Microplastic Distribution in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence: A Case Study in Sasebo City, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
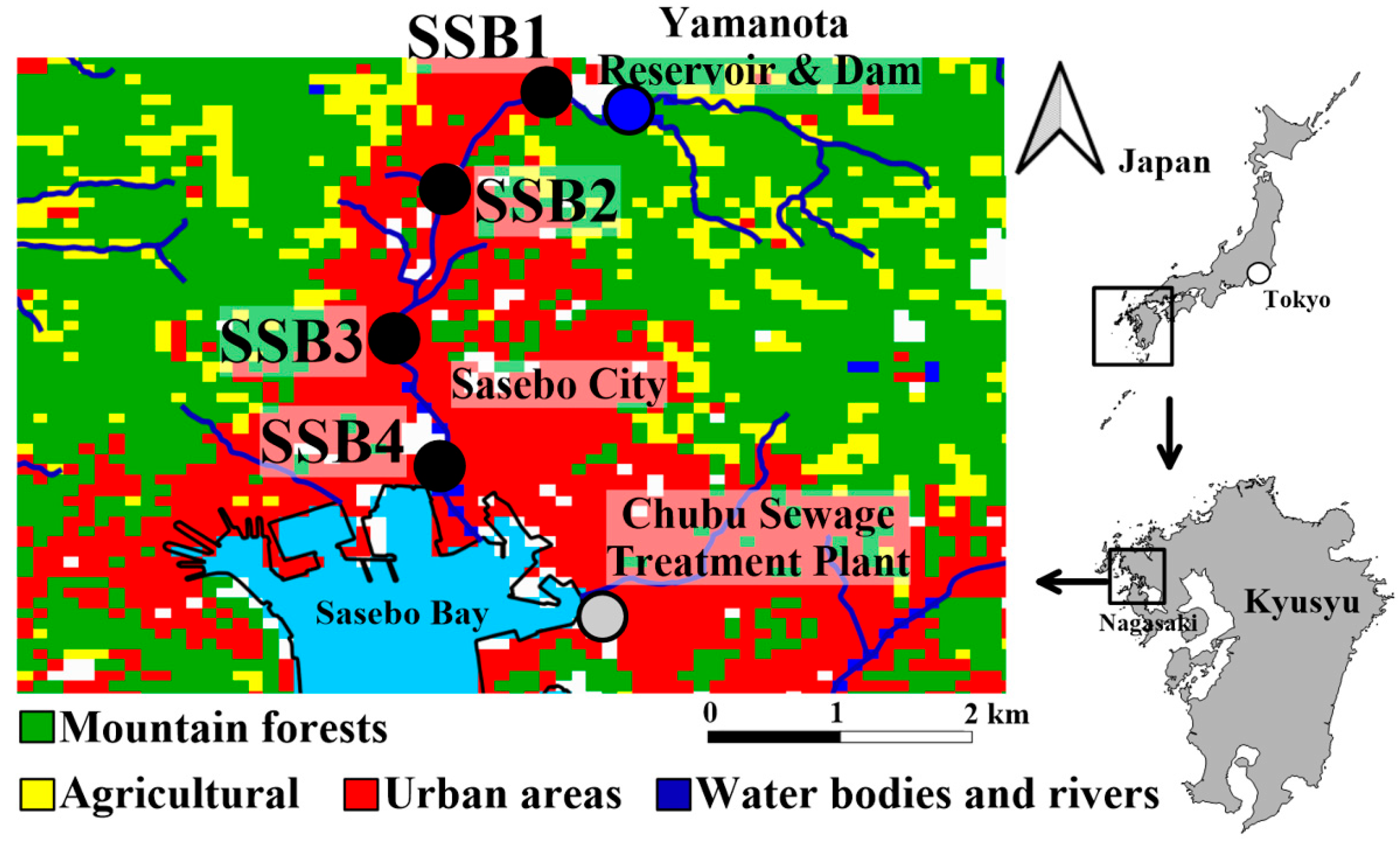
2.1. Microplastic (MP) Sample Collection
2.2. Surface Water Flow Velocity and Salinity
2.3. Laboratory Pretreatment of MP Samples
2.4. MP Polymer Identification
2.5. MP Shape and Size Classification
2.6. Quality Control Procedures
2.7. Literature Survey
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Flow Velocity and Salinity Profiles
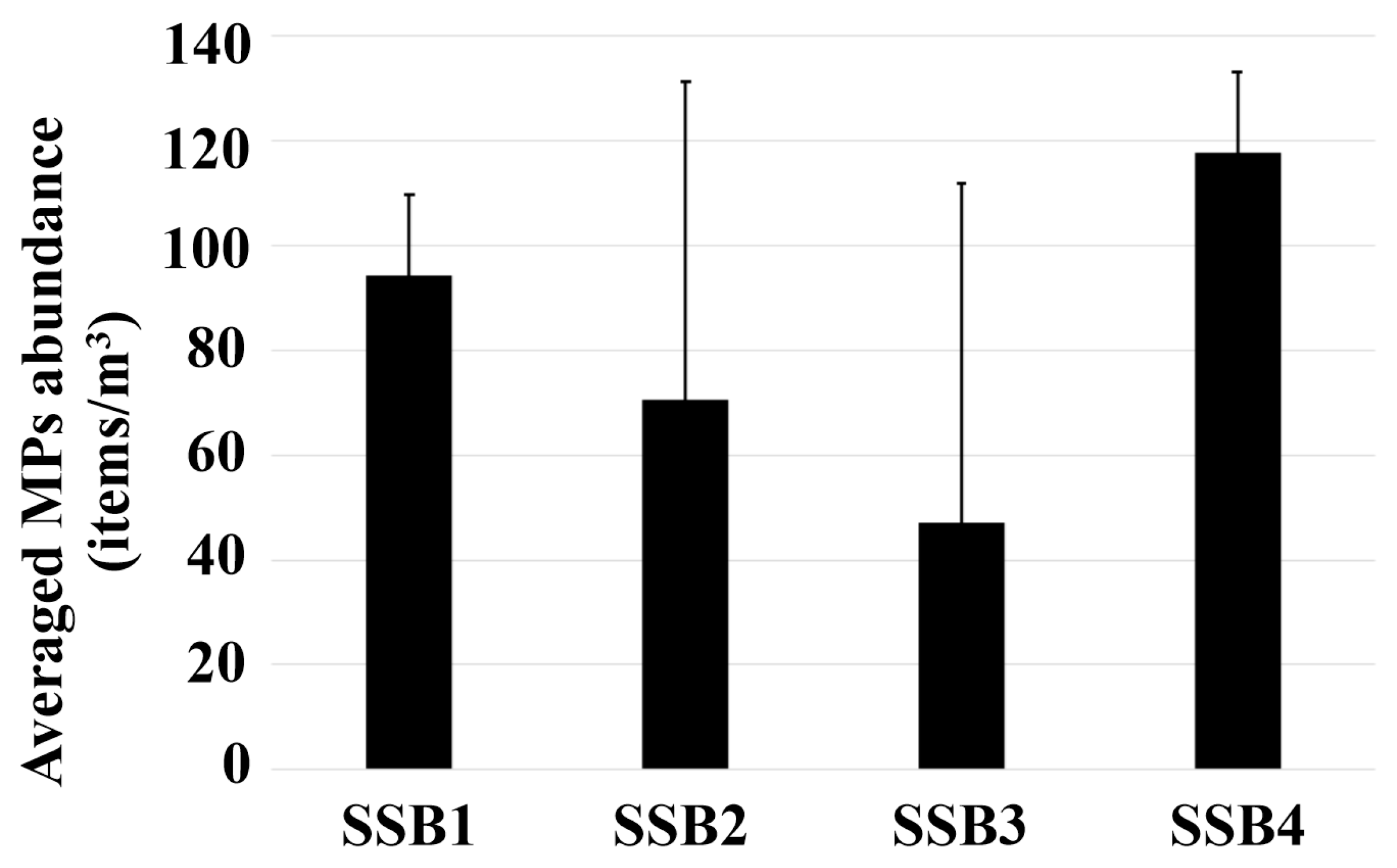
3.2. Numerical Abundance of MPs
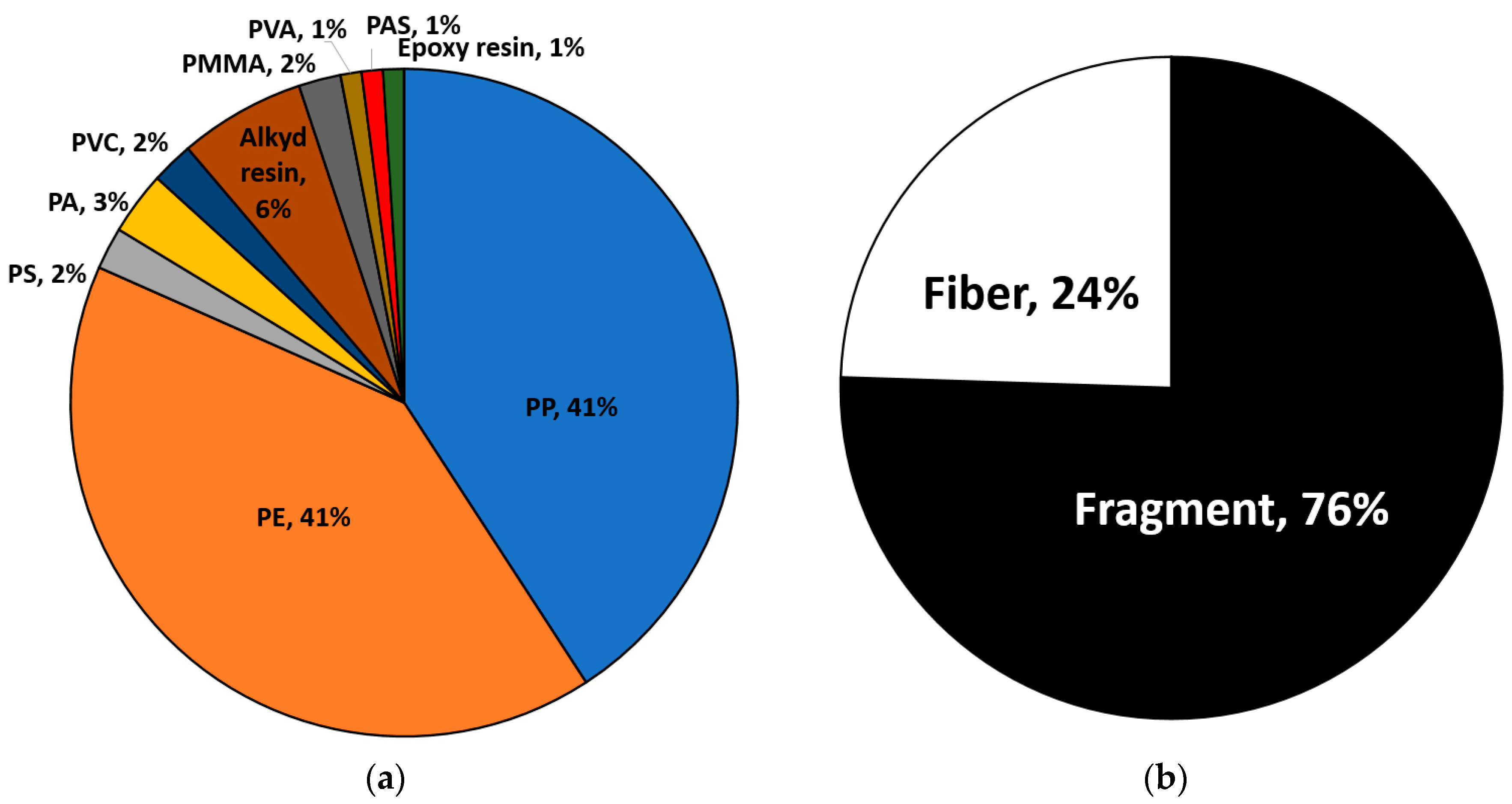
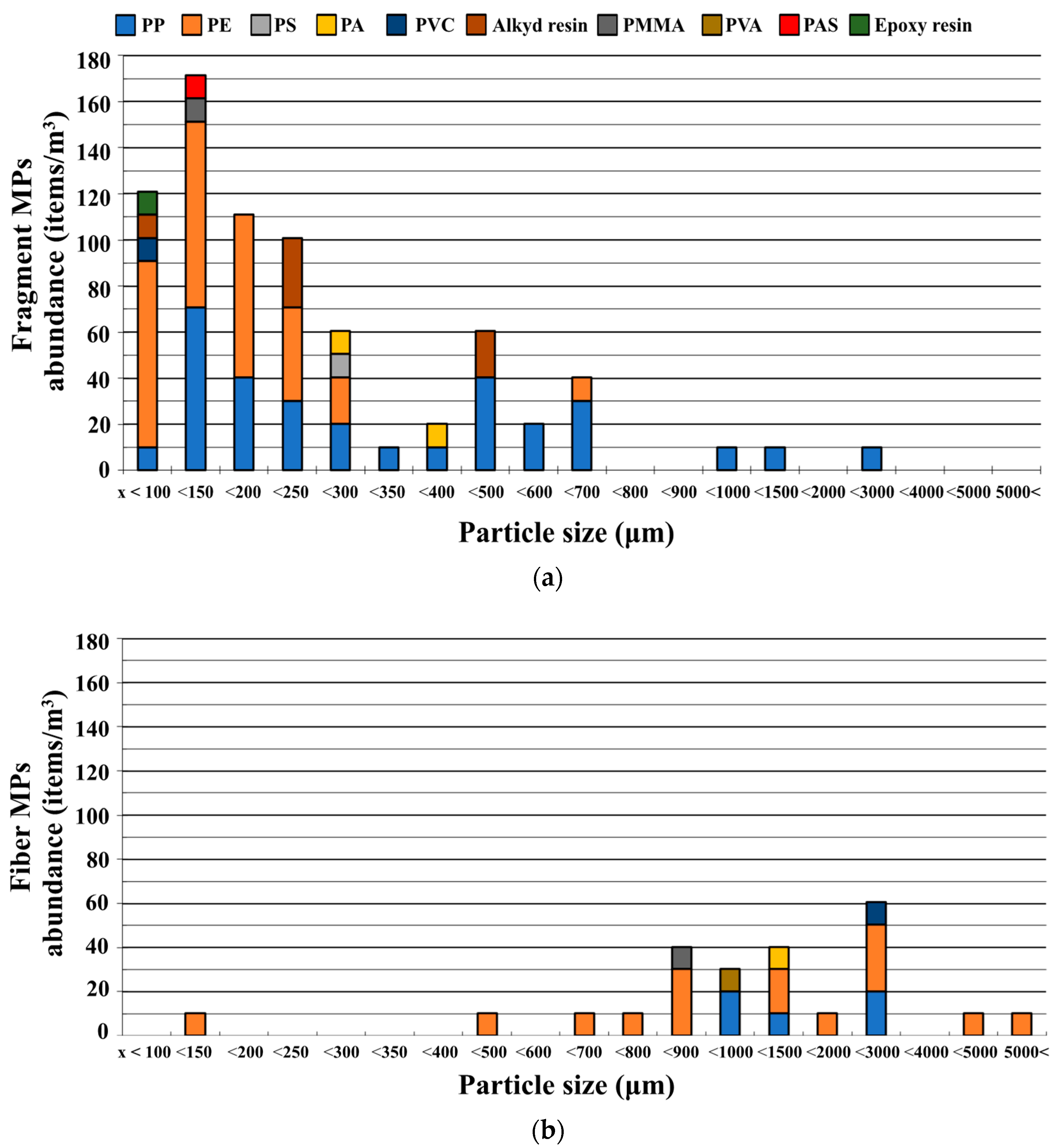
3.3. Overall Distributions of MP Polymer Types, Shapes, and Sizes
3.4. MP Polymer and Shape Distributions by Sampling Points
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Group A (positive PC1, negative PC2) included only SSB1, characterized by stagnant freshwater conditions. A wide variety of polymer types and shapes was present in this area, likely due to the limited water movement.
- Group B (negative PC1, negative PC2) included SSB2 and SSB3, marked by high water velocity and reduced diversity and abundance of MPs. PMMA fragments and fibers, uniquely detected at SSB2, contributed modestly and negatively to the PCs.
- Group C (negative PC1, positive PC2) corresponded to SSB4, where low water velocity and elevated salinity were observed. The MPs in this area, particularly those positively associated with PC2, might be affected by seawater.
4. Discussions
4.1. Microplastic Distribution Patterns in the Aquatic System of Sasebo City
4.2. Baseline MP Abundance in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP Guidlines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter in the Ocean. Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/publications/guidelines-for-the-monitoring-and-assessment-of-plastic-litter-in-the-ocean (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Akoueson, F.; Sheldon, L.M.; Danopoulos, E.; Morris, S.; Hotten, J.; Chapman, E.; Li, J.; Rotchell, J.M. A Preliminary Analysis of Microplastics in Edible versus Non-Edible Tissues from Seafood Samples. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human Health Concerns Regarding Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment—From Marine to Food Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, P.; Bessa, F.; Otero, V.; Henriques, B.; Raimundo, J.; Caetano, M.; Vale, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics in Wild Fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and Its Potential for Causing Neurotoxic Effects, Lipid Oxidative Damage, and Human Health Risks Associated with Ingestion Exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 134625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, F.; Barria, P.; Neto, J.M.; Frias, J.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P.; Marques, J.C. Occurrence of Microplastics in Commercial Fish from a Natural Estuarine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Çevik, C.; Temiz Ataş, N. Occurrence of Microplastics in the Gastrointestinal Tracts of Some Edible Fish Speciealong the Turkish Coast. Turk. J. Zool. 2020, 44, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Zoh, K.D. Occurrence of Microplastics in the Han River and Riverine Fish in South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.B.; Ashraf, P.M.; Thomas, S.N.; Thomson, K.T. Microplastics in the Edible Tissues of Shellfishes Sold for Human Consumption. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, E.; Jenner, L.C.; Twiddy, M.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastic Contamination of Seafood Intended for Human Consumption: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 126002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneechan, W.; On Prommi, T. Occurrence of Microplastics in Edible Aquatic Insect Pantala Sp. (Odonata: Libellulidae) from Rice Fields. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, K.; Green, D. The Potential Effects of Microplastics on Human Health: What Is Known and What Is Unknown. Ambio 2022, 51, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, W. Low-Dose of Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Cardiotoxicity in Mice and Human-Originated Cardiac Organoids. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue Using ΜFTIR Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.E.; Hare, J.T.; Khamis, Z.I.; Hua, T.; Sang, Q.X.A. Exposure of Human Lung Cells to Polystyrene Microplastics Significantly Retards Cell Proliferation and Triggers Morphological Changes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, E.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Grootaert, C.; Jelsbak, L.; Syberg, K.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Microplastics in the Human Digestive Environment: A Focus on the Potential and Challenges Facing in Vitro Gut Model Development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Yue, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Microplastics Reduce Lipid Digestion in Simulated Human Gastrointestinal System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12285–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österlund, H.; Blecken, G.; Lange, K.; Marsalek, J.; Gopinath, K.; Viklander, M. Microplastics in Urban Catchments: Review of Sources, Pathways, and Entry into Stormwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, T.; Hurley, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Rico, A.; Vighi, M. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Microplastics in a Mediterranean River Catchment: The Importance of Wastewater as an Environmental Pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kudou, K.; Hinata, H. Assessment of the Sources and Inflow Processes of Microplastics in the River Environments of Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Oh, M.J.; Kim, P.G.; Kim, G.; Jeong, D.H.; Ju, B.K.; Lee, W.S.; Chung, H.M.; Kang, H.J.; Kwon, J.H. National Reconnaissance Survey of Microplastics in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in Korea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.-K.; Cho, C.-R.; Cheon, H.-S.; Soh, H.-Y.; Cho, H.-S. A Study on the Distribution of Microplastics in the South Coast of Korea and Gwangyang Bay. Microplastics 2024, 3, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Jeong, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.K.; Cho, C.R.; Soh, H.Y.; Ishibashi, Y.; Cho, H.S. Microplastic Distribution Characteristics Considering the Marine Environment Based on Surface Seawater Quality Parameters in Southern Sea of Korea, 2019. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.K.; Jeong, H.H.; Ju, M.J.; Ko, U.; Dae, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, C.R.; Soh, H.Y.; Ishibashi, Y.; Cho, H.S. Baseline Study on Microplastic Distribution in the Open Surface Waters of the Korean Southwest Sea. Water 2023, 15, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Liu, X.; Jiang, F.; Ding, J.; Yin, X.; Sun, C. Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in the Seawater and Sediment: A Case Study in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Novirsa, R.; Cahya Nugraha, W.; Addai-Arhin, S.; Dinh, Q.P.; Fukushima, S.; Fujita, E.; Bambang, W.; Kameda, Y.; Ishibashi, Y.; et al. The Distributions of Microplastics (MPs) in the Citarum River Basin, West Java, Indonesia. J. Environ. Saf. 2021, 12, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.Z.; Watts, A.J.R.; Winslow, B.O.; Galloway, T.S.; Barrows, A.P.W. Mountains to the Sea: River Study of Plastic and Non-Plastic Microfiber Pollution in the Northeast USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M.; Takada, H.; Takada, N.; Mizukawa, K.; Tsuyuki, S. Microplastics in Urban Wastewater and Estuarine Water: Importance of Street Runoff. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2021, 1, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Sekine, M. Wastewater Treatment Plants Elevating Microplastic Abundances, Ecological Risks, and Loads in Japanese Rivers: A Source-to-Sink Perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 96499–96514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Rao, Q.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Rainfall Is a Significant Environmental Factor of Microplastic Pollution in Inland Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, S.R.; Löder, M.G.J.; Herrmann, F.; Laforsch, C. Seasonal Variations of Microplastic Pollution in the German River Weser. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, B.; Pais, J.; Antunes, J.; Pequeno, J.; Pires, A.; Sobral, P. Seasonal Abundance and Distribution Patterns of Microplastics in the Lis River, Portugal. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñon-Colin, T.J.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R.; Rogel-Hernandez, E.; Alvarez-Andrade, A.; Wakida, F.T. Microplastics in Stormwater Runoff in a Semiarid Region, Tijuana, Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Sekine, M.; Imai, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kanno, A.; Higuchi, T. Assessing Small-Scale Freshwater Microplastics Pollution, Land-Use, Source-to-Sink Conduits, and Pollution Risks: Perspectives from Japanese Rivers Polluted with Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahens, L.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Dris, R.; Boukerma, K.; Rinnert, E.; Gasperi, J.; Tassin, B. Macroplastic and Microplastic Contamination Assessment of a Tropical River (Saigon River, Vietnam) Transversed by a Developing Megacity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameda, Y.; Yamada, N.; Fujita, E. Source- and Polymer-Specific Size Distributions of Fine Microplastics in Surface Water in an Urban River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, K.; Takaoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kitaura, F. Estimation of Temporal Variations and Annual Flux of Microplastics in Rivers under Low- and High-Flow Condistions. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 (Hydraul. Eng.) 2018, 74, I_529–I_534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankoda, K.; Yamada, Y. Occurrence, Distribution, and Possible Sources of Microplastics in the Surface River Water in the Arakawa River Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27474–27480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki Prefecture in Japan Annaul Stastics in Nagasaki Prefecture. Volume 47. Available online: https://www.pref.nagasaki.jp/bunrui/kenseijoho/toukeijoho/kankoubutsu/nenkan/33937.html (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Nagasaki Prefecture in Japan Annual Stastics in Nagasaki Prefecture. Volume 69. Available online: https://www.pref.nagasaki.jp/bunrui/kenseijoho/toukeijoho/kankoubutsu/nenkan/599095.html (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- General Oceanics Inc. 2030 and 2031 Series Mechanical and Electronic Digital Flowmeter Operators Manual. Available online: https://www.generaloceanics.com/media/hexaattachment/products/attachments/2030_MANUAL.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments. Available online: https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-604 (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Michida, Y.; Chavanich, S.; Chiba, S.; Cordova, M.R.; Cózar, C.A.; Galgani, F.; Hagmann, P.; Hinata, H.; Isobe, A.; Kershaw, P.; et al. Guidelines for Harmonizing Ocean Surface Microplastic Monitoring Methods. Version 1.1. Available online: https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-867 (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Prata, J.C.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for Sampling and Detection of Microplastics in Water and Sediment: A Critical Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagg, A.S.; Harrison, J.P.; Ju-Nam, Y.; Sapp, M.; Bradley, E.L.; Sinclair, C.J.; Ojeda, J.J. Fenton’s Reagent for the Rapid and Efficient Isolation of Microplastics from Wastewater. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Kusano, T.; Addai-Arhin, S.; Nugraha, W.C.; Novirsa, R.; Phan Dinh, Q.; Shirosaki, T.; Fujita, E.; Kameda, Y.; Cho, H.S.; et al. Differences in Microplastic Distributions on the Surface Freshwater Collected Using 100– and 355–μm Meshes. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2022, 2, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corami, F.; Rosso, B.; Bravo, B.; Gambaro, A.; Barbante, C. A Novel Method for Purification, Quantitative Analysis and Characterization of Microplastic Fibers Using Micro-FTIR. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, W.H. Feret‘s Statistical Diameter as a Measure of Particle Size. Nature 1948, 162, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Jung, H.; Lee, J.; Cho, H. The Characteristics of Methylsiloxane Distribution in the Marine Surface Sediment, Masan Bay, Korea, in August 2018 and Suggesting Directions for Further Studies. Water 2024, 16, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, S.-D.; Cho, H.-S. Characteristics of Hypoxic Water Mass Occurrence in the Northwestern Gamak Bay, Korea, 2017. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2021, 27, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbke, H.P.; Banton, M.; Block, C.; Dawkins, G.; Eisert, R.; Leibold, E.; Pemberton, M.; Puijk, I.M.; Sakoda, A.; Yasukawa, A. Risk Assessment for Migration of Styrene Oligomers into Food from Polystyrene Food Containers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Tang, X.; Gong, X.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Development and Application of a Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantifying Nylon Microplastics in Environment. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13930–13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the Aquatic and Terrestrial Environment: Sources (with a Specific Focus on Personal Care Products), Fate and Effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastics in the Sea Surface Microlayer in Jinhae Bay, South Korea. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, D.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Pereira, T. Ingestion of Microplastics by Commercial Fish off the Portuguese Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Isama, K.; Matsuoka, A. Analysis of Phthalic Acid Diesters, Monoester, and Other Plasticizers in Polyvinyl Chloride Household Products in Japan. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2011, 46, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.A. Modern Plastics Handbook, 1st ed.; Harper, C.A., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0070267146. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.R.; Li, S.F.; Chow, W.K. Preliminary Studies on Burning Behavior of Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). J. Fire Sci. 2002, 20, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H. A Study on the Proper Sampling Method for Microplastic Distributions in the Surface Freshwater: From Case Studies in Japan and Indonesia. Ph.D. Thesis, Prefectural University of Kumamoto, Kumamoto, Japan, 2021. Available online: http://rp-kumakendai.pu-kumamoto.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/123456789/2099/3/2021-kan-zenbun-jeong.pdf (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Capparelli, M.V.; Molinero, J.; Moulatlet, G.M.; Barrado, M.; Prado-Alcívar, S.; Cabrera, M.; Gimiliani, G.; Ñacato, C.; Pinos-Velez, V.; Cipriani-Avila, I. Microplastics in Rivers and Coastal Waters of the Province of Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; fan Mao, R.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in Surface Waters and Sediments of the Wei River, in the Northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Lu, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiayihazi, N. Occurrence and Pollution Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Water of the Manas River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Jin, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, C.; Qiu, Z. Distinct Profile of Bacterial Community and Antibiotic Resistance Genes on Microplastics in Ganjiang River at the Watershed Level. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, H.; Gu, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; He, Q. Distribution and Characteristics of Microplastics in the Yulin River, China: Role of Environmental and Spatial Factors. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.K.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Annual Load of Microplastics in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water Res. 2019, 160, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Characterization of Microplastics in the Surface Seawater of the South Yellow Sea as Affected by Season. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Watanabe, K.; Todoroki, S.; Suemori, H.; Shinjyo, R. Study on Performance of PVA Fiber Reinforced Concrete Exposed for 10 Years to Seawater Spray. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2018, 16, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Goncalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Goncalves, A.M.M. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Microplastics in Water and Sediments of a Freshwater System (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of Microplastics in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Pelagic and Demersal Fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The Physical Impacts of Microplastics on Marine Organisms: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, B. Ingestion of Microplastics by Fish and Its Potential Consequences from a Physical Perspective. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrendt, C.; Perez-Venegas, D.J.; Urbina, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Echeveste, P.; Aldana, M.; Pulgar, J.; Galbán-Malagón, C. Microplastic Ingestion Cause Intestinal Lesions in the Intertidal Fish Girella Laevifrons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradney, L.; Wijesekara, H.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Obadamudalige, N.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kirkham, M.B. Particulate Plastics as a Vector for Toxic Trace-Element Uptake by Aquatic and Terrestrial Organisms and Human Health Risk. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Biswas, C.; Banerjee, S.; Guchhait, R.; Adhikari, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Pramanick, K. Interaction of Plastic Particles with Heavy Metals and the Resulting Toxicological Impacts: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60291–60307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamahara, S.; Nakata, H. Road Dust-Associated Microplastics as a Carrier of Plastic Additives in Urban Small-Scale River Sediment. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2025, 5, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Transport of Persistent Organic Pollutants by Microplastics in Estuarine Conditions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokai, T.; Uchida, K.; Kuroda, M.; Isobe, A. Mesh Selectivity of Neuston Nets for Microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 165, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, A.P.W.; Neumann, C.A.; Berger, M.L.; Shaw, S.D. Grab: Vs. Neuston Tow Net: A Microplastic Sampling Performance Comparison and Possible Advances in the Field. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbulana, S.; Tanaka, S.; Yukioka, S.; Oluwoye, I. Occurrence and Distribution of Plastic Particles (10–25,000 Μm) and Microfibers in the Surface Water of an Urban River Network in Japan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihei, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kataoka, T.; Ogata, R. High-Resolution Mapping of Japanese Microplastic and Macroplastic Emissions from the Land into the Sea. Water 2020, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Cui, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. A Case Study on Small-Size Microplastics in Water and Snails in an Urban River. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, E.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y. Microplastics in the Surface Water of Small-Scale Estuaries in Shanghai. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; He, J.; Sun, H. Influence of Ongoing Discharge from Multiple Wastewater Treatment Plants on Microplastic Patterns in Small-Scale Receiving Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büngener, L.; Schäffer, S.-M.; Schwarz, A.; Schwalb, A. Microplastics in a Small River: Occurrence and Influencing Factors along the River Oker, Northern Germany. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 264, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matjašič, T.; Mori, N.; Hostnik, I.; Bajt, O.; Viršek, M.K. Microplastic Pollution in Small Rivers along Rural–Urban Gradients: Variations across Catchments and between Water Column and Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Basic Information about Nonpoint Source (NPS) Pollution. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nps/basic-information-about-nonpoint-source-nps-pollution (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of Microplastics from Land to Sea. A Modelling Approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerranti, C.; Martellini, T.; Perra, G.; Scopetani, C.; Cincinelli, A. Microplastics in Cosmetics: Environmental Issues and Needs for Global Bans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Basu, S.; Shetti, N.P.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Microplastics in the Environment: Occurrence, Perils, and Eradication. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.F.; Harrad, S.; Millette, J.R.; Holbrook, R.D.; Davis, J.M.; Stapleton, H.M.; Allen, J.G.; McClean, M.D.; Ibarra, C.; Abdallah, M.A.E.; et al. Identifying Transfer Mechanisms and Sources of Decabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE 209) in Indoor Environments Using Environmental Forensic Microscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sui, Q.; Xu, D.; Qu, H.; Yu, G. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastics in Domestic, Industrial, Agricultural and Aquacultural Wastewater Sources: A Case Study in Changzhou, China. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.C.; Sembiring, E.; Muntalif, B.S.; Suendo, V. Microplastic Distribution in Surface Water and Sediment River around Slum and Industrial Area (Case Study: Ciwalengke River, Majalaya District, Indonesia). Chemosphere 2019, 224, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, J.; Chae, K.J. Eye-Glass Polishing Wastewater as Significant Microplastic Source: Microplastic Identification and Quantification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, C.; Gonzalez-Pleiter, M.; Leganes, F.; Fernandez-Pinas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants and Their Environmental Dispersion with Effluent and Sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbulana, S.; Tanaka, S.; Oluwoye, I. Quantifying Annual Microplastic Emissions of an Urban Catchment: Surface Runoff vs Wastewater Sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic Contamination in an Urban Area: A Case Study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.; Woodward, J.; Rothwell, J.J. Microplastic Contamination of River Beds Significantly Reduced by Catchment-Wide Flooding. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, A.; de Pooter, L.; Dröge, R.; Kuenen, J.; Valk, E. Emission of Microplastics and Potential Mitigation Measures Abrasive Cleaning Agents, Paints and Tyre Wear. Available online: https://rivm.openrepository.com/server/api/core/bitstreams/a53256d6-26bb-47bd-86e3-e3671a85b491/content (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Katsumi, N.; Kusube, T.; Nagao, S.; Okochi, H. The Role of Coated Fertilizer Used in Paddy Fields as a Source of Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamrat, R.; Taweesan, A.; Pussayanavin, T. Assessment of Microplastics Distribution and Related Water Quality in an Urban Canal, Thailand. Pollution 2022, 8, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, W.; Żmijewska, A.; Stasińska, E.; Zieliński, P. Spatial–Temporal Distribution of Microplastics in Lowland Rivers Flowing through Two Cities (Ne Poland). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasebo City in Japan The Raywa 5-Year Edition of Sasebo City Statistics (34th). Available online: https://www.city.sasebo.lg.jp/kikaku/seisak/r5toukeisyo.html (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Nagasaki Prefecture in Japan The Results of Water Quality Measurement of Public Water Area and Groundwater in Reiwa 4-Year. Available online: https://www.pref.nagasaki.jp/shared/uploads/2024/04/1712911053.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Japan Meteorological Agency Historical Weather Records for Sasebo City. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/stats/etrn/index.php?prec_no=84&block_no=47812&year=&month=&day=&view=h0 (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Huang, D.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. The Occurrence and Abundance of Microplastics in Surface Water and Sediment of the West River Downstream, in the South of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Christie-Oleza, J.A.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Lin, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. Environmental Fate of Microplastics in the World’s Third-Largest River: Basin-Wide Investigation and Microplastic Community Analysis. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, J. Microplastic Pollution and Characteristics in the Surface Waters of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Han River along Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 10205–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, A.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Vighi, M.; Waichman, A.V.; de Souza Nunes, G.S.; de Oliveira, R.; Singdahl-Larsen, C.; Hurley, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Schell, T. Large-Scale Monitoring and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Amazon River. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Takada, H.; Nihei, Y.; Kameda, Y.; Nishikawa, K. Current Status and Issues of Microplastic Pollution Research. J. Jpn. Sociery Water Environ. 2021, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.R.; Pise, M.; Kumkar, P.; Gosavi, S.M.; Kalous, L. Microplastic Contamination in Ulhas River Flowing through India’s Most Populous Metropolitan Area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Nan, B.; Craig, N.J.; Pettigrove, V. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Microplastics in Roadside Dust from Rural and Urban Victoria, Australia: Implications for Diffuse Pollution. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Principal Components (PCs) | PC 1 | PC 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 7.416 | 6.154 | ||
| Proportion (%) | 43.6 | 36.2 | ||
| Accumulative Proportion (%) | 43.6 | 79.8 | ||
| Parameters | Loading Factors | Eigenvectors | ||
| PC 1 | PC 2 | PC 1 | PC 2 | |
| PP fragment | −0.449 | 0.780 | −0.048 | 0.104 |
| PE fragment | −0.089 | 0.888 | 0.007 | 0.178 |
| PS fragment | 0.613 | 0.694 | 0.096 | 0.112 |
| PA fragment | 0.647 | −0.166 | 0.088 | 0.024 |
| PAS fragment | 0.989 | −0.100 | 0.133 | −0.004 |
| Alkyd resin fragment | 0.991 | 0.118 | 0.138 | 0.043 |
| PMMA fragment | −0.242 | −0.092 | −0.031 | 0.032 |
| PAS fragment | 0.989 | −0.100 | 0.133 | −0.004 |
| Epoxy resin fragment | −0.282 | 0.901 | −0.023 | 0.134 |
| PP fiber | 0.258 | 0.922 | 0.054 | 0.182 |
| PE fiber | 0.836 | −0.540 | 0.104 | −0.073 |
| PA fiber | 0.989 | −0.100 | 0.133 | −0.004 |
| PVC fiber | 0.989 | −0.100 | 0.133 | −0.004 |
| PMMA fiber | −0.242 | −0.092 | −0.031 | 0.032 |
| PVA fiber | −0.282 | 0.901 | −0.023 | 0.134 |
| Velocity | −0.629 | −0.775 | −0.101 | −0.151 |
| Salinity | −0.282 | 0.901 | −0.023 | 0.134 |
| Study Area | River | Mesh Size | Filtered Water Volume | Numerical Abundance of MPs | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Basin Area | Min | Max | Mean | SD | ||||
| (km) | (km2) | (μm) | (L) | (items/m3) | |||||
| Small-Scale Aquatic Environments with Limited Anthropogenic Influence | |||||||||
| Sasebo River, Japan | 5.2 | 14.7 | 100< | 300 | 0.0 | 131.1 | 82.4 | 47.7 | this study |
| Small-Scale Aquatic Environments with Intense Anthropogenic Influence * | |||||||||
| Tsurumi River, Japan | 42.5 | 235 | 10< | 20 | 298 | 1240 | n/a | n/a | [37] |
| Awano River, Japan | 29.3 | 177 | 50< | 1 | 102,000 | 146,000 | 132,800 | 15,730 | [35] |
| Ayaragi River, Japan | 9.5 | 20 | 86,000 | 148,000 | 111,880 | 21,420 | |||
| Asa River, Japan | 44 | 232 | 87,000 | 172,000 | 130,000 | 27,840 | |||
| Majime River, Japan | 8.3 | 12 | 99,000 | 1,061,000 | 272,500 | 299,150 | |||
| Saba River–Shimaji River, Japan | 172.17 | 464 | 50–1000 | 1 | 11,000 | 256,000 | 88,500 | 46,410 | [30] |
| Koya River, Japan | 44 | 264 | 82,250 | 72,530 | |||||
| Fushino River, Japan | 30 | 322.4 | 87,800 | 48,750 | |||||
| Nishiki River, Japan | 110 | 884.2 | 38,730 | 24,200 | |||||
| Semiarid region, Tijuana, Mexico | n/a | 0.038–1.75 | 25< | 1 | 88,000 | 289,000 | n/a | n/a | [34] |
| Sean Saep Canal, Bangkok, Thailand | 72 | n/a | 100–1000 | n/a | 307 | 1113 | 479 (300–1000 μm) 261 (100–300 μm) | n/a | [102] |
| Lis River, Portugal | 39.5 | 850 | 150< | n/a | 0.05 | 3422.22 | 203.6 | 727.8 | [33] |
| Biała River, Białystok City, Poland | 17.02 ** | 102 *** | 40< | 50 | 5100 | 23,600 | 10,830 | 3960 | [103] |
| Czarna Hańcza River, Suwałki City, Poland | 10.90 ** | 65.5 *** | 40< | 50 | 4900 | 25,200 | 10,290 | 3900 | |
| Large-Scale Aquatic Environments with Intense Anthropogenic Influence * | |||||||||
| Saigon River, Vietnam | 250 | 4717 | 50< | 0.3 | 172,000 | 519,000 | n/a | n/a | [36] |
| Nakdong River Upstream, Republic of Korea | n/a | 9336 | 20< | 100 | 293 | 2167 | n/a | n/a | [67] |
| Nakdong River Midstream, Republic of Korea | n/a | 5991 | 20< | 100 | 1400 | 2613 | n/a | n/a | |
| Nakdong River Downstream, Republic of Korea | n/a | 6261 | 20< | 100 | 360 | 1273 | n/a | n/a | |
| Wei River, China | 818 | 134,766 | 75< | 5 | 3670 | 10,700 | n/a | n/a | [63] |
| Manas River, China | 450 | 33,500 | 100< | 5000 | 21,000 | 49,000 | n/a | n/a | [64] |
| Ganjian River, China | 766 | 83,500 | 50< | 50 | 160 | 720 | 407 | n/a | [65] |
| West River Down Stream, in Pearl River, China | 173 ** | 353,120 | 75 | 30 | 2990 | 9870 | n/a | n/a | [107] |
| Yangtze River, China | 6300 | n/a | 48< | 50 | 20 | 2580 | 1270 | 830 | [108] |
| Han River Middle and Lower Reaches, China | 940 ** | 151,000 | 25< | n/a | 2315 | 8406 | 4218 | 806 | [109] |
| Citarum River, Indonesia | n/a | 13,000 | 100< | 0.05 | 0 | 350,000 | 210,000 | 130,000 | [27] |
| Weser River, Germany | 744 | 49,000 | 10–500 | 622 ± 167 | 157 | 14,536 | n/a | n/a | [32] |
| Large-Scale Aquatic Environments with Limited Anthropogenic Influence * | |||||||||
| The anonymous 1st-grade river, Japan | 213 | 5090 | 100< | 3200 | 3.2 | 38.8 | 14.1 | 10.7 | [47] |
| Yulin River, China | 20 ** | 3861 | 64< | 50 | 7 | 17 | 13 | n/a | [66] |
| Amazon River, Brazil | 1500 | n/a | 55< | 300–4600 | 8 | 39 | n/a | n/a | [110] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Fukuda, D.; Elwaleed, A.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Soe, P.S.; Min, B.K.; Cho, H.S.; Agusa, T.; Ishibashi, Y. Microplastic Distribution in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence: A Case Study in Sasebo City, Japan. Microplastics 2025, 4, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030055
Jeong H, Fukuda D, Elwaleed A, Nguyen QT, Soe PS, Min BK, Cho HS, Agusa T, Ishibashi Y. Microplastic Distribution in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence: A Case Study in Sasebo City, Japan. Microplastics. 2025; 4(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Huiho, Daigo Fukuda, Ahmed Elwaleed, Quynh Thi Nguyen, Pyae Sone Soe, Byeong Kyu Min, Hyeon Seo Cho, Tetsuro Agusa, and Yasuhiro Ishibashi. 2025. "Microplastic Distribution in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence: A Case Study in Sasebo City, Japan" Microplastics 4, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030055
APA StyleJeong, H., Fukuda, D., Elwaleed, A., Nguyen, Q. T., Soe, P. S., Min, B. K., Cho, H. S., Agusa, T., & Ishibashi, Y. (2025). Microplastic Distribution in a Small-Scale Aquatic System with Limited Anthropogenic Influence: A Case Study in Sasebo City, Japan. Microplastics, 4(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4030055







