From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
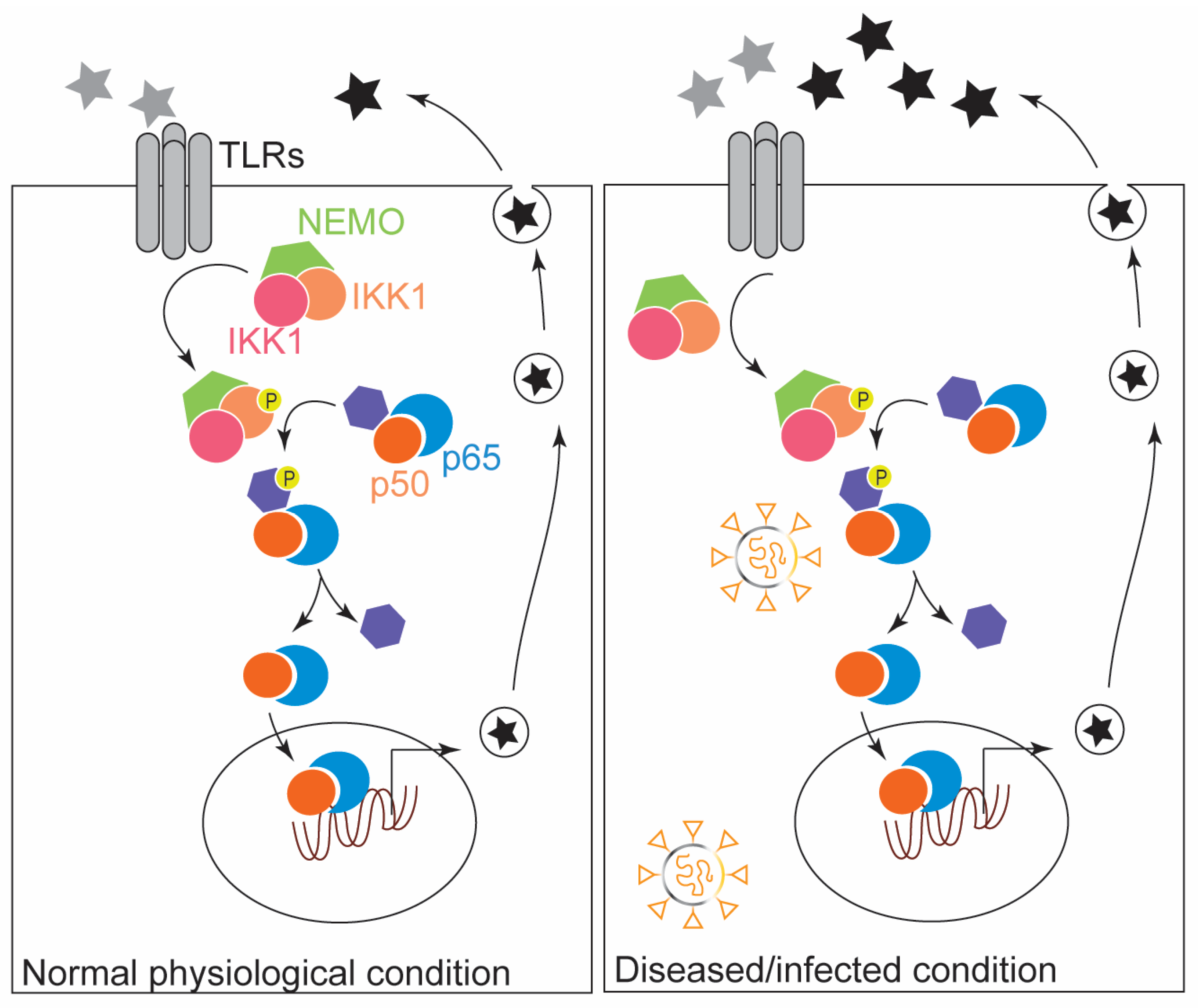
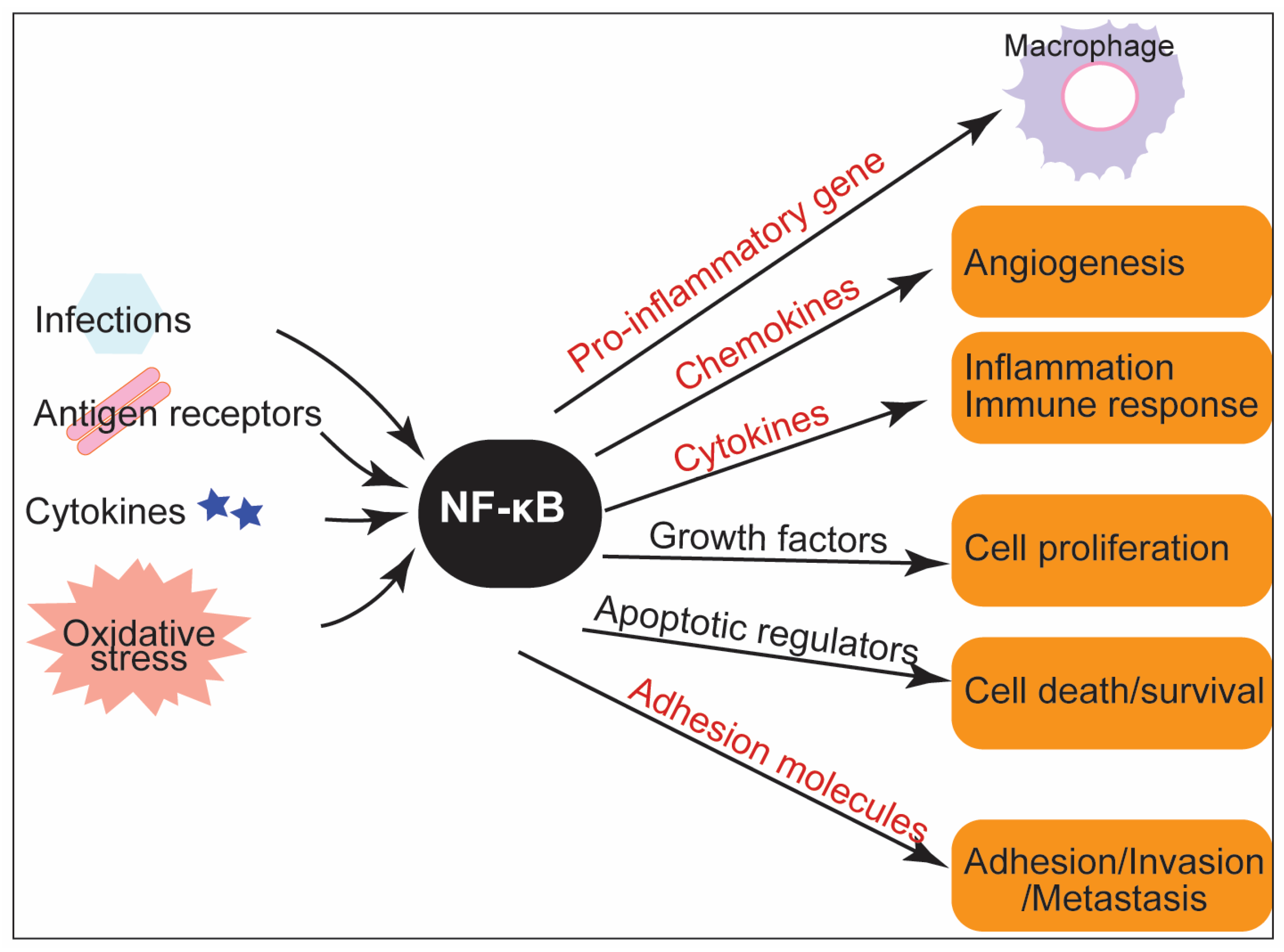
2. The Modulatory Role of NF-κB in the Innate Immune Response: Inflammation and ROS Production
3. NF-κB in Inflammatory Diseases
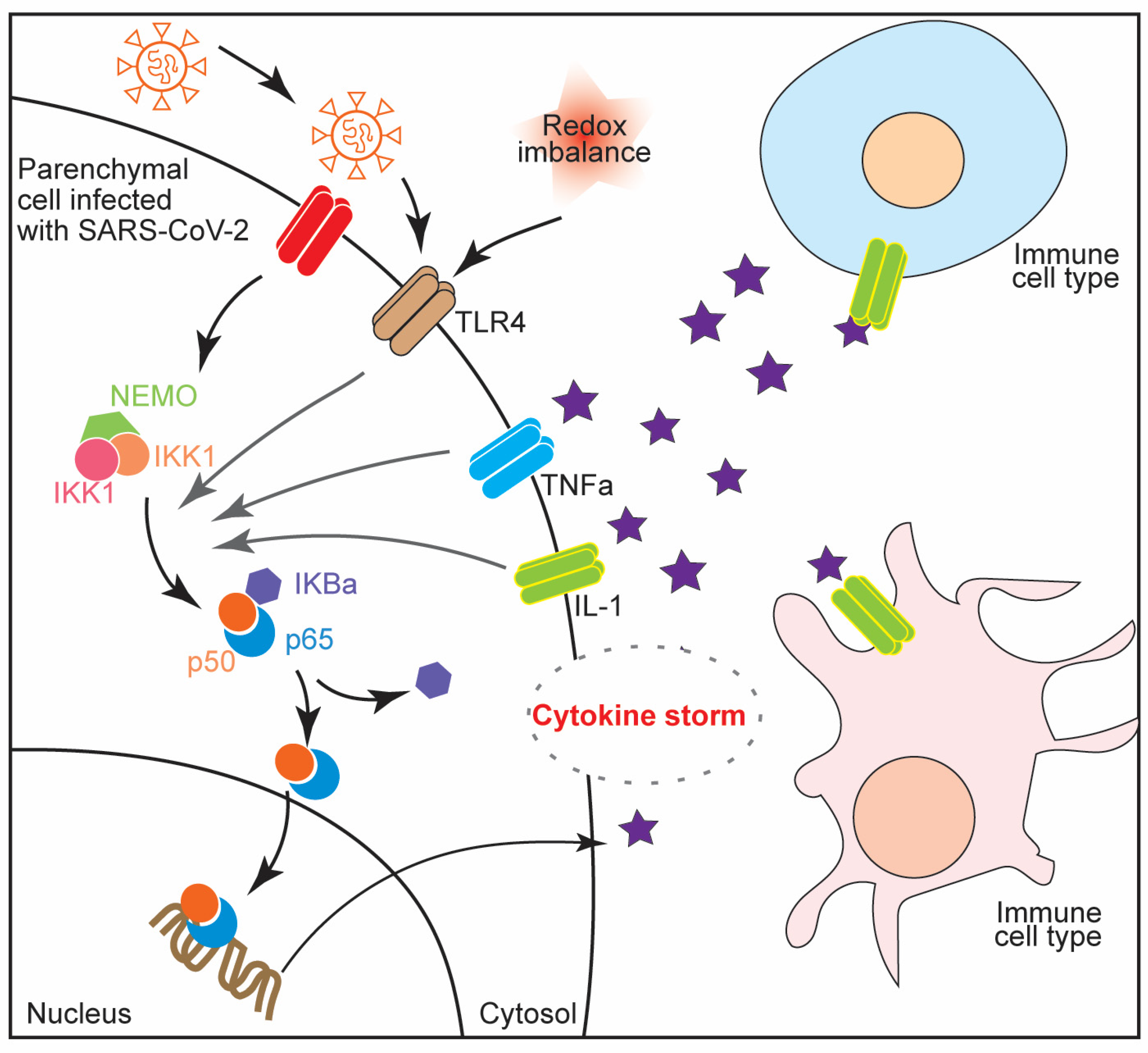
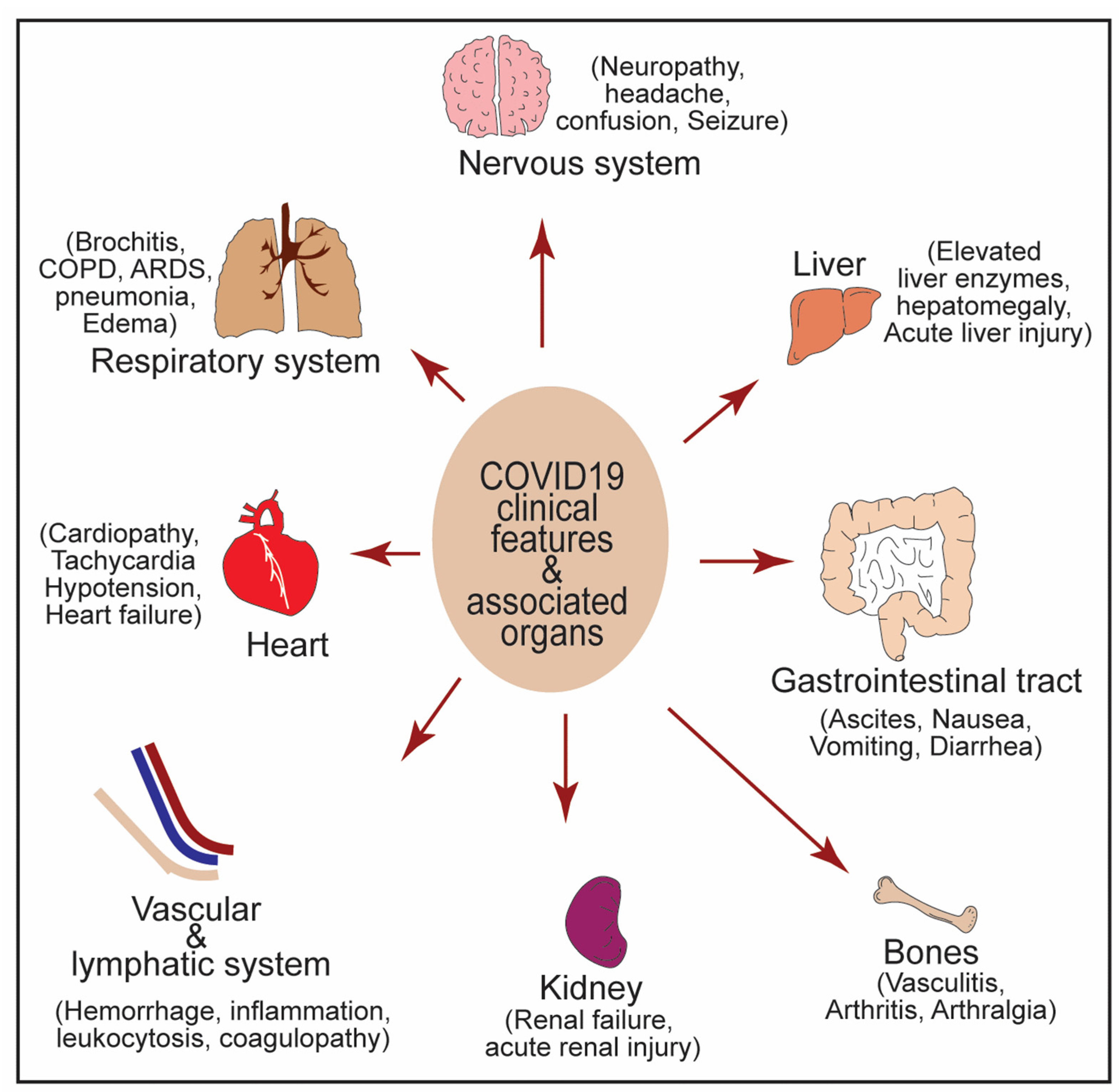
4. NF-κB Activation in Cytokine Storm Syndrome and Multiple Organ Failure during
5. NF-κB in Crosstalk between COVID-19 and Associated Comorbidities
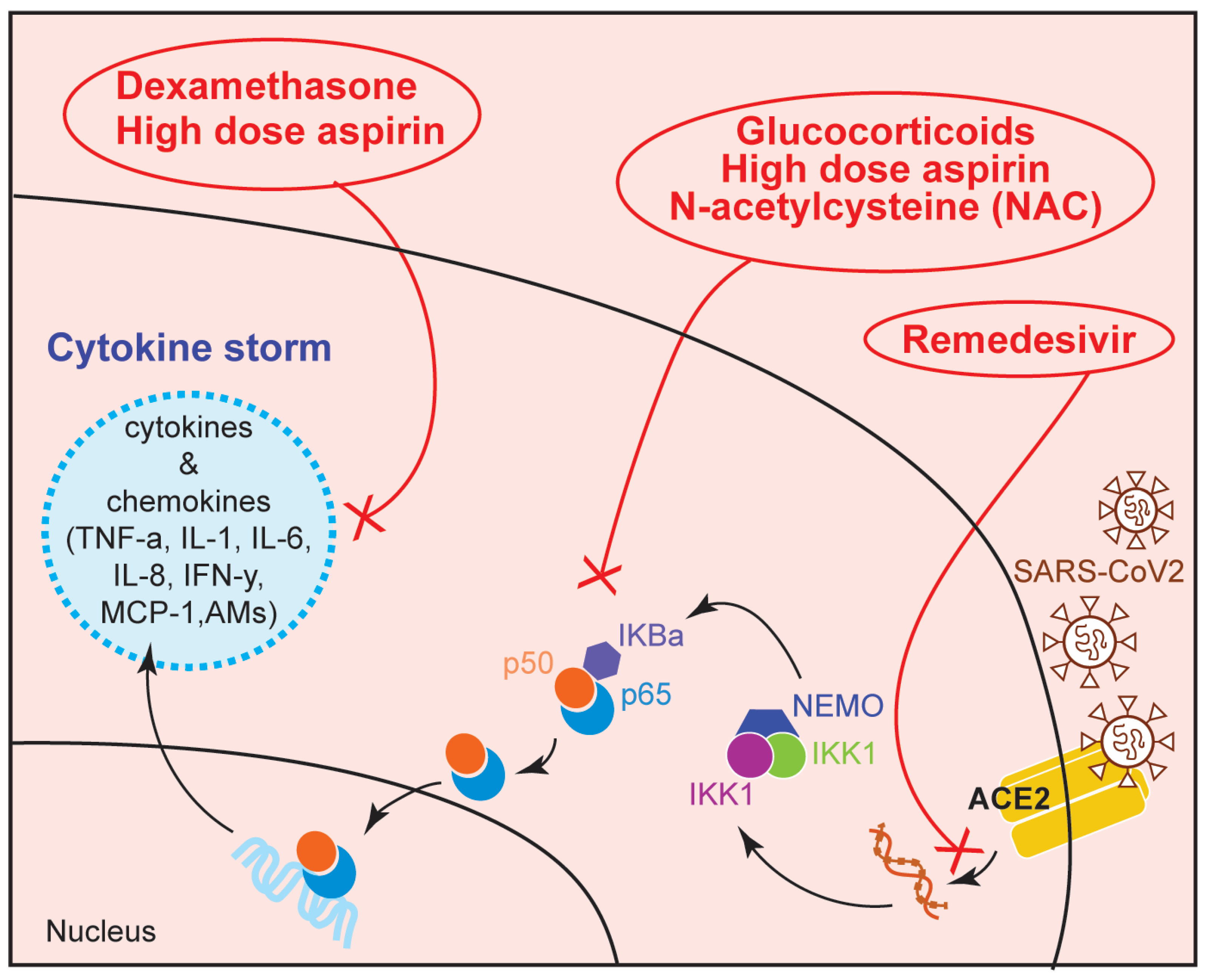
6. Therapeutic Use of NF-κB Modulators in COVID-19
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB Family of Transcription Factors and Its Regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.-C.; Chang, J.-H.; Jin, J. Regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; on behalf of theHLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, L.; Ye, L.; Li, B.; Gao, B.; Zeng, Y.; Kong, L.; Fang, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Z.; et al. Up-regulation of IL-6 and TNF-alphaα induced by SARS-coronavirus spike protein in murine macrophages via NF-kappaκB pathway. Virus Res. 2007, 128, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus—Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Rao, Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L.M.; Zanetti, L.C.; Weinlich, R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Shafiei, M.S.; Longoria, C.; Schoggins, J.W.; Savani, R.C.; Zaki, H. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway. eLife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Karki, R.; Williams, E.P.; Yang, D.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Vogel, P.; Jonsson, C.B.; Kanneganti, T.-D. TLR2 senses the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein to produce inflammatory cytokines. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, K.; Dixit, V.M. Signaling in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a006049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaκB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-kappa B Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.-G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaκB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulsen, C.; Carroll, K.S. Orchestrating Redox Signaling Networks through Regulatory Cysteine Switches. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toledano, M.B.; Leonard, W.J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4328–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pai, S.; Thomas, R. Immune deficiency or hyperactivity-Nf-kappaκb illuminates autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaκB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goverman, J. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussman, J.; Beecham, A.H.; Schmidt, M.; Martin, E.R.; McCauley, J.L.; Vance, J.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. GWAS analysis implicates NF-κB-mediated induction of inflammatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun. 2016, 17, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallace, K.L.; Zheng, L.B.; Kanazawa, Y.; Shih, D.Q. Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J.H. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Stirling, B.; Temmerman, S.T.; Ma, C.A.; Fuss, I.J.; Derry, J.M.J.; Jain, A. Impaired regulation of NF-κB and increased susceptibility to colitis-associated tumorigenesis in CYLD-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3042–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Fuss, I.J.; Preiß, J.; Strober, W.; Kitani, A. Treatment of murine Th1- and Th2-mediated inflammatory bowel disease with NF-kappa B decoy oligonucleotides. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3057–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, M.R.; Bartlett, N.W.; Clarke, D.; Birrell, M.; Belvisi, M.; Johnston, S.L. Targeting the NF-κB pathway in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuliga, M. NF-kappaB Signaling in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1266–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramori, G.; Romagnoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Bellettato, C.; Casoni, G.L.; Boschetto, P.; Chung, K.F.; Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.; Ciaccia, A.; et al. Nuclear localisation of p65 in sputum macrophages but not in sputum neutrophils during COPD exacerbations. Thorax 2003, 58, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gagliardo, R.; Chanez, P.; Mathieu, M.; Bruno, A.; Costanzo, G.; Gougat, C.; Vachier, I.; Bousquet, J.; Bonsignore, G.; Vignola, A.M. Persistent Activation of Nuclear Factor–κB Signaling Pathway in Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, D.; Ng, N.; Lee, S.; Batzer, G.; Horner, A.A. Airway House Dust Extract Exposures Modify Allergen-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity Responses by TLR4-Dependent and Independent Pathways. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Chu, C.; You, H.; Jin, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, W.; Ji, W. Ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma is Toll-like receptor 2 dependent. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014, 35, e15–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Anti-inflammatory Actions of Glucocorticoids: Molecular Mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998, 94, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swinney, D.C.; Xu, Y.-Z.; Scarafia, L.E.; Lee, I.; Mak, A.Y.; Gan, Q.-F.; Ramesha, C.S.; Mulkins, M.A.; Dunn, J.; So, O.-Y.; et al. A Small Molecule Ubiquitination Inhibitor Blocks NF-κB-dependent Cytokine Expression in Cells and Rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23573–23581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, D.; Guido, G.; Zerunian, M.; Polidori, T.; Lucertini, E.; Pucciarelli, F.; Polici, M.; Rucci, C.; Bracci, B.; Nicolai, M.; et al. Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 Pneumonia: Six-month Chest CT Follow-up. Radiology 2021, 301, E396–E405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myall, K.J.; Mukherjee, B.; Castanheira, A.M.; Lam, J.L.; Benedetti, G.; Mak, S.M.; Preston, R.; Thillai, M.; Dewar, A.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. Persistent Post–COVID-19 Interstitial Lung Disease. An Observational Study of Corticosteroid Treatment. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahanic, S.; Tymoszuk, P.; Ausserhofer, D.; Rass, V.; Pizzini, A.; Nordmeyer, G.; Hüfner, K.; Kurz, K.; Weber, P.M.; Sonnweber, T.; et al. Phenotyping of Acute and Persistent Coronavirus Disease 2019 Features in the Outpatient Setting: Exploratory Analysis of an International Cross-sectional Online Survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnweber, T.; Tymoszuk, P.; Sahanic, S.; Boehm, A.; Pizzini, A.; Luger, A.; Schwabl, C.; Nairz, M.; Grubwieser, P.; Kurz, K.; et al. Investigating phenotypes of pulmonary COVID-19 recovery: A longitudinal observational prospective multicenter trial. eLife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attiq, A.; Yao, L.J.; Afzal, S.; Khan, M.A. The triumvirate of NF-κB, inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barh, D.; Aljabali, A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Tiwari, S.; Serrano-Aroca, A.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Silva Andrade, B.S.; Azevedo, V.; Ganguly, N.K.; Lundstrom, K. Predicting COVID-19—Comorbidity Pathway Crosstalk-Based Targets and Drugs: Towards Personalized COVID-19 Management. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.-J.; Liang, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.-R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-Q.; Chen, R.-C.; Tang, C.-L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y. The Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Severe COVID-19. Gerontology 2021, 67, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Patidar, R.; Younis, K.; Desai, P.; Hosein, Z.; Padda, I.; Mangat, J.; Altaf, M. Comorbidity and its Impact on Patients with COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.; Nee, S.; Hickey, N.S.; Marschollek, M. Risk factors for Covid-19 severity and fatality: A structured literature review. Infection 2021, 49, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyerovich, K.; Ortis, F.; Cardozo, A.K. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway and its contribution to β-cell failure in diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, F1–F6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruglikov, I.L.; Scherer, P.E. Preexisting and inducible endotoxemia as crucial contributors to the severity of COVID-19 outcomes. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, G.; Dinakaran, V.; Rajendhran, J.; Swaminathan, K. Blood Microbiota and Circulating Microbial Metabolites in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.A.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Albensi, B.C. The Effect of COVID-19 on NF-κB and Neurological Manifestations of Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4178–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prescott, J.A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Cook, S.J. Inhibitory feedback control of NF-κB signalling in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2619–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Fett, C.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L. Inhibition of NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-Infected Mice Increases Survival. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, I.; Pranata, R. Lymphopenia in severe coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolpour, S.; Rakhshandehroo, T.; Wei, E.X.; Rashidian, M. Lymphopenia during the COVID-19 infection: What it shows and what can be learned. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 225, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, M. NF-κB signalling as a pharmacological target in COVID-19: Potential roles for IKKβ inhibitors. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 2021, 394, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y. The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, Z.; Tomita, M.; Katano, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Ahmed, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Sata, T.; Mori, N.; Yamamoto, N. An HIV protease inhibitor, ritonavir targets the nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibits the tumor growth and infiltration of EBV-positive lymphoblastoid B cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariya, R.; Taura, M.; Suzu, S.; Kai, H.; Katano, H.; Okada, S. HIV protease inhibitor Lopinavir induces apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells via suppression of NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett. 2014, 342, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, B.; Lu, R.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liang, C.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Immunosuppressive effects of hydroxychloroquine and artemisinin combination therapy via the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in lupus nephritis mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kircheis, R.; Haasbach, E.; Lueftenegger, D.; Heyken, W.T.; Ocker, M.; Planz, O. NF-κB Pathway as a Potential Target for Treatment of Critical Stage COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 598444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretta, A.A.; Silveira, M.A.D.; Capcha, J.M.C.; De Jong, D. Propolis and its potential against SARS-CoV-2 infection mechanisms and COVID-19 disease: Running title: Propolis against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, J.; Bhadra, B.; Dattaroy, T.; Nagle, V.; Dasgupta, S. Potential of natural astaxanthin in alleviating the risk of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Management of Acute Lung Injury: Palmitoylethanolamide as a New Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandey, A.; Mishra, A.K. From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19. Physiologia 2022, 2, 34-45. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2020004
Pandey A, Mishra AK. From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19. Physiologia. 2022; 2(2):34-45. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2020004
Chicago/Turabian StylePandey, Ashutosh, and Abhinava K. Mishra. 2022. "From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19" Physiologia 2, no. 2: 34-45. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2020004
APA StylePandey, A., & Mishra, A. K. (2022). From Innate Immunity to Inflammation: A Primer on Multiple Facets of NF-κB Signaling in COVID-19. Physiologia, 2(2), 34-45. https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2020004






