From Counters to Telemetry: A Survey of Programmable Network-Wide Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Conceptual Framework: We define and distinguish network-wide monitoring from traditional monitoring approaches, positioning it as a necessary evolution in response to modern network demands.
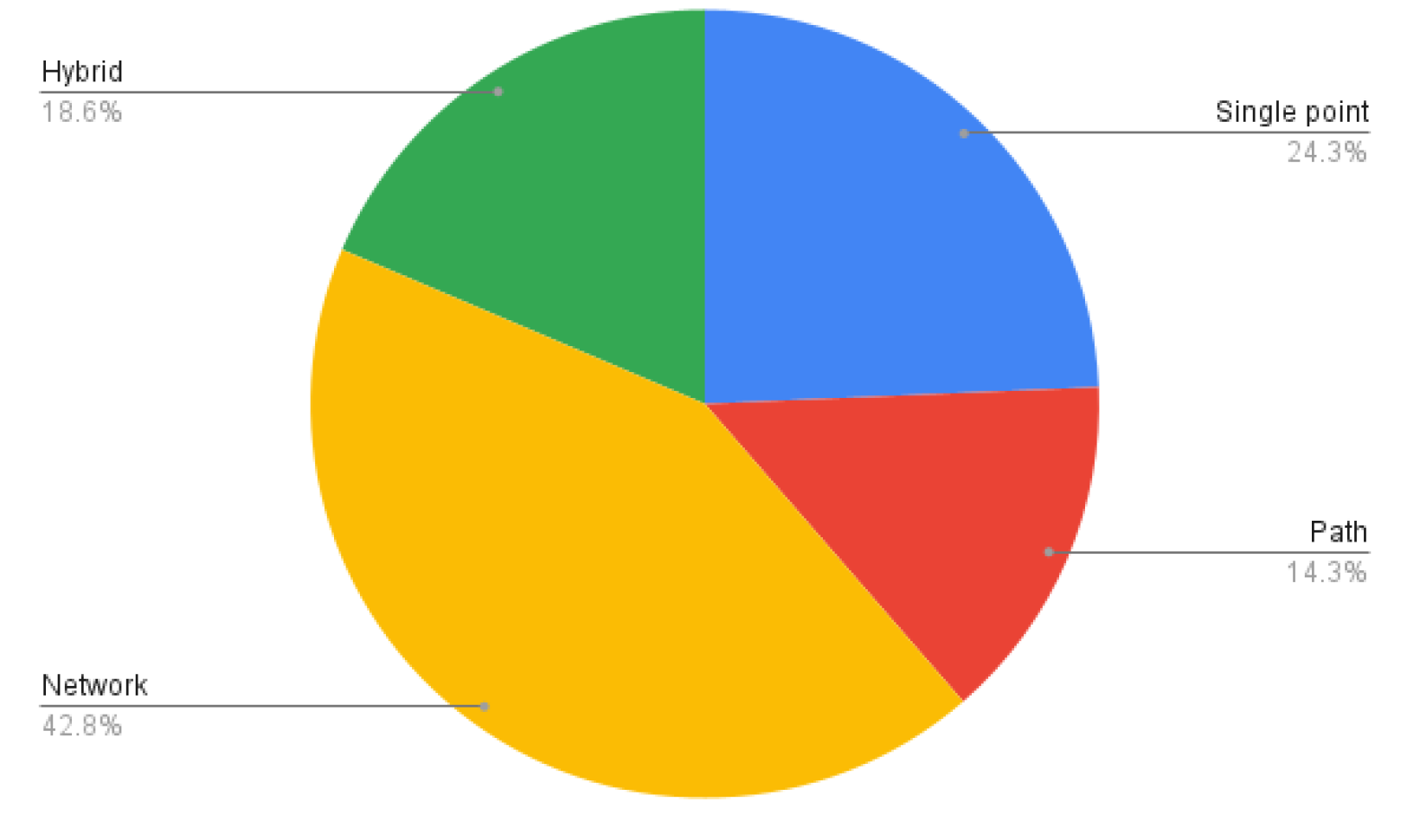
- Taxonomy of Monitoring Architectures: We present an updated taxonomy of monitoring approaches, ranging from single point (device local) techniques and path level measurements to whole network frameworks and hybrid strategies.
- Comprehensive Survey: We review and synthesize over a decade of research on network monitoring systems, covering both foundational technologies (e.g., SNMP, NetFlow/IPFIX) and emerging paradigms (e.g., SDN, INT, programmable switches).
- Future Directions: We outline open research challenges and future directions for enabling robust, scalable, and intelligent network-wide monitoring.
2. Methodology
2.1. Related Surveys
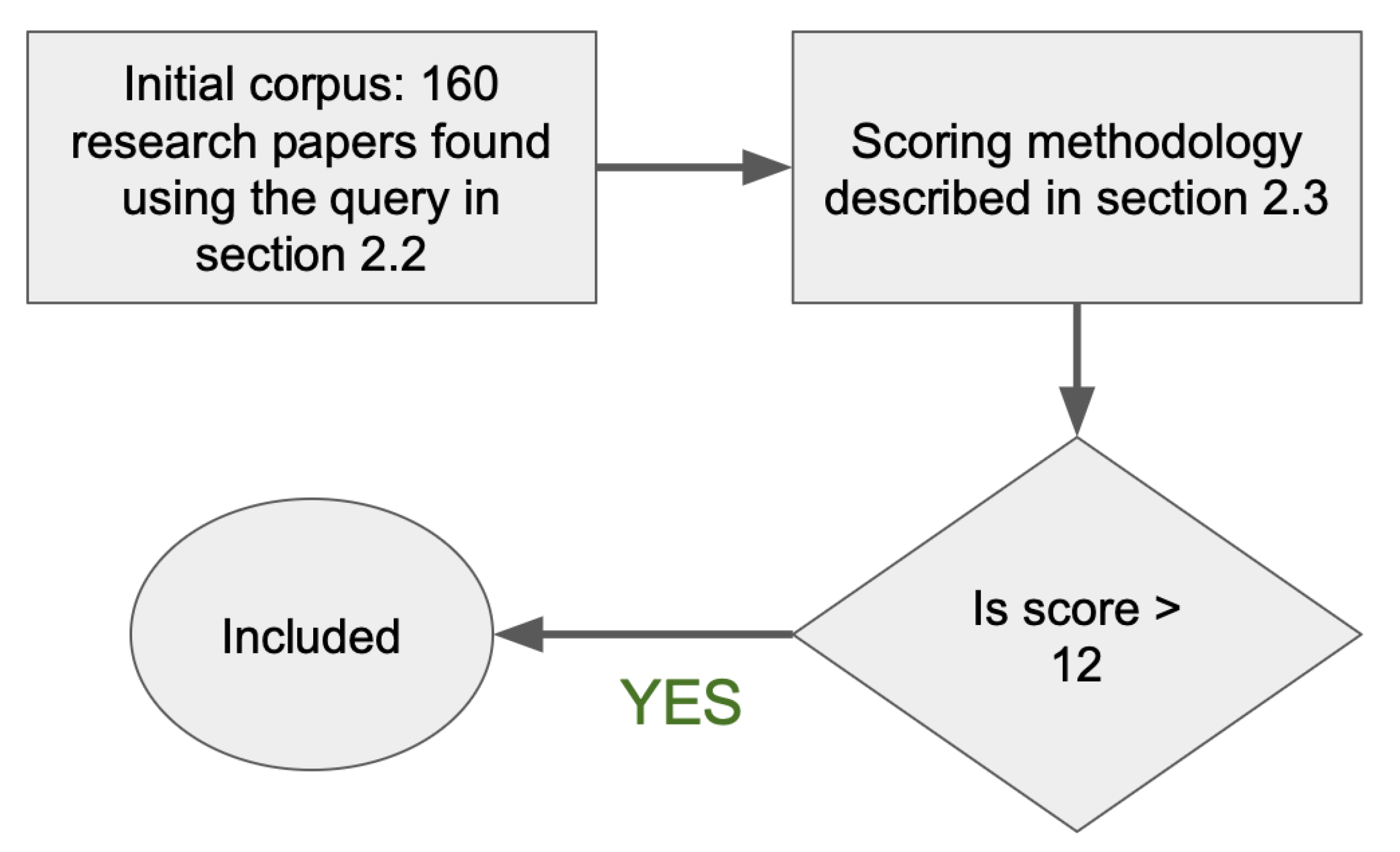
2.2. Article Search and Selection
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library
- Google Scholar
- ACM Digital Library
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Normalized citation impact (0–10)
- Recency (0–5), binned by publication year (<2000 → 0; 2000–2004 → 1; 2005–2009 → 2; 2010–2014 → 3; 2015–2019 → 4; 2020+ → 5)
- Relevance (0–10), an expert assessment of direct fit to network-wide monitoring, technical depth, generality, and evidence of practice.
3. Background in Network Monitoring
3.1. Key Concepts and Terminology
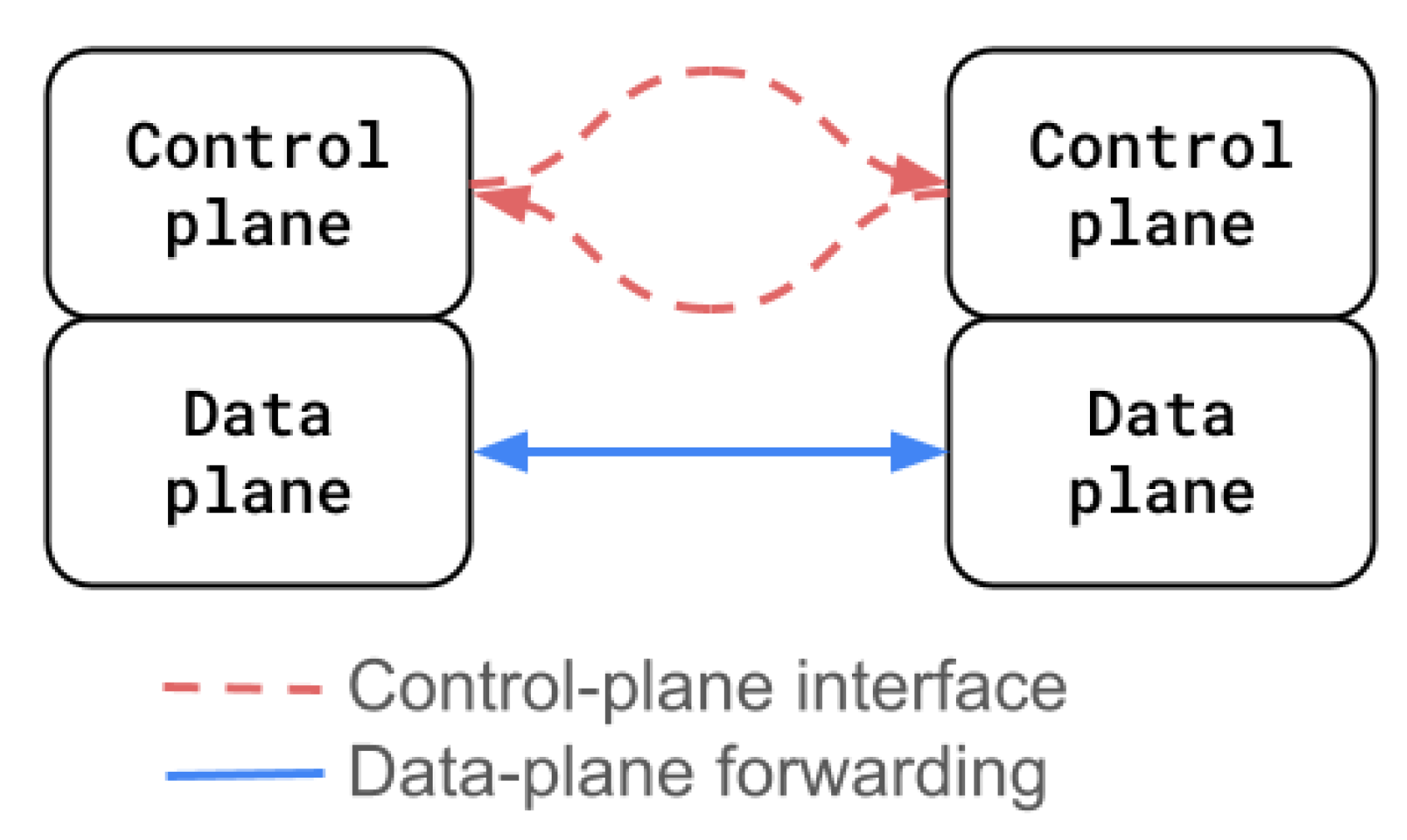
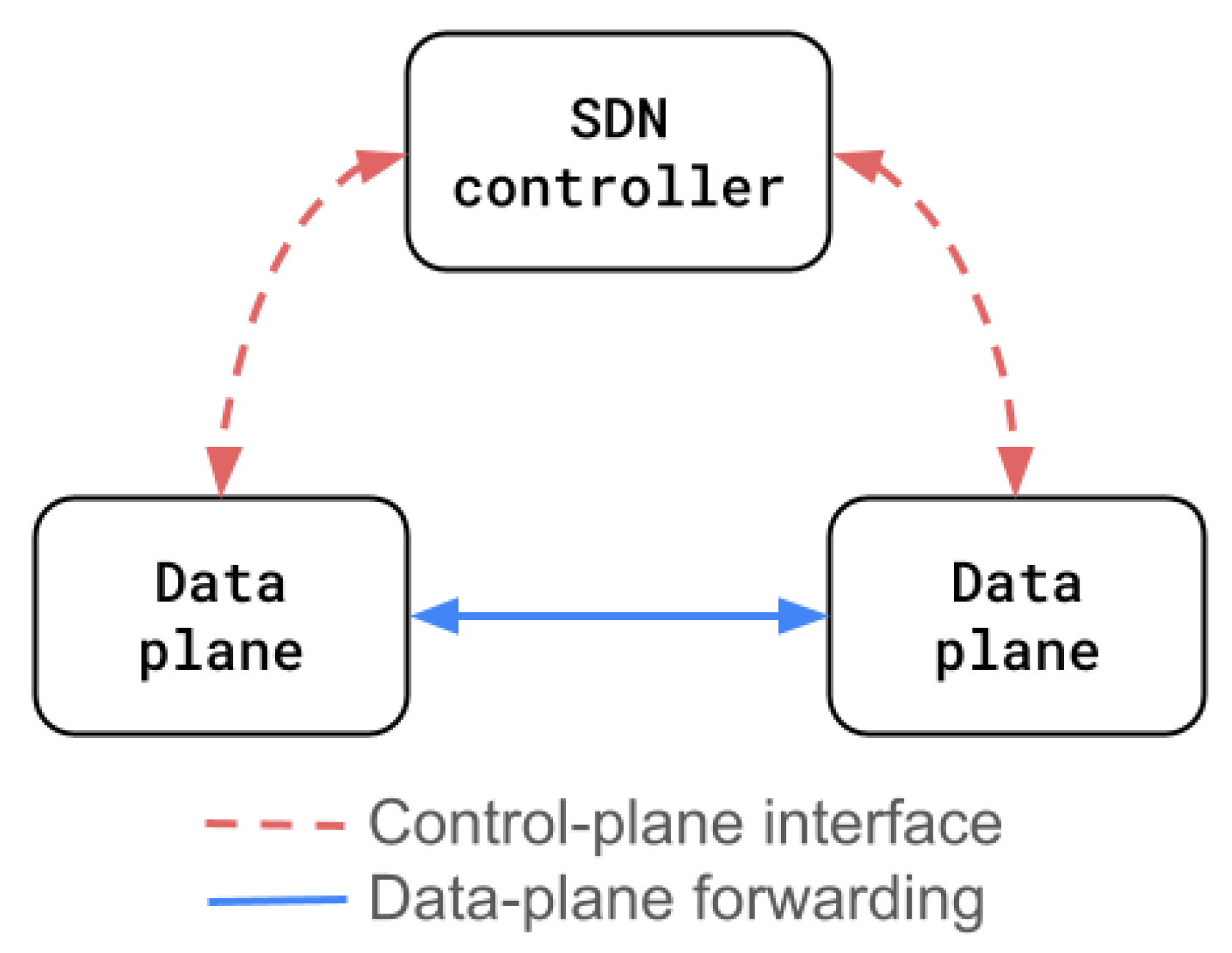
3.2. Architectural Paradigms: Traditional, Software-Defined, and Programmable Networks
3.3. Taxonomy
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. Single Point Monitoring
4.2. Path-Based Monitoring
4.3. Network-Wide Monitoring
4.4. Hybrid
5. Open Issues and Future Research Directions
5.1. Scalability
5.2. Performance
5.3. Maintenance and Deployment
5.4. Intent-Based Observability
5.5. Self-Driving Networks
5.6. AI Engineering for Network Monitoring
- Data scarcity and generalization: rare failures and proprietary traces limit pretraining. Synthetic data, transfer learning, federation, and large-scale simulators are needed.
- Latency/compute: inline detection demands model compression, efficient TSFM designs, and edge/offload inference.
- Interpretability/trust: operators need attributions linking anomalies to specific signals or protocol states.
- Systems integration: fit into existing net operation workflows and guardrails.
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5G | Fifth Generation Mobile Network |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| ASIC | Application Specific Integrated Circuit |
| AS | Autonomous System |
| BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| DCM | Distributed and Collaborative Monitoring |
| DPDK | Data Plane Development Kit |
| DDoS | Distributed Denial of Service |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| IBN | Intent-Based Networking |
| INT | In-Band Network Telemetry |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IPFIX | IP Flow Information eXport |
| ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MTU | Maximum Transmission Unit |
| NFV | Network Function Virtualization |
| NMS | Network Management System |
| OSPF | Open Shortest Path First |
| P4 | Programming Protocol-independent Packet Processors |
| PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| SLA | Service Level Agreement |
| SLO | Service Level Objective |
| SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| SR | Segment Routing |
| TCAM | Ternary Content Addressable Memory |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| TTL | Time to Live |
| VLAN | Virtual Local Area Network |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Roughan, M. A case study of the accuracy of SNMP measurements. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2010, 2010, 812979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claise, B. Cisco Systems NetFlow Services Export Version 9. RFC 3954, 2004. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17487/RFC3954 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Li, Y.; Miao, R.; Kim, C.; Yu, M. FlowRadar: A Better NetFlow for Data Centers. In Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 16), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Levanti, K.; Kim, H.S. Network monitoring: Present and future. Comput. Netw. 2014, 65, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Ghafir, I.; Prenosil, V. Network Monitoring Approaches: An Overview. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Netw. Its Secur.—IJCNS 2015, 5, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- So-In, C. A Survey of Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis Tools. 2006. Available online: https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-06/ftp/net_traffic_monitors3.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Kore, A.; Bhat, M.; Gorana, O.; Ghugul, A.; Saha, S. Survey on monitoring of network using open source software. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. (IJRAR) 2019, 6, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Moceri, P. SNMP and Beyond: A Survey of Network Performance Monitoring Tools. 2006. Available online: https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-06/ftp/net_traffic_monitors2.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Tsai, P.W.; Tsai, C.W.; Hsu, C.W.; Yang, C.S. Network Monitoring in Software-Defined Networking: A Review. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 12, 3958–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, C.; Cheng, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Xia, R.; et al. Rethinking Fine-Grained Measurement From Software-Defined Perspective: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 15, 3649–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alconzo, A.; Drago, I.; Morichetta, A.; Mellia, M.; Casas, P. A Survey on Big Data for Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2019, 16, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, J.C.; Mozzaquatro, B.A.; Granville, L.Z. Network-Wide Initiatives to Control Measurement Mechanisms: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 1475–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Su, W.; Zhang, W.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, N. In-band Network Telemetry: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2021, 186, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, N.; Anderson, T.; Balakrishnan, H.; Parulkar, G.; Peterson, L.; Rexford, J.; Shenker, S.; Turner, J. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2008, 38, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bosshart, P.; Daly, D.; Gibb, G.; Izzard, M.; McKeown, N.; Rexford, J.; Schlesinger, C.; Talayco, D.; Vahdat, A.; Varghese, G.; et al. P4: Programming protocol-independent packet processors. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2014, 44, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estan, C.; Keys, K.; Moore, D.; Varghese, G. Building a better NetFlow. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2004, 34, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chuah, C.N.; Mohapatra, P. ProgME: Towards programmable network measurement. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2007, 37, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.R.; Kim, W.; Yalagandula, P. Mahout: Low-overhead datacenter traffic management using end-host-based elephant detection. In Proceedings of the 2011 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 10–15 April 2011; pp. 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Jose, L.; Miao, R. Software defined traffic measurement with OpenSketch. In Proceedings of the 10th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, NSDI’13, Lombard, IL, USA, 2–5 April 2013; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Lumezanu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Singh, V.; Jiang, G.; Madhyastha, H.V. FlowSense: Monitoring Network Utilization with Zero Measurement Cost. In Proceedings of the Passive and Active Measurement, Hong Kong, China, 18–19 March 2013; Roughan, M., Chang, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Malboubi, M.; Wang, L.; Chuah, C.N.; Sharma, P. Intelligent SDN based traffic (de)Aggregation and Measurement Paradigm (iSTAMP). In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2014 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27 April–2 May 2014; pp. 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, J.; He, J.; Gui, J.; Huang, Q. OmniWindow: A General and Efficient Window Mechanism Framework for Network Telemetry. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2023 Conference, ACM SIGCOMM ’23, New York, NY, USA, 10–14 September 2023; pp. 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau-Feibish, S.; Liu, Z.; Rexford, J. Compact Data Structures for Network Telemetry. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Confluence: Improving network monitoring accuracy on multi-pipeline data plane. Comput. J. 2025, bxaf039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Sivaraman, A.; Nathan, V.; Goyal, P.; Arun, V.; Alizadeh, M.; Jeyakumar, V.; Kim, C. Language-Directed Hardware Design for Network Performance Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’17, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–25 August 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Harrison, R.; Canini, M.; Feamster, N.; Rexford, J.; Willinger, W. Sonata: Query-driven streaming network telemetry. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’18, Budapest, Hungary, 20–25 August 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonchack, J.; Michel, O.; Aviv, A.J.; Keller, E.; Smith, J.M. Scaling Hardware Accelerated Network Monitoring to Concurrent and Dynamic Queries With *Flow. In Proceedings of the 2018 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 18), Boston, MA, USA, 11–13 July 2018; pp. 823–835. [Google Scholar]
- Chiesa, M.; Verdi, F.L. Network Monitoring on Multi-Pipe Switches. Proc. Acm Meas. Anal. Comput. Syst. 2023, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, G.S. Traceroute Using an IP Option. RFC 1393. 1993. Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc1393 (accessed on 12 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Snell, Q.O.; Mikler, A.R.; Gustafson, J.L. NetPIPE: A Network Protocol Independent Performance Evaluator. 1996. p. 6. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2813386_NetPIPE_A_Network_Protocol_Independent_Performance_Evaluator (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Katz-Bassett, E.; Madhyastha, H.V.; Adhikari, V.K.; Scott, C.; Sherry, J.; Van Wesep, P.; Anderson, T.; Krishnamurthy, A. Reverse traceroute. In Proceedings of the 7th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, NSDI’10, San Jose, CA, USA, 28–30 April 2010; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Kang, N.; Cao, J.; Greenberg, A.; Lu, G.; Mahajan, R.; Maltz, D.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, B.Y.; et al. Packet-Level Telemetry in Large Datacenter Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Conference on Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’15, London, UK, 17–21 August 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Sivaraman, A.; Katta, N.; Bas, A.; Dixit, A.; Wobker, L.J. In-band Network Telemetry via Programmable Dataplanes. 2015. Available online: https://nkatta.github.io/papers/int-demo.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Kim, Y.; Suh, D.; Pack, S. Selective In-band Network Telemetry for Overhead Reduction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cloud Networking (CloudNet), Tokyo, Japan, 22–24 October 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Basat, R.; Ramanathan, S.; Li, Y.; Antichi, G.; Yu, M.; Mitzenmacher, M. PINT: Probabilistic In-band Network Telemetry. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication on the Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, SIGCOMM ’20, Virtual Event, 10–14 August 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, K.; Papadimitriou, P.; Papagianni, C. Deterministic and Probabilistic P4-Enabled Lightweight In-Band Network Telemetry. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 4909–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Cui, L.; Tso, F.P.; Deng, Y.; Jia, W. OffsetINT: Achieving High Accuracy and Low Bandwidth for In-Band Network Telemetry. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2024, 17, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Yoon, S.; Hong, J.; Pack, S.; Lee, D. Quantized In-band Network Telemetry for Low Bandwidth Overhead Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Prague, Czech Republic, 28–31 October 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, D.; Dang, Y.; Huang, R.; Maltz, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, V.; Pang, B.; Chen, H.; et al. Pingmesh: A Large-Scale System for Data Center Network Latency Measurement and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM Conference on Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’15, London, UK, 17–21 August 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.A.; Luizelli, M.C.; da Costa Filho, R.I.T.; Gaspary, L.P. An optimization-based approach for efficient network monitoring using in-band network telemetry. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Song, E.; Bian, Z.; Lin, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. INT-path: Towards Optimal Path Planning for In-band Network-Wide Telemetry. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Jin, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Deng, K.; Bi, D.; Xiang, D. NetBouncer: Active Device and Link Failure Localization in Data Center Networks. In Proceedings of the 16th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 19), Boston, MA, USA, 26–28 February 2019; pp. 599–614. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, F.; Pan, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. INT-react: An O(E) Path Planner for Resilient Network-Wide Telemetry Over Megascale Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 30th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP), Lexington, KY, USA, 30 October–2 November 2022; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.; Gaspary, L. Advancing Network Monitoring and Operation with In-band Network Telemetry and Data Plane Programmability. In Proceedings of the NOMS 2023–2023 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Miami, FL, USA, 8–12 May 2023; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Su, W.; Shi, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W. GrayINT—Detection and Localization of Gray Failures via Hybrid In-band Network Telemetry. In Proceedings of the 2023 24st Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Sejong, Republic of Korea, 6–8 September 2023; pp. 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Zheng, Y.; Song, E.; Liu, J.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y. INT-Balance: In-Band Network-Wide Telemetry with Balanced Monitoring Path Planning. In Proceedings of the ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 28 May–1 June 2023; pp. 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Pi, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, J. AdapINT: A Flexible and Adaptive In-Band Network Telemetry System Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 5505–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yuan, Q.; Pan, T.; Wang, X.; Cao, J. MTU-Adaptive In-Band Network-Wide Telemetry. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2024, 32, 2315–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverini, M.; Sardellitti, S.; Barbarossa, S.; Cianfrani, A.; Di Lorenzo, P.; Listanti, M. Reducing the In band Network Telemetry overhead through the spatial sampling: Theory and experimental results. Comput. Netw. 2024, 242, 110269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.; Guo, Y.; Kurose, J.; Towsley, D. Locating network monitors: Complexity, heuristics, and coverage. In Proceedings of the Proceedings IEEE 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Miami, FL, USA, 13–17 March 2005; Volume 1, pp. 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, V.; Reiter, M.K.; Willinger, W.; Zhang, H.; Kompella, R.R.; Andersen, D.G. CSAMP: A system for network-wide flow monitoring. In Proceedings of the 5th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, NSDI’08, San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–18 April 2008; pp. 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Malboubi, A.; Chuah, C.N. OpenMeasure: Adaptive flow measurement & inference with online learning in SDN. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 April 2016; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Song, C.; Dai, H.; Shi, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, L. ACM: Accuracy-Aware Collaborative Monitoring for Software-Defined Network-Wide Measurement. Sensors 2022, 22, 7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Liu, Z.; Seshan, S. HeteroSketch: Coordinating Network-wide Monitoring in Heterogeneous and Dynamic Networks. In Proceedings of the 19th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 22), Renton, WA, USA, 4–6 April 2022; pp. 719–741. [Google Scholar]
- Tootoonchian, A.; Ghobadi, M.; Ganjali, Y. OpenTM: Traffic Matrix Estimator for OpenFlow Networks. In Proceedings of the Passive and Active Measurement, Zurich, Switzerland, 7–9 April 2010; Krishnamurthy, A., Plattner, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Wang, T.; Xia, Y.; Hamdi, M. CeMon: A cost-effective flow monitoring system in software defined networks. Comput. Netw. 2015, 92, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, N.; Sonchack, J.; Liu, V. Synchronized network snapshots. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’18, Budapest, Hungary, 20–25 August 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, H.; Lee, P.P.C.; Bai, W.; Zhu, F.; Bao, Y. OmniMon: Re-architecting Network Telemetry with Resource Efficiency and Full Accuracy. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication on the Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, SIGCOMM ’20, Virtual Event, 10–14 August 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 404–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Foster, N.; Schneider, F.B. Causal network telemetry. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on P4 in Europe, EuroP4 ’22, Rome, Italy, 9 December 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudet, C.; Fleury, E.; Lassous, I.G.; Rivano, H.; Voge, M.E. Optimal positioning of active and passive monitoring devices. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM Conference on Emerging Network Experiment and Technology, CoNEXT ’05, Toulouse, France, 24–27 October 2005; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrichem, N.; Doerr, C.; Kuipers, F. OpenNetMon: Network monitoring in OpenFlow Software-Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS), Krakow, Poland, 5–9 May 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Qian, C.; Li, X. Distributed and collaborative traffic monitoring in software defined networks. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, HotSDN ’14, Chicago, IL, USA, 22 August 2014; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Savi, M.; Antichi, G.; Siracusa, D. An Incrementally-Deployable P4-Enabled Architecture for Network-Wide Heavy-Hitter Detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W. Hawkeye: Efficient In-band Network Telemetry with Hybrid Proactive-Passive Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking (ISPA/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom), Melbourne, Australia, 17–19 December 2022; pp. 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummar, D.; Nawab, I.; Kulkarni, S.G. Distributed In-band Network Telemetry. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 23rd International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing Workshops (CCGridW), Bangalore, India, 1–4 May 2023; pp. 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, C.; Bhatia, R.; Gupta, A.; Harrison, R.; Lokshtanov, D.; Willinger, W. Query Planning for Robust and Scalable Hybrid Network Telemetry Systems. Proc. ACM Netw. 2024, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.R.; Rae, I.; Akella, A. Extensible and scalable network monitoring using OpenSAFE. In Proceedings of the 2010 Internet Network Management Conference on Research on Enterprise Networking, INM/WREN’10, San Jose, CA, USA, 27 April 2010; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Bari, M.F.; Ahmed, R.; Boutaba, R. PayLess: A low cost network monitoring framework for Software Defined Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS), Krakow, Poland, 5–9 May 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y. NetVision: Towards Network Telemetry as a Service. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 26th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP), Cambridge, UK, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, D.; Niu, B.; Peng, J.; Zhu, Z. Sel-INT: A Runtime-Programmable Selective In-Band Network Telemetry System. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Zhao, D.; Lu, H. The Processing Method of the Message Based on the In-band Network Telemetry Technology. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Service Science (ICSS), Zhuhai, China, 13–15 May 2022; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handigol, N.; Heller, B.; Jeyakumar, V.; Mazières, D.; McKeown, N. I know what your packet did last hop: Using packet histories to troubleshoot networks. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, NSDI’14, Seattle, WA, USA, 2–4 April 2014; pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Rasley, J.; Stephens, B.; Dixon, C.; Rozner, E.; Felter, W.; Agarwal, K.; Carter, J.; Fonseca, R. Planck: Millisecond-scale monitoring and control for commodity networks. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2014, 44, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Kwon, T.; Dixon, C.; Felter, W.; Carter, J. OpenSample: A Low-Latency, Sampling-Based Measurement Platform for Commodity SDN. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 34th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Madrid, Spain, 30 June–3 July 2014; pp. 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Manousis, A.; Vorsanger, G.; Sekar, V.; Braverman, V. One Sketch to Rule Them All: Rethinking Network Flow Monitoring with UnivMon. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGCOMM Conference, SIGCOMM ’16, Florianopolis, Brazil, 22–26 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.; Cai, Q.; Gupta, A.; Rexford, J. Network-Wide Heavy Hitter Detection with Commodity Switches. In Proceedings of the Symposium on SDN Research, SOSR ’18, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 28–29 March 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hu, G.; Xing, C.; Zu, J.; Liu, Y. FINT: Flexible In-band Network Telemetry method for data center network. Comput. Netw. 2022, 216, 109232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Greenberg, A.; Maltz, D.; Rexford, J.; Yuan, L.; Kandula, S.; Kim, C. Profiling network performance for multi-tier data center applications. In Proceedings of the 8th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, NSDI’11, Boston, MA, USA, 30 March–1 April 2011; pp. 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Moshref, M.; Yu, M.; Govindan, R.; Vahdat, A. Trumpet: Timely and Precise Triggers in Data Centers. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGCOMM Conference, SIGCOMM ’16, Florianopolis, Brazil, 22–26 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jin, X.; Lee, P.P.C.; Li, R.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhang, G. SketchVisor: Robust Network Measurement for Software Packet Processing. In Proceedings of the Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, SIGCOMM ’17, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–25 August 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammana, P.; Agarwal, R.; Lee, M. Distributed Network Monitoring and Debugging with SwitchPointer. In Proceedings of the 15th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 18), Renton, WA, USA, 9–11 April 2018; pp. 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Flajolet, P.; Fusy, É.; Gandouet, O.; Meunier, F. Hyperloglog: The analysis of a near-optimal cardinality estimation algorithm. Discret. Math. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2007, AH, 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Datadog AI. Available online: https://www.datadoghq.com/about/latest-news/press-releases/datadog-ai-research-launches-new-open-weights-ai-foundation-model-and-observability-benchmark/#:~:text=for%20various%20applications (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Cisco AI. Available online: https://blogs.cisco.com/innovation/network-operations-for-the-ai-age (accessed on 18 August 2025).

| Prior Survey(s) | Scope/Perspective | How This Survey Differs |
|---|---|---|
| Lee et al. [4]; Svoboda et al. [5] | Overview of traditional monitoring: SNMP, flow-level analysis, passive methods. | Updates the landscape to SDNs, programmable networks and network-wide monitoring. |
| SoIn [6]; Kore [7]; Moceri [8] | Network monitoring tools | Shifts focus from individual tools to system level design principles and end-to-end architectures for next generation network-wide observability. |
| Tsia et al. [9]; Zheng et al. [10] | SDN enabled monitoring | Unifies traditional, SDN, and programmable/hybrid settings within a single taxonomy spanning data sources, deployment models, and orchestration |
| D’Alconzo et al. [11] | Big data for traffic monitoring | Centers architectural and systemic design: telemetry sources (counters, sketches, probes), placement/orchestration, and deployment trade-offs beyond analytics |
| Nobre et al. [12] | Control and configuration aspects of measurements | Integrates control/intent with a broader end-to-end taxonomy: telemetry substrates, deployment models (SDN, INT, hybrid), and orchestration frameworks. |
| Tan et al. [13] | In-band Network Telemetry (INT). | Generalizes INT as one telemetry pillar within a comprehensive taxonomy spanning traditional polling/counters to programmable and hybrid models. |
| Category | Mechanism | List of Papers |
|---|---|---|
| Single point | Local sampling, counters, sketches, message interception to controller | [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] |
| Polling/querying individual nodes | [25,26,27,28] | |
| Path | Active probing to discover paths and measure path performance | [29,30,31,32] |
| In band network telemetry | [33,34,35,36,37,38] | |
| Network | Probes designed to collectively cover entire network | [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] |
| Optimally placing (or updating) monitors to cover all flows, possibly adaptive | [50,51,52,53,54] | |
| Optimally polling switches to cover all flows | [55,56] | |
| Taking causally consistent snapshots of the network | [57,58,59] | |
| Globally optimized distributed measurement tasks and load balancing | [60,61,62,63,64,65,66] | |
| Collecting measurements for subset of flows | [67,68] | |
| Hybrid | Use probes to collect data across switches and bring to central controller | [69,70,71] |
| Switches report, possibly based on thresholds; data aggregated centrally for correlation | [72,73,74,75,76,77] | |
| Event or load driven probes starting from local observations to achieve broader insight | [78,79,80] | |
| Switch store pointers to data on end-hosts | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaseen, N. From Counters to Telemetry: A Survey of Programmable Network-Wide Monitoring. Network 2025, 5, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5030038
Yaseen N. From Counters to Telemetry: A Survey of Programmable Network-Wide Monitoring. Network. 2025; 5(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaseen, Nofel. 2025. "From Counters to Telemetry: A Survey of Programmable Network-Wide Monitoring" Network 5, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5030038
APA StyleYaseen, N. (2025). From Counters to Telemetry: A Survey of Programmable Network-Wide Monitoring. Network, 5(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/network5030038






