Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Spondin-Like and Fasciclin-Like Genes in Neopyropia yezoensis, A Marine Red Alga
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Materials and Treatments
2.2. Transcriptional Analysis of NySPL and NyFAL Genes
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Spondin Domain-Containing Proteins
3.2. Characterization of Fasciclin Domain-Containing Proteins
3.3. Expression Profiles of NySPL Genes at Different Developmental Stages
3.4. Expression Profiles of NyFAL Genes at Different Developmental Stages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hynes, R.O. The Extracellular Matrix: Not Just Pretty Fibrils. Science 2009, 326, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Turnbull, J.; Guimond, S. Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: The dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 209, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloareg, B.; Badis, Y.; Cock, J.M.; Michel, G. Role and Evolution of the Extracellular Matrix in the Acquisition of Complex Multicellularity in Eukaryotes: A Macroalgal Perspective. Genes 2021, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Poza, S.; Leandro, A.; Cotas, C.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The Evolution Road of Seaweed Aquaculture: Cultivation Technologies and the Industry 4.0. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Bio. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.J.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harburger, D.S.; Calderwood, D.A. Integrin signalling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drew, K. Life-history of Porphyra. Nature 1954, 173, 1243–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurogi, M. Study of the life-history of Porphyra. I. The germination and development of carpospores. Bull. Tohoku Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1953, 2, 67–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, L.S.; Craigie, J.S.; Brown, R.G. Chemical composition and structure of the cell walls of the conchocelis and thallus phases of Porphyra tenera (Rhodophyceae). J. Phycol. 1981, 17, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingson, J.; Nelson, W. Cell wall polysaccharides are informative in Porphyra species taxonomy. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.; Carol, C.M.; Reid, P.E.; Sheath, R.G. Comparative studies on the cell walls of sexual and asexual Bangia atropurpurea (Rhodophyta). I. Histochemistry of polysaccharides. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.; Park, C.M.; Reid, P.E. Comparative studies on the cell walls of sexual and asexual Bangia atropurpurea (Rhodophyta). II. Electrophoretic patterns of polysaccharides. J. Phycol. 1986, 22, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Ojima, N.; Yasuike, M.; Shigenobu, Y.; Satomi, M.; Fukuma, Y.; Shiwaku, K.; Tsujimoto, A.; et al. The first symbiont-free genome sequence of marine red alga, susabi-nori (Pyropia yezoensis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brawley, S.H.; Blouin, N.A.; Ficko-Blean, E.; Wheeler, G.L.; Lohr, M.; Goodson, H.V.; Jenkins, J.W.; Blaby-Haas, C.E.; Helliwell, K.E.; Chan, C.X.; et al. Insights into the red algae and eukaryotic evolution from the genome of Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiophyceae, Rhodophyta). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6361–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Xu, K.P.; Yu, X.Z.; Bi, G.Q.; Liu, Y.; Kong, F.N.; Sun, P.P.; Tang, X.H.; Du, G.Y.; Ge, Y.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of Pyropia haitanensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feinstein, Y.; Borrell, V.; Garcia, C.; Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Tzarfaty, V.; Frumkin, A.; Nose, A.; Okamoto, H.; Higashijima, S.; Soriano, E.; et al. F-spondin and mindin: Two structurally and functionally related genes expressed in the hippocampus that promote outgrowth of embryonic hippocampal neurons. Development 1999, 126, 3637–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashijima, S.; Nose, A.; Eguchi, G.; Hotta, Y.; Okamoto, H. Mindin/F-spondin family: Novel ECM proteins expressed in the zebrafish embryonic axis. Dev. Biol. 1997, 192, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umemiya, T.; Takeichi, M.; Nose, A. M-spondin, a novel ECM protein highly homologous to vertebrate F-spondin, is localized at the muscle attachment sites in the Drosophila embryo. Dev. Biol. 1997, 186, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.; Lawler, J. The structure of the Ca2+-binding, glycosylated F-spondin domain of F-spondin—A C2-domain variant in an extracellular matrix protein. BMC Struct. Biol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klar, A.; Baldassare, M.; Jessell, T.M. F-spondin—A gene expressed at high-levels in the floor plate encodes a secreted protein that promotes neural cell-adhesion and neurite extension. Cell 1992, 69, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaba, A.R.I.; Cox, C.; Jessell, T.M.; Klar, A. Ectopic neural expression of a floor plate marker in frog embryos injected with the midline transcription factor Pintallavis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8268–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzarfati-Majar, V.; Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Klar, A. F-spondin is a contact-repellent molecule for embryonic motor neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4722–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seifert, G.J. Fascinating Fasciclins: A surprisingly widespread family of proteins that mediate interactions between the cell exterior and the cell surface. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastiani, M.J.; Harrelson, A.L.; Snow, P.M.; Goodman, C.S. Expression of fasciclin I and II glycoproteins on subsets of axon pathways during neuronal development in the grasshopper. Cell 1987, 48, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Shanley, J. Altered nerve terminal arborization and synaptic transmission in Drosophila mutants of cell adhesion molecule fasciclin I. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6679–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Jeong, H.W.; Nam, J.O.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, R.W.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, I.S. Identification of motifs in the fasciclin domains of the transforming growth factor-β-induced matrix protein βig-h3 that interact with the αvβ5 integrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46159–46165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seifert, G.J.; Roberts, K. The biology of arabinogalactan proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, M.A.; Geng, L.L.; Zhao, J. The fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein gene, FLA3, is involved in microspore development of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2010, 64, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Kibble, N.A.J.; Bacic, A.; Schultz, C.J. A Fasciclin-Like Arabinogalactan-Protein (FLA) Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana, fla1, Shows Defects in Shoot Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.; Pereira, A.M.; Pinto, S.C.; Silva, J.; Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S. In silico and expression analyses of fasciclin-like arabinogalactan proteins reveal functional conservation during embryo and seed development. Plant Reprod. 2019, 32, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Kim, Y.; Guo, Y. The Arabidopsis SOS5 locus encodes a putative cell surface adhesion protein and is required for normal cell expansion. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, D.; Tian, L.; Debrosse, T.; Poirier, E.; Emch, K.; Herock, H.; Travers, A.; Showalter, M.A. Glycosylation of a fasciclin-like arabinogalactan-protein (SOS5) mediates root growth and seed mucilage adherence via a cell wall receptor-like kinase (FEI1/FEI2) pathway in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashagre, A.H.; Zaltzman, D.; Idan-Molakandov, A.; Romano, H.; Tzfadia, O.; Harpaz-Saad, S. FASCICLIN-LIKE 18 is a new player regulating root elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 645286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, N.J. Bangiomorpha pubescens n. gen., n. sp.: Implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes. Paleobiology 2000, 26, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.M.; Shih, P.M.; Cumming, V.M.; Fischer, W.W.; Crockford, P.W.; Hodgskiss, M.S.W.; Worndle, S.; Creaser, R.A.; Rainbird, R.H.; Skulski, T.M.; et al. Precise age of Bangiomorpha pubescens dates the origin of eukaryotic photosynthesis. Geology 2018, 46, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuwano, K.; Aruga, Y.; Saga, N. Cryopreservation of clonal gametophytic thalli of Porphyra (Rhodophyta). Plant Sci. 1996, 116, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provasoli, L. Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In Culture and Collections of Algae, Proceedings of US-Japan Conference, Hakone, September 1966; Watanabe, A., Hattori, A., Eds.; Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists: Tokyo, Japan, 1968; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Uji, T.; Matsuda, R.; Takechi, K.; Takano, H.; Mizuta, H.; Takio, S. Ethylene regulation of sexual reproduction in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, T.; Mizuta, H. Treatment with heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibitors induces asexual life cycle in the marine red alga Neopyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6814–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, T.; Gondaira, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Mizuta, H.; Saga, N. Characterization and expression profiles of small heat shock proteins in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2019, 24, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Uji, T.; Takahashi, M.; Saga, N.; Mikami, K. Visualization of nuclear localization of transcription factors with cyan and green fluorescent proteins in the red alga Porphyra yezoensis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Kim, B.H.; Grishin, N.V. PROMALS3D: A tool for multiple protein sequence and structure alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, K.; Horton, P. PSORT: A program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999, 24, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.L.; Cao, C.Z.; Jia, W.; Yu, L.L.; Mo, M.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.P.; Lim, J.M.; Ishihara, M.; Wells, L.; et al. Structure of the F-spondin domain of mindin, an integrin ligand and pattern recognition molecule. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.L.; Jones, B.J.; Bacic, A.; Schultz, C.J. The fasciclin-like arabinogalactan proteins of Arabidopsis. A multigene family of putative cell adhesion molecules. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1911–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, B.H.; Park, R.W.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, I.S. Identification of motifs for cell adhesion within the repeated domains of transforming growth factor-beta-induced gene, beta ig-h3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30907–30915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.L.; Yan, C.C.; Li, H.M.; Wu, W.T.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.; Ma, H.L. Bioinformatics prediction and evolution analysis of arabinogalactan proteins in the plant kingdom. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.L.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the arabinogalactan protein gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2647–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, T.; Endo, H.; Mizuta, H. Sexual reproduction via a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid-dependent pathway through redox modulation in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, H.; Mizuta, H.; Uji, T. α-aminoisobutyric acid mimics the effect of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid to promote sexual reproduction in the marine red alga Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G.J.; Blaukopf, C. Irritable Walls: The Plant Extracellular Matrix and Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Cho, W. Roles of calcium ions in the membrane binding of C2 domains. Biochem. J. 2001, 359, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinstein, Y.; Klar, A. The neuronal class 2 TSR proteins F-spondin and Mindin: A small family with divergent biological activities. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, O.; Sumper, M. Algal-CAMs: Isoforms of a cell adhesion molecule in embryos of the alga Volvox with homology to Drosophila fasciclin I. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4212–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drew, K. Studies in the Bangioideae III. The Life-history of Porphyra umbilicalis (L.) Kütz. var. lociniata (Lightf.) J. Ag.: A. The Conchocelis-Phase in culture. Ann. Bot. 1954, 18, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.Y.; Kunieda, T.; Rogalski, J.; Foster, L.J.; Ellis, B.E.; Haughn, G.W. Identification and characterization of Arabidopsis seed coat mucilage proteins. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouriques, L.C.; Schmidt, E.C.; Bouzon, Z.L. The mechanism of adhesion and germination in the carpospores of Porphyra spiralis var. amplifolia (Rhodophyta, Bangiales). Micron 2012, 43, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.G.; Isaji, T.; Xu, Q.S.; Kariya, Y.; Gu, W.; Fukuda, T.; Du, Y.G. Potential roles of N-glycosylation in cell adhesion. Glycoconj. J. 2012, 29, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, M.E.; Litynska, A.; Vereecken, P. Cell migration-The role of integrin glycosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, R.; Sekine, N.; Mizuta, H.; Uji, T. Transcriptomic analysis under ethylene precursor treatment uncovers the regulation of gene expression linked to sexual reproduction in the dioecious red alga Pyropia pseudolinearis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3317–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
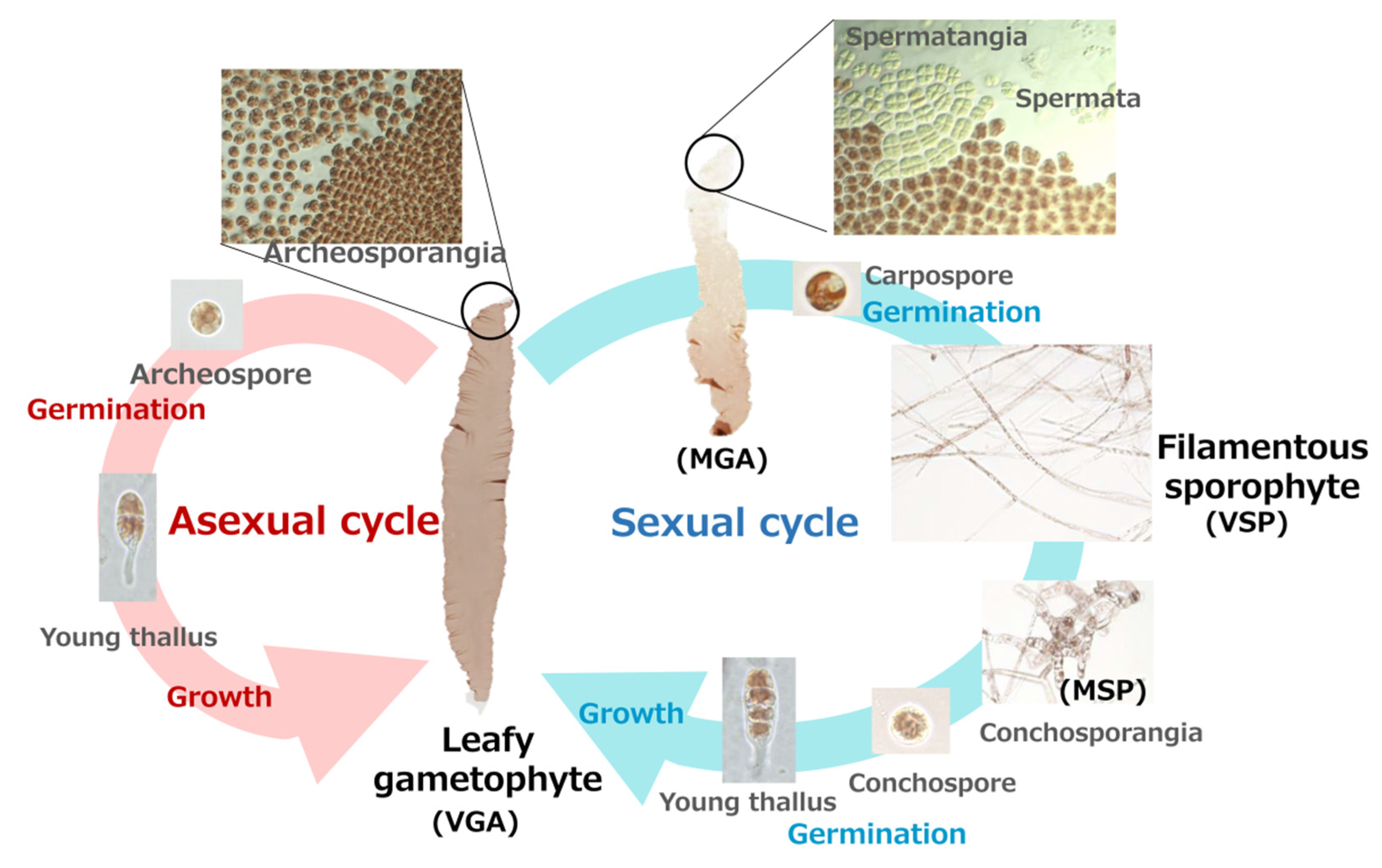
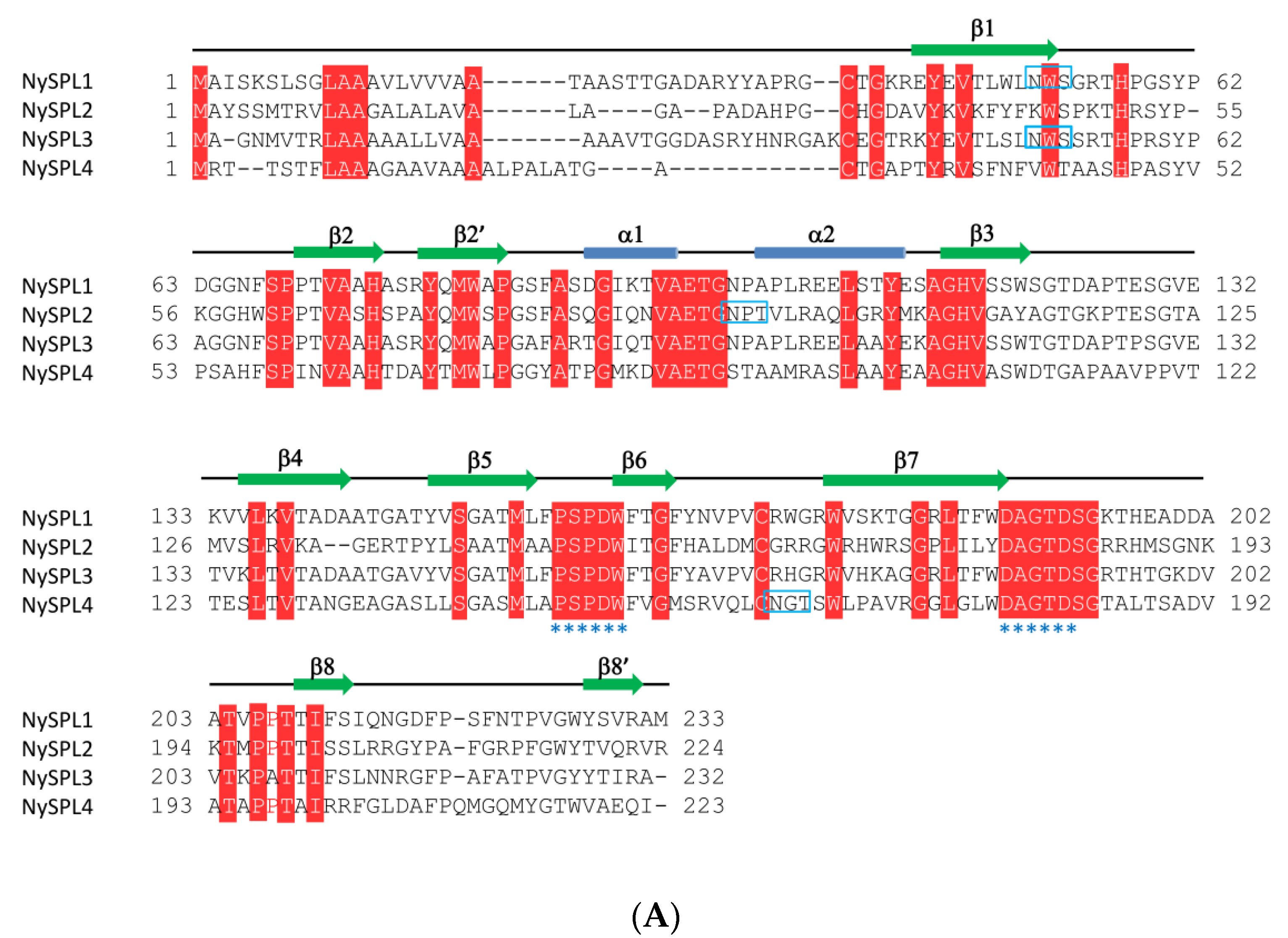
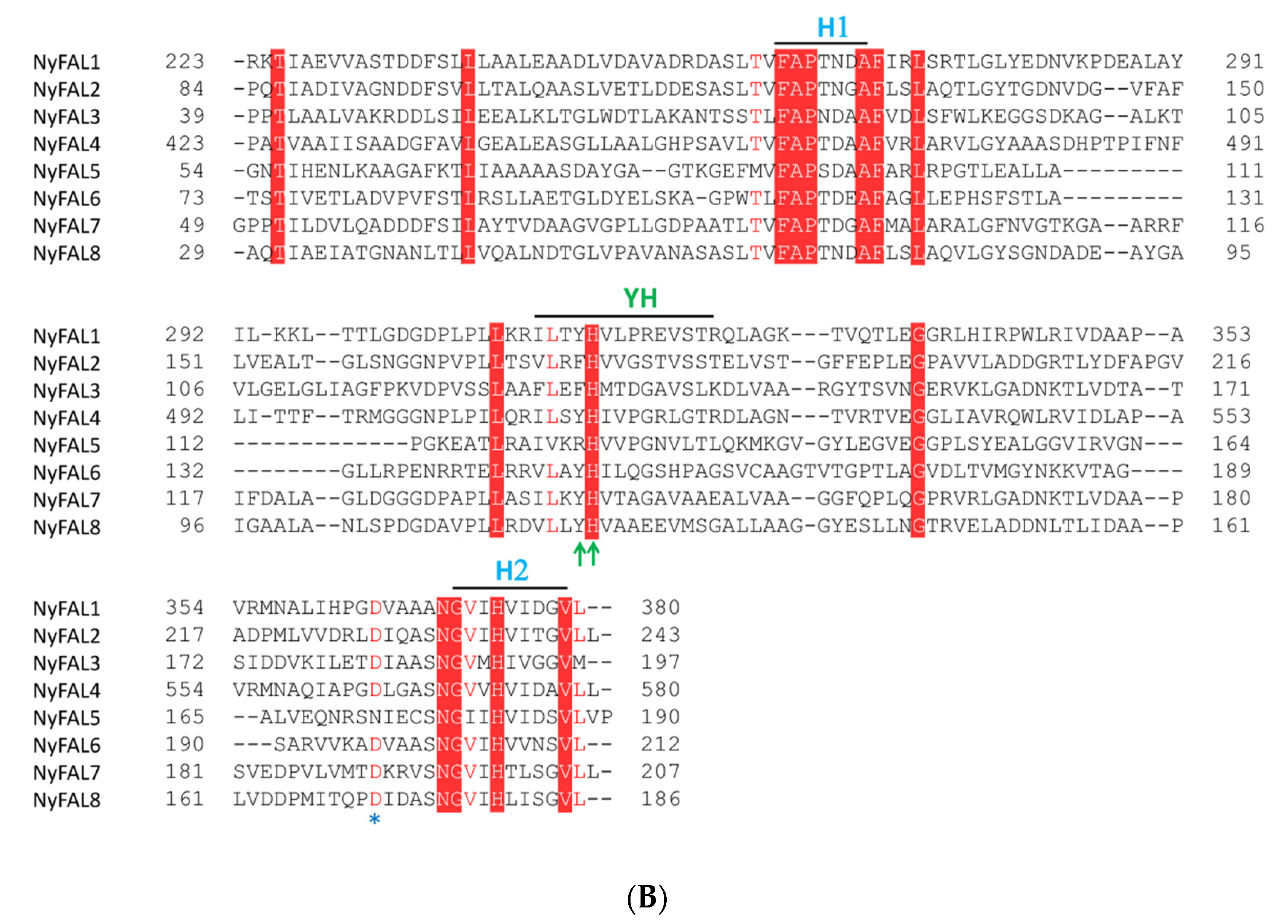


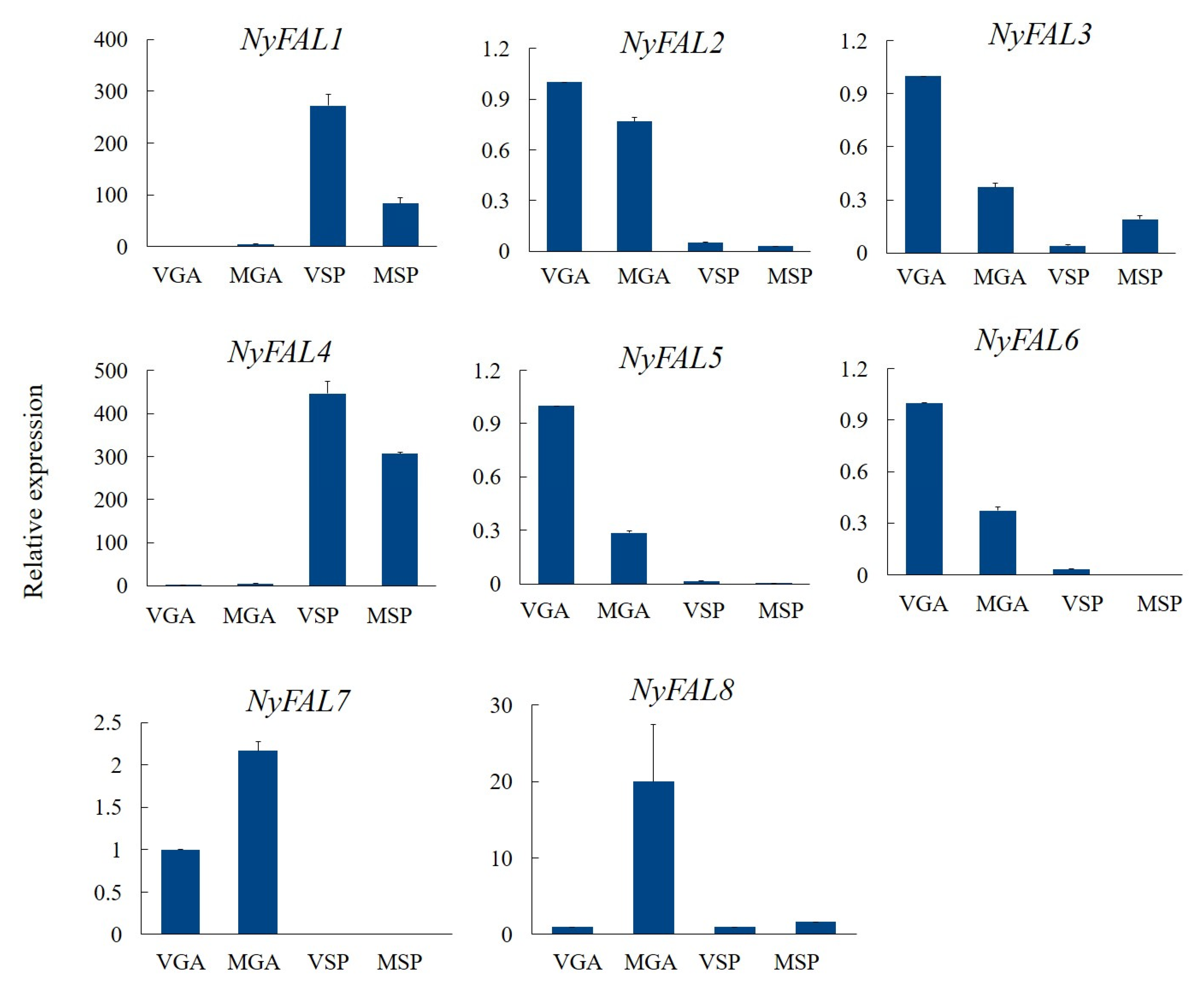
| Name | Contig ID | Size (aa) | pI | Mw (KDa) | Predicted Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NySPL1 | contig_17719_g4350 | 228 | 5.78 | 24.64 | extracellular |
| NySPL2 | contig_23899_g5890 | 223 | 10.37 | 24.18 | extracellular |
| NySPL3 | contig_29619_g7276 | 232 | 9.69 | 24.46 | extracellular |
| NySPL4 | contig_33564_g8106 | 224 | 5.13 | 22.55 | extracellular |
| Name | Contig ID | Size (aa) | pI | Mw (KDa) | Predicted Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NyFAL1 | contig_12094_g2891 | 414 | 8.59 | 43.5 | extracellular |
| NyFAL2 | contig_12570_g3010 | 1124 | 4.06 | 114.15 | membrane |
| NyFAL3 | contig_15884_g3808 | 204 | 5.37 | 20.89 | cytoplasmic |
| NyFAL4 | contig_23059_g5692 | 611 | 11.25 | 61.98 | membrane |
| NyFAL5 | contig_29738_g7294 | 336 | 8.98 | 34.6 | mitochondria |
| NyFAL6 | contig_33001_g7988 | 266 | 8.55 | 27.48 | endoplasmic reticulum |
| NyFAL7 | contig_38449_g8982 | 442 | 5.01 | 44.87 | mitochondria |
| NyFAL8 | contig_39761_g9180 | 406 | 4.54 | 40.53 | extracellular |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uji, T.; Ueda, S.; Mizuta, H. Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Spondin-Like and Fasciclin-Like Genes in Neopyropia yezoensis, A Marine Red Alga. Phycology 2022, 2, 45-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology2010003
Uji T, Ueda S, Mizuta H. Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Spondin-Like and Fasciclin-Like Genes in Neopyropia yezoensis, A Marine Red Alga. Phycology. 2022; 2(1):45-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleUji, Toshiki, Shinnosuke Ueda, and Hiroyuki Mizuta. 2022. "Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Spondin-Like and Fasciclin-Like Genes in Neopyropia yezoensis, A Marine Red Alga" Phycology 2, no. 1: 45-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology2010003
APA StyleUji, T., Ueda, S., & Mizuta, H. (2022). Identification, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of Spondin-Like and Fasciclin-Like Genes in Neopyropia yezoensis, A Marine Red Alga. Phycology, 2(1), 45-59. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology2010003






