Analysis of the Effect on Denture Base Metal of Cleaning with Denture Cleanser Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
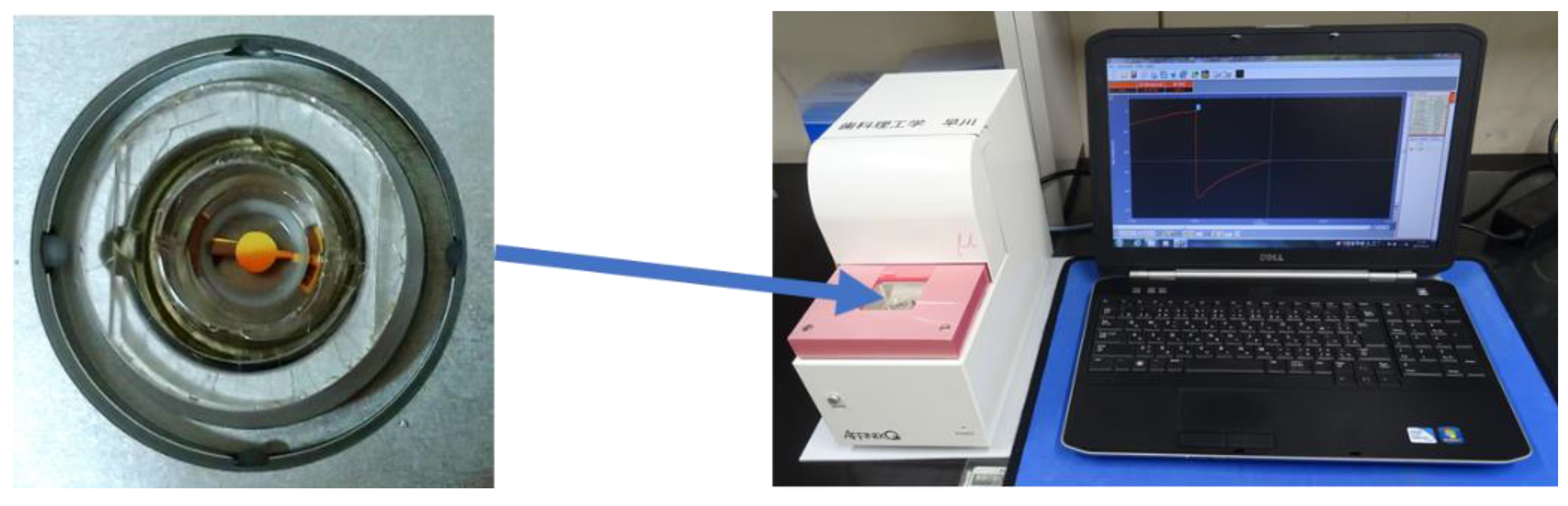
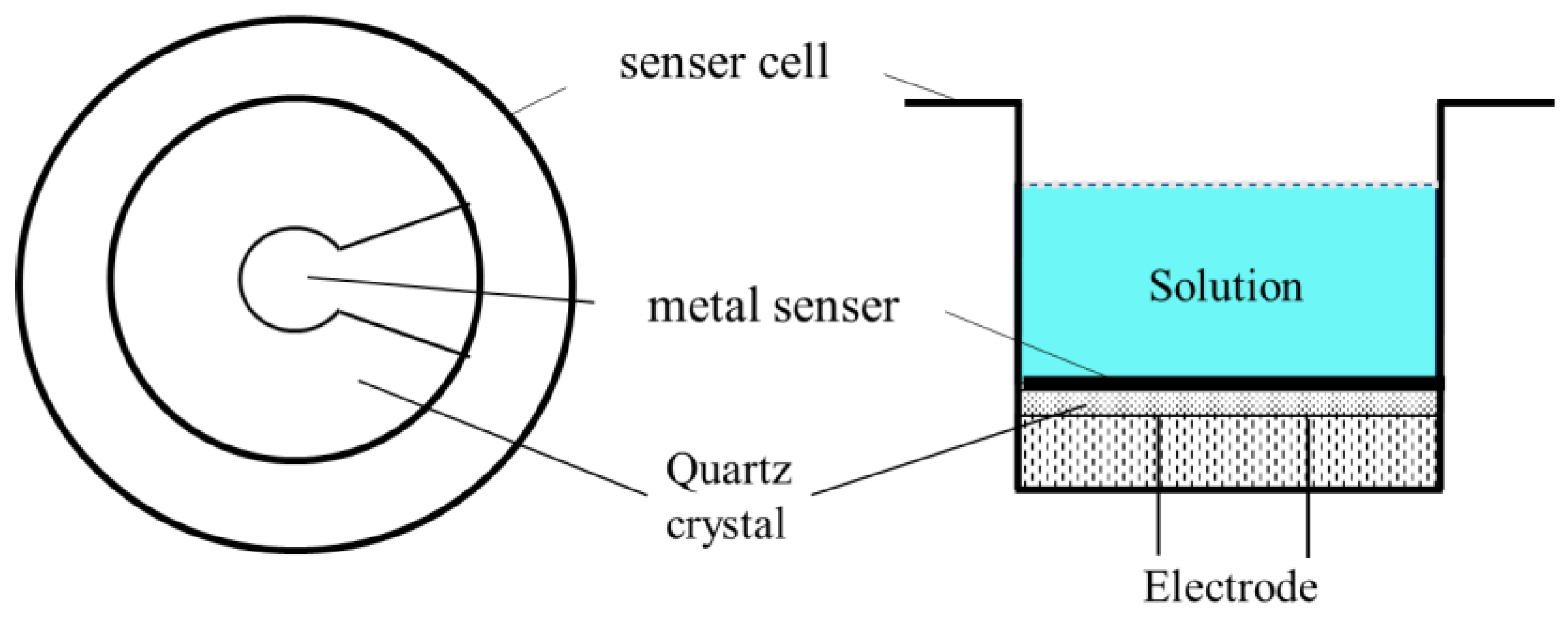
2.1. QCM Apparatus and Sensors
- ΔF: frequency changes (Hz);
- Δm: mass change (g);
- F0: fundamental frequency of the quartz crystal (27 × 106 Hz);
- A: electrode area (0.049 cm2);
- : density of quartz (2.65 gcm−3);
- : shear modulus of quartz (2.95 × 1011 dyncm−2).
2.2. Measurements of Contact Angle
2.3. QCM Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
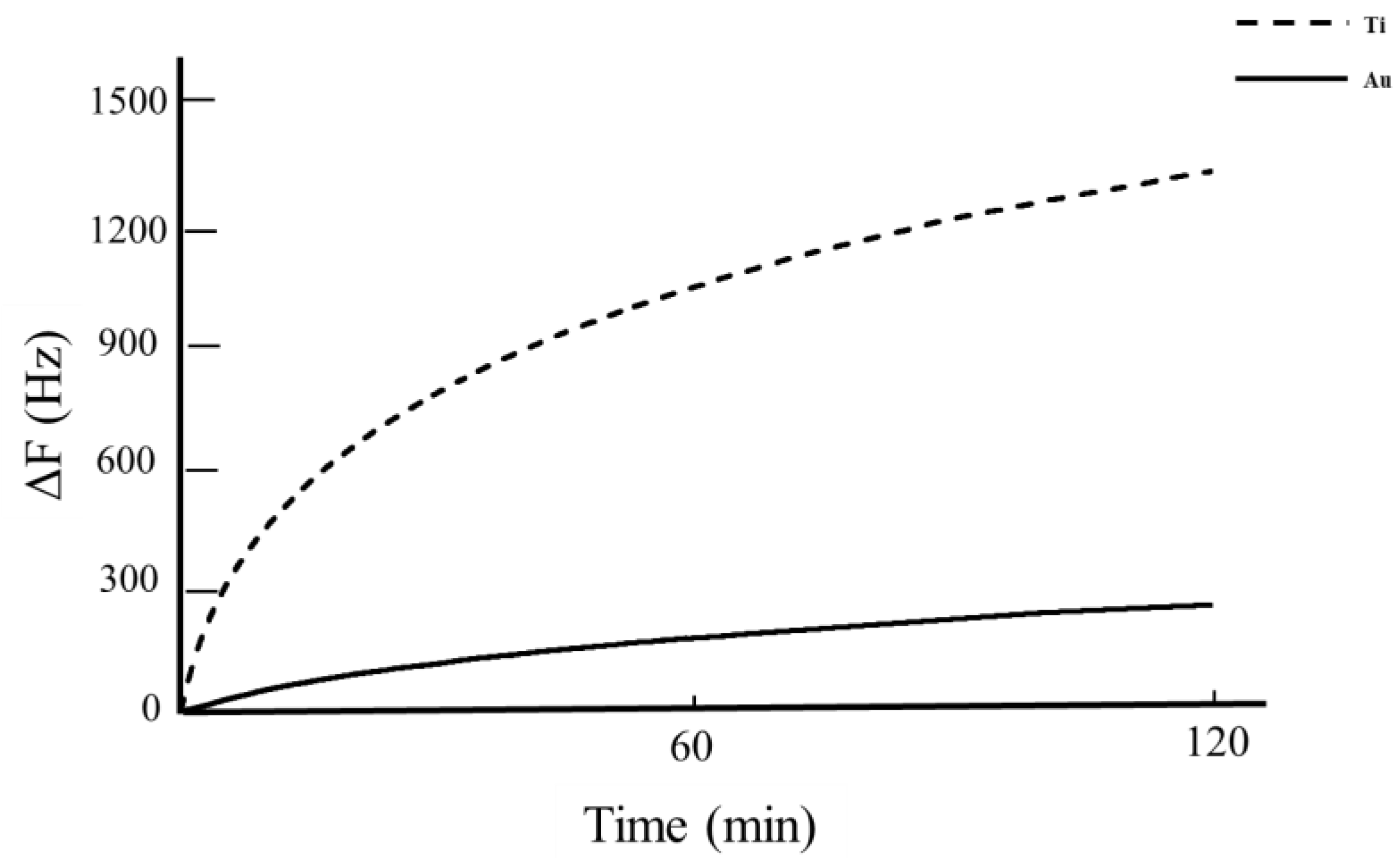
3. Results
3.1. Contact Angles
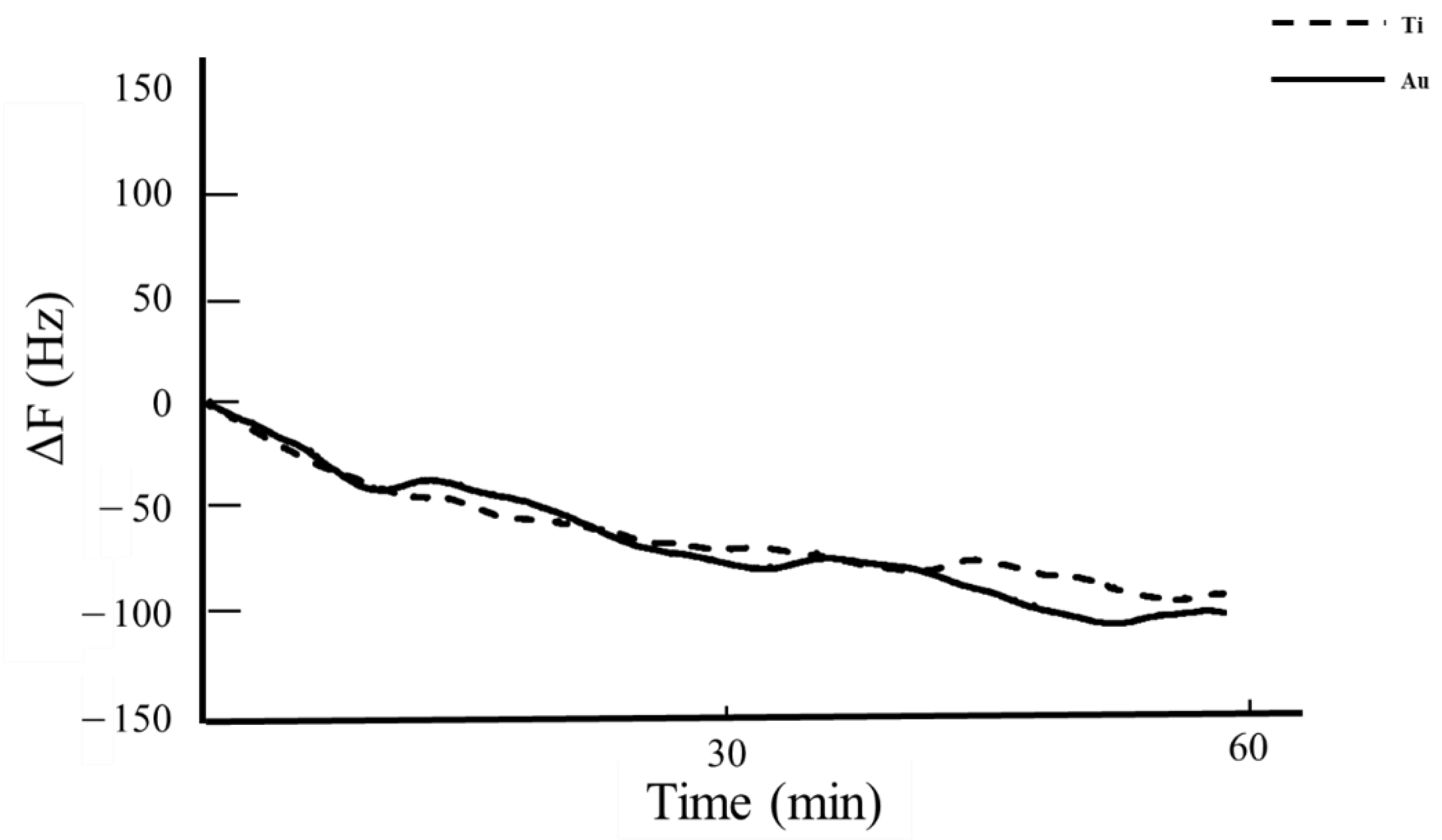
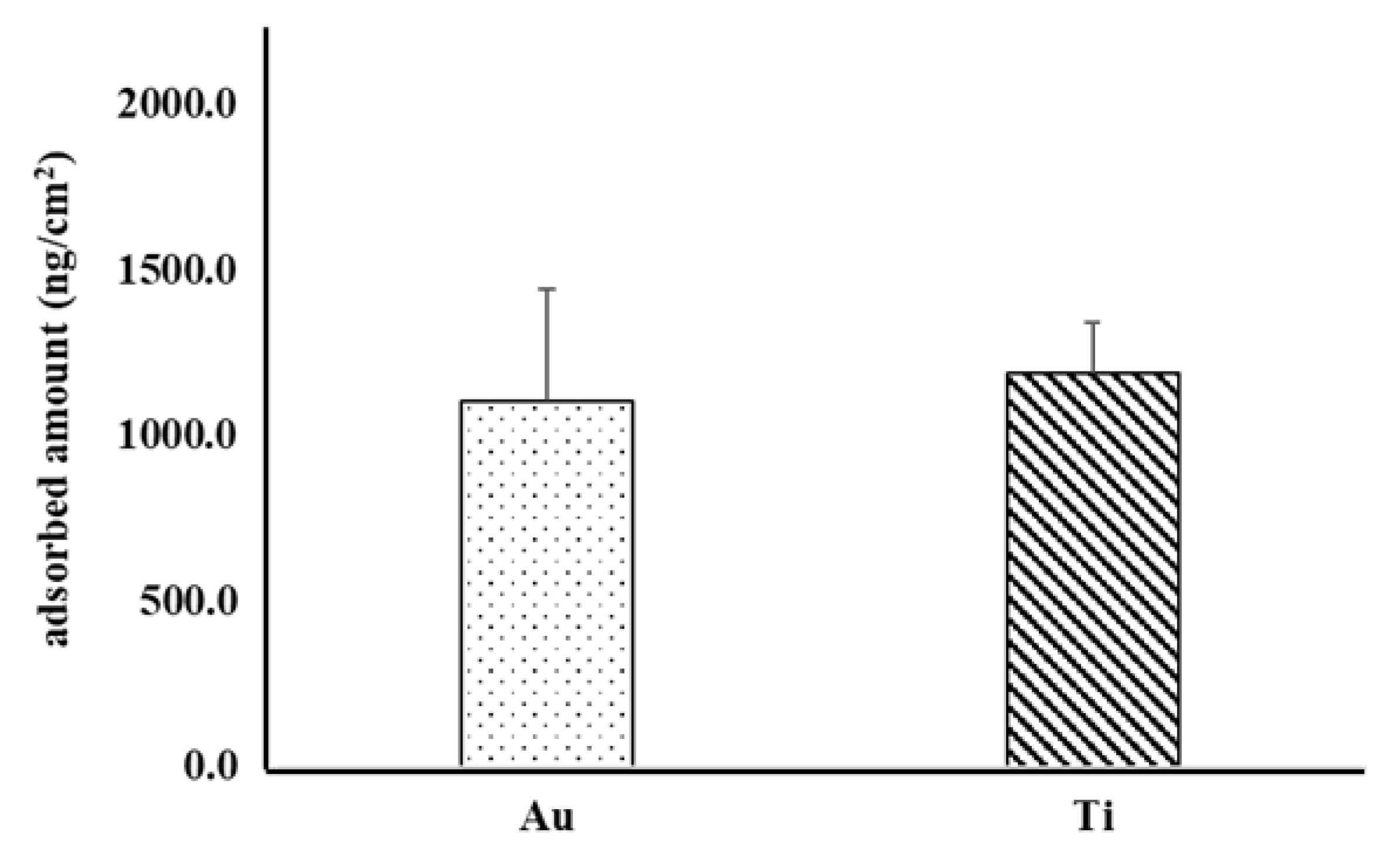
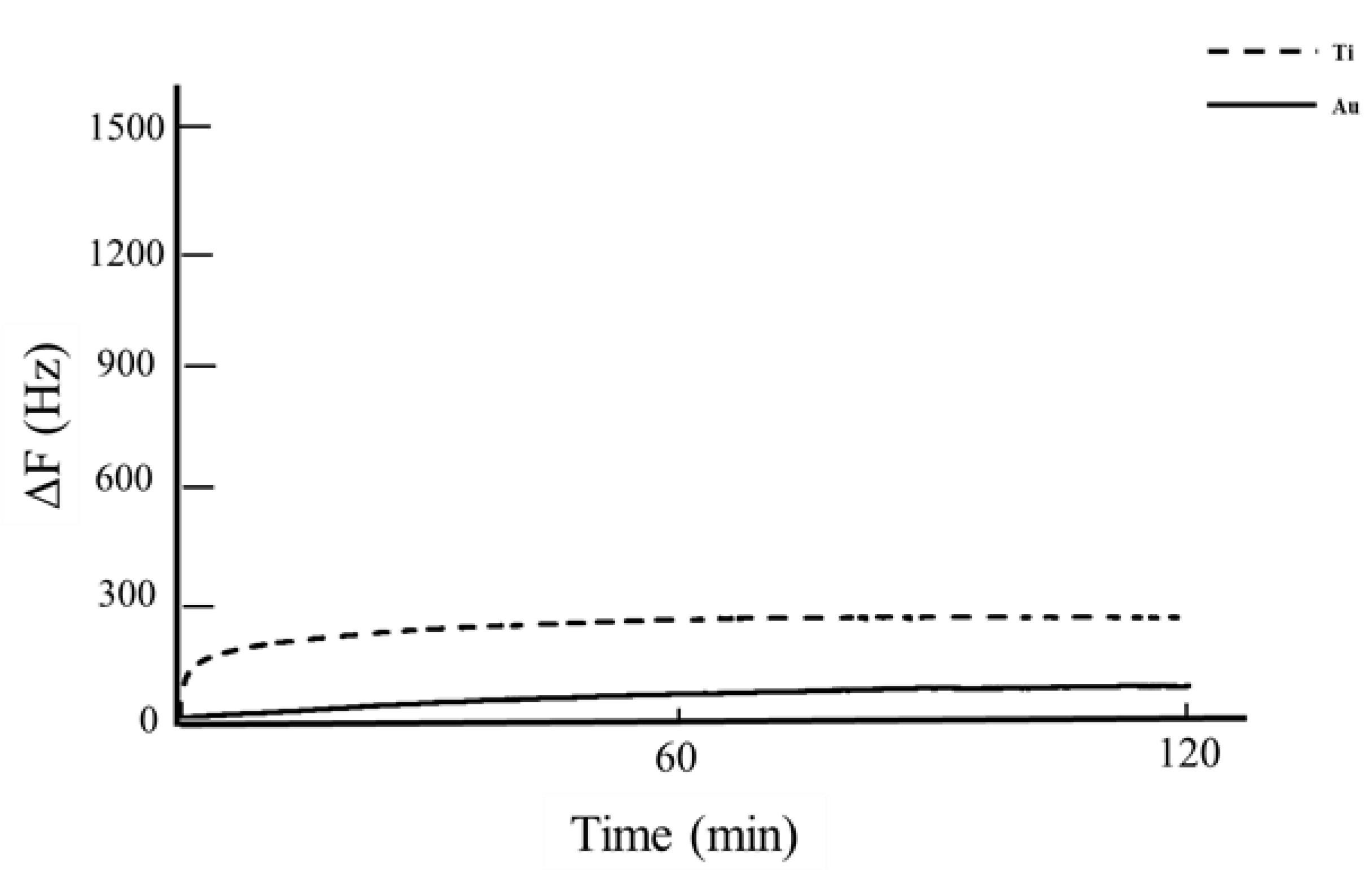
3.2. QCM Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The contact angle of Au was significantly higher than that of Ti. Second item.
- There was no significant difference between the amounts of BSA adsorbed by Au and Ti sensors.
- The frequency increased when using Dentmousse and Polident, and frequency shifts were observed in the removal of BSA after using various denture cleansers.
- The BSA removal amount of Ti was significantly higher than that of Au when using Dentmousse and Polident.
- The comparison of BSA removal rates of denture cleansers at different times of day showed that the removal rate of Ti was significantly greater than that of Au within one hour after injection of the cleaning agents, but the removal rate decreased after one hour.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Lin, J.; Ng, L.; Needleman, I.; Walsh, T.; Li, C. Oral care measures for preventing nursing home-acquired pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Yoneyama, T.; Akagawa, Y. Oral care reduces pneumonia of elderly patients in nursing homes, irrespective of dentate or edentate status. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 2001, 38, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarel-Wierink, C.D.; Vanobbergen, J.N.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Schols, J.M.; de Baat, C. Oral health care and aspiration pneumonia in frail older people: A systematic literature review. Gerodontology 2013, 30, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, T.; Yoshida, M.; Ohrui, T.; Mukaiyama, H.; Okamoto, H.; Hoshiba, K.; Ihara, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Ariumi, S.; Morita, T.; et al. Oral care reduces pneumonia in older patients in nursing homes. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, Y.; Kagami, H.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Kakinoki, Y.; Haruguchi, Y.; Miyamoto, H. High correlation between the bacterial species in denture plaque and pharyngeal microflora. Gerodontology 2003, 20, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Torii, M.; Urushibara, Y.; Kawai, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Maeda, N.; Ohkubo, C.; Ohshima, T. Analysis of plaque microbiota and salivary proteins adhering to dental materials. J. Oral Biosci. 2020, 62, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninagi, T. Studies of the Formation of Initial Denture Plaque. J. Kyushu Dent. Soc. 1987, 41, 1123–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irahara, A.; Ishihara, O.; Miki, K.; Ikeda, M.; Isikawa, J.; Hoshino, T. Plaque adhesion on mucosal surface of denture base. J. Hokkaido Dent. Assoc. 1975, 30, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Nikawa, H.; Mikihira, S.; Egusa, H.; Fukushima, H.; Kawabata, R.; Hamada, T.; Yatani, H. Candida Adherence and Biofilm Formation on Oral Surfaces. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 2005, 46, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Seto, K.; Kamashita, Y.; Take, C.; Kurono, A.; Nagaoka, E. Examination of denture-cleaning methods based on the quantity of microorganisms adhering to a denture. Gerodontology 2012, 29, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Sato, Y.; Owada, G.; Minakuchi, S. Effectiveness of a combination denture-cleaning method versus a mechanical method: Comparison of denture cleanliness, patient satisfaction, and oral health-related quality of life. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Adriana, Z.; Donald, C.; Leighann, S.; Colin, M.; Mary, F.; Zvi, L.; Daryll, J. A Comparative In Vitro Study of Two Denture Cleaning Techniques as an Effective Strategy for Inhibiting Candida albicans Biofilms on Denture Surfaces and Reducing Inflammation. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 21, 516–522. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Ohshima, T.; Maeda, N.; Ohkubo, C. Removal Effectiveness of Biofilms and Changes in Surface Roughness by Cleaning Methods of Denture Base Resin. Ann. Jpn. Prosthodont. Soc. 2013, 5, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heath, J.; Davenport, C.; Jones, A. The abrasion of acrylic resin by cleaning paste. J. Oral Rehabil. 1983, 10, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadamori, S.; Kotani, H.; Nikawa, H.; Hamada, T. Clinical Survey on Denture Stomatitis Part 2. The Relation between the Maintenance of Denture and Denture Stomatitis. J. Jpn. Prosthodont. Soc. 1990, 34, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urushibara, Y.; Ohshima, T.; Sato, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Maeda, N.; Ohkubo, C. An analysis of the biofilms adhered to framework alloys using in vitro denture plaque models. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granick, S.; Sinclair, P.; Sassa, S.; Grieninger, G. Effects by heme, insulin, and serum albumin on heme and protein synthesis in chick embryo liver cells cultured in a chemically defined medium, and a spectrofluorometric assay for porphyrin composition. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 9215–9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengvall, P.; Lundström, I.; Liedberg, B. Protein adsorption studies on model organic surfaces: An ellipsometric and infrared spectroscopic approach. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falb, R.; Takahashi, M.; Grode, G.; Leininger, R. Studies on the stability and protein adsorption characteristics of heparinized polymer surfaces by radioisotope labeling techniques. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1967, 1, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niegelhell, K.; Ganner, T.; Plank, H.; Jantscher-Krenn, E.; Spirk, S. Lectins at Interfaces-An Atomic Force Microscopy and Multi-Parameter-Surface Plasmon Resonance Study. Materials 2018, 11, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Luna-Velasco, A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Field, J. Assessing protein oxidation by inorganic nanoparticles with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.; Craig, R.; Filisko, F.; Zand, R. Preparation and characterization of high-surface-area polymer substrates for microcalorimetry. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 31, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.C.; Sousa, S.R.; Antunes, J.C.; Barbos, M.A. Protein adsorption characterization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 811, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, T. Analysis of Protein Adsorption Using 27 MHz Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. J. Jpn. Soc. Dent. Prod. 2012, 26, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xinge, X.; Isabelle, I.; Niyonshuti, N.; Yu, L.; Ying, F.; Jingyi, C.; Yanbin, L. Label-Free Quartz Crystal Microbalance Biosensor Based on Aptamer-Capped Gold Nanocages Loaded with Polyamidoamine for Thrombin Detection. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 10047–10054. [Google Scholar]
- Dongsheng, L.; Zihao, X.; Mengjiao, Q.; Qian, Z.; Yongqing, F.; Jin, X. Virtual Sensor Array Based on Butterworth–Van Dyke Equivalent Model of QCM for Selective Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 39, 47043–47051. [Google Scholar]
- Semra, A.; Dilek, B.; Serkan, Y.; Handan, Y.; Adil, D. Rapid and sensitive detection of synthetic cannabinoids JWH-018, JWH-073 and their metabolites using molecularly imprinted polymer-coated QCM nanosensor in artificial saliva. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104454. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, I.; Kozaki, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Fukazawa, K. Biomimetic phospholipid polymers for suppressing adsorption of saliva proteins on dental hydroxyapatite substrate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakawa, Y.; Yoshida, E.; Hayakawa, T. Protein Adsorption to Titanium and Zirconia Using a Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1521593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, E.; Hayakawa, T. Adsorption study of pellicle proteins to gold, silica and titanium by quartz crystal microbalance method. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, N.; Yamachika, R.; Sakurai, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Hosoya, N. Bone Response to Titanium Implants Coated with Double- or Single-Stranded DNA. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9204391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, E.; Hayakawa, T. Adsorption Analysis of Lactoferrin to Titanium, Stainless Steel, Zirconia, and Polymethyl Methacrylate Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3961286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Tashiro, Y.; Inui, S.; Kusumoto, T.; Nishizaki, H.; Sekino, T.; et al. Optimized Surface Characteristics and Enhanced in Vivo Osseointegration of Alkali-Treated Titanium with Nanonetwork Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, E.; Hayakawa, T. Influence of mucin pre-adsorption for lipoteichoic acid adsorption on titanium surfaces. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Komasa, S.; Komasa, Y. Development of new denture cleaning agent for home health care Study on adhesion of denture plaque using a biosensor that simulates the denture surface. J. Osaka Odontol. Soc. 2017, 80, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, M.; Hayakawa, T. Adsorption behaviors of salivary pellicle proteins onto denture base metals using 27-MHz quartz crystal microbalance. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, A.; Komasa, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Komasa, Y.; Okazaki, J. Adsorption of Saliva Related Protein on Denture Materials: An X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Quartz Crystal Microbalance Study. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wagung dunner Schichten und zur Mikrowagung. Z Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, L.; Gerd, G.; Michael, J.; Sylwia, M.; Franz, D.; Anton, L. Softlithography in Chemical Sensing—Analytes from Molecules to Cells. Sensors 2005, 5, 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Serro, A.; Fernandes, A.; Saramago, B.; Norde, W. Bovine serum albumin adsorption on titania surfaces and its relation to wettability aspects. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, O.; Munoz, A.; Mischler, S. An Overview of Serum Albumin Interactions with Biomedical Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaurav, A.; Zhang, F.; Robert, J.L.; Georges, B. Protein-Associated Water and Secondary Structure Effect Removal of Blood Proteins from Metallic Substrates. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Thyparambil, A.; Wei, Y.; Latour, R. Experimental characterization of adsorbed protein orientation, conformation, and bioactivity. Biointerphases 2015, 10, 019002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberi, J.; Spriano, S. Titanium and Protein Adsorption: An Overview of Mechanisms and Effects of Surface Features. Materials 2021, 14, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Tashiro, Y.; Komasa, S.; Miyake, A.; Komasa, Y.; Okazaki, J. Effects of Surface Modification on Adsorption Behavior of Cell and Protein on Titanium Surface by Using Quartz Crystal Microbalance System. Materials 2020, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matei, I.; Buta, M.; Turcu, M.; Culita, D.; Munteanu, C.; Ionita, G. Formation and Stabilization of Gold Nanoparticles in Bovine Serum Albumin Solution. Molecules 2019, 24, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Ferreira, P.; Saramago, B.; Melo, L.; Barbosa, M. Human Serum Albumin Adsorption on TiO2 from Single Protein Solutions and from Plasma. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9745–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sensor | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| Au | 40.1 ± 1.1 a |
| Ti | 21.3 ± 1.6 b |
| Denture Cleanser | Sensor | Removal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Polident | Au | 15.8 ± 3.4 a,d |
| Ti | 69.1 ± 4.6 b | |
| Dentmousse | Au | 4.8 ± 0.9 c,d |
| Ti | 9.8 ± 1.3 a,c,d |
| Time Period | Sensor | Removal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ① | Au | 3.2 ± 0.9 a,d |
| Ti | 9.4 ± 1.5 b,c | |
| ② | Au | 1.4 ± 0.3 a,d |
| Ti | 0.7 ± 0.6 a,d |
| Time Period | Sensor | Removal Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ① | Au | 10.9 ± 2.6 a |
| Ti | 54.3 ± 3.7 b | |
| ② | Au | 4.8 ± 2.0 a |
| Ti | 32.2 ± 4.5 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imaizumi, N.; Sakurai, T.; Hirota, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Ohkubo, C. Analysis of the Effect on Denture Base Metal of Cleaning with Denture Cleanser Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. Hygiene 2021, 1, 129-139. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene1030012
Imaizumi N, Sakurai T, Hirota M, Hayakawa T, Ohkubo C. Analysis of the Effect on Denture Base Metal of Cleaning with Denture Cleanser Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. Hygiene. 2021; 1(3):129-139. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene1030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleImaizumi, Naoya, Toshitsugu Sakurai, Masatsugu Hirota, Tohru Hayakawa, and Chikahiro Ohkubo. 2021. "Analysis of the Effect on Denture Base Metal of Cleaning with Denture Cleanser Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method" Hygiene 1, no. 3: 129-139. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene1030012
APA StyleImaizumi, N., Sakurai, T., Hirota, M., Hayakawa, T., & Ohkubo, C. (2021). Analysis of the Effect on Denture Base Metal of Cleaning with Denture Cleanser Using the Quartz Crystal Microbalance Method. Hygiene, 1(3), 129-139. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene1030012





