Abstract
Objective: The objective of this systematic review is to analyze the effects of strength training on the quality of life (QoL) of older adults diagnosed with sarcopenia, contributing to a better understanding of the impact of this intervention on the physical and psychological well-being of this population. Methods: A systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines. The search was conducted on the Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed databases, including studies published until 2025. Randomized controlled trials that applied strength training interventions in individuals aged 60 years or older with sarcopenia were included, evaluating QoL as the primary outcome. Data screening, extraction, and analysis were performed by two independent investigators. Results: Three studies from the United Kingdom, Saudi Arabia, and China were included, with interventions ranging from 6 to 16 weeks. The results showed that strength training can improve the quality of life of older adults with sarcopenia (instruments: SarQoL, SF-36, WHOQOL-BREF), being more effective in high-intensity and supervised interventions. One of the studies revealed significant improvements (p < 0.001), while the others showed non-significant increases. Conclusions: Strength training proved to be a promising intervention for promoting improvements in the quality of life of older adults with sarcopenia, especially when performed at adequate intensity and with regular monitoring. However, further studies with larger samples, long-term follow-up, and standardization of QoL assessment tools are needed.
1. Introduction
The prevalence of sarcopenia among older adults is significantly variable in diagnostic criteria used, clinical settings, and comorbidity contexts, according to criteria and age group, observational studies show. Global data indicates the prevalence is between 8% and 40% for community-dwelling older adults (≥60 years) and higher levels (30–50%) for patients in both the acute care and long-term care contexts due to their greater fragility and comorbidities [1,2]. Obviously, the condition of sarcopenia is influenced by age, sex, or gender. For example, sarcopenia appears to be more prevalent in older men at 12–40% than older women at 8–30%, although women tend to experience a more accelerated decline in muscle mass and strength after menopause due to hormonal changes [3,4]. In Latin American populations, Brazil, particularly, some epidemiological studies, such as the SABE study, report prevalence rates of sarcopenia at 16–33% [5], depending on the criteria applied, validating the significance of the topic in middle-income macro contexts. These variations across regions underscore the urgent need for effective, evidence-based interventions that not only mitigate muscle loss but also improve quality of life (QoL) outcomes specific to sarcopenic older adults. This global and multidimensional impact highlights the relevance of the present review. These variations underscore the necessity for standardization in operationalized diagnostic workups (e.g., applying EWGSOP2 criteria) and for starting early true pathophysiological interventions, particularly in higher-risk subgroups (older adults ≥80 years, or adults living with chronic diseases). A 2022 systematic review including over 9400 Brazilian participants aged ≥ 60 years estimated an overall prevalence of approximately 17% (95% CI: 13–22%), with slightly higher rates among women than men [5].
Given this context, there is a greater demand for effective, safe, and accessible solutions to limit the effects of sarcopenia, maintain functionality, and promote healthy and active aging [6]. Amongst non-pharmacological interventions, physical exercise, especially strength training, stands out as one of the most efficacious [7,8]. Evidence from the sciences suggests that the implementation of structured, progressive strength training programs with adequate supervision could lead to large increases in strength, enhance functional performance, and demonstrate positive influences on the quality of life of older adults with sarcopenia [9].
From a physiological perspective, strength training demonstrates several advantageous effects that explain its role in sarcopenia. Specifically, strength training promotes muscle protein synthesis and decreases catabolism, assisting in the maintenance or increase in lean mass [10,11]. Furthermore, it induces neuromuscular adaptations, enhances motor coordination, increases motor unit activation, and improves muscular recruitment [12]. Moreover, evidence shows that strength training decreases chronic inflammatory states and increases insulin sensitivity, both of which are associated with muscle declines in aging [13,14]. These combined mechanisms translate not only into physical gains but also into greater autonomy, a lower risk of falls, and, consequently, better quality of life [15].
However, the literature also has significant limitations that need to be recognized. There is high heterogeneity in intervention protocols (e.g., duration, frequency, intensity, and type of exercises), which limits the ability to replicate results and infer generalizable outcomes [16]. Furthermore, there is a great deal of variance with regard to the instruments used to assess QoL, which limits the ability to make direct comparisons [15]. Another major limitation is the number of randomized clinical trials that focus on QoL as a primary outcome, where most studies simply consider it a secondary outcome that is only referenced. Many studies mention physical indicators and do not explore QoL as a primary indicator [17].
Therefore, clearly understanding the relationship between strength training and QoL in older adults with sarcopenia must include methodologically sound options with a standardized protocol and valid instruments [1]. This will facilitate recommendations to clinicians and public health systems, as well as public health policies to inform community initiatives to promote healthy aging [18].
In clinical and social terms, effective sarcopenia interventions could potentially prevent falls, fractures, and hospitalizations, lower healthcare costs, and postpone frail older adult institutionalizations [19]. Thus, in addition to enhancing individual quality of life, strengthening the scientific evidence on strength training may help develop policies that promote a more active, autonomous, and economically sustainable aging process [6].
Given the growing prevalence of sarcopenia and its profound impact on physical and psychosocial well-being, it is essential to identify interventions that not only prevent muscle decline but also enhance quality of life. Previous systematic reviews have primarily focused on physical performance outcomes, often treating QoL as a secondary measure. Therefore, the present review addresses a critical gap by synthesizing evidence exclusively from randomized controlled trials that evaluate quality of life as a primary outcome in older adults diagnosed with sarcopenia. This approach provides a more specific and clinically relevant understanding of the role of strength training in promoting holistic well-being among this population. In this context, the present study aims to conduct a systematic review of the scientific literature, specifically analyzing the effects of strength training on the quality of life of older adults with a clinical diagnosis of sarcopenia. It was hypothesized that strength training interventions would significantly improve quality of life outcomes in older adults diagnosed with sarcopenia.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [18]. The review protocol was registered in the PROSPERO database under the ID CRD420251090162.
2.1. Literature Search, Manuscript Selection, and Eligibility Criteria
To carry out this systematic review, articles were retrieved from two electronic databases: Web of Science (WOS), Scopus, and PubMed (the research was updated on 30 July 2025). The search strategy aimed to gather all studies that used the following terms: (“resistance training” OR “strength training” OR “resistance exercise” OR “strength exercise” OR “weight training” OR “muscle strengthening” OR “progressive resistance training”) AND (“older adults” OR elderly OR “older people” OR aged OR aging OR geriatric OR seniors OR “older individuals”) AND (sarcopenia) AND (“quality of life”). The selection criteria were defined based on the PICOS framework, considering the following studies: P (Population): studies involving older adults with sarcopenia aged 60 years or older; I (Intervention): studies that assessed the effects of a strength training program; C (Comparator): studies comparing other types of exercise (e.g., walking), a control group, or pre–post intervention comparisons; O (Outcomes): studies that evaluated quality of life construct and its dimensions/domains; and S (Study design): RCT studies.
The inclusion criteria for this review were as follows: (i) participants aged 60 years or older; (ii) interventions focused on strength training in individuals clinically diagnosed with sarcopenia; (iii) studies that included quality of life as one of the assessed outcomes; and (iv) randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The exclusion criteria included the following: (i) studies with participants under 60 years of age; (ii) studies involving individuals without sarcopenia; (iii) studies that did not include quality of life as one of the outcomes evaluated; (iv) the gray literature (in order to increase the scientific robustness of studies); (v) articles not published in English or Portuguese; and (vi) studies involving multicomponent interventions.
2.2. Data Extraction
First author (L.F.) began the article search and subsequently screened the identified titles and abstracts for possible inclusion. All disagreements and uncertainties were discussed with the last author (M.J.), and consensus on inclusion was achieved. When this consensus was not possible, a third investigator was invited to collaborate. Reference management and importing of records from databases were performed using EndNote X7 (Clarivate, Philadelphia, PA, USA). Duplicates were also automatically eliminated by the software.
The key information from the studies included in this systematic review was extracted in a consistent manner, including author, year published, sample size, mean and standard deviation, type of exercise, frequency and duration of training sessions, design of study, assessment instrument, and outcome variable. Studies with essential information that was missing or ambiguous were not included in the final selection. Data extraction was conducted independently by first author (L.F.), with any discrepancies or uncertainties were resolved with the last author (M.J.).
2.3. Methodological Quality Assessment
The methodological quality of the randomized clinical trials included in this review was assessed using the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) Scale, a widely used and validated tool in the field of rehabilitation. This scale has good reliability and validity and is recognized for its ability to consistently measure the methodological rigor of studies. Its application ensures greater robustness, transparency, and comparability of results between systematic reviews in physical therapy. The PEDro Scale is made up of 11 items. Ten of these items are scored and consist of items pertaining to randomization, blinding, statistical analysis, and data integrity. Two authors independently evaluated each study using the PEDro Scale, and consensus was reached for discrepancies. Studies rated below 4 were deemed to be low quality, scores of 4 to 6 were considered moderate quality, and scores of 7 and above were considered high quality. Overall, the PEDro Scale allows for a consistent and open assessment of all studies’ methodological quality.
3. Results
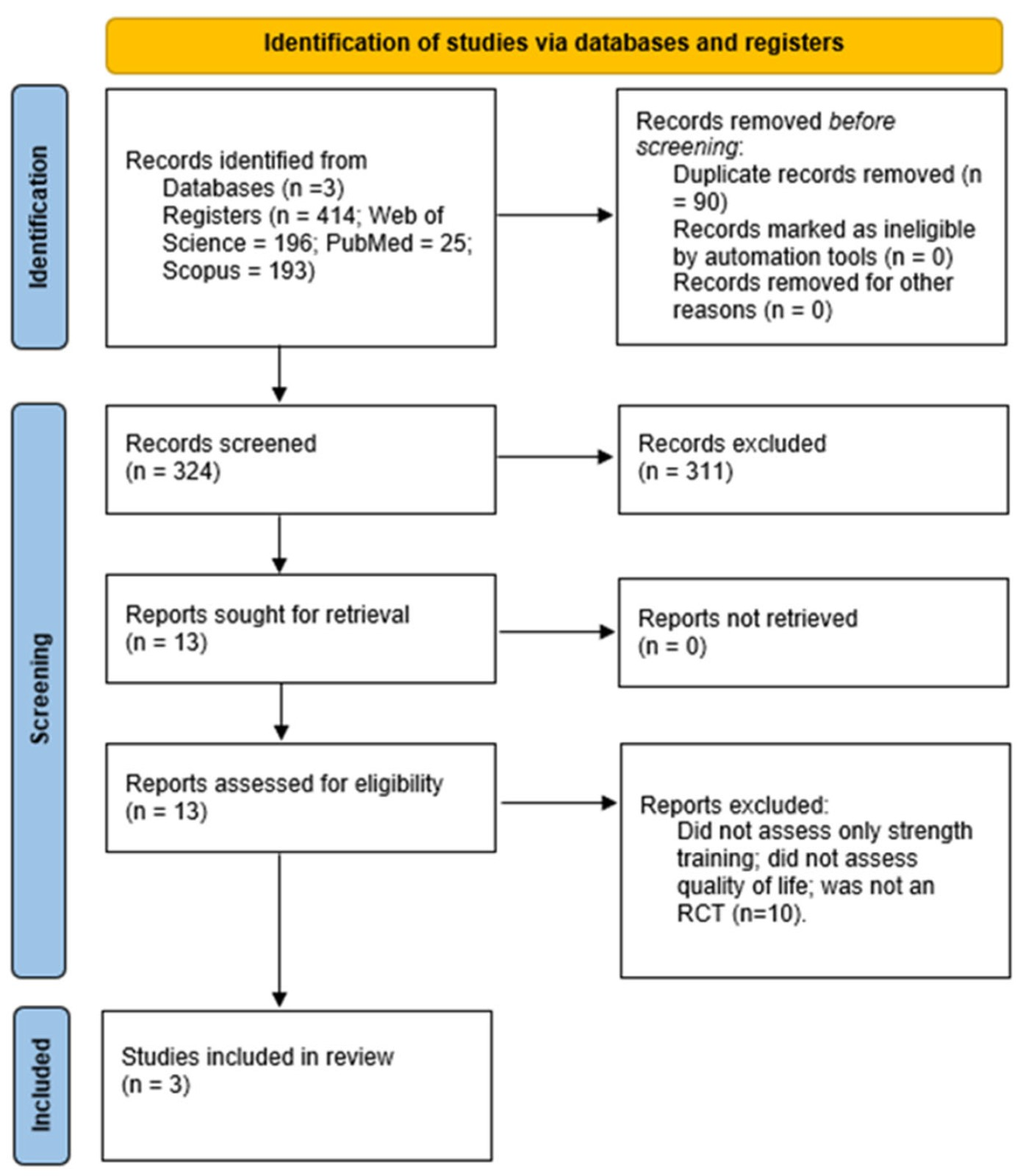
Of the 414 articles retrieved from the databases, 311 were excluded after screening their titles and abstracts, and 9 were excluded after full-text review. Only three studies met all the inclusion criteria and were deemed eligible for this systematic review (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Flow diagram PRISMA for the included studies.
These studies were conducted between 2020 and 2024 across different geographical regions: the United Kingdom, Pakistan, and China. All selected studies employed experimental designs with randomized groups and evaluated the impact of strength training on the quality of life (QoL) of older adults with sarcopenia (Table 1).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included studies.
3.1. Type of Study
The three studies included in this systematic review used experimental designs in the context of RCTs, which accounted for the inclusion criteria of this review, as RCTs are the gold standard in evaluating the efficacy of interventions. Randomization was outlined in all three studies and, therefore, each had a fair allocation of participants and reduced selection bias. Of the three studies, one study implemented a non-intervention control group, whereas the other two studies also included groups with different types of intervention. This experimental design adds to the internal validity of the findings, even though the protocols were all different and created challenges in making direct comparisons of the outcomes. For the purposes of this review, only the methods and outcomes of the strength training groups were included.
3.2. Intervention
All studies had the shared purpose of assessing the effects of strength training on QoL in older adults with sarcopenia; however, there were differences in intensity, frequency, duration, load progression, and mode of exercise.
3.2.1. Study by Kirk et al. [20]
The study by Kirk et al. [20] assessed a supervised strength training protocol for 8 weeks, at a frequency of two sessions per week. The training consisted of multi-joint and single-joint exercises (e.g., leg press, chest press, shoulder press) to failure in two sets. The load increased when the participant could perform 12 repetitions for 2 consecutive sets (+2.5 kg upper body, +5 kg lower body). Also included was a functional circuit of 12 stations with muscular endurance exercises.
3.2.2. Study by Ibrahim et al. [21]
In the study by Ibrahim et al. [21], a supervised high-intensity progressive resistive strength training was prescribed (up to 65% of 10RM). Training was performed using dumbbells, resistance bands, and sandbags (1–3 kg) in 2 sets of 10–12 repetitions with a 2-min rest, three days a week for 6 weeks. The load progression was self-determined, using perceived exertion at a target of 12–14 Borg scale.
3.2.3. Study by Zhuang et al. [22]
The study by Zhuang et al. [22] used a supervised progressive strength training protocol that lasted for 12 weeks, increasing in intensity by 5%: 60% of 1RM (1–4 weeks), 65% of 1RM (5–8 weeks), and 70% (9–12 weeks). The protocol included upper and lower-body exercises (e.g., shoulder external rotation, squats with abduction, lunges) in 3 sets × 10 repetitions, lasting a total of 30 min (including warm-up and cool-down), three days a week. In all the studies, the supervised programs should be considered a safety and adherence issue that was rightly thought to contribute to the outcomes. This evidence supports the inclusion of professionally supervised exercise sessions as a core component of interventions targeting sarcopenia management.
3.3. Intervention Outcomes
Only Kirk et al. [20], Ibrahim et al. [21], and Zhuang et al. [22] assessed quality of life (QoL) outcomes through quantitative measures; however, they all saw improvements, specificity, and standard deviations in the measurement of the improvements. The improvements were greater than expected in Ibrahim et al. and Zhuang et al. Kirk et al. [20] demonstrated a small increase in participant perception of overall quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) in the exercise group (4.19 ± 0.93 → 4.33 ± 0.80); however, the increase in QoL perception was not statistically significant. Ibrahim et al. [21] reported significant improvements in the SarQoL questionnaire relative to high-intensity training (66.45 ± 4.57 → 73.30 ± 4.39; p < 0.001). Zhuang et al. [22] reported significant improvements in several SF-36 domains, particularly in physical functioning, role—physical, general health, mental health, and health transition (all p < 0.05). Other domains, such as bodily pain, vitality, social functioning, and role—emotional, did not show statistically significant changes. These results highlight that the effects of resistance training were more pronounced in the physical and mental health components of QoL. Zhuang et al. is of particular interest as it is important to analyze multidimensional improvements in QoL from progressive resistance training.
Overall, it seems that with an intervention conducted at a higher intensity, with progressions conceived to increase and with greater reciprocal duration, overall improvements in QoL—especially in physical and mental aspects—achieved through participation in endurance exercise, can be more remarkable.
3.4. Methodological Quality Assessment Results
The studies showed moderate methodological quality overall. The PEDro scores ranged from 5 to 6. All the studies were reasonably good at random allocation, and the baseline characteristics for each group were balanced. Data reporting was acceptable, and the statistical analysis was appropriate. Due to the nature of supervised physical interventions, none of the studies used blinding for participants, therapists, or assessors, which compromises the internal validity of the research. The absence of intention-to-treat analysis from all studies poses a consistent challenge to the quality of the research. Of the three included studies, Kirk et al. [20] received the lowest score (5/10) due to somewhat less clear methodology and weaker statistical comparisons, while Ibrahim et al. [21] and Zhuang et al. [22] had more rigorous statistical analyses and adherence to the physical activity interventions.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to critically evaluate the effects of strength training on the QoL of older adults with sarcopenia. By analyzing recent studies, we sought to overcome the limitations of previous reviews [8,23] through a rigorous methodological approach that considered both physical and psychosocial parameters of QoL.
The results of this systematic review corroborate established evidence that strength training is an effective strategy to mitigate the impacts of sarcopenia, promoting consistent gains in QoL. Meta-analyses, such as those by Peterson et al. [8] and Kashi et al. [23], had already demonstrated that strength training programs, especially when progressively structured and supervised, generate substantial improvements in physical performance and subjective perception of QoL. Also, a meta-analysis by Yoshimura et al. (2022) reported moderate pooled effects of resistance exercise on physical function (standardized mean difference = 0.58, 95% CI 0.32–0.84), whereas effects on QoL were smaller and less consistent [24]. However, our investigation provided more specific results than previous studies, showing that strength training is effective for improving QoL in older adults with sarcopenia.
The studies included in this review reinforce this trend, highlighting the work by Ibrahim et al. [21] and Zhuang et al. [22], who applied protocols of higher intensity and progression, achieving statistically significant effects in multiple QoL domains. Both studies advocated the use of loads equal to or greater than 65% of 1RM as a safe and effective threshold to optimize muscular and functional gains, as previously suggested [16]. Ibrahim et al. [21] drew attention to the efficacy of short (6-week) high-intensity interventions, while Zhuang et al. [22] focused on not only physical but also mental aspects. Although high-intensity training has been shown to have positive effects on quality of life and muscle function, it may pose increased risks for frail individuals, making professional supervision, gradual progression of load, and individual assessment of tolerance essential. On the other hand, Kirk et al. [20] reported only modest gains in overall QoL perception. Various adaptations, such as increasing weekly frequency, lengthening intervention duration (8 weeks), or adjusting prescription, could lead to a significant impact. Although multimodal approaches are recommended in rehabilitation contexts [25], the combined prescription of strength and resistance training (through functional training) may reduce the specific impact of isolated strength training on certain parameters, such as QoL. This methodological heterogeneity among studies, regarding intensity, frequency, duration, and exercise types, complicates direct comparisons and underscores the need for more homogeneous and standardized protocols, as also noted by Beaudart et al. [18].
When considering exclusively the impact on QoL of older adults with sarcopenia, strength training shows superior results compared to other intervention modalities. Aerobic exercise programs, while contributing to improvements in cardiovascular health and general conditioning, demonstrate limited effects on the physical and psychosocial domains of QoL [26,27]. Multicomponent interventions, combining strength training, balance, and functional activities, have shown broader gains in autonomy and functionality [20,25], but with less pronounced effects on global health perception compared to progressive high-intensity strength training. Nutritional strategies, such as protein or amino acid supplementation, have also been associated with modest improvements in QoL, mainly when combined with exercise [28,29], but alone, they do not produce the same effect. Thus, the data suggests that supervised and progressive strength training appears to be the most consistent intervention to promote significant and comprehensive improvements in the QoL of older adults with sarcopenia, outperforming isolated modalities and gaining special relevance when integrated with nutritional strategies.
Another relevant finding of the present work concerns professional supervision. Supervised interventions, such as those by Ibrahim et al. [21] and Zhuang et al. [22], showed high adherence rates and appropriate progression, contrasting with the inconsistent results observed in studies with unsupervised programs [30]. This disparity supports the guidelines of the American College of Sports Medicine [7], which emphasize specialized supervision as critical for the safety and efficacy of programs, especially in older adults with sarcopenia and associated comorbidities.
Regarding assessment instruments, this review identified significant limitations in the use of generic QoL questionnaires. While the SF-36 captured improvements limited to specific domains [22], the SarQoL, developed specifically for individuals with sarcopenia, demonstrated greater sensitivity to detect changes in psychosocial and functional aspects [18,21]. These results reinforce criticisms about the inadequacy of generic instruments and support the need for methodological standardization in evaluations [31].
Although this review reported positive outcomes, there are some limitations to consider, including (1) the small number of included studies limits generalization of results; (2) the training protocols are heterogeneous (i.e., intensity, frequency, duration, and type of exercise); (3) the different instruments used to assess QoL (e.g., WHOQOL-BREF, SarQoL, SF-36) prevent comparisons across studies; and (4) language bias may have occurred since only English and Portuguese publications were included. Future research should use larger and more macroscopically representative randomized controlled trials and longitudinal follow-up to confirm the lasting effects of strength training on QoL and ascertain variations and differential responses between subgroups of the population (for example, sex and homogeneity of baseline functional level).
From a clinical and community perspective, the findings of this review strongly support the inclusion of supervised and progressive strength training programs within prevention and rehabilitation services targeting sarcopenia and the promotion of quality of life (QoL) in older adults. Short-term high-intensity training may be as effective as longer moderate-intensity training has been shown to enhance not only functional capacity but also subjective QoL dimensions, including autonomy, psychological well-being, and perceived health status. Beyond individual benefits, these structured programs may contribute to broader public health outcomes by reducing the incidence of falls, fractures, and hospitalizations, thereby lowering healthcare costs and delaying the onset of frailty and institutionalization [19]. Consequently, the integration of evidence-based strength training protocols into community and clinical settings could represent a cost-effective and sustainable strategy to foster active, independent, and healthy aging among older adults with sarcopenia.
5. Conclusions
Based on the limited number of randomized controlled trials available, strength training shows promising potential to improve QoL among older adults with sarcopenia. However, current evidence remains preliminary and should be interpreted with caution. Larger and more methodologically robust trials are needed to confirm these effects and establish optimal training parameters.
In conclusion, strength training/education should be a large component in current prevention and rehabilitation programs for older adults aging with sarcopenia when aimed at later life active, independent, and healthy aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F. and M.J.; methodology, L.F. and M.J.; software, L.F. and M.J.; validation, R.A., R.M., D.M., N.A., N.C. and M.J.; formal analysis, M.J.; investigation, L.F. and M.J.; resources, L.F. and M.J.; data curation, L.F. and M.J.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F. and M.J.; writing—review and editing, L.F., N.C. and M.J.; visualization, R.A., R.M., D.M., N.A., N.C. and M.J.; supervision, M.J.; project administration, L.F. and M.J.; funding acquisition, R.A., R.M., D.M., N.A., N.C. and M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by National Funds from FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology, under the following project UID/04045: Research Center in Sports Sciences, Health Sciences, and Human Development.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizako, H.; Nakai, Y.; Tomioka, K.; Taniguchi, Y. Prevalence of Sarcopenia Defined Using the Asia Working Group for Sarcopenia Criteria in Japanese Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. Res. 2019, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; He, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tong, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Liu, K. The Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Risk Factors in the Older Adult in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz, J.B.M.; Leopoldino, A.A.O.; Moreira, B.d.S.; Henschke, N.; Dias, R.C.; Pereira, L.S.M.; Oliveira, V.C. Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Older Brazilians: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Cesari, M.; Di Bari, M.; Cherubini, A.; Collamati, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Pahor, M.; Bernabei, R.; et al. Sarcopenia: An Overview. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P.; American College of Sports Medicine. Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory, Musculoskeletal, and Neuromotor Fitness in Apparently Healthy Adults: Guidance for Prescribing Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.D.; Rhea, M.R.; Sen, A.; Gordon, P.M. Resistance Exercise for Muscular Strength in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zou, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z. Exercise Programs for Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, T.D.; Clark, L.A.; Clark, B.C. Resistance Exercise to Prevent and Manage Sarcopenia and Dynapenia. Annu. Rev. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 36, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.W.; Murphy, K.T.; McKellar, S.R.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Henselmans, M.; Helms, E.; Aragon, A.A.; Devries, M.C.; Banfield, L.; Krieger, J.W.; et al. A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of the Effect of Protein Supplementation on Resistance Training-Induced Gains in Muscle Mass and Strength in Healthy Adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, P.; Suetta, C.; Caserotti, P.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M. Role of the Nervous System in Sarcopenia and Muscle Atrophy with Aging: Strength Training as a Countermeasure. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.F.; Fielding, R.A. Skeletal Muscle Power: A Critical Determinant of Physical Functioning in Older Adults. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2012, 40, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Assar, M.; Álvarez-Bustos, A.; Sosa, P.; Angulo, J.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Effect of Physical Activity/Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Muscle and Vascular Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Zaaria, M.; Pasleau, F.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Bruyère, O. Health Outcomes of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragala, M.S.; Cadore, E.L.; Dorgo, S.; Izquierdo, M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Peterson, M.D.; Ryan, E.D. Resistance Training for Older Adults: Position Statement From the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekoura, M.; Kastrinis, A.; Katsoulaki, M.; Billis, E.; Gliatis, J. Sarcopenia and Its Impact on Quality of Life. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 987, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Biver, E.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Rolland, Y.; Bautmans, I.; Petermans, J.; Gillain, S.; Buckinx, F.; Dardenne, N.; et al. Validation of the SarQoL®, a Specific Health-Related Quality of Life Questionnaire for Sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, A.C.; Araújo, D.A.; Veríssimo, M.T.; Amaral, T. Sarcopenia and Hospitalisation Costs in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 74, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, B.; Mooney, K.; Cousins, R.; Angell, P.; Jackson, M.; Pugh, J.N.; Coyles, G.; Amirabdollahian, F.; Khaiyat, O. Effects of Exercise and Whey Protein on Muscle Mass, Fat Mass, Myoelectrical Muscle Fatigue and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Adults: A Secondary Analysis of the Liverpool Hope University-Sarcopenia Ageing Trial (LHU-SAT). Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Dewir, I.M.; Abu El Kasem, S.T.; Ragab, M.M.; Abdel-Fattah, M.S.; Hussein, H.M. Influences of High vs. Low-Intensity Exercises on Muscle Strength, Function, and Quality of Life in Post-COVID-19 Patients with Sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 9530–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Chen, N. Effects of 12-Week Whole-Body Vibration Training versus Resistance Training in Older People with Sarcopenia. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodadad Kashi, S.; Mirzazadeh, Z.S.; Saatchian, V. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Resistance Training on Quality of Life, Depression, Muscle Strength, and Functional Exercise Capacity in Older Adults Aged 60 Years or More. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2023, 25, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yamada, M.; Kim, H.; Harada, A.; Arai, H. Interventions for Treating Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 553.e1–553.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Risk of Falls, Gait Ability, and Balance in Physically Frail Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-J.; Latham, N.K. Progressive Resistance Strength Training for Improving Physical Function in Older Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 2009, CD002759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Sports Medicine; Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.; Fiatarone Singh, M.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and Physical Activity for Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Pan, T.; Tong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The Effects of Nutritional Supplementation on Older Sarcopenic Individuals Who Engage in Resistance Training: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Klersy, C.; Terracol, G.; Talluri, J.; Maugeri, R.; Guido, D.; Faliva, M.A.; Solerte, B.S.; Fioravanti, M.; Lukaski, H.; et al. Whey Protein, Amino Acids, and Vitamin D Supplementation with Physical Activity Increases Fat-Free Mass and Strength, Functionality, and Quality of Life and Decreases Inflammation in Sarcopenic Elderly. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, A.; Hortobágyi, T.; Beurskens, R.; Granacher, U. Effects of Supervised vs. Unsupervised Training Programs on Balance and Muscle Strength in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2341–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Demonceau, C.; Reginster, J.; Locquet, M.; Cesari, M.; Cruz Jentoft, A.J.; Bruyère, O. Sarcopenia and Health-related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).