyltrifluoroacetone via GF-AAS. Appl. Chem. 2021, 1, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, N.; Hieda, S.; Yamada, M.; Yasui, R.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguch, S. Formation of a liquid organic ion associate in aqueous solution and its application to the GF-AAS determination of trace cadmium in environmental water as a complex with 2-(5-bromo-2-pyridylazo)5-(N-propyl-N-sulfopropylamino)phenol. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, S.; Takamura, Y. Liquid Electrode Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry Combined with Multi-Element Concentration Using Liquid Organic Ion Associate Extraction for Simultaneous Determination of Trace Metals in Water. Bunseki Kagaku 2012, 60, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.M.A.; Murashima, R.; Okazaki, T.; Taguchi, S.; Kuramitz, H.; Hata, N. Micro-organic Ion-associate Phase Extraction/micro-volume Back-extraction for the Preconcentration and GF-AAS Determination of Cadmium, Nickel and Lead in Environmental Water. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, N.; Yuwatini, E.; Ando, K.; Yamada, M.; Kasahara, I.; Taguchi, S. Micro-organic ion-associate phase extraction via in situ fresh phase formation for the preconcentration and determination of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in river water by HPLC. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, S.; Kasahara, I.; Fukushima, Y.; Goto, K. An application of bis[2-(5-chloro-2-pyridylazo)-5-diethylaminophenolato]cobalt(III) chloride to the extraction and spectrophotometric determination of sulphonated and sulphated surfactants. Talanta 1981, 28, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, I.; Hashimoto, K.; Kawabe, T.; Kunita, A.; Magawa, K.; Hata, N.; Taguchi, S.; Goto, K. Spectrophotometric determination of anionic surfactants in sea-water based on ion-pair extraction with bis[2-(5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridylazo)-5-diethylaminophenolato]cobalt(III) as counter ion. Analyst 1995, 120, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, M.; Shemirani, F. In situ solvent formation microextraction based on ionic liquids: A novel sample preparation technique for determination of inorganic species in saline solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 634, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Caravaca, M.; Soto-Meca, A.; Francisco-Ortíz, Ó.D.; Fernández-López, C. In Situ Formation of Ionic Liquid by Metathesis Reaction for the Rapid Removal of Bisphenol A from Aqueous Solutions. Water 2019, 11, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M. Simultaneous Concentration and Determination of Cadmium and Lead Ions Using In Situ Solvent Formation Microextraction Method Based on Functionalized Ionic Liquid. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 76, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaver, M.; Chapana, A.L.; Wuilloud, R.G. Simultaneous and highly sensitive determination of selenium and tellurium species in environmental samples by on-line ionic liquid based in-situ solvent formation microextraction with hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry detection. Talanta 2021, 222, 121460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Caravaca, M.; Soto-Meca, A. Non-chromatographic speciation of arsenic by successive dispersive liquidliquid microextraction and in situ formation of an ionic liquid in water samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jin, Y.; Jung, D.; Park, K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. In situ formation of thymol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Application to antibiotics analysis in surface water based on liquid-liquid microextraction followed by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ma, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Fei, Q. Application of an in-situ formulated magnetic deep eutectic solvent for the determination of triazine herbicides in rice. Talanta 2021, 222, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, S.; Sellitepe, H.E. Vortex assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on in situ formation of a natural deep eutectic solvent by microwave irradiation for the determination of beta-blockers in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1642, 462007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the preconcentration and HPLC analysis of five rice paddy herbicides in water samples. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Sazawa, K.; Okazaki, T.; Islam, M.S.; Hata, N.; Sugawara, K.; Kuramitz, H. Adsorptive Voltammetry for the Determination of Ochratoxin A Using Enrichment Effect by Cationic Surfactants. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; Incorporating the 1st addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Japan. Drinking Water Quality Standards, Water Quality Control Target Setting Items. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/topics/bukyoku/kenkou/suido/kijun/kijunchi.html#01 (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA, Washington, DC, USA). KOWWIN 1.68 in “Estimation Programs Interface Suite™ for Microsoft® Windows, v 4.11]”. 2012. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/oppt/exposure/pubs/episuite.htm (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Bakanov, N.; Wieczorek, M.V.; Schulz, R. Retention of plant protection products (PPPs) by aquatic plants in flow-through systems. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikushi, H.; Hirota, K.; Yoshida, N.; Edamura, T.; Toda, K. Simple water analysis of golf link pesticides by means of batch-wise adsorption and supercritical fluid extraction. Talanta 2009, 80, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hata, N.; Igarashi, A.; Yasui, R.; Matsushita, M.; Kohama, N.; Komiyama, T.; Sazawa, K.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguchi, S. Evaluation of an Ion-Associate Phase Formed In Situ from the Aqueous Phase by Adding Benzethonium Chloride and Sodium Ethylbenzenesulfonate for Microextraction. AppliedChem 2023, 3, 32-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010003
Hata N, Igarashi A, Yasui R, Matsushita M, Kohama N, Komiyama T, Sazawa K, Kuramitz H, Taguchi S. Evaluation of an Ion-Associate Phase Formed In Situ from the Aqueous Phase by Adding Benzethonium Chloride and Sodium Ethylbenzenesulfonate for Microextraction. AppliedChem. 2023; 3(1):32-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHata, Noriko, Akane Igarashi, Rie Yasui, Maho Matsushita, Nozomi Kohama, Tomoka Komiyama, Kazuto Sazawa, Hideki Kuramitz, and Shigeru Taguchi. 2023. "Evaluation of an Ion-Associate Phase Formed In Situ from the Aqueous Phase by Adding Benzethonium Chloride and Sodium Ethylbenzenesulfonate for Microextraction" AppliedChem 3, no. 1: 32-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010003
APA StyleHata, N., Igarashi, A., Yasui, R., Matsushita, M., Kohama, N., Komiyama, T., Sazawa, K., Kuramitz, H., & Taguchi, S. (2023). Evaluation of an Ion-Associate Phase Formed In Situ from the Aqueous Phase by Adding Benzethonium Chloride and Sodium Ethylbenzenesulfonate for Microextraction. AppliedChem, 3(1), 32-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3010003