Fate of Microplastics in Deep Gravel Riverbeds: Evidence for Direct Transfer from River Water to Groundwater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
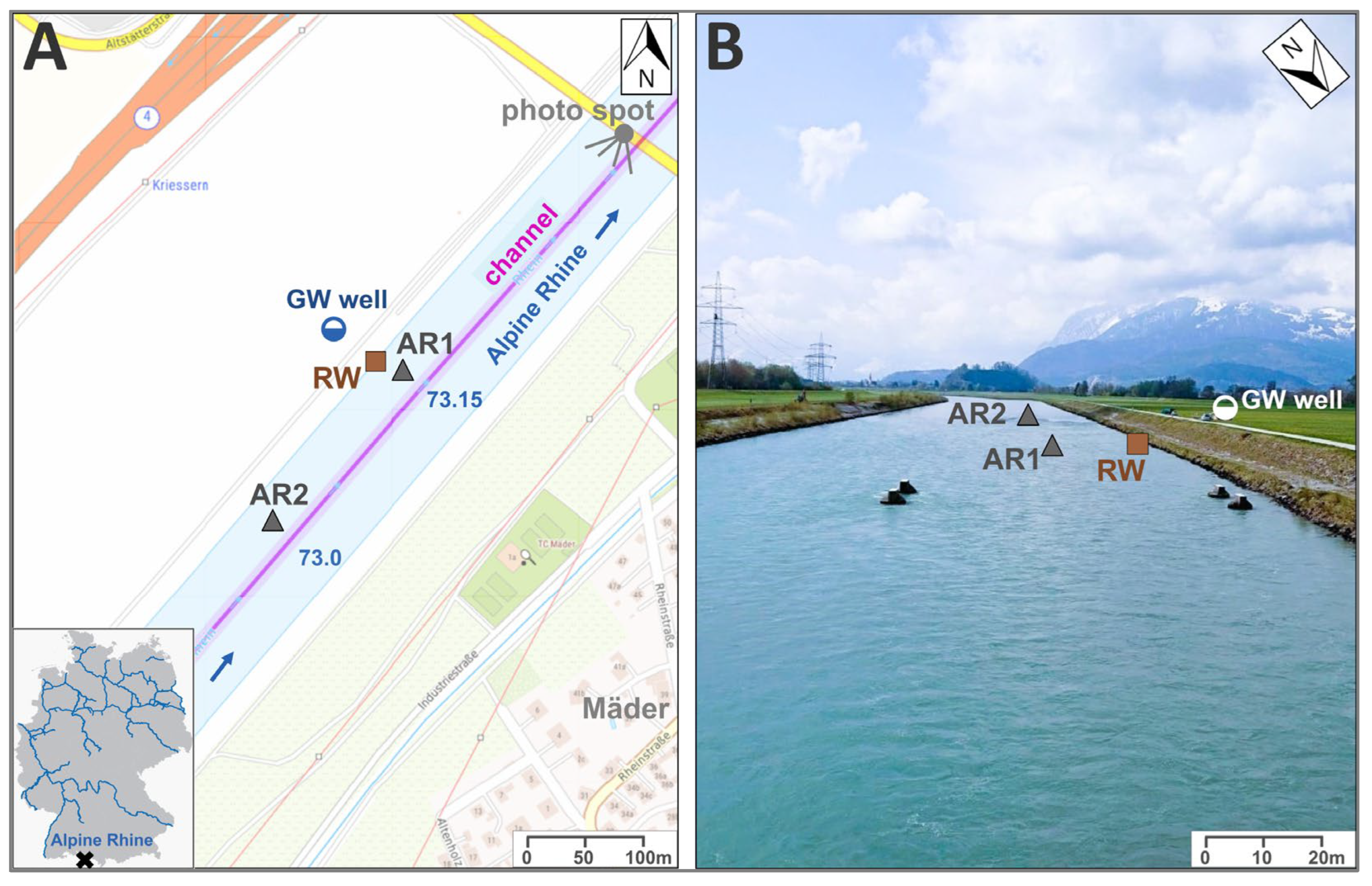
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Contamination Control
3. Results and Discussion
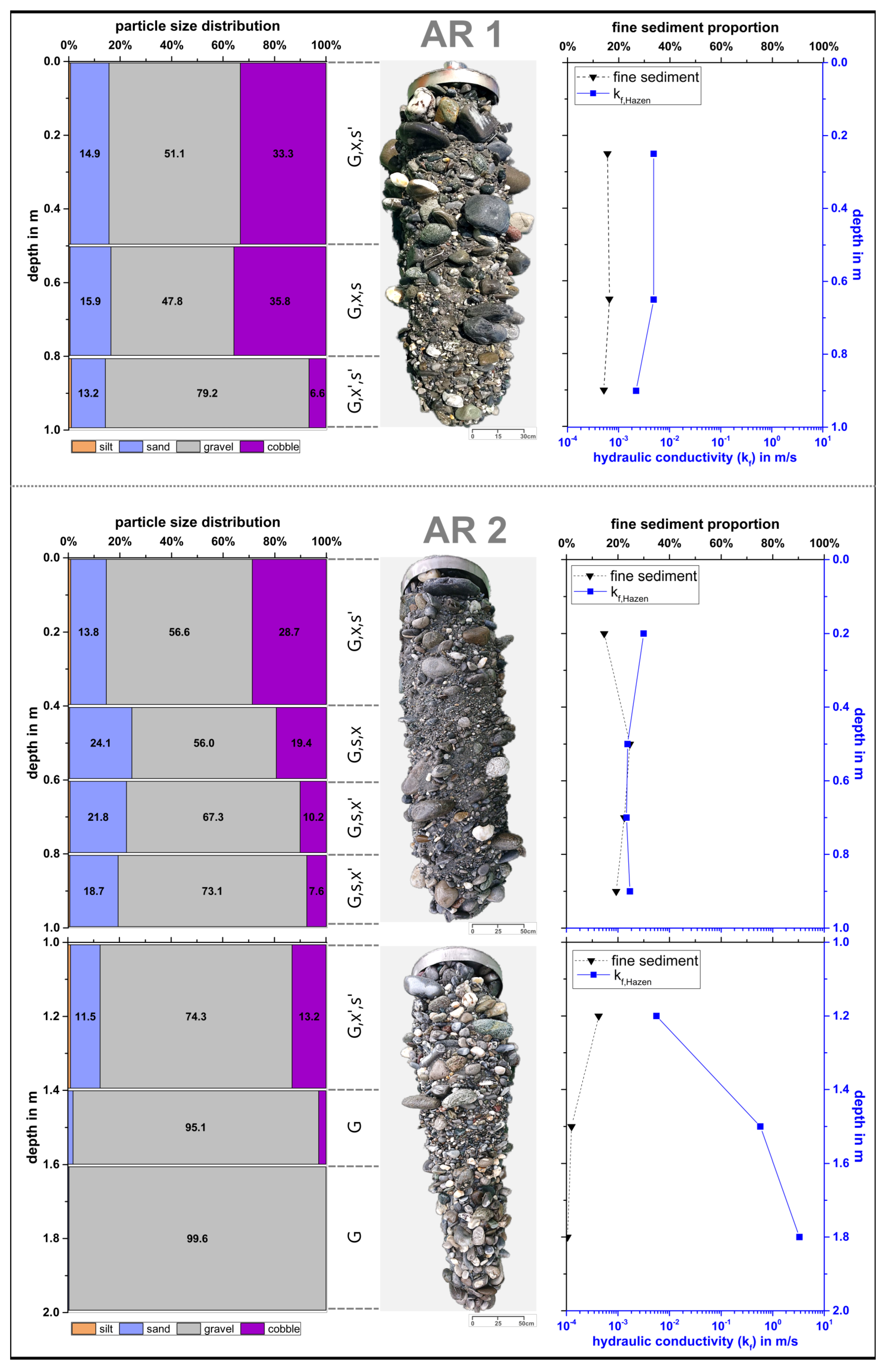
3.1. Characteristics of the Riverbed Sediments
3.2. Depth-Specific MP Distribution in Riverbed Sediments
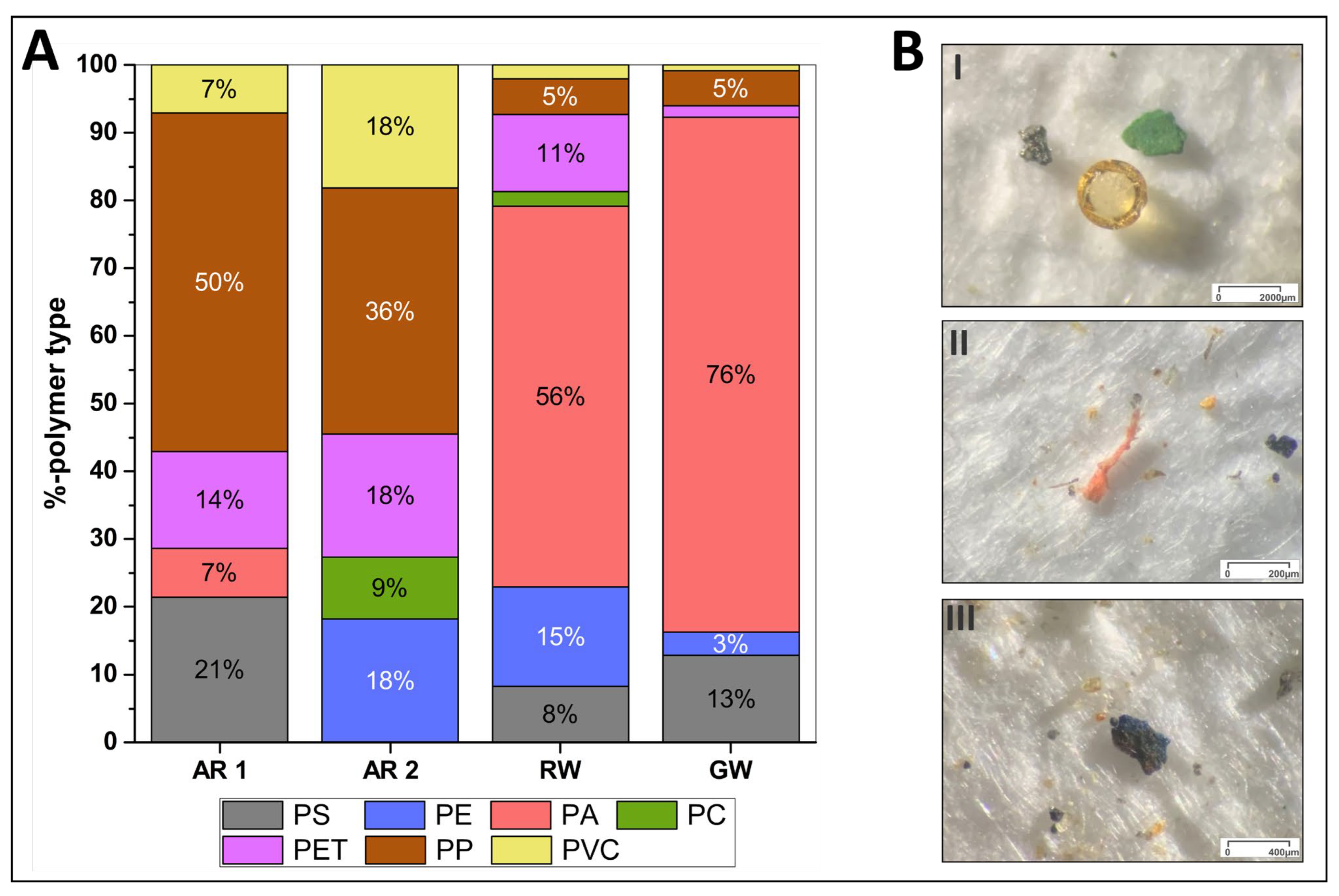
3.3. MP Concentration in River Water and Groundwater
3.4. Polymer Composition in Sediment, Groundwater, and River Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Attenuated total reflection |
| CA | Cellulose acetate |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| GF | Glass fiber |
| GW | Groundwater |
| HQ | High-water discharge |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| MQ | Mean volumetric discharge |
| MP | Microplastic particle |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NNQ | Low-water discharge |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PFA | Perfluoroalkoxy alkane |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| RW | River water |
| µ-FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared microspectroscopy |
| µ-Raman | Raman microspectroscopy |
References
- Gao, S.; Orlowski, N.; Bopf, F.K.; Breuer, L. A review on microplastics in major European rivers. WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Galafassi, S.; Volta, P.; Bettinetti, R. Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L.C.M. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, aaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.-W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.L.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyers, L.J.; van Emmerik, T.; Huthoff, F.; Collas, F.P.; Wegman, C.; Vriend, P.; Boon, A.; de Winter, W.; Oswald, S.B.; Schoor, M.M.; et al. River plastic transport and storage budget. Water Res. 2024, 259, 121786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Emmerik, T.; Mellink, Y.; Hauk, R.; Waldschläger, K.; Schreyers, L.J. Rivers as Plastic Reservoirs. Front. Water 2022, 3, 786936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkham, S.; Aminul Islam, M.; Adhikari, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Sakunkoo, P.; Bhattacharya, P.; Tiwari, A. Evidence of microplastics in groundwater: A growing risk for human health. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, W.W. Groundwater-Surface Water Exchange; The Groundwater Project: Waterloo, ON, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-7770541-5-1. [Google Scholar]
- Irvine, D.J.; Singha, K.; Kurylyk, B.L.; Briggs, M.A.; Sebastian, Y.; Tait, D.R.; Helton, A.M. Groundwater-Surface water interactions research: Past trends and future directions. J. Hydrol. 2024, 644, 132061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, M.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C.; van Wezel, A.P.; Koelmans, A.A. Modeling the Fate and Transport of Plastic Debris in Freshwaters: Review and Guidance. In Freshwater Microplastics: The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, 58th ed.; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 125–152. ISBN 978-3-319-61615-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, D.; Kowalski, N.; Waniek, J.J. Effects of biofouling on the sinking behavior of microplastics. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. New insights into the vertical distribution and microbial degradation of microplastics in urban river sediments. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Schüttrumpf, H. Infiltration Behavior of Microplastic Particles with Different Densities, Sizes, and Shapes–From Glass Spheres to Natural Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9366–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munz, M.; Loui, C.; Postler, D.; Pittroff, M.; Oswald, S.E. Transport and retention of micro-polystyrene in coarse riverbed sediments: Effects of flow velocity, particle and sediment sizes. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2024, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, S.; Piehl, S.; Gilfedder, B.S.; Löder, M.G.J.; Krutzke, J.; Wilhelm, L.; Laforsch, C. Occurence of microplastics in the hyporheic zone of rivers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, P. Plastic in agricultural soils—A global risk for groundwater systems and drinking water supplies?—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, J.-P.; Gilfedder, B.S.; Frei, S. Tracking Microplastics Across the Streambed Interface: Using Laser-Induced-Fluorescence to Quantitatively Analyze Microplastic Transport in an Experimental Flume. Water Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR031064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, S.V.; Kelly, W.R.; Scott, J.; Zheng, W.; McNeish, R.E.; Holm, N.; Hoellein, T.J.; Baranski, E.L. Microplastic Contamination in Karst Groundwater Systems. Groundwater 2019, 57, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.M.; Prioleau, M.D.; Borchardt, M.A.; Hynds, P.D. Review: Epidemiological evidence of groundwater contribution to global enteric disease, 1948–2015. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 981–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divine, C.; Killingstad, M.; Mortensen, L.; Beciragic, A.; Dettmer, A.; Alspach, B. The Plastiverse Extends to Hydrogeologic Systems: Microplastics Are an Important Emerging Groundwater Contaminant Class. Groundw. Monit. R. 2024, 44, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Ball, H.; Cross, R.; Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Read, D.S.; Vollertsen, J.; Svendsen, C. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Potable Water and Their Sources within Water Treatment Works in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12326–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, E.; Ducci, L.; Sutti, A.; Robottom, S.; Sutti, S.; Celico, F. River–Groundwater Interaction and Recharge Effects on Microplastics Contamination of Groundwater in Confined Alluvial Aquifers. Water 2022, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, M.; Kreiß, J.; Krüger, L.; Schmidt, L.K.; Bochow, M.; Bednarz, M.; Bannick, C.G.; Oswald, S.E. Application of High-Resolution Near-Infrared Imaging Spectroscopy to Detect Microplastic Particles in Different Environmental Compartments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittroff, M.; Loui, C.; Oswald, S.E.; Bochow, M.; Kamp, J.; Dierkes, G.; Lensing, H.-J.; Munz, M. Riverbed depth-specific microplastics distribution and potential use as process marker. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 45326–45340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Gan, W.; Sun, J.; Lin, B.; Chen, Z. Depth profiles of microplastics in sediments from inland water to coast and their influential factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Lechthaler, S. Plastics as a stratigraphic marker in fluvial deposits. Anthropocene 2021, 36, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Opp, C.; Prume, J.A.; Koch, M.; Andersen, T.J.; Chifflard, P. Deposition and in-situ translocation of microplastics in floodplain soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, G.; Peng, X. Distribution, sedimentary record, and persistence of microplastics in the Pearl River catchment, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H. Vertical microplastic distribution in sediments of Fuhe River estuary to Baiyangdian Wetland in Northern China. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, K.; Jiang, H.; Su, P.; Lu, P.; Yan, Z. Vertical Profiles of Microplastics in the Hyporheic Zone Sediment: A Case Study in the Yangtze River, Nanjing Section. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Liu, J. Sampling of micro- and nano-plastics in environmental matrixes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazne, M.; Schneidewind, U.; Haverson, L.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Simon, L.; Nel, H.A.; Krause, S. Does what we find depend on how we sample? Measured streambed microplastic concentrations can be affected by the choice of sampling method. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, D.; Lensing, H.-J.; Nuber, T.; Richter, D.; Frank, S.; Goeppert, N.; Goldscheider, N. Improved geohydraulic characterization of river bed sediments based on freeze-core sampling—Development and evaluation of a new measurement approach. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, Z.S.; Williams, D.D. Freezing core method for describing the vertical distribution of sediments in a streambed. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRR. Technischer Bericht Dekolmationsversuch: Hochwasserschutz Alpenrhein Internationale Strecke km 65–km 91 Genehmigungsprojekt; Teil C: Sonstige Unterlagen; Internationale Rheinregulierung (IRR): St. Margrethen, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17892-4:2016; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 4: Determination of Particle Size Distribution. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2016; ICS: 93.020 13.080.20 (ISO/TC 182). [CrossRef]
- ISO 14688-1:2017; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Identification and Classification of Soil—Part 1: Identification and Description. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2017; ICS: 93.020 (ISO/TC 182). [CrossRef]
- DIN 18128:2002-12; Soil—Investigation and Testing—Determination of Ignition Loss. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Hazen, A. Some physical properties of sands and gravels with special reference to their use in filtration. In 24th Annual Report Massachusetts State Board of Health; 1892; pp. 539–556. [CrossRef]
- Pittroff, M.; Müller, Y.K.; Witzig, C.S.; Scheurer, M.; Storck, F.R.; Zumbülte, N. Microplastic analysis in drinking water based on fractionated filtration sampling and Raman microspectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59439–59451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Ewins, C. Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzawi, M.S.M.; Kefer, S.; Weißer, J.; Reichel, J.; Schwaller, C.; Glas, K.; Knoop, O.; Drewes, J.E. Validation of Sample Preparation Methods for Microplastic Analysis in Wastewater Matrices—Reproducibility and Standardization. Water 2020, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzawi, M.S.; Knoop, O.; Drewes, J.E. Validation of sample preparation methods for small microplastics (≤10 µm) in wastewater effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Primpke, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastic Pollution in Benthic Midstream Sediments of the Rhine River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in River Shore Sediments of the Rhine-Main Area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoellein, T.J.; Shogren, A.J.; Tank, J.L.; Risteca, P.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic deposition velocity in streams follows patterns for naturally occurring allochthonous particles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Brookson, C.; Bikker, J.; Djuric, N.; Earn, A.; Bucci, K.; Athey, S.; Huntington, A.; McIlwraith, H.; Munno, K.; et al. Rethinking microplastics as a diverse contaminant suite. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschläger, K.; Brückner, M.Z.; Carney Almroth, B.; Hackney, C.R.; Adyel, T.M.; Alimi, O.S.; Belontz, S.L.; Cowger, W.; Doyle, D.; Gray, A.; et al. Learning from natural sediments to tackle microplastics challenges: A multidisciplinary perspective. Earth Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molazadeh, M.; Liu, F.; Simon-Sánchez, L.; Vollersten, J. Buoyant microplastics in freshwater sediments—How do they get there? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Smith, M.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Rintoul, L.; Goonetilleke, A. Dispersal and transport of microplastics in river sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boos, J.-P.; Dichgans, F.; Fleckenstein, J.H.; Gilfedder, B.S.; Frei, S. Assessing the Behavior of Microplastics in Fluvial Systems: Infiltration and Retention Dynamics in Streambed Sediments. Water Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Weber, A.; Stock, F.; Vurusic, S.; Egerci, H.; Kochleus, C.; Arendt, N.; Földi, C.; Dierkes, G.; Wagner, M.; et al. Comparative assessment of microplastics in water and sediment of a large European river. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piehl, S.; Atwood, E.C.; Bochow, M.; Imhof, H.K.; Franke, J.; Siegert, F.; Laforsch, C. Can Water Constituents Be Used as Proxy to Map Microplastic Dispersal Within Transitional and Coastal Waters? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, L.; Zimmermann, T.; Primpke, S.; Fischer, D.; Gerdts, G.; Pröfrock, D. Comparison and uncertainty evaluation of two centrifugal separators for microplastic sampling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, T.; Blarer, P.; Storck, F.R.; Pittroff, M.; Wernicke, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Repeated detection of polystyrene microbeads in the Lower Rhine River. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Seasonal microplastics variation in nival and pluvial stretches of the Rhine River—From the Swiss catchment towards the North Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Imhof, H.K.; Moses, S.R.; Heß, M.; Schwaiger, J.; Laforsch, C. Riverine microplastic contamination in southwest Germany: A large-scale survey. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 794250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Rao, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics across the watershed of the world’s third-largest river. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zuo, R.; Wu, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z. Global distribution, drivers, and potential hazards of microplastics in groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Cha, J.; Ha, K.; Viaroli, S. Microplastic pollution in groundwater: A systematic review. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2024, 36, 2299545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laermanns, H.; Reifferscheid, G.; Kruse, J.; Földi, C.; Dierkes, G.; Schaefer, D.; Scherer, C.; Bogner, C.; Stock, F. Microplastic in Water and Sediments at the Confluence of the Elbe and Mulde Rivers in Germany. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 794895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Keckeis, H.; Lumesberger-Loisl, F.; Zens, B.; Krusch, R.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Schludermann, E. The Danube so colourful: A potpourri of plastic litter outnumbers fish larvae in Europe’s second largest river. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
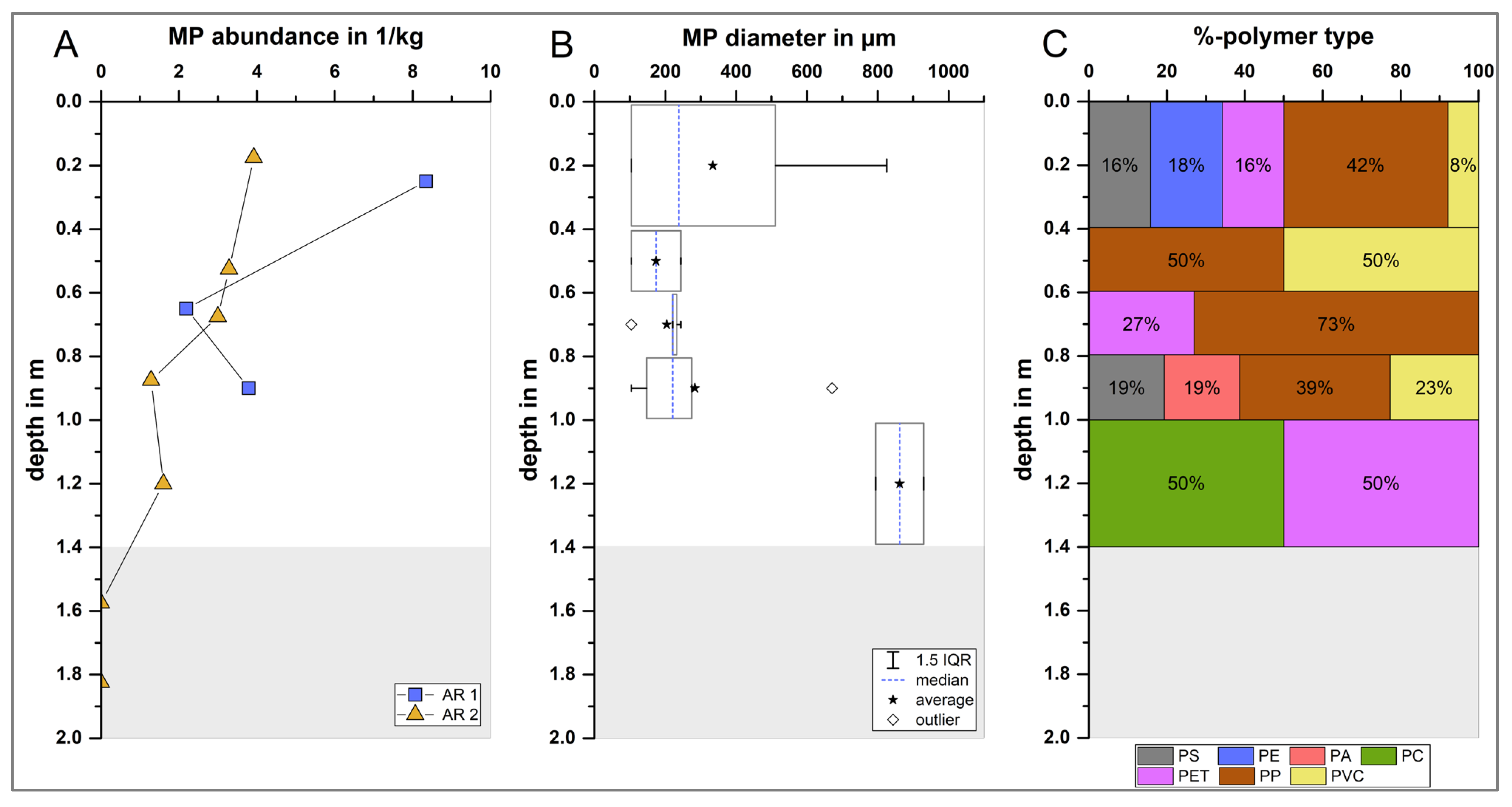
| Sediment Core | Depth Segment [cm] | Sediment Dry Weight [g] | Fine Sediment Fraction [%] | MP Abundance [MP/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR 1 | 0–50 | 5832 | 15.6 | 8.3 |
| 50–80 | 4967 | 16.4 | 2.2 | |
| 80–100 | 6330 | 14.2 | 3.8 | |
| AR 2 | 0–40 | 5104 | 14.7 | 3.9 |
| 40–60 | 5218 | 24.6 | 3.3 | |
| 60–80 | 2789 | 22.5 | 3.0 | |
| 80–100 | 2466 | 19.3 | 1.3 | |
| 100–140 | 2858 | 12.5 | 1.6 | |
| 140–160 | 3192 | 2 | 0 * | |
| 160–200 | 2867 | 0.4 | 0 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pittroff, M.; Munz, M.; Valenti, B.; Loui, C.; Lensing, H.-J. Fate of Microplastics in Deep Gravel Riverbeds: Evidence for Direct Transfer from River Water to Groundwater. Microplastics 2025, 4, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020026
Pittroff M, Munz M, Valenti B, Loui C, Lensing H-J. Fate of Microplastics in Deep Gravel Riverbeds: Evidence for Direct Transfer from River Water to Groundwater. Microplastics. 2025; 4(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020026
Chicago/Turabian StylePittroff, Marco, Matthias Munz, Bernhard Valenti, Constantin Loui, and Hermann-Josef Lensing. 2025. "Fate of Microplastics in Deep Gravel Riverbeds: Evidence for Direct Transfer from River Water to Groundwater" Microplastics 4, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020026
APA StylePittroff, M., Munz, M., Valenti, B., Loui, C., & Lensing, H.-J. (2025). Fate of Microplastics in Deep Gravel Riverbeds: Evidence for Direct Transfer from River Water to Groundwater. Microplastics, 4(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4020026





