Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Einstein Relativistic Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach
2.2. Synchronization of Clocks in General Relativity: The Ramsey Approach
2.3. Ramsey Approach to Quantum Synchronization of Clocks
2.4. Ramsey Approach to Synchronization of Logical Clocks
2.5. Synchronization of Clocks and Symmetry
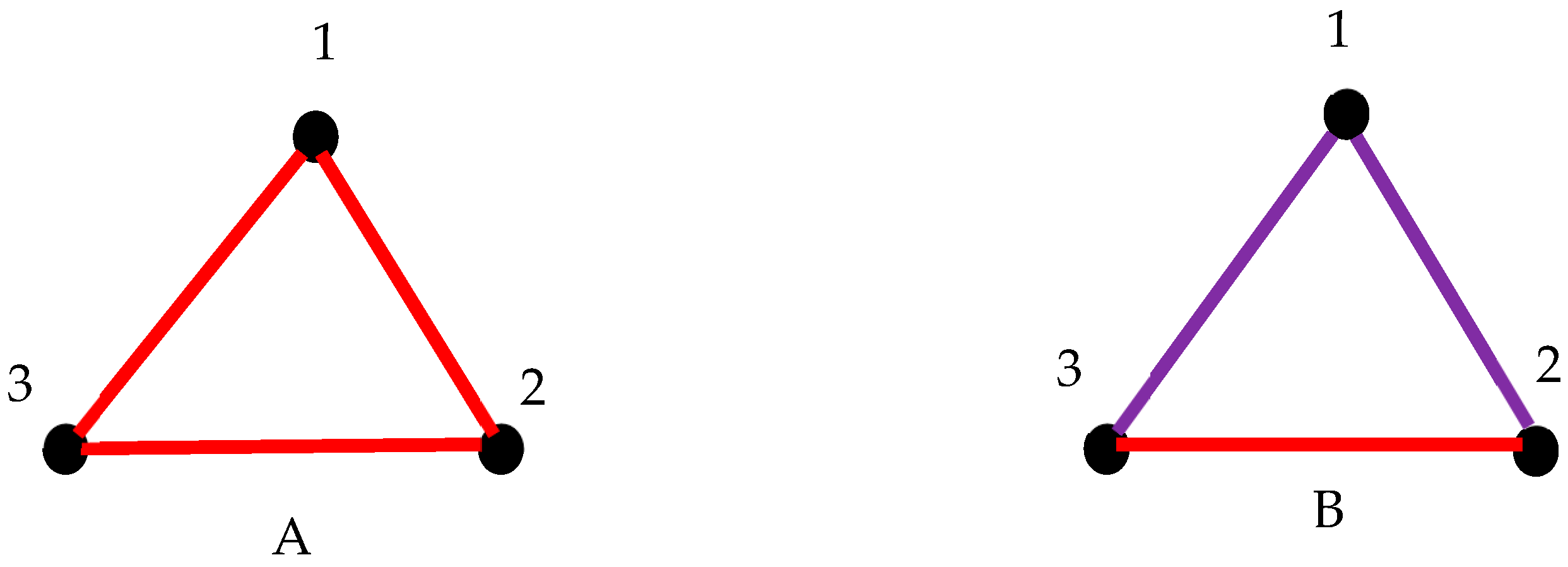
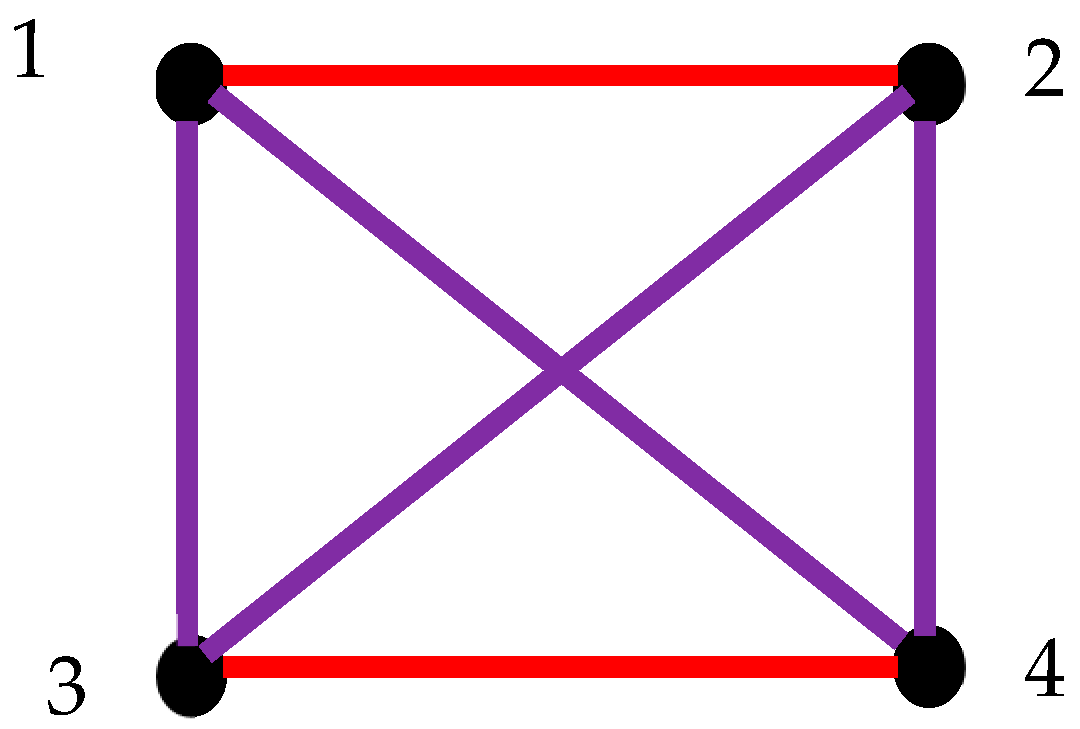
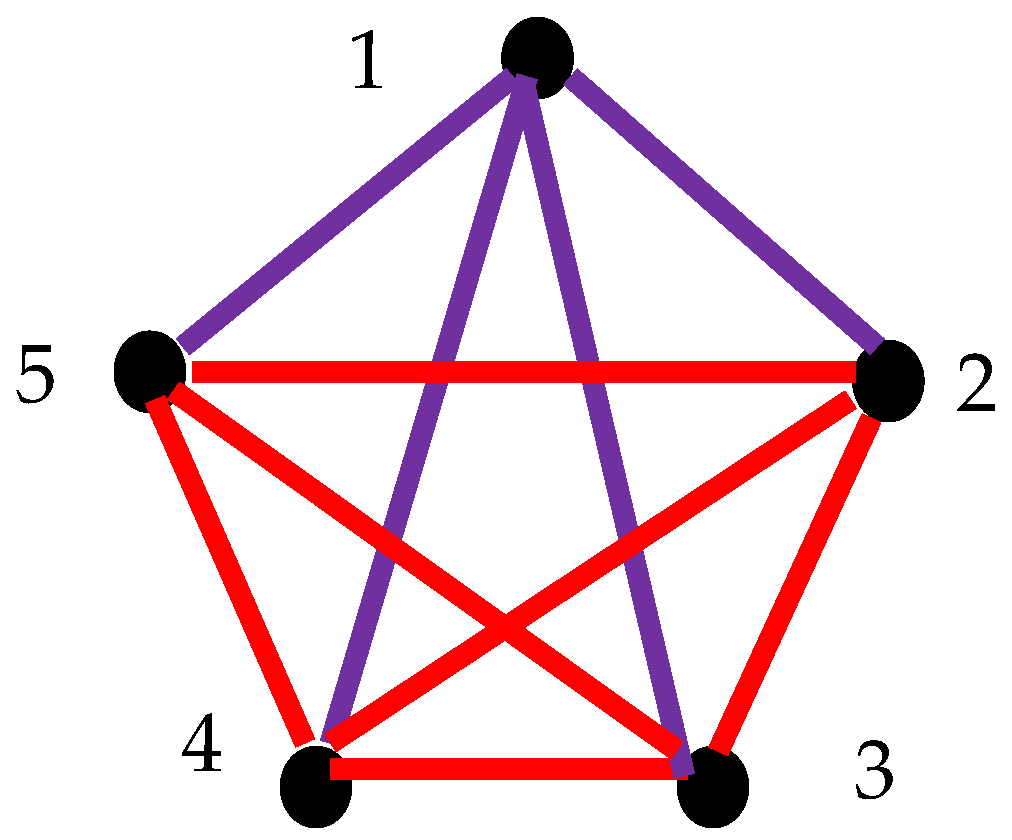
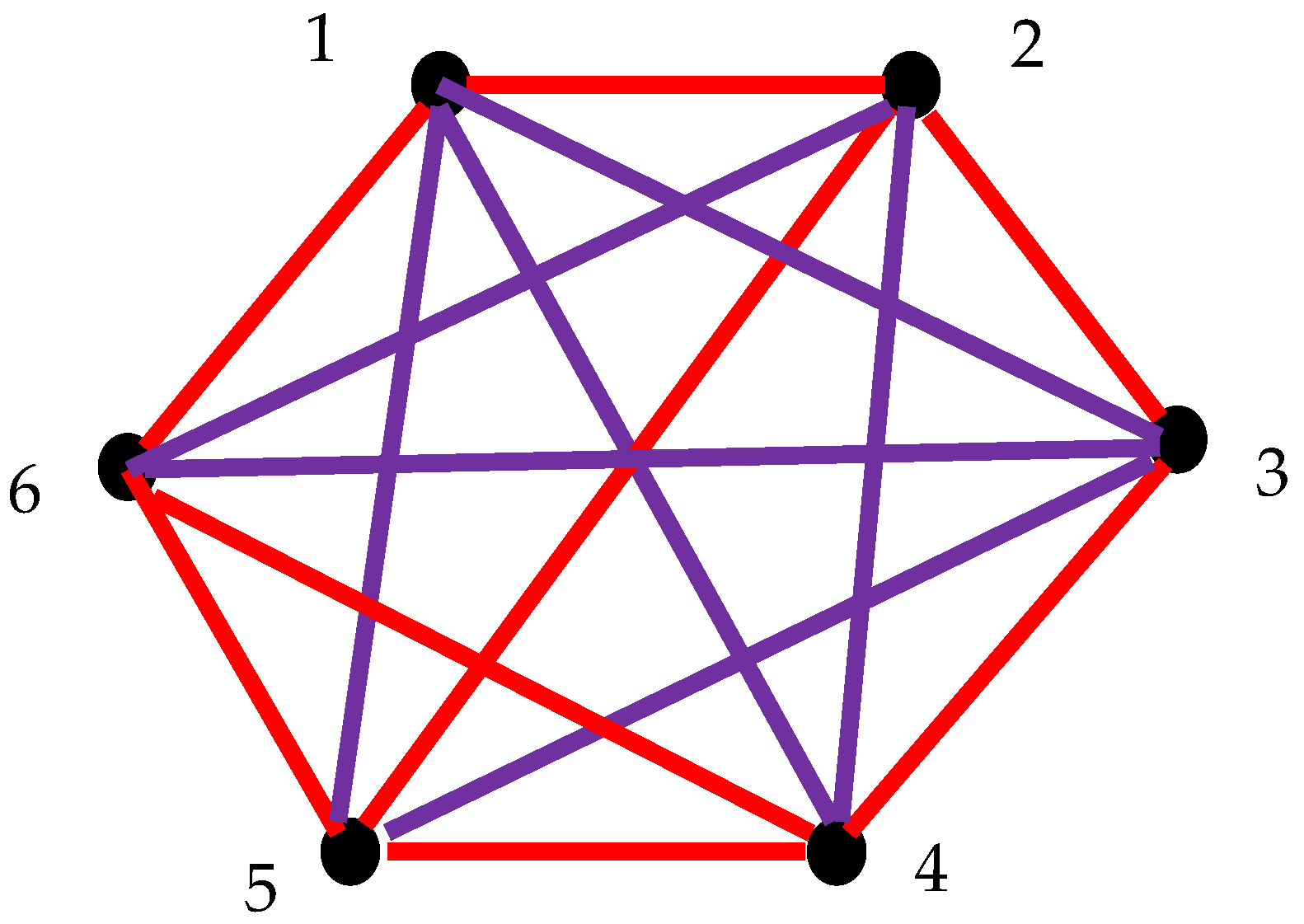
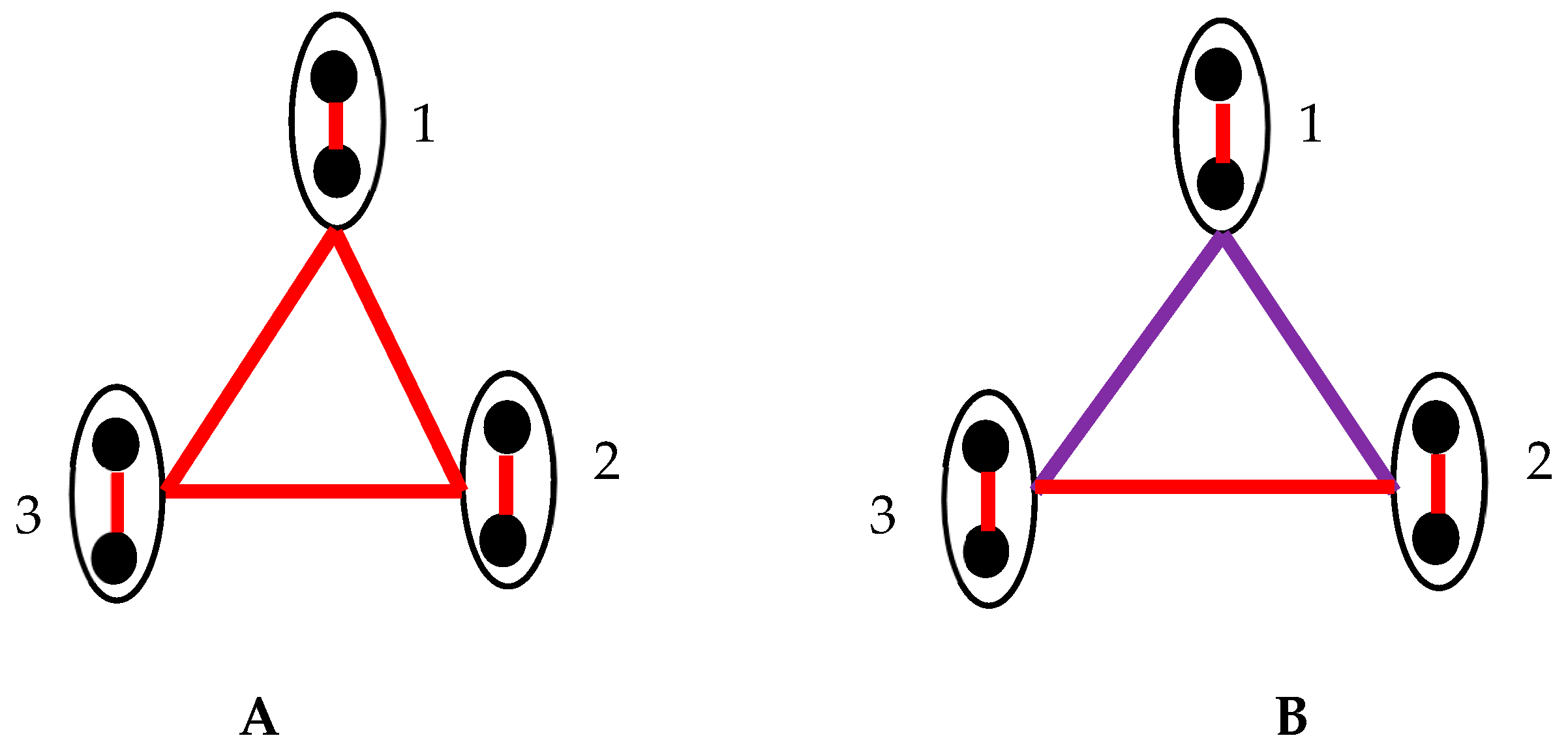
2.6. Generalization of Suggested Approach: Pairs of Synchronized Clocks Seen as the Vertices of Bi-Colored, Complete Graph
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landau, L.; Lifshitz, E.M. The Classical Theory of Fields, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1975; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tolman, R.C. Relativity, Thermodynamics and Cosmology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, D. The Special Theory of Relativity; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Moller, C. The Theory of Relativity, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- DiSalle, R. Understanding Space-Time: The Philosophical Development of Physics from Newton to Einstein; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- DiSalle, R. Absolute space and Newton’s theory of relativity. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. 2020, 71, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussotti, P.; Lotti, B. Newton and His System of the World. In Cosmology in the Early Modern Age: A Web of Ideas; Logic, Epistemology, and the Unity of Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Eddington, A.S. The Mathematical Theory of Relativity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.; Vetharaniam, I.; Stedman, G.E. Conventionality of synchronisation, gauge dependence and test theories of relativity. Phys. Rep. 1998, 295, 93–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samain, E.; Fridelance, P. Time Transfer by Laser Link (T2L2) experiment on Mir. Metrologia 1998, 35, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, P. Zeroth law of thermodynamics and transitivity of simultaneity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1997, 36, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klioner, S.A. The problem of clock synchronization: A relativistic approach. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 1992, 53, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Burgh, M.; Bartlett, S.D. Quantum methods for clock synchronization: Beating the standard quantum limit without entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilo-Okeke, E.O.; Tessler, L.; Dowling, J.P.; Byrnes, T. Remote quantum clock synchronization without synchronized clocks. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2018, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirov, O.; Shepelyansky, D. Quantum synchronization. Eur. Phys. J. D 2006, 38, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokur, V.M.; Baturina, T.I.; Fistul, M.V.; Mironov, A.Y.; Baklanov, M.R.; Strunk, C. Superinsulator and quantum synchronization. Nature 2008, 452, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulet, A.; Bruder, C. Quantum Synchronization and Entanglement Generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 063601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohe, M.A. Quantum synchronization over quantum networks. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2010, 43, 465301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, J.A.; Murty, U.S.R. Graph Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bollobás, B. Modern Graph Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 184. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.L.; Rothschild, B.L.; Spencer, J.H. Ramsey Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience Series in Discrete Mathematics and Optimization; A Wiley-Interscience Publication; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 10–110. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.; Butler, S. Rudiments of Ramsey Theory, 2nd ed.; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2015; pp. 7–46. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nasso, M.; Goldbring, I.; Lupini, M. Nonstandard Methods in Combinatorial Number Theory; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2239. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, M.; Reimann, J. An Introduction to Ramsey Theory: Fast Functions, Infinity, and Metamathematics; Student Mathematical Library; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2018; Volume 87, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, E.F.; Wheeler, J.H. Spacetime Physics, 2nd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gilevich, A.; Shoval, S.; Nosonovsky, M.; Frenkel, M.; Bormashenko, E. Converting Tessellations into Graphs: From Voronoi Tessellations to Complete Graphs. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, L. Time, clocks, and the ordering of events in a distributed system. Commun. ACM 1978, 21, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Demirbas, M.; Madappa, D.; Avva, B.; Leone, M. Logical Physical Clocks. In Principles of Distributed Systems, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, OPODIS 2014, Cortina d’Ampezzo, Italy, 16–19 December 2014; Aguilera, M.K., Querzoni, L., Shapiro, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8878. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, J. Symmetry in Science: An Introduction to the General Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weyl, H. Symmetry; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bormashenko, E. Universe as a Graph (Ramsey Approach to Analysis of Physical Systems). World J. Phys. 2023, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- de Gois, C.; Hansenne, K.; Gühne, O. Uncertainty relations from graph theory. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 107, 062211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-P.; Schwonnek, R.; Winter, A. Bounding the Joint Numerical Range of Pauli Strings by Graph Parameters. PRX Quantum. 2024, 5, 020318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansenne, K.; Qu, R.; Weinbrenner, L.T.; de Gois, C.; Wang, H.; Ming, Y.; Yang, Z.; Horodecki, P.; Gao, W.; Gühne, O. Optimal overlapping tomography. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.05730. [Google Scholar]
- Wouters, J.; Giotis, A.; Kang, R.; Schuricht, D.; Fritz, L. Lower bounds for Ramsey numbers as a statistical physics problem. J. Stat. Mech. 2022, 2022, 033211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Shvalb, N. A Ramsey-Theory-Based Approach to the Dynamics of Systems of Material Points. Dynamics 2024, 4, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvalb, N.; Frenkel, M.; Shoval, S.; Bormashenko, E. Dynamic Ramsey Theory of Mechanical Systems Forming a Complete Graph and Vibrations of Cyclic Compounds. Dynamics 2023, 3, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Chudak, F.; Macready, W.G.; Clark, L.; Gaitan, F. Experimental Determination of Ramsey Numbers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 130505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitan, F.; Clark, L. Ramsey Numbers and Adiabatic Quantum Computing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 010501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Braun, T.; Dimitrova, D.C. Methodology for GPS Synchronization Evaluation with High Accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Glasgow, UK, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pallier, D.; Le Cam, V.; Pillement, S. Energy-Efficient GPS Synchronization for Wireless Nodes. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 5221–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefrour, D. Evolution of network time synchronization towards nanoseconds accuracy: A survey. Comput. Commun. 2022, 191, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, A.G.; Asali, Y.; Márka, Z.; Sigg, D.; Countryman, S.; Bartos, I.; Kawabe, K.; Pirello, M.D.; Thomas, M.; Shaffer, T.J.; et al. Timing system of LIGO discoveries. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremaschini, C.; Tessarotto, M. Hamiltonian approach to GR–Part 1: Covariant theory of classical gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremaschini, C.; Tessarotto, M. Hamiltonian approach to GR–Part 2: Covariant theory of quantum gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A. New Variables for Classical and Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bormashenko, E. Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach. Foundations 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020015
Bormashenko E. Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach. Foundations. 2025; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBormashenko, Edward. 2025. "Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach" Foundations 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020015
APA StyleBormashenko, E. (2025). Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach. Foundations, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020015





