Reliable River Microplastic Monitoring Using Innovative Fluorescence Dyes—A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
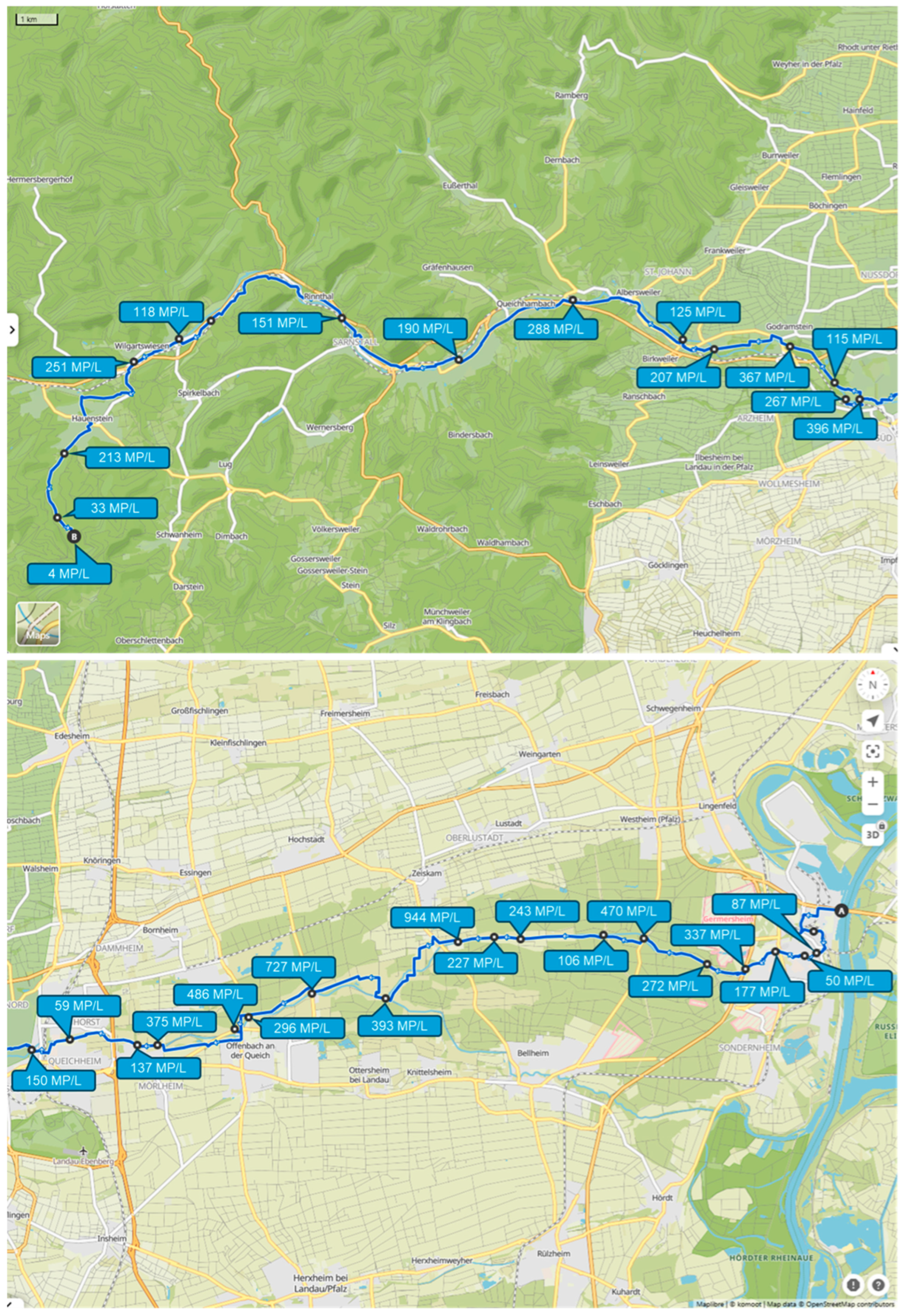
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Sampling Dates
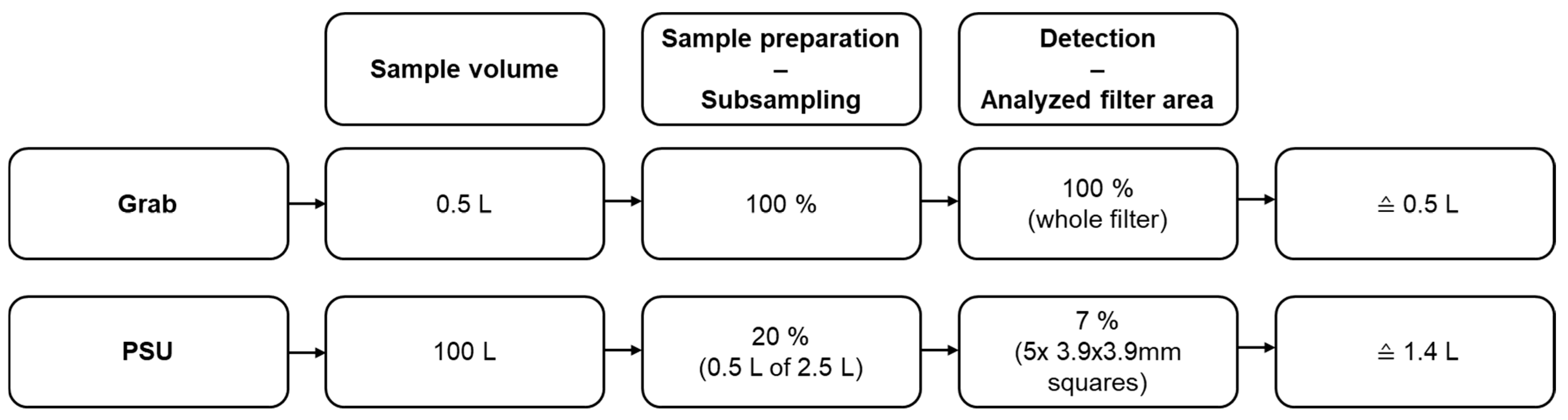
2.3. Sampling Method
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Fluorescent Imaging and Microplastic Detection
2.6. Contamination Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sampling Along the Three Rivers
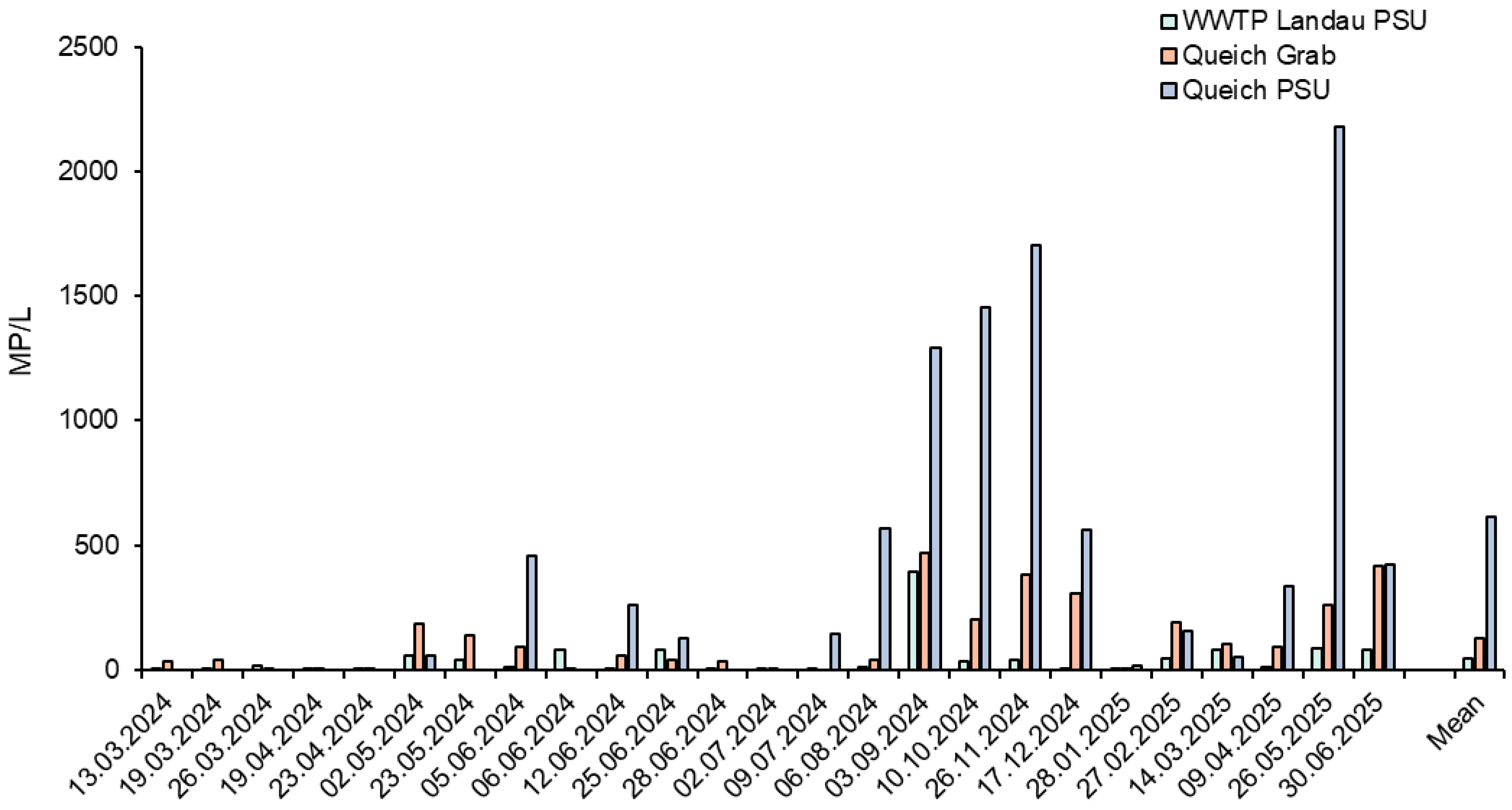
3.2. Temporal Variations and Sampling Method Comparison
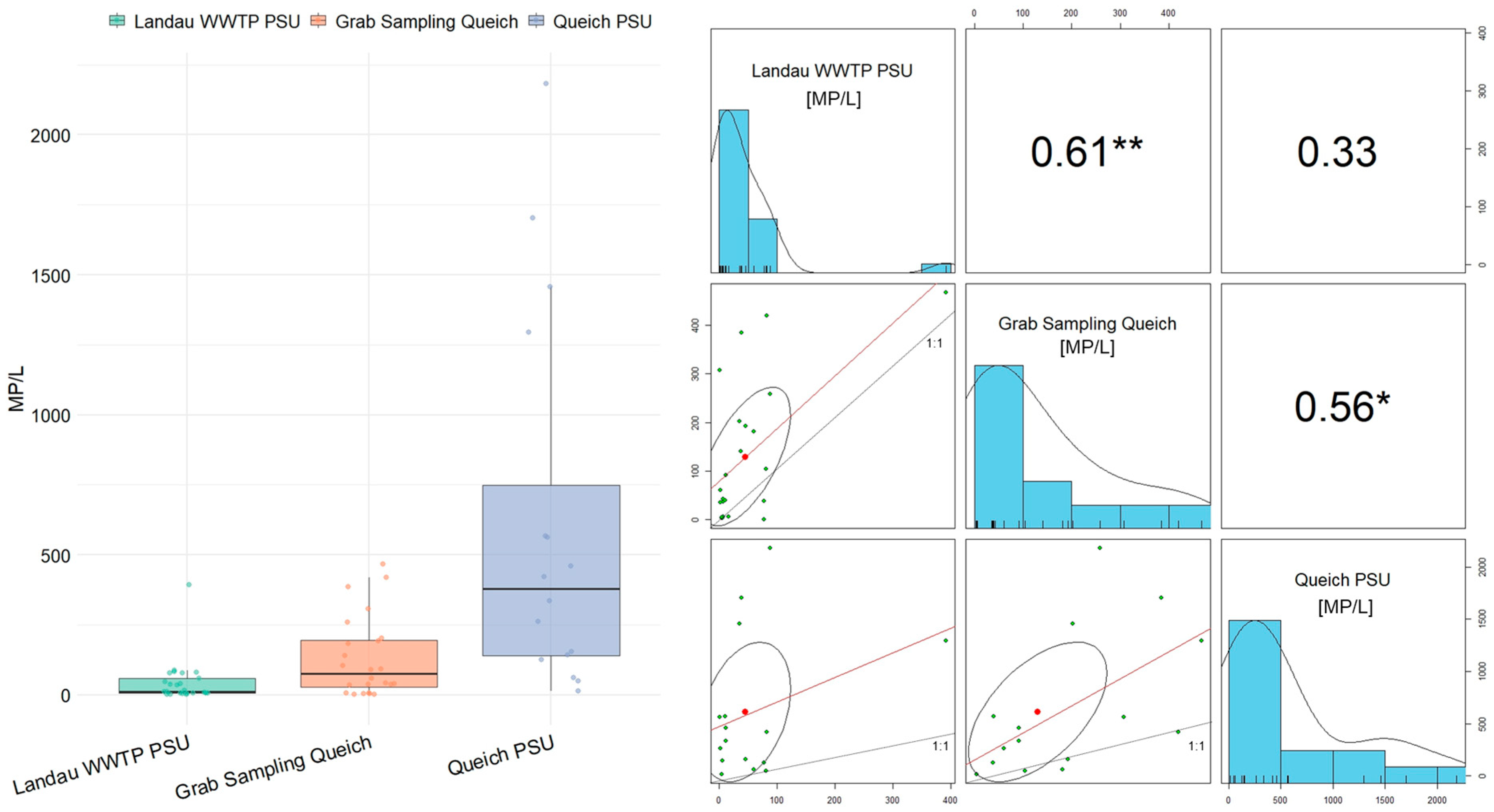
3.3. Comparison of Grab and PSU Sample Fluctuations
3.4. Correlation Analysis with Environmental Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPs | Microplastics |
| TSS | Total suspended solids |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. JGR Oceans 2020, 125, e2018JC014719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seewoo, B.J.; Goodes, L.M.; Thomas, K.V.; Rauert, C.; Elagali, A.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Symeonides, C.; Dunlop, S.A. How do plastics, including microplastics and plastic-associated chemicals, affect human health? Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3036–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Orlowski, N.; Bopf, F.K.; Breuer, L. A review on microplastics in major European rivers. WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owowenu, E.K.; Nnadozie, C.F.; Akamagwuna, F.; Noundou, X.S.; Uku, J.E.; Odume, O.N. A critical review of envi-ronmental factors influencing the transport dynamics of microplastics in riverine systems: Implications for ecological studies. Aquat. Ecol. 2023, 57, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, B.; Woodward, J.C.; Shiels, H.A. Riverine microplastics and their interaction with freshwater fish. Water Biol. Secur. 2023, 2, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Pojar, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sam-pling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, H. Analytical methods for microplastics in the environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mourik, L.M.; Crum, S.; Martinez-Frances, E.; van Bavel, B.; Leslie, H.A.; de Boer, J.H.; Cofino, W.P. Results of WEPALQUASIMEME/NORMANs first global interlaboratory study on microplastics reveal urgent need for harmonization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.K.; Roberts, S.L.; Jürgens, M.D.; Johnson, A.C.; Davis, C.W.; Gouin, T. Ensuring representative sample volume predictions in microplastic monitoring. Micropl. Nanopl. 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Suona, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X. Overview of analytical methods for the determination of microplastics: Current status and trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Shim, W.J. A comparison of spectroscopic analysis methods for microplastics: Manual, semi-automated, and automated Fourier transform infrared and Raman techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy to Assess the Degree of Alteration of Artificially Aged and Environmentally Weathered Microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, V.; Andrade-Garda, J.M.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Impact of weathering on the chemical identification of microplastics from usual packaging polymers in the marine environment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, M.E.; Lynch, J.M. Previous successes and untapped potential of pyrolysis-GC/MS for the analysis of plastic pollution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittner, M.; Eisentraut, P.; Dittmann, D.; Braun, U. Decomposability versus detectability: First validation of TED-GC/MS for microplastic detection in different environmental matrices. Appl. Res. 2024, 3, e202200089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, N.; Catarino, A.I.; Declercq, A.M.; Brenan, A.; Devriese, L.; Vandegehuchte, M.; de Witte, B.; Janssen, C.; Everaert, G. Microplastic detection and identification by Nile red staining: Towards a semi-automated, cost- and time-effective technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; Gomes, R.L.; Needham, T.; Burson, A. Exploring the Efficacy of Nile Red in Microplastic Quantification: A Costaining Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, H.A.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Kelleher, L.; Lynch, I.; Mansfield, I.; Margenat, H.; Onoja, S.; Goldberg Oppenheimer, P.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Krause, S. Detection limits are central to improve reporting standards when using Nile red for microplastic quantification. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Wontor, K.; Cizdziel, J.V. Labeling Microplastics with Fluorescent Dyes for Detection, Recovery, and Degradation Experiments. Molecules 2022, 27, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbone, L.; Panebianco, A.; Giarratana, F.; Russell, M. Nile Red staining for detecting microplastics in biota: Preliminary evidence. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Horn, H.; Schuhen, K. The potential of fluorescent dyes-comparative study of Nile red and three derivatives for the detection of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Myers, E.; Schober, D.; Korzin, A.; Schuhen, K. Development of an Inexpensive and Comparable Microplastic Detection Method Using Fluorescent Staining with Novel Nile Red Derivatives. Analytica 2023, 4, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Myers, E.; Korzin, A.; Polierer, S.; Schober, D.; Schuhen, K. Fast Forward: Optimized Sample Preparation and Fluorescent Staining for Microplastic Detection. Microplastics 2023, 2, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Analyzing microplastics with Nile Red: Emerging trends, challenges, and prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; Reis, V.; Matos, J.T.V.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. A new approach for routine quantification of microplastics using Nile Red and automated software (MP-VAT). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Alves, J.R.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Major factors influencing the quantification of Nile Red stained microplastics and improved automatic quantification (MP-VAT 2.0). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Argyropoulou, D.; Myers, E.; Korzin, A.; Ronsse, P.; Zernikel, O.; Schober, D.; Schuhen, K. Comparative Long-Term Monitoring of Microplastics in the Effluent of Three Different Wastewater Treatment Plants with Two, Three, and Four Treatment Stages. Water 2025, 17, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.T.; Myers, E.; Korzin, A.; Schober, D.; Schuhen, K. Long-Term Monitoring of Microplastics in a German Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Microplastics 2024, 3, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesamt für Umwelt Rheinland-Pfalz. Steckbriefe der Oberflächenwasserkörper. Available online: https://wasserportal.rlp-umwelt.de/auskunftssysteme/wasserkoerper-steckbriefe-wrrl (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Landesamt für Umwelt Rheinland-Pfalz. Hochwasservorhersagezentrale Rheinland-Pfalz—Pegel Siebeldingen/Queich. Available online: https://www.hochwasser.rlp.de/flussgebiet/oberrhein/siebeldingen#pegelkennwerte (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Landesanstalt für Umwelt Baden-Württemberg. Pegel—Ettlingen/Alb. Available online: https://www.hvz.baden-wuerttemberg.de/pegel.html?id=00110 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Moses, S.R.; Löder, M.G.J.; Herrmann, F.; Laforsch, C. Seasonal variations of microplastic pollution in the German River Weser. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocca, M.; Di Pace, E.; Errico, M.E.; Gentile, G.; Montarsolo, A.; Mossotti, R.; Avella, M. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-45908-6. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J. Seasonal pulse effect of microplastics in the river catchment-From tributary catchment to mainstream. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofty, J.; Sonnino Sorisio, G.; Kelleher, L.; Krause, S.; Ouro, P.; Wilson, C. Hydrological and hydraulic drivers of mi-croplastics in a rural river sourced from the UK’s largest opencast coal mine. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbulana, S.; Tanaka, S.; Moriya, A.; Oluwoye, I. Inter-event and intra-event dynamics of microplastic emissions in an urban river during rainfall episodes. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A.; Rosik-Dulewska, C. Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Characteristics, Occurrence and Removal Technologies. Water 2024, 16, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, L.; Grabinski, L.; Salameh, S. Microplastic pollution in aquatic environments: A meta-analysis of influencing factors and methodological recommendations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1600570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Li, Z.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardan, J.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Heděnec, P.; Li, Z.; Yuan, C.; Yuan, J.; et al. Quantitative assessment on the distribution patterns of microplastics in global inland waters. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Imhof, H.K.; Moses, S.R.; Heß, M.; Schwaiger, J.; Laforsch, C. Riverine microplastic contamination in southwest Germany: A large-scale survey. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 794250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, F.; Liao, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, F. Pollution characterization and multi-index ecological risk assessment of microplastics in urban rivers from a Chinese megacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Bai, G.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y. On microplastics abundance in waters of Guizhou, China. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2025, 43, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzig, C.S.; Fiener, P.; König, M.; Zumbülte, N. Temporal Variability of Microplastic Concentrations in Inland Waters: An Automated, Semicontinuous Sampling of Microplastics ≥11 μm in a Stream in Southern Germany. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Deng, L.; Rao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.; Qian, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of microplastics in an urban river network area. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.; Balla, A.; Kiss, T. High spatiotemporal resolution analysis on suspended sediment and microplastic transport of a lowland river. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chifflard, P.; Nather, T.; Weber, C.J. Transport of (Micro)plastic Within a River Cross-Section—Spatio-Temporal Variations and Loads. Microplastics 2024, 3, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Jin, H.; Yao, J.; Wang, X. Spatial–Temporal and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Surface Water of the Qinhuai River during Different Rainfall Seasons in Nanjing City, China. Water 2024, 16, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; He, J.; Sun, H. Influence of ongoing discharge from multiple wastewater treatment plants on microplastic patterns in small-scale receiving rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecinos, S.; Gil, M.; Tognana, S.; Salgueiro, W.; Amalvy, J. Distribution of microplastics present in a stream that receives discharge from wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkmann-Metaj, L.; Weber, F.; Bitter, H.; Wolff, S.; Lackner, S.; Kerpen, J.; Engelhart, M. Quantification of micro-plastics in wastewater systems of German industrial parks and their wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscher, L.; Halbach, M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Hebeler, M.; Luschtinetz, F.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Microplastics in two German wastewater treatment plants: Year-long effluent analysis with FTIR and Py-GC/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treilles, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Rabier, A.; Breton, J.; Rocher, V.; Guérin, S.; Tassin, B. Macro and Microplastics in Stormwater and Combined Sewer Overflows in Paris Megacity. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea; Cocca, M., Di Pace, E., Errico, M.E., Gentile, G., Montarsolo, A., Mossotti, R., Avella, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 145–151, ISBN 978-3-030-45908-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, A.; Jiang, J.; Liang, Y.; Cao, X.; He, D. Removal of microplastics in water: Technology progress and green strategies. Green. Anal. Chem. 2022, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y. Variance and precision of microplastic sampling in urban rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruge, A.; Dhamelincourt, M.; Lanceleur, L.; Monperrus, M.; Gasperi, J.; Tassin, B. A first estimation of uncertainties related to microplastic sampling in rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-W.; Li, Y.-L.; Lin, C.; Bui, X.-T.; Vo, T.-D.-H.; Ngo, H.H. Seasonal influence on pollution index and risk of multiple compositions of microplastics in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, G.; Doyen, P.; Dehaut, A.; Veillet, G.; Duflos, G.; Amara, R. Vertical distribution of microplastics in a river water column using an innovative sampling method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Verma, A.; Jha, P.K.; Singh, P.; Gupta, P.K.; Chandra, R.; Prasad, P.V.V. Effect of Physical Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Conditions on Transport and Deposition of Microplastics in Riverine Ecosystem. Water 2021, 13, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Location | Mean | S.D. | Median | Min | Max | No. Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | MP/L | MP/L | MP/L | MP/L | MP/L | n |
| Queich | 264 | 195 | 235 | 4 | 944 | 32 |
| Alb | 98 | 54 | 78 | 27 | 188 | 21 |
| Rehbach | 540 | 476 | 359 | 123 | 1761 | 10 |
| Sample Type Queich | Total MP/s | WWTP MP/s | WWTP Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grab | 224,580 | 7\z480 | 3.33% |
| PSU | 1,028,560 | 0.73% |
| Date | MP Concentration [MP/L] |
|---|---|
| 03.01.2024 | 41 |
| 22.02.2024 | 86 |
| 17.05.2024 | 2255 |
| 09.01.2025 | 190 |
| 27.01.2025 | 314 |
| Mean | 577 |
| S.D. | 844 |
| Max | 2255 |
| Min | 41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sturm, M.T.; Korzin, A.; Ronsse, P.; Myers, E.; Zernikel, O.; Schober, D.; Schuhen, K. Reliable River Microplastic Monitoring Using Innovative Fluorescence Dyes—A Case Study. Microplastics 2025, 4, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030063
Sturm MT, Korzin A, Ronsse P, Myers E, Zernikel O, Schober D, Schuhen K. Reliable River Microplastic Monitoring Using Innovative Fluorescence Dyes—A Case Study. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleSturm, Michael Toni, Anika Korzin, Pieter Ronsse, Erika Myers, Oleg Zernikel, Dennis Schober, and Katrin Schuhen. 2025. "Reliable River Microplastic Monitoring Using Innovative Fluorescence Dyes—A Case Study" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030063
APA StyleSturm, M. T., Korzin, A., Ronsse, P., Myers, E., Zernikel, O., Schober, D., & Schuhen, K. (2025). Reliable River Microplastic Monitoring Using Innovative Fluorescence Dyes—A Case Study. Microplastics, 4(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030063







