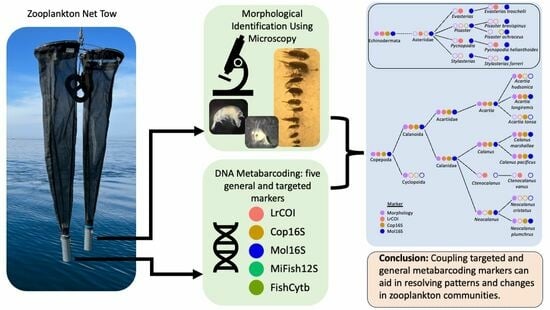
Evaluating Metabarcoding Markers for Identifying Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities to Species in the Salish Sea: Morphological Comparisons and Rare, Threatened or Invasive Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Zooplankton Community and Approach
1.2. Metabarcoding Markers Evaluated for the Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities
1.3. Project Aim and Scientific Question
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Metadata, and Morphological Identifications
2.2. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Metabarcoding
2.3. Bioinformatic Processing
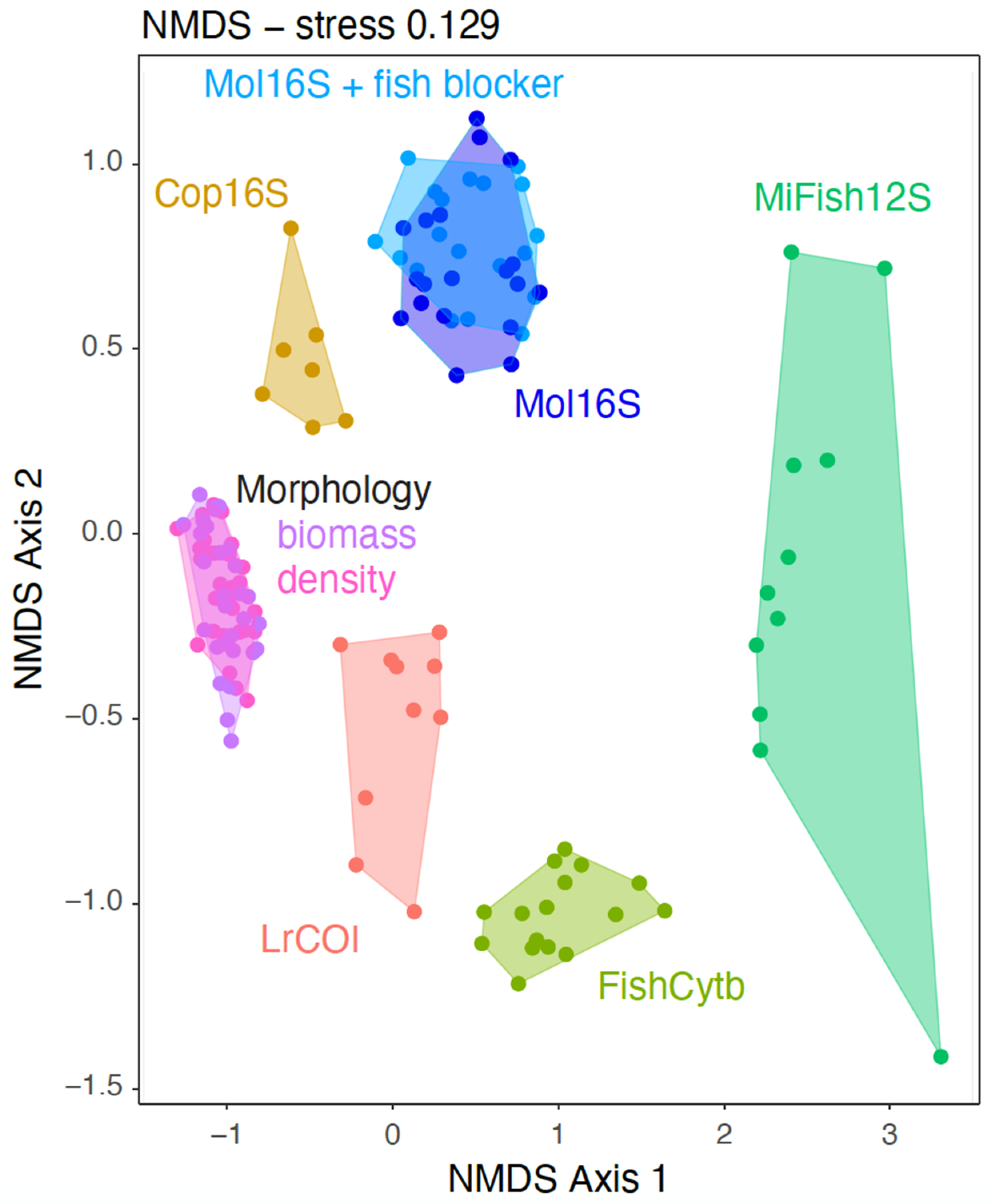
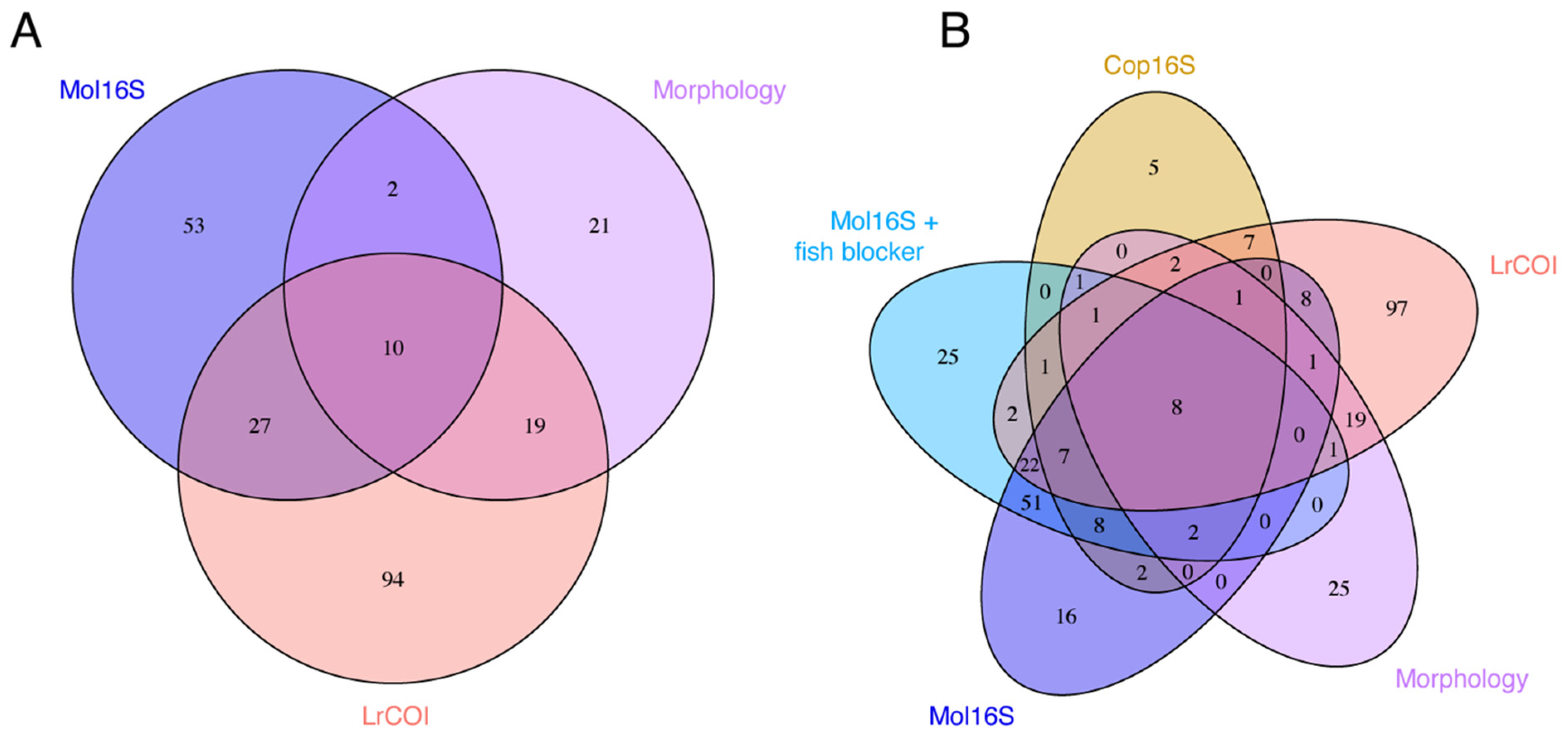
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Marker Strengths and Limitations
3.1.1. LrCOI
3.1.2. Cop16S
3.1.3. Mol16S
3.1.4. MiFish12S
3.1.5. FishCytb
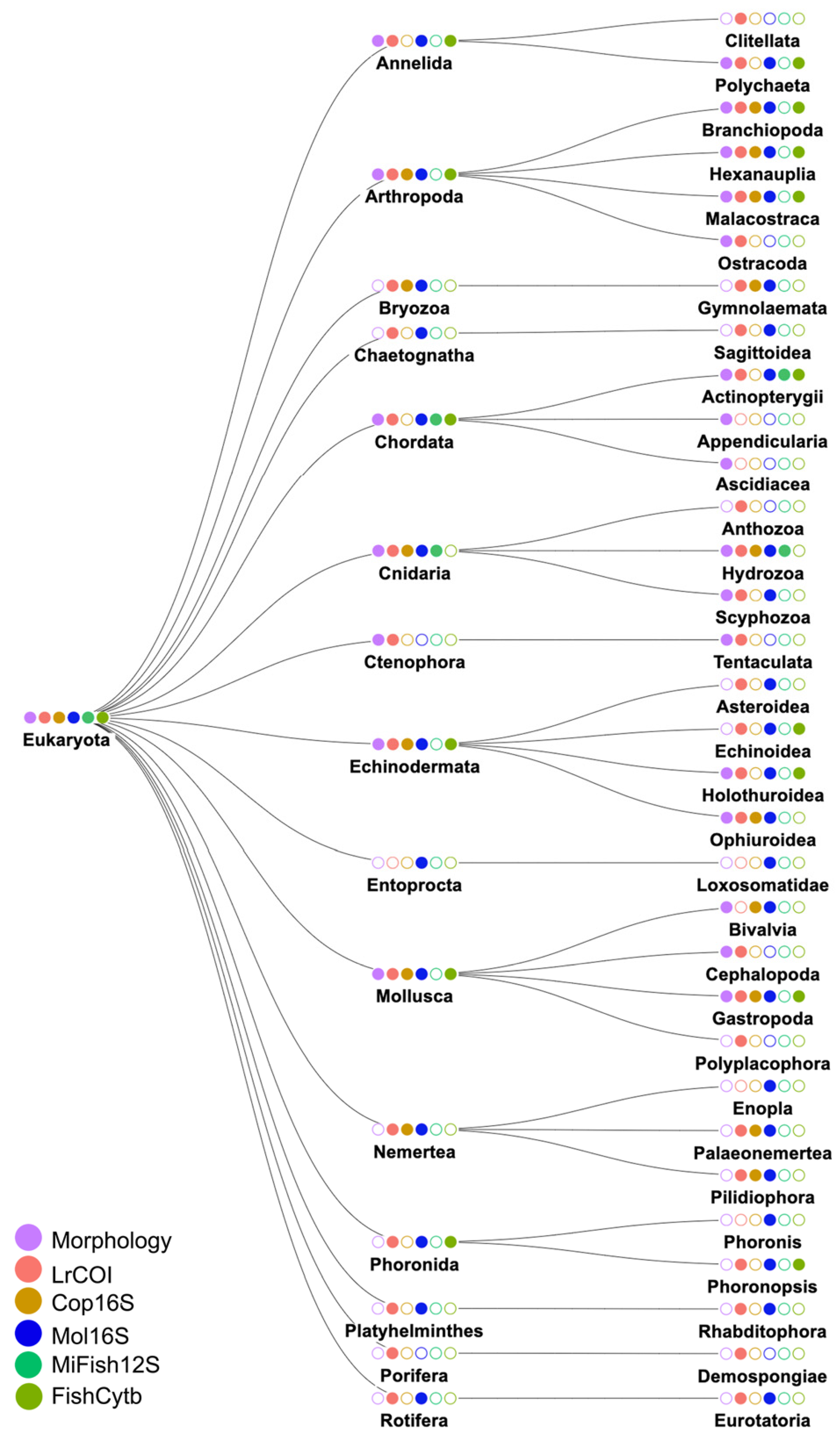
3.2. Species Identities and Distributions of Major Taxa
3.2.1. Phylum Annelida: Class Polychaeta (Bristleworms, Fanworms, Clamworms) (Figure 6B, Supplementary Table S4)
3.2.2. Phylum Arthropoda: Class Crustacea (Supplementary Table S4)
3.2.3. Phylum Cnidaria (Supplementary Figure S2B, Supplementary Table S4)
3.2.4. Phylum Echinodermata (Supplementary Figure S2C, Supplementary Table S4)
3.2.5. Phylum Mollusca (Supplementary Table S4)
3.2.6. Phylum Chordata: Class Osteichthyes (bony fishes) (Figure 6E, Supplementary Figure S2E)
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabarcoding Marker Specificities
4.2. Species Detected by Morphology and Missed by Metabarcoding
4.3. Sequence Read Proportion Relationships and Potential Biases
4.4. Threatened or Vulnerable Fishery Species
4.5. Non-Indigenous Species Detections
4.6. Species Identifications and Reference Libraries
4.7. Ecological Patterns and Trends
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coyle, K.O.; Pinchuk, A.K.; Eisner, L.B.; Napp, J.M. Zooplankton species composition, abundance and biomass on the eastern Bering Sea shelf during summer: The potential role of water-column stability and nutrients in structuring the zooplankton community. Deep. Sea Res. Part II 2008, 55, 1755–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerleau, C.; Sastri, A.R.; Beisner, B.E. Evaluation of functional trait diversity for marine zooplankton communities in the Northeast subarctic Pacific Ocean. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, J.; Katakura, S.; Kasai, H.; Nagai, S. Cryptic zooplankton diversity revealed by a metagenetic approach to monitoring metazoan communities in the coastal waters of the Okhotsk Sea, Northeastern Hokkaido. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Baumann, H. Hypoxia and acidification in ocean ecosystems: Coupled dynamics and effects on marine life. Biol. Lett. 2016, 5, 20150976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitburg, D. Effects of hypoxia, and the balance between hypoxia and enrichment, on coastal fishes and fisheries. Estuaries 2002, 25, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, K.E.; Klinger, T.; Keister, J.E.; McLaskey, A.K. Comparative sensitivities of zooplankton to ocean acidification conditions in experimental and natural settings. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 86, 613778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, M.; Hunt, G.; Dowsett, H.J.; Robinson, M.M.; Stoll, D.K. Latitudinal species diversity gradient of marine zooplankton for the last three million years. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, B.; Marco, T.; Angela, C. Interannual summer biodiversity changes in ichthyoplankton assemblages of the Strait of Sicily (Central Mediterranean) over the period 2001–2016. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 960929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebitz, A.S.; Hoffman, J.C.; Darling, J.A.; Pilgrim, E.M.; Kelly, J.R.; Brown, E.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Egan, S.P.; Grey, E.K.; Hashsham, S.A.; et al. Early detection monitoring for aquatic non-indigenous species: Optimizing surveillance, incorporating advanced technologies, and identifying research needs. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebitz, A.S.; Hoffman, J.C.; Darling, J.A.; Pilgrim, E.M.; Kelly, J.R.; Brown, E.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Egan, S.P.; Grey, E.K.; Hashsham, S.A.; et al. Diversity and distribution of meroplanktonic larvae in the Pacific Arctic and connectivity with adult benthic invertebrate communities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, F.C.; Uren Webster, T.M.; Rodriguez-Barreto, D.; O’Rorke, R.; Garcia de Leaniz, C.; Consuegra, S. Quantitative assessment of fish larvae community composition in spawning areas using metabarcoding of bulk samples. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonico, G.; Buttigieg, P.L.; Montes, E.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Stepien, C.; Wright, D.; Benson, A.; Helmuth, B.; Costello, M.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; et al. Global observational needs and resources for marine biodiversity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.; Batta-Lona, P.G.; Questel, J.M.; Wiebe, P.H.; Richardson, D.E.; Copley, N.J.; Benson, A.L.; Helmuth, B.; Costello, M.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; et al. COI metabarcoding of zooplankton species diversity for time-series monitoring of the NW Atlantic continental shelf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z. Standards for methods utilizing environmental DNA for detection of fish species: Review. Genes 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, T.; Orr, J.W. Fishes of the Salish Sea: Puget Sound and the Straits of Georgia and Juan de Fuca; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019; p. 1074. ISBN 9780295743745. [Google Scholar]
- Keister, J.E.; Winans, A.K.; Herrmann, B. Zooplankton community response to seasonal hypoxia: A test of three hypotheses. Diversity 2020, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 2003, 425, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, A.; Hales, B.; Waldbusser, G.C.; Langdon, C.; Feely, R.A. The Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, shows negative correlation to naturally elevated carbon dioxide levels: Implications for near-term ocean acidification effects. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Doney, S.C.; Cooley, S.R. Ocean acidification: Present conditions and future changes in a high-CO2 world. Oceanography 2009, 22, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Alin, S.R.; Newton, J.; Sabine, C.L.; Warner, M.; Devol, A.; Krembs, C.; Maloy, C. The combined effects of ocean acidification, mixing, and respiration on pH and carbonate saturation in an urbanized estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feely, R.A.; Alin, S.R.; Carter, B.; Dunne, J.P.; Gledhill, D.K.; Jiang, L.; Lance, V.; Stepien, C.A.; Sutton, A.; Wanninkhof, R. 2020: Open Ocean Region Acidification Research. NOAA Ocean, Coastal, and Great Lakes Acidification Research Plan: 2020–2029. Available online: https://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/files/noaa-oa-researchplan2020-2029.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Zark, M.; Broda, N.K.; Hornick, T.; Grossart, H.-P.; Riebesell, U.; Dittmar, T. Ocean acidification experiments in large-scale mesocosms reveal similar dynamics of dissolved organic matter production and viotransformation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Fitzer, S. The impact of environmental acidification on the microstructure and mechanical integrity of marine invertebrate skeletons. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coz062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaskey, A.K.; Keister, J.E.; McElhany, P.; Olson, M.B.; Busch, D.S.; Maher, M.; Winans, A.K. Development of Euphausia pacifica (krill) larvae is impaired under pCO2 levels currently observed in the Northeast Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2016, 555, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daewe, U.; Hjøllo, S.S.; Huret, M.; Ji, R.; Maar, M.; Niiranen, S.; Travers-Trolet, M.; Peck, M.A.; van de Wolfshaar, K.E. Predation control of zooplankton dynamics: A review of observations and models. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, G.D.; Kleppel, G.S.; Dempsey, M. Apparent predation on ichthyoplankton by zooplankton and fishes in nearshore waters of southern California. Mar. Biol. 1984, 80, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, M.; Edwards, M.; Richardson, A.J.; Halliday, N.C.; Wanless, S. From plankton to top predators: Bottom-up control of a marine food web across four trophic levels. J. Anim. Ecol. 2006, 75, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeque, P.K.; Parry, H.E.; Harmer, R.A.; Somerfield, P.J.; Atkinson, A. Next generation sequencing reveals the hidden diversity of zooplankton assemblages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Loos, L.M.; Nijand, R. Biases in bulk: DNA metabarcoding of marine communities and the methods involved. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2021, 30, 3270–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Choi, H.; Jeon, M.S.; Kim, E.-J.; Jeong, H.G.; Kim, S.; Hwang, H.; Purnaningtyas, D.W.; Lee, S.; Eyun, S.; et al. Zooplankton diversity monitoring strategy for the urban coastal region using metabarcoding analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.T.; Stepien, C.A. Macroinvertebrate community diversity and habitat quality relationships along a large river from targeted eDNA metabarcoding assays. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claver, C.; Canals, O.; de Amézaga, L.G.; Mendibil, I.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N. An automated workflow to assess completeness and curate GenBank for environmental DNA metabarcoding: The marine fish assemblage as case study. Environ. DNA 2023, 5, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Leese, F. Validation and development of COI metabarcoding primers for freshwater macroinvertebrate bioassessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.K.; Chain, F.J.J.; Abbot, C.L.; Cristescu, M.E. Metabarcoding using multiplexed markers increases species detection in complex zooplankton communities. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Sado, T.; Gotoh, R.O.; Watanabe, S.; Tsukamoto, K.; Miya, M. New PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from freshwater eels, genus Anguilla. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klymus, K.E.; Marshall, N.T.; Stepien, C.A. Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding assays to detect invasive invertebrate species in the Great Lakes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.R.; Yoon, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Kang, C.-K.; Kim, H.-W. Metabarcoding analysis of ichthyoplankton in the East/Japan Sea using the novel fish-specific universal primer set. Front. Mar. Sci. 2012, 8, 614394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, T.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Meyer, A.; Edwards, V.; Paabo, S.; Villablanca, F.X.; Wilson, A.C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: Amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6196–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbi, S. Chapter 7—Nucleic Acids II: The polymerase chain reaction. In Molecular Systematics, 2nd ed.; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B.K., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 205–248. ISBN 0878932828/978-0878932825. [Google Scholar]
- Stepien, C.A.; Kocher, T.D. Chapter 1—Molecules and morphology in studies of fish evolution. In Molecular Systematics of Fishes; Kocher, T.D., Stepien, C.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, D.V. Mitochondrial genomes in invertebrate animals. In Molecular Life Sciences; Bell, E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.W. The evolution of per-cell organelle number. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.; Steinke, D.; Blanco-Bercial, L. DNA barcoding of marine Metazoa. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 471–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Knowlton, N. DNA barcoding and metabarcoding of standardized samples reveal patterns of marine benthic diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, B.; Knebelsberger, T.; Neumann, H.; Laakmann, S.; Arbizu, P.M. Metabarcoding of marine environmental DNA based on mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulovici, A.E.; Vieira, P.E.; Duarte, S.; Teixeira, M.A.L.; Borges, L.M.S.; Deagle, B.E.; Majaneva, S.; Redmond, N.; Schultz, J.A.; Costa, F.O. Revision and annotation of DNA barcode records for marine invertebrates: Report of the 8th iBOL conference hackathon. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2021, 5, e67862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoon, M.; Kim, H.J. The complete mitochondrial genome of rockfish Sebastes oculatus Valenciennes, 1833 from southwest Atlantic Ocean. Mitochondrial DNA Part B Resour. 2019, 4, 3407–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leray, M.; Yang, J.Y.; Meyer, C.P.; Mills, S.C.; Agudelo, N.; Ranwez, V.; Boehm, J.T.; Machida, R.J. A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: Application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, J.; Meyer, C.; Hawk, H. Redesign of PCR primers for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I for marine invertebrates and application in all-taxa biotic surveys. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.M.; Ransome, E.; Collins, A.G.; Mahardini, A.; Kurniasih, E.M.; Sembiring, A.; Schiettekatte, N.M.D.; Cahyani, N.K.D.; Anggoro, A.W.; Moore, M.; et al. DNA metabarcoding marker choice skews perception of marine eukaryotic biodiversity. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1229–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, P.; Collins, A.G.; Pagenkopp Lohan, K.M.; Hanson, K.M.; Truskey, S.B.; Jaeckle, W.; Ames, C.L.; Goodheart, J.A.; Bush, S.L.; Biancani, L.M.; et al. The role of taxonomic expertise in interpretation of metabarcoding studies. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 3397–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Wang, D.; Xue, L.; Guan, M.; Huang, T.; Li, R. Species identification through mitochondrial rRNA genetic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-C. Secondary structure of mitochondrial 12S rRNA among fish and its phylogenetic applications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 19, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.J.; Beard, J.M.; Swadling, K.M.; Deagle, B.E. Effect of marker choice and thermal cycling protocol on zooplankton DNA metabarcoding studies. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Andrews, K.; Elz, A.; Marshall, N.T.; Snyder, M.R. Understanding marine community responses in species composition, diversity, and population genetics: Targeted metagenomics from environmental DNA and plankton samples. In Proceedings of the Application and Innovation in the Use of Environmental DNA (eDNA) for Use with Aquatic Species, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 21 August 2018; American Fisheries Society Annual Meeting. American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://afs.confex.com/afs/2018/oral/papers/viewonly.cgi?password=299439&username=32989 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Strong, E.E.; Gargominy, O.; Ponder, W.F.; Bouchet, P. 2008. Global diversity of gastropods (Gastropoda; Mollusca) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Stepien, C.A.; Nuc, Z. Neocosmopolitan distributions of invertebrate aquatic invasive species due to euryhaline geographic history and human-mediated dispersal: Ponto-Caspian versus other geographic origins. Ecol. Process. 2023, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Adolf, J.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Dunton, K.J.; Hinks, G.; VanMorter, S.M. Trawl and eDNA assessment of marine fish diversity, seasonality, and relative abundance in coastal New Jersey, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Adolf, J.; Ausubel, J.H.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Dunton, K.J.; Hinks, G. Current laboratory protocols for detecting fish species with environmental DNA optimize sensitivity and reproducibility, especially for more abundant populations. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.R.; Stepien, C.A. Increasing confidence for discerning species and population compositions from metabarcoding assays of environmental samples. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2020, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.R.; Stepien, C.A.; Marshall, N.T.; Scheppler, H.; Black, C.; Czajkowski, K. Detecting aquatic invasive species in bait and pond stores with targeted environmental DNA high-throughput sequencing metabarcode assays: Angler, retailer, and manager implications. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 245, 108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrete, V.G.; Wiens, J.J. Why are there so few fish in the sea? Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northwest Association of Networked Ocean Observing Systems (NANOOS); Pacific Northwest Regional Association of the Integrated Ocean Observing System (IOOS). NVS Salish Cruises Reports. Available online: https://nvs.nanoos.org/CruiseSalish (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Winans, A.K.; Herrmann, B.; Keister, J.E. Spatio-temporal variation in zooplankton community composition in the southern Salish Sea: Changes during the 2015–2016 Pacific marine heatwave. Prog. Oceanogr. 2023, 214, 103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A. Methods for population genetic analysis of zooplankton. In ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Harris, R., Wiebe, P., Lenz, J., Skjoldal, H.R., Huntley, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 533–570. ISBN 9780123276452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G.A.; Szabo, I. British Columbia Pelagic Marine Copepoda: An Identification Manual and Annotated Bibliography; Department of Fisheries and Oceans: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1982; Available online: http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2016/mpo-dfo/Fs41-31-62-eng.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Shanks, A.L. An Identification Guide to the Larval Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest, 1st ed.; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780870715310. [Google Scholar]
- Light, S.F.; Carlton, J.T. The Light and Smith Manual: Intertidal Invertebrates from Central California to Oregon, 4th ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0520239395. [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel, D.; Mills, C. Pacific Coast Pelagic Invertebrates: A Guide to the Common Gelatinous Animals; Sea Challengers, Monterey Bay Aquarium: Monterey, CA, USA, 1998; ISBN 9780930118235. [Google Scholar]
- Lough, R.G. Dynamics of Crab Larvae (Anomura, Brachyura) off the Central Oregon Coast, 1969–1971. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1975; pp. 28–83. Available online: https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/concern/parent/j098zc90v/file_sets/rx913s09f (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Sorochan, K.A.; Duguid, W.D.P.; Quijón, P.A. Diagnostic morphological characteristics of laboratory-reared Cancer oregonensis (Brachyura: Cancridae) with recommendations for identifying cancrid zoeae in the Salish Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, E.; Ohman, M.D.; Townsend, A.W.; Knight, M.D.; Bridgeman, A.L. Euphausiids of the World Ocean, 2015, v. 1.1. Available online: https://euphausiids.linnaeus.naturalis.nl/linnaeus_ng/app/views/introduction/topic.php?id=11(accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Thorp, J.H.; Covich, A.P. (Eds.) Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Academic Press, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1991; p. 911. ISBN 9780080530673. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, T.; Wood, T.S. Results of a freshwater bryozoan survey in the Pacific Northwest. In Bryozoan Studies; Jackson, W., Jones, B., Jones, S., Eds.; Swets and Zeitlinger: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 90-5809-388-3. [Google Scholar]
- Van Guelpen, L.; Markle, D.F.; Duggan, D.J. An evaluation of accuracy, precision, and speed of several zooplankton subsampling techniques. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1982, 40, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D.M.; Mable, B.K.; Larson, A.; Davis, S.K.; Zimmer, E.A. Chapter 9—Nucleic Acids IV: Sequencing and cloning. In Molecular Systematics, 2nd ed.; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B.K., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 321–384. ISBN 0878932828/978-087893282578. [Google Scholar]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeqplatform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wen, C.; Qin, Y.; Yin, H.; Tu, Q.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J. Phasing amplicon sequencing on Illumina Miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, S.M.; Norton, E.L.; Galaska, M.P. REVAMP: Rapid Exploration and Visualization through an Automated Metabarcoding Pipeline. Oceanography 2023, 36, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI); National Institutes of Health (NIH); National Library of Medicine, USA. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. 2021. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastHome (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Menzel, P. Subtree Program in: Taxonomy Tools. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/pmenzel/taxonomy-tools (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Shen, W.; Ren, H. TaxonKit: A practical and efficient NCBI taxonomy toolkit. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. NMDS Phyloseq. Classification Clustering Genetic Variability Metagenomics Microbiome Multiple Comparison Sequencing Software Visualization. 2022. Available online: https://rdrr.io/github/schuyler-smith/phyloschuyler/man/nmds_phyloseq.html (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- visNetwork, an R Package for Interactive Network Visualization, r. 2.1.1. 2022. Available online: https://datastorm-open.github.io/visNetwork/ (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.; Burgiel, S.; Brantley, K.; Daniel, W.M.; Darling, J.; Davis, J.; Franklin, T.; Gaddis, K.; Hunter, M.; Lance, R.; et al. Strategic considerations for invasive species managers in the utilization of environmental DNA (eDNA): Steps for incorporating this powerful surveillance tool. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2021, 12, 747–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, C.N.; Brown, S.D.; McAllister, S.M.; Winans, A.K.; Keister, J.E.; Galaska, M.P. The complete mitochondrial genome of Cyphocaris challengeri (Amphipoda: Cyphocarididae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2023, 8, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.-T.; Hendrycks, E.A. A new species and new records of the genus Vibilia Milne Edwards, 1830 (Amphipoda: Hyperiidea: Vibiliidae) occurring in the eastern Pacific Ocean. J. Nat. Hist. 2003, 37, 253–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikou, C.; Passamaneck, Y.J.; Lowe, C.J.; Martindale, M.Q.; Hejnol, A. Molecular patterning during the development of Phoronopsis harmeri reveals similarities to rhynchonelliform brachiopods. EvoDevo 2019, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G. Proceraea Okadai: Annelids-Polychaetes. Smithsonian Environmental Research Center’s National Estuarine and Marine Exotic Species Information System (NEMESIS). Available online: https://invasions.si.edu/nemesis/species_summary/-683 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Nishizawa, R.; Sato, M.; Furota, T.; Tosuji, H. Cryptic invasion of northeast Pacific estuaries by the Asian polychaete, Hediste diadroma (Nereididae). Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.R. Environmental DNA Detection and Population Genetic Patterns of Native and Invasive Great Lakes Fishes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, 2019. Available online: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=toledo1564680483342507 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Ershova, E.A.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Descoteaux, R.; Barth-Jensen, C.; Præbel, K. Metabarcoding as a quantitative tool for estimating biodiversity and relative biomass of marine zooplankton. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 3342–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.A.; Goetze, E.; Ohman, M.D. Recommendations for interpreting zooplankton metabarcoding and integrating molecular methods with morphological analyses. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.T.; Stepien, C.A. Invasion genetics from eDNA and thousands of larvae: A targeted metabarcoding assay that distinguishes species and population variation of zebra and quagga mussels. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3515–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänfling, B.; Handley, L.L.; Read, D.S.; Hahn, C.; Li, J.; Nichols, P.; Blackman, R.C.; Oliver, A.; Winfield, I.J. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of lake fish communities reflects long-term data from established survey methods. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3101–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Knudsen, S.W.; Jørgensen, O.A.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA from seawater samples correlate with trawl catches of subarctic, deepwater fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, K.M.; Everett, M.; Dahlheim, M.; Park, L. Water, water everywhere: Environmental DNA can unlock population structure in elusive marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.L.A.; Clarke, L.J.; Wedderburn, S.D.; Barnes, T.C.; Weyrich, L.S.; Cooper, A. Comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and conventional fish survey methods in a river system. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 197, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, B.; Cottet, M.; Destanque, T.; Kue, K.; Descloux, S.; Chanudet, V.; Hughes, S. Direct fishing and eDNA metabarcoding for biomonitoring during a 3-year survey significantly improves number of fish detected around a South East Asian reservoir. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, P.D.; Hunter, E.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Creer, S.; Davies, R.G.; Taylor, M.I. How quantitative is metabarcoding: A meta-analytical approach. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Gold, Z.J.; Jensen, A.J.; D′Agnese, E.; Allan, E.A.; Van Cise, A.; Gallego, R.; Ramón-Laca, A.; Garber-Yonts, M.; Parsons, K.; et al. Toward quantitative metabarcoding. Ecology 2023, 104, e3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Li, H.; Zhan, A. Early detection of invasive species in marine ecosystems using high-throughput sequencing: Technical challenges and possible solutions. Mar. Biol. 2022, 163, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Bohmann, K. Scrutinizing key steps for reliable metabarcoding of environmental samples. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 9, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñol, J.; Mir, G.; Gomez-Polo, P.; Agustí, N. Universal and blocking primer mismatches limit the use of high-throughput DNA sequencing for the quantitative metabarcoding of arthropods. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2015, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.D.; Bloom, R.J.; Jiang, S.; Durand, H.K.; Dallow, E.; Mukherjee, S.; David, L.A. Measuring and mitigating PCR bias in microbiota datasets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Nakao, R.; Doi, H.; Minamoto, T. Simultaneous absolute quantification and sequencing of fish environmental DNA in a mesocosm by quantitative sequencing technique. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, Z.; Kelly, R.P.; Shelton, A.O.; Thompson, A.R.; Goodwin, K.D.; Gallego, R.; Parsons, K.M.; Thompson, L.R.; Kacev, D.; Barber, P.H. Archived DNA reveals marine heatwave-associated shifts in fish assemblages. Environ. DNA 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.; Rajabi, H.; McClenaghan, B.; Fahner, N.A.; Porter, E.; Singer, G.A.C.; Hajibabaei, M. Comparative analysis of fish eDNA reveals higher sensitivity achieved through targeted sequence-based metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2022, 23, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Lusana, J.L.; Chen, Y. High-throughput DNA metabarcoding as an approach for ichthyoplankton survey in Oujiang River Estuary, China. Diversity 2022, 14, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, A.B.; Freitas-Souza, D.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Nobile, M.L.M.O.; Costa, G.O.; de Lima, F.P.; Camacho, J.P.M.; Foresti, F.; Oliveira, C. DNA metabarcoding of Neotropical ichthyoplankton: Enabling high accuracy with lower cost. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2019, 3, e35060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariac, C.; Renno, J.-F.; Garcia-Davila, C.; Vigouroux, Y.; Mejia, E.; Angulo, C.; Ruiz, D.C.; Estivals, G.; Nolorbe, C.; Vasquez, A.G.; et al. Species-level ichthyoplankton dynamics for 97 fishes in two major river basins of the Amazon using quantitative metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 1627–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOAA Fisheries. Chum Salmon-Protected. 2022. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/chum-salmon-protected (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. Chum Salmon, (Hood Canal Summer ESU) (ONCORHYNCHUS keta pop. 2). Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/species/oncorhynchus-keta-pop-2 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. Walleye Pollock (South Puget Sound) (Gadus chalcogrammus). Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/species/gadus-chalcogrammus#desc-range (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Small, M.P.; Loxterman, J.L.; Frye, A.E.; Vonbargen, J.F.; Bowman, C.; Young, S.F. Temporal and spatial genetic structure among some Pacific herring populations in Puget Sound and the Southern Strait of Georgia. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2005, 134, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Fisheries. Species Directory. Pacific Herring. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/pacific-herring (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. Pacific Herring (Clupea pallasii). Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/species/clupea-pallasii#conservation (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. Pacific Hake (Merluccius productus). Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/species/merluccius-productus (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Chittaro, P.; Grandin, C.; Pacunski, R.; Zabel, R. Five decades of change in somatic growth of Pacific hake from Puget Sound and Strait of Georgia. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytsma, M.D.; Cordell, J.R.; Chapman, J.W. Lower Columbia River Aquatic Nonindigenous Species Survey 2001–2004. In Annual Progress Report to Pacific States Fisheries Commission; Final Technical Report; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. Available online: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=&httpsredir=1&article=1022&context=centerforlakes_pub (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Emmett, R.L.; Stone, S.L.; Hinton, S.A.; Monaco, M.E. Volume II: Species Life History Summaries. In Distribution and Abundance of Fishes and Invertebrates in West Coast Estuaries; ELMR Rep. No. 8; NOAA/NOS Strategic Environmental Assessments Division: Rockville, MD, USA, 1991; p. 329. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/2871 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Hasselman, D.J.; Hinrichsen, R.A.; Shields, B.A.; Ebbesmeyer, C.C. The rapid establishment, dispersal, and increased abundance of invasive American shad in the Pacific Northwest. Fisheries 2012, 37, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grason, E.W.; McDonald, P.S.; Adams, J.W.; Litle, K.; Apple, J.K.; Pleus, A. Citizen science program detects range expansion of the globally invasive European green crab in Washington State (USA). Manag. Biol. Invasion 2018, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens Yamada, S.; Thomson, R.E.; Gillespie, G.E.; Norgard, T.C. Lifting barriers to range expansion: The European green crab Carcinus maenas (Linnaeus, 1758) enters the Salish Sea. J. Shellfish. Res. 2017, 36, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife. European Green Crab (Carcinus maenas). 2023. Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/invasive/carcinus-maenas#desc-range (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Westfall, K.M.; Therriault, T.W.; Abbott, C.L. Targeted next-generation sequencing of environmental DNA improves detection of invasive European green crab (Carcinus maenas). Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, F.Á.; Machordom, A. DNA barcoding reveals a cryptic nemertean invasion in Atlantic and Mediterranean waters. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2013, 67, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS (US Geological Survey). Invasive Species Program: National Early Detection and Rapid Response (EDRR) Framework. 2023. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/tools/national-early-detection-and-rapid-response-edrr-framework (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Bianchi, F.M.; Gonçalves, L.T. Getting science priorities straight: How to increase the reliability of specimen identification? Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20200874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, J.W.; Spies, I.; Stevenson, D.E.; Longo, G.C.; Kai, Y.; Ghods, S.; Hollowed, M. Molecular phylogenetics of snailfishes (Cottoidei: Liparidae) based on mtDNA and RADseq genomic analyses, with comments on selected morphological characters. Zootaxa 2019, 4642, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, M.L.; Whitney, J.; Collins, A.G.; Meyer, C.; Murphy, K.R.; Reft, A.J.; Bemis, K.E. Skimming for barcodes: Rapid production of mitochondrial genome and nuclear ribosomal repeat reference markers through shallow shotgun sequencing. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithsonian/NOAA/BOEM and Partners Genome Skimming Project. 2023. Available online: https://geome-db.org/workbench/project-overview?projectId=446 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Bucklin, A.; Peijnenburg, K.T.C.A.; Kosobokova, K.N.; O’Brien, T.D.; Blanco-Bercial, L.; Cornils, A.; Falkenhaug, T.; Hopcroft, R.R.; Hosia, A.; Laakmann, S.; et al. Toward a global reference database of COI barcodes for marine zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Duffy, E.; Collins, A.; Paulay, G.; Wetzer, R. The US Ocean Biocode. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2021, 55, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH (National Institutes of Health). NOAA Genome Skimming of Marine Animals Inhabiting the US Exclusive Economic Zone. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/720393 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Gold, Z.; Wall, A.R.; Schweizer, T.M.; Pentcheff, N.D.; Curd, E.E.; Barber, P.H.; Meyer, R.S.; Wayne, R.; Stolzenbach, K.; Prickett, K.; et al. A manager’s guide to using eDNA metabarcoding in marine ecosystems. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiasny, M.H.; Mittermayer, F.H.; Sswat, M.; Voss, R.; Jutfelt, F.; Chierici, M.; Puvanendran, V.; Mortensen, A.; Reusch, T.B.; Clemmesen, C. Ocean acidification effects on Atlantic cod larval survival and recruitment to the fished population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, S.A.; Van Woudenberg, L.; Lenz, P.H.; Cepeda, G.; Goetze, E. Vertical gradients in species richness and community composition across the twilight zone in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6136–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, L.; Pearman, J.K.; Irigoien, X. Metabarcoding reveals seasonal and temperature-dependent succession of zooplankton communities in the Red Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, J.; Tachibana, A.; Tsuda, A. Large-scale metabarcoding analysis of epipelagic and mesopelagic copepods in the Pacific. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobari, T.; Tokumo, Y.; Sato, I.; Kume, G.; Hirai, J. Metabarcoding analysis of trophic sources and linkages in the plankton community of the Kuroshio and neighboring waters. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Site and Season | Latitude | Longitude | SamplingDate | Tow Start Time | Salinity (PSU) Range (and Mean) | Fluorescence (mg/m3) Range (and Mean) | pH Range (and Mean) | Temp. (°C) Range (and Mean) | Diss.O2 (mg/L) Range (and Mean) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (P22) Spring | 48.2723 | −123.0212 | 04/08/18 | 11:46 | 30.49–32.91 (31.62) | 0.15–0.45 (0.30) | 7.70–7.80 (7.75) | 8.15–8.57 (8.28) | 4.96–8.10 (6.64) |
| B (P4) Spring | 48.2437 | −122.5562 | 04/07/18 | 20:20 | 24.69–29.41 (27.97) | 0.24–1.20 (0.51) | 7.56–7.84 (7.63) | 8.70–9.57 (9.07) | 3.72–9.29 (6.23) |
| C (P8) Spring | 47.8989 | −122.6054 | 04/09/18 | 07:29 | 29.10–30.62 (30.08) | 0.32–0.89 (0.46) | 7.73–7.85 (7.79) | 8.44–9.19 (8.61) | 7.81–9.09 (8.21) |
| D (P28) Spring | 47.7047 | −122.4544 | 04/07/18 | 12:39 | 28.97–29.65 (29.47) | 0.20–0.77 (0.33) | 7.74–7.76 (7.75) | 8.32–8.73 (8.38) | 3.34–3.69 (3.42) |
| E (P38) Spring | 47.2776 | −122.7085 | 04/11/18 | 10:55 | 28.42–28.91 (28.78) | 0.41–21.20 (3.06) | 7.72–8.19 (7.81) | 8.43–9.47 (8.64) | 8.12–12.64 (9.06) |
| F (P402) Spring | 47.3558 | −123.0239 | 04/09/18 | 17:10 | 25.94–30.07 (29.65) | 0.21–6.61 (0.68) | 7.43–7.79 (7.48) | 10.15–10.97 (10.26) | 3.51–9.21 (4.20) |
| G (P12) Spring | 47.4256 | −123.1074 | 04/09/18 | 14:59 | 26.92–30.39 (30.01) | 0.12–1.32 (0.24) | 7.41–7.55 (7.48) | 9.54–10.58 (10.11) | 3.14–7.43 (4.24) |
| A (P22) Autumn | 48.27268 | −123.02076 | 09/12/18 | 08:49 | 31.43–32.99 (32.26) | 0.12–0.46 (0.24) | 7.62–7.75 (7.67) | 8.81–11.01 (9.85) | 4.38–5.37 (4.91) |
| B (P4) Autumn | 48.2428 | −122.55274 | 09/11/18 | 18:17 | 26.91–30.18 (29.62) | 0.17–12.51 (1.87) | 7.42–8.27 (7.53) | 10.95–14.50 (11.51) | 5.64–7.03 (5.76) |
| C (P8) Autumn | 47.89546 | −122.60412 | 09/12/18 | 15:36 | 29.81–31.01 (30.83) | 0.44–3.80 (0.78) | 7.72–7.83 (7.74) | 11.84–12.93 (12.03) | 5.79–6.55 (6.11) |
| D (P28) Autumn | 47.70974 | −122.45264 | 09/11/18 | 11:44 | 30.05–30.69 (30.52) | 0.13–0.87 (0.26) | 7.68–7.79 (7.73) | 12.30–13.59 (12.56) | 5.61–6.91 (5.82) |
| E (P38) Autumn | 47.2767 | −122.7086 | 09/15/18 | 11:30 | 29.62–30.12 (30.00) | 0.09–6.02 (0.59) | 7.71–7.95 (7.75) | 13.38–14.75 (13.60) | 6.24–7.45 (6.57) |
| F (P402) Autumn | 47.35682 | −123.02252 | 09/13/18 | 16:26 | 28.55–30.42 (29.88) | 0.12–5.76 (0.74) | 7.24–8.33 (7.30) | 9.86–17.01 (10.39) | 1.10–10.68 (2.02) |
| G (P12) Autumn | 47.42576 | −123.10922 | 09/13/18 | 14:00 | 27.89–30.30 (29.92) | 0.05–5.24 (0.51) | 7.32–7.65 (7.38) | 9.82–13.01 (10.29) | 2.50–5.72 (3.05) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stepien, C.A.; Schultz, H.K.; McAllister, S.M.; Norton, E.L.; Keister, J.E. Evaluating Metabarcoding Markers for Identifying Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities to Species in the Salish Sea: Morphological Comparisons and Rare, Threatened or Invasive Species. DNA 2024, 4, 1-33. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4010001
Stepien CA, Schultz HK, McAllister SM, Norton EL, Keister JE. Evaluating Metabarcoding Markers for Identifying Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities to Species in the Salish Sea: Morphological Comparisons and Rare, Threatened or Invasive Species. DNA. 2024; 4(1):1-33. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleStepien, Carol A., Haila K. Schultz, Sean M. McAllister, Emily L. Norton, and Julie E. Keister. 2024. "Evaluating Metabarcoding Markers for Identifying Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities to Species in the Salish Sea: Morphological Comparisons and Rare, Threatened or Invasive Species" DNA 4, no. 1: 1-33. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4010001
APA StyleStepien, C. A., Schultz, H. K., McAllister, S. M., Norton, E. L., & Keister, J. E. (2024). Evaluating Metabarcoding Markers for Identifying Zooplankton and Ichthyoplankton Communities to Species in the Salish Sea: Morphological Comparisons and Rare, Threatened or Invasive Species. DNA, 4(1), 1-33. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4010001