A Multimodal Omics Exploration of the Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. RNA-Sequencing from Monocyte Samples
2.3. Metabolomics and Lipidomics
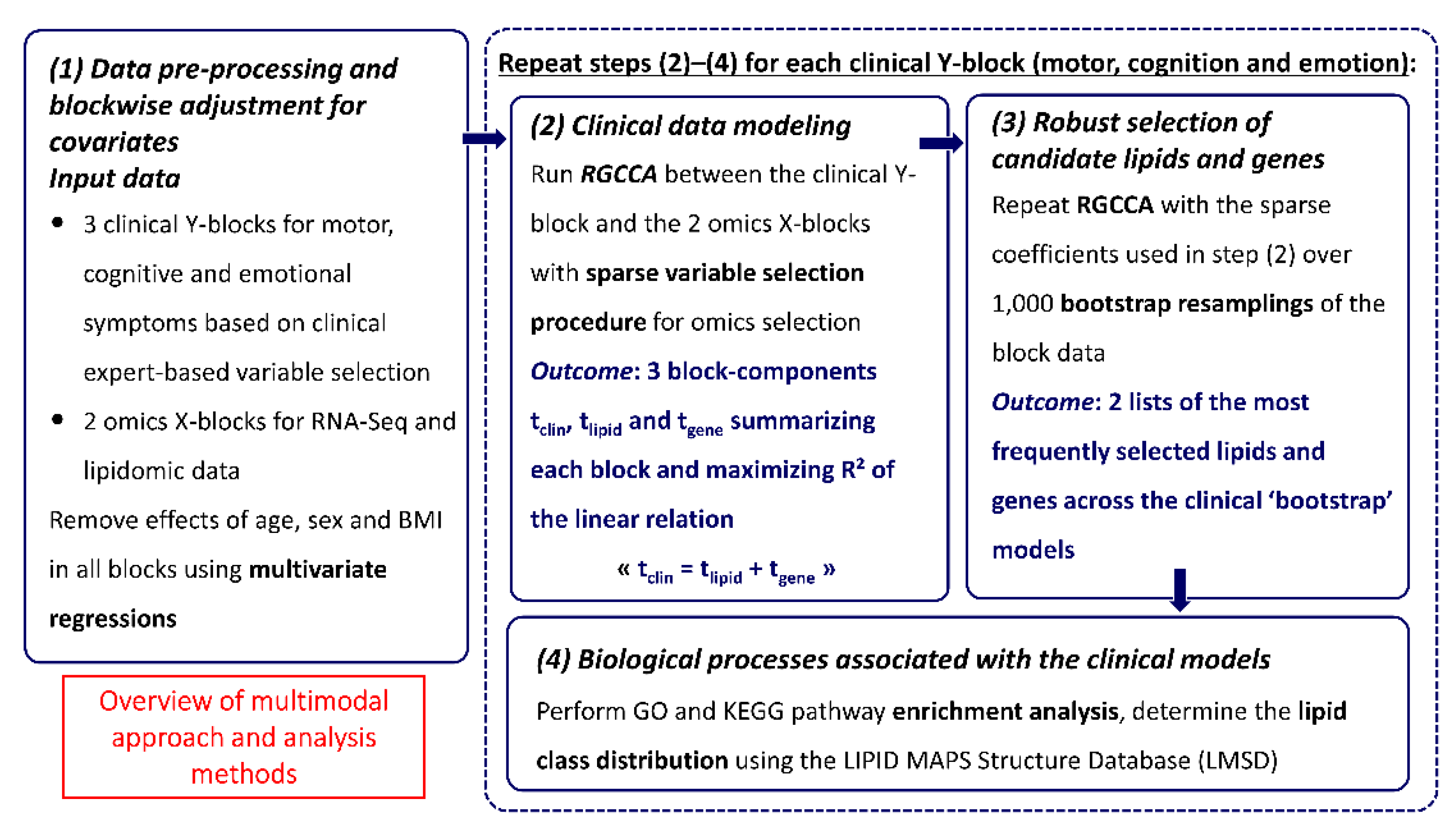
2.4. Integrative Analysis
2.5. Data Pre-Processing
2.6. Multiblock Data Analysis
2.7. Stability of the Omics Selections
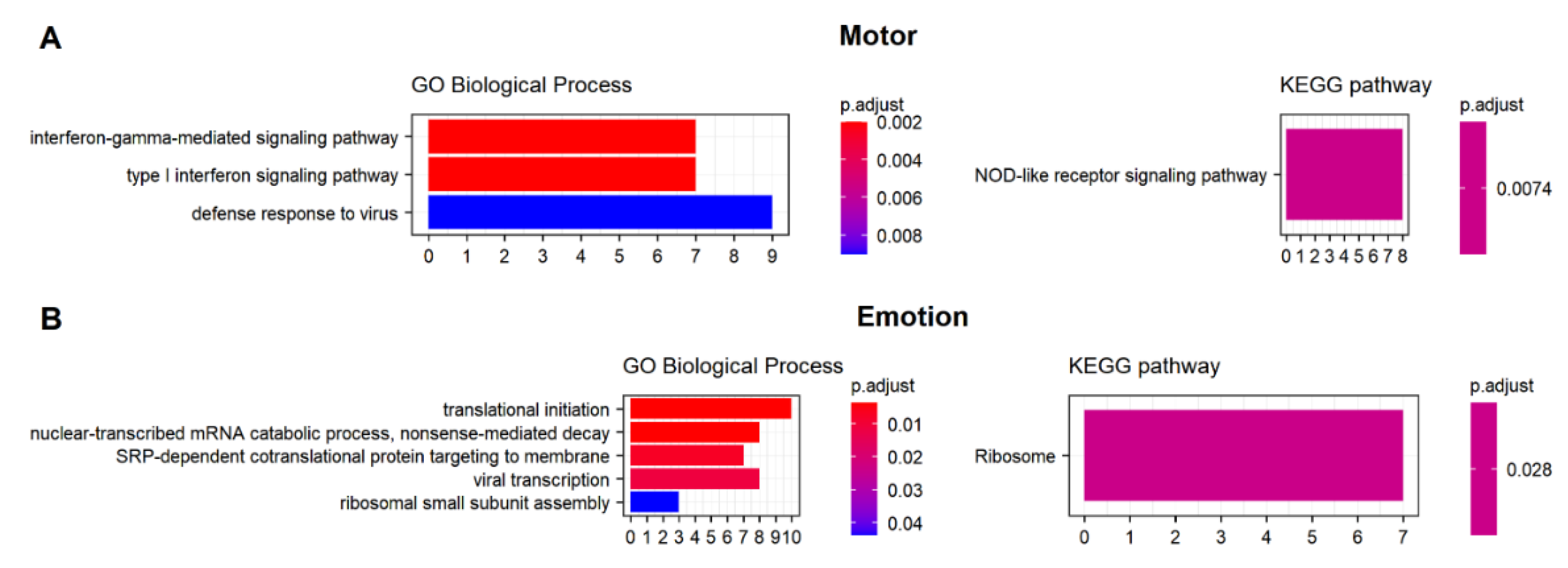
2.8. Biological Processes
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
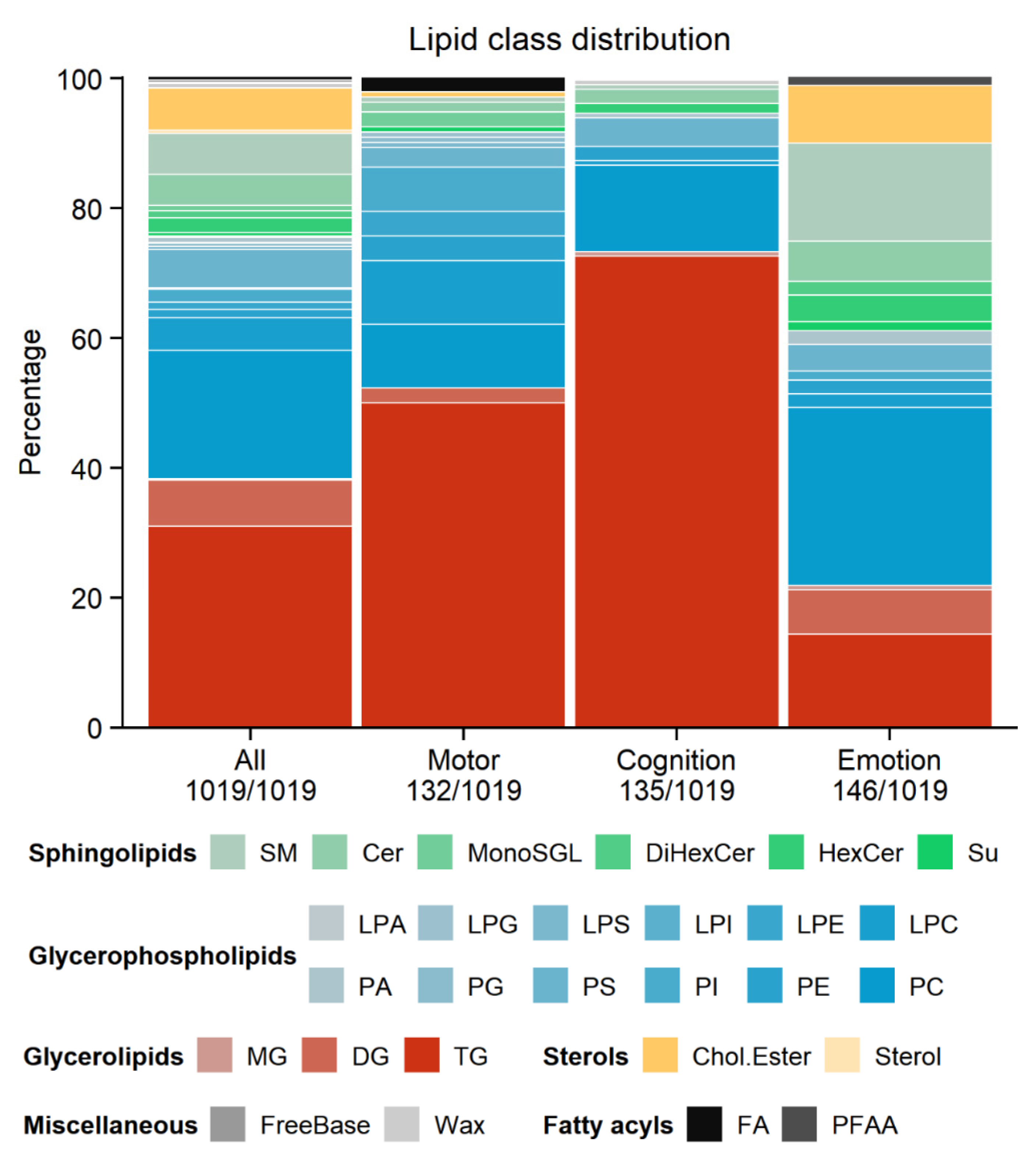
3.2. Omics Analyses
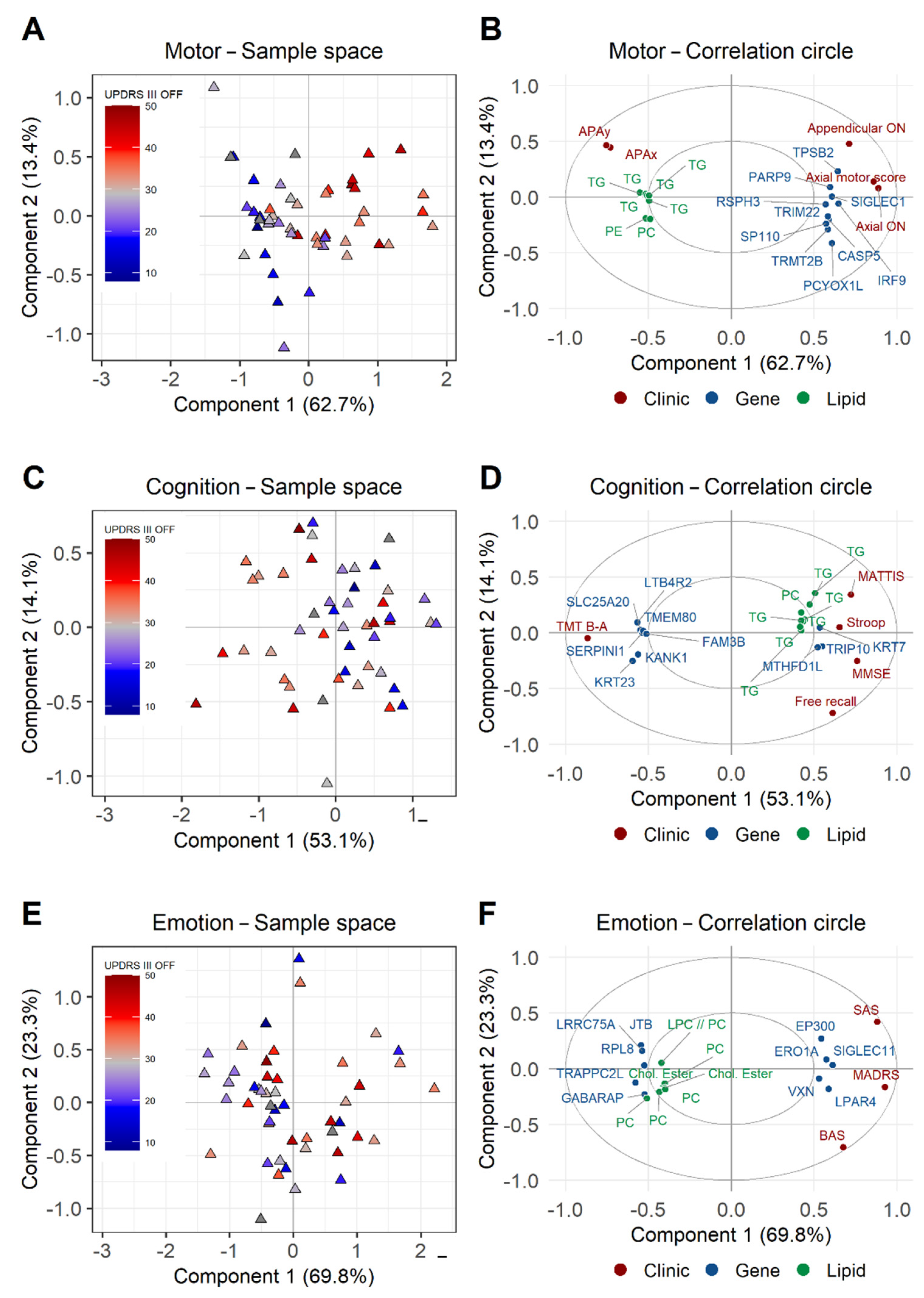
3.3. Multiblock Models for Omics–Clinical Associations
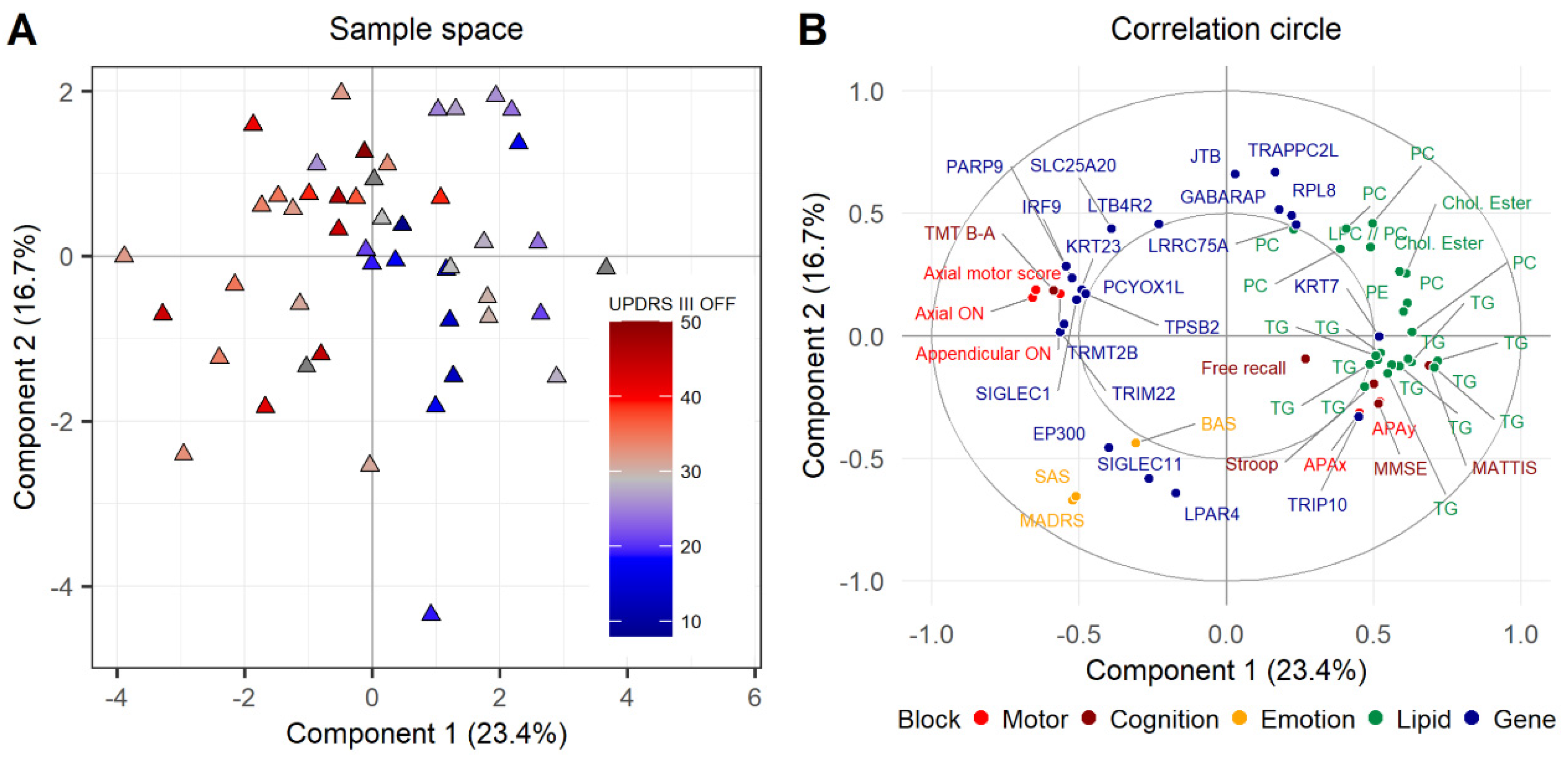
3.4. Consensus Integrative Analysis
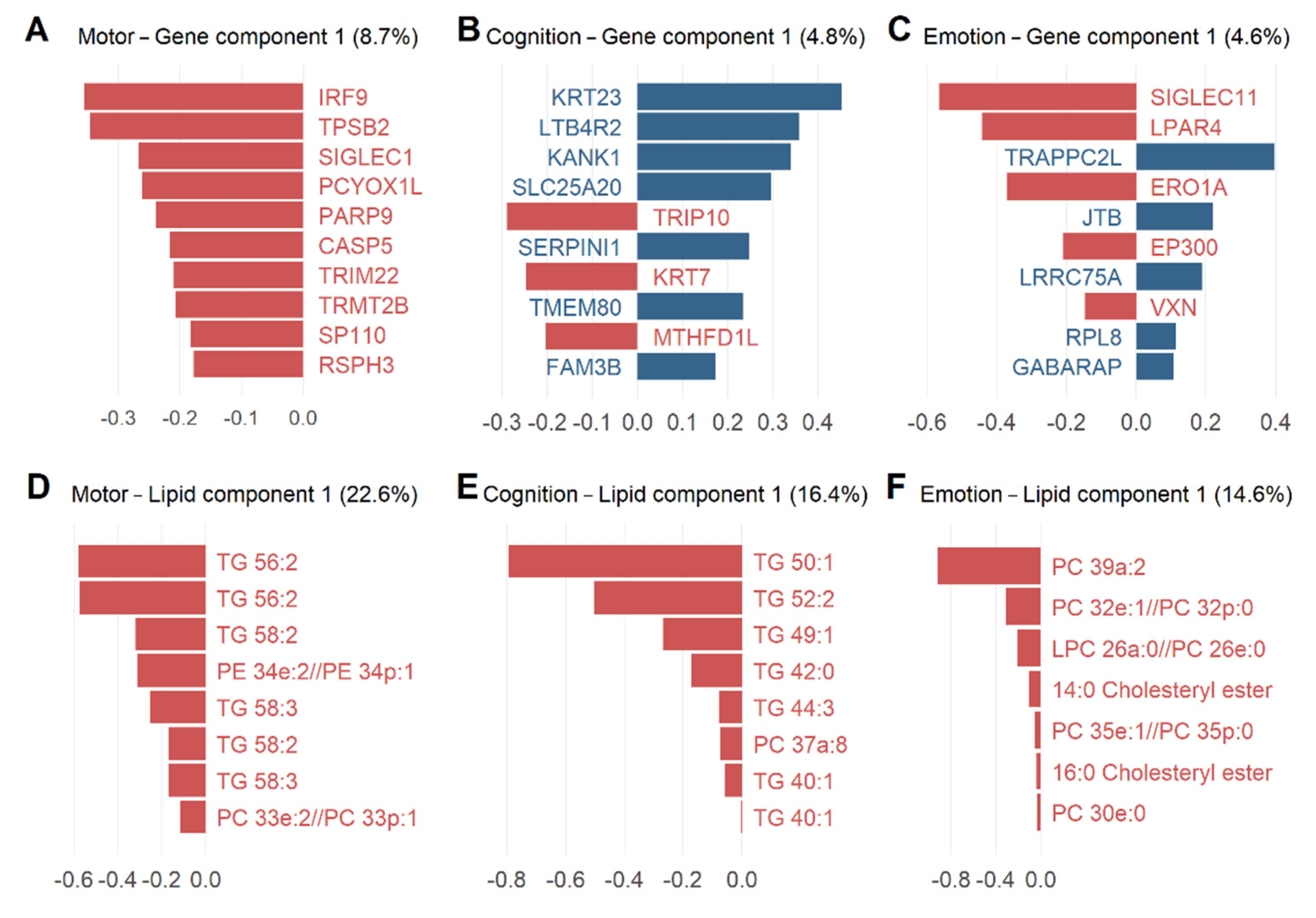
3.5. Potential Candidate Lipids and Genes Associated with Clinical Models
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Lorenzo, D.; Longo-Dos Santos, C.; Ewenczyk, C.; Leu-Semenescu, S.; Gallea, C.; Quattrocchi, G.; Pita Lobo, P.; Poupon, C.; Benali, H.; Arnulf, I.; et al. The Coeruleus/Subcoeruleus Complex in Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2013, 136, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallea, C.; Ewenczyk, C.; Degos, B.; Welter, M.L.; Grabli, D.; Leu-Semenescu, S.; Valabregue, R.; Berroir, P.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Bertasi, E.; et al. Pedunculopontine Network Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease with Postural Control and Sleep Disorders. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2017, 32, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewenczyk, C.; Mesmoudi, S.; Gallea, C.; Welter, M.L.; Gaymard, B.; Demain, A.; Yahia Cherif, L.; Degos, B.; Benali, H.; Pouget, P.; et al. Antisaccades in Parkinson Disease: A New Marker of Postural Control? Neurology 2017, 88, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallea, C.; Wicki, B.; Ewenczyk, C.; Rivaud-Péchoux, S.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Pouget, P.; Vidailhet, M.; Hainque, E. Antisaccade, a Predictive Marker for Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s Disease and Gait/Gaze Network Connectivity. Brain J. Neurol. 2021, 144, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargouri, F.; Gallea, C.; Mongin, M.; Pyatigorskaya, N.; Valabregue, R.; Ewenczyk, C.; Sarazin, M.; Yahia-Cherif, L.; Vidailhet, M.; Lehéricy, S. Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Investigation of Basal Forebrain Damage and Cognitive Deficits in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2019, 34, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redenšek, S.; Dolžan, V.; Kunej, T. From Genomics to Omics Landscapes of Parkinson’s Disease: Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2018, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrageiro, G.; Haylett, W.; Seedat, S.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Bardien, S. A Review of Genome-Wide Transcriptomics Studies in Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreq, L.; Ben-Shaul, Y.; Israel, Z.; Bergman, H.Z.; Soreq, H. Meta-Analysis of Genetic and Environmental Parkinson’s Disease Models Reveals a Common Role of Mitochondrial Protection Pathways. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Wang, C.; Zheng, C.; Wei, H.; Song, X. A Meta-Analysis of Public Microarray Data Identifies Biological Regulatory Networks in Parkinson’s Disease. BMC Med. Genomics 2018, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaab, E.; Schneider, R. Comparative Pathway and Network Analysis of Brain Transcriptome Changes during Adult Aging and in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C.J.H.M.; Martens, G.J.M.; Sharma, M.; Martens, M.B.; Isacson, O.; Gasser, T.; Visser, J.E.; Poelmans, G. Integrated Molecular Landscape of Parkinson’s Disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2017, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xicoy, H.; Wieringa, B.; Martens, G.J.M. The Role of Lipids in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, S.; Selkoe, D.; Dettmer, U. Parkinson’s Disease: Proteinopathy or Lipidopathy? NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avisar, H.; Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Surface, M.; Chan, A.; Alcalay, R.N.; Lerner, B. Lipidomics Prediction of Parkinson’s Disease Severity: A Machine-Learning Analysis. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardini Buzatto, A.; Tatlay, J.; Bajwa, B.; Mung, D.; Camicioli, R.; Dixon, R.A.; Li, L. Comprehensive Serum Lipidomics for Detecting Incipient Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 4053–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.B.; Perotte, A.J.; Zhou, B.; Liong, C.; Shorr, E.J.; Marder, K.S.; Kang, U.J.; Waters, C.H.; Levy, O.A.; Xu, Y.; et al. Elevated GM3 Plasma Concentration in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: A Lipidomic Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alecu, I.; Bennett, S.A.L. Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism and Its Role in α-Synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, S.; Haque, A.; Imberdis, T.; Baru, V.; Barrasa, M.I.; Nuber, S.; Termine, D.; Ramalingam, N.; Ho, G.P.H.; Noble, T.; et al. Lipidomic Analysis of α-Synuclein Neurotoxicity Identifies Stearoyl CoA Desaturase as a Target for Parkinson Treatment. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 1001–1014.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardi, S.P.; Viel, C.; Clarke, J.; Treleaven, C.M.; Richards, A.M.; Park, H.; Olszewski, M.A.; Dodge, J.; Marshall, J.; Makino, E.; et al. Glucosylceramide Synthase Inhibition Alleviates Aberrations in Synucleinopathy Models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017, 114, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, S.; Elton, R.L. Members of the UPDRS Development Committee Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale. In Recent Developments in Parkinsons Disease; Fahn, S., Marsden, C.D., Calne, D.B., Goldstein, M., Eds.; Macmillan Healthcare Information: Florham Park, NJ, USA, 1987; Volume 2, pp. 153–163, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Garali, I.; Adanyeguh, I.M.; Ichou, F.; Perlbarg, V.; Seyer, A.; Colsch, B.; Moszer, I.; Guillemot, V.; Durr, A.; Mochel, F.; et al. A Strategy for Multimodal Data Integration: Application to Biomarkers Identification in Spinocerebellar Ataxia. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1356–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenhaus, A.; Tenenhaus, M. Regularized Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis. Psychometrika 2011, 76, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicota, L.; Ichou, F.; Lejeune, F.X.; Colsch, B.; Tenenhaus, A.; Leroy, I.; Fontaine, G.; Lhomme, M.; Bertin, H.; Habert, M.O.; et al. Multi-Omics Signature of Brain Amyloid Deposition in Asymptomatic Individuals at-Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease: The INSIGHT-PreAD Study. eBioMedicine 2019, 47, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenenhaus, A.; Philippe, C.; Guillemot, V.; Le Cao, K.A.; Grill, J.; Frouin, V. Variable Selection for Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis. Biostat. Oxf. Engl. 2014, 15, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of Clinical Diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: A Clinico-Pathological Study of 100 Cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism: Onset, Progression, and Mortality. Neurology 1967, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate Alignment of Transcriptomes in the Presence of Insertions, Deletions and Gene Fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python Framework to Work with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessner, D.; Chambers, M.; Burke, R.; Agus, D.; Mallick, P. ProteoWizard: Open Source Software for Rapid Proteomics Tools Development. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomoni, F.; Le Corguillé, G.; Monsoor, M.; Landi, M.; Pericard, P.; Pétéra, M.; Duperier, C.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Martin, J.F.; Jacob, D.; et al. Workflow4Metabolomics: A Collaborative Research Infrastructure for Computational Metabolomics. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for Large-Scale Metabolic Profiling of Serum and Plasma Using Gas Chromatography and Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyer, A.; Boudah, S.; Broudin, S.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B. Annotation of the Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Lipidome Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and a Dedicated Data Processing Workflow. Metabolomics Off. J. Metabolomic Soc. 2016, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Jankovic, J.; Suteerawattananon, M.; Wankadia, S.; Caroline, K.S.; Vuong, K.D.; Protas, E. Clinical Gait and Balance Scale (GABS): Validation and Utilization. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 217, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”. A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattis, S. Mental Status Examination for Organic Mental Syndrome in the Elderly Patient; Bellack, L., Karusu, T.B., Eds.; Geriatric Psychiatry, Grune & Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 77–121. [Google Scholar]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of Interference in Serial Verbal Reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 1935, 18, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitan, R.M. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an Indicator of Organic Brain Damage. Percept. Mot. Skills 1958, 8, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, J.D.; Hinkeldey, N.S. Relationships between Parts A and B of the Trail Making Test. J. Clin. Psychol. 1987, 43, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkstein, S.E.; Mayberg, H.S.; Preziosi, T.J.; Andrezejewski, P.; Leiguarda, R.; Robinson, R.G. Reliability, Validity, and Clinical Correlates of Apathy in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.A.; Asberg, M. A New Depression Scale Designed to Be Sensitive to Change. Br. J. Psychiatry J. Ment. Sci. 1979, 134, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, K.; de Pretis, S.; Lister, R.; Morelli, M.J.; Bianchi, V.; Amati, B.; Ecker, J.R.; Pelizzola, M. MethylPipe and CompEpiTools: A Suite of R Packages for the Integrative Analysis of Epigenomics Data. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Nishijima, M.; Raetz, C.R.H.; Shimizu, T.; Spener, F.; van Meer, G.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Dennis, E.A. Update of the LIPID MAPS Comprehensive Classification System for Lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu-Sekine, B.; Goldschmidt, H.; Raben, D.M. Diacylglycerol, Phosphatidic Acid, and Their Metabolic Enzymes in Synaptic Vesicle Recycling. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 57, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohanian, J.; Ohanian, V. Lipid Second Messenger Regulation: The Role of Diacylglycerol Kinases and Their Relevance to Hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2001, 15, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, N.; Sancak, Y.; Frasor, J.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E. A Protective Role for Triacylglycerols during Apoptosis. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Song, W.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Cao, B.; Huang, R.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Shang, H.F. The Serum Lipid Profile of Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Study from China. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, K. Reduced Serum Levels of Triglyceride, Very Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alza, N.P.; Conde, M.A.; Scodelaro-Bilbao, P.G.; Salvador, G.A. Neutral Lipids as Early Biomarkers of Cellular Fate: The Case of α-Synuclein Overexpression. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Campos, S.; Alza, N.P.; Salvador, G.A. Lipid Metabolism Alterations in the Neuronal Response to A53T α-Synuclein and Fe-Induced Injury. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 655, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, C. High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Based Quantitative Lipidomics Study of Ganglioside-NANA-3 Plasma to Establish Its Association with Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 5345–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, M.A.S.; Colombo, N.; Fuertes-Alvarez, S.; Nicklas, S.; Cano, L.G.; Marín, M.; Goncalves, J.; Schwamborn, J.C. Expression of the Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Gene Alpha-Synuclein Is Regulated by the Neuronal Cell Fate Determinant TRIM32. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4257–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozina, E.; Sadasivan, S.; Jiao, Y.; Dou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Tan, H.; Kodali, K.; Shaw, T.; Peng, J.; Smeyne, R.J. Mutant LRRK2 Mediates Peripheral and Central Immune Responses Leading to Neurodegeneration in Vivo. Brain J. Neurol. 2018, 141, 1753–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.K.; Chao, Y.X.; West, A.; Chan, L.L.; Poewe, W.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson Disease and the Immune System—Associations, Mechanisms and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.D.; Li, G.Q.; Wu, Z.S.; Liu, X.Q.; Yang, X.X.; Wang, J.H. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Parkinson’s Disease in Patients with Mutations in the Glucocerebrosidase Gene. Neuroreport 2021, 32, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaare, J.J.; Nido, G.S.; Sztromwasser, P.; Knappskog, P.M.; Dahl, O.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Maple-Grødem, J.; Alves, G.; Tysnes, O.B.; Johansson, S.; et al. Rare Genetic Variation in Mitochondrial Pathways Influences the Risk for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lejeune, F.-X.; Ichou, F.; Camenen, E.; Colsch, B.; Mauger, F.; Peltier, C.; Moszer, I.; Gilson, E.; Pierre-Jean, M.; Floch, E.L.; et al. A Multimodal Omics Exploration of the Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 2, 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2010009
Lejeune F-X, Ichou F, Camenen E, Colsch B, Mauger F, Peltier C, Moszer I, Gilson E, Pierre-Jean M, Floch EL, et al. A Multimodal Omics Exploration of the Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Translational Medicine. 2022; 2(1):97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLejeune, François-Xavier, Farid Ichou, Etienne Camenen, Benoit Colsch, Florence Mauger, Caroline Peltier, Ivan Moszer, Emmanuel Gilson, Morgane Pierre-Jean, Edith Le Floch, and et al. 2022. "A Multimodal Omics Exploration of the Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Translational Medicine 2, no. 1: 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2010009
APA StyleLejeune, F.-X., Ichou, F., Camenen, E., Colsch, B., Mauger, F., Peltier, C., Moszer, I., Gilson, E., Pierre-Jean, M., Floch, E. L., Sabarly, V., Tenenhaus, A., Deleuze, J.-F., Ewenczyk, C., Vidailhet, M., & Mochel, F. (2022). A Multimodal Omics Exploration of the Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Translational Medicine, 2(1), 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2010009






