An NLP Approach for Extracting Practical Knowledge from a CMS-Based Community of Practice in E-Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ 1: What are the text characteristics, most frequent words, and word sequences used in the online community?
- RQ 2: What are the characteristics of sentiment, named entities, and relationships among entities in the online community?
- RQ 3: What are the latent topic structures in the online community?
2. Background
2.1. Communities of Practice in Instructional Design
2.2. Instructional Design Competencies
2.3. Tacit Knowledge Characteristics and Extraction
- Tacit knowledge as a competence refers to the skills and abilities acquired through apprenticeships and face-to-face interactions.
- Tacit background knowledge is the regulations, codes of conduct, and processes of acculturation to which individuals adhere, based on their context.
- Tacit knowledge acts as a mechanism for creating new knowledge and assessing the accuracy of information itself.
2.4. NLP Studies on Online News Sources
3. Materials and Methods
Ethical Considerations
4. Results
4.1. RQ1: What Are the Text Characteristics, Most Frequent Words, and Word Sequences Used in the Online Community?
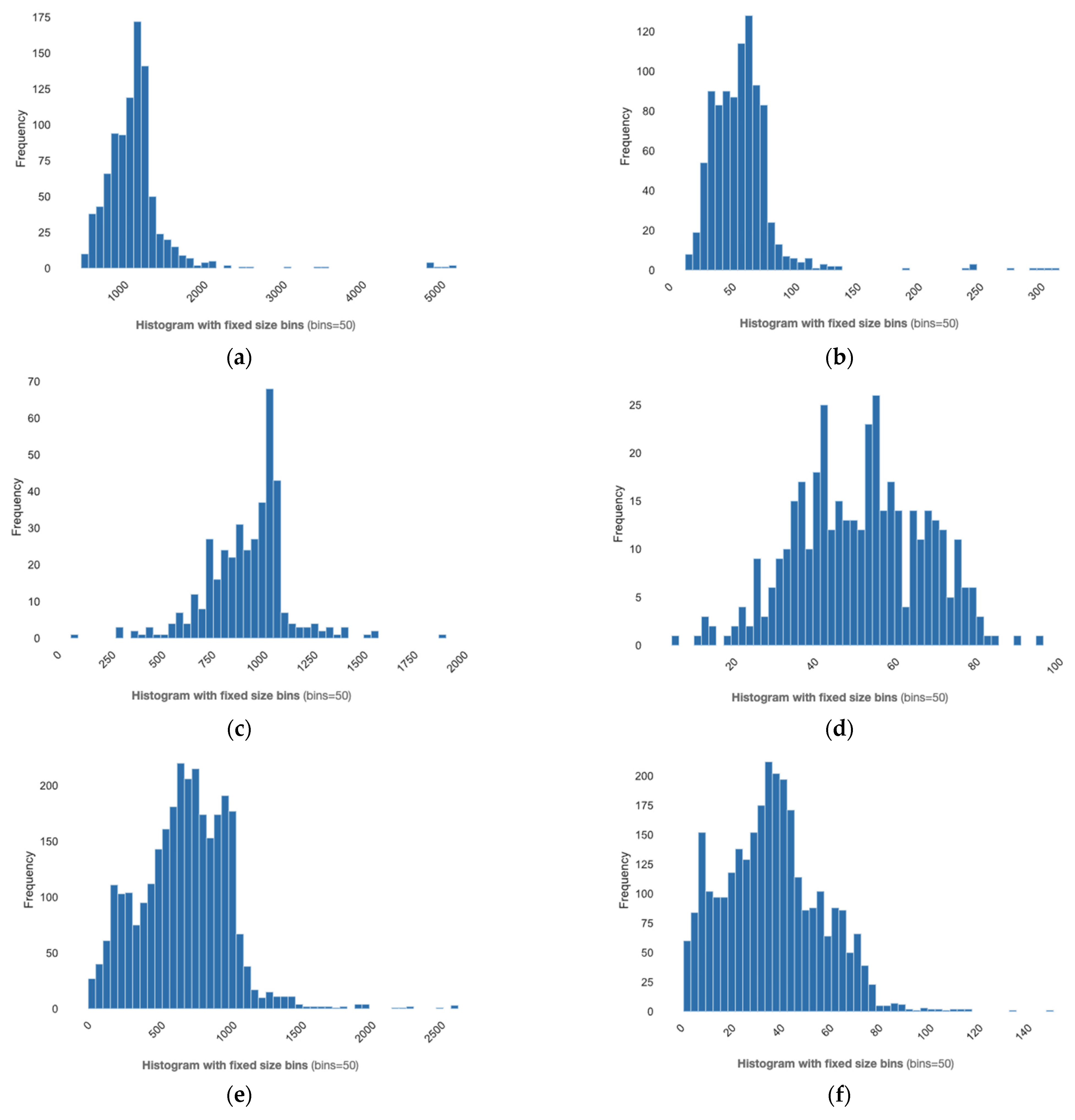
4.1.1. Text Characteristics
4.1.2. Word Frequencies
- Category 3: E-Learning Trends (36,321 words);
- Category 4: Design and Development (30,808 words);
- Category 5: Instructional Design (19,615 words);
- Category 6: Best Practices (19,102 words);
- Category 1: Learning Management System (17,580 words);
- Category 2: E-Learning Software (11,325 words);
- Category 7: Free Resources (9481 words).
4.1.3. N-Grams
4.2. RQ2: What Are the Characteristics of Sentiment, Named Entities, and Relationships among Entities in the Online Community?
4.2.1. Sentiment
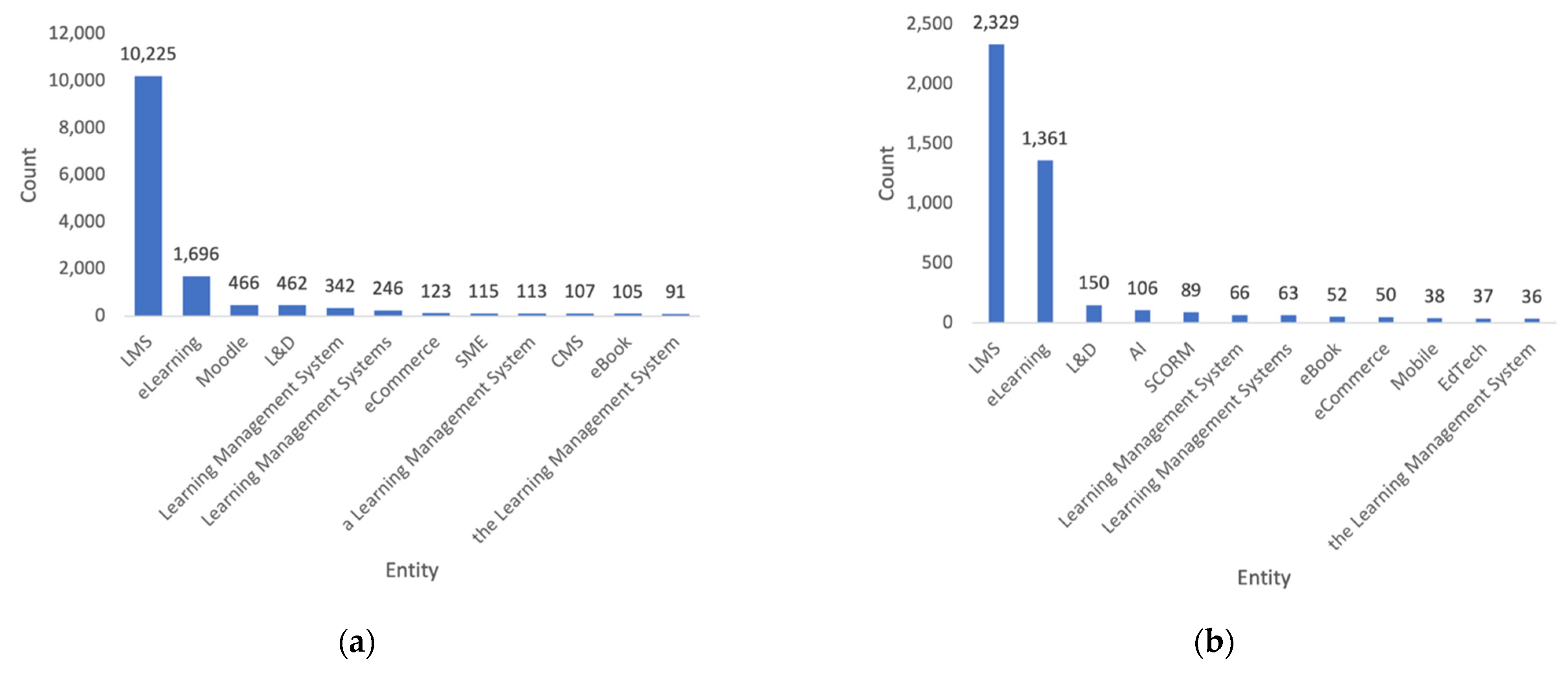
4.2.2. Recognized Entities
- Category 3: E-Learning Trends (58,606 entities);
- Category 4: Design and Development (50,326 entities);
- Category 1: Learning Management System (35,747 entities);
- Category 5: Instructional Design (24,097 entities);
- Category 6: Best Practices (18,944 entities);
- Category 2: E-Learning Software (12,562 entities);
- Category 7: Free Resources (6939 entities).
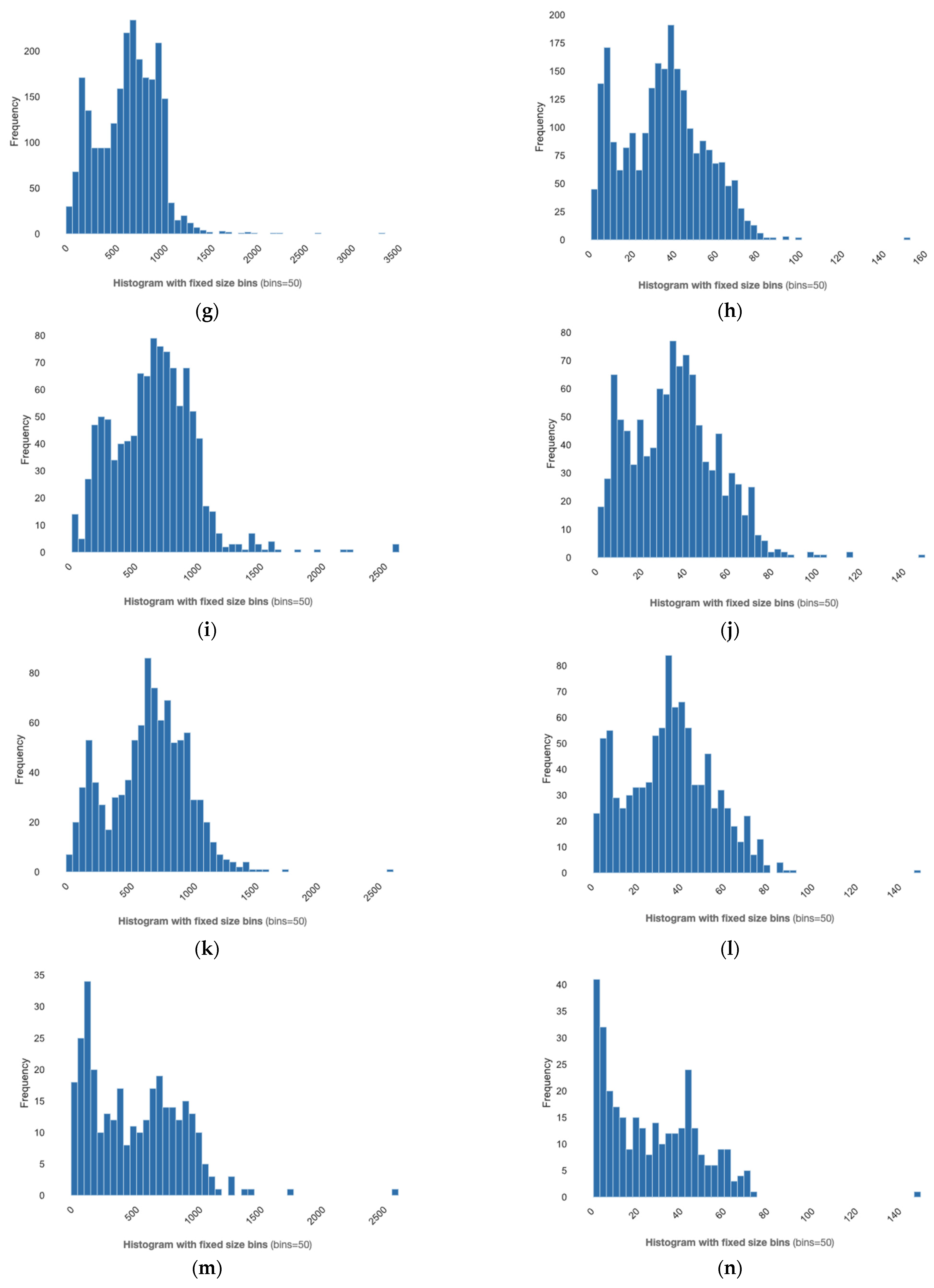
4.2.3. Entity Relationships
- Category 3: E-Learning Trends (1326 entity relationships);
- Category 4: Design and Development (1174 entity relationships);
- Category 6: Best Practices (626 entity relationships);
- Category 5: Instructional Design (611 entity relationships);
- Category 2: E-Learning Software (300 entity relationships);
- Category 7: Free Resources (236 entity relationships);
- Category 1: Learning Management System (213 entity relationships).
4.3. RQ3: What Are the Latent Topic Structures in the Online Community?
4.3.1. Category 1: Learning Management System
4.3.2. Category 2: E-Learning Software
4.3.3. Category 3: E-Learning Trends
4.3.4. Category 4: Design and Development
4.3.5. Category 5: Instructional Design
4.3.6. Category 6: Best Practices
4.3.7. Category 7: Free Resources
5. Discussion
5.1. Priorities of the Online CoP
5.2. E-Learning Materials Production as the Purpose of the Community
5.3. Implications for Research and Practice
5.4. Recommendations
5.5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanchar, S.C.; Hawkley, M.N. Instructional design and professional informal learning: Practices, tensions, and ironies. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 424–434. [Google Scholar]
- Clinton, G.; Rieber, L.P. The Studio experience at the University of Georgia: An example of constructionist learning for adults. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2010, 58, 755–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Stepich, D.A.; York, C.S.; Stickman, A.; Wu, X.; Zurek, S.; Goktas, Y. How instructional design experts use knowledge and experience to solve ill-structured problems. Perform. Improv. Q. 2008, 21, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardré, P.L.; Ge, X.; Thomas, M.K. An Investigation of Development Toward Instructional Design Expertise. Perform. Improv. Q. 2008, 19, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.H.; You, J.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J. Instructional design for adult and continuing higher education: Theoretical and practical considerations. Res. Anthol. Adult Educ. Dev. Lifelong Learn. 2021, 1018–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peñalvo, F.J. Informal Learning Management Experiences. Int. J. Hum. Cap. Inf. Technol. Prof. 2014, 5, iv–ix. [Google Scholar]
- Önday, Ö. Web 6.0: Journey from Web 1.0 to Web 6.0. J. Media Manag. 2019, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.; Whiting, J. Designing Informal Learning Environments. In Design for Learning: Principles, Processes, and Praxis; McDonald, J.K., West, R.E., Eds.; EdTech Books: Online, 2021; Available online: https://edtechbooks.org/id/designing_informal (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Abramenka-Lachheb, V.; Lachheb, A.; Leung, J.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Seo, G.Z. Instructional Designers’ Use of Informal Learning: How Can We All Support Each Other in Times of Crisis? J. Appl. Instr. Des. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, T.J. A review of informal learning literature, theory and implications for practice in developing global professional competence. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2004, 28, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Karlsven, M.; Perry, S.B. Informal Learning. In The Students’ Guide to Learning Design and Research; Kimmons, R., Ed.; EdTech Books: Online, 2018; Available online: https://edtechbooks.org/studentguide/informal_learning (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Detect which CMS a Site is Using-What CMS? What CMS Is This Site Using? Available online: https://whatcms.org/?s=elearningindustry.com (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- elearning Industry Inc. About. Elearning Industry. Available online: https://elearningindustry.com/about-us (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- ICANN. Registration Data Lookup Tool. Available online: http://maintenance.icann.org/lookup (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Similarweb. Available online: https://www.similarweb.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wenger, E. Communities of practice: Learning as a social system. Syst. Think. 1998, 9, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, E.C.; Snyder, W.M. Communities of practice: The organizational frontier. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2000, 78, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, B. Informal learning in an online community of practice. Int. J. E-Learn. Distance Educ./La Revue Internationale de l’Apprentissage en Ligne et de l’Enseignment À Distance 2004, 19, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Schwier, R.A.; Campbell, K.; Kenny, R. Instructional designers’ observations about identity, communities of practice and change agency. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2004, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwier, R.A.; Campbell, K.; Kenny, R.F. Instructional designers’ perceptions of their agency: Tales of change and community. In Instructional Design: Case Studies in Communities of Practice; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Access the Capability Model. American Talent Development. Available online: https://www.td.org/capability-model/access (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Instructional Designer Competencies. Welcome to Ibstpi. 21 April 2016. Available online: https://ibstpi.org/instructional-design-competencies/ (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Martin, F.; Ritzhaupt, A.D. Standards and Competencies for Instructional Design and Technology Professionals [E-book]. In Design for Learning; 2020; p. 20. Available online: https://edtechbooks.org/id/standards_and_competencies (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- ISTE Standards: Educators|ISTE. ISTE Standards: Educators. Available online: https://www.iste.org/standards/iste-standards-for-teachers (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Polanyi, M. The Tacit Dimension, 2009th ed.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, R.K.; Sternberg, R.J. Practical intelligence in real-world pursuits: The role of tacit knowledge. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1985, 49, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, R.; Mason, B.; McCrory, J. Exploring the dichotomies within the tacit knowledge literature: Towards a process of tacit knowing in organizations. J. Knowl. Manag. 2007, 11, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, R.; Pozzali, A. Cognitive Aspects of Tacit Knowledge and Cultural Diversity. Model-Based Reason. Sci. Technol. Med. 2007, 64, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, D.M.; Steiger, N.M. Instance-based cognitive mapping: A process for discovering a knowledge worker’s tacit mental model. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2008, 6, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Laird, P.; Byrne, R. Mental models website: A gentle introduction. Recuper. El 2000, 22. Available online: http://www.tcd.ie/Psychology/Ruth_Byrne/mental_models/index.html (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Bolade, S.; Sindakis, S. Micro-Foundation of Knowledge Creation Theory: Development of a Conceptual Framework Theory. J. Knowl. Econ. 2019, 11, 1556–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Saeedi, M. Building a Trust Model in the Online Market Place. J. Internet Commer. 2006, 5, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, A.; Patalas-Maliszewska, J. A Model of a Tacit Knowledge Transformation for the Service Department in a Manufacturing Company: A Case Study. Found. Manag. 2016, 8, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.W.; Tedmori, S.; Hinde, C.J.; Bani-Hani, A. The Boundaries of Natural Language Processing Techniques in Extracting Knowledge from Emails. J. Emerg. Technol. Web Intell. 2012, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohanan, M.; Samuel, P. Software Requirement Elicitation Using Natural Language Processing. In Innovations in Bio-Inspired Computing and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsangi, P. Automation of Tacit Knowledge Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Soft Computing & Machine Intelligence (ISCMI), Johannesburg, South Africa, 19–20 November 2019; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, A.; Sawyer, P. Identifying tacit knowledge-based requirements. IEE Proc. Softw. 2006, 153, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambliss, M.J.; Garner, R. Do Adults Change their Minds after Reading Persuasive Text? Writ. Commun. 1996, 13, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.; Singh, S. Proposed Model for Context Topic Identification of English and Hindi News Article Through LDA Approach with NLP Technique. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. B 2021, 103, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Peng, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Khan, S.; Xie, L.; Fang, Y.; Vincent, S. DIANES: A DEI Audit Toolkit for News Sources. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11383. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, Y.C.; Lee, L.K.; Chui, K.T.; Cheung, G.H.K.; Tang, C.H.; Wong, S.M. Sentiment Analysis and Summarization of Facebook Posts on News Media. In Data Mining Approaches for Big Data and Sentiment Analysis in Social Media; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S. Text Similarity Measures in News Articles by Vector Space Model Using NLP. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. B 2020, 102, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Martino, G.D.S.; Nakov, P. Experiments in detecting persuasion techniques in the news. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.06815. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Touran, A.; Wang, Q. Mining and Visualizing Cost and Schedule Risks from News Articles with NLP and Network Analysis. Constr. Res. Congr. 2022, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaidka, K.; Ceolin, A.; Singh, I.; Chhaya, N.; Ungar, L. WikiTalkEdit: A Dataset for modeling Editors’ behaviors on Wikipedia. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2191–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Brugman, S. Introduction—Pandas-Profiling 3.0.0 Documentation. Pandas Profiling. 2021. Available online: https://pandas-profiling.github.io/pandas-profiling/docs/master/rtd/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Mueller, A. WordCloud for Python Documentation—Wordcloud 1.8.1 Documentation. WordCloud for Python. 2020. Available online: http://amueller.github.io/word_cloud/ (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Kaur, J.; Buttar, P.K. A systematic review on stopword removal algorithms. Int. J. Future Revolut. Comput. Sci. Commun. Eng. 2018, 4, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, M.; Shi, H.; Amaral, L.A.N. A universal information theoretic approach to the identification of stopwords. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Language Toolkit—NLTK 3.6.2 Documentation. Natural Language Processing Toolkit-NLTK. Available online: https://www.nltk.org/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Lorian, S. TextBlob: Simplified Text Processing—TextBlob 0.16.0 documentation. TextBlob: Simplified Text Processing. Available online: https://textblob.readthedocs.io/en/dev/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- spaCy. Industrial-strength Natural Language Processing in Python. spaCy-Industrial-Strength Natural Language Processing. Available online: https://spacy.io/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Řehůřek, R. Gensim: Topic Modelling for Humans. 2009. Available online: https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/ (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Grootendorst, M. GitHub-MaartenGr/BERTopic: Leveraging BERT and c-TF-IDF to Create Easily Interpretable Topics. BERTopic. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/MaartenGr/BERTopic (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Reimers, N. Pretrained Models—Sentence-Transformers Documentation. Pre-Trained Models. 2021. Available online: https://www.sbert.net/docs/pretrained_models.html (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Chang, J.; Gerrish, S.; Wang, C.; Boyd-Graber, J.; Blei, D. Reading tea leaves: How humans interpret topic models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–10 December 2009; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Rosner, F.; Hinneburg, A.; Röder, M.; Nettling, M.; Both, A. Evaluating topic coherence measures. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.6397. [Google Scholar]
- Krotov, V.; Murray State University; Johnson, L.; Silva, L. University of Houston Legality and Ethics of Web Scraping. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2020, 47, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancosu, M.; Vegetti, F. What You Can Scrape and What Is Right to Scrape: A Proposal for a Tool to Collect Public Facebook Data. Soc. Media Soc. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, S.A.; De Meo, P.; Ferrara, E.; Fiumara, G.; Provetti, A. Crawling facebook for social network analysis purposes. In Proceedings of the international conference on web intelligence, mining and semantics, Sogndal, Norway, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Washburn, A.N.; Hanson, B.E.; Motyl, M.; Skitka, L.J.; Yantis, C.; Wong, K.M.; Sun, J.; Prims, J.P.; Mueller, A.B.; Melton, Z.J.; et al. Why Do Some Psychology Researchers Resist Adopting Proposed Reforms to Research Practices? A Description of Researchers’ Rationales. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 1, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.M.; Roque, G. Resisting the Deprofessionalization of Instructional Design. In Optimizing Instructional Design Methods in Higher Education; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, C. The Accidental Instructional Designer: Learning Design for the Digital Age; American Society for Training and Development: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- North, C.; Shortt, M.; Bowman, M.A.; Akinkuolie, B. How Instructional Design Is Operationalized in Various Industries for job-Seeking Learning Designers: Engaging the Talent Development Capability Model. TechTrends 2021, 65, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| News Category | Number of Articles |
|---|---|
| Learning Management System | 927 |
| E-Learning Software | 400 |
| E-Learning Trends | 2934 |
| Design and Development | 2415 |
| Instructional Design | 1065 |
| Best Practices | 972 |
| Free Resources | 320 |
| Total | 9033 |
| NLP Task | Python Package |
|---|---|
| Text characteristics | Lambda functions to calculate average word and sentence lengths |
| Visualization | Profile Report to visualize text characteristics |
| Sentiment analysis | TextBlob |
| Trigrams | NLTK |
| NER | spaCy |
| Topic modeling | Gensim for Latent Dirichlet Allocation and BERTopic (stsb-bert-large pre-trained model) |
| News Category | C_v | N_Topics Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Learning Management System | 0.488 | 7 |
| 2. E-Learning Software | 0.437 | 4 |
| 3. E-Learning Trends | 0.465 | 3 |
| 4. Design and Development | 0.377 | 9 |
| 5. Instructional Design | 0.438 | 5 |
| 6. Best Practices | 0.422 | 3 |
| 7. Free Resources | 0.356 | 10 |
| News Category | Trigram | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Management System | [learning management system] | 1511 |
| [online training course] | 407 | |
| [extended enterprise lms] | 313 | |
| [running a small business] | 293 | |
| [help free tool] | 291 | |
| [homebase help free] | 291 | |
| [manage team visit] | 291 | |
| [business never harder] | 291 | |
| [time manage team] | 291 | |
| [make work easier] | 291 | |
| E-Learning Software | [elearning authoring tool] | 406 |
| [learning management system] | 319 | |
| [online training course] | 283 | |
| [online training content] | 169 | |
| [online training software] | 163 | |
| [employee training software] | 163 | |
| [online training resource] | 104 | |
| [lms training company] | 94 | |
| [employee training participant] | 87 | |
| [value money lms] | 82 | |
| E-Learning Trends | [learning management system] | 609 |
| [online training course] | 319 | |
| [subject matter expert] | 255 | |
| [instructional design model] | 252 | |
| [mobile learning strategy] | 209 | |
| [online training resource] | 207 | |
| [mobile learning solution] | 192 | |
| [elearning authoring tool] | 189 | |
| [elearning course design] | 169 | |
| [online training program] | 147 | |
| Design and Development | [learning management system] | 409 |
| [online training course] | 381 | |
| [elearning authoring tool] | 336 | |
| [elearning course design] | 321 | |
| [subject matter expert] | 275 | |
| [online training resource] | 192 | |
| [elearning content development] | 181 | |
| [elearning content provider] | 169 | |
| [online training content] | 156 | |
| [online training program] | 119 | |
| Instructional Design | [instructional design model] | 252 |
| [subject matter expert] | 180 | |
| [online training course] | 132 | |
| [elearning course design] | 119 | |
| [design model theory] | 114 | |
| [learning management system] | 107 | |
| [learning battle card] | 85 | |
| [online learner able] | 71 | |
| [give online learner] | 69 | |
| [elearning authoring tool] | 61 | |
| Best Practices | [learning management system] | 143 |
| [online training resource] | 92 | |
| [elearning course design] | 90 | |
| [online training course] | 90 | |
| [elearning authoring tool] | 90 | |
| [subject matter expert] | 65 | |
| [online training content] | 55 | |
| [curated elearning content] | 50 | |
| [online training program] | 49 | |
| [elearning content curation] | 47 | |
| Free Resources | [learning management system] | 49 |
| [free video tutorial] | 36 | |
| [elearning course design] | 33 | |
| [elearning infographic template] | 29 | |
| [camstasia studio 8] | 28 | |
| [top elearning blog] | 27 | |
| [adobe captivate 7] | 22 | |
| [elearning authoring tool] | 21 | |
| [free moodle video] | 20 | |
| [mobile apps learning] | 18 |
| News Category | Positive | Neutral | Negative | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Management System | 927 | 0 | 0 | 927 |
| E-Learning Software | 399 | 0 | 1 | 400 |
| E-Learning Trends | 2908 | 10 | 16 | 2934 |
| Design and Development | 2404 | 5 | 6 | 2415 |
| Instructional Design | 1061 | 0 | 4 | 1065 |
| Best Practices | 964 | 3 | 5 | 972 |
| Free Resources | 318 | 1 | 1 | 320 |
| Total | 8981 | 19 | 33 | 9033 |
| News Category | Entity | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Management System | website | 509 |
| read | 67 | |
| published | 35 | |
| want | 14 | |
| captivate prime | 12 | |
| means | 8 | |
| features | 6 | |
| allow | 5 | |
| help | 5 | |
| take free | 5 | |
| E-Learning Software | studio | 8 |
| references | 6 | |
| costs | 5 | |
| use | 4 | |
| features | 4 | |
| take | 4 | |
| conclusion | 4 | |
| need | 3 | |
| help | 3 | |
| halfpoint | 2 | |
| E-Learning Trends | read | 77 |
| need | 25 | |
| used | 24 | |
| want | 22 | |
| check | 21 | |
| use | 21 | |
| help | 21 | |
| leave | 20 | |
| studio | 20 | |
| find | 18 | |
| Design and Development | read | 107 |
| use | 33 | |
| help | 27 | |
| find | 23 | |
| take | 20 | |
| make | 19 | |
| create | 18 | |
| need | 15 | |
| professional | 15 | |
| keep | 15 | |
| Instructional Design | read | 41 |
| leave | 12 | |
| used | 11 | |
| think | 9 | |
| check | 9 | |
| find | 9 | |
| images | 8 | |
| offer instructional | 8 | |
| know | 7 | |
| learning | 7 | |
| Best Practices | read | 35 |
| use | 13 | |
| images | 12 | |
| help | 11 | |
| make | 10 | |
| want | 8 | |
| studio | 8 | |
| learn | 7 | |
| let | 7 | |
| find | 7 | |
| Free Resources | join free | 6 |
| use | 5 | |
| visit | 5 | |
| find | 4 | |
| help | 4 | |
| read | 4 | |
| missed free | 4 | |
| captivate | 4 | |
| see | 4 | |
| want | 3 |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Employee Onboarding | Employee Training |
| Topic 2 | Custom Online Training | Online Compliance Training |
| Topic 3 | LMS Requirements | LMS User and Content Management |
| Topic 4 | Online Compliance Training | LMS Implementation |
| Topic 5 | LMS Implementation | Employee Training |
| Topic 6 | Employee Training | LMS Implementation |
| Topic 7 | LMS User and Content Management | Online Employee Training Costs |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Language Courses | LMS Requirements |
| Topic 2 | Employee Onboarding | Employee Onboarding |
| Topic 3 | Online Compliance Training | Technology in Educational Settings |
| Topic 4 | E-Learning Authoring Tools | LMS in Corporate Settings |
| Topic 5 | Technology in Educational Settings | |
| Topic 6 | LMS User and Content Management | |
| Topic 7 | Mobile Learning | |
| Topic 8 | E-Learning Authoring Tools |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Gamification | Instructional Design Process |
| Topic 2 | E-Learning Development | Microlearning |
| Topic 3 | Mobile Learning | Collaboration and Networking |
| Topic 4 | Employee Onboarding | |
| Topic 5 | Learning Theories |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Mobile Learning | Educational Animation |
| Topic 2 | E-Learning Development | Course Translation |
| Topic 3 | E-Learning Templates | Assessment |
| Topic 4 | Employee Training | Voiceover |
| Topic 5 | Voiceover | Learning Theories |
| Topic 6 | E-Learning Examples | Learning Objectives |
| Topic 7 | Engaging E-Learning | |
| Topic 8 | Course Translation | |
| Topic 9 | Assessment |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Estimate Development Time | E-Learning Development |
| Topic 2 | Employee Training | Learning Theories |
| Topic 3 | E-Learning Development | Adult Learning |
| Topic 4 | E-Learning Development | Video Development |
| Topic 5 | Learning Theories | User Interface Design |
| Topic 6 | Instructional Design Jobs |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | E-Learning Development | Online Learning |
| Topic 2 | Course Translation | Language Courses |
| Topic 3 | E-Learning Development | Student Feedback |
| Topic 4 | Video Development |
| Topic | Bag-of-Words | Sentence Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | Multimedia Resources | Training Resources |
| Topic 2 | Video Development | Adobe and Camtasia |
| Topic 3 | Adobe Captivate | Infographic Resources |
| Topic 4 | Employee Training | Apps |
| Topic 5 | Storyboarding | |
| Topic 6 | Professional Development | |
| Topic 7 | Infographics | |
| Topic 8 | Webinars | |
| Topic 9 | Multimedia Resources | |
| Topic 10 | Multimedia Resources |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leung, J. An NLP Approach for Extracting Practical Knowledge from a CMS-Based Community of Practice in E-Learning. Knowledge 2022, 2, 310-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge2020018
Leung J. An NLP Approach for Extracting Practical Knowledge from a CMS-Based Community of Practice in E-Learning. Knowledge. 2022; 2(2):310-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge2020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeung, Javier. 2022. "An NLP Approach for Extracting Practical Knowledge from a CMS-Based Community of Practice in E-Learning" Knowledge 2, no. 2: 310-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge2020018
APA StyleLeung, J. (2022). An NLP Approach for Extracting Practical Knowledge from a CMS-Based Community of Practice in E-Learning. Knowledge, 2(2), 310-336. https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge2020018






