Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the Detection of Marine Vertebrate Diversity in Maltese Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Møller, P.R.; Rasmussen, M.; Willerslev, E. Detection of a diverse marine fish fauna using environmental DNA from seawater samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jiao, L.; Ni, L.; Wang, M.; You, P. Bridging the gap: The integration of eDNA techniques and traditional sampling in fish diversity analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1289589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeglédi, I.; Sály, P.; Specziár, A.; Preiszner, B.; Szalóky, Z.; Maroda, Á.; Pont, D.; Meulenbroek, P.; Valentini, A.; Erős, T. Congruency between two traditional and eDNA-based sampling methods in characterising taxonomic and trait-based structure of fish communities and community-environment relationships in lentic environment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBattista, J.D.; Fowler, A.M.; Riley, I.J.; Reader, S.; Hay, A.; Parkinson, K.; Hobbs, J.P.A. The use of environmental DNA to monitor impacted coastal estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Jin, D.; Govindarajan, A.F. Applying environmental DNA approaches to inform marine biodiversity conservation: The case of the Ocean Twilight Zone. Mar. Policy 2024, 165, 106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresa, K.J.; Lodgea, D.M.; Andrésa, J. Environmental DNA reveals the genetic diversity and population structure of an invasive species in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2307345120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaither, M.R.; DiBattista, J.D.; Leray, M.; von der Heyden, S. Metabarcoding the marine environment: From single species to biogeographic patterns. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicala, D.; Maiello, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Garofalo, G.; Massi, D.; Sbrana, A.; Mariani, S.; D’Alessandro, S.; Stefani, M.; Perrodin, L.; et al. Spatial analysis of demersal food webs through integration of eDNA metabarcoding with fishing activities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1209093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.A.; Whitmore, L.; Mashkour, N.; Rollinson, D.R.; Rachel, R.; Catherine, S.T.; Burkhalter, B.; Yetsko, K.; Mott, C.; Wood, L.; et al. Detection and population genomics of sea turtle species via noninvasive environmental DNA analysis of nesting beach sand tracks and oceanic water. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2471–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Singh, M.; Amin, A.; Malik, M.M.; Qadri, S.N.; Abubakr, A.; Teja, S.S.; Dar, S.A.; Ahmad, I. A systematic review on environmental DNA (eDNA) science: An eco-friendly survey method for conservation and restoration of fragile ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 173, 113441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevellec, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Normandeau, E.; Bernatchez, L.; Howland, K.L. Effect of eDNA metabarcoding temporal sampling strategies on detection of coastal biodiversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1522677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Rivera, A.; Skern-Mauritzen, R.; Dahle, G.; Sundby, S.; Mozfar, B.; Thorsen, A.; Wehde, H.; Krafft, B.A. Comparison of visual and molecular taxonomic methods to identify ichthyoplankton in the North Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2020, 18, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyanandan, M.; Madhusoodhanan, R.; Al-Said, T.; Ahmed, A.; Al-Haddad, S.; Al-Zekri, W.; Al-Yamani, F. Molecular taxonomy of fish larvae in the Northwestern Arabian gulf: A baseline study from Kuwait’s first marine protected area. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, I.; Carvalho, G.R.; Walsh, K.; Seymour, M.; Hajibabaei, M.; Lallias, D.; Christmas, M.; Creer, S. Annual time-series analysis of aqueous eDNA reveals ecologically relevant dynamics of lake ecosystem biodiversity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirimin, L.; Desmet, S.; Romero, D.L.; Fernandez, S.F.; Miller, D.L.; Mynott, S.; Brincau, A.G.; Stefanni, S.; Berry, A.; Gaughan, P.; et al. Don’t catch me if you can—Using cabled observatories as multidisciplinary platforms for marine fish community monitoring: An in situ case study combining underwater video and environmental DNA data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Yao, M. Angling and trolling for eDNA: A novel and effective approach for passive eDNA capture in natural waters. Environ. Int. 2024, 194, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, A.; Reyna, P.B.; Giménez, D.R.; Tatián, M. Disembarking in port: Early detection of the ascidian Ascidiella scabra (Müller, 1776) in a SW Atlantic port and forecast of its worldwide environmental suitability. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 272, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Bylemans, J.; Goodman, S.J.; Lombardi, R.; Carr, I.; Castellano, L.; Galimberti, A.; Galli, P. Novel universal primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA surveys of marine mammals and other marine vertebrates. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Arcangeli, A.; Lombardi, R.; Boyse, E.; Carr, I.M.; Galli, P.; Goodman, S.J. Ferries and environmental DNA: Underway sampling from commercial vessels provides new opportunities for systematic genetic surveys of marine biodiversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 704786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Jensen, M.R.; Winkelmann, I.E.; Møller, P.R.; Hansen, M.M.; Thomsen, P.F. Population-level inferences from environmental DNA—Current status and future perspectives. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Côté, G.; Leclerc, V.; Bernatchez, L. Quantifying relative fish abundance with eDNA: A promising tool for fisheries management. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Kelly, R.P.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Park, L.; Schwenke, P.; Greene, C.; Henderson, R.A.; Beamer, E.M. Environmental DNA provides quantitative estimates of a threatened salmon species. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Koseff, J.R.; Fringer, O.B.; Ouellette, N.T.; Lowe, A.B.; Edwards, C.A.; Boehm, A.B. Modeling environmental DNA transport in the coastal ocean using Lagrangian particle tracking. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissinger, K.; Fernandes, C.; Formenti, G.; Bista, I.; Berg, P.R.; Bleidorn, C.; Bombarely, A.; Crottini, A.; Gallo, G.R.; Godoy, J.A.; et al. How genomics can help biodiversity conservation. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Vella, N.; Schembri, S. A molecular approach towards taxonomic identification of elasmobranch species from Maltese fisheries landings. Mar. Genom. 2017, 36, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantera, I.; Cilleros, K.; Valentini, A.; Cerdan, A.; Dejean, T.; Iribar, A.; Taberlet, P.; Vigouroux, R.; Brosse, S. Optimizing environmental DNA sampling effort for fish inventories in tropical streams and rivers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majaneva, M.; Diserud, O.H.; Eagle, S.H.C.; Boström, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ekrem, T. Environmental DNA filtration techniques affect recovered biodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Minamoto, T. Spatiotemporal changes in environmental DNA concentrations caused by fish spawning activity. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERA Natura 2000 Datasheets & Maps. Available online: https://era.org.mt/topic/natura-2000-datasheets-maps/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Ragkousis, M.; Zenetos, A.; Souissi, J.B.; Hoffman, R.; Ghanem, R.; Taşkın, E.; Muresan, M.; Karpova, E.; Slynko, E.; Dağlı, E.; et al. Unpublished Mediterranean and Black Sea records of marine alien, cryptogenic, and neonative species. BioInvasions Rec. 2023, 12, 339–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Scicluna, Y.; Mifsud, C.M.; Monaco, C.; Peri, I.; Tibullo, D.; Tiralongo, F.; Vella, N. The first record of the marbled spinefoot, Siganus rivulatus Forsskål & Niebuhr, 1775 and further records of the dusky spinefoot, Siganus luridus (Rüppell, 1829) from Malta. BioInvasions Rec. 2023, 12, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Giarrusso, E.; Monaco, C.; Mifsud, C.M.; Darmanin, S.A.; Raffa, A.; Tumino, C.; Peri, I.; Vella, N. New Records of Callinectes sapidus (Crustacea, Portunidae) from Malta and the San Leonardo River Estuary in Sicily (Central Mediterranean). Diversity 2023, 15, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikliras, A.C.; Antonopoulou, E.; Stergiou, K.I. Spawning period of Mediterranean marine fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2010, 20, 499–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Baillie, C.; Halliday, N.C.; Rainbird, S.; Sims, D.W.; Mariani, S.; Genner, M.J. Reproduction influences seasonal eDNA variation in a temperate marine fish community. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2022, 7, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA NATURA 2000 VIEWER. Available online: https://natura2000.eea.europa.eu/expertviewer/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Google Earth Maltese Islands and Surrounding Waters. Available online: https://earth.google.com/ (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Shokralla, S.; Gibson, J.F.; Nikbakht, H.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Hajibabaei, M. Next-generation DNA barcoding: Using next-generation sequencing to enhance and accelerate DNA barcode capture from single specimens. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, I.B.; Bohmann, K.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Tag jumps illuminated—Reducing sequence-to-sample misidentifications in metabarcoding studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.M.; Jusino, M.A.; Banik, M.T.; Lindner, D.L. Non-biological synthetic spike-in controls and the AMPtk software pipeline improve mycobiome data. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Flyvbjerg, H. Error filtering, pair assembly and error correction for next-generation sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgulis, A.; Coulouris, G.; Raytselis, Y.; Madden, T.L.; Agarwala, R.; Schäffer, A.A. Database indexing for production MegaBLAST searches. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WoRMS Editorial Board World Register of Marine Species. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Froese; Pauly, D. Fishbase. Available online: https://www.fishbase.se/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Golani, D.; Azzurro, E.; Dulčić, J.; Massuti, E.; Orsi-Relini, L. Atlas of Exotic Fishes in the Mediterranean Sea, 2nd ed.; CIESM PUBLISHERS/Paris: Monaco City, Monaco, 2021; ISBN 978-92-99003-5-9. [Google Scholar]
- Deidun, A.; Zava, B.; Marrone, A.; Galdies, J.; Sciberras, A.; Corsini-Foka, M. The confirmed occurrence of Schedophilus medusophagus (Cocco, 1839) and Petromyzon marinus Linnaeus, 1758 in Maltese waters, Central Mediterranean Sea. Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2023, 33, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Vella, N. Jellyfish blooming in Maltese waters and its socio-economic interactions. In Jellyfish: Ecology, Distribution Patterns and Human Interactions; Mariottini, G.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 163–188. ISBN 9781634856881. [Google Scholar]
- Vella, N.; Vella, A. Characterization of the complete mitogenome of Haifa grouper, Hyporthodus haifensis (Perciformes: Serranidae), and its phylogenetic position within Epinephelini. Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2021, 6, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Everts, T.; Van Driessche, C.; Neyrinck, S. Combining multiple markers significantly increases the sensitivity and precision of eDNA-based single-species analyses. Environ. DNA 2023, 5, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cananzi, G.; Tatini, I.; Li, T.; Montagna, M.; Serra, V.; Petroni, G. Active or passive? A multi-marker approach to compare active and passive eDNA sampling in riverine environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 974, 179247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Combining Multiple Markers in Environmental DNA Metabarcoding to Assess Deep-Sea Benthic Biodiversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 684955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Carroll, B.; Stewart, K.A. Transforming marine monitoring: Using eDNA metabarcoding to improve the monitoring of the Mediterranean Marine Protected Areas network. Mar. Policy 2023, 156, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglieri, G.; Quattrocchi, F.; Mariani, S.; Baillie, C.; Spatafora, D.; Di Franco, A.; Turco, G.; Tolone, M.; Di Gerlando, R.; Milazzo, M. Fish eDNA detections in ports mirror fishing fleet activities and highlight the spread of non-indigenous species in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulčić, J.; Golani, D. First record of Cyclopterus lumpus L., 1758 (Osteichthyes: Cyclopteridae) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Poursanidis, D.; Hoffman, R.; Rizgalla, J.; Rothman, S.B.S.; Levitt-Barmats, Y.; Hadjioannou, L.; Trkov, D.; Garmendia, J.M.; Rizzo, M.; et al. Unpublished mediterranean records of marine alien and cryptogenic species. BioInvasions Rec. 2020, 9, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Yildirim, D.; Ballesteros, E. Alien Marine Fishes Deplete Algal Biomass in the Eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.G.; Davison, P.I.; Creach, V.; Stone, D.; Bass, D.; Tidbury, H.J. The Application of eDNA for Monitoring Aquatic Non-Indigenous Species: Practical and Policy Considerations. Diversity 2023, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, S.W.; Hesselsøe, M.; Thaulow, J.; Agersnap, S.; Hansen, B.K.; Jacobsen, M.W.; Bekkevold, D.; Jensen, S.K.S.; Møller, P.R.; Andersen, J.H. Monitoring of environmental DNA from nonindigenous species of algae, dinoflagellates and animals in the North East Atlantic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Wangensteen, O.S.; O’Gorman, E.J.; Mariani, S.; Sims, D.W.; Genner, M.J. Persistence of environmental DNA in marine systems. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plön, S.; Andra, K.; Auditore, L.; Gegout, C.; Hale, P.J.; Hampe, O.; Ramilo-Henry, M.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Jaigirdar, A.M.; Klein, L.; et al. Marine mammals as indicators of Anthropocene Ocean Health. Npj Biodivers. 2024, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Tabor, G. Introduction: Marine vertebrates as sentinels of marine ecosystem health. Ecohealth 2004, 1, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukan, N.; Cornelis, I.; Maes, S.; Hostens, K.; De Backer, A.; Derycke, S. Vertical and horizontal environmental DNA (eDNA) patterns of fish in a shallow and well-mixed North Sea area. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westgaard, J.I.; Præbel, K.; Arneberg, P.; Ulaski, B.P.; Ingvaldsen, R.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Johansen, T. Towards eDNA informed biodiversity studies—Comparing water derived molecular taxa with traditional survey methods. Prog. Oceanogr. 2024, 222, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Knudsen, S.W.; Jørgensen, O.A.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA from seawater samples correlate with trawl catches of subarctic, deepwater fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Murakami, H.; Masuda, R.; Sakata, M.K.; Yamamoto, S.; Minamoto, T. Rapid degradation of longer DNA fragments enables the improved estimation of distribution and biomass using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, e25–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.V.; Vollmers, C.; Newsom, L.A.; Wang, Y.; Heintzman, P.D.; Leighton, M.; Green, R.E.; Shapiro, B. Minimizing polymerase biases in metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daban, I.B.; Ismen, A.; Ihsanoglu, M.A.; Cabbar, K. Age, growth and reproductive biology of the saddled seabream (Oblada melanura) in the North Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2020, 49, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafalah, F. Some Aspects of the Reproductive Biology of the Saddled Sea Bream Oblada Melanura (Linnaeus, 1758) in Benghazi Coast –Eastern Libya. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2018, 29, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Iijima, T.; Kakuzen, W.; Watanabe, S.; Yamada, Y.; Okamura, A.; Horie, N.; Mikawa, N.; Miller, M.J.; Kojima, T.; et al. Release of eDNA by different life history stages and during spawning activities of laboratory-reared Japanese eels for interpretation of oceanic survey data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Statistics Office. Malta News Release 207/2022. 16 Novemb. 2022; Malta National Statistics Office: Valletta, Malta, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, A. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in water biology and security. Water Biol. Secur. 2025, 12, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Sha, N.; Wang, J.; Qiu, G.; Chang, M. Application of eDNA Metabarcoding Technology to Monitor the Health of Aquatic Ecosystems. Water 2025, 17, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, O.; Mendibil, I.; Santos, M.; Irigoien, X.; Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N. Vertical stratification of environmental DNA in the open ocean captures ecological patterns and behavior of deep-sea fishes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2021, 6, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
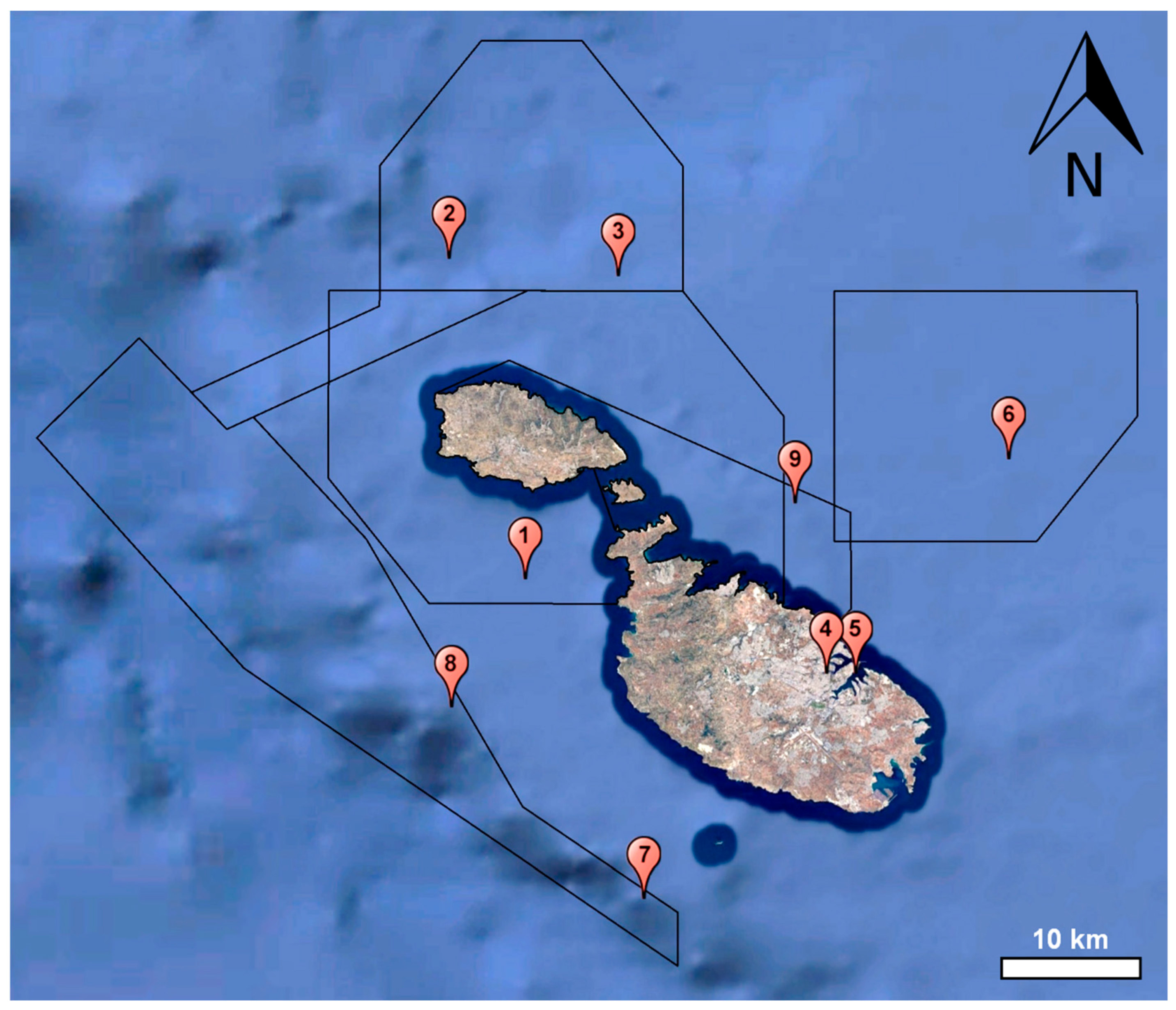
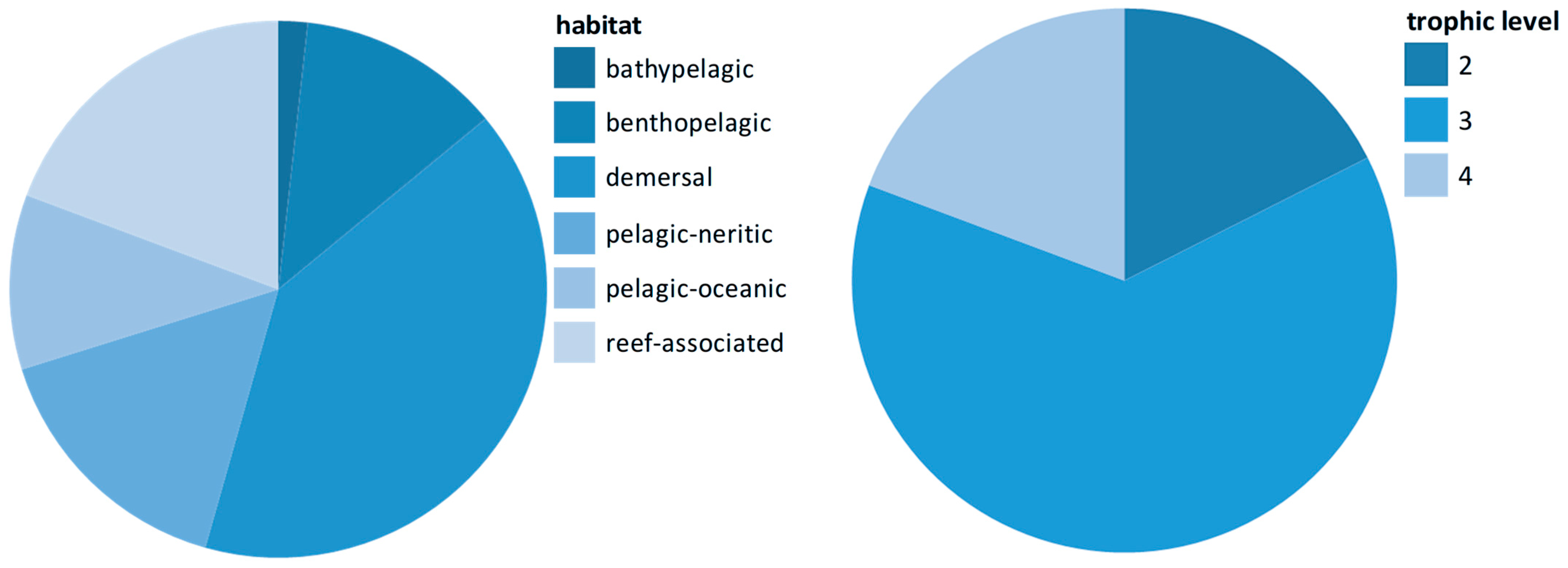
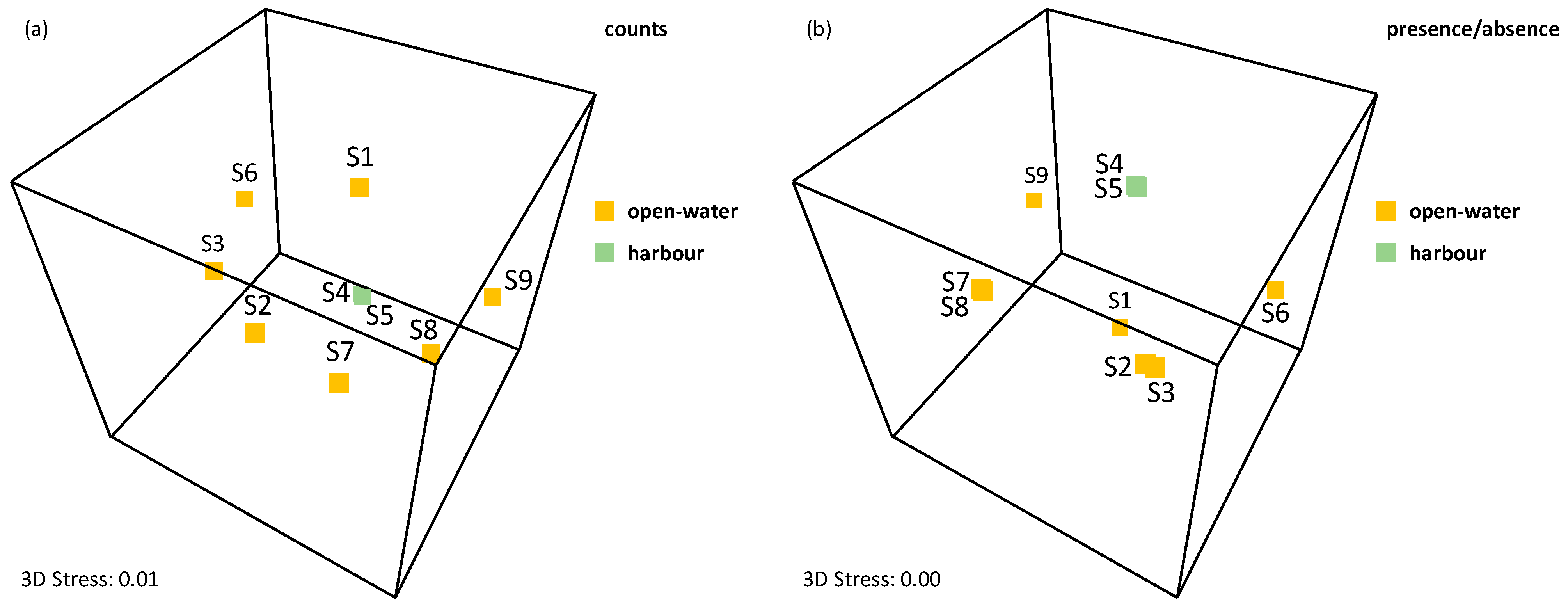
| Sample | Sampling Month | GPS | Description | Natura 2000 Site Code [37] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | May 2021 | 35.956; 14.256 | 6 km off-shore | MT0000112 |
| S2 | May 2021 | 36.161; 14.195 | 9 km off-shore | MT0000115 |
| S3 | June 2021 | 36.150; 14.329 | 10 km off-shore | MT0000115 |
| S4 | June 2021 | 35.896; 14.494 | Marsamxett Harbour | – |
| S5 | June 2021 | 35.896; 14.517 | Grand Harbour | – |
| S6 | June 2021 | 36.033; 14.638 | 18 km off-shore | MT0000107 |
| S7 | July 2021 | 35.752; 14.350 | 10 km off-shore | MT0000113 |
| S8 | July 2021 | 35.874; 14.198 | 12 km off-shore | MT0000113 |
| S9 | August 2021 | 36.005; 14.469 | 6 km off-shore | MT0000105 |
| Family | 12S | 16S | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species (Trophic Level) | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 |
| Delphinidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stenella coeruleoalba | 835 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tursiops truncatus | 32 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cheloniidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Caretta caretta | 853 | 189 | ||||||||||||||||
| Rajidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Raja clavata (3.8) | 620 | 2067 | ||||||||||||||||
| Torpedinidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Torpedo marmorata (4.5) | 985 | |||||||||||||||||
| Alosidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sardina pilchardus (3.1) | 433 | 1370 | ||||||||||||||||
| Atherinidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Atherina boyeri (3.2) | 6146 | 2838 | 408 | 944 | ||||||||||||||
| Atherina sp.1 | 36 | |||||||||||||||||
| Atherina sp.2 | 2666 | 2123 | ||||||||||||||||
| Atherina hepsetus (3.2) | 1664 | 1165 | 492 | |||||||||||||||
| Blenniidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Blennidae sp.1 | 5062 | |||||||||||||||||
| Blennidae sp.2 | 2595 | |||||||||||||||||
| Parablennius gattorugine (3.6) | 4038 | |||||||||||||||||
| Parablennius incognitus (2.7) | 6709 | 13,819 | ||||||||||||||||
| Parablennius sanguinolentus (2.1) | 855 | |||||||||||||||||
| Salaria pavo (3.6) | 12,060 | 2486 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scartella cristata (2.5) | 2205 | 2489 | ||||||||||||||||
| Carangidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Caranx crysos (4.1) | 4297 | 2745 | 837 | 6213 | 69 | 1234 | ||||||||||||
| Trachinotus ovatus (4.2) | 347 | |||||||||||||||||
| Trachurus mediterraneus (3.8) | 434 | 113 | ||||||||||||||||
| Centrolophidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schedophilus medusophagus (4.0) | 782 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cyclopteridae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cyclopterus lumpus (3.9) | 1088 | |||||||||||||||||
| Dorosomatidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sardinella aurita (3.4) | 219 | 25 | 525 | 663 | ||||||||||||||
| Engraulidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Engraulis encrasicolus (3.1) | 197 | 968 | 824 | 345 | 508 | 937 | ||||||||||||
| Epinephelinae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hyporthodus haifensis (4.0) | 614 | 53 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gobiesocidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lepadogaster candolli (2.8) | 1025 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobiidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aphia minuta (3.2) | 222 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobiidae sp.1 | 165 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius bucchichi (3.1) | 1223 | 1355 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gobius couchi (2.9) | 430 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius niger (3.3) | 840 | 578 | 1262 | |||||||||||||||
| Gobius sp.1 | 849 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius sp.2 | 650 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius sp.3 | 301 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius sp.4 | 156 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gobius paganellus (3.3) | 2311 | 332 | ||||||||||||||||
| Millerigobius macrocephalus (3.2) | 445 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||
| Zebrus zebrus (3.2) | 107 | 291 | ||||||||||||||||
| Labridae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coris julis (3.4) | 1245 | |||||||||||||||||
| Symphodus roissali (3.5) | 301 | 158 | ||||||||||||||||
| Symphodus tinca (3.3) | 1476 | 2216 | 1870 | 325 | ||||||||||||||
| Xyrichtys novacula (3.5) | 368 | |||||||||||||||||
| Molidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mola mola (3.1) | 454 | |||||||||||||||||
| Moronidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dicentrarchus labrax (3.5) | 7411 | 11,776 | 377 | 266 | 855 | |||||||||||||
| Mugilidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chelon auratus (2.8) | 2515 | 1523 | 319 | 2760 | 198 | 467 | ||||||||||||
| Mullidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mullus barbatus (3.1) | 2375 | 1449 | 33 | 1431 | ||||||||||||||
| Mullus surmuletus (3.5) | 436 | 21 | 1161 | |||||||||||||||
| Muraenidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Muraena helena (4.2) | 1270 | 251 | ||||||||||||||||
| Myctophidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ceratoscopelus maderensis (3.3) | 219 | |||||||||||||||||
| Pomacentridae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chromis chromis (3.8) | 26 | 79 | 2218 | 16,381 | 17,119 | |||||||||||||
| Scaridae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sparisoma cretense (2.9) | 75 | |||||||||||||||||
| Scombridae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Auxis rochei (4.4) | 699 | 2621 | 229 | |||||||||||||||
| Euthynnus alletteratus (4.5) | 574 | |||||||||||||||||
| Thunnus thynnus (4.5) | 831 | 866 | 1241 | |||||||||||||||
| Thunnus sp. | 39 | 200 | ||||||||||||||||
| Scorpaenidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scorpaena notata (3.7) | 365 | 282 | ||||||||||||||||
| Serranidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serranus scriba (3.8) | 2535 | 1273 | 641 | 315 | 29 | |||||||||||||
| Siganidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Siganus luridus (2.0) | 36 | 698 | ||||||||||||||||
| Sparidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Boops boops (2.8) | 493 | 2784 | 931 | 1551 | 262 | 1001 | ||||||||||||
| Diplodus annularis (3.6) | 2180 | 521 | 47 | |||||||||||||||
| Diplodus puntazzo (3.2) | 66 | |||||||||||||||||
| Diplodus vulgaris (3.5) | 1378 | 1421 | 2705 | 998 | ||||||||||||||
| Lithognathus mormyrus (3.5) | 110 | |||||||||||||||||
| Oblada melanura (3.4) | 29 | 560 | 1087 | 16,672 | 3339 | 822 | 228 | 5825 | 42 | 1278 | ||||||||
| Pagellus bogaraveo (4.2) | 56 | 48 | 841 | 268 | ||||||||||||||
| Sarpa salpa (2.0) | 70 | 5681 | 261 | 52 | 2415 | 20 | ||||||||||||
| Sparus aurata (3.7) | 52 | 13,744 | 2343 | 895 | 117 | 31,657 | 761 | |||||||||||
| Spicara smaris (3.0) | 316 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tripterygiidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tripterygion tripteronotum (3.4) | 1033 | 1181 | ||||||||||||||||
| Xiphiidae | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xiphias gladius (4.5) | 197 | 230 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total reads | 4569 | 757 | 2321 | 65,278 | 45,806 | 4307 | 1132 | 5399 | 3367 | 14,623 | 508 | 2348 | 103,552 | 55,660 | 4403 | 479 | 2185 | 695 |
| MOTUs | 8 | 2 | 3 | 18 | 23 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 35 | 38 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vella, A.; Mifsud, C.M.; Vella, N. Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the Detection of Marine Vertebrate Diversity in Maltese Waters. DNA 2025, 5, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040050
Vella A, Mifsud CM, Vella N. Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the Detection of Marine Vertebrate Diversity in Maltese Waters. DNA. 2025; 5(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleVella, Adriana, Clare Marie Mifsud, and Noel Vella. 2025. "Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the Detection of Marine Vertebrate Diversity in Maltese Waters" DNA 5, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040050
APA StyleVella, A., Mifsud, C. M., & Vella, N. (2025). Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the Detection of Marine Vertebrate Diversity in Maltese Waters. DNA, 5(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040050







