Abstract
Substantial amounts of organo-pollutants, often persistent and toxic, are generated globally each year, posing a threat to soil, water, groundwater, and air. The pollutants encompass a wide range of substances from various sources, which include solid as well as liquid ones, such as landfill leachates and wastewaters. The compounds include paper and pulp mill byproducts, pharmaceuticals, diverse types of plastics, hydrocarbons, pigments, and dyes, as well as pesticides and insecticides. Fungal bioremediation stands out as a promising technology that uses the metabolic potential of fungi to eliminate or mitigate the impact of pollutants. Notably, species of the genus Pycnoporus exhibit significant capabilities for degrading a broad spectrum of toxic molecules. This degradation is facilitated by released ligninolytic enzymes, especially laccase, and cellular enzymes pertaining to the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system. The laccase, which is overproduced by the genus Pycnoporus, is quite remarkable for its high redox potential. The objective of this review is to highlight the proficiency of the Pycnoporus genus in the degradation of pollutants in submerged and solid-state fermentation. Recent studies conducted over the past decade consistently highlight the Pycnoporus genus as a robust contender in the realm of white biotechnology.
1. Introduction
Numerous studies highlight the efficacy of fungi in breaking down various pollutants, which is largely due to their metabolic versatility [1]. This versatility gives these organisms a significant role in the decomposition of organic matter in soils. Within the fungal realm, white-rot fungi (WRF) emerge as a notable group. It is worth emphasizing that white-rot fungi do not form a taxonomic category but rather consist of fungal species from the basidiomycetes class with the unique ability to degrade lignin. Noteworthy members of this group include Phanerochaete, Pleurotus, Trametes, Ganoderma, and Bjerkandera [2,3]. These fungi showcase impressive bioremediation capabilities, primarily attributed to their ligninolytic enzymatic system. Lignin degradation by WRF is made possible by a group of enzymes generally known as lignin-modifying enzymes (LMEs). These enzymes are released as multiple isoforms by the various WRF species, depending on the environmental conditions. The group of LMEs consists of a phenoloxidase, laccase (Lcc, EC 1.10.3.2), and three types of peroxidases (class II peroxidases with high oxidation potential). These enzymes are lignin peroxidase (LiP, EC 1.11.1.14), manganese-dependent peroxidase (MnP, EC 1.11.1.13), and versatile peroxidase (VP, 1.11.1.16) [4,5,6,7]. Thanks to their lack of substrate specificities, these enzymes exhibit potential for degrading various pollutants, including paper and pulp mill byproducts, pharmaceuticals, diverse types of plastics, hydrocarbons, pigments, and dyes, as well as pesticides and insecticides. Over the last few decades, research on the application of white-rot fungi in pollutant bioremediation has been steadily growing.
Fungi from the Polyporaceae family, which belongs to the order Polyporales and class Agaricomycetes, are popularly known as wood ear or urupê [8]. As of 2018, the Index Fungorum lists 1621 species for the 114 genera belonging to the Polyporaceae family. This family is one of the most representative of saprotrophic homobasidiomycetes that cause wood rot, with recognized lignocellulolytic potential [9]. The genus Trametes stands out in this family, with 195 species, as does the genus Fomes, with 59 species. The genus Pycnoporus, with only four known species, has been studied in several areas of research thanks to its enzymatic arsenal, which includes a series of hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes, in addition to its ability to mineralize a wide variety of highly toxic and recalcitrant compounds found in the environment as a consequence of industrial and agricultural activities and inappropriately discarded [9]. The list includes polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, synthetic dyes, herbicides, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, microorganisms of this genus have been listed as producers of molecules useful in foods and cosmetics [10,11]. Considering the potential presented by this genus, this review aims to evaluate potential applications of Pycnoporus spp. and its enzymes in bioremediation processes, emphasizing the findings of the last decade (2012–2023). The emphasis was placed on articles where the metabolic routes and degradation intermediates of pollutants were identified. Additionally, current trends in the research field and neglected aspects are discussed.
2. The genus Pycnoporus
Pycnoporus is akin to the genus Trametes with respect to all its morphological characteristics if one excludes the intense bright orange-red color of its basidiocarp [12]. This color is caused by several phenoxazine-3-one pigments, including cinnabarinic acid [9,13]. The genus Pycnoporus is made up of 4 widely distributed species: P. coccineus (Fr.) Bondartsev and Singer 1851; P. cinnabarinus (Jacq.) P. Karst 1881; P. puniceus (Fr.) Ryvarden 1972; and P. sanguineus (L.) Murril 1994 (Figure 1).
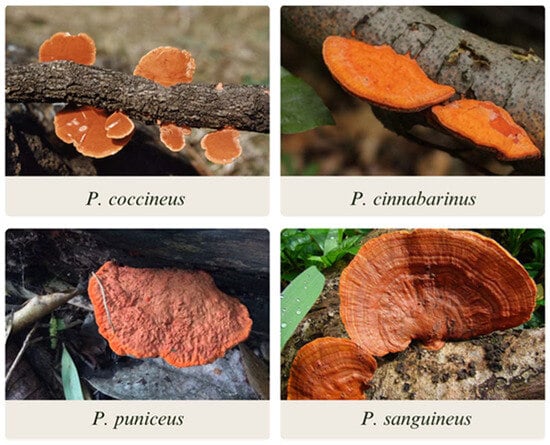

Figure 1.
The four species of the genus Pycnoporus.
P. cinnabarinus is found mainly in the Northern Hemisphere; P. puniceus, is sparsely distributed over Africa, India, Malaysia, and New Caledonia; P. sanguineus is a species belonging to tropical and subtropical regions whereas P. coccineus is found along the coasts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans [14]. Until 2013 there were no in-depth genomic and transcriptomic studies with species of the genus Pycnoporus. The first determination of the transcriptome of P. sanguineus was performed in 2013 [15]. Many transcripts were identified which encode enzymes involved in the synthesis of important sesquiterpenoids, precursors of triterpenoids and sterols and glutathione S-transferases and cytochrome P450 monooxygenases, which are frequently involved in the biodegradation of pollutants and detoxification of lignin degradation products.
When the delignification capacity of the genus Pycnoporus was studied [16], several genes encoding laccase and AA2 peroxidases (MnP, LiP or VP) were identified in P. cinnabarinus. Seven laccases have been identified and 22 genes have been demonstrated to operate in the kynurenine pathway. In the latter, laccases transform the intermediate metabolite 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid into cinnabarinic acid [17]. The genomes of the species P. sanguineus, P. coccineus and P. cinnabarinus, are home of the genes that encode the enzyme complex for the degradation of lignin, especially peroxidases and a fair number of auxiliary enzymes for the production of H2O2, important in the degradation of pectin, hemicellulose, and cellulose [18]. More recently, a bioprocess for recovering cellulose from cactus waste, consisting in lignin depolymerization by P. cinnabarinus, was optimized [19].
Pycnoporus spp. have been described for their capacity to synthesize high-value-added substances, including antioxidants, antibiotics, flavorings, and antivirals [9,20,21]. Recently, a Pycnoporus sanguineus SYBC-L7 variant was discovered, in which its pigments, composed of cinnabarinic acid, tramesanguine, and 2-amino-9-formylphenoxazone-1-carbonic acid, showed significant antibacterial action against several species, mainly Gram-positive ones [22].
Enzymes are the most studied biomolecules produced by Pycnoporus spp. Pycnoporus enzymes as well as enzymes from all white-rot basidiomycetous fungi can be obtained using submerged fermentation (SmF) or solid-state fermentation (SSF) [23]. SSF and SmF are two distinct methods used in biotechnology for the production of various biochemical products. In solid-state fermentation, microorganisms grow on a solid substrate with limited moisture content, typically agricultural residues like wheat bran or rice husk. This method offers advantages such as lower energy requirements, reduced contamination risk, and higher product yields due to better control over microbial growth. However, SSF also has limitations, including slower fermentation rates, difficulties in controlling process parameters, and challenges in scaling up production. On the other hand, submerged fermentation involves the cultivation of microorganisms in a liquid medium, providing better control over process conditions such as pH, temperature, and nutrient availability. This method often yields faster fermentation rates, higher biomass concentrations, and easier monitoring and scaling up of production. Nevertheless, submerged fermentation has drawbacks such as higher energy consumption, increased risk of contamination, and the requirement for sterile conditions, which can escalate production costs. Therefore, the choice between SSF and SmF depends on the specific requirements of the fermentation process and the desired product. As spending on culture media is considered one of the main determinants of high enzyme production costs [24], SSF has been considered a cheaper alternative to submerged processes as it allows the use of organic matter available in abundance [25,26]. Wood chips and bran were recently used as substrates for SSF of various white-rot fungi, including P. sanguineus, aiming at bioremediating diesel oil-contaminated soils [27]. However, both types of fermentation have been used to cultivate Pycnoporus spp., aimed at its use and the use of its enzymes in biodegradation processes. Pycnoporus sp. strain P6 was used to treat vinasse through both submerged and solid-state processes. Both processes resulted in reductions of color, phenolic compound content, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and toxicity. A recent study aimed at deciphering ligninolytic enzymes in the secretome of Pycnoporus sp. and correlating them, especially crude laccase and crude Mn peroxidase, in the degradation of 2-chlorophenol (2-CPs) [28]. The crude ligninolytic enzymes secreted by Pycnoporus sp. could effectively degrade 2-CPs and reduce their toxicity within a relatively short time frame of 16 h.
Pycnoporus spp. are known as producers of different oxidative and hydrolytic enzymes. Pycnoporus sanguineus, grown under submerged conditions with corn cobs as a carbon source, produced several carbohydrases, including cellulases, xylanases, and polygalacturonases [29,30]. A carboxylic acid reductase of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus (PcCAR2) was recently expressed in Escherichia coli [31]. The carboxylic reductases (CARs, E.C. 1.2.1.30) are known for their highly selective single-step reduction of carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acid reductases are versatile enzymes for the transformation of long-chain carboxylic acids into fuels and chemical commodities [32]. A new chymotrypsin-like protease from P. sanguineus was produced via solid-state fermentation using wheat bran, an agro-industrial residue, as the culture substrate. This protease was claimed to coagulate both reconstituted skim milk and whole milk in the presence or absence of calcium [33].
Pycnoporus spp. are especially explored as efficient producers of ligninolytic enzymes, laccases (p-diphenol:oxygen oxidoreductases, EC 1.10.3.2), and Mn peroxidase (MnP, EC 1.11.1.13) [34,35,36]. The laccases from Pycnoporus spp. are especially interesting due to their higher redox potential (high-redox potential laccases, or HRPLs; 0.720–0.790 V vs. NHE) when compared to other fungal, bacterial, or plant laccases (0.400–0.700 V vs. NHE) [37]: the laccases from P. coccineus and P. sanguineus presented redox potentials between 0.7 and 0.75 V [38]; the redox potential of the Pycnoporus sanguineus RP15 laccase was found to be 0.747 V [39]. Pycnoporus laccases are enzymes with intriguing phyco-chemical properties that make them valuable in various industrial and biotechnological applications. One notable characteristic is that Pycnoporus laccases exhibit impressive thermostability, being active at low temperatures [40] and retaining their enzymatic activity at elevated temperatures [39].
The addition of an appropriate inducer to the medium, such as syringaldehyde, p-coumaric acid, ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), or lignocellulosic agro-wastes, has been considered an effective procedure for regulating and increasing laccase production from Pycnoporus spp. [41,42,43]. The 17-ethinyl estradiol molecule helped to increase the expression of laccase by P. sanguineus in crops using cupuaçu (Theobroma grandiflorum) residues [44]. Lignocellulosic food, agricultural residues, and forestry residues are suitable and inexpensive choices of substrates in SSF. Billions of tons of organic waste are generated each year around the world, and this amount is constantly increasing [45]. The use of agricultural food waste as a substrate in SSF should be preferred because it helps to solve environmental problems associated with their treatment and disposal. At the same time, it provides a similar natural habitat for fungal growth. Lignocellulosic wastes provide appropriate nutrients with easy assimilation by microorganisms in a simple, green, and inexpensive process [25,46]. Figure 2 offers views of Pycnoporus sanguineus as found in nature, in a culture developed in potato dextrose agar, and in a SSF culture using wheat bran as substrate. Residues, such as corn cobs, sugar cane bagasse, and wheat bran supplemented or not with sources of nitrogen, and phosphate, among other salts and organic compounds, are frequently used as substrates in Pycnoporus cultivation [29,31,47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. Scalable laccase production by Pycnoporus sp. SYBC-L3 has already been accomplished at pilot scale in a 500-L and a 5-ton bioreactor, where the highest activities around 60 U/mL and 80 U/mL, respectively, were obtained [54].
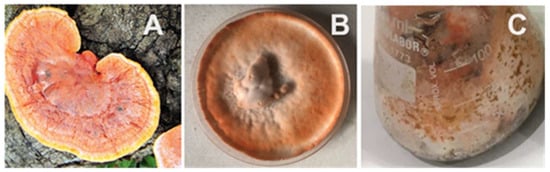
Figure 2.
Pycnoporus sanguineus. (A): Basidioma in nature; (B): Mycelia cultivated in PDA; (C): Mycelia cultivated in SSF using wheat bran as substrate.
3. General Mechanisms Used by Pycnoporus spp. for the Biodegradation of Pollutants
Pycnoporus spp., as well as several other WRF, are capable of biodegrading/bioremediating different pollutants quite efficiently for four main reasons. First, they express ligninolytic enzymes, which are nonspecific and therefore capable of oxidizing different types of organic compounds [55,56,57,58]. Second, when compared to other eukaryotes, ligninolytic fungi are less harmed by high concentrations of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [59]. One of the causes of this resistance is the fact that ROS are necessary, for example, for the initial degradation processes of the wood cell wall [60]. The third characteristic worth mentioning is that, like other eukaryotes, white wood rot fungi have specific mechanisms of detoxification against excess ROS, including enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, for example, and other low molecular weight agents such as glutathione, which act as antioxidant defenses [61,62]. And, finally, the fourth feature favoring the ligninolytic action of the fungi is the biodegradation of pollutants by the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system [63,64].
Recent studies with different WRF show that their ligninolytic enzymes are capable of degrading in vitro different pollutants such as chlorophenols, hydroxyphenylureas, and glyphosate [65,66]. These observations confirm that ligninolytic enzymes are, at least in part important agents participating in the in vivo transformation of pollutants. Investigations of the biodegradation of herbicides by ligninolytic fungi have revealed interesting facts. For example, the herbicides bentazon, diuron, and paraquat, widely used in Brazil, are classified as photosynthesis inhibitors [67]. They act by inhibiting electron transport, as they cause the removal or inactivation of one or more intermediate electron transport carriers. They also catalyze the excessive generation of superoxide anionic radicals and, consequently, of other reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated through reactions like the Fenton reaction [67,68]. Several studies, in which it was not possible to find a correlation between the biodegradation of different pollutants by ligninolytic fungi and the expression of ligninolytic enzymes, led to the assumption that intracellular factors may be involved in the propensity of ligninolytic fungi to break down pollutants. For example, oxygenation reactions mediated by cytochrome P-450 make an outstanding contribution during the metabolization of recalcitrant pollutant compounds in several ligninolytic fungi [64].
Studies in which Pycnoporus spp. were used in the bioremediation of different pollutants have focused on the use of fungal mycelial mass or on the exploration of the capability of free oxidative enzymes, especially laccases. To expand the applicability of Pycnoporus laccases, researchers have also invested in the co-producing oxidative enzymes system using fungal consortium [69], in the immobilization of enzymes [70,71,72,73,74] and in the immobilization of fungal cells [75]. The laccase from P. sanguineus CS43, for example, was entrapped in LentiKats®, a particulate commercial polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) gel. The immobilized enzyme revealed remarkable capacity for breaking down m-cresol within 24 h. The kinetics of m-cresol degradation by the LentiKats® captured enzyme were of the Michaelis-Menten type [71]. Another example is the immobilized laccase from P. sanguineus CS43, produced in a relatively large bioreactor (10 L), which was used for breaking down bisphenol A (BPA). Laccases were also entrapped by a multichannel ceramic membrane with 4% glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking inducer. In this case, 100% BPA degradation was seen in less than 24 h when 620 U/L of laccase were added [76]. However, the number of studies dealing with the immobilization of laccases from Pycnoporus spp. is still scarce when compared with the large number of laccases from other WRF that were hitherto immobilized, particularly those of Trametes versicolor [77].
4. Degradation of Pharmaceuticals
The utilization of pharmaceuticals plays a crucial role in safeguarding human health, promoting treatment efficacy, and sustaining the overall productivity of various organisms. However, the widespread use of these pharmaceuticals raises environmental apprehensions due to their frequent presence in both wastewater and drinking water. Following consumption, surplus pharmaceuticals, along with partially metabolized and conjugated forms, typically find their way into wastewater treatment systems. These non-conventional contaminants, also known as emerging contaminants (ECs), exhibit considerable persistence and can evoke undesirable biological effects in aquatic and land-dwelling organisms, frequently at very low concentrations [78].
A combined culture of P. sanguineus and Alcaligenes faecalis was used to develop an effective, renewable, and cheap procedure for breaking down sulfonamides. Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) is a strong inhibitor of the laccase of P. sanguineus. The enhancement of laccase activity by a combined culture of A. faecalis and P. sanguineus significantly improved the elimination of SMX, with simultaneous lowering of the accumulation of N-hydroxy-SMX and consequent diminution of the cytotoxicity of the corresponding end-products. Biotransformation, much more likely than absorption, plays the dominant role in the eradication of SMX by the simultaneous culture of A. faecalis and P. sanguineus [79].
An artificial fungal consortium of P. chrysosporium and P. sanguineus was constructed aiming at exploring the breakdown effectiveness of the antibiotics ciprofloxacin (CIP), norfloxacin (NOR), and sulfamethoxazole (SMX), or combinations of the three compounds. The pure culture of P. sanguineus removed CIP, NOR, and SMX by 98.5%, 96.4%, and 100%, respectively, within two days. The mixture of the three compounds was eliminated from the medium by 100% without biosorption during the same time period. The pure culture of P. chrysosporium was less effective, and removal occurred by both biosorption and biotransformation. The coculture of P. sanguineus with P. chrysosporium was more effective in removing the antibiotics than the culture of P. chrysosporium alone. It is probable that both the laccase and the cytochrome P450 system participated in the breakdown reactions. The MnP possibly participated solely in the SMX removal [69]. The proposed biotransformation pathway of ciprofloxacin and norfluxacin by the fungal consortium of P. chrysosporium and P. sanguineus is illustrated by Figure 3 [69]. The authors used liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC/ESI/MS) in order to identify the compounds resulting from the degradation reactions. The transformation of CIP and NOR in the pure P. chrysosporium culture was proposed to occur by three different routes: (1) defluorination or dehydration; (2) decarboxylation; and (3) oxidation of the piperazinyl substituent. Other pathways also occurred in co-culture and pure P. sanguineus culture, namely (4) monohydroxylation and (5) demethylation or deethylation.
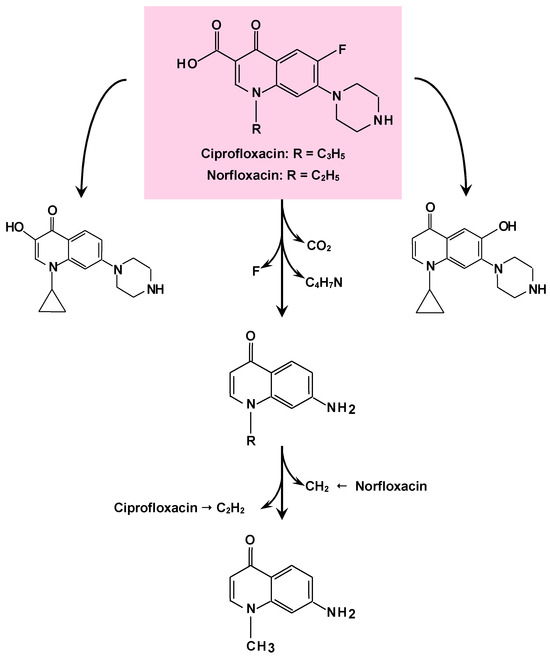
Figure 3.
Proposed biotransformation pathway of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin by the fungal combination of P. chrysosporium and P. sanguineus [69].
A highly resistant laccase (Lac-Q), thermally stable and well adapted to low temperatures, was obtained from Pycnoporus sp. SYBC-L10 [40]. This enzyme was applied to the degradation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline. When coupled to 1.0 mmol/L ABTS, it was able to decompose 100% of tetracycline or oxytetracycline (50 mg/L) within 5 min under static incubation. The Mn2+ ion was inhibitory to tetracycline degradation. Figure 4 illustrates the sequence of reactions that were proposed [40], starting with oxytetracycline, which is based on the identified intermediates during the laccase-mediated oxidation process. The whole process includes deamination, dehydration, and demethylation reactions. It was proposed to use the laccase-Q-ABTS system for treating wastewater containing antibiotics under various temperatures and eventually contaminated with metal ions [40].
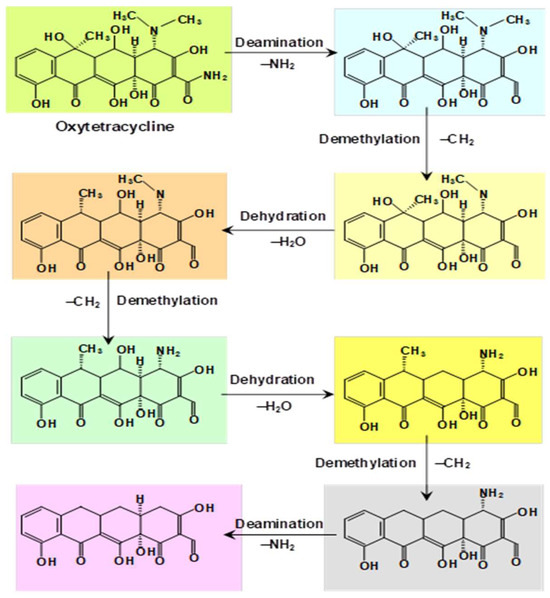
Figure 4.
The proposed sequence of transformation reactions undergone by oxytetracycline in the presence of laccase-Q-ABTS [40].
A Mexican wild strain of P. sanguineus was cultivated in a bioreactor (10 L, stirred) using tomato juice as a growth substrate and CuSO4 plus soybean oil as inducers. Under these conditions, 143,000 IU/L of laccase were obtained, as measured with ABTS as substrate at pH 3.0. Purification revealed two molecular forms (LacI and LacII). Both were used in the decomposition of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), more specifically nonyl-phenol (NP) and the antibacterial agent triclosan (TCS). Both purified laccases, LacI and LacII, were able to remove NP and TCS after 8 h of treatment. The outstanding characteristic of these laccases is their pronounced thermal stability, as indicated by their half-life of 6.1 h at 60 °C [43,80].
Another laccase offering favorable perspectives was isolated from P. sanguineus CS43. This enzyme removed β-naphthol (97%), 2,4-dichlorophenol (71%), and diclofenac (50%) within 8 h. It was more efficient in transforming 5,7-diiodo-8-hydroxyquinoline, with 78% degradation after 3.5 h [81].
5. Decolorization and Degradation of Synthetic Dyes by Pycnoporus spp. and Their Enzymes
Pollution by synthetic dyes is one of the major environmental problems worldwide. The dyeing process of textiles demands large water volumes. Even if the concentration of dyes is relatively low in industrial effluents, they are highly visible for obvious reasons and constitute a quite undesirable phenomenon [82]. Dyes in solution are difficult to eliminate, and simple exposure to light, water, and even chemicals is not very effective in this respect due to their chemical structure. Additionally, aerobic treatment by sewerage systems scarcely contributes to the decolorization of textile dye effluents. For all these reasons, dyes are by far the main pollutants released into the environment by the textile industry [83]. The problem is further enhanced by the fact that 80% of the total discharge from the industries goes into the water stream. The development of efficient dye decolorization methods is, thus, a crucial issue, and this is a topic where WRF and laccases could play an important role [84]. However, the number of attempts at using cells of Pycnoporus spp. and their enzymes in the decomposition of dyes, as outlined below, is still relatively small.
Dye removal must not necessarily imply chemical transformation, as physical methods can equally be used. Adsorption is one such method, which was employed using P. sanguineus loaded on magnetic alginate beads for removing the synthetic dye malachite green from an aqueous solution [85]. The immobilized cells of P. sanguineus efficiently removed malachite green. In this work, no attempts were made at evaluating the participation of P. sanguineus enzymes in the decolorization of malachite green, a phenomenon that might, notwithstanding, have occurred.
Recent investigations have shown that laccases from Pycnoporus spp. have potential for use in the degradation of dyes, differing substantially in structural terms. In a response surface optimization study, the Pycnoporus sanguineus RP15 laccase was obtained by growing the fungus on wheat bran and corncob under solid-state fermentation. The laccases effectively discolored the dyes Bromophenol Blue, Remazol Brilliant Blue R, and Reactive Blue 4 [86]. An optimized culture broth (containing mainly laccase) of a new strain of P. sanguineus, isolated from forested areas in Uruguay, revealed a pronounced ability to decolorize various recalcitrant synthetic pigments, such as, for example, Acid Red 88 (AR88), Reactive Black 5 (RB5), and Lanaset Grey G (LG). At appropriate enzyme concentrations and reaction times, almost 70% of AR88 was transformed without adding redox mediators. For the two other dyes, however, the addition of redox mediators was necessary for achieving decolorization. Methyl syringate was the most effective mediator for AR88 (reaching a discoloration degree of over 90%) and RB5 (nearly 70%). Around 80% of LG could be decolorized using violuric acid [87]. Laccase from P. sanguineus MUCL 38531 was able to decolorize the dyes Reactive Black (93.2%), Crystal Violet (90%), Basic Fuchsin (83.4%), and Congo Red (88.2%) [42]. The crude laccase extract from P. sanguineus CS43 was purified, and the laccase fractions (Lac-I and Lac-II) were used to remove the RBBR dye. In this case, the decomposition efficiencies were between 82 and 88% after 3 h for both laccase fractions [71].
6. Degradation of Flame Retardants and Pesticides
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) stands out as one of the most extensively utilized brominated flame retardants, finding widespread application in electronic devices, furniture, plastics, and textiles. Its presence is recurrently detected in water, soil, air, and living organisms, including humans, prompting concerns within the scientific community regarding potential adverse health implications. Human exposure to TBBPA primarily occurs through dietary intake, inhalation, and skin contact. A plethora of in vivo and in vitro investigations employing animal and cellular models have showcased TBBPA’s capacity to elicit diverse effects on both cells and animals, potentially leading to toxicities to the kidneys, liver, heart, nerves, and reproductive system. Nonetheless, conflicting reports exist asserting the safety of TBBPA as a chemical [88]. Mycelia from P. sanguineus obtained in liquid medium were used in the removal of TBBPA and Cr(VI) combined pollutants [88,89]. In the first study, it was observed that augmentation of the Cr(VI) levels was prejudicial to the removal of TBBPA, the fungal growth, and intracellular protein synthesis. This inhibition led to decreased cell viability as well as compromised cell membrane integrity and alterations in cell morphology and structure. Notably, the study did not explore the involvement of lignin-degrading enzymes in the process [89]. In a subsequent investigation, the activities of two common extracellular lignin-degrading enzymes of P. sanguineus, namely Mn peroxidase and laccase, were found to decrease with higher Cr(VI) levels. The elevated Cr(VI) levels also impeded the gene expression of four intracellular enzymes associated with TBBPA decomposition. The enzymes were two cytochrome P450s, glutathione S-transferases, and pentachlorophenol 4-monooxygenase. These suppressions determined a reduced efficiency of TBBPA decomposition by the fungal cells and decreased levels of intracellular enzymes [90].
Triphenyl phosphate (TPhP), belonging to the group of aryl organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs), has found extensive application in a wide array of industrial items, such as, for example, plastics, electrical devices, building materials, textiles, and paints [91]. The ease with which TPhP can permeate the environment is attributed to its physical addition to products without being covalently bound to the polymer matrix [92]. With its usage on the rise, TPhP has been consistently identified in most environments in recent years, from air to water and from soil to sediments [93,94].
For the reasons delineated above, the potential of P. sanguineus to degrade TPhP was further evaluated [90]. Around 63% of 5 mg/L TPhP was biodegraded by P. sanguineus. Seven biodegradation products were found. Their structures, shown in Figure 5, indicate that TPhP underwent oxidative cleavage, hydroxylation, and methylation. The proteomic analysis revealed that cytochrome P450s, aromatic compound dioxygenase, oxidizing species-generating enzymes, methyltransferases, and MFS general substrate transporters are probably involved in the TPhP biotransformation. Carboxylesterase and glutathione S-transferase were induced to resist TPhP stress [90].

Figure 5.
The proposed transformations suffered by triphenyl phosphate in a culture of P. sanguineus [90].
The degradation of well-known pesticides by Pycnoporus sanguineus was also the objective of some recent studies. Such liquid cultures of P. sanguineus MCA16 transformed diuron by 56% in 40 days of cultivation. This was accompanied by the production of three metabolites with higher polarity. Two of them could be identified and were DCPU (N-3,4-dichlorophenylurea) and DCPMU (N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methylurea) [95]. Diuron was a strong inducer of laccase, but the enzyme failed to catalyze the transformation of the herbicide in vitro. This observation allows us to infer that the biodegradation of diuron by the fungus was not caused by the laccase. This leads to the hypothesis that cytochrome P450 enzymes can probably be the catalytic agents involved, as illustrated by Figure 6. The cytochrome P450 (CYP450) protein family comprises versatile oxidoreductases found widely across living organisms, initially identified in the early 1960s [96]. Belonging to the oxygenase enzyme group, CYP450s facilitate electron transfer to oxygen, thereby catalyzing the oxidation of diverse organic compounds. The general reaction for CYP450s can be succinctly expressed as: RH + NAD(P)H + H+ + O2 → ROH + NAD(P)+ + H2O. Because of their potent capabilities, a broad spectrum of substrates, and the ability to catalyze diverse reactions, CYP450s exhibit significant potential for practical applications. Additionally, CYP450s play a crucial role in the degradation of various organic pollutants by white rot fungi [64,97].
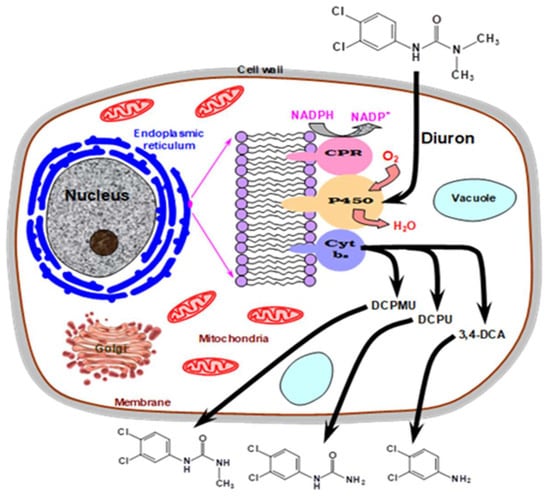
Figure 6.
Involvement of cellular components of P. sanguineus MCA16 in the transformation suffered by the pesticide diuron. Abbreviations: CPR, cytochrome P450 reductase; P450, cytochrome P450; Cyt b5, cytochrome b5; DCPMU, N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methylurea; DCPU, N-3,4-; 3,4-DCA, N-3,4-diphenyl amine. The scheme above was inspired in a similar illustration presented in [95].
P. sanguineus H1 was cultured in mineral liquid medium, and the degradation breakdown of anthracene and pyrene was studied using intra- and extracellular systems. P. sanguineus H1 degraded both anthracene and pyrene. Anthracene is metabolized by this fungus via intracellular cytochrome P450 and by both mycelium-associated and extracellular laccases. On the other hand, pyrene seems to be degraded only by cytochrome P450. In vitro, laccase degraded 59.9% of a solution of 1 mg/L of anthracene after 24 h [98].
7. Perspectives and Conclusions
Despite the numerous benefits associated with the use of Pycnoporus spp. in bioremediation, as outlined in the various sections of this review, their widespread application in this field is often impeded by certain factors. A primary challenge lies in the fact that among the four Pycnoporus species, only P. sanguineus has found extensive use in pollutant bioremediation, while those from P. cinnabarinus, P. puniceus, and P. coccineus have only been sporadically employed in such studies. Consequently, the potentialities of the latter three species are largely unknown, making further studies highly desirable.
The second hindrance is linked to the limited availability of commercial laccases from Pycnoporus spp. Currently, six major laccase suppliers globally—Novozymes, DuPont, Amano Enzyme, Yiduoli, Sunson, and Denykem—largely offer laccases sourced from Trametes sp. [99]. It is crucial to emphasize that increased research efforts are necessary to produce substantial quantities of Pycnoporus laccases on a laboratory scale. It is hoped that the promising data summarized in the present review can attract biotechnology companies to invest in large-scale enzyme production, given the distinctive advantages of Pycnoporus sanguineus laccase, including ease of cultivation and the potential for high production yields. Two characteristics make Pycnoporus laccases particularly useful for application in large-scale bioremediation processes: high redox potential and high thermostability. Such characteristics have already been well established in studies of enzyme production and in the bioremediation processes of different pollutants in laboratory-scale crops. In terms of these factors, the Pycnoporus sanguineus enzyme is poised to competitively match its Trametes sp. counterpart.
Author Contributions
V.M.S.C.: Investigation, Methodology. T.M.U.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology. L.F.O.d.S.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology. E.B.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology. M.P.D.: Formal analysis, Investigation; Validation. A.G.C.: Writing—review and editing. R.C.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. C.G.M.d.S.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. R.C.G.C.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. A.B.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. R.M.P.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank the Foundation for Research Support of Paraná (Fundação Araucária), and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento) for the financial support for this research. R.M. Peralta, and A. Bracht are research fellows of CNPq. R.C.G. Corrêa is a research fellow of Cesumar Institute of Science, Technology and Innovation (ICETI). A.G. Contato is research fellow of São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP Process n.° 2023/08824-4).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data were created in the present work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Navina, B.K.; Velmurugan, N.K.; Kumar, P.S.; Rangasamy, G.; Palanivelu, J.; Thamarai, P.; Vickram, A.S.; Saravanan, A.; Shakoor, A. Fungal bioremediation approaches for the removal of toxic pollutants: Mechanistic understanding for biorefinery applications. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, R.M.; da Silva, B.P.; Côrrea, R.C.G.; Kato, C.G.; Seixas, F.A.V.; Bracht, A. Enzymes from basidiomycetes—Peculiar and efficient tools for biotechnology. In Biotechnology of Microbial, Enzymes; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 119–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voběrková, S.; Solčány, V.; Vršanská, M.; Adam, V. Immobilization of ligninolytic enzymes from white-rot fungi in cross-linked aggregates. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andlar, M.; Rezić, T.; Marđetko, N.; Kracher, D.; Ludwig, R.; Šantek, B. Lignocellulose degradation: An overview of fungi and fungal enzymes involved in lignocellulose degradation. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakratsas, G.; Antoniadis, K.; Athanasiou, P.E.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H. Laccase and Biomass Production via Submerged Cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus using wine lees. Biomass 2024, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uber, T.M.; Backes, E.; Saute, V.M.S.; Silva, B.P.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Kato, C.G.; Seixas, F.A.V.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Enzymes from basidiomycetes—Peculiar and efficient tools for biotechnology. In Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes—Production, Catalysis, and Industrial Applications; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Chapter 6; pp. 129–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, C.; Sain, M.; Qin, W. Lignin utilization: A review of lignin depolymerization from various aspects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, A.; Hibbett, D.S. Phylogenetic classification of Trametes (Basidiomycota, Polyporales) based on a five–marker dataset. Taxon 2011, 60, 1567–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téllez-Téllez, M.; Villegas, E.; Rodríguez, A.; Acosta-Urdapilleta, M.L.; O’Donovan, A.; Díaz-Godínez, G. Fungi of Pycnoporus: Morphological and moleculer identification, worldwide distribution and biotechnological potential. Mycosphere 2016, 11, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomascolo, A.; Uzan-Boukhris, E.; Herpoel-Gimbert, I.; Sigoillot, J.C.; Lesage-Meessen, L. Peculiarities of Pycnoporus species for applications in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 1129–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinar, E.; Rios, N.; Spadafora, C.; Arnold, A.E.; Coley, P.D.; Kursar, T.A.; Gerwick, W.H.; Cubilla-Rios, L. Coibanoles, a new class of meroterpenoids produced by Pycnoporus sanguineus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welti, S.; Moreau, P.; Favel, A.; Courtecuisse, R.; Haon, M.; Navarro, D.; Taussac, S.; Lesage-Meessen, L. Molecular phylogeny of Trametes and related genera, and description of a new genus Leiotrametes. Fungal Divers. 2012, 55, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinagl, C.W.; Siewert, B.; Hammerle, F.; Spes, G.; Peintner, U.; Schlierenzauer, M.; Vrabl, P. Growth, morphology, and formation of cinnabarin in Pycnoporus cinnabarinus in relation to different irradiation spectra. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2023, 22, 2861–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage-Meessen, L.; Haon, M.; Uzan, E.; Levasseur, A.; Piumi, F.; Navarro, D.; Taussac, S.; Favel, A.; Lomascolo, A. Phylogeographic relationships in the polypore fungus Pycnoporus inferred from molecular data. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 325, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, C.O.; Levin, L.; Mentaberry, A.; Wirth, S. A First Insight into Pycnoporus sanguineus BAFC 2126 Transcriptome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur, A.; Lomascolo, A.; Chabrol, O.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Boukhris-Uzan, E.; Piumi, F.; Kües, U.; Ram, A.F.J.; Murat, C.; Haon, M.; et al. The genome of the white-rot fungus Pycnoporus cinnabarinus: A basidiomycete model with a versatile arsenal for lignocellulosic biomass breakdown. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Jia, G.; Sun, H.; Sun, T.; Hou, D. Genome sequence of the fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus, which produces cinnabarinic acid and pH-and thermo-stable laccases. Gene 2020, 742, 144586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, S.; Hage, H.; Drula, É.; Lesage-Meessen, L.; Berrin, J.; Navarro, D.; Favel, A.; Chaduli, D.; Grisel, S.; Haon, M.; et al. Conserved white-rot enzymatic mechanism for wood decay in the Basidiomycota genus Pycnoporus. DNA Res. 2020, 27, dsaa011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, R.G.; Brambila, O.M.G.; Bedrán, H.V.; Martínez, J.C.G.; Luna, J.A.C.; Brambila, M.M.G. Depolymerization of lignin by extracellular activity of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus, to obtain cellulose. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2023, 21, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asther, M.; Lomascolo, A.; Mi, A.; Moukha, S.; Lesage-Meessen, L. Metabolic pathways of biotransformation and biosynthesis of aromatic compounds for the flavour industry by the basidiomycete Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Micol. Neotrop. Apl. 1998, 11, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Smânia, A.; Marques, C.J.S.; Smânia, E.F.A.; Zanetti, C.R.; Carobrez, S.G.; Tramonte, R.; Loguercio-Leite, C. Toxicity and antiviral activity of cinnabarin obtained from Pycnoporus sanguineus (Fr.) Murr. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Shao, X.; Luo, S.P.; Tian, Q.; Liao, X. Pigment production by a newly isolated strain Pycnoporus sanguineus SYBC-L7 in solid-state fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1015913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentil, J.A.; Thygesen, A.; Mensah, M.; Lange, L.; Meyer, A.S. Cellulase production by white rot basidiomycetous fungi: Solid state versus submerged cultivation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5827–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattanakitjanukul, N.; Sukkasem, C.; Chiersilp, B.; Boonsawang, P. Use of palm empty fruit bunches for the production of ligninolytic enzymes by Xylaria sp. in solid state fermentation. Waste Biomass Valori. 2020, 11, 3953–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, A.N.; Barrena, R.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A. Solid-state fermentation as a novel paradigm for organic waste valorization: A review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, P.M.; Álvarez, A.; De Figueroa, L.I.C.; Pajot, H.F. Boldly going green: Utilizing Pycnoporus sp. for laccase production and sustainable vinasse treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Gao, D. Bioremediation of Diesel-Contaminated Soil by Fungal Solid-State Fermentation. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 112, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, R.S.; Mehant, A.; Suman, S.K. Deciphering ligninolytic enzymes in the secretome of Pycnoporus sp. and their potential in degradation of 2-chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 92830–92841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkoski, D.L.; Guimarães, V.M.; de Almeida, M.N.; Alfenas, A.C.; Colodette, J.L.; de Rezende, S.T. Characterization of cellulolytic extract from Pycnoporus sanguineus PF-2 and its application in biomass saccharification. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1586–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, M.A.A.M.; Jalil, R.; Kalil, M.S. Production of Cellulase from Pycnoporus sanguineus. Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphatsoe, M.M.; Hashem, C.; Ling, J.G.; Horvat, M.; Rumbold, K.; Bakar, F.D.A.; Winkler, M. Characterization and immobilization of Pycnoporus cinnabarinus carboxylic acid reductase, PcCAR2. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 345, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.K.; Turner, N.J.; Jones, P.R. Carboxylic acid reductase is a versatile enzyme for the conversion of fatty acids into fuels and chemical commodities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.N.; Silva, A.T.; Nascimento, J.S.D.; De Souza, C.B.; Da Costa Silva, M.; Grillo, L.A.M.; Da Luz, J.M.R.; Pereira, H.J.V. Production, characterization, and application of a new chymotrypsin-like protease from Pycnoporus sanguineus. Biocatal. Biotransfor. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Zhao, Y. Hazardous contaminants in the environment and their laccase-assisted degradation—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, J.C.P.; Marques, N.P.; Monteiro, D.A.; Martins, G.M.; de Paula, A.V.; Silva, R.; Gomes, E.; Cocchini, D.A. Saccharification of pretreated sugarcane bagasse using enzymes solution from Pycnoporus sanguineus MCA 16 and cellulosic ethanol production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Z.; Ma, H.; Terry, N. Fungal laccase production from lignocellulosic agricultural wastes by solid-state fermentation: A review. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber-Zucker, S.; Mateljak, I.; Goldsmith, M.; Kupervaser, M.; Alcalde, M.; Fleishman, S.J. Designed High-Redox Potential Laccases exhibit high functional diversity. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 13164–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzan, E.; Nousiainen, P.; Balland, V.; Sipila, J.; Piumi, F.; Navarro, D.; Asther, M.; Record, E.; Lomascolo, E. High redox potential laccases from the ligninolytic fungi Pycnoporus coccineus and Pycnoporus sanguineus suitable for white biotechnology: From gene cloning to enzyme characterization and applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 2199–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbardi, A.L.R.L.; Camargo, P.F.; Carli, S.; Neto, S.A.; Meleiro, L.P.; Rosa, J.C.; De Andrade, A.R.; Jorge, J.A.; Furriel, R.P.M. A high redox potential laccase from Pycnoporus sanguineus RP15: Potential application for dye decolorization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Dou, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Meng, D.; Zhai, L.; Shen, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, G.; Liao, X. Characterization of a robust cold-adapted and thermostable laccase from Pycnoporus sp. SYBC-L10 with a strong ability for the degradation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline by laccase-mediated oxidation. J. Hazard. Mat. 2020, 382, 121084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardado, A.L.P.; Belleville, M.P.; Alanis, M.J.R.; Sanches-Marcan, J. Effect of redox mediators in pharmaceuticals degradation by laccase: A comparative study. Process Biochem. 2019, 78, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malci, K.; Kurt-Gur, G.; Tamerler, C.; Yazgan-Karatas, A. Combinatorial decolorization performance of Pycnoporus sanguineus MUCL 38531 sourced recombinant laccase/mediator systems on toxic textile dyes. Int. J. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2023, 20, 951–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Cavazos, L.I.; Junghanns, C.; Nair, R.; Cardenas-Chavez, D.L.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Agathos, S.N.; Parra, R. Enhanced production of thermostable laccases from a native strain of Pycnoporus sanguineus using central composite design. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golveia, J.C.S.; Santiago, M.F.; Sales, P.T.F.; Sartoratto, A.; Ponezi, A.N.; Thomaz, D.V.; Gil, E.S.; Bara, M.T.F. Cupuaçu (Theobroma grandiflorum) residue and its potential application in the bioremediation of 17-A-ethinylestradiol as a Pycnoporus sanguineus laccase inducer. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 48, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, J.W.C. Sustainable composting and its environmental implications. In Sustainable Resource Recovery and Zero Waste Approaches; Mohammad, J.T., Bolton, K., Wong, J., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheute, V.M.S.; Backes, E.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Corrêa, V.G.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. The global market for mushrooms, their uses as dietary supplements and associated safety issues. In Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis; Stojkovic, D., Barros, L., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Chapter 11; pp. 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Soto, G.; Medina González, G.E.; García Zambrano, E.A.; Treviño Ramírez, J.E.; Hernández Luna, C.E. Selection and characterization of a native Pycnoporus sanguineus strain as a lignocellulolytic extract producer from submerged cultures of various agroindustrial wastes. Bioresources 2015, 10, 3564–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.D.; Paiva, I.M.A.; Castrillo, M.L.; Zapata, P.D.; Villalba, L.L. KH2PO4 improves cellulase production of Irpex lacteus and Pycnoporus sanguineus. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saat, M.N.; Annuar, M.S.M.; Alias, Z.; Chuan, L.T.; Chisti, Y. Modeling of growth and laccase production by Pycnoporus sanguineus. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Feng, M.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Degradation of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether by Pycnoporus sanguineus in the presence of copper ions. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, M.; Piumi, F.; Cullen, D.; Record, E.; Faulds, C.B. Heterologous production and characterization of two glyoxal oxidases from Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4867–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Godínez, G.; Téllez-Téllez, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Obregón-Barbosa, V.; Acosta-Urdapilleta, M.D.L.; Villegas, E. Enzymatic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and insecticidal activities of Pleurotus pulmonarius and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus grown separately in an airlift reactor. Bioresources 2016, 11, 4186–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niderhaus, C.; Garrido, M.; Insani, M.; Campos, E.; Wirth, S. Heterologous production and characterization of a thermostable GH10 family endo-xylanase from Pycnoporus sanguineus BAFC 2126. Proc. Biochem. 2018, 67, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhonghua, Y.; Liao, X.; Liu, J.; Mao, F.; Huang, Q. Scalable production, fast purification, and spray drying of native Pycnoporus laccase and circular dichroism characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echezonachi, S.O. The role of white rot fungi in bioremediation. In Microbes and Microbial Biotechnology for Green Remediation Elsevier eBooks; Malik, J.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, R.; Fan, F. A comprehensive insight into the application of white rot fungi and their lignocellulolytic enzymes in the removal of organic pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellouze, M.; Sayadi, S. White-rot fungi and their enzymes as a biotechnological tool for xenobiotic bioremediation. In Management of Hazardous Wastes; El-Din, H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, R.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Ashraf, S.S. Laccases and peroxidases: The smart, greener and futuristic biocatalytic tools to mitigate recalcitrant emerging pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.K.; Österman-Udd, J.; Mali, T.; Lundell, T. Basidiomycota Fungi and ROS: Genomic Perspective on Key Enzymes Involved in Generation and Mitigation of Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Fungal Biol. 2022, 3, 837605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R. ROS are good. Trends Plants Sci. 2017, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, G.M.; Inácio, F.D.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Castoldi, R.; Comar, J.F.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Response of Ganoderma lucidum and Trametes sp. to the herbicide picloram: Tolerance, antioxidants and production of ligninolytic enzymes. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 105, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, E.; Kato, C.G.; De Oliveira, V.A.; Uber, T.M.; Santos, L.F.O.D.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Overproduction of Laccase by Trametes versicolor and Pycnoporus sanguineus in Farnesol-Pineapple Waste Solid Fermentation. Fermentation 2023, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresnar, B.; Petric, S. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in the fungal kingdom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wei, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhuo, R. Bioremediation of organic pollutants by white rot fungal cytochrome P450: The role and mechanism of CYP450 in biodegradation. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łebkowska, M.; Załęska-Radziwiłł, M. Application of white-rot fungi for biodegradation of refractory organic compounds—A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 3708–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijoma, G.N.; Tekere, M. Potential microbial applications of co-cultures involving ligninolytic fungi in the bioremediation of recalcitrant xenobiotic compounds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1787–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.E.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Putti, F.F.; Santos, F.A.; Forti, J.C. Degradation of commercial glyphosate-based herbicide via advanced oxidative processes in aqueous media and phytotoxicity evaluation using maize seeds. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, J.C.; Loretti, G.H.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; de Andrade, A.R. A phytotoxicity assessment of the efficiency 2,4-D degradation by different oxidative processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Liu, C.X.; Xu, Q.M.; Cheng, J.S.; Yuan, Y.J. Simultaneous removal of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, sulfamethoxazole by co-producing oxidative enzymes system of Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pycnoporus sanguineus. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.F.; Lacerda, M.F.A.R.; Thomaz, D.V.; de Souza-Golveia, J.C.; Pereira, M.D.G.C.; de Souza-Gil, E.; Schimidt, F.; Santiago, M.F. Optimization of laccase–alginate–chitosan-based matrix toward 17 α-ethinylestradiol removal. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Coronel, L.A.; Cobas, M.; Rostro-Alanis, M.J.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á. Immobilization of laccase of Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Long, S.Y.; Huang, J.; Xiao, H.; Ju-Ying, Z. Immobilization of Pycnoporus sanguineus laccase on magnetic chitosan microspheres. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 25, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, R.; García-García, A.; Orana-Navar, C.; Osma, J.F.; Nigam, K.D.P.; Ornelas-Soto, N. Biotransformation of emerging pollutants in groundwater by laccase from P. sanguineus CS43 immobilized onto titania nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Delgado, M.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Martínez-Lorán, E.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; García-García, A.; Contreras-Torres, F.F. Enhanced enzymatic activity of laccase (from Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43) immobilized on sputtered nanostructured gold thin films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.S.; Don, M.M. Optimization of process variables for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Pycnoporus sanguineus using statistical experimental design. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2013, 56, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Estrada, C.; Rostro-Alanis, M.J.; Parra, A.L.; Belleville, M.P.; Sanchez-Marcano, J.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldivar, T. Potentialities of active membranes with immobilized laccase for Bisphenol A degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyomuhimbo, H.D.; Brink, H.G. Applications and immobilization strategies of the copper-centred laccase enzyme: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uber, T.M.; Buzzo, A.J.D.R.; Scaratti, G.; De Amorim, S.M.; Helm, C.V.; Maciel, G.M.; Peralta, R.A.; Moreira, R.F.P.M.; Bracht, A. Comparative detoxification of Remazol Brilliant Blue R by free and immobilized laccase of Oudemansiella canarii. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2022, 40, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Q.M.; Cheng, J.S.; Yuan, Y.J. Improving the bioremoval of sulfamethoxazole and alleviating cytotoxicity of its biotransformation by laccase producing system under coculture of Pycnoporus sanguineus and Alcaligenes faecalis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Cavazos, L.I.; Junghanns, C.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Cardenas-Chávez, D.L.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Demarche, P.; Enaud, E.; Garcia-Morales, R.; Agathos, S.N.; Parra, R. Purification and characterization of two thermostable laccases from Pycnoporus sanguineus and potential role in degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 108, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Delgado, M.; Orona-Navar, C.; García-Morales, R.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Parra, R.; Mahlknecht, J.; Ornelas-Soto, N. Biotransformation kinetics of pharmaceutical and industrial micropollutants in groundwaters by a laccase cocktail from Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43 fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 108, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.S.; Udayanga, D.; Jayasanka, D.J.; Hewawasam, C. Textile dye decolorization by white rot fungi–A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouni, A.; Fersi, C.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Bes-Piá, A.; Alcaina–Miranda, M.I.; Dhahbim, M. Reactive dyes rejection and textile effluent treatment study using ultrafiltration and nanofiltration processes. Desalination 2012, 297, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyabalan, J.; Veluchamy, A.; Priyan, V.V.; Kumar, A.; Chandrasekar, R.; Narayanasamy, S. A review on the laccase assisted decolourization of dyes: Recent trends and research progress. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Shih, M.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Huang, K.S. Magnetic Pycnoporus sanguineus-loaded alginate composite beads for removing dye from aqueous solutions. Molecules 2014, 19, 8276–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iracheta-Cárdenas, M.M.; Rocha-Peña, M.A.; Galán-Wong, L.J.; Arévalo-Niño, K.; Tovar-Herrera, O.E. A Pycnoporus sanguineus laccase for denim bleaching and its comparison with an enzymatic commercial formulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 77, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, L.; Manta, C.; Ovsejevi, K.; Burgueño, J.; Menéndez, P.; Rodriguez-Couto, S. Enhancing laccase production by a newly-isolated strain of Pycnoporus sanguineus with high potential for dye decolouration. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 34096–34103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Li, H.; You, S.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, M.; Zhou, J. Effect of hexavalent chromium on the biodegradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) by Pycnoporus sanguineus. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Influence of co-existed tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) and hexavalent chromium on the cellular characteristics of Pycnoporus sanguineus during their removal and reduction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Zhou, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Mao, W. Bioremediation of triphenyl phosphate by Pycnoporus sanguineus: Metabolic pathway, proteomic mechanism and biotoxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, X.; Thai, P.K.; Baduel, C.; Gallen, C.; Banks, A.P.W.; Bainton, P.; English, K.; Mueller, J.F. Organophosphate and brominated flame retardants in Australian indoor environments: Levels, sources, and preliminary assessment of human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Li, D.Q.; Mu-Ning, Z.; Liao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Z. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: Sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, H.J.; Choi, W.; Moon, H. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in water and sediment: Occurrence, distribution, and hotspots of contamination of Lake Shihwa, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, R.; He, J.; Ma, H.; Zhao, F.; Tao, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, J. Triphenyl phosphate at environmental levels retarded ovary development and reduced egg production in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14709–14715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, C.; Arakaki, R.M.; Monteiro, D.A.; Boscolo, M.; Da Silva, R.; Gomes, E. Degradation of the organochlorinated herbicide diuron by rainforest basidiomycetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5324391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Waterman, M.R.; Egli, M. Recent structural insights into cytochrome P450 function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Moreira, J.S.; Brugnari, T.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; Castoldi, R.; de Souza, C.G.M.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Evaluation of diuron tolerance and biotransformation by the white-rot fungus Ganoderma Lucidum. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ning, Y.N.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, K.; Yang, S.; La, G.; Sun, X.; Li, X. Contrasting characteristics of anthracene and pyrene degradation by wood rot fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus H1. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerva, A.; Simić, S.; Topakas, E.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Applications of Microbial laccases: Patent Review of the past decade (2009–2019). Catalysts 2019, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).