Genomic, Epigenomic, and Immuno-Genomic Regulations of Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Literature Review and In Silico Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
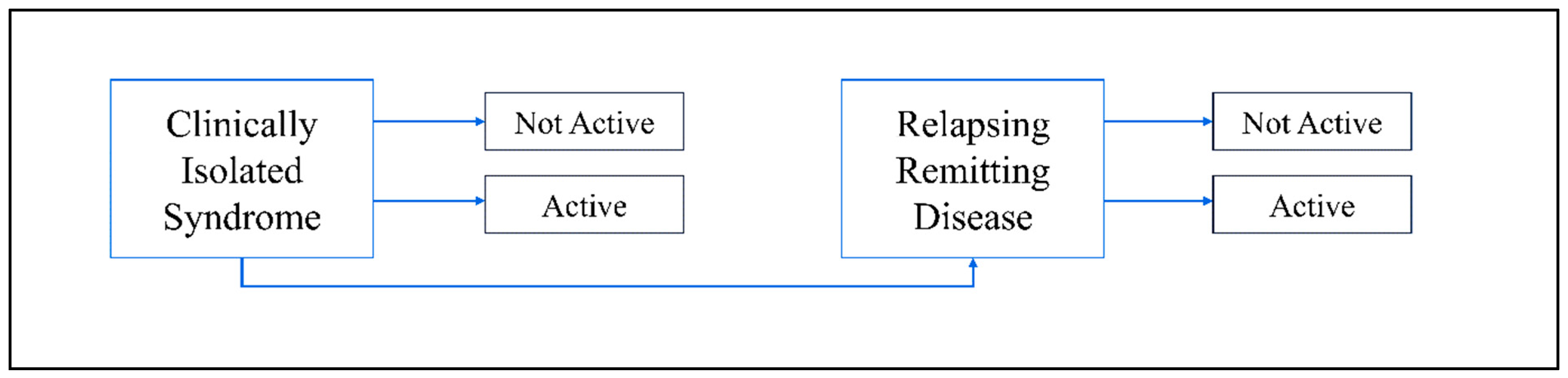
2. Epidemiology
3. Factors Leading to Multiple Sclerosis
3.1. Epigenetic Factors
3.2. Genetic Factors
3.3. Immunological Factors
3.4. Substantial Nigra in MS
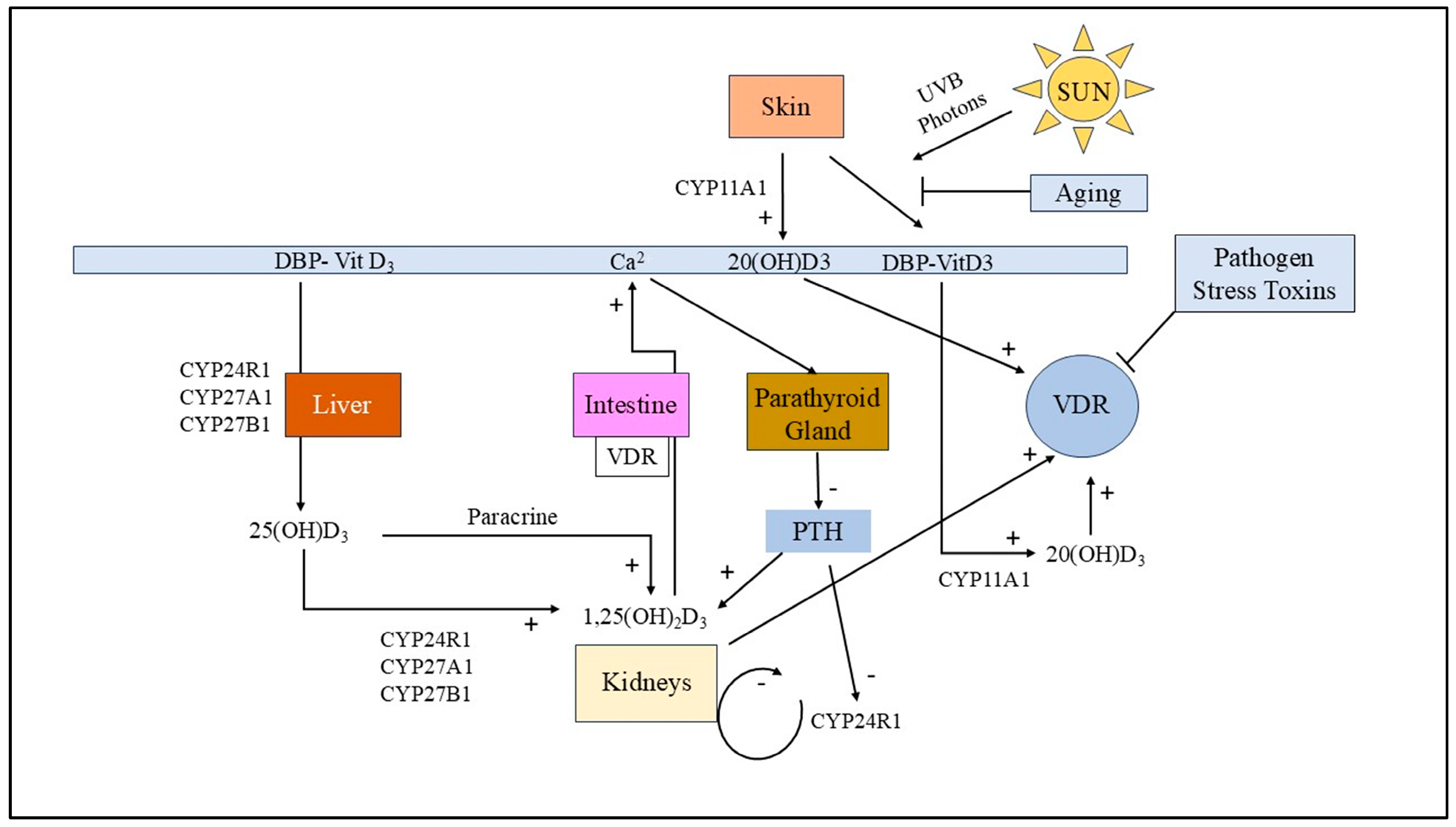
3.5. Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Dysfunction in MS
4. Bioinformatics-Based Meta-Analysis of Molecular Dysregulation in Multiple Sclerosis
4.1. Protein–Protein Interactions in MS
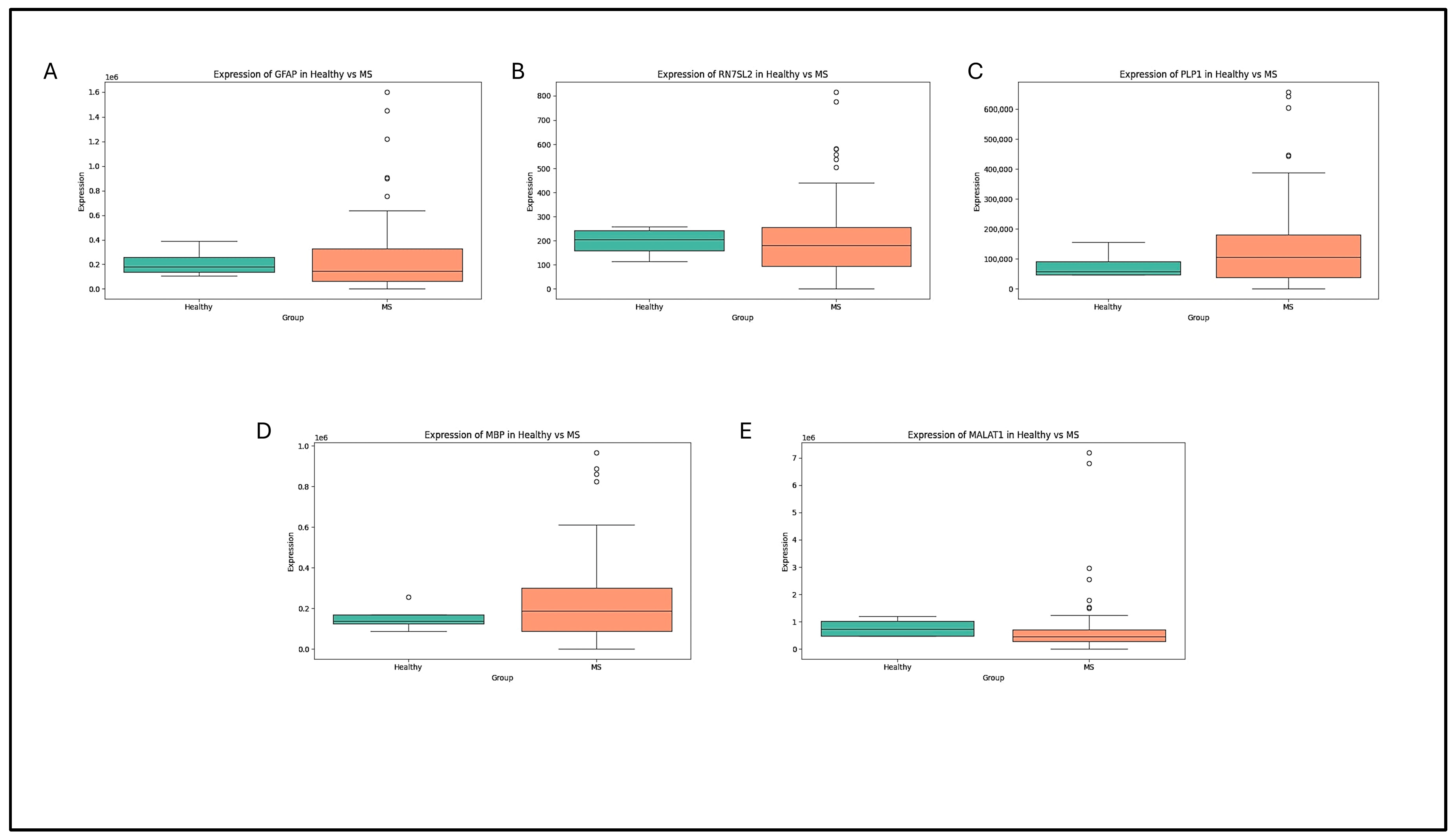
4.2. Box-Plot Analysis of the Retrieved Data in MS
4.3. Volcano-Plot Analysis of the Retrieved Data in MS
5. Effect of Vitamin D in Multiple Sclerosis
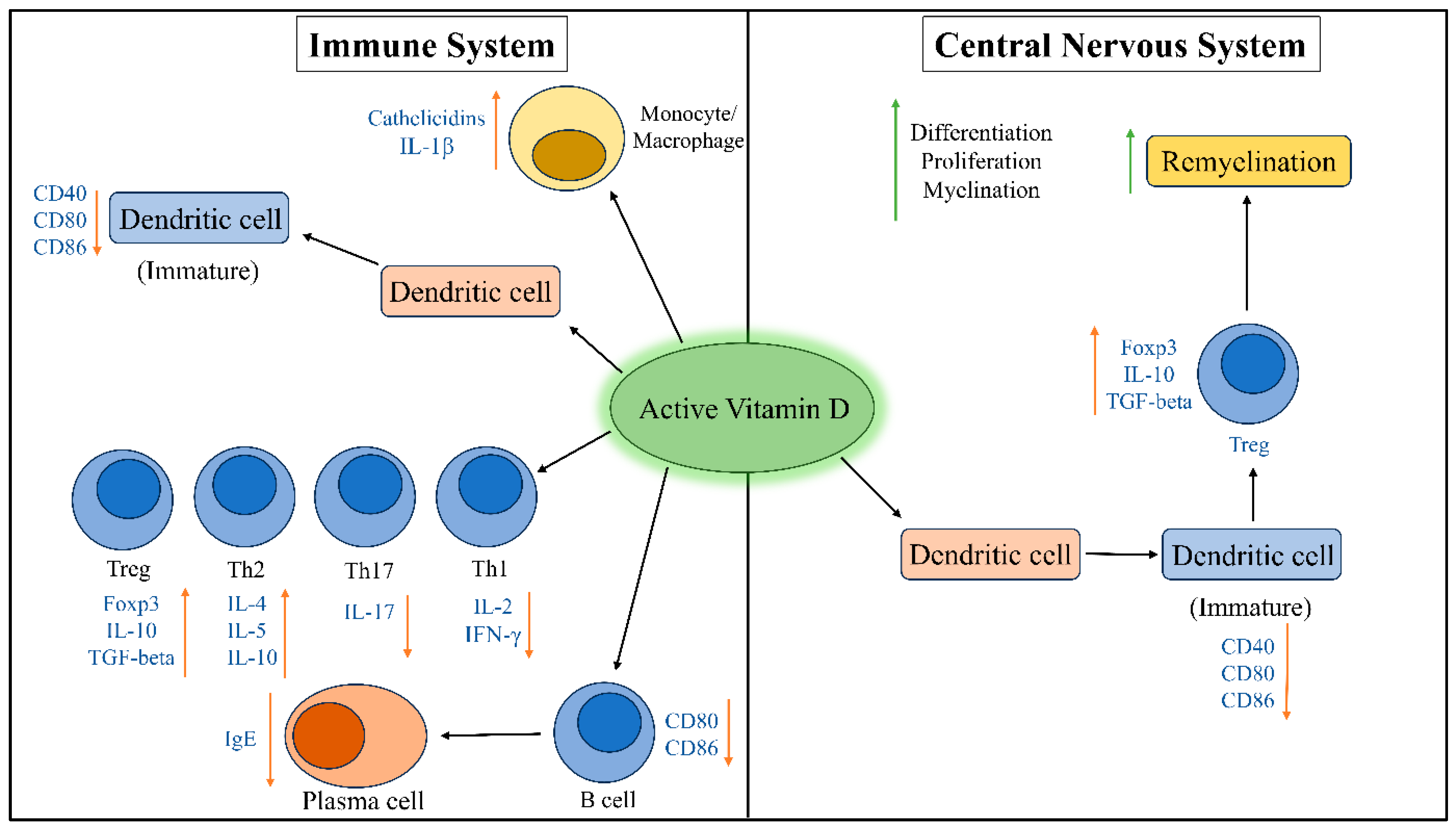
5.1. Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System
5.2. Effects of Vitamin D on Substantial Nigra
5.3. Effects of Vitamin D in Epigenetic Regulation of MS
5.4. Effects of Vitamin D on Oxidative Stress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doshi, A.; Chataway, J. Multiple Sclerosis, a Treatable Disease. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klineova, S.; Lublin, F.D. Clinical Course of Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekerle, H.; Lassmann, H. The Immunology of Inflammatory Demyelinating Disease. In McAlpine’s Multiple Sclerosis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 491–555. ISBN 9780443072710. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, B.F.G.; Pirko, I.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis: Where Do We Stand? Continuum 2013, 19, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Di Dario, M.; Russo, A.; Menon, R.; Brini, E.; Romeo, M.; Sangalli, F.; Costa, G.D.; Rodegher, M.; Radaelli, M.; et al. Dysregulation of MS Risk Genes and Pathways at Distinct Stages of Disease. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Ma, Y.; Qin, F.; Han, F.; Zhang, C. Brain Proteome-wide Association Study Linking-genes in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Xu, X. Multiple Sclerosis: An Overview of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Serological Biomarkers. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2024, 2024, 7372789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Bali, P.; Chowdhary, R. Epidemiology and Genetic Aspects of Multiple Sclerosis in India. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2015, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Casaccia, P. Epigenetic Modifications in Brain and Immune Cells of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Mult. Scler. 2018, 24, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscarello, M.A.; Mastronardi, F.G.; Wood, D.D. The Role of Citrullinated Proteins Suggests a Novel Mechanism in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mu, P.; Li, Y.; Singh, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. Expression, Regulation and Function of MicroRNAs in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Takahashi, T.; Golstein, P.; Nagata, S. Molecular Cloning and Expression of the Fas Ligand, a Novel Member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Family. Cell 1993, 75, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, M.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Degn, M. B Cell Follicle-like Structures in Multiple Sclerosis—With Focus on the Role of B Cell Activating Factor. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Touil, H.; Pikor, N.B.; Gommerman, J.L.; Prat, A.; Bar-Or, A. B Cells in the Multiple Sclerosis Central Nervous System: Trafficking and Contribution to CNS-Compartmentalized Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Weng, T.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Xiong, H.; Huang, B.; Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Fu, X. IFN-γ-Induced ER Stress Impairs Autophagy and Triggers Apoptosis in Lung Cancer Cells. OncoImmunology 2021, 10, 1962591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimova, T.; Beier, U.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hancock, W.W. Histone/Protein Deacetylases and T-Cell Immune Responses. Blood 2012, 119, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, F.; Yang, B. The Tale of Histone Modifications and Its Role in Multiple Sclerosis. Hum. Genom. 2018, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Hernandez, A.; Perez-Guerrero, E.E.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; Nava-Valdivia, C.A.; Villagomez-Vega, A.; Contreras-Haro, B.; Garcia-Ortega, Y.E.; Esparza-Guerrero, Y.; Gallardo-Moya, S.G.; Gamez-Nava, J.I.; et al. Polymorphisms CYP2R1 Rs10766197 and CYP27B1 Rs10877012 in Multiple Sclerosis: A Case-Control Study. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, J.C.; Perez, T.H.; Albert, P.J. Reversing Bacteria-induced Vitamin D Receptor Dysfunction Is Key to Autoimmune Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakos, S.; Dhawan, P.; Verstuyf, A.; Verlinden, L.; Carmeliet, G. Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, G.N.; Cavagnola, R.; Sacco, D.; Costantino, L.; Bernardinelli, L.; Gentilini, D. Exploring the Complexities of Epigenetics in Multiple Sclerosis: A Study Involving Meta-Analysis of DNA Methylation Profiles, Epigenetic Drift, and Rare Epivariations. Multiple Sclerosis. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2024, 10, 20552173241296726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribbin, J.; Wolujewicz, P.; Soda, K.J. X Chromosome Analysis in Multiple Sclerosis for Identification of Genes Implicated in Female-Biased Disease Presentation (S42.007). Neurology 2024, 102, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandler, J.M.; Härtl, J.; Cordts, I.; Sturm, M.; Hedderich, D.M.; Bafligil, C.; Baki, E.; Becker, B.; Machetanz, G.; Haack, T.B.; et al. Uncovering Genetic Mimics in Multiple Sclerosis: A Single-Center Clinical Exome Sequencing Study. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2024, 10, 20552173241263491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Mendell, J.T. MicroRNAs in Cell Proliferation, Cell Death, and Tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, A.; Pender, M.P.; Khanna, R.; Steinman, L.; Hartung, H.-P.; Maniar, T.; Croze, E.; Aftab, B.T.; Giovannoni, G.; Joshi, M.A. Epstein–Barr Virus in Multiple Sclerosis: Theory and Emerging Immunotherapies. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.R. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation and Therapeutic Inhibitors. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskov, H.; Orhan, A.; Christensen, J.P.; Gögenur, I. Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells in Cancer and Cancer Immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahad, D.H.; Trapp, B.D.; Lassmann, H. Pathological Mechanisms in Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, L.; Trauger, S.A.; Blain, M.; Nadeau, M.; Patel, B.; Alvarez, J.I.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Yeste, A.; Kivisäkk, P.; Kallas, K.; et al. Regulation of Astrocyte Activation by Glycolipids Drives Chronic CNS Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Pelekanos, M.; Liu, P.-Y.; Burne, T.H.J.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D.W. The vitamin D receptor in dopamine neurons; its presence in human substantia nigra and its ontogenesis in rat midbrain. Neuroscience 2013, 236, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogias, C.; Gold, R.; Chan, A.; Triantafyllou, N.; Voumvourakis, K.; Tsivgoulis, G. Brain Hyperechogenicities Are Not Associated with Venous Insufficiency in Multiple Sclerosis: A Pilot Neurosonology Study. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.; Vernooij, M.W.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; Larsson, E.-M.; Jäger, H.R.; Barkhof, F. Cerebral Microbleeds: Imaging and Clinical Significance. Radiology 2018, 287, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, D.; Razi, B.; Motallebnezhad, M.; Rezaei, R. Association between Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Polymorphisms and the Risk of Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An Updated Meta-Analysis. BMC Neurol 2019, 19, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonne, J.; Reddy, V.; Beato, M.R. Neuroanatomy, Substantia Nigra. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, A.; Carboni, E.; Gomes, L.C.; Roudeau, S.; Maass, F.; Lenz, C.; Ortega, R.; Lingor, P. Metal Dyshomeostasis in the Substantia Nigra of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease or Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 2024, 168, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellino, M.; Masera, S.; Lorenzatti, M.; Condello, C.; Merola, A.; Mattioda, A.; Tribolo, A.; Capello, E.; Mancardi, G.L.; Mutani, R.; et al. Demyelination, Inflammation, and Neurodegeneration in Multiple Sclerosis Deep Gray Matter. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Roy, D.; Dubey, S.; Das, S.; Benito-León, J. Movement Disorders in Multiple Sclerosis: An Update. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczyk, A.; Stolarz-Skrzypek, K.; Wesołowska, A.; Czarnecka, D. Vitamin D and vitamin D receptor activators in treatment of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2014, 14, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Meng, X. Vitamin D and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosni, H.A.; Fouad, A.M.; Ibrahim, N.W.; Sharaf, S.A.E.-A. Investigating the Role of VDR Gene Variants in Multiple Sclerosis Susceptibility: A Case–Control Study in Egypt. Egypt J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2024, 60, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioka, C.; Papakonstantinou, S.; Markoula, S.; Gkartziou, F.; Georgiou, A.; Georgiou, I.; Pelidou, S.-H.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Fotopoulos, A. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms in Multiple Sclerosis Patients in Northwest Greece. J Negat Results BioMed 2011, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.G.; Ochalek, J.T.; Kaufmann, M.; Jones, G.; DeLuca, H.F. CYP2R1 Is a Major, but Not Exclusive, Contributor to 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Production in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15650–15655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluca, H.F. Recent Advances in Our Understanding of the Vitamin D Endocrine System. J. Steroid Biochem. 1979, 11, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Sharma, A. Challenges in the diagnosis & treatment of miliary tuberculosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 703–730. [Google Scholar]
- Śliwka, P.; Ochocka, M.; Skaradzińska, A. Applications of Bacteriophages against Intracellular Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Teh, T.M.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ang, E.L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Identification and Characterization of the Biosynthetic Pathway of the Sulfonolipid Capnine. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbanat, D.R.; Leadbetter, E.R.; Godchaux, W.; Escher, A. Sulphonolipids Are Molecular Determinants of Gliding Motility. Nature 1986, 324, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryabor, G.; Gholijani, N.; Kahmini, F.R. A Review of the Critical Role of Vitamin D Axis on the Immune System. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 132–133, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, T.; Kikuta, J.; Ishii, M. The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.; Lahore, H.; McDonnell, S.; Baggerly, C.; French, C.; Aliano, J.; Bhattoa, H. Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths. Nutrients 2020, 12, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpe, K.O. Olmesartan Compared with Other Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists: Head-to-Head Trials. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, A33–A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sag, D.; Ayyildiz, Z.O.; Gunalp, S.; Wingender, G. The Role of TRAIL/DRs in the Modulation of Immune Cells and Responses. Cancers 2019, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falschlehner, C.; Schaefer, U.; Walczak, H. Following TRAIL’s path in the immune system. Immunology 2009, 127, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossin, A.; Miloro, G.; Hueber, A.O. TRAIL and FasL Functions in Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases: Towards an Increasing Complexity. Cancers 2019, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisato, V.; Gonelli, A.; Voltan, R.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G. Clinical Perspectives of TRAIL: Insights into Central Nervous System Disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyuan, I.-T.; Tsai, H.-F.; Wu, C.-S.; Sung, C.-C.; Hsu, P.-N. TRAIL-Mediated Suppression of T Cell Receptor Signaling Inhibits T Cell Activation and Inflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Miyagishi, R.; Fukazawa, T.; Yabe, I.; Miyazaki, Y.; Sasaki, H. TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Gene Polymorphism in Japanese Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 167, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gómez, C.; Fernández, Ó.; García-León, J.A.; Pinto-Medel, M.J.; Oliver-Martos, B.; Ortega-Pinazo, J.; Suardíaz, M.; García-Trujillo, L.; Guijarro-Castro, C.; Benito-León, J.; et al. TRAIL/TRAIL Receptor System and Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandinger, K.-P.; Lünemann, J.D.; Wengert, O.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; Aktas, O.; Weber, A.; Grundström, E.; Ehrlich, S.; Wernecke, K.-D.; Volk, H.-D.; et al. TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) as a Potential Response Marker for Interferon-Beta Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis. Lancet 2003, 361, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y. Expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in serum of patients with periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with these diseases. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 57, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaei, S.; Sahraian, M.; Mohammadifar, M.; Ramagopalan, S.; Ghajarzadeh, M. Effect of Vitamin D Supplements on Relapse Rate and Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) in Multiple Sclerosis (MS): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, S., Jr.; Der Mei, I.V.; Taylor, B. The Role of Vitamin D in Multiple Sclerosis: Biology and Biochemistry, Epidemiology and Potential Roles in Treatment. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.; Moser, T.; Bieler, L.; Schwenker, K.; Hauer, L.; Sellner, J. Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Critical Analysis of Potentials and Threats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.S.; Mesler, D.E.; Snipes, R.G.; Gray, T.K. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 activates secretion of hydrogen peroxide by human monocytes. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.N.; Wong, M.T.; Zhang, A.L.; Winer, D.; Suhoski, M.M.; Tolentino, L.L.; Gaitan, J.; Davidson, M.G.; Kung, T.H.; Galel, D.M.; et al. TH1, TH2, and TH17 Cells Instruct Monocytes to Differentiate into Specialized Dendritic Cell Subsets. Blood 2011, 118, 3311–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sims, G.P.; Chen, X.X.; Gu, Y.Y.; Chen, S.; Lipsky, P.E. Modulatory Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Human B Cell Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csuka, D.; Simon, D.; Hóbor, R.; Uray, K.; Prohászka, Z.; Bánlaki, Z.; Jani, P.K.; Szilágyi, Á.; Hudecz, F.; Rajczy, K.; et al. Serum Concentration of Immunoglobulin G-Type Antibodies against the Whole Epstein–Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 and Its Aa35–58 or Aa398–404 Fragments in the Sera of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 171, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pludowski, P.; Holick, M.F.; Grant, W.B.; Konstantynowicz, J.; Mascarenhas, M.R.; Haq, A.; Povoroznyuk, V.; Balatska, N.; Barbosa, A.P.; Karonova, T.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation Guidelines. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, T.; Cicero, S.; Pan, H.; Carter, K.; Dubey, S.; Chu, R.; Glanz, B.; Hurwitz, S.; Tauhid, S.; Park, M.-A.; et al. Regional Microglial Activation in the Substantia Nigra Is Linked with Fatigue in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W.; Smith, S.; Kinobe, R.; Hewison, M.; McGrath, J.J. Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2005, 29, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, E.; Galeel, A.A.; Ramadan, I.; Gaber, D.; Mustafa, H.; Mekky, J. Iron Deposition in Multiple Sclerosis: Overall Load or Distribution Alteration? Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zughaier, S.M.; Alvarez, J.A.; Sloan, J.H.; Konrad, R.J.; Tangpricha, V. The Role of Vitamin D in Regulating the Iron-Hepcidin-Ferroportin Axis in Monocytes. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2014, 1, e19–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Benzi, A.; Sturla, L.; Marubbi, D.; Frumento, D.; Spinelli, S.; Abbotto, E.; Ivaldi, F.; Von Holtey, M.; Murone, M.; et al. Sirt6 Inhibition Delays the Onset of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Reducing Dendritic Cell Migration. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangha, A.; Quon, M.; Pfeffer, G.; Orton, S.-M. The Role of Vitamin D in Neuroprotection in Multiple Sclerosis: An Update. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltjes, R.; Knippenberg, S.; Gerlach, O.; Hupperts, R.; Damoiseaux, J. Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: An Expert Opinion Based on the Review of Current Evidence. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuso, T.; Aznar, P.; Soriano, L.; Olaskoaga, A.; Roldán, M.; Otano, M.; Ajuria, I.; Soriano, G.; Lacruz, F.; Mendioroz, M. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Is Epigenetically Altered and Transcriptionally Up-Regulated in Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetahu, I.S.; Habaus, J.; Kállay, E. Vitamin D and the Epigenome. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-J.; Li, L.-J.; Yang, X.-K.; Yu, T.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Altered microRNAs Expression in T Cells of Patients with SLE Involved in the Lack of Vitamin D. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62099–62110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huynh, J.L.; Casaccia, P. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Multiple Sclerosis: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Olsen, N.; Zheng, S.G. Vitamin D and Chronic Diseases. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, M.; Niedziela, N.; Adamczyk-Zostawa, J.; Zalejska-Fiolka, J.; Szczygieł, J.; Sowa, A.; Świętek, A.; Adamczyk-Sowa, M. Comparative Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Oxidative Stress in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 14119–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.R.C.; Mimura, L.A.N.; Fraga-Silva, T.F.D.C.; Ishikawa, L.L.W.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Zorzella-Pezavento, S.F.G.; Sartori, A. Calcitriol Prevents Neuroinflammation and Reduces Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Local Macrophage/Microglia Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Steele, S.; Cassard, S.; Waubant, E.; Calabresi, P.; Mowry, E. Vitamin D Supplementation Reduces Markers of Oxidative Stress Measured by Untargeted Metabolomics in Healthy Controls but Not in Multiple Sclerosis Patients (P3.006). Neurology 2016, 86, P3.006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Salgado-Cámara, P.; García-Martín, E.; Agúndez, J.A.G. Oxidative Stress Markers in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñar-Morales, R.; Durán, R.; Bautista-García, A.; García-Mansilla, M.J.; Aliaga-Gaspar, P.; Vives-Montero, F.; Barrero-Hernández, F.J. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Symptoms Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene/miRNA | Expression in MS | Function/Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PADI2 | Upregulated (hypomethylation) | Citrullinates MBP → demyelination | [10] |
| MBP | Downregulated | Major myelin protein; degraded during demyelination | [10] |
| FOXP3 | Downregulated (hypermethylation) | Treg suppression → immune imbalance | [9] |
| miR-155 | Upregulated | Pro-inflammatory; TRAIL-regulated | [11] |
| miR-326 | Upregulated | Promotes Th17 cell development | [11] |
| miR-146a | Upregulated | Regulates innate immune responses | [11] |
| miR-142-3p | Upregulated | Immune regulation | [11] |
| miR-18b/599 | Upregulated | Relapse markers | [11] |
| miR-96 | Downregulated | Remission marker | [11] |
| FAS/FASL | Upregulated | Fas–FasL mediated apoptosis in oligodendrocytes | [12] |
| CXCL13 | Upregulated | B-cell recruitment into CNS | [13] |
| IL-6 | Upregulated | Pro-inflammatory cytokine | [14] |
| IL-10/IL-35 | Downregulated | Anti-inflammatory cytokines | [14] |
| IFNG (IFN-γ) | Upregulated | Enhances glutamate toxicity in neurons | [15] |
| HDAC1/2 | Upregulated | Histone deacetylation → transcriptional repression | [16] |
| DNMT1/3A | Dysregulated | DNA methylation; gene silencing or activation | [9] |
| KAT2A/B, CREBBP, EP300 | Upregulated | Histone acetyltransferases → promote gene expression | [17] |
| TET enzymes | Dysregulated | DNA demethylation; affects T-cell lineage commitment | [9] |
| CYP27B1 | Downregulated | Vitamin D activation enzyme | [18] |
| VDR | Dysfunctional | Vitamin D receptor; immune modulation | [19] |
| NFE2L2 (Nrf2) | Downregulated | Redox master regulator | [20] |
| SHMT1/FAM120B | Upregulated | Folate metabolism, lipid metabolism | [6] |
| ICA1L/TRIM47 | Downregulated | Vascular remodelling, protein degradation | [6] |
| NAV2/KCNQ4/KAZN/CADM1 | Hypermethylated | Neurodevelopment, cell adhesion regulation | [21] |
| METTL21C | Hypomethylated | Protein methylation | [21] |
| JDP2/MAF/MAPK3/RGS1/BACH2/IKZF3/FOXP1/ZNF438/IL7R | Up/Down regulated | Stage-specific MS gene expression | [22] |
| TLR7/TLR8 | Female-specific upregulation | Innate immune response (X chromosome) | [22] |
| NOTCH3 | Mutated (monogenic mimic) | CADASIL—MS-like clinical presentation | [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modak, P.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Ghosh, K. Genomic, Epigenomic, and Immuno-Genomic Regulations of Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Literature Review and In Silico Meta-Analysis. DNA 2025, 5, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040048
Modak P, Bhattacharjee P, Ghosh K. Genomic, Epigenomic, and Immuno-Genomic Regulations of Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Literature Review and In Silico Meta-Analysis. DNA. 2025; 5(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleModak, Preetam, Pritha Bhattacharjee, and Krishnendu Ghosh. 2025. "Genomic, Epigenomic, and Immuno-Genomic Regulations of Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Literature Review and In Silico Meta-Analysis" DNA 5, no. 4: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040048
APA StyleModak, P., Bhattacharjee, P., & Ghosh, K. (2025). Genomic, Epigenomic, and Immuno-Genomic Regulations of Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Literature Review and In Silico Meta-Analysis. DNA, 5(4), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5040048






