Accumulation Evaluation of Potential Microplastic Particles in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Goro Sacca (Adriatic Sea, Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
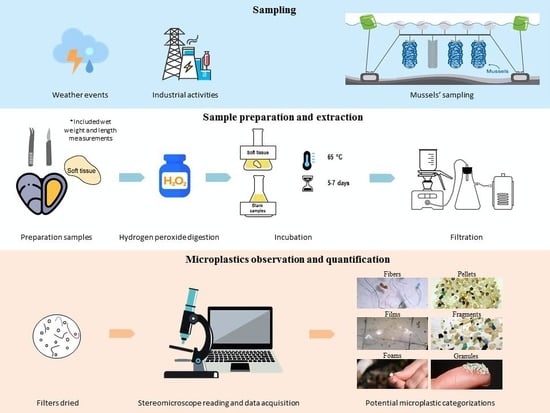
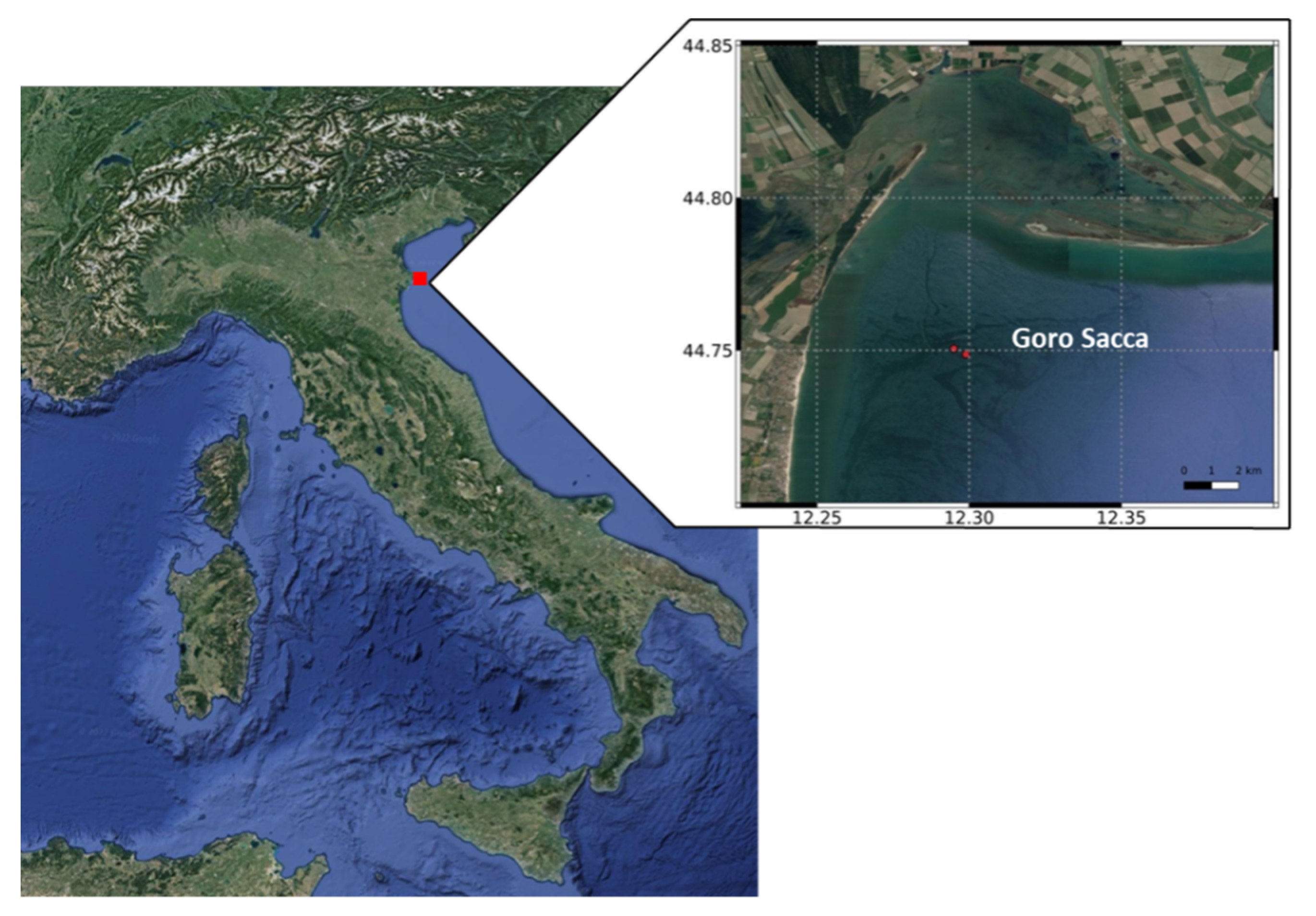
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
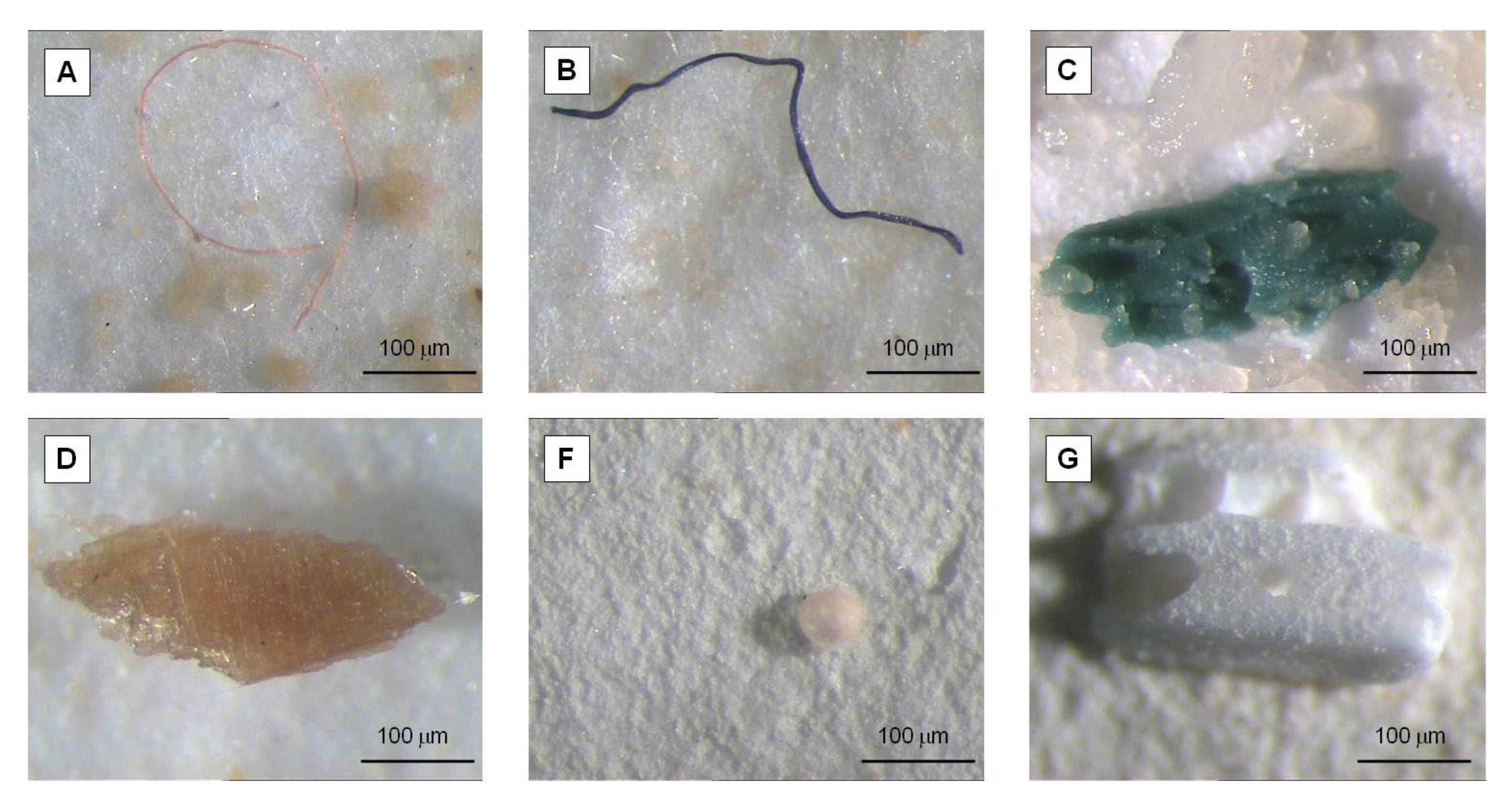
2.3. MP Observation and Quantification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
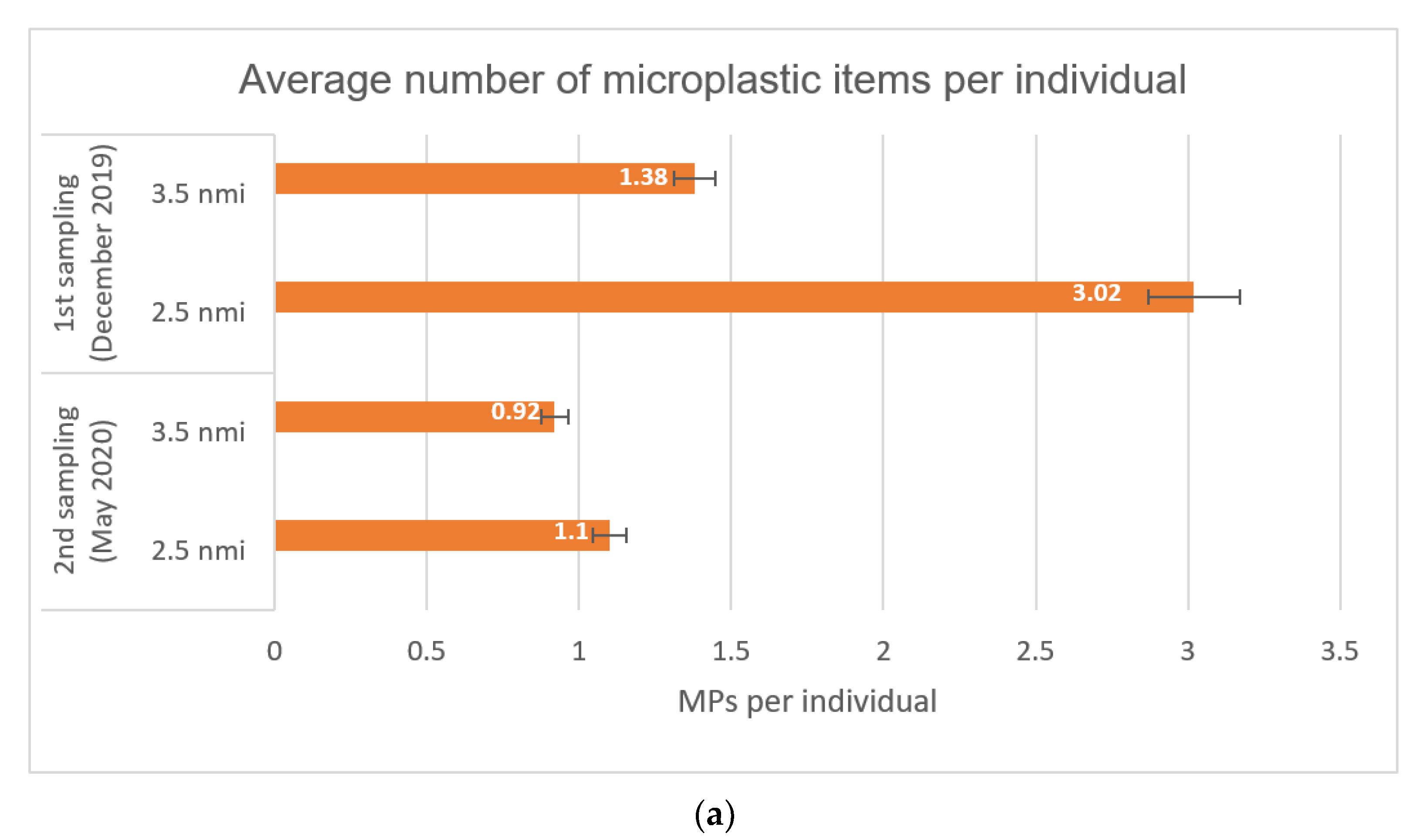
3.1. Abundance of Microplastics
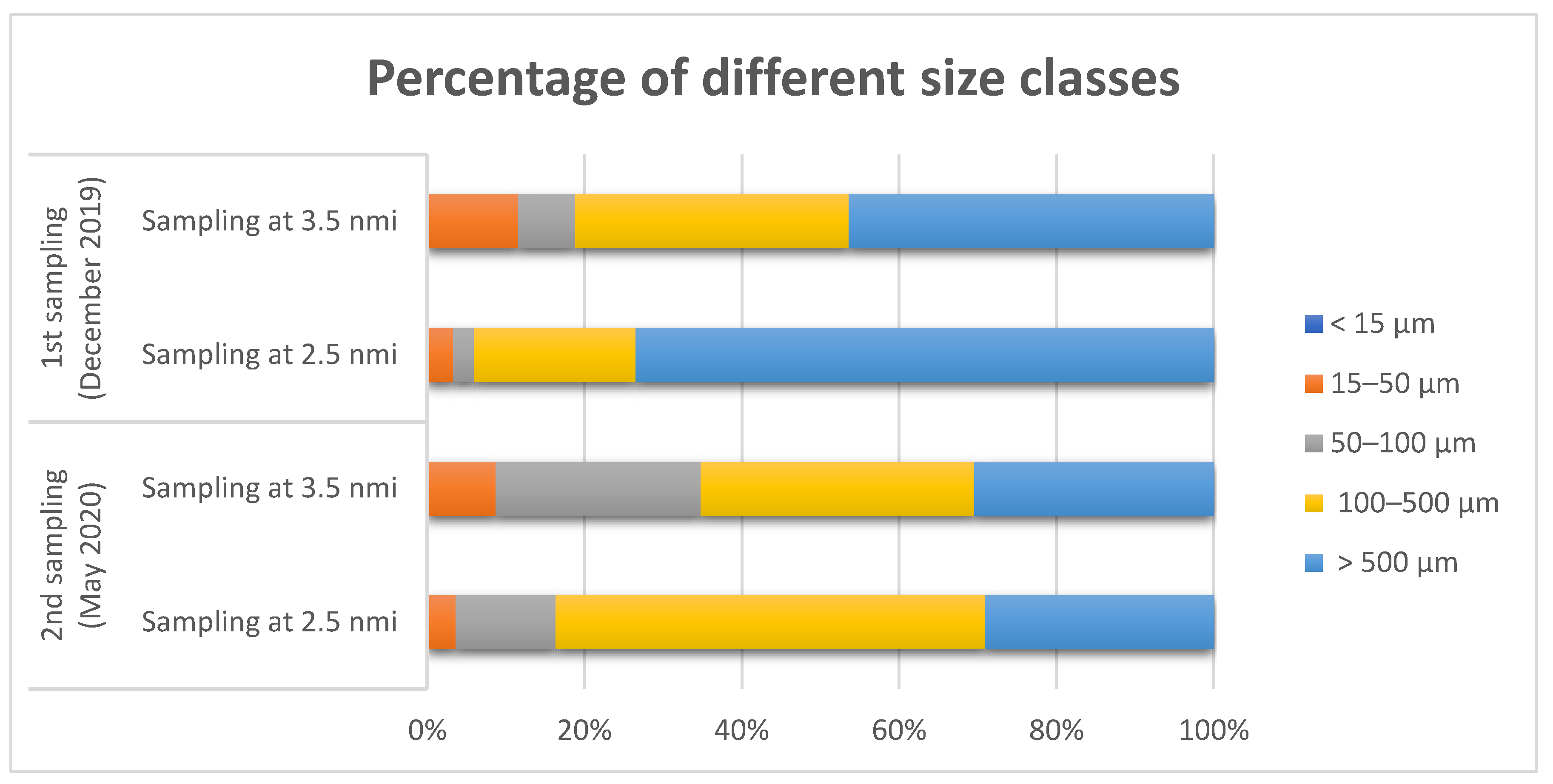
3.2. Shape, Color, and Size Class of Microplastics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bråte, I.L.N.; Hurley, R.; Iversen, K.; Beyer, J.; Thomas, K.; Steindal, C.C.; Green, N.W.; Olsen, M.; Lusher, A. Mytilus spp. as sentinels for monitoring microplastic pollution in Norwegian coastal waters: A qualitative and quantitative study. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.; Sun, C.; Shahadat Hossain, M.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezania, S.; Parka, J.; Din, M.F.M.; Taib, S.M.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Yadav, K.K.; Kamyabe, H. Microplastics pollution in different aquatic environments and biota: A review of recent studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; van der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zeng, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, W. Status of marine microplastic pollution and its ecotoxicological effects on marine fish. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 41, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, C.J.; Feiner, Z.S.; Malinich, T.D.; Höök, T.O. A meta-analysis of the effects of exposure to microplastics on fish and aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F. Marine litter, future prospects for research. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Distribution, Interactions and Effects. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 245–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ory, N.C.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Thiel, M. AmberstripescadDecapterusmuroadsi (Carangidae) fish ingest blue microplastics resembling their copepod prey along the coast of Rapa Nui (Easter Island) in the South Pacific subtropical gyre. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Rowe, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1031–R1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naji, A.; Nuri, M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics contamination in molluscs from the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutantsbioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, F.; Barría, P.; Neto, J.M.; Frias, J.P.G.L.; Otero, V.; Sobral, P.; Marques, J.C. Occurrence of microplasticsiin commercial fish from a natural estuarine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenet, T.; Mancia, A.; Bono, G.; Falsone, F.; Scannella, D.; Vaccaro, C.; Baldi, A.; Catani, M.; Cavazzini, A.; Pasti, L. Plastic ingestion by Atlantic horsemackerel (Trachurustrachurus) from centralMediterranean Sea: A potential cause for endocrine disruption. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.I.; Van de Meulen, M.D.; Maes, T.; Bekaert, K.; Paul-Pont, I.; Frère, L.; Robbens, J.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastic contamination in brown shrimp (Crangoncrangon, Linnaeus 1758) from coastal waters of the southern north sea and channel area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Jiang, F.; He, C.; Zhang, M.; Ju, P.; Ding, N.X. An examination of the occurrence and potential risks of microplastics across various shellfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Sun, C.; He, C.; Li, J.; Ju, P.; Li, F. Microplastics in four bivalve species and basis for using bivalves as bioindicators of microplastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Su, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Li, D.; Shi, H. Microplastics in mussels along the coastal waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Green, C.; Reynolds, A.; Shi, H.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 67, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, D.A.; Carvalho-Souza, G.F. Are we eating plastic-ingesting fish? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.F.M.; Ascer, L.G.; Custodio, M.R.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Moreira, F.; Turra, A. Microplastics contamination in mussels’ natural beds from a Brazilian urbanized coastal region: An initial evaluation for further bioassessments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Su, L.; Ruan, H.D.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Lee, C.H.; Jiang, S.Y. Quantitative and qualitative determination of microplastics in oyster, seawater and sediment from the coastal areas in Zhuhai, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 112000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Part 2 of a Global Assessment. GESAMP Reports and Studies, 2016; 220p. Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/site/assets/files/1275/sources-fate-and-effects-of-microplastics-in-the-marine-environment-part-2-of-a-global-assessment-en.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.L.; Welden, N.A.; Sobral, P.; Cole, M. Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.L. Plastics in the marine environment. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digka, N.; Tsangaris, C.; Torre, M.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Zeri, C. Microplastics in mussels and fish from the northern Ionian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeersch, G.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R.; Marques, A.; Granby, K.; Fait, G.; Kotterman, M.J.J.; Diogene, J.; Bekaert, K.; Robbens, J.; et al. A critical review on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathalon, A.; Hill, P. Microplasticfibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding halifaxharbor, nova scotia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Claessens, M.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics are taken up by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and lugworms (Arenicola marina) living in natural habitats. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Guerranti, C.; Blašković, A. Microplastic contents from maricultured and natural mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, B.; Devriese, L.; Bekaert, K.; Hoffman, S.; Vandermeersch, G.; Cooreman, K.; Robbens, J. Quality assessment of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis): Comparison between commercial and wild types. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Su, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Shi, H. Assessing the relationship between the abundance and properties of microplastics in water and in mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in market bivalves from South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, C.; Awe, A.; Maneveld, J. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in retail mussels from Cape Town, South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Deng, H.; Li, B.; Chen, Q.; Pettigrove, V.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. The occurrence of microplastic in specific organs in commercially caught fishes from coast and estuary area of east China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkinshaw, C.; Lindeque, P.K.; Thompson, R.; Tolhurst, T.; Cole, M. Microplastics and seafood: Lower trophic organisms at highest risk of contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deme, G.G.; Ewusi-Mensah, D.; Olagbaju, O.A.; Okeke, E.S.; Okoye, C.O.; Odii, E.C.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Igun, E.; Onyekwere, J.O.; Oderinde, O.K.; et al. Macro problems from microplastics: Toward a sustainable policy framework for managing microplastic waste in Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bolan, N.; Tsang, D.; Sarkar, B.; Bradney, L.; Li, Y. A review of microplastics aggregation in aquatic environment: Influence factors, analytical methods, and environmental implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, M.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Rillig, M.C.; Koelmans, A.A.; Metian, M.; Wright, S.; Provencher, J.F.; Sanden, M.; et al. Global plastic pollution observation system to aid policy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7770–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igalavithana, A.D.; Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Gajanayake, P.; Abeynayaka, A.; Gamaralalage, P.J.D.; Ohgaki, M.; Takenaka, M.; Fukai, T.; Istubo, N. Microplastics and Potentially Toxic Elements: Potential Human Exposure Pathways through Agricultural Lands and Policy Based Countermeasures. Microplastics 2022, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K.A. Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcieri, F.M.; Benetazzo, A.; Sclavo, M.; Russo, A.; Carniel, S. Po River plume pattern variability investigated from model data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 87, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, E.C.; Falcieri, F.M.; Piehl, S.; Bochow, M.; Matthies, M.; Franke, J.; Carniel, S.; Sclavo, M.; Laforsch, C.; Siegert, F. Coastal accumulation of microplastic particles emitted from the Po River, Northern Italy: Comparing remote sensing and hydrodynamic modelling within situ sample collections. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomiero, A.; Strafella, P.; Øysæd, K.B.; Fabi, G. First occurrence and composition assessment of microplastics in native mussels collected from coastal and offshore areas of the northern and central Adriatic Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 24407–24416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liubartseva, S.; Coppini, G.; Lecci, R.; Creti, S. Regional approach to modeling the transport of floating plastic debris in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, A.; Da Ros, L.; Boldrin, A.; Marceta, T.; Moschino, V. First evaluation of floating microplastics in the Northwestern Adriatic Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 28546–28561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpae Emilia-Romagna. Servizio IdroMeteoClima. Available online: https://www.arpae.it/sim/?osservazioni_e_dati/richiestadati (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Bessa, F.; Frias, J.; Kögel, T.; Lusher, A.; Andrade, J.; Antunes, J.; Sobral, P.; Pagter, E.; Nash, R.; O’Connor, I.; et al. Harmonized Protocol for Monitoring Microplastics in Biota. JPI-Oceans BASEMAN Project: 2019; 30p. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332157735_Harmonized_protocol_for_monitoring_microplastics_in_biota (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic debris in 29 Great Lakes tributaries: Relations to watershed attributes and hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Ho, Y.B.; Larat, V.; Salamatinia, B. Microplastics in eviscerated flesh and excised organs of dried fish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.K.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Spatiotemporal distribution and annual load of microplastics in the Nakdong River, South Korea. Water Res. 2019, 160, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballent, A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Madden, O.; Helm, P.A.; Longstaffe, F.J. Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario nearshore, tributary and beach sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Nationwide monitoring of microplastics in bivalves from the coastal environment of Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, A.I.; Macchia, V.; Sanderson, W.G.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Low levels of microplastics (MP) in wild mussels indicate that MP ingestion by humans is minimal compared to exposure via household fibres fallout during a meal. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; MacNaughtan, W.; Gomes, R.L. Freshwater and airborne textile fibre populations are dominated by ‘natural’, not microplastic, fibres. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suaria, G.; Achtypi, A.; Perold, V.; Lee, J.R.; Pierucci, A.; Bornman, T.G.; Aliani, S.; Ryan, P. Microfibers in oceanic surface waters: A global characterization. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, A.; Rees, A.; Rowe, R.; Stevens, J.; Wright, P. Microplastics in the Solent estuarine complex, UK: An initial assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Shim, W.J.; Cho, Y.; Han, G.M.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H. A close relationship between microplastic contamination and coastal area use pattern. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Cardelli, L.R.; Gorbi, S.; Pellegrini, D.; Regoli, F. Microplastics pollution after the removal of the Costa Concordia wreck: First evidences from a biomonitoring case study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.N.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A.; Kamari, A.; Mouneyrac, C.; Amiard, F.; Poirier, L.; Lagarde, F. Quantification and characterization of microplastics in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis): Protocol setup and preliminary data on the contamination of the French Atlantic coast. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6135–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Norkko, J.; Lehtiniemi, M. Feeding type affects microplastic ingestion in a coastal invertebrate community. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
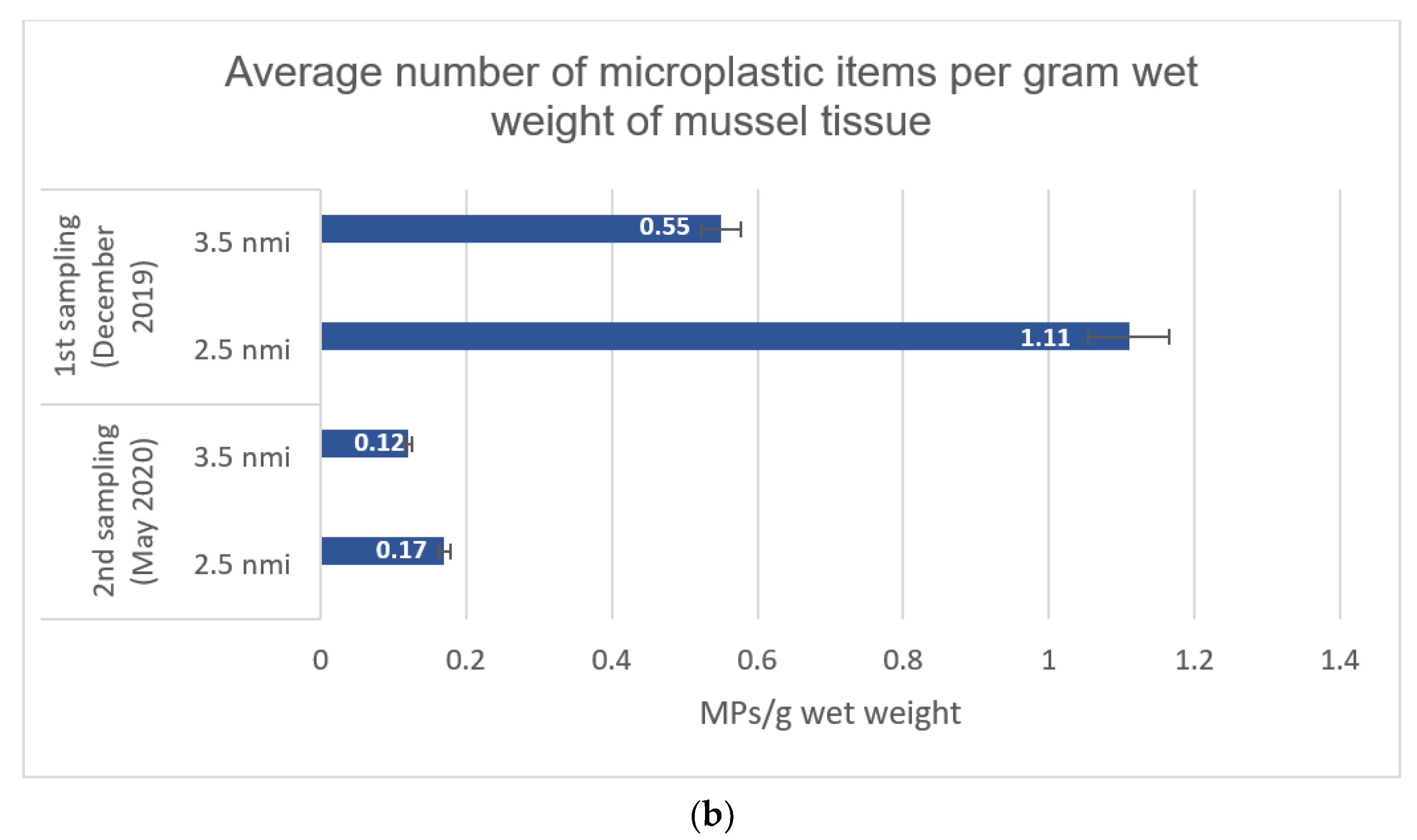
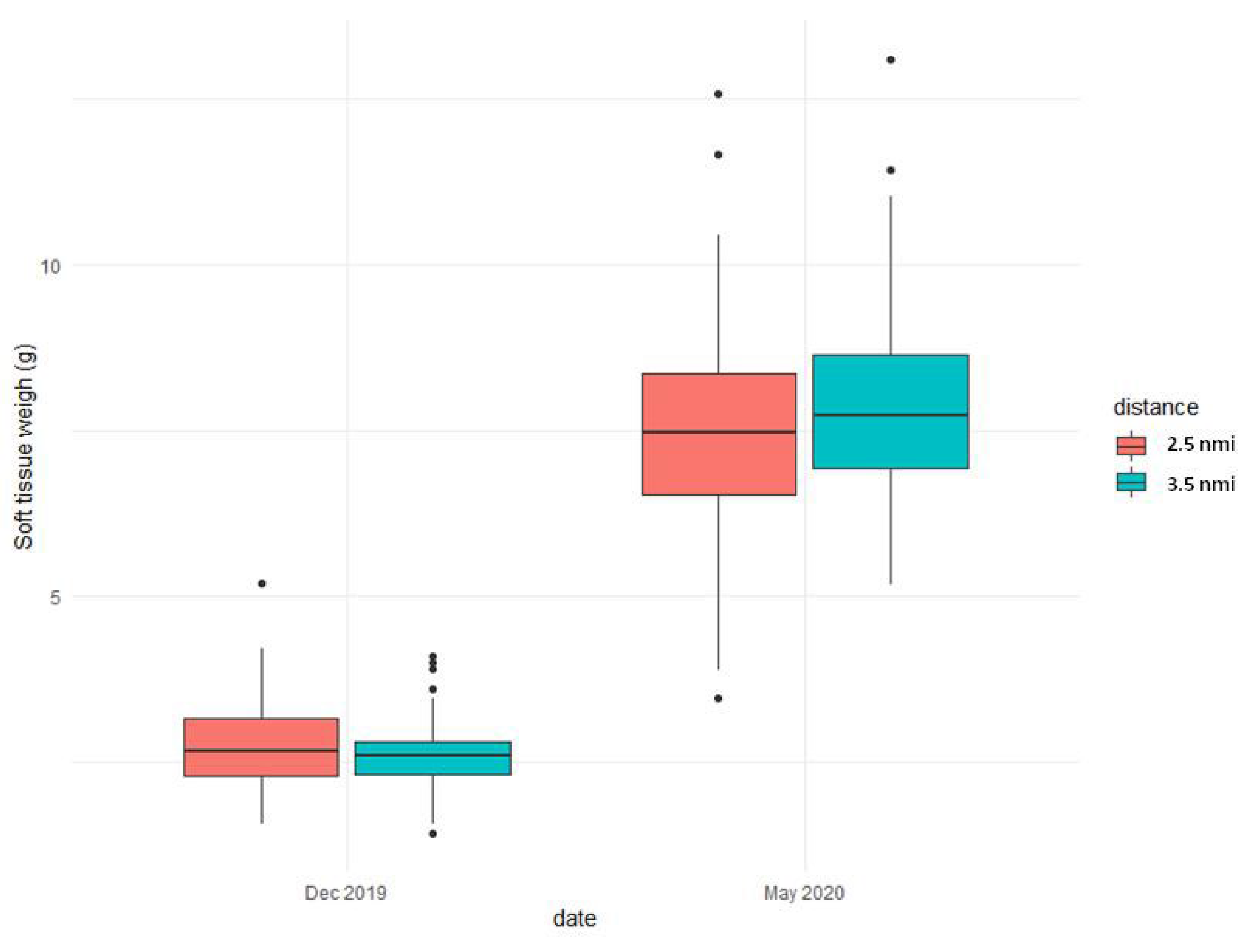
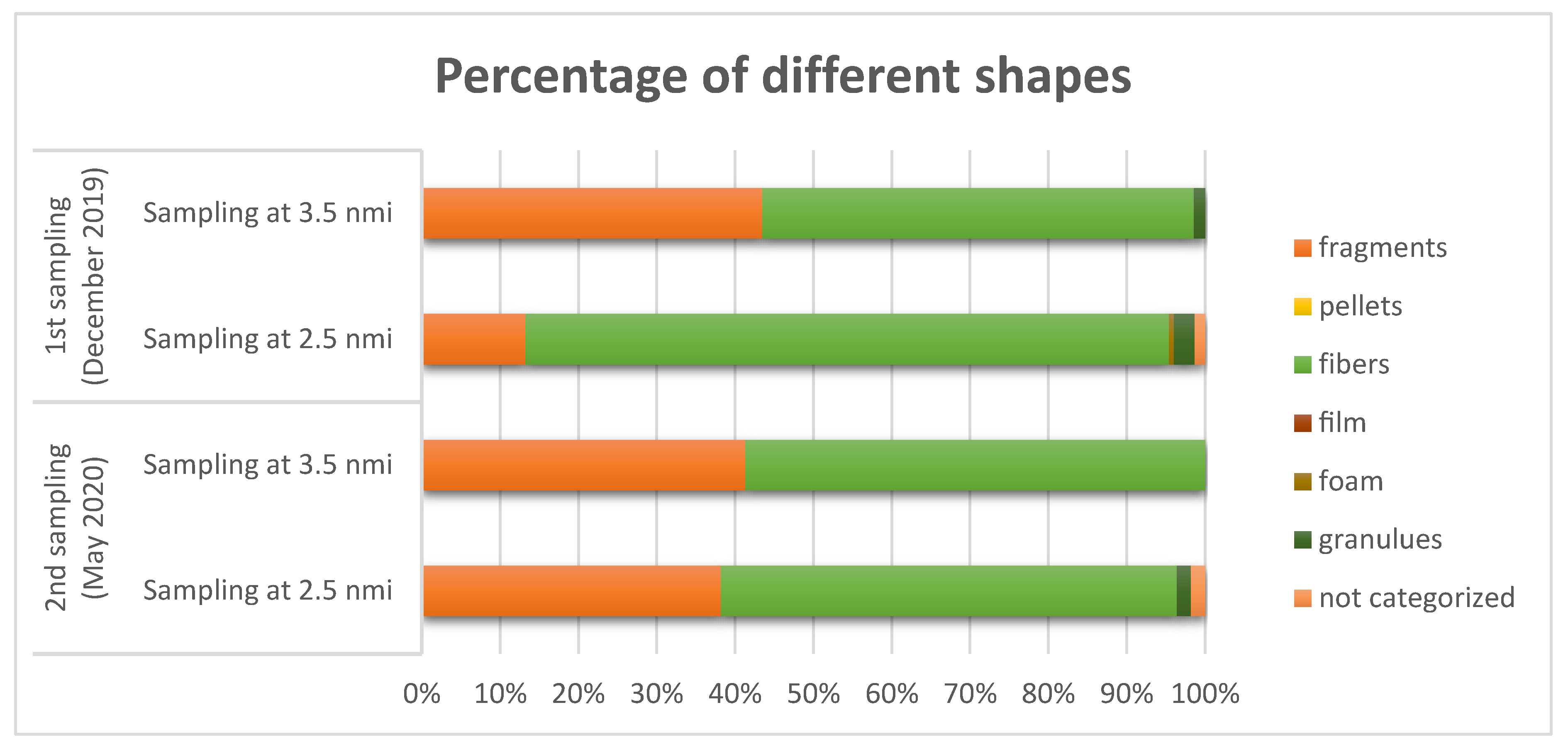
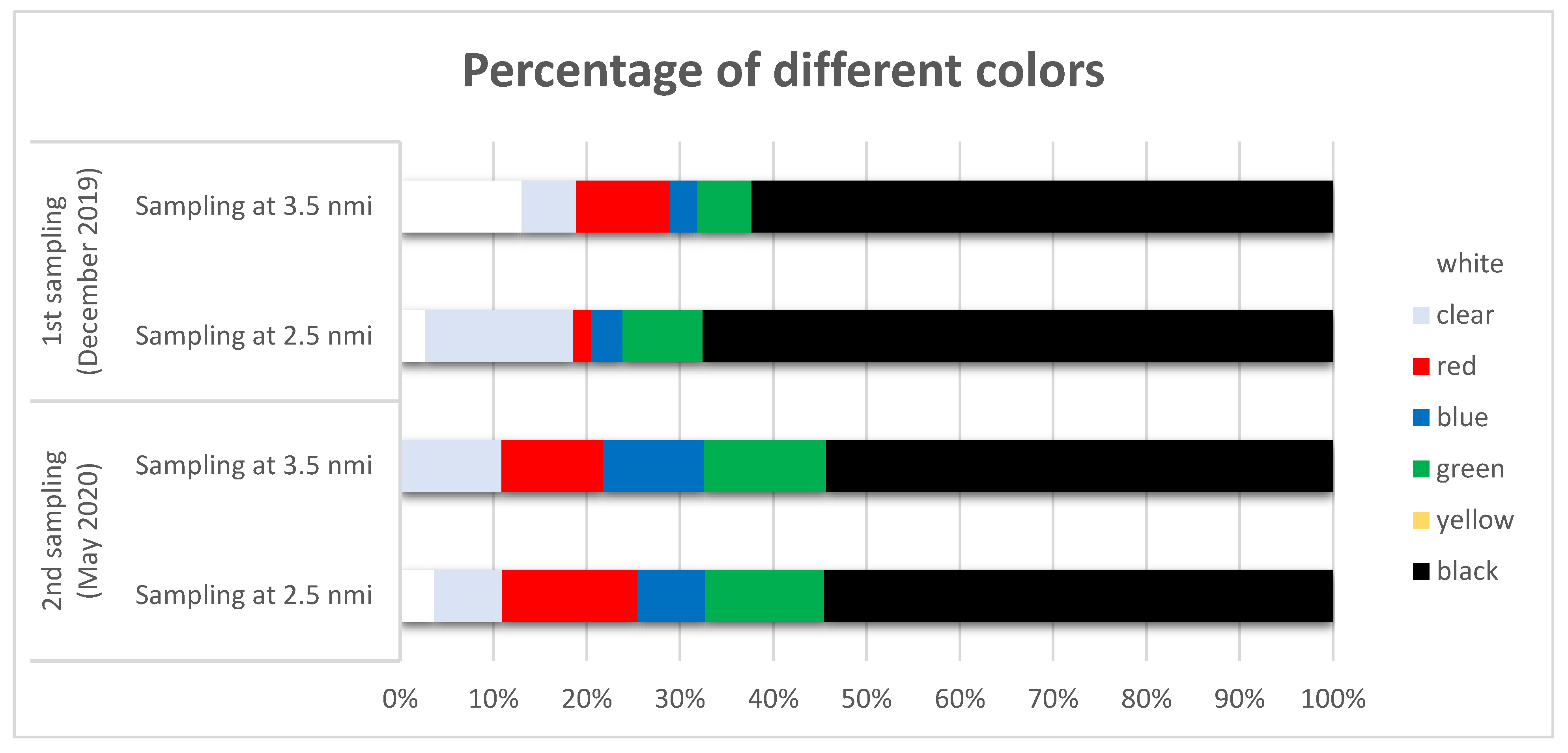
| Period | December 2019 | May 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Week before sampling | 6643.68 | 1527.07 |
| Week of sampling | 4504.70 | 1037.93 |
| Site | Geographic Position | Sampling Period | Collected Mussels | Shell Length (cm) | Soft Tissue Weight (g/Individual) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goro Sacca Station 1 (2.5 nmi) | 44°44.920′ N 12°17.936′ E | December 2019 | 50 | 5.32 ± 0.36 | 2.84 ± 0.74 |
| 44°44.920′ N 12°17.936′ E | May 2020 | 50 | 6.97 ± 4.3 | 7.46 ± 1.87 | |
| Goro Sacca Station 2 (3.5 nmi) | 44°45.031′ N 12°17.699′ E | December 2019 | 50 | 4.81 ± 0.36 | 2.64 ± 0.59 |
| 44°45.031′ N 12°17.699′ E | May 2020 | 50 | 6.24 ± 0.48 | 7.90 ± 1.61 |
| Sampling | Station 1 at 2.5 nmi (December 2019) | Station 2 at 3.5 nmi (December 2019) | Station 1 at 2.5 nmi (May 2020) | Station 2 at 3.5 nmi (May 2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of mussels examined | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Number of mussels containing microplastics | 43 | 36 | 27 | 27 |
| Microplastics frequency of occurence | 86% | 72% | 54% | 54% |
| Microplastics number | 151 | 69 | 55 | 46 |
| Microplastics mean size | 1892.7 µm | 1343.9 µm | 1162.02 µm | 496.15 µm |
| Microplastics size class range more present | >500 µm | >500 µm | 100–500 µm | 100–500 µm |
| Minimum particle size | 21.6 µm | 38 µm | 22 µm | 25 µm |
| Microplastic Abundance | ||||
| (a) Average number of microplastic items per individual | 3.02 ± 2.28 | 1.38 ± 1.24 | 1.1 ± 1.46 | 0.92 ± 1.04 |
| (b) Average number of microplastic items per gram wet weight of mussel tissue | 1.11 ± 0.92 | 0.55 ± 0.56 | 0.17 ± 0.21 | 0.12 ± 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizzurro, F.; Recchi, S.; Nerone, E.; Salini, R.; Barile, N.B. Accumulation Evaluation of Potential Microplastic Particles in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Goro Sacca (Adriatic Sea, Italy). Microplastics 2022, 1, 303-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020022
Pizzurro F, Recchi S, Nerone E, Salini R, Barile NB. Accumulation Evaluation of Potential Microplastic Particles in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Goro Sacca (Adriatic Sea, Italy). Microplastics. 2022; 1(2):303-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020022
Chicago/Turabian StylePizzurro, Federica, Sara Recchi, Eliana Nerone, Romolo Salini, and Nadia Beatrice Barile. 2022. "Accumulation Evaluation of Potential Microplastic Particles in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Goro Sacca (Adriatic Sea, Italy)" Microplastics 1, no. 2: 303-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020022
APA StylePizzurro, F., Recchi, S., Nerone, E., Salini, R., & Barile, N. B. (2022). Accumulation Evaluation of Potential Microplastic Particles in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Goro Sacca (Adriatic Sea, Italy). Microplastics, 1(2), 303-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1020022