Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
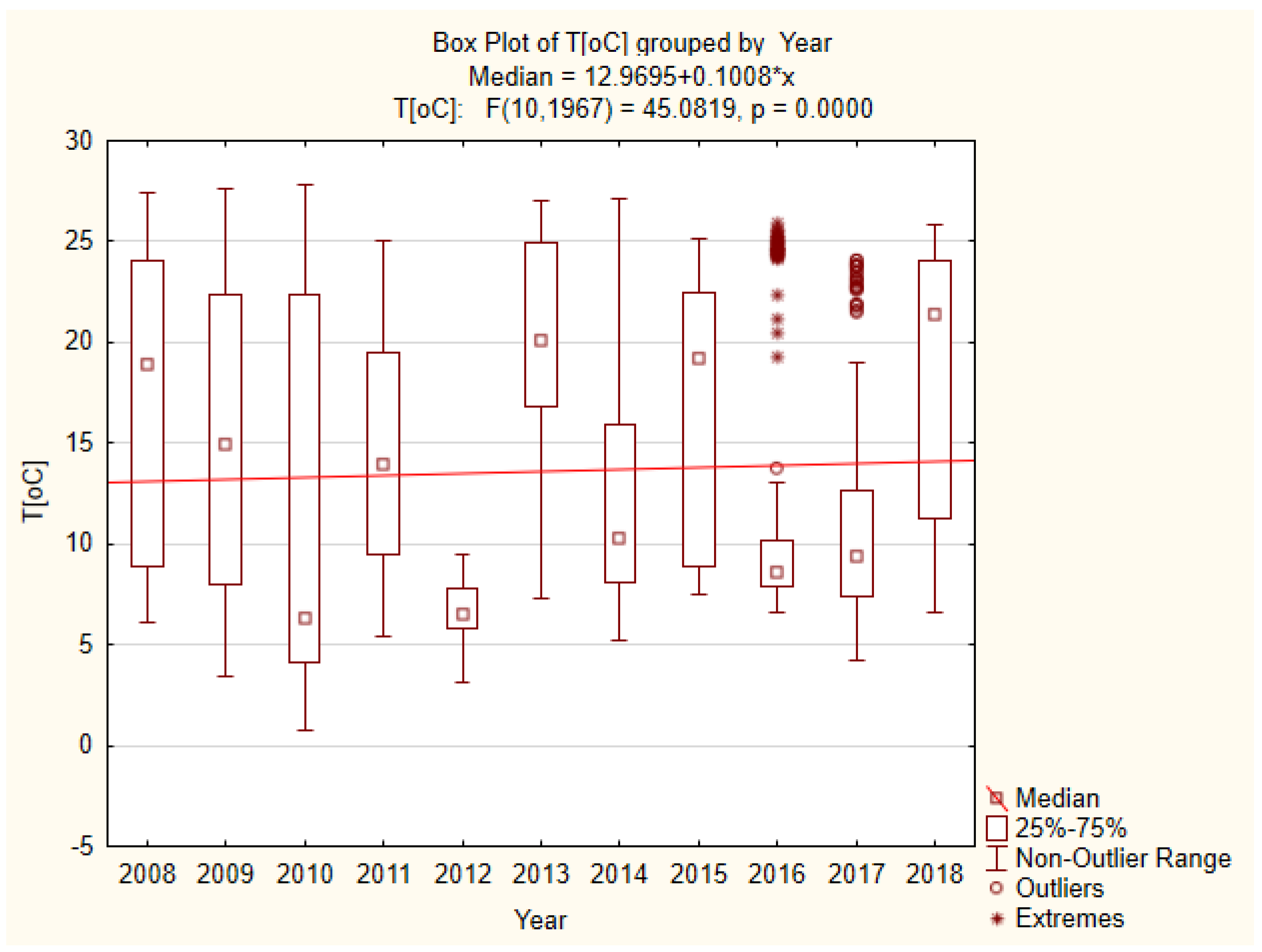
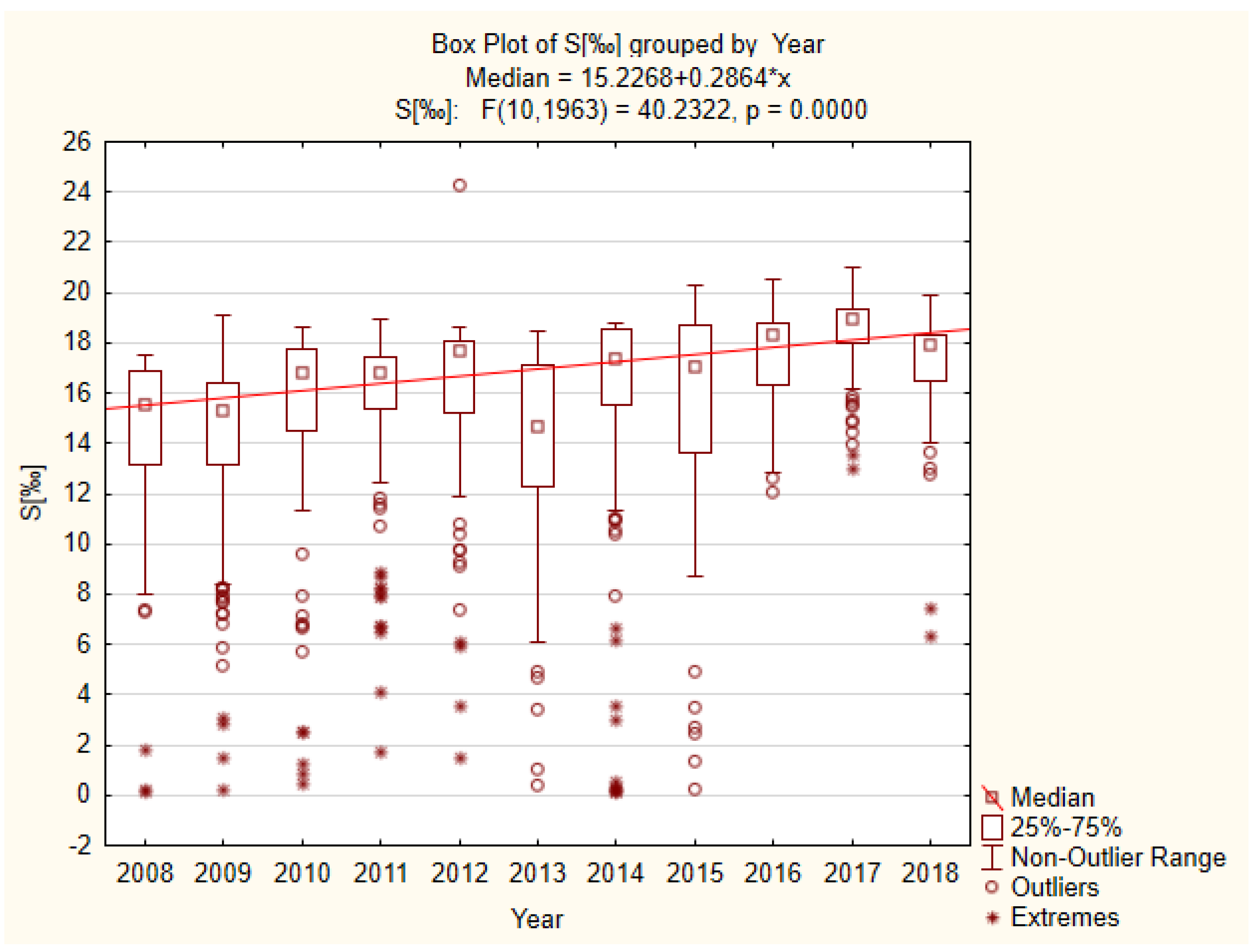
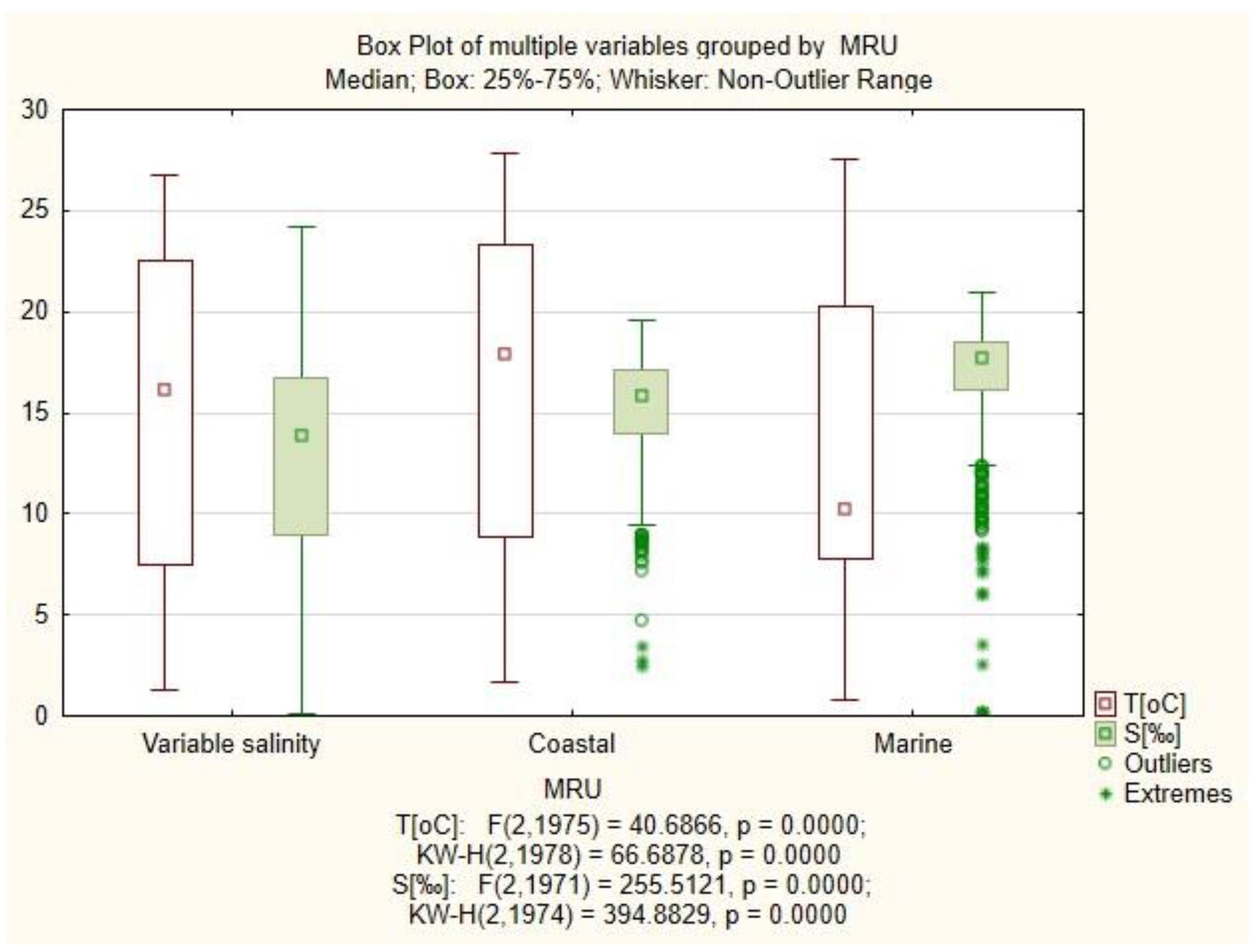
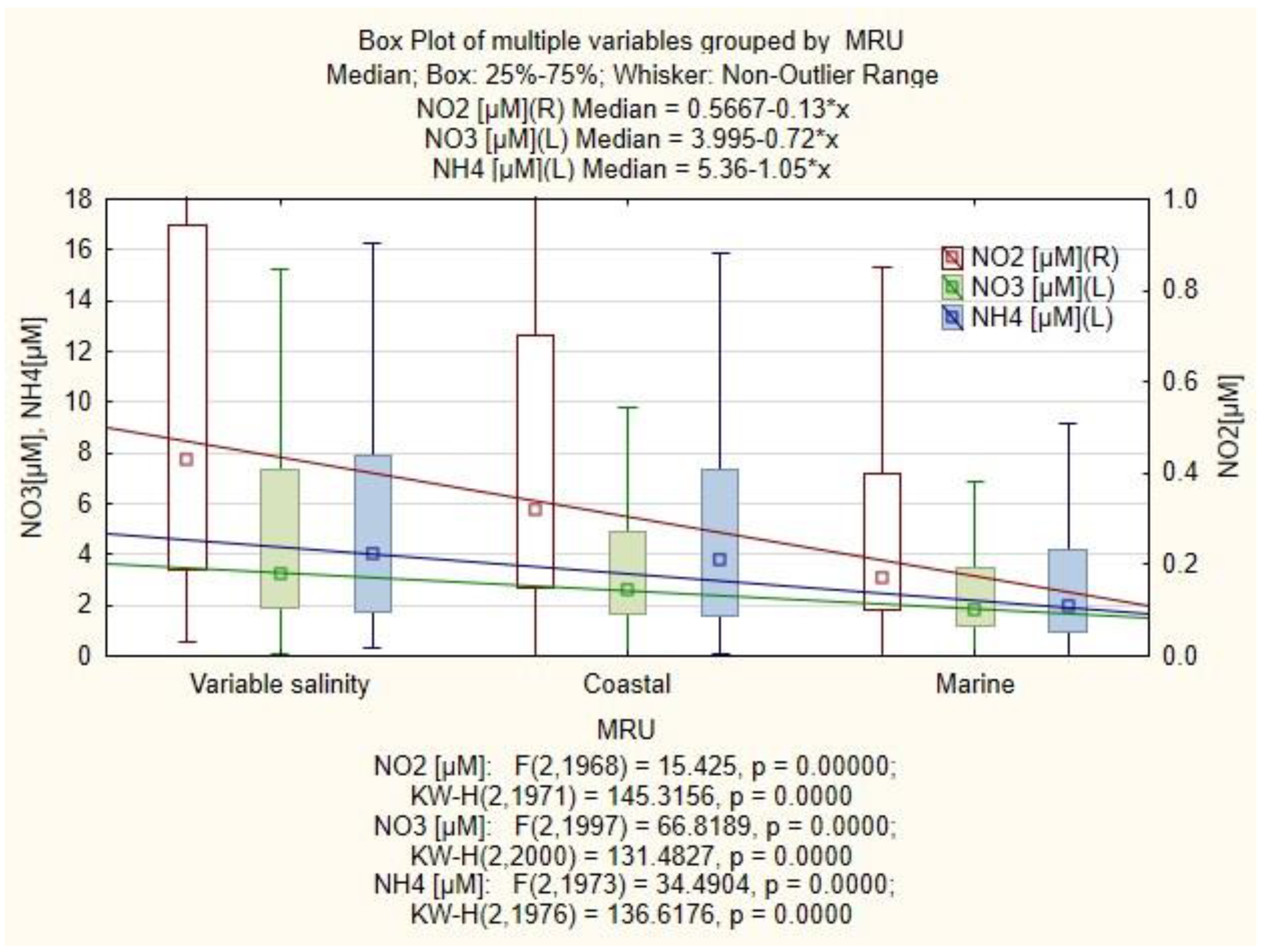
3.1. Physicochemical Factors
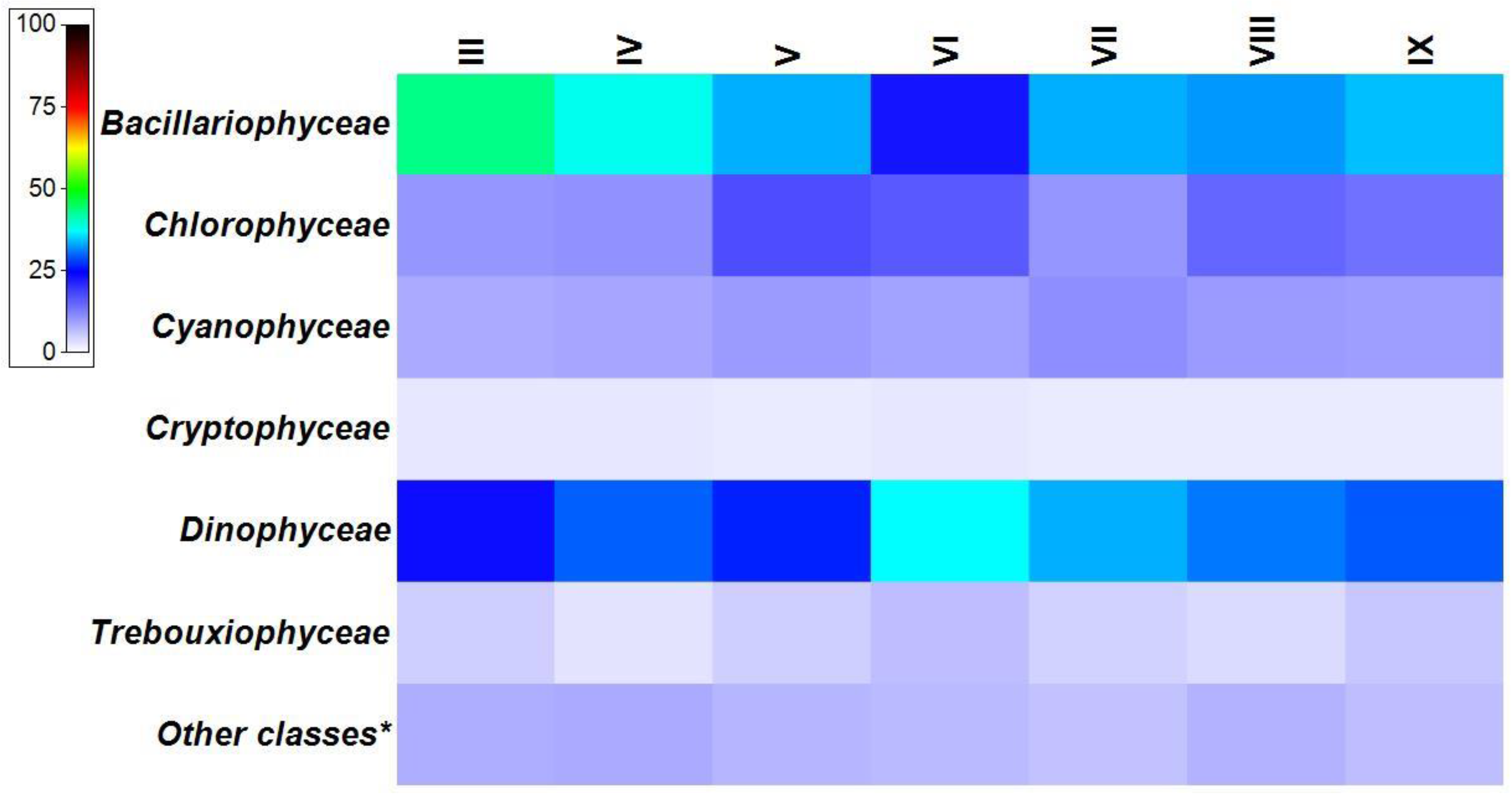
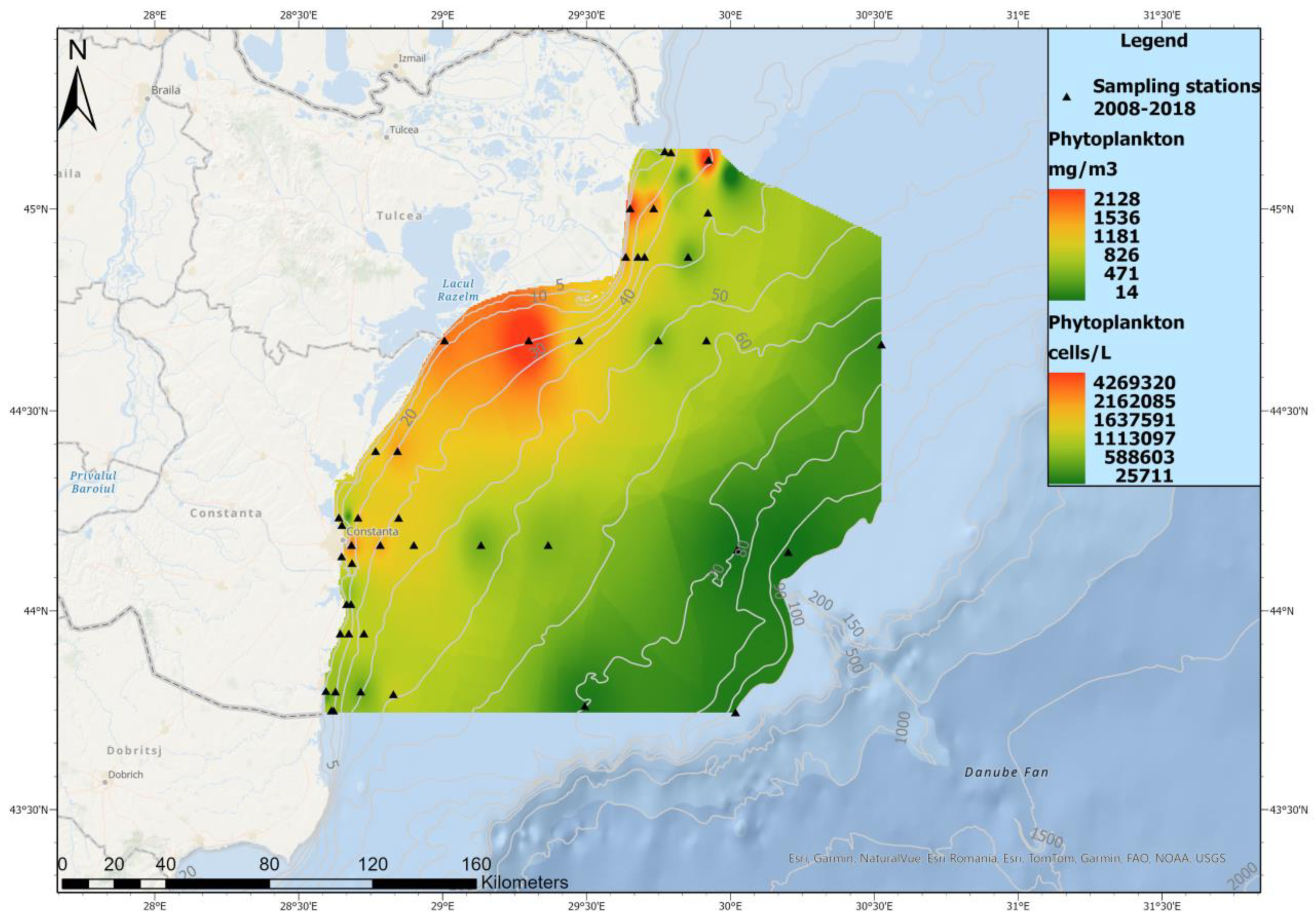
3.2. Phytoplankton Spatial Distribution in 2008–2018
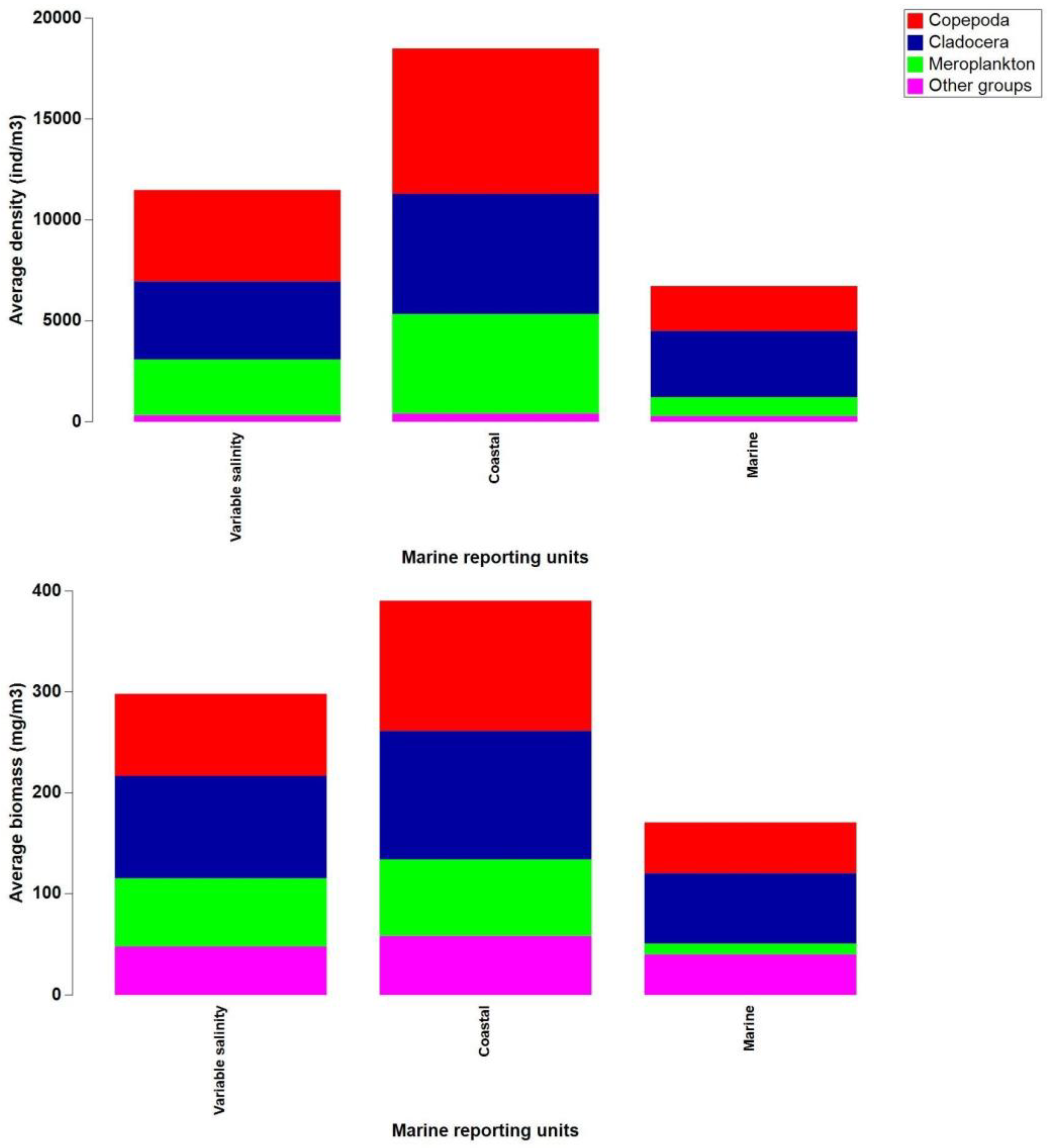
3.3. Zooplankton Spatial Distribution in 2008–2018
3.4. Semi-Quantitative Models of the Causal Relationships between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton and Physico-Chemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irigoien, X.; Huisman, J.; Harris, R.P. Global Biodiversity Patterns of Marine Phytoplankton and Zooplankton. Nature 2004, 429, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.F.; Karl, D.M. Genomic Perspectives in Microbial Oceanography. Nature 2005, 437, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ding, D.; Gu, T.; Jiang, T.; Qu, K.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z. Different Responses of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Communities to Current Changing Coastal Environments. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, P. Role of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton as Health Indicators of Aquatic Ecosystem: A Review. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2013, 2, 489–500. [Google Scholar]
- Onyema, I.C.; Lawal-Are, A.O.; Bassey, T.A.; Bassey, O.B. Water Quality Parameters, Chlorophyll a and Zooplankton of an Estuarine Creek in Lagos. J. Am. Sci. 2009, 5, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, G.; Richardson, A.; Robinson, C. Climate Change and Marine Plankton. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.D.; Irwin, A.J.; Finkel, Z.V.; Stock, C.A. Anthropogenic Climate Change Drives Shift and Shuffle in North Atlantic Phytoplankton Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2964–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.; Richardson, A.J. Impact of Climate Change on Marine Pelagic Phenology and Trophic Mismatch. Nature 2004, 430, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Pei, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, C. Harvesting of a Phytoplankton-Zooplankton Model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 3608–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, D. The Ecology of the Fish Pond Ecosystem with Special Reference to Africa; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Tas, B.; Gonulol, A. An Ecologic and Taxonomic Study on Phytoplankton of a Shallow Lake, Turkey. J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 28, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, J.J.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Nandini, S. Seasonal Changes in the Rotifer (Rotifera) Diversity from a Tropical High Altitude Reservoir (Valle de Bravo, Mexico). J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandran, R.; Jaiswar, A.K.; Raizada, S.; Mandal, S.; Mayekar, T.S.; Bisht, A.S.; Singh, S.K.; Mohindra, V.; Lal, K.K.; Tyagi, L.K. Plankton Dynamics and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors Shape Fish Community Structure in Fluvial Ecosystem: A Case Study. Indian J. Fish. 2021, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Zanre, E.; Gray, S. Fuzzy Cognitive Maps as Representations of Mental Models and Group Beliefs. In Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Applied Sciences and Engineering: From Fundamentals to Extensions and Learning Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, K.; Espitia, E.; Breuer, L.; Correa, A. Using Fuzzy Cognitive Maps to Promote Nature-Based Solutions for Water Quality Improvement in Developing-Country Communities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, L.; Jernberg, S.; Korn, P.; Puntila-Dodd, R.; Skyttä, A.; Vikström, S. Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping of Baltic Archipelago Sea Food Webs Reveals No Cliqued Views of the System Structure between Stakeholder Groups. Socio-Environ. Syst. Model. 2020, 2, 16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, A.C.; Samhouri, J.F.; Gray, S.; Martone, R.G.; Mach, M.E.; Halpern, B.S.; Kappel, C.V.; Scarborough, C.; Levin, P.S. Integrating Expert Perceptions into Food Web Conservation and Management. Conserv. Lett. 2017, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetter, A.J.; Kok, K. Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Futures Studies—A Methodological Assessment of Concepts and Methods. Futures 2014, 61, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özesmi, U.; Özesmi, S.L. Ecological Models Based on People’s Knowledge: A Multi-Step Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping Approach. Ecol. Model. 2004, 176, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.A.; Gray, S.; Cox, L.J.; Henly-Shepard, S. Mental Modeler: A Fuzzy-Logic Cognitive Mapping Modeling Tool for Adaptive Environmental Management. In Proceedings of the 2013 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Wailea, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2013; pp. 965–973. [Google Scholar]
- Stanev, E.V.; Peneva, E.; Chtirkova, B. Climate Change and Regional Ocean Water Mass Disappearance: Case of the Black Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 4803–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliozzi, C.; Palma, M.; Druon, J.-N.; Palialexis, A.; Abigail, M.-G.; Ioanna, V.; Rafael, G.-Q.; Elena, G.; Birgit, H.; Laura, B.; et al. Status of Pelagic Habitats within the EU-Marine Strategy Framework Directive: Proposals for Improving Consistency and Representativeness of the Assessment. Mar. Policy 2023, 148, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. (Ed.) State of the Environment of the Black Sea (2001-2006/7); Publications of the Commission on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution (BSC): Istanbul, Turkey, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Konovalov, S.K.; Murray, J.W. Variations in the Chemistry of the Black Sea on a Time Scale of ž/Decades 1960–1995. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 31, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, L.-I.; Tanase, V.-M.; Rusu, E. An Evaluation of the Wind Energy along the Romanian Black Sea Coast. Inventions 2023, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailov, M.E.; Tomescu-Chivu, M.I.; Dima, V. Black Sea Water Dynamics on the Romanian Littoral—Case Study: The Upwelling Phenomena. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2012, 64, 232–245. [Google Scholar]
- Lazăr, L. (Ed.) Anthropogenic Pressures and Impacts on the Black Sea Coastal Ecosystem; CD Press: Constanta, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lazăr, L. (Ed.) Impact of the Rivers on the Black Sea Ecosystem; CD Press: Constanta, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moncheva, S.; Parr, B. Manual for Phytoplankton Sampling and Analysis in the Black Sea; Black Sea Commission: Istanbul, Turkey, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kisselew, I.A. Dinoflagellata; Fauna URSS: Moscova, Russia, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Proshkina-Lavrenko, A.I. (Ed.) Planktonic Diatoms from the Black Sea; Fauna URSS: Moscova, Russia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Carmelo, R.T. (Ed.) Identifying Marine Diatoms and Dinoflagellataes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, J. (Ed.) Dinoflagellatae, Rabenhorst’s Cryptogamen—Flora Leipzig II; Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft M. B. H.: Leipzig, Germany, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Moncheva, S.; Doncheva, V.; Boicenco, L.; Sahin, F.; Slabakova, N.; Culcea, O. Report on the MISIS Cruise Intercalibration Exercise: Phytoplankton; Ex. Ponto: Constanta, Romania, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, G.E. (Ed.) A Treatise on Limnology. In Introduction to Lake Biology and the Limnoplankton; J. Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, B.; Arashkevich, E.; Gubanova, A.; Korshenko, A. Manual for Mesozooplankton Sampling and Analysis in the Black Sea Monitoring; Black Sea Commission: Istanbul, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mordukhay-Boltovskoy, F.D. (Ed.) Identification Manual on the Fauna of the Black and Azov Seas; Naukova Dumka Pub: Kiev, Ukraine, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Mordukhay-Boltovskoy, F.D. (Ed.) Guide of the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov Fauna; Naukova Dumka Pub: Kiev, Ukraine, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Petipa, T.S. On the Mean Weight of the Principle Forms of Zooplankton in the Black Sea. Sevast. Biol. Station 1957, 9, 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) Methods of Seawater Analysis; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mullin, J.B.; Riley, J.P. The Spectrophotometric Determination of Nitrate in Natural Waters, with Particular Reference to Sea-Water. Anal. Chim. Acta 1955, 12, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis, 3rd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Addinsoft, Inc. Addinsoft XLSTAT Software; Version 2021.2.1; Addinsoft, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- TIBCO Software, Inc. TIBCO Statistica; Version 14.0.1.25; TIBCO Software, Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ESRI. ArcGIS Desktop; Version 10.7; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mamoori, S.K.; Al-Maliki, L.A.; Al-Sulttani, A.H.; El-Tawil, K.; Al-Ansari, N. Statistical Analysis of the Best GIS Interpolation Method for Bearing Capacity Estimation in An-Najaf City, Iraq. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.; Lewis, S.; Kurniasih, E.; Prabuning, D.; Faiqoh, E. Plankton Biomass Models Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Predicting Marine Megafauna Hotspots in the Solor Waters. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 47, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytan, U.; Senturk, Y. Dynamics of Noctiluca Scintillans (Macartney) Kofoid & Swezy and Its Contribution to Mesozooplankton in the Southeastern Black Sea. Aquat. Sci. Eng. 2018, 33, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollevier, A.; Mortelmans, J.; Aubert, A.; Deneudt, K.; Vandegehuchte, M.B. Noctiluca Scintillans: Dynamics, Size Measurements and Relationships with Small Soft-Bodied Plankton in the Belgian Part of the North Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 777999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonda Umani, S. Noctiluca Scintillans MACARTNEY in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Long-Term Dynamics, Relationships with Temperature and Eutrophication, and Role in the Food Web. J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrächter, M.; Qi, Z. Aspects of Noctiluca (Dinophyceae) Population Dynamics. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Turkoglu, M. Red Tides of the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca Scintillans Associated with Eutrophication in the Sea of Marmara (the Dardanelles, Turkey). Oceanologia 2013, 55, 709–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaguchi, H.; Fujiki, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Toda, T. Relationship between the Bloom of Noctiluca Scintillans and Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters of Sagami Bay, Japan. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. Biomass, Feeding and Production of Noctiluca Scintillans in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihnea, P.E. Qualitative and Quantitative Aspects of the Alga Eutreptia Lanowii (Steuer) in Relation to the Coastal Pollution Phenomenon. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 1978, 11, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bartram, J.; Balance, R. (Eds.) Water Quality Monitoring: A Practical Guide to the Design Implementation of Freshwater Quality Studies and Monitoring Programmes; TJ Press: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gogoi, P.; Sinha, A.; Das Sarkar, S.; Chanu, T.N.; Yadav, A.K.; Koushlesh, S.K.; Borah, S.; Das, S.K.; Das, B.K. Seasonal Influence of Physicochemical Parameters on Phytoplankton Diversity and Assemblage Pattern in Kailash Khal, a Tropical Wetland, Sundarbans, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmakh, L.; Kovrigina, N.; Gorbunova, T. Phytoplankton Seasonal Dynamics under Conditions of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Pollution in the Western Coastal Waters of the Black Sea (Sevastopol Region). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.; Parveen, S.; Khan, A.A.; Kabir, H.A.; Mola, H.R.A.; Ganai, A.H. Zooplankton Population in Relation to Physico-Chemical Factors of a Sewage Fed Pond of Aligarh (UP), India. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Limbu, S.M.; Kyewalyanga, M.S. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Composition and Biomass in Coral Reef Areas around Unguja, Zanzibar, Tanzania. Springerplus 2015, 4, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyewalyanga, M.S. Seasonality in Phytoplankton Species Composition and Their Influence on Small Pelagic Fish along the Western Pemba Channel. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2022, 48, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Thirumala, S.; Ravind, H.B. Zooplankton Diversity and Its Relationship with Physico-Chemical Parameters in Kundavada Lake, of Davangere District. ProEnviron. Promediu 2011, 4, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U.; Padisák, J.; Reynolds, C.S.; Juhász-Nagy, P. Hutchinson’s Heritage: The Diversity-Disturbance Relationship in Phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 1993, 249, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talling, J.E. The Phytoplankton of Lake Victoria (East Africa). Arch. Hydrobiol. 1987, 25, 229–256. [Google Scholar]
- Pijanowska, J. Cyclomorphosis in Daphnia: An Adaptation to Avoid Invertebrate Predation. Hydrobiologia 1990, 198, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.H. Seasonal and Spatial Variation of Phytoplankton Assemblages, Biomass and Cell Size from Spring to Summer across the North-Eastern New Zealand Continental Shelf. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, A.L.; Cobb, T.P.; Vinebrooke, R.D. Effects of Experimental Greenhouse Warming on Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Communities in Fishless Alpine Ponds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarbalz, F.M.; Henry, N.; Brandão, M.C.; Martini, S.; Busseni, G.; Byrne, H.; Coelho, L.P.; Endo, H.; Gasol, J.M.; Gregory, A.C.; et al. Global Trends in Marine Plankton Diversity across Kingdoms of Life. Cell 2019, 179, 1084–1097.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Folt, C.L. Consequences of Fall Warming for Zooplankton over Wintering Success. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buana, S.; Tambaru, R.; Selamat, M.B.; Lanuru, M.; Massinai, A. The Role of Salinity and Total Suspended Solids (TSS) to Abundance and Structure of Phytoplankton Communities in Estuary Saddang Pinrang. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 860, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parab, S.G.; Matondkar, S.G.P.; Gomes, H.d.R.; Goes, J.I. Effect of Freshwater Influx on Phytoplankton in the Mandovi Estuary (Goa, India) during Monsoon Season: Chemotaxonomy. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhudessai, S.S.; Vishal, C.R.; Rivonker, C.U. Antonymous Nature of Freshwater Phytoplankton in the Tropical Estuarine Environments of Goa, Southwest Coast of India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 32, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.A.M.; Lewandowska, A.M. Zooplankton Dominance Shift in Response to Climate-Driven Salinity Change: A Mesocosm Study. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 861297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Mills, M.M.; Arrigo, K.R.; Berman-Frank, I.; Bopp, L.; Boyd, P.W.; Galbraith, E.D.; Geider, R.J.; Guieu, C.; Jaccard, S.L.; et al. Processes and Patterns of Oceanic Nutrient Limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Miralto, A.; Poulet, S.A.; Carotenuto, Y.; Buttino, I.; Romano, G.; Casotti, R.; Pohnert, G.; Wichard, T.; Colucci-D’Amato, L.; et al. Aldehyde Suppression of Copepod Recruitment in Blooms of a Ubiquitous Planktonic Diatom. Nature 2004, 429, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Caldwell, G.S.; Casotti, R.; Cembella, A.D.; Engström-Öst, J.; Halsband, C.; Sonnenschein, E.; Legrand, C.; Llewellyn, C.A.; et al. The Relevance of Marine Chemical Ecology to Plankton and Ecosystem Function: An Emerging Field. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcelos Ramos, E.J.; Schulz, K.G.; Voss, M.; Narciso, Á.; Müller, M.N.; Reis, F.V.; Cachão, M.; Azevedo, E.B. Nutrient-Specific Responses of a Phytoplankton Community: A Case Study of the North Atlantic Gyre, Azores. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redden, A.M.; Rukminasari, N. Effects of Increases in Salinity on Phytoplankton in the Broadwater of the Myall Lakes, NSW, Australia. Hydrobiologia 2008, 608, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, A.J.; Finkel, Z.V.; Schofield, O.M.E.; Falkowski, P.G. Scaling-up from Nutrient Physiology to the Size-Structure of Phytoplankton Communities. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K. Physical Oceanography, Food Chains, and Fish Stocks: A Review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1993, 50, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, H.G. Evolutionary Adaptation of Marine Zooplankton to Global Change. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Berglund, E.C.; Engström, P.; Berggren, F.; Eklund, J.; Harðardóttir, S.; Lundholm, N.; Grebner, W.; Andersson, M.X. Copepods Drive Large-Scale Trait-Mediated Effects in Marine Plankton. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaat5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMott, W.R.; Moxter, F. Foraging Cyanobacteria by Copepods: Responses to Chemical Defense and Resource Abundance. Ecology 1991, 72, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kate, B.N.; Banerjee, U.C. Bioactive Compounds from Cyanobacteria and Microalgae: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.A.; Martínez, R.A.; Escribano, R.; Lagos, N.A. Seasonal Relative Influence of Food Quantity, Quality, and Feeding Behaviour on Zooplankton Growth Regulation in Coastal Food Webs. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, U.; Pandey, J. Enhanced Production of δ-Aminolevulinic Acid, Bilipigments, and Antioxidants from Tropical Algae of India. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogfors, H.; Motwani, N.H.; Hajdu, S.; El-Shehawy, R.; Holmborn, T.; Vehmaa, A.; Engström-Öst, J.; Brutemark, A.; Gorokhova, E. Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Support Copepod Reproduction and Development in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Work, K.A.; Havens, K.E. Zooplankton Grazing on Bacteria and Cyanobacteria in a Eutrophic Lake. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.-E. A Numerical Study of the Effect of Periodic Nutrient Supply on Pathways of Carbon in a Coastal Upwelling Regime. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 491–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.D.D.A.; Quintanilha, J.; Monteiro-Ribas, W.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, E.; Coutinho, R. Seasonal and Interannual Coupling between Sea Surface Temperature, Phytoplankton and Meroplankton in the Subtropical South-Western Atlantic Ocean. J. Plankton Res. 2012, 34, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Pinedo, S.; Sardá, R. Grazing by Meroplanktonic Polychaete Larvae May Help to Control Nanoplankton in the NW Mediterranean Littoral: In Situ Experimental Evidence. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 143, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.G.; Christy, J.H. Planktivorous Fishes as Selective Agents for Reproductive Synchrony. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 209, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.; Beaugrand, G.; Lindley, J.; Richardson, A.; Edwards, M.; Reid, P. Climate Effects and Benthic; Pelagic Coupling in the North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 330, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.R.; Beaugrand, G.; Lindley, J.A. Climate-induced Effects on the Meroplankton and the Benthic-pelagic Ecology of the North Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkin, V.A.; Pautova, L.A.; Giordano, M.; Chasovnikov, V.K.; Vostokov, S.V.; Podymov, O.I.; Pakhomova, S.V.; Moskalenko, L.V. Drivers of Phytoplankton Blooms in the Northeastern Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodeanu, N.; Andrei, C.; Boicenco, L.; Popa, L.; Sburlea, A. A new trend of the phytoplankton structure and dynamics in the Romanian marine waters. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2004, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Velikova, V.; Moncheva, S.; Petrova, D. Phytoplankton Dynamics and Red Tides (1987–1997) in the Bulgarian Black Sea. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncheva, S.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Krastev, A. Phytoplankton Blooms in Black Sea and Mediterranean Coastal Ecosystems Subjected to Anthropogenic Eutrophication: Similarities and Differences. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 53, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, D.H. Plankton Production and Year-Class Strength in Fish Populations: An Update of the Match/Mismatch Hypothesis. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1990, 26, 249–293. [Google Scholar]
- Henson, S.A.; Robinson, I.; Allen, J.T.; Waniek, J.J. Effect of Meteorological Conditions on Interannual Variability in Timing and Magnitude of the Spring Bloom in the Irminger Basin, North Atlantic. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Chai, F. Impacts of the Unique Landfall Typhoons Damrey on Chlorophyll-a in the Yellow Sea off Jiangsu Province, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 39, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Zhu, L.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, S. Phytoplankton Blooms and Its Influencing Environmental Factors in the Southern Yellow Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.; Niu, X. Effect of Water Temperature on the Dynamic Behavior of Phytoplankton–Zooplankton Model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 378, 125211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, L.; Boicenco, L.; Pantea, E.; Timofte, F.; Vlas, O.; Bișinicu, E. Modeling Dynamic Processes in the Black Sea Pelagic Habitat—Causal Connections between Abiotic and Biotic Factors in Two Climate Change Scenarios. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bișinicu, E.; Abaza, V.; Cristea, V.; Harcotă, G.E.; Lazar, L.; Tabarcea, C.; Timofte, F. The Assessment of the Mesozooplankton Community from the Romanian Black Sea Waters and the Relationship to Environmental Factors. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2021, 51, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, L.; Boicenco, L.; Marin, O.; Culcea, O.; Pantea, E.; Bișinicu, E.; Timofte, F.; Mihailov, M.-E. Black Sea Eutrophication Dynamics from Causes to Effects. Cercet. Mar. Rech. Mar. 2018, 48, 100–117. [Google Scholar]




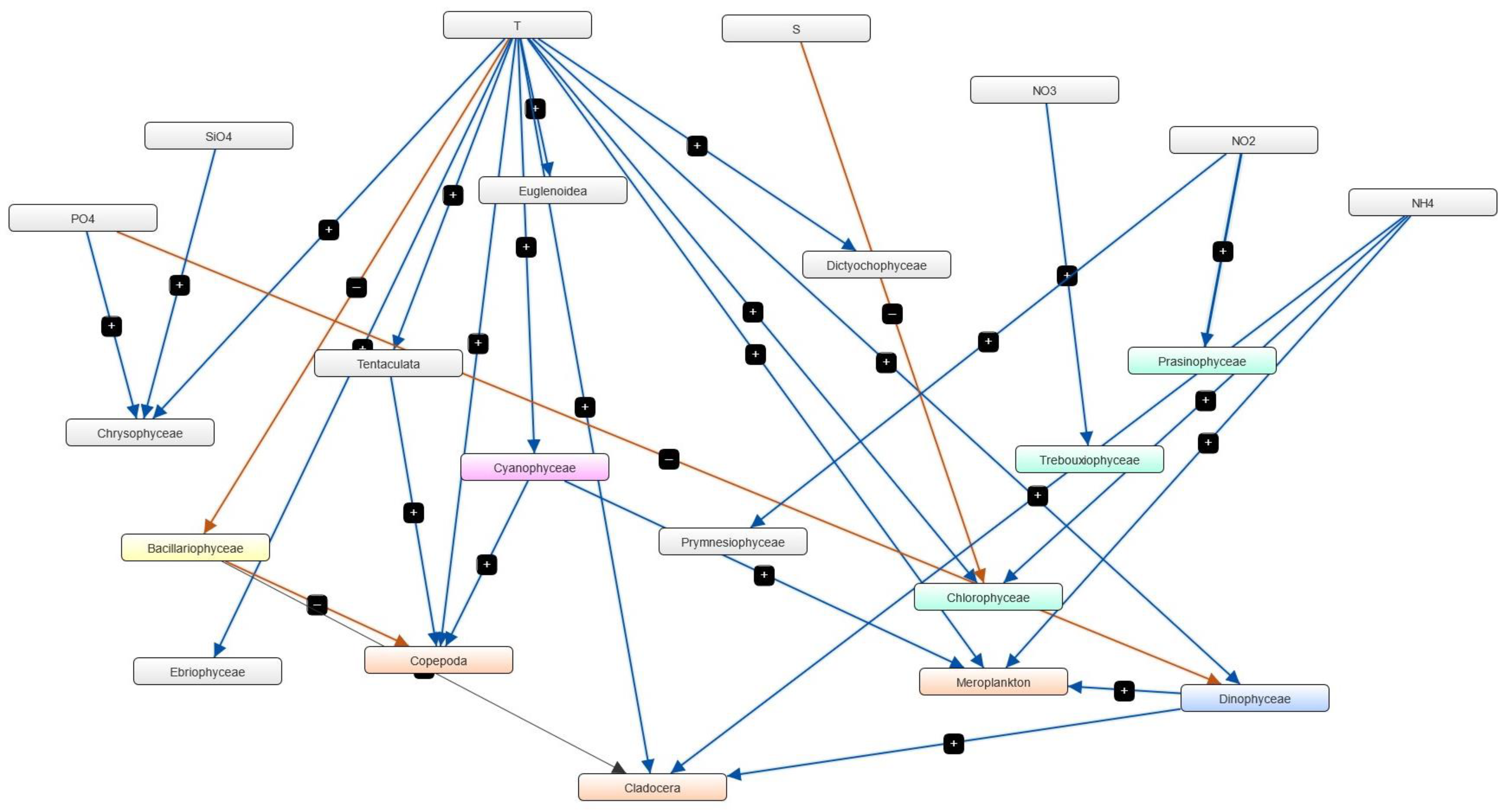

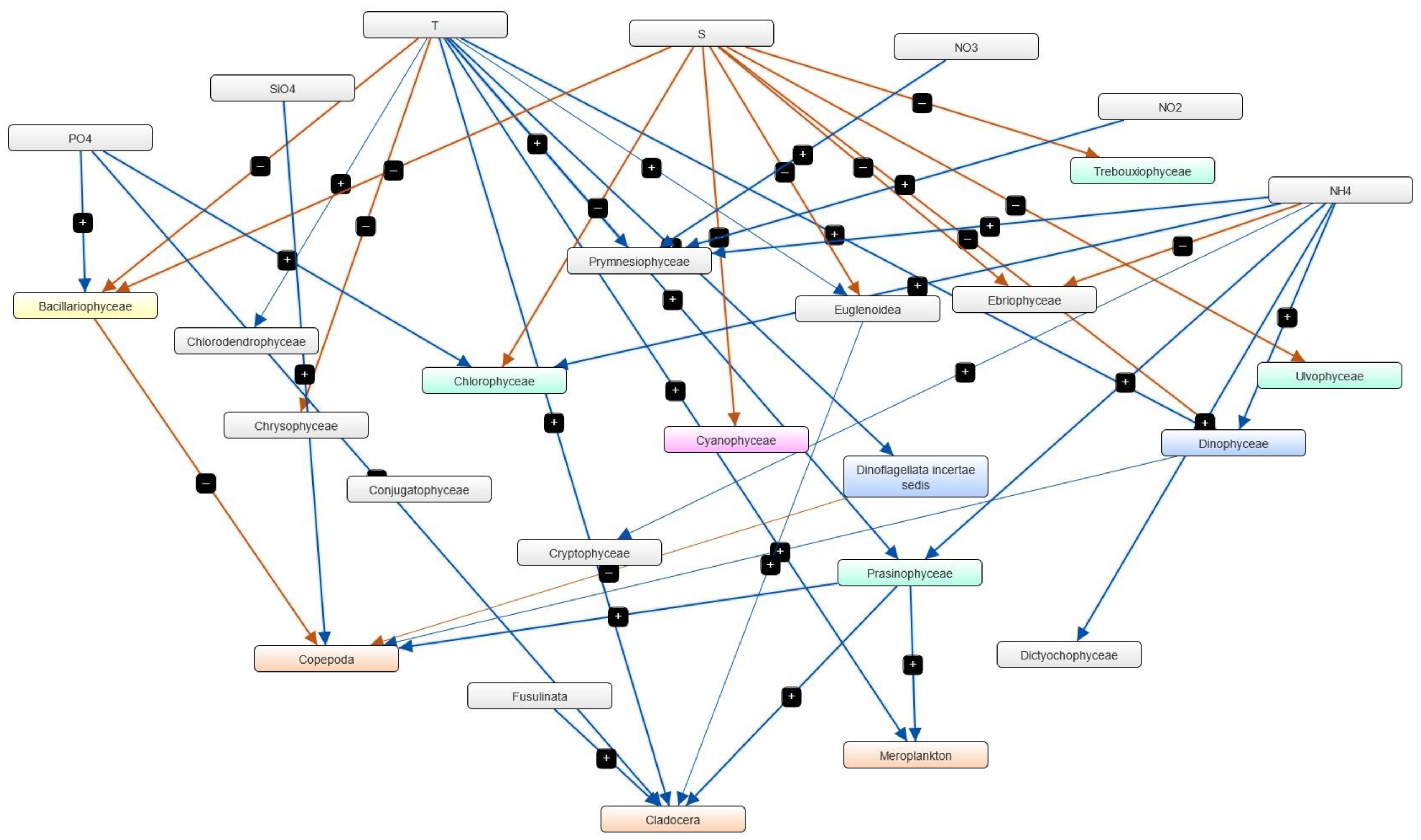

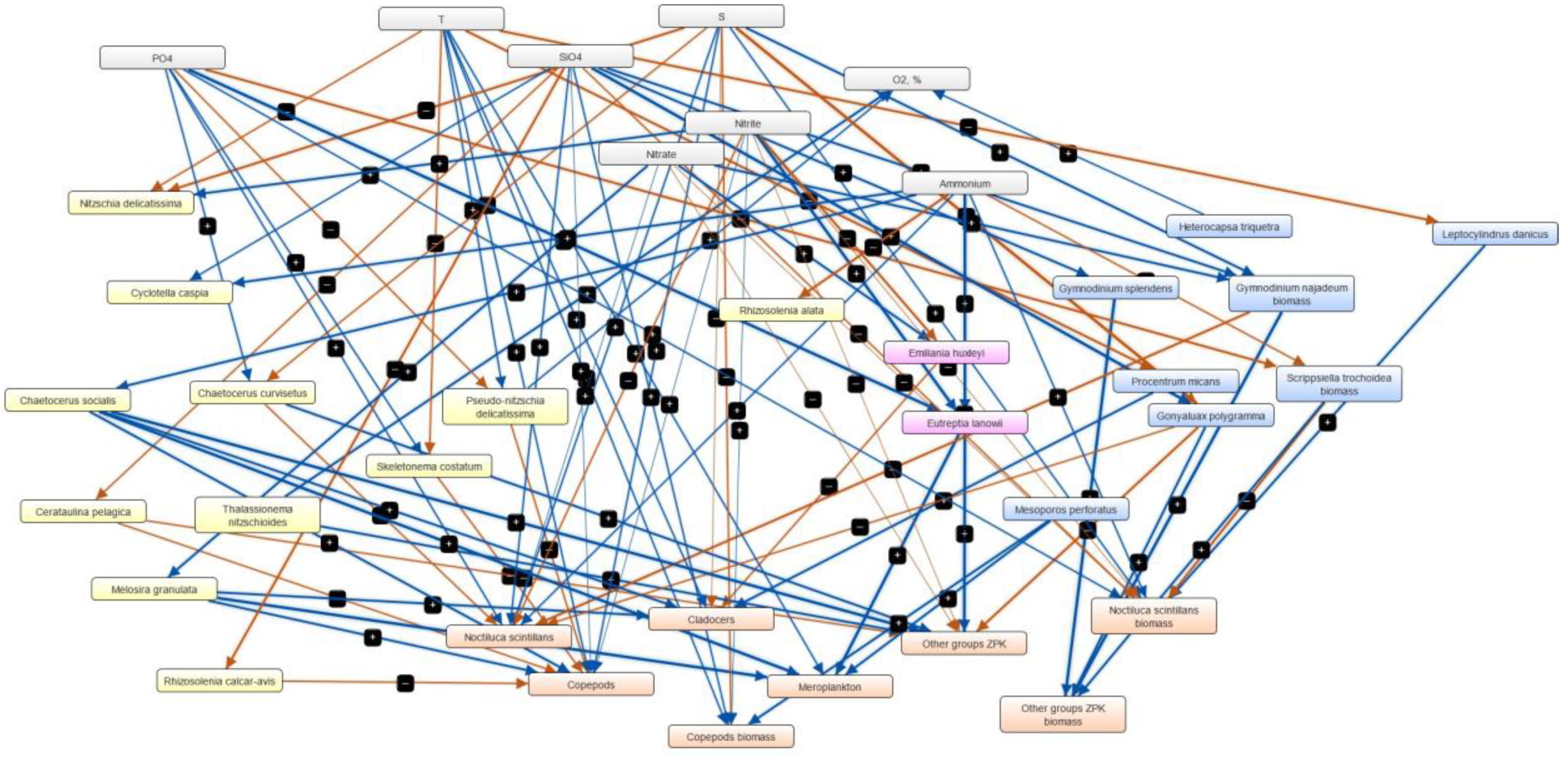
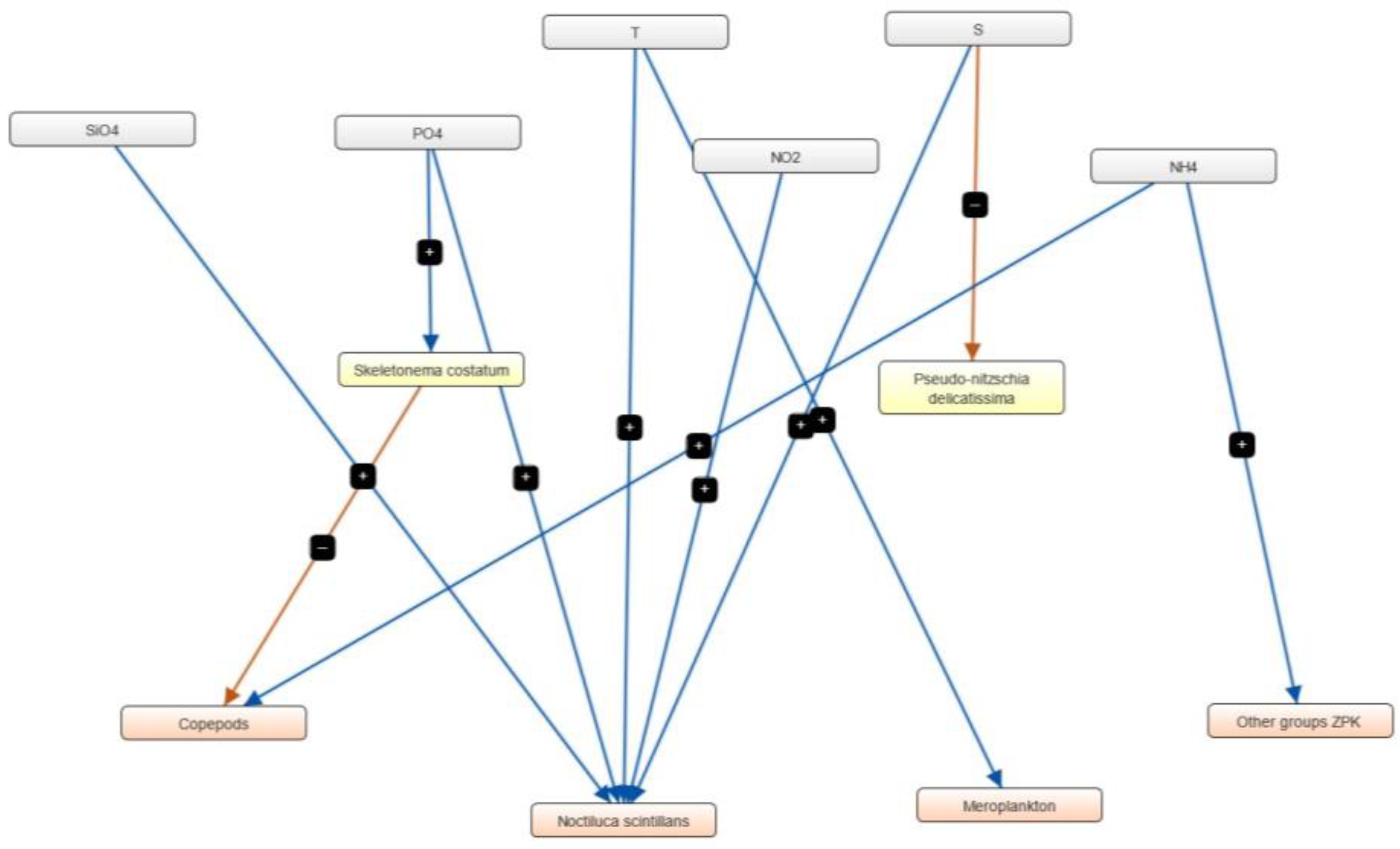
| Marine Reporting Unit | Variable Salinity | Coastal | Marine |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 97 | 172 | 193 |
| Total components | 22 | 24 | 27 |
| Total connections | 28 | 35 | 36 |
| Drivers—Components in a system that affect other components and which are not affected by other parts of the system | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| Receiver—Components in a system that are affected by other components and do not affect other parts of the system | 11 | 12 | 12 |
| Ordinary—both influenced and influencing components | 4 | 4 | 7 |
| Complexity score | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bișinicu, E.; Boicenco, L.; Pantea, E.; Timofte, F.; Lazăr, L.; Vlas, O. Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea. Phycology 2024, 4, 168-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010010
Bișinicu E, Boicenco L, Pantea E, Timofte F, Lazăr L, Vlas O. Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea. Phycology. 2024; 4(1):168-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBișinicu, Elena, Laura Boicenco, Elena Pantea, Florin Timofte, Luminița Lazăr, and Oana Vlas. 2024. "Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea" Phycology 4, no. 1: 168-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010010
APA StyleBișinicu, E., Boicenco, L., Pantea, E., Timofte, F., Lazăr, L., & Vlas, O. (2024). Qualitative Model of the Causal Interactions between Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, and Environmental Factors in the Romanian Black Sea. Phycology, 4(1), 168-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4010010








