Abstract
Zinc is integral to diverse biological functions, acting catalytically, structurally, and supportively in essential enzyme cycles, despite its limited amounts in the body. Targeting zinc enzymes with potent drugs, such as Vorinostat, demonstrates the therapeutic efficacy of zinc-binding ligands, notably in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma treatments. Our study merges experimental and theoretical approaches to analyze the coordination of 8-hydroxylquinoline (8HQ) inhibitors with biomimetic zinc complexes and human histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8), a monozinc hydrolase enzyme. Assessing 10 8HQ derivatives for structural and electronic characteristics against these models, we observe minimal inhibition efficacy, corroborated through protein–ligand docking analyses, highlighting the complexities of inhibitor–zinc enzyme interactions and suggesting intricate noncovalent interactions that are important for ligand binding to enzymes not accounted for in model zinc hydrolase mimics.
1. Introduction
Zinc is an essential metal ion that is found in various biological processes, which can include serving as a cofactor in structural, regulatory, and biochemical transformations. Zinc-dependent enzymes can be categorized into three types: structural, catalytic, or co-catalytic. Among catalytic zinc enzymes, zinc hydrolases are particularly abundant and play important roles in biochemical reactions [1,2]. In zinc hydrolases, zinc acts as a Lewis acid, activating a substrate such as water/hydroxide or a serine or tyrosine residue, which increases their nucleophilicities. In most cases, the zinc ion is bound to a combination of 3 histidine and/or glutamate/aspartate amino acid residues. What sets zinc apart from other biologically important metals is that it exists in nature solely as Zn2+, which has filled d orbitals and is redox-benign, meaning its main role in catalysis is as a Lewis acid. For zinc to function in a catalytic capacity, there must be an open coordination site for a substrate to bind. In zinc hydrolases, the metal adopts a tetrahedral or trigonal bipyramidal geometry, unlike small-molecule zinc complexes that have higher coordination and often do not exhibit hydrolase activity [3,4].
Zinc enzymes have been successfully targeted with drugs that bind strongly to zinc. For example, Vorinostat (also known as suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA), a broad-spectrum drug that targets the mono-zinc enzyme family of histone deacetylases (HDAC), has been used in cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) treatments [5,6]. In another example, treatment of glaucoma is performed using sulfonamides such as dorzolamide, which targets the zinc center in carbonic anhydrase [7]. Another example of a zinc-dependent enzyme targeted with drugs is the di-zinc alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme. ALP is a non-specific enzyme that is known to hydrolyze a variety of phosphate-containing compounds such as glucose phosphate, phospholipids, and other phosphatides [8,9]. ALP is also responsible for the production of the important signaling molecule, adenosine, via the hydrolysis of adenosine monophosphate. The inhibition of alkaline phosphatase has been shown to improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus by preventing calcification. Cardiovascular events can be caused by an imbalance between the promoters and inhibitors of mineralization, a process akin to skeletal mineralization that is regulated by ALP [10,11]. The overexpression of tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNLAP) induces calcification, cardiac hypertrophy, and subsequently death, mimicking the phenotype found in chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus [12]. These examples in drug discovery highlight the value of targeting zinc-based enzymes and developing better zinc-binding drugs.
The inhibition of zinc-containing enzymes via zinc-binding drugs is an important area of study because these enzymes can influence biological systems via covalent modifications. These covalent modifications dominate the regulation of processes within a cell. Phosphorylation, methylation, ubiquitination, adenosine diphosphate ribosylation, acetylation, and deacetylation all play a variety of roles in healthy tissue as well as in disease progression [13,14]. The enzymes responsible for the acetylation and deacetylation of histones important for the formation of chromatin and regulation of transcription are monozinc enzymes, histone acetyltransferases (HATs), and HDACs. HDACs along with HATs operate in a balanced manner that influences and regulates various cellular processes from the cell cycle and DNA damage repair to apoptosis, all of which culminate in the maintenance of homeostasis within a cell. While the enzyme class is called histone deacetylase, histones are not the only, or even the primary target, of HDACs. HDAC has activity on a wide array of nonhistone proteins, which is why it is able to have such an impact on maintaining cellular homeostasis [5,14,15].
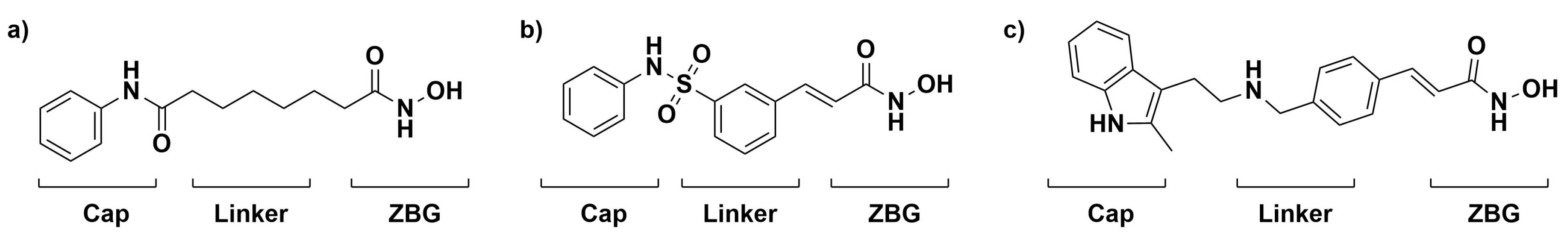
HDAC has been highly implicated in many different cancers as its expression is usually upregulated in tumor cells. For example, tumor cells are able to evade cell cycle arrest through the inactivation of the tumor suppressor gene p53 via the upregulation of HDAC activity [16]. The ability to restore the balance of HDACs and HATs could be an essential component of a chemotherapeutic approach to treating cancer [6,17]. One way to restore this balance is through the inhibition of HDAC, such as through the widely studied HDAC inhibitor (HDACi) Vorinostat, also known as SAHA. SAHA follows a common HDACi motif that consists of a zinc-binding group that chelates the zinc in the active site, an organic linker that packs into the active site tunnel, and a cap group that protrudes from the active site. Several successful HDAC inhibitors follow this motif, as shown in Figure 1 [18,19]. The interplay between HDACs, HATs, and tumor suppressors/proto-oncogenes allows for the inhibition of HDAC to be a viable chemotherapeutic target. The structure of the enzyme and its active site tunnel is depicted in Figure 2.
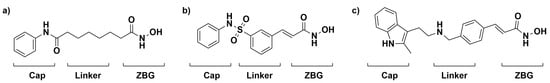
Figure 1.
FDA-approved treatments for the inhibition of HDAC, Vorinostat (a), Belinostat (b), and Panobinostat (c) are shown with the cap group, linker, and zinc-binding group (ZBG) moieties known to be important for the inhibition of HDAC.
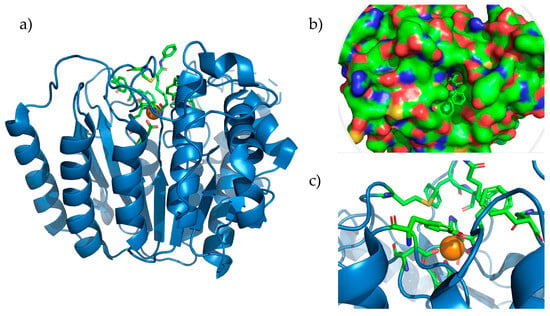
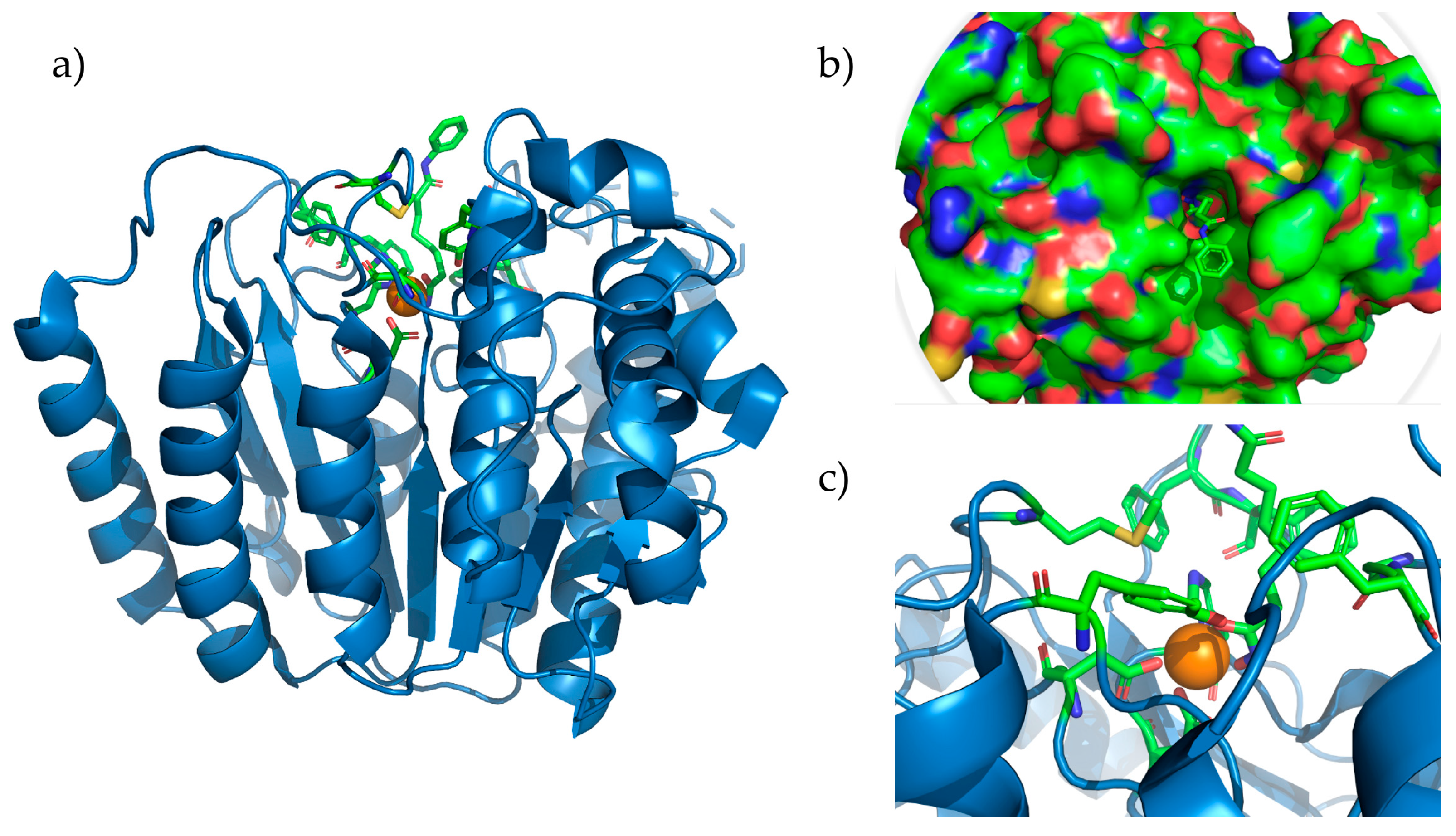
Figure 2.
HDAC8 complexed with SAHA (pdb accession: 1T69). (a) Entire HDAC8 enzyme with the Zn2+ ion depicted as the orange sphere. (b) Representation of the surface of HDAC8 showing bound Vorinostat that is reaching the surface. (c) Active site of HDAC8 showing amino acids Asp178, Asp267, and His180, coordinated with Zn2+ and the residues forming the hydrophobic tunnel.
The specific functional group within SAHA that binds zinc is the hydroxamic acid moiety. Once the O-H is deprotonated, the hydroxamates bind as bidentate anionic chelators. The strength of the zinc–hydroxamate interaction prevents the zinc active sites in enzymes like HDAC from binding their normal substrates, thus inhibiting the enzymes’ functions [20]. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) has been used to study the binding of hydroxamic acids to zinc compounds, and small-molecule models of enzyme active sites have been crystallized with hydroxamate bound to them. Notably, the ITC studies showed that 8-hydroxyquinoline (8HQ), another anionic bidentate chelator, bound zinc more strongly than hydroxamic acids in the buffer. In addition, 8HQ could displace SAHA bound to a small-molecule zinc center supported by a bulky trispyrazolylborate (Tp) framework, further supporting it as a stronger chelator than hydroxamic acids [21]. The ZnTp framework has been used to study a variety of zinc-binding bioisosteres with various coordination geometries [22,23].
In drug discovery, a privileged structure is a useful strategy in the design of lead drug candidates via the rational modification of a previously known bioactive structure that may lead to more potent ligands with favorable properties for diverse targets. For example, hydroxamic acids would be an example of such a structure. However, there are many other privileged structures. Quinolines have been identified as an important bioactive pharmacophore for a broad range of biological effects [24]. Among the quinolines, 8-hydroxyquinoline (8HQ) has emerged recently as a privileged drug scaffold due to its strong metal binding properties, lending itself to a wide variety of pharmacological applications: metal chelators for neuroprotection, anticancer, anti-HIV, antifungal, antibacterial, and antischistosomal therapies [25,26,27]. This privileged nature of 8HQ provides an exciting opportunity to explore zinc-binding interactions with 8HQ derivatives and how these compounds inhibit Zn-dependent metalloenzyme catalytic activity for a range of pharmacological applications. The 8HQ scaffold was chosen for this current study due to an earlier account showing better zinc binding than hydroxamic acids [21]. The fact that 8HQs bind small-molecule zinc species that are stronger than hydroxamates in buffers and organic solvents also supports the idea that 8HQs may be superior to hydroxamic acids for targeting zinc hydrolases.
There needs to be more connectivity between the structure and activity of enzymes and small-molecule zinc complexes that have been used to attempt to mimic the active sites structurally. Further, a better understanding of structure–activity relationships for drug molecule interactions with the enzymes is needed for effective drug development. This study explores the intersection of drug discovery and small-molecule zinc coordination chemistry, leading to design principles for better drugs targeting the function of zinc hydrolase enzymes. This study focuses on the zinc hydrolase HDAC8 as the model enzyme to explore these principles by combining the modeling of zinc enzyme active sites with small molecules with computational and experimental studies of zinc enzymes relevant to disease states in order to discover better zinc-binding drug molecules for various pharmacological applications. A key focus is understanding how substituents in 8-hydroxyquinoline ligands affect their binding to small-molecule zinc complexes and if these lessons translate to the binding of the same molecules to HDAC8, a zinc hydrolase enzyme. Our results are reported below.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Considerations
All reactions were carried out on the bench in the presence of air unless otherwise noted. NMR spectra were collected by a Bruker Avance 300 MHz or a Neo 400 MHz spectrometer. Unless otherwise noted, chemicals were used as received from commercial suppliers. Acetonitrile was purified using an Innovative Technologies solvent purification system under N2. The syntheses of KTp and ZnTpOH were carried out as previously reported [21]. All other chemicals were used as received from commercial suppliers. Absorbance values for the HDAC8 activity assay were measured using a Multiskan FC microplate reader.
2.2. Synthesis of ZnTp(X-H)
Syntheses of the TpZn8HQ species were carried out similarly to the reported procedure for TpZn(A-H) [21]. Generally, these reactions were carried out on a 30–150 mg scale of TpZnOH with one equivalent of the appropriate hydroxyquinoline in a small amount (ca. 5–20 mL) of a polar solvent such as dichloromethane, methanol, acetone, and acetonitrile in a 20 mL scintillation vial equipped with a Teflon-covered stir bar. Upon mixing, the solution became yellow or yellow-orange in color, reflecting the formation of a deprotonated 8HQ metal complex. The reactions were stirred on a stir plate at room temperature (ca. 18–21 °C) under air for at least 15 min, and then the solvent was removed via rotary evaporation. Product identity and relative purity were assessed via 1H NMR spectroscopy, and they were consistent with the expected structure and similar to the reported values of TpZn(A-H) [21]. The primary species in the 1H NMR spectra were the TpZn(X-H) species, with solvents as the only other identifiable species. Yields were generally within the range of 40–90%. Because the focus of the work was structural comparison, further purification or spectroscopic characterizations were not performed, and the materials were used to grow single crystals of the species. Single crystals for X-ray crystallography were generally grown via cooling concentrated acetonitrile solutions of the TpZn(X-H) species in the freezer.
NMR data in ppm (CDCl3): TpZn(B-H): 7.75 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.71 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 7.37–7.4 (m, TpPh, 6H), 7.03 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.88–6.90 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.55 (dd, 8HQ, 1H), 6.17 (s, Tp, 3H). 2.59 (s, TpMe, 9H).
TpZn(C-H): 8.89 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 8.57 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.24–7.27 (m, TpPh, 6H), 7.08 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 6.84–6.86 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.64 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 6.38 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.17 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.59 (s, TpMe, 9H).
TpZn(D-H): 7.77 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.42–7.43 (d, TpPh, 6H), 7.34 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.06 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.82–6.88 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.57 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.46 (dd, 8HQ 1 H), 6.19 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.60 (s, TpMe, 9H).
TpZn(E-H): 7.56 (br m, TpPh, 6H), 7.31 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.84 (br m, TpPh, 9H), 6.76 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.57 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.21 (s, Tp, 3H), 6.18 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 2.60 (s, TpMe, 9H), 1.14 (s, 8HQMe, 3H).
TpZn(F-H): 7.67–7.69 (m, TpPh, 6H), 7.05 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 6.99 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 6.81 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.32 (m, 8HQ, 1H), 6.18 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.59 (s, TpMe, 9H), 2.30 (s, 8HQMe, 3H), 2.09 (s, 8HQMe, 3H).
TpZn(G-H): 7.70 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.51 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.41 (d, TpPh, 6H), 7.03 (m, 8HQ, 1H), 6.82–6.90 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.54 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.46 (dd, 8HQ, 1H), 6.18 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.59 (s, TpMe, 3H).
TpZn(H-H): 7.53 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.48 (d, TpPh, 6H), 7.41 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 7.02 (s, 8HQ, 1H), 6.88–6.90 (m, TpPh, 9H), 6.45 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.41 (m, 8HQ, 1H), 6.21 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.62 (s, TpMe, 9H).
TpZn(I-H): 7.37 (d, TpPh, 6H), 7.35 (m, 8HQ, 1H), 6.79–6.88 (m, TpPh and 8HQ, 10H), 6.74 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.67 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.59 (d, 8HQ, 1H), 6.19 (s, Tp, 3H), 2.59 (s, TpMe, 9H).
2.3. Density Functional Theory Calculations
Density Functional Theory was carried out with Gaussian 16 and visualized with GaussView [28]. The MN15-L functional was used with the def2-TZVP basis set [29]. Optimized geometries were analyzed for frequencies to ensure that structures were at a ground state and not on other parts of the potential energy surface. Optimized .xyz coordinates are included as supporting information. Calculations were performed in the gas phase without any solvation model.
2.4. X-ray Structures
X-ray crystallography was carried out via RDS, DJW, and ARJ. X-ray diffraction data compounds TpZn(G-H), TpZn(H-H), and TpZn(I-H) were collected on a Bruker D8 Diffractometer with an APEX-II CCD detector. Data collection was carried out using sealed-tube Mo K⍺ radiation. The structure was solved and refined using Bruker APEX3 V3 software and XSHELL V6.3.1. Further details of the crystal structures can be found in their .cif files, which have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre’s (CCDC) Cambridge Structural Database (CSD). The deposition numbers are shown in Table 1 (vide infra).
2.5. Ligand Docking of Human HDAC8
Docking was performed using the webserver docking program DockThor Version 2.0 [30,31]. The 1T69 crystal structure from the protein databank was used [32]. Before uploading to DockThor, the water, zinc cofactor, and bound SAHA were removed from the crystal structure. Cofactor files were uploaded in the .mol2 format, and ligands were uploaded in the .SDF format. A grid of 20 angstroms was centered around the original zinc cofactor in the crystal structure. Coordinates for the zinc were also obtained in PyMOL Version 3.0.3, and any images generated were also from PyMOL [33]. No docking prep using chimera is necessary when using DockThor.
2.6. Recombinant Expression of Human HDAC8
The HDAC8 gene (UniProt ID: Q9BY41) was cloned into the pET-28a plasmid between the BamHI and HindIII restriction sites via Twist Bioscience. The plasmid was transformed into both BL21(DE3) and BLR(DE3) chemically competent cells purchased from New England Biolabs and Novagen, respectively. BLR(DE3) was chosen for continuation in further studies due to increased protein yields and activity compared to BL21(DE3) cells. Starters for 500 mL cultures of HDAC8-containing BLR cells were grown in 10 mL of terrific broth (TB) media containing kanamycin at a final concentration of 0.05 mg/mL and 1% glucose. These starters were grown overnight (about 14 h) at 37 °C and added to 500 mL of TB kanamycin media the following morning. The 500 mL culture was grown to an OD600 of 0.7–0.9 and induced with isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) to a final concentration of 0.8 mM. Zinc sulfate was also added to a final concentration of 0.2 mM. The cultures were incubated for another 16–18 h at 26 °C.
2.7. Purification of Recombinant HDAC8
Cells were harvested via centrifugation at 4500× g for 10 min and lysed in a lysis buffer (25 mM Tris, 3 mM MgCl2, 300 mM NaCl, 30 mM imidazole, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0, supplemented with PMSF) via ultrasonication, and they were clarified via centrifugation 4000× g for 4 h at 4 °C. Then, 10 mL of lysis buffer was added for each gram of cell pellet harvested from the cultures and pooled for sonication. HDAC8 was purified using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) performed on an ÅKTA Start from Cytiva. The wash buffer (25 mM Tris, 3 mM MgCl2, 300 mM NaCl, 30 mM imidazole, pH 8.0), elution buffer (wash buffer containing 300 mM imidazole) and storage buffer (10 mM Tris, 3 mM MgCl2, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, 10% glycerol, pH 7.5) were modified recipes from two separate studies [34,35]. The clarified and filtered lysate was loaded onto the column and washed for 15 column volumes with wash buffer, continuing with 30 mM imidazole and then 10 column volumes with wash buffers containing 100 mM imidazole. This was carried out on the ÅKTA FPLC by mixing the wash and elution buffers at a ratio to attain a final concentration of 100 mM imidazole. After elution and verifying which fractions to pool via SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, the protein was desalted using a PD-10 desalting column packed with Sephadex G-25 from Cytiva that was equilibrated with the storage buffer. The desalted eluate was concentrated to a point where 100 μg could be obtained from 85 μL or less using Amicon® (Millipore Sigma, Darmstadt, Germany) ultra centrifugal filters. This protein product was stored at −80 °C and used for assays within 2–3 days.
2.8. Colorimetric HDAC Activity Assay
HDAC activity was ascertained using a colorimetric HDAC assay kit from Abcam (ab1432) following the provided protocol with a few adjustments. In total, 2 μL of 5 mM zinc sulfate solution was added to increase enzyme activity, the amount of added HDAC8 was kept consistent at 100 μg per well, and the assay incubation time was 1 h and 30 min instead of the recommended hour. For assaying the activity with inhibitors, 2 μL of 1 mM of each inhibitor was added to the respective wells.
3. Results and Discussion
Clinically relevant HDAC inhibitors are in a variety of chemical classes such as hydroxamic acids, carboxylic acids, benzamides, or cyclic peptides [36,37]. Shown in Figure 2 is HDAC8 with SAHA coordinated with the zinc in its active site, highlighting its accessibility to the surface of the enzyme through a hydrophobic tunnel formed by Phe152, Gly151, His180, Phe208, Met274, and Tyr306. At the base of the hydrophobic tunnel is the catalytic Zn2+, which is coordinated by two Asp residues and one His residue, and normally, it has an activated water molecule (displaced by SAHA). The SAHA linker transcends the hydrophobic pocket, and the hydroxamic acid group binds the active site Zn2+. We will utilize HDAC8 as our model zinc enzyme to compare zinc complexes with the ligand scaffold (shown in Figure 3) and trispyrazolylborate (Tp) ligand (specifically the hydrotris(3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borate ligand, hereafter referred to as Tp). The ZnTp system has been used before to examine the interaction of zinc-binding groups in drug molecules with a mononuclear zinc center, modeling another zinc hydrolase and matrix metalloprotease.
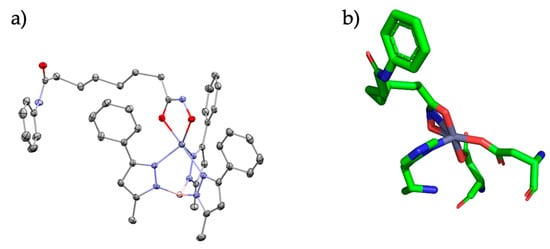
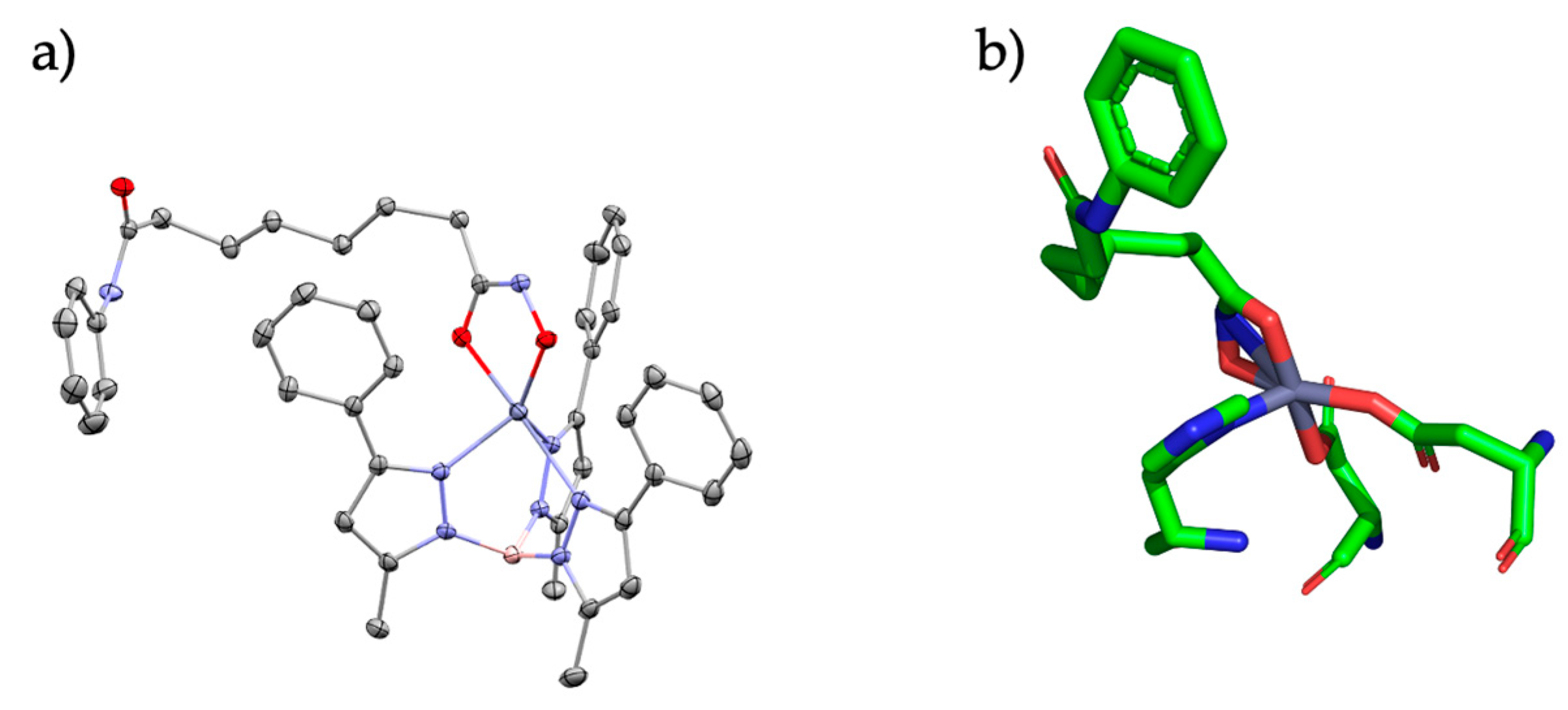
Figure 3.
(a) SAHA bound to the TpZn motif and (b) SAHA bound to the HDAC active site. Relevant bond lengths are as follows: for (a) Zn-O1 (1.94 Å) and Zn-O2 (2.14 Å); (b) Zn-O1 (2.0 Å) and Zn-O2 (2.0 Å).
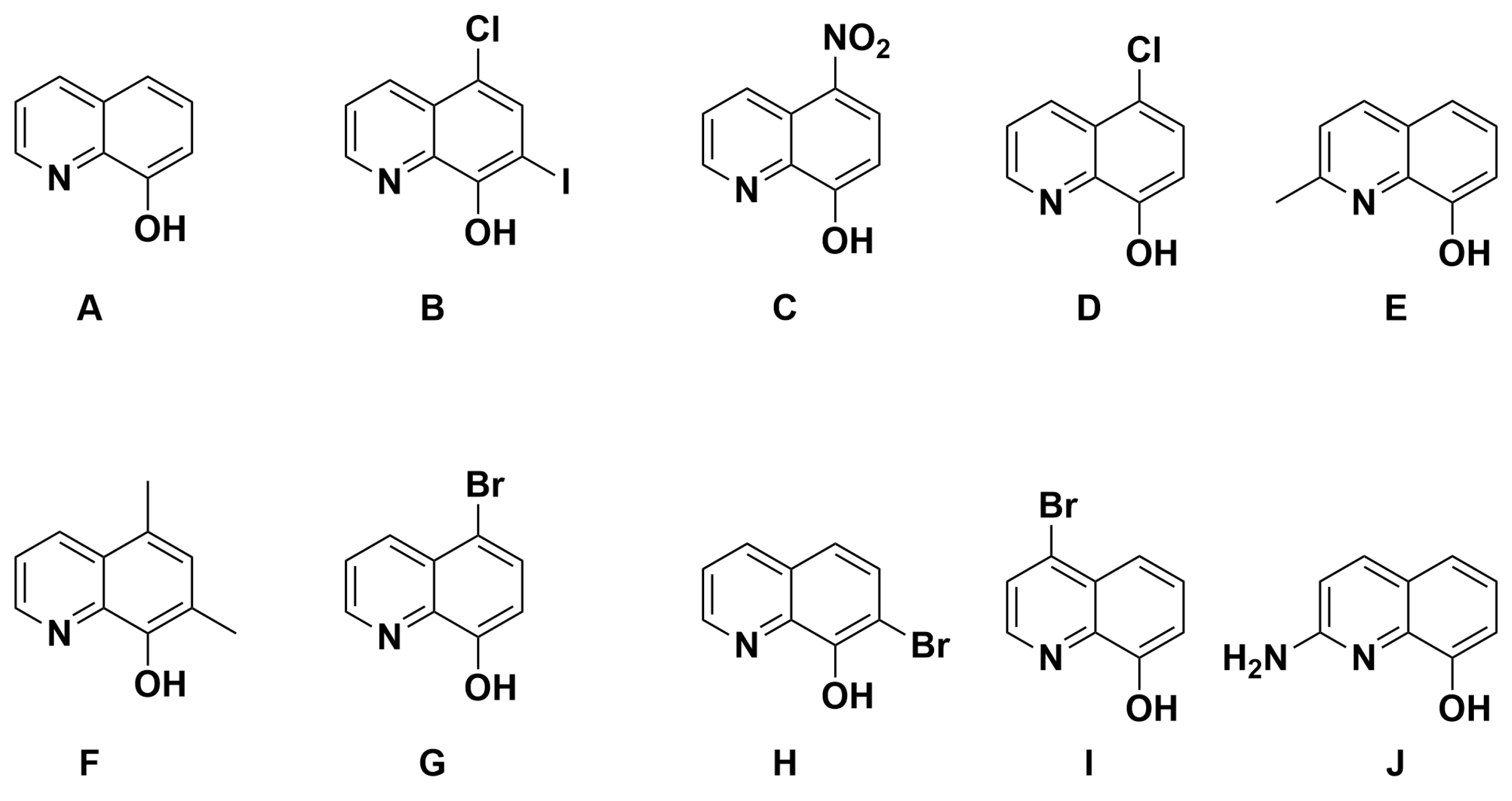
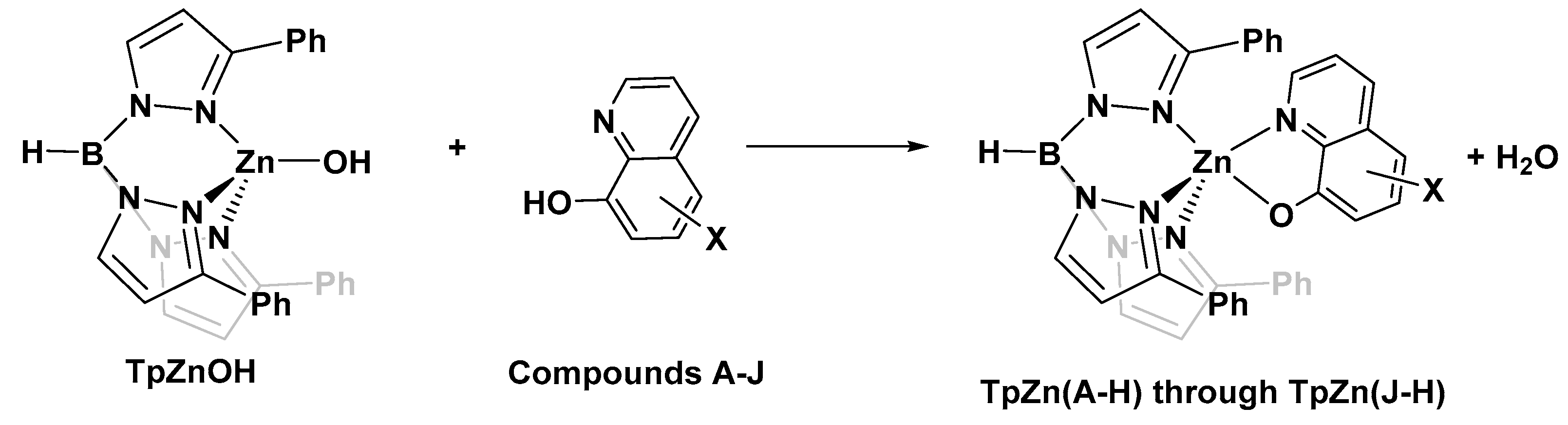
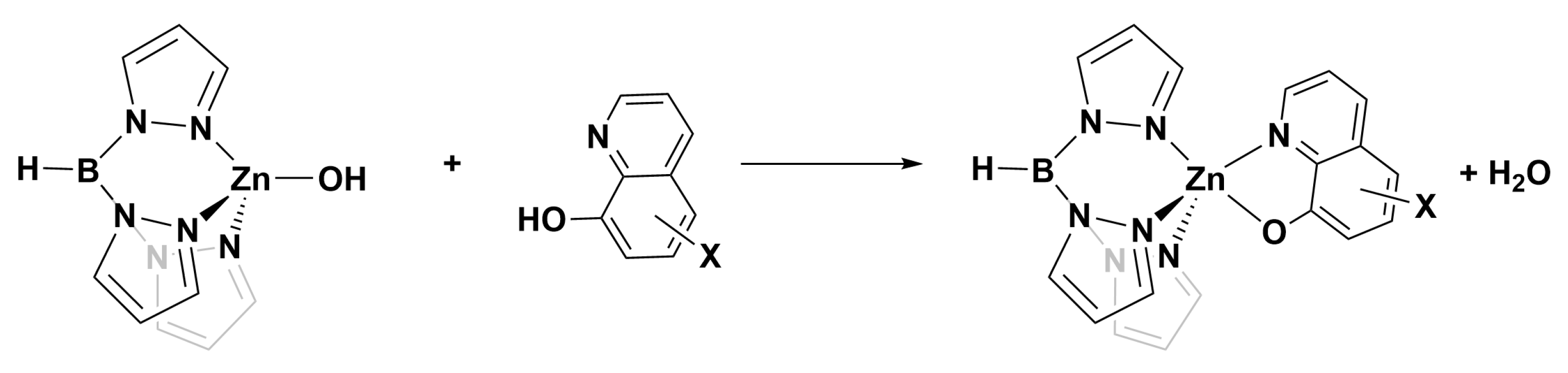
3.1. Structures of TpZn Bound to 8HQ Derivatives
With the knowledge that 8HQs bind more strongly than hydroxamates, we selected 10 8HQ derivative molecules to examine which have a variety of electron-donating or -withdrawing substituents in several different locations (Figure 4). These initial 10 were selected based on their commercial availability. Of these, only the unsubstituted ligand A has been bound, binding the TpZn system. To our knowledge, 8HQs have not been studied versus HDAC8, but they have been used to target a variety of other metal-based proteins. Compound B is clioquinol, which has been used as an antibacterial and antifungal compound [38,39], and compound C is nitroxoline, which has been used as an antibacterial compound and has shown promise as an anti-amoeba treatment [40,41]. The TpZnOH complex was synthesized as per previous reports and reacted with compounds A–J to form TPZn(A–J). The products were generally yellow to orange powders. The reaction scheme is shown in Figure 5.
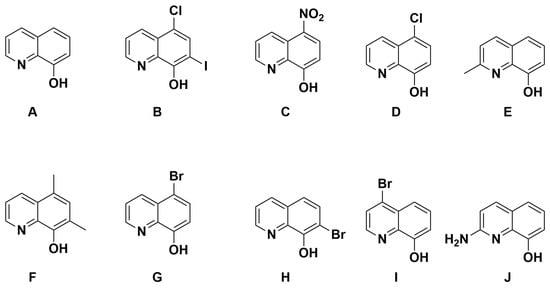
Figure 4.
The 8HQ compounds examined in this study.
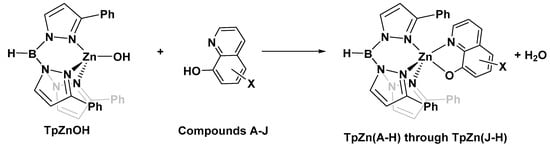
Figure 5.
Common reaction scheme for the synthesis of complexes in this study.
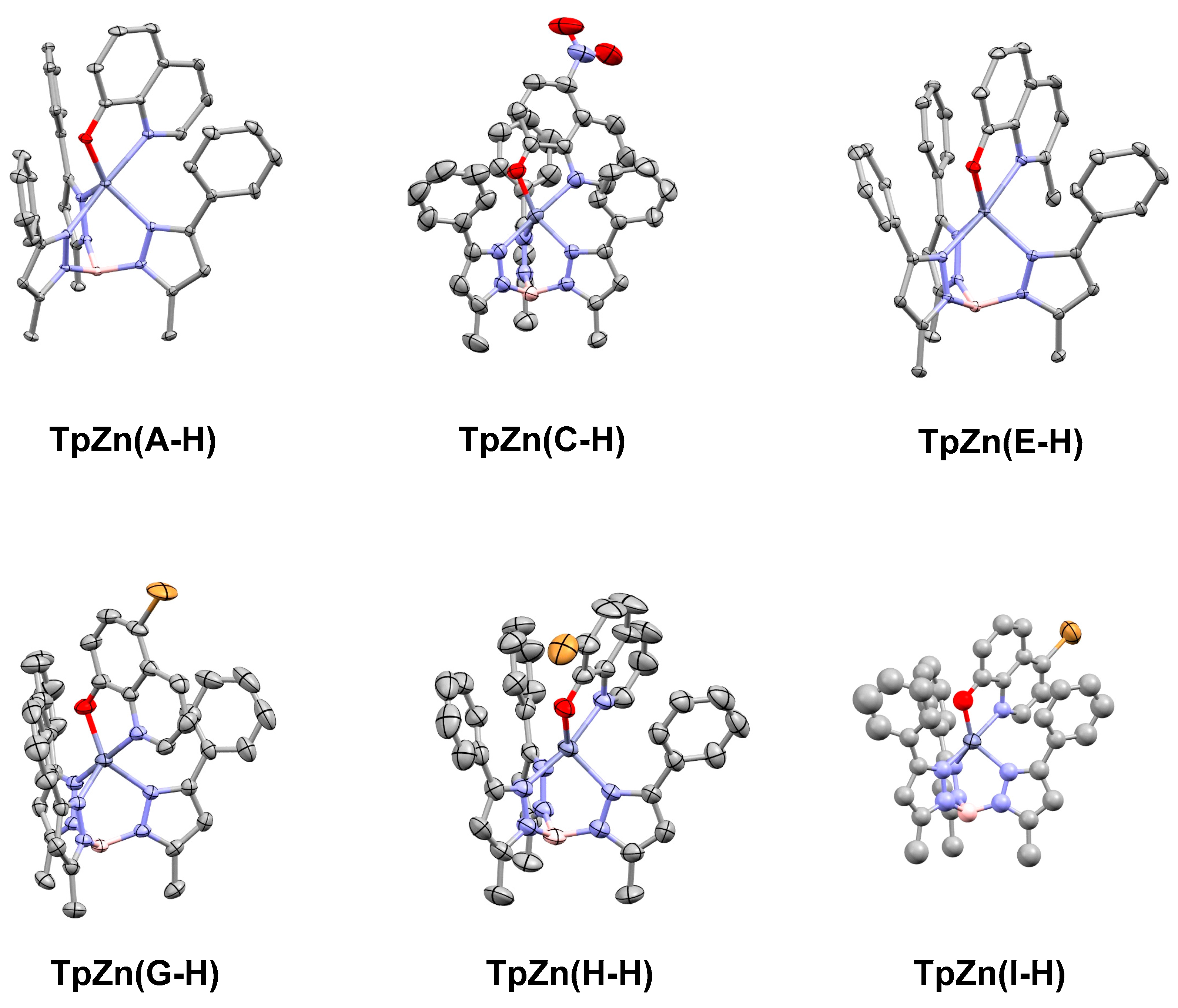
We have previously used the tridentate anionic trispyrazolylborate framework to obtain an X-ray crystallographic structure of the parent 8HQ, A, bound to zinc [21]. In order to compare the binding of the other 8HQs, we set out to obtain single X-ray crystal structures of the other inhibitors studied in this work. We were successful for complexes based on C, E, G, H, and I, and their structures are shown below in Figure 6.
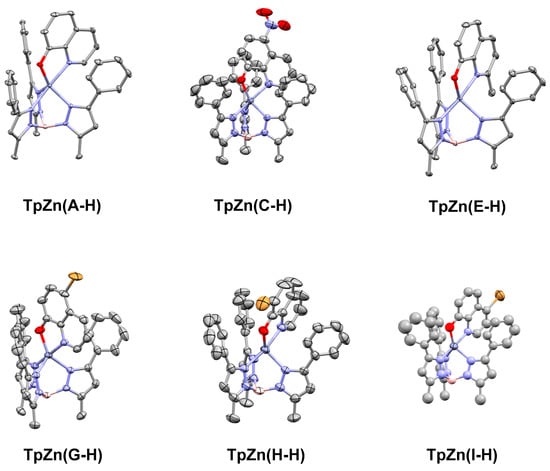
Figure 6.
Single crystal X-ray structures of TpZn(A-H), TpZn(B-H), TpZn(C-H), TpZn(E-H), TpZn(G-H), TpZn(H-H), and TpZn(I-H), with ellipsoids shown at 50% probability and hydrogen atoms excluded for clarity. Co-crystallized solvents were also excluded. The CCDC numbers are listed in Table 1. TpZn(H-H) is of poor quality but shows overall connectivity.
With these structures in hand, we could compare the Zn-O and Zn-N bond lengths of the structures, with the guiding principle that a shorter distance generally reflects a stronger bond. The bond lengths from these structures are summarized below in Table 1.

Table 1.
Relevant bond lengths between the Zn and 8HQ ligands from the crystal structures of A-H.
Table 1.
Relevant bond lengths between the Zn and 8HQ ligands from the crystal structures of A-H.
| Compound | Zn-O Bond (Å) | Zn-N Bond (Å) | Sum | Reference | CCDC # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TpZn(A-H) | 1.9442(6) | 2.1905(7) | 4.135 | [21] | 1,429,136 |
| TpZn(B-H) | - | - | - | - | - |
| TpZn(C-H) | 1.963(2) | 2.219(2) | 4.182 | This work | 2,225,097 |
| TpZn(D-H) | - | - | - | - | - |
| TpZn(E-H) | 1.9334(8) | 2.199(1) | 4.132 | This work | 2,361,176 |
| TpZn(F-H) | - | - | - | - | - |
| TpZn(G-H) | 1.945(2) | 2.207(3) | 4.152 | This work | 2,359,443 |
| TpZn(H-H) | 1.955(2) | 2.165(5) | 4.120 | This work | 2,359,448 |
| TpZn(I-H) | 1.94(2) | 2.24(1) | 4.180 | This work | 2,359,447 |
| TpZn(J-H) | - | - | - | - | - |
As can be seen in Table 1, TpZn(E-H) is has the shortest Zn-O bond, and TpZn(B-H) has the longest Zn-O bond. The shorter Zn-O bonds generally correspond to the un-substituted phenol 8HQs. In addition, TpZn(H-H) has the shortest Zn-N bond of the complexes, while TpZn(I-H) has the longest Zn-N bond. Given the concept that the shorter bonds are generally stronger bonds, it appears that the 8HQs H, E, and A bind the best to TpZn, based on comparing the sum of the Zn-O and Zn-N 8HQ bonds. However, bond lengths can be affected by packing forces and potentially by interactions between the Tp phenyl groups and the 8HQs. Therefore, we used DFT calculations to further examine Zn–8HQ interactions.
3.2. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations
In order to understand the thermodynamics of 8HQ binding to Zn, we used density functional theory (DFT) at the MN15-L/def2TZVP level of theory to study the reaction in Scheme 1. For the sake of computational speed, the Ph and Me groups on the Tp ligand were replaced with hydrogen atoms. This also removes any energetic effect from the interaction of the 8HQs with the phenyl groups, such as potential π–π interactions. The free energy of reactions in the gas phase was calculated for compounds A-J using the standard “products minus reactants” approach for thermochemistry in Gaussian 16 and they are shown in the table below, along with Zn-O and Zn-N bond lengths for the products [42].
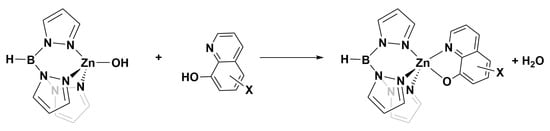
Scheme 1.
Reaction for which deltaG298K was calculated using DFT.
As can be seen in the data in Table 2, there is no clear correlation between bond lengths and the energy of the reaction. The ΔG values likely correlate to the acidity of 8-hydroxyquinolines, as the nitro-substituted species would be expected to be the most acidic. Disagreement is also seen between these calculations and the X-ray structures, as the species with the shortest calculated 8HQ bond lengths are F and J, which have not been crystallized; 8HQs A and I also have relatively short bonds but were found to have longer bonds in the corresponding crystal structure. Fundamentally, the disagreement between theory and X-ray structures indicates that packing forces may play significant roles in the Zn-O and Zn-N bonds in crystal structures. We next sought to study these 8HQs as ligands of the zinc active site of HDAC8 and the inhibitors of hydrolase activity.

Table 2.
Bond lengths and reaction energies for forming TpZn(A-H) through TpZn(J-H).
3.3. Protein–Ligand Docking of HDAC8
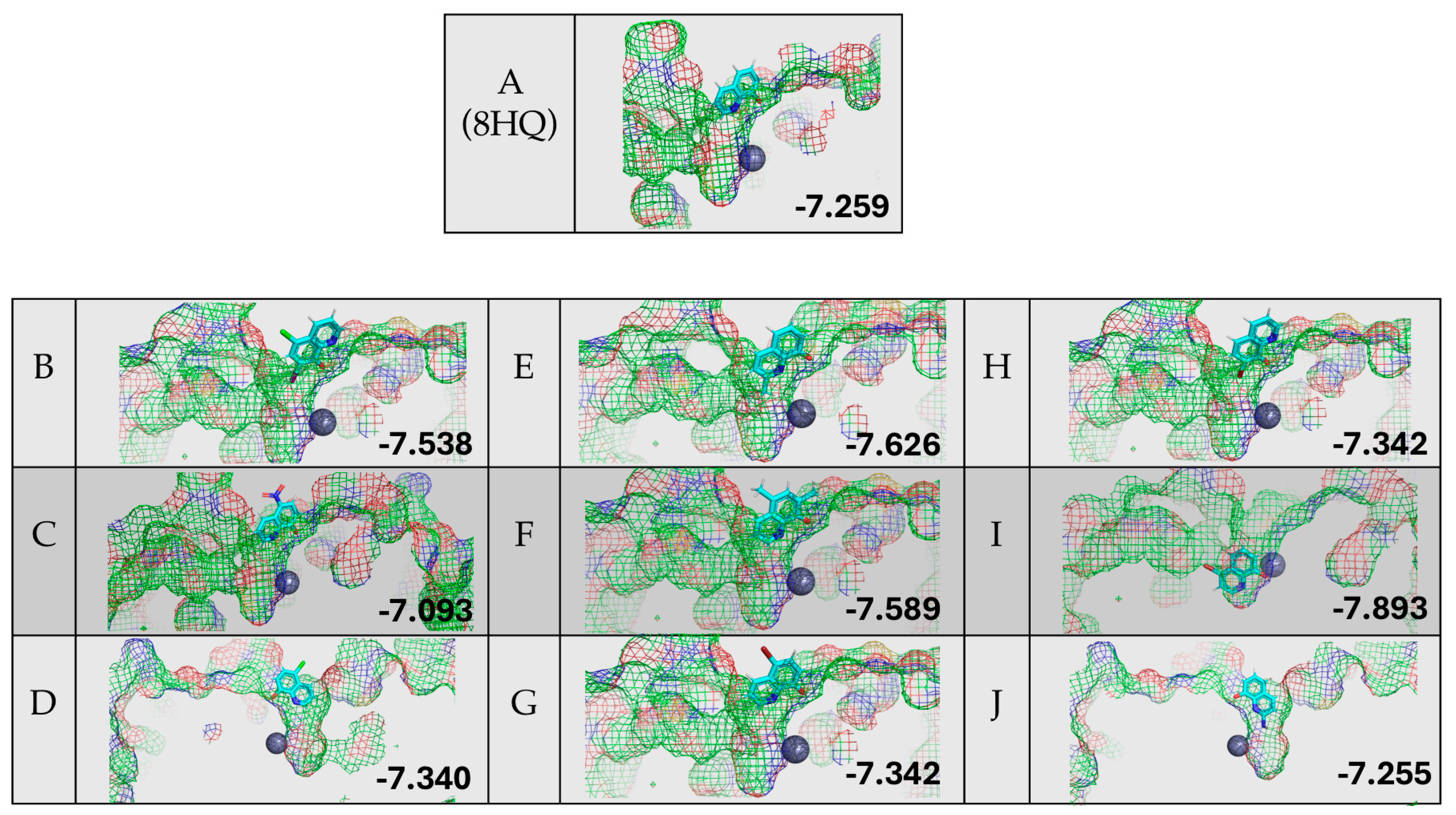
Figure 7 shows the results of the protein–ligand docking of 8HQ derivatives and their relative docking scores reported in kcal/mol. All but one 8HQ, ligand I, did not bind to the zinc center in HDAC8 in this study but rather sat above the active site. This does not align with the small-molecule zinc hydrolase mimic chemistry, where TpZnOH reacted readily with 8HQ species, suggesting that the shape of the substrate channel = allowing access to the relatively buried active site of HDAC8 does not work well with simple 8HQs.
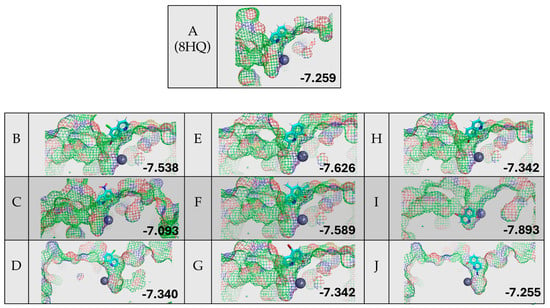
Figure 7.
Protein–ligand docking of 8HQ derivatives with HDAC8 and their associated docking scores reported in kcal/mol, with the letter of the compound shown to the left of the electrostatic potential map of the protein–ligand complex.
Although the zinc-binding group of 8HQ inhibitors only enters the active site in the case of inhibitor I, without the direct binding of zinc, it does not rule out possible inhibition through zinc binding or other mechanisms. For example, 8HQ could block the access of the substrate to the active site in an alternative way. Proteins are flexible structures and can accommodate the bulky structure of 8HQs, which is something that is not accounted for in the DockThor algorithm, which uses a static protein structure. It should also be noted that all inhibitors scored in the −7.2 to −7.9 kcal/mol range, making the determination of the ranking of inhibitors not feasible due to the similarity of the docking scores. Given the experimental and computational studies reported above, an examination of residual enzyme activity in the presence of 8HQ derivatives was performed utilizing an in vitro inhibition assay specific for HDACs.
3.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant HDAC8
The expression and purification of recombinant HDAC8 were adapted with variations from two previous protocols, [34,35]. During expression, 0.8 mM IPTG and 0.2 mM ZnSO4 were introduced upon induction for 16–18 h at 25 °C. Typical yields from a 500 mL culture ranged from 3 to 7 mg, but samples were very pure from IMAC alone following this protocol and required no further purification steps, as shown in Figure S2. The modification of purification protocol is as follows: wash and elution buffers at a pH of 8, 300 mM NaCl to prevent nonspecific electrostatic interactions, and 10% glycerol to increase solvent density and help solubilize and stabilize HDAC8 prior to column loading. Buffers originally tested at a pH of 7.5 with a 100 mM imidazole wash step compared to the buffers with a pH of 8 resulted in more nonspecific proteins only eluting after the addition of 300 mM imidazole, as seen in the SDS- PAGE gels shown in Figures S1 and S2. Then, 100 mM imidazole at a pH of 8 pulled off the nonspecific proteins with very minimal loss relative to HDAC.
3.5. HDAC8 Enzyme Inhibition Studies
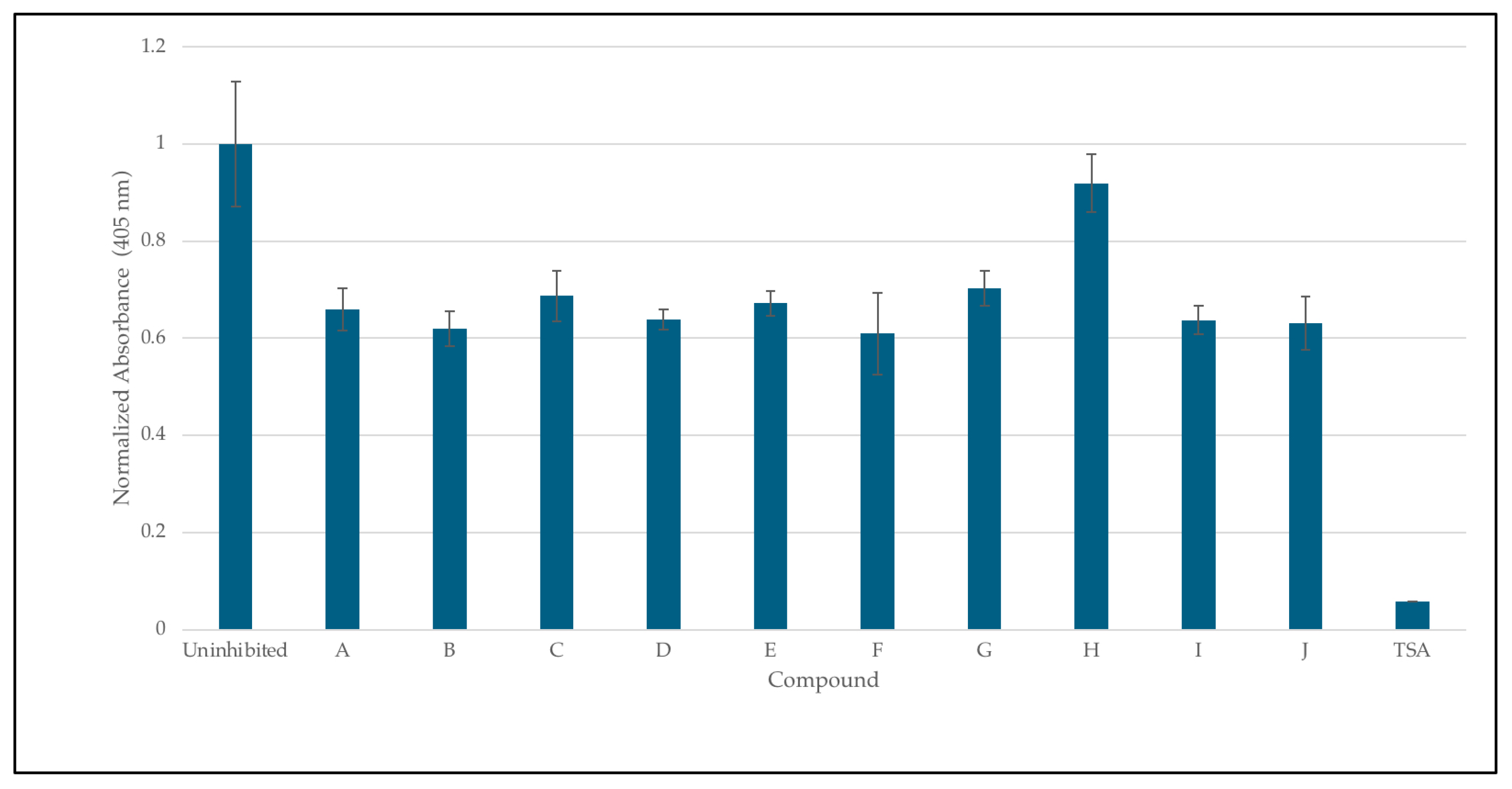
The inhibition of HDAC8 via 8HQs, as shown in Figure 8, shows that 8HQs are not as effective as the hydroxamic acid TSA, which is similar to Vorinostat’s structure and also features a cap, tail, and zinc-binding group. TSA is crystallized and bound to HDAC [32]. The 8HQ inhibition data are consistent with the predictions made via molecular docking using DockThor. For example, docking the predicted inhibitor C would result in the least amount of inhibition, while inhibition assays show C on the lower end of inhibition in comparison to other molecules. Docking the predicted inhibitor I would perform the best, and the results show I as one of the better-performing inhibitors. An outlier is inhibitor H, which has a binding score of −7.342 kcal/mol, falling in the middle of the range of all inhibitors. Docking predicted that the performance of inhibitor H would be in the middle when in fact it provided the least inhibition with respect to enzyme activity. The fact that, in direct competition assays, 8HQs were able to outcompete SAHA for zinc binding. In the case of HDAC8, zinc binding is not the only important interaction when it comes to inhibiting HDAC8. An inhibitor needs to be able to fit in the active site tunnel and interact with residues in that tunnel even if it is only through Van der Waals interactions; hence, the linear chain structure of the linker group on SAHA is part of the pharmacophore. The linker and cap group on SAHA and TSA clearly provide an advantage over 8HQs in terms of zinc binding to HDAC8 due to the accessibility of the zinc ion.
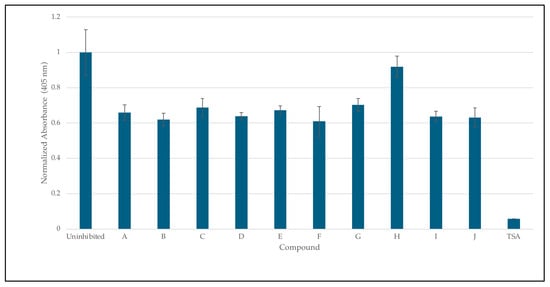
Figure 8.
Inhibition studies of HDAC 8 with 8HQ derivatives. The negative control was shown as an uninhibited enzyme, and the positive control was shown as trichostatin A (TSA) a stand-in for SAHA. Error bars are displayed, and all compounds are significantly significant (p < 0.05) except for H (0.19).
The data clearly show that the TpZn framework, while valuable for studying small molecules bound to zinc, is not a good framework for understanding the binding of drug molecules to HDAC8 or similar proteins. The tertiary structure of the protein plays an important role, and the “linker and cap” structures of SAHA and TSA appear to make them significantly superior to 8HQ, even though 8HQ binds better to zinc compared to hydroxamic acids in small-molecule complexes.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we examined the role of substituents on 10 different 8-hydroxyquinolines binding to a zinc small-molecule structure and the use of 8HQs as inhibitors for the zinc-dependent enzyme HDAC8. We obtained five new crystal structures of substituted 8-hydroxyquinolines bound to the TpZn framework. The bond lengths between Zn and 8-hydroxyquinolines were compared, but a clear trend was not observed. Further, DFT calculations of the related TpZn species did not correlate well with the X-ray structures. When docking studies were performed with the 8HQs and an HDAC8 crystal structure, the 8HQs did not bind to the zinc atom in the active site, and they primarily did not fit well into the active site as a class of molecules. This poor binding behavior was consistent with the in vitro inhibition assay studies of HDAC8, where all 8HQs did not inhibit hydrolase activity to a large degree in comparison to a known hydroxamic acid inhibitor with a linker, cap, and zinc-binding group. This study is limited due to the ineffective modeling of the enzyme active in the small-molecule system. Overall, the TpZn framework should not be considered a good model of HDACs because it does not account for the hydrophobic tunnel that provides substrate access to the zinc ion.
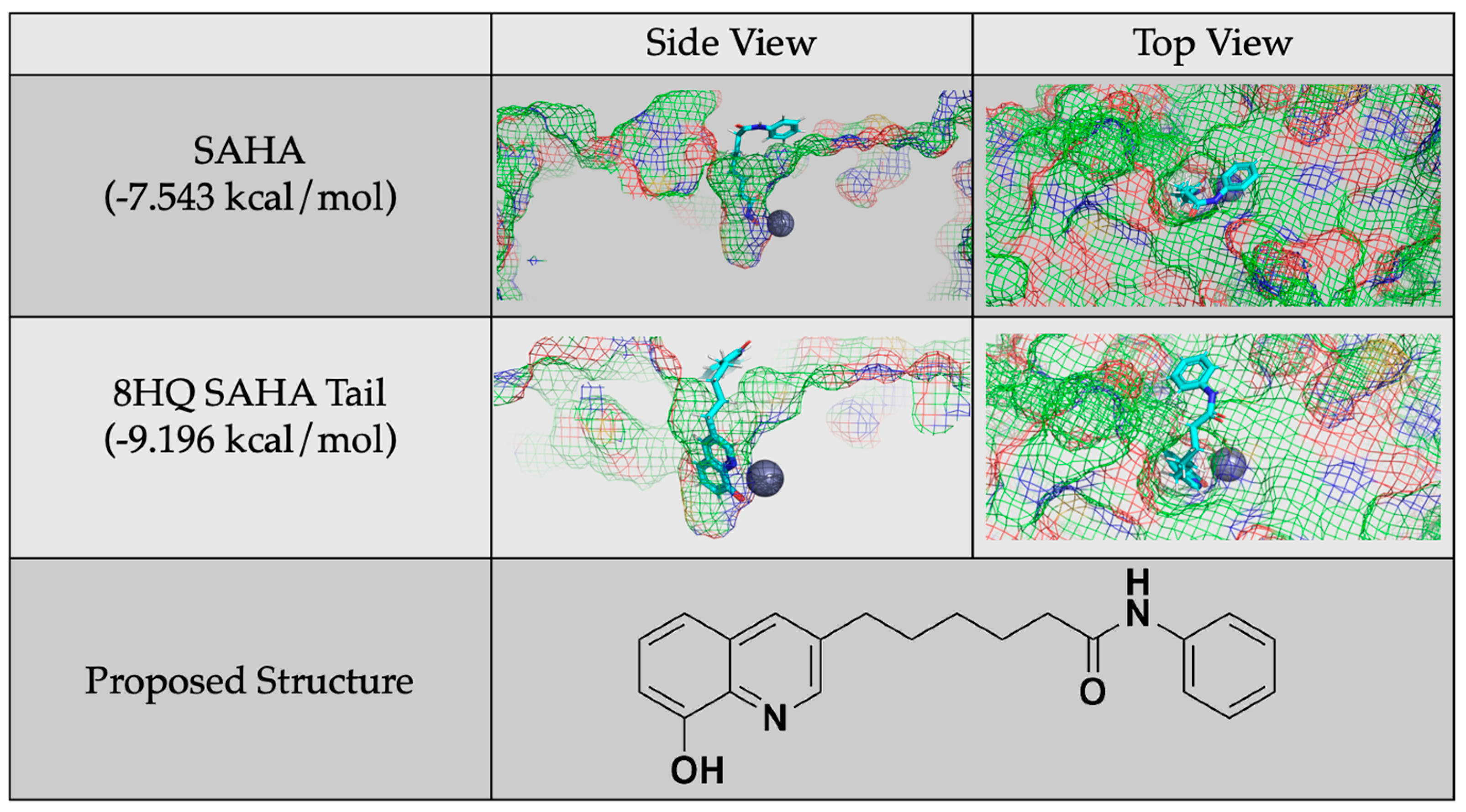
Given these conclusions, future studies will focus on generating inhibitors based on 8HQ fragments with the linker and cap groups associated with the HDAC pharmacophore, such as the proposed molecule shown in Figure 9. It is important to note that these future studies are in reference to HDAC8 and are not generalizable to other zinc-containing enzymes as it is the structure of the cavity that is being exploited. As a comparison with the smaller 8HQs A-J, this compound was docked with HDAC8 and did show zinc binding, and it accommodated the linker and cap groups. The overall docking score was better than the known inhibitor SAHA. This proposed structure and similar molecules will be synthesized and tested as inhibitors in future work.
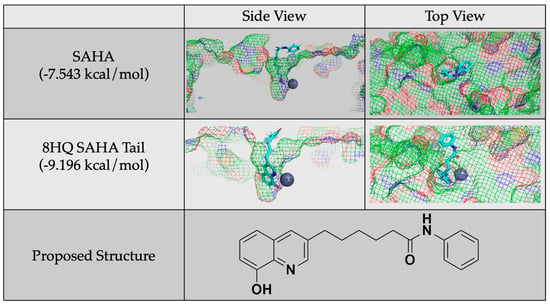
Figure 9.
Protein–ligand docking of a proposed molecule for future study generated by adding a SAHA tail to 8HQ and a comparison of its docking and docking score to that of SAHA.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/foundations4030024/s1. Figure S1: Amino acid sequence of human histone deacetylase 8; Figure S2: SDS-PAGE showing FPLC run from the original purification protocol; Figure S3: SDS-PAGE showing FPLC run from the modified purification protocol; Figure S4: NMR spectrum of TpZn(B-H) in CDCl3 at 300 MHz; Figure S5: NMR spectrum of TpZn(C-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz; Figure S6: NMR spectrum of TpZn(D-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz; Figure S7: NMR spectrum of TpZn(E-H) in CDCl3 at 300 MHz; Figure S8: NMR spectrum of TpZn(F-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz; Figure S9: NMR spectrum of TpZn(G-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz; Figure S10: NMR spectrum of TpZn(H-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz; Figure S11: NMR spectrum of TpZn(I-H) in CDCl3 at 400 MHz. Reference [43] is cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Methodology, K.L.S., K.A.G. and A.M.B.; investigation, K.L.S., K.A.G., A.M.B., E.M., H.F.C., M.J.T., X.A.A. and P.S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.B., K.L.S. and K.A.G.; writing—review and editing, A.M.B., K.L.S. and K.A.G.; supervision, K.L.S. and K.A.G.; project administration, K.L.S. and K.A.G.; X-ray crystal structures, R.D.S., A.R.J. and D.J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the following individuals who have offered support and expertise: John Kurowski, Nicole Staszak, John Zakhari, and Lihua Jin. Matthew L. Brown is acknowledged for valuable discussions about crystallography.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Anzellotti, A.I.; Farrell, N.P. Zinc Metalloproteins as Medicinal Targets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Pecoraro, V.L. Designing Hydrolytic Zinc Metalloenzymes. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 957–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, K.A.; Huang, C.; Fierke, C.A. Function and Mechanism of Zinc Metalloenzymes. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1437S–1446S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.W. Regulation of Zinc-Dependent Enzymes by Metal Carrier Proteins. Biometals 2022, 35, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, W.-G. Targeting Histone Deacetylases for Cancer Therapy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Ramos, J.; Luo, W.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Buggy, J.J. A Novel Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8)-Specific Inhibitor PCI-34051 Induces Apoptosis in T-Cell Lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A. Sulfonamides and Their Isosters as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashida, M.; Iqbal, J. Inhibition of Alkaline Phosphatase: An Emerging New Drug Target. MRMC 2015, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Alkaline Phosphatase. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, 2020, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarhaus, M.; Cianciolo, G.; Barbuto, S.; La Manna, G.; Gasperoni, L.; Tripepi, G.; Plebani, M.; Fusaro, M.; Magnusson, P. Alkaline Phosphatase: An Old Friend as Treatment Target for Cardiovascular and Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarhaus, M.; Brandenburg, V.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Magnusson, P. Alkaline Phosphatase: A Novel Treatment Target for Cardiovascular Disease in CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, D.; Liang, M.; Wang, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Huo, Y.; et al. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase Levels and the Risk of New-Onset Diabetes in Hypertensive Adults. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Overview and Perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of Histone Acetylation: The Histone Deacetylase Enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogal, A.; Abdulkadir, S.A. Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (HDACi); Trichostatin-A (TSA) on the Expression of Housekeeping Genes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2006, 20, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, W.-G. The Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Their Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 576946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and Emerging HDAC Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Yang, H.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferrajoli, A.; Cortes, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Faderl, S.; Koller, C.; Morris, G.; Rosner, G.; et al. Phase 1 Study of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Vorinostat (Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid [SAHA]) in Patients with Advanced Leukemias and Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Blood 2008, 111, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, L.M.; Zhou, X.; Xu, W.-S.; Scher, H.I.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor SAHA Arrests Cancer Cell Growth, up-Regulates Thioredoxin-Binding Protein-2, and down-Regulates Thioredoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11700–11705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Song, J.; Sun, M.; Shan, C. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi), the Ongoing Epigenetic Agents to Enhance Chemotherapy Sensitization. In Epigenetic Regulation in Overcoming Chemoresistance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun Cao, P.; Sommer, R.D.; Grice, K.A. Structural Comparison of Suberanilohydroxamic Acid (SAHA) and Other Zinc-Enzyme Inhibitors Bound to a Monomeric Zinc Species. Polyhedron 2016, 114, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.G.; Burns, P.T.; Miceli, A.M.; Grice, K.A.; Karver, C.E.; Jin, L. Calorimetric Studies of the Interactions of Metalloenzyme Active Site Mimetics with Zinc-Binding Inhibitors. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11817–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Jackl, M.K.; Kalaj, M.; Cohen, S.M. Developing Metal-Binding Isosteres of 8-Hydroxyquinoline as Metalloenzyme Inhibitor Scaffolds. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 7631–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Shah, K. Quinolines, a Perpetual, Multipurpose Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. 8-Hydroxyquinoline: A Privileged Structure with a Broad-Ranging Pharmacological Potential. Med. Chem. Commun. 2015, 6, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.M.; Cole, K.E.; Dowling, D.P.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, Mechanism, and Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases and Related Metalloenzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knez, D.; Sosič, I.; Pišlar, A.; Mitrović, A.; Jukič, M.; Kos, J.; Gobec, S. Biological Evaluation of 8-Hydroxyquinolines as Multi-Target Directed Ligands for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian. Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.S.; He, X.; Truhlar, D.G. MN15-L: A New Local Exchange-Correlation Functional for Kohn–Sham Density Functional Theory with Broad Accuracy for Atoms, Molecules, and Solids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.A.; Costa, L.S.C.; Dos Santos, K.B.; Karl, A.L.M.; Rocha, G.K.; Teixeira, I.M.; Galheigo, M.M.; Medeiros, V.; Krempser, E.; Custódio, F.L.; et al. Drug Design and Repurposing with DockThor-VS Web Server Focusing on SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Targets and Their Non-Synonym Variants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.B.; Guedes, I.A.; Karl, A.L.M.; Dardenne, L.E. Highly Flexible Ligand Docking: Benchmarking of the DockThor Program on the LEADS-PEP Protein–Peptide Data Set. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somoza, J.R.; Skene, R.J.; Katz, B.A.; Mol, C.; Ho, J.D.; Jennings, A.J.; Luong, C.; Arvai, A.; Buggy, J.J.; Chi, E.; et al. Structural Snapshots of Human HDAC8 Provide Insights into the Class I Histone Deacetylases. Structure 2004, 12, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 3..0.3; Schrödinger LLC: San Diego, CA, USA.
- Hu, E.; Chen, Z.; Fredrickson, T.; Zhu, Y.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Zhang, G.-F.; Johanson, K.; Sung, C.-M.; Liu, R.; Winkler, J. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Human Class I Histone Deacetylase That Functions as a Transcription Repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15254–15264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantt, S.L.; Gattis, S.G.; Fierke, C.A. Catalytic Activity and Inhibition of Human Histone Deacetylase 8 Is Dependent on the Identity of the Active Site Metal Ion. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6170–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.S.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Ganesan, A. Thirty Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 Insight and Hindsight. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12460–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Yuan, H.; Hu, J.; Zhao, C.; Chai, R.; Cao, H. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Nitro Oxide Donating N-Hydroxycinnamamide Derivatives as Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- You, Z.; Ran, X.; Dai, Y.; Ran, Y. Clioquinol, an Alternative Antimicrobial Agent against Common Pathogenic Microbe. J. Mycol. Médicale 2018, 28, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ran, Y. The Effects of Clioquinol in Morphogenesis, Cell Membrane and Ion Homeostasis in Candida Albicans. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijma, R.A.; Huttner, A.; Koch, B.C.P.; Mouton, J.W.; Muller, A.E. Review of the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Nitrofurantoin and Nitroxoline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2916–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao-Pellicer, J.; Arberas-Jiménez, I.; Fuchs, F.; Sifaoui, I.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Scheid, P. Repurposing of Nitroxoline as an Alternative Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis Treatment. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochterski, J. Thermochemistry in Gaussian; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Benchling. Available online: https://www.benchling.com/ (accessed on 6 June 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).