Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Signaling Pathways in Tetrahymena pyriformis Exposed to Micro- and Nanoplastics
Abstract
1. Introduction
Impact of Microplastics on Various Signaling Pathways
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Vitro Culture of Tetrahymena
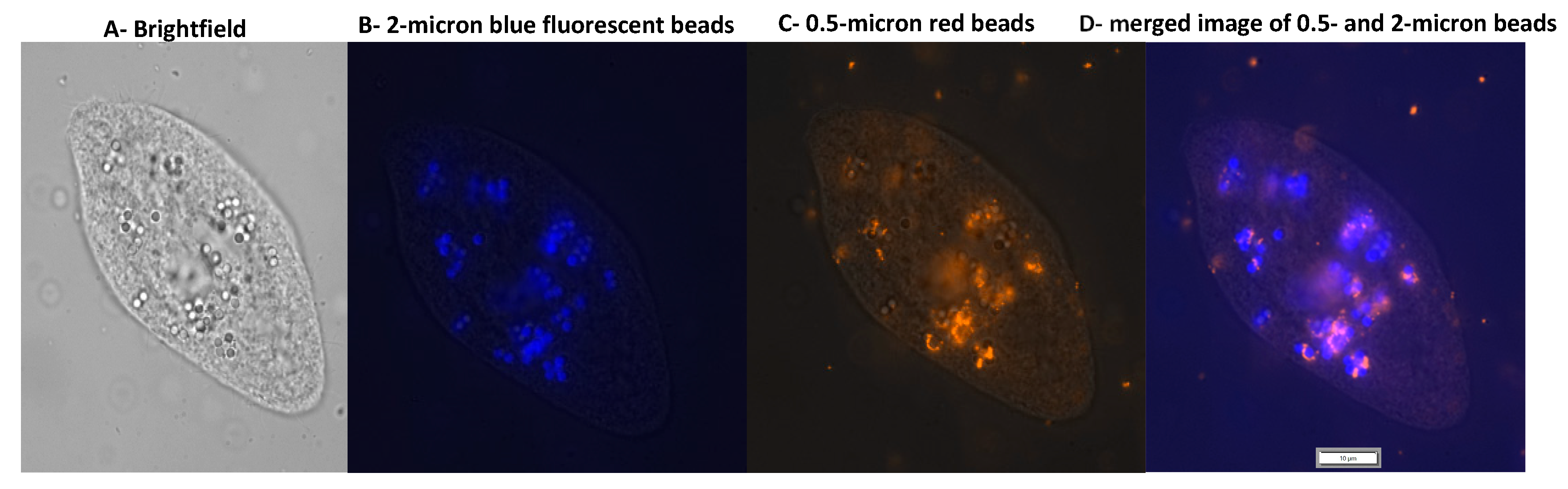
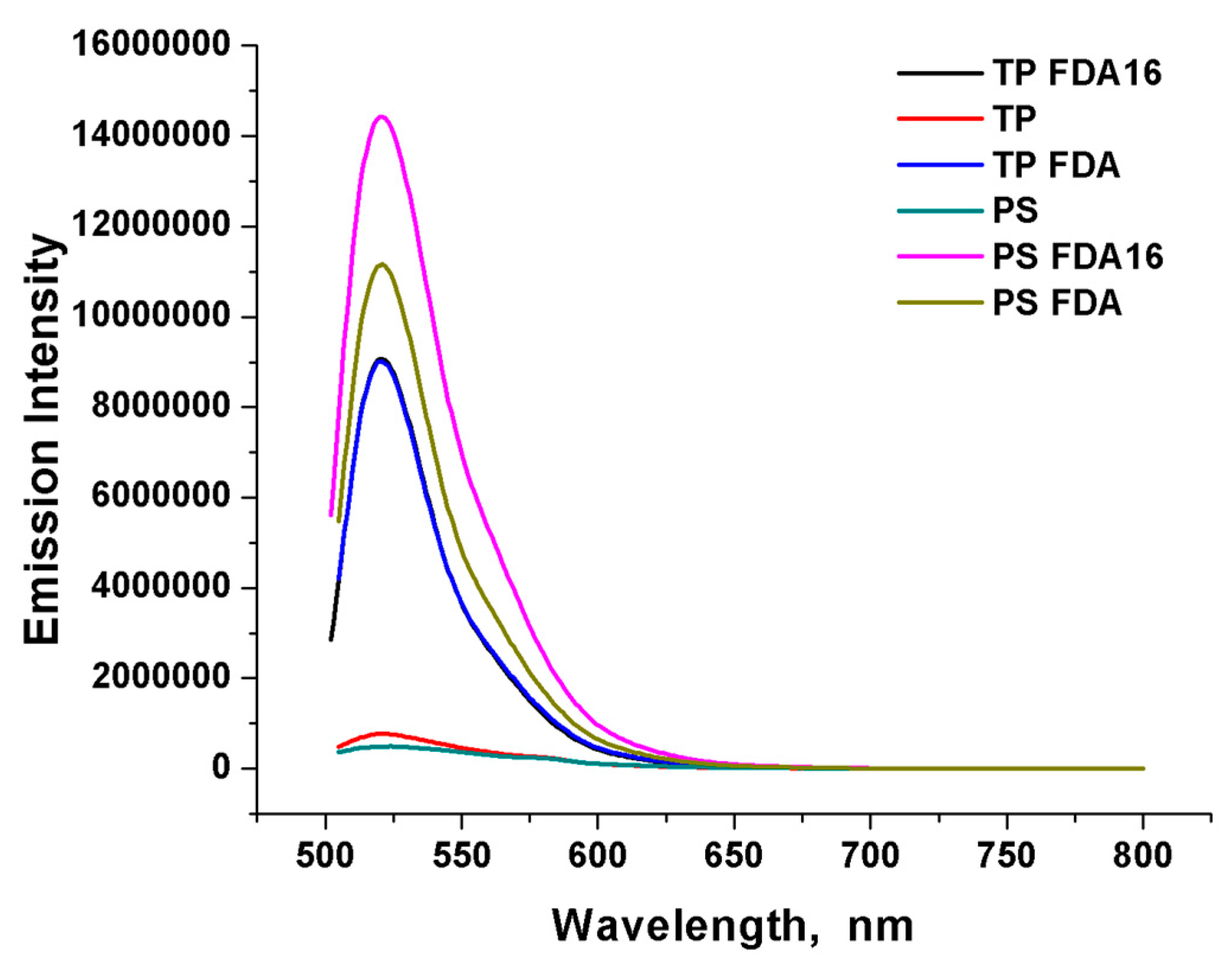
2.3. Uptake of MPs by T. pyriformis
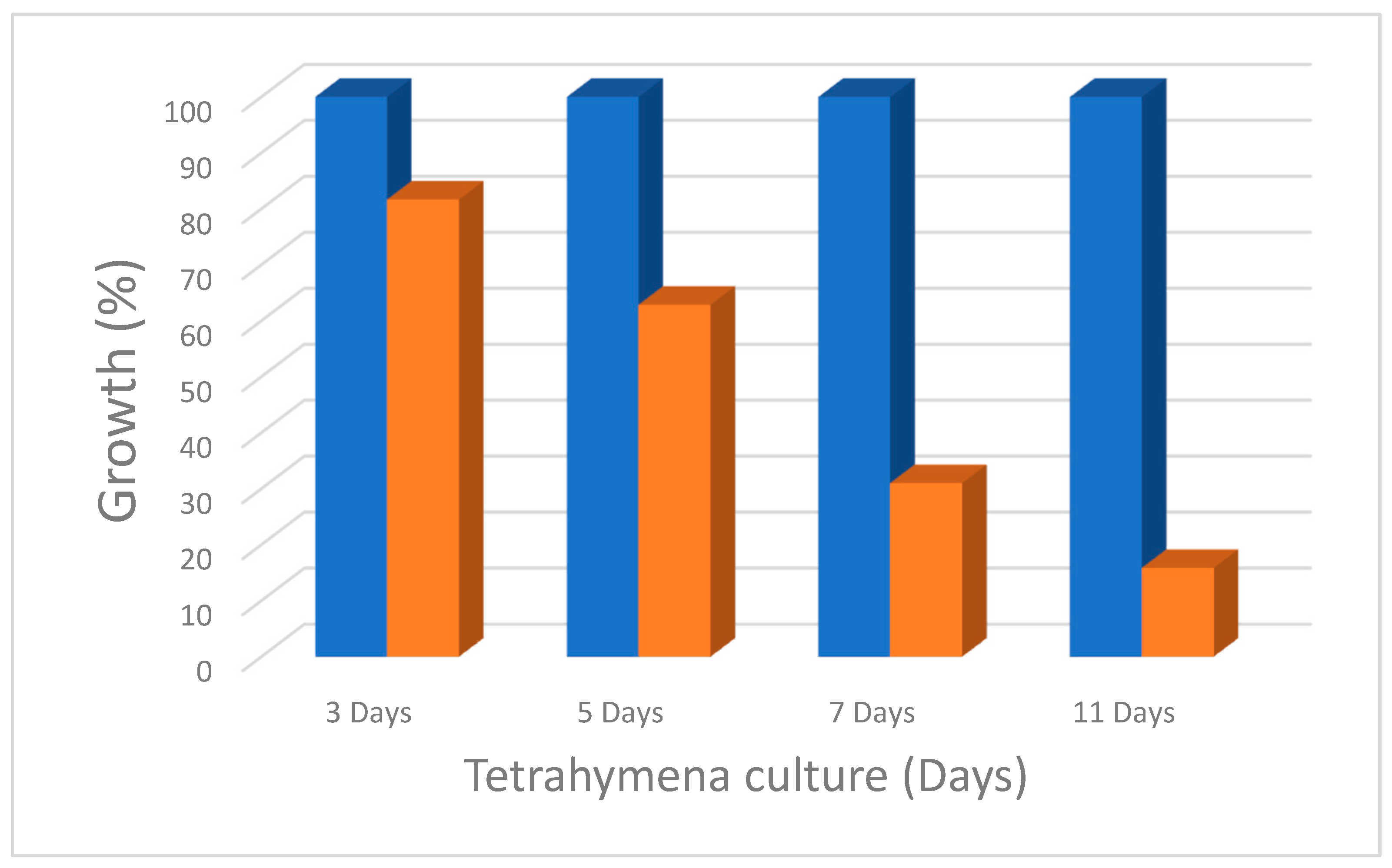
2.4. Measurement of Growth Inhibition
2.5. Measurement of the Level of Reactive Oxygen Species
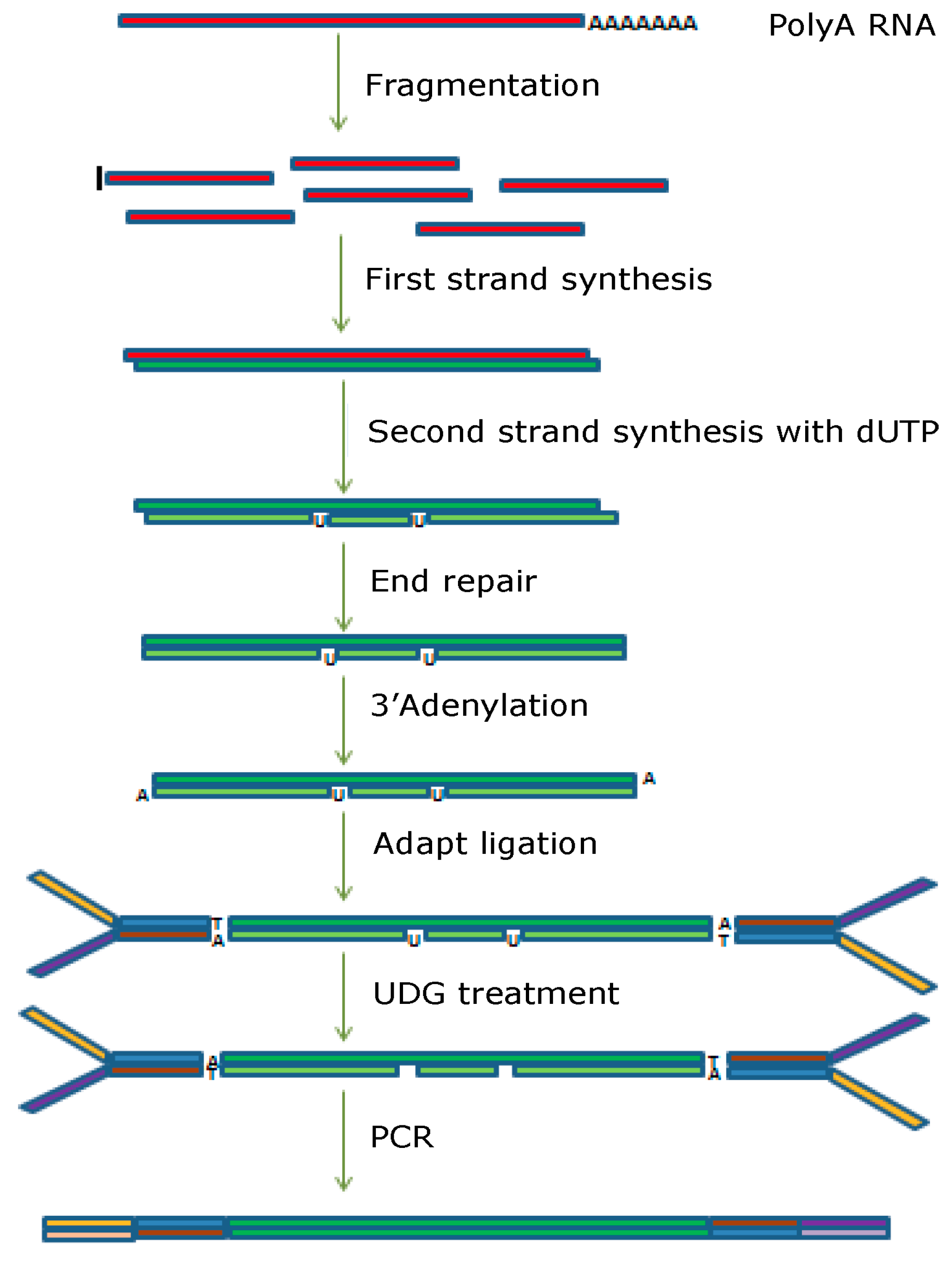
2.6. Differential Gene Expression Analysis by RNA Sequencing
Library Construction and Sequencing
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7.1. De Novo Assembly, Unigene Annotation, and Functional Classification
2.7.2. Differential Expression Analysis of Unigenes
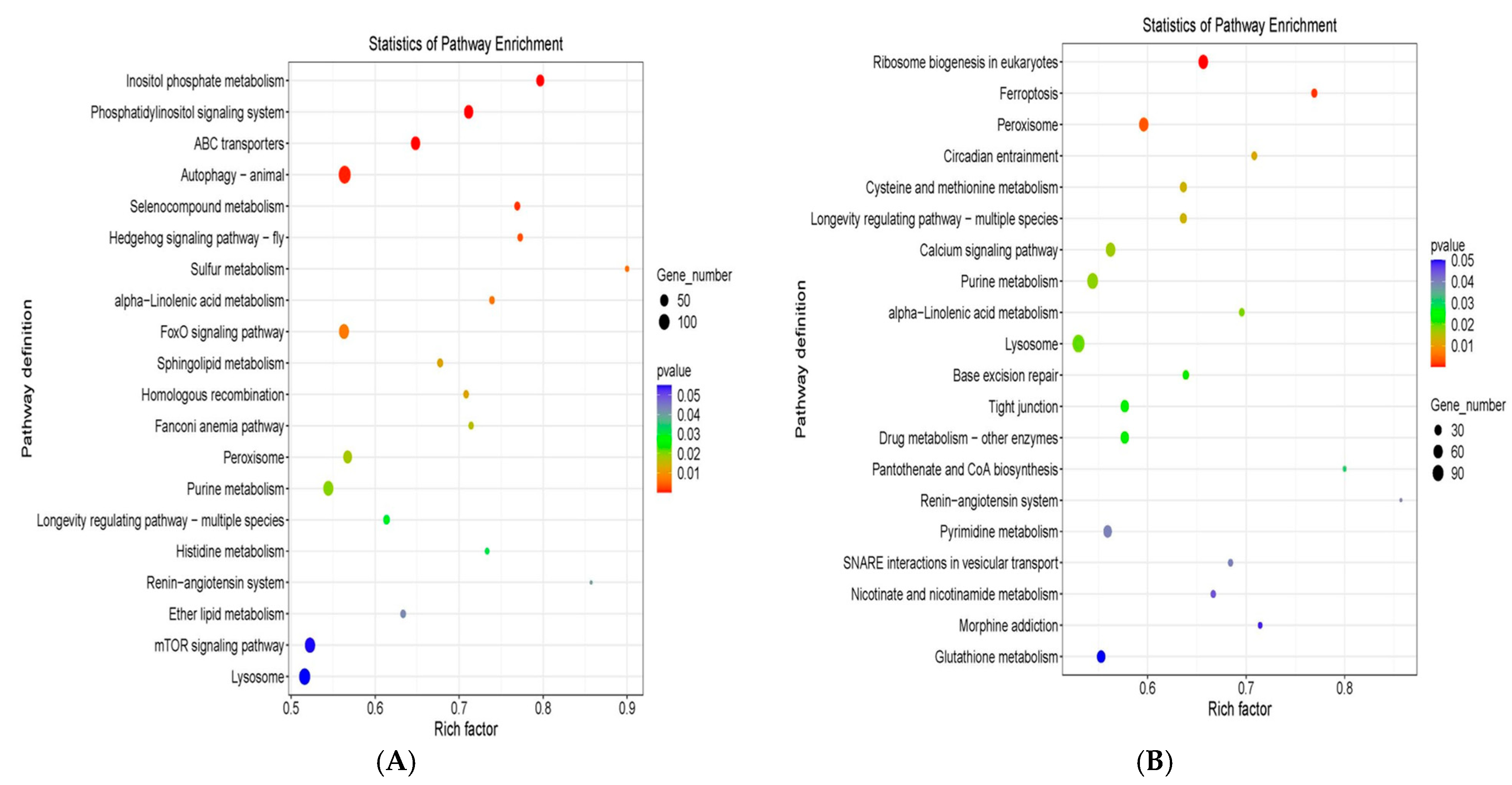
2.7.3. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
3. Results
3.1. Uptake of MPs and NPs by Tetrahymena pyriformis
3.2. Growth Inhibition of T. pyriformis by Polystyrene Micro and Nano Plastics
3.3. RNA-Seq (Transcriptome) Analysis of PS-MP and PMA-MP Exposed T. pyriformis
3.4. The Mechanism of Growth Inhibition
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Modifications of PS-MP and PMA-MP Particles and Their Effect on the Growth Inhibition Response in T. pyriformis
4.2. Variation in the Oxidative Damage Caused by Various Types of MPs and NPs
4.3. Alteration of PS-MP and PMS-MP-Induced Transcriptome Changes in T. pyriformis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, T.S. Micro- and nano-plastics and human health. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Raveendran, S.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Environmental impacts of microplastics and nanoplastics: A current overview. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 768297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S. Micro- and nanoplastics in the environment: Research priorities for the near future. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 257, pp. 163–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, D. Cellular uptake, transport, and organelle response after exposure to microplastics and nanoplastics: Current knowledge and perspectives for environmental and health risks. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehle, M.D.; Orias, E.; Pearson, C.G. Tetrahymena as a unicellular model eukaryote: Genetic and genomic tools. Genetics 2016, 203, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Tian, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Fu, C.; Orias, E.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of the model protozoan, Tetrahymena thermophila, using deep RNA sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Liver injury induced by exposure to polystyrene microplastics alone or in combination with cadmium in mice is mediated by oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, E.; Mychasiuk, R.; Hibbs, M.L.; Semple, B.D. Dysregulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in microglia: Shaping chronic neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Cockcroft, S. Phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate: Diverse functions at the plasma membrane. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Islinger, M.; Worthy, H.; Carmichael, R.; Schrader, M. The peroxisome: An update on mysteries 3.0. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 161, 99–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Iron metabolism in ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 590226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, M.; Ferraro, M.G.; Iazzetti, F.; Santamaria, R.; Irace, C. Insight into iron, oxidative stress and ferroptosis: Therapy targets for approaching anticancer strategies. Cancers 2024, 16, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito WA, S.; Mutter, F.; Wende, K.; Cecchini, A.L.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Consequences of nano and microplastic exposure in rodent models: The known and unknown. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.Z.; Li, R.; Lai, K.P.; Zhang, X.X. Biological exposure to microplastics and nanoplastics and plastic additives: Impairment of glycolipid metabolism and adverse effects on metabolic diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 60778–60791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondellini, S.; Schwarzer, M.; Völkl, M.; Jasinski, J.; Jérôme, V.; Scheibel, T.; Laforsch, C.; Freitag, R. Size-dependent uptake and trophic transfer of polystyrene microplastics in unicellular freshwater eukaryotes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-H.; Choi, S.; Kim, D.; Park, H.J.; Bian, Y.; Choi, S.H.; Chung, H.Y.; Bae, O.-N. Amine-modified nanoplastics promote the procoagulant activation of isolated human red blood cells and thrombus formation in rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Johnson, B.; Williams, C. Localization of nanoplastics in T. pyriformis. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.; Lee, E. Uptake mechanisms of microplastics in protozoa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, F.; Green, G.; Black, H. Chemical modifications and growth inhibition in T. pyriformis. Environ. Res. 2023, 56, 200–215. [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt, S.; Gorokhova, E. Micro- and nanoplastic exposure effects in microalgae: A meta-analysis of standard growth inhibition tests. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, B.R.; Kopperi, H.; Mohan, S.V. Micro/nano-plastics occurrence, identification, risk analysis and mitigation: Challenges and perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2022, 21, 169–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattichizzo, F.; Ceriello, A.; Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Graciotti, L.; Olivieri, F.; Paolisso, P.; D’Agostino, B.; Iovino, P.; Balestrieri, M.L. Micro-nanoplastics and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma AM, G.; Morciano, P.; Aloisi, M. Beyond genetics: Can micro and nanoplastics induce epigenetic and gene-expression modifications? Front. Epigenetics Epigenomics 2023, 1, 1241583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Irvine, R.F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature 1989, 341, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divecha, N.; Irvine, R.F. Phospholipid signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-W.; Feng, J.-N.; Cao, Y.; Meng, L.-P.; Wang, S.-L. Autophagy prevents autophagic cell death in Tetrahymena in response to oxidative stress. Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, A.; Xie, S.; Xiang, Q.; Song, E.; Zou, J. Induction of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and DNA damage by koumine in Tetrahymena thermophila. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, P.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. Effects of pyraclostrobin on growth, oxidative stress, and gene expression related to stress and ATP-binding cassette transporters in Tetrahymena thermophila. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cat # | Type of Microplastics | Surface Functional Group | Average Particle Size Micron (Mean Diameter) | Dye Content (%) | Polymer Density (g/mL) | Solid Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L0780 | Polystyrene | Amine Modified | 0.045–0.055 | ≥0.1 (blue Fluorescent) | 1.04–1.06 | ≥2.5 |
| L3280 | Polystyrene | Carboxylate Modified | 0.4–0.6 | 0.2–0.6 (red fluorescent) | 1.04–1.05 | 2.5 |
| L0280 | Polystyrene | Amine Modified | 1.90–2.20 | ≥0.1 (blue fluorescent) | 1.04–1.06 | 2.4–2.6 |
| 90,875 | Polymethacrylate | None | 0.92–1.0 | Non-fluorescent | 1.19 | 10 |
| Sample | Raw_Reads | Raw_Bases | Valid_Reads |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA1 | 42,055,924 | 6.31G | 41,495,164 |
| PMMA2 | 49,347,144 | 7.40G | 48,728,388 |
| PS1 | 46,459,334 | 6.97G | 45,922,588 |
| PS2 | 42,432,942 | 6.36G | 41,856,014 |
| Tp | 41,112,544 | 6.17G | 40,552,504 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajapandi, T.; Adeleke, A.; Jiru, M. Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Signaling Pathways in Tetrahymena pyriformis Exposed to Micro- and Nanoplastics. Microplastics 2025, 4, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020033
Rajapandi T, Adeleke A, Jiru M. Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Signaling Pathways in Tetrahymena pyriformis Exposed to Micro- and Nanoplastics. Microplastics. 2025; 4(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajapandi, Thavamani, Adewale Adeleke, and Mintesinot Jiru. 2025. "Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Signaling Pathways in Tetrahymena pyriformis Exposed to Micro- and Nanoplastics" Microplastics 4, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020033
APA StyleRajapandi, T., Adeleke, A., & Jiru, M. (2025). Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Related Signaling Pathways in Tetrahymena pyriformis Exposed to Micro- and Nanoplastics. Microplastics, 4(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020033






