The Wind Dynamics of Super-Eddington Sources in FRADO
Abstract
1. Introduction
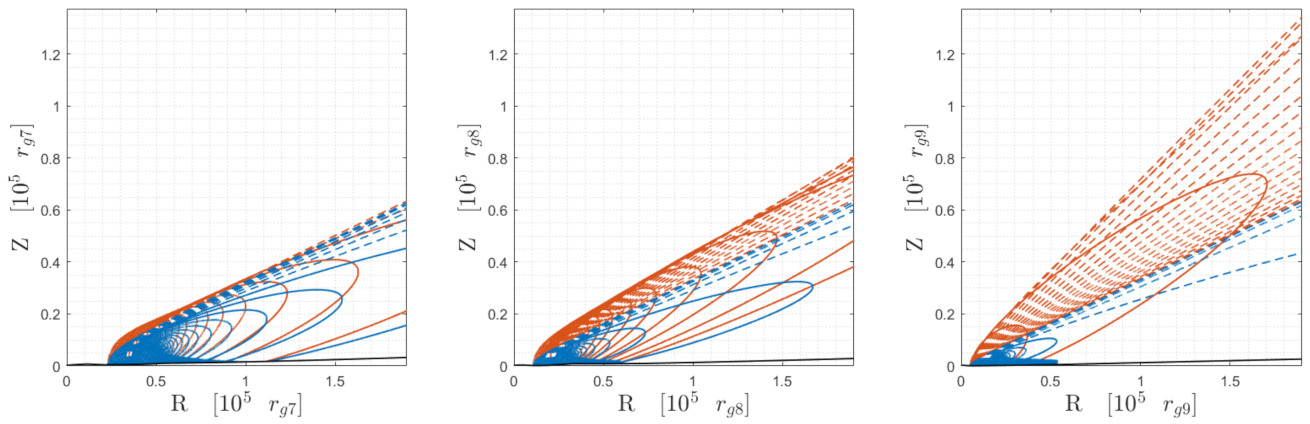
2. Dynamics in 2.5D Frado Model
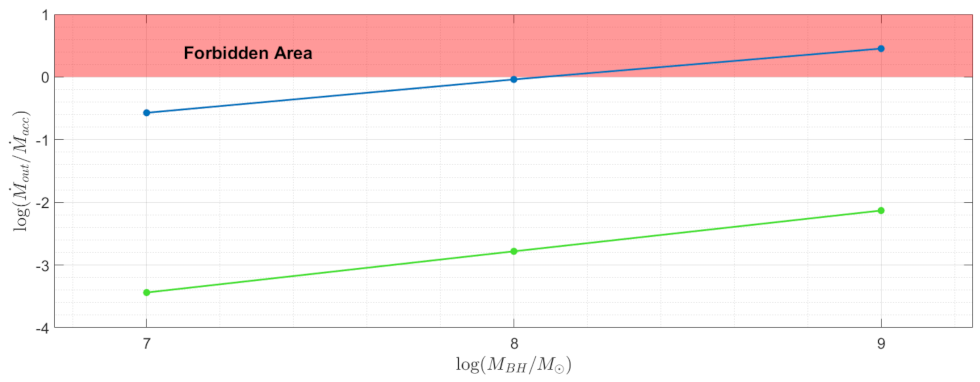
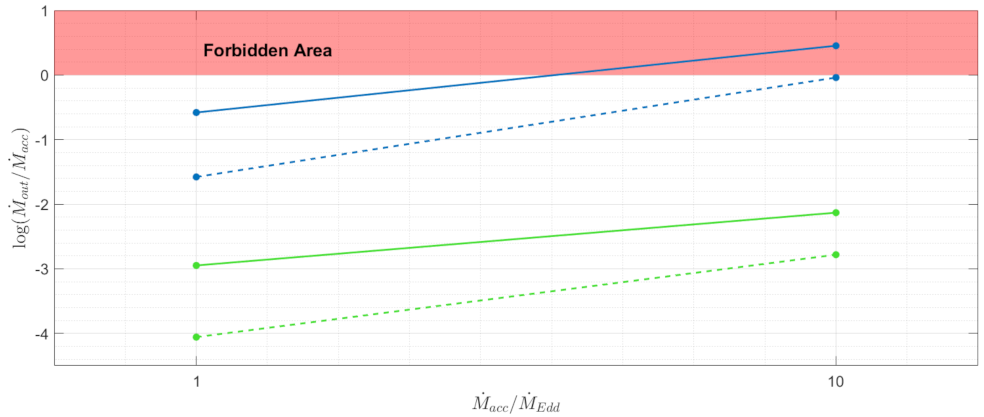
3. Mass-Loss Rate Due to Dusty-Driven Outflow
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kollmeier, J.A.; Onken, C.A.; Kochanek, C.S.; Gould, A.; Weinberg, D.H.; Dietrich, M.; Cool, R.; Dey, A.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Jannuzi, B.T.; et al. Black Hole Masses and Eddington Ratios at 0.3 < z < 4. Astrophys. J. 2006, 648, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komossa, S.; Voges, W.; Xu, D.; Mathur, S.; Adorf, H.M.; Lemson, G.; Duschl, W.J.; Grupe, D. Radio-loud Narrow-Line Type 1 Quasars. Astron. J. 2006, 132, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Done, C.; Ward, M. Strong constraints on a super-Eddington accretion flow: XMM-Newton observations of an intermediate-mass black hole. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; Marziani, P.; Dultzin-Hacyan, D. Phenomenology of Broad Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 38, 521–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Brandt, W.N.; Hall, P.B.; Wu, J.; Anderson, S.F.; Garmire, G.P.; Gibson, R.R.; Plotkin, R.M.; Richards, G.T.; Schneider, D.P.; et al. X-ray Insights into the Nature of PHL 1811 Analogs and Weak Emission-line Quasars: Unification with a Geometrically Thick Accretion Disk? Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begelman, M.C.; Volonteri, M. Hyperaccreting black holes in galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, M.J. Tidal disruption of stars by black holes of 106–108 solar masses in nearby galaxies. Nature 1988, 333, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Wang, J.M.; Hu, C.; Valls-Gabaud, D.; Baldwin, J.A.; Ge, J.Q.; Xue, S.J. Outflows from active galactic nuclei: The BLR-NLR metallicity correlation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Hu, C.; Lu, K.X.; Huang, Y.K.; Cheng, C.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.W.; Fan, X.L.; Bai, J.M.; et al. Supermassive Black Holes with High Accretion Rates in Active Galactic Nuclei. IV. Hβ Time Lags and Implications for Super-Eddington Accretion. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, K.X.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.R.; Bai, J.M.; Bian, W.H.; et al. Supermassive Black Holes with High Accretion Rates in Active Galactic Nuclei. IX. 10 New Observations of Reverberation Mapping and Shortened Hβ Lags. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete, C.A.; Dultzin, D.; Marziani, P.; Esparza, D.; Sulentic, J.W.; del Olmo, A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; García López, A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Bon, N.; et al. Highly accreting quasars: The SDSS low-redshift catalog. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Kawaguchi, T. Super-Eddington accretion rates in Narrow Line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 426, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayoshi, K.; Nakatani, R.; Toyouchi, D.; Hosokawa, T.; Kuiper, R.; Onoue, M. Rapid Growth of Seed Black Holes during Early Bulge Formation. Astrophys. J. 2022, 927, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, D.; Efstathiou, A.; Afonso, J.; Bernard-Salas, J.; Cairns, J.; Clements, D.L.; Croker, K.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Joyce, M.; Lacy, M.; et al. Stellar and black hole assembly in z < 0.3 infrared-luminous mergers: Intermittent starbursts versus super-Eddington accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 4770–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziani, P.; Dultzin, D.; Sulentic, J.W.; Del Olmo, A.; Negrete, C.A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; D’Onofrio, M.; Bon, E.; Bon, N.; Stirpe, G.M. A main sequence for quasars. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śniegowska, M.; Czerny, B.; You, B.; Panda, S.; Wang, J.M.; Hryniewicz, K.; Wildy, C. Properties of active galaxies at the extreme of Eigenvector 1. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 613, A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xing, F.; Zhang, K.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S. Outflow and Hot Dust Emission in High-redshift Quasars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 776, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Du, P.; Hu, C.; Netzer, H.; Bai, J.M.; Lu, K.X.; Kaspi, S.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y.R.; Wang, F.; et al. Supermassive Black Holes with High Accretion Rates in Active Galactic Nuclei. II. The Most Luminous Standard Candles in the Universe. Astrophys. J. 2014, 793, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dultzin, D.; Marziani, P.; de Diego, J.A.; Negrete, C.A.; Del Olmo, A.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; D’Onofrio, M.; Bon, E.; Bon, N.; Stirpe, G.M. Extreme quasars as distance indicators in cosmology. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2020, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukue, J. Critical Accretion Disk. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 56, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotti, L.; Ostriker, J.P.; Proga, D. Feedback from Central Black Holes in Elliptical Galaxies. III. Models with Both Radiative and Mechanical Feedback. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormendy, J.; Ho, L.C. Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Host Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 511–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsuga, K.; Mori, M.; Nakamoto, T.; Mineshige, S. Supercritical Accretion Flows around Black Holes: Two-dimensional, Radiation Pressure-dominated Disks with Photon Trapping. Astrophys. J. 2005, 628, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Stone, J.M.; Davis, S.W. A Global Three-dimensional Radiation Magneto-hydrodynamic Simulation of Super-Eddington Accretion Disks. Astrophys. J. 2014, 796, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sądowski, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C.; Tchekhovskoy, A. Numerical simulations of super-critical black hole accretion flows in general relativity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M.H.; Czerny, B.; Szczerba, R. The Picture of BLR in 2.5D FRADO: Dynamics and Geometry. Astrophys. J. 2021, 920, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, B.; Hryniewicz, K. The origin of the broad line region in active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 525, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, B.; Li, Y.R.; Hryniewicz, K.; Panda, S.; Wildy, C.; Sniegowska, M.; Wang, J.M.; Sredzinska, J.; Karas, V. Failed Radiatively Accelerated Dusty Outflow Model of the Broad Line Region in Active Galactic Nuclei. I. Analytical Solution. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspi, S.; Smith, P.S.; Netzer, H.; Maoz, D.; Jannuzi, B.T.; Giveon, U. Reverberation Measurements for 17 Quasars and the Size-Mass-Luminosity Relations in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2000, 533, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.M.; Ferrarese, L.; Gilbert, K.M.; Kaspi, S.; Malkan, M.A.; Maoz, D.; Merritt, D.; Netzer, H.; Onken, C.A.; Pogge, R.W.; et al. Central Masses and Broad-Line Region Sizes of Active Galactic Nuclei. II. A Homogeneous Analysis of a Large Reverberation-Mapping Database. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, M.C.; Walsh, J.L.; Barth, A.J.; Baliber, N.; Bennert, V.N.; Canalizo, G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Ganeshalingam, M.; Gates, E.L.; Greene, J.E.; et al. The Lick AGN Monitoring Project: Broad-line Region Radii and Black Hole Masses from Reverberation Mapping of Hβ. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, C.J.; Peterson, B.M.; Horne, K.; Bentz, M.C.; Pogge, R.W.; Denney, K.D.; De Rosa, G.; Martini, P.; Kochanek, C.S.; Zu, Y.; et al. The Structure of the Broad-line Region in Active Galactic Nuclei. I. Reconstructed Velocity-delay Maps. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, A.; Hüttemann, A.; Kiefer, C.; Britzen, S.; Zajaček, M.; Lämmerzahl, C.; Stöckler, M.; Valencia-S, M.; Karas, V.; García-Marín, M. The Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole: How Good a Case Is It? Found. Phys. 2017, 47, 553–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, V.; Svoboda, J.; Zajaček, M. Selected Chapters on Active Galactic Nuclei as Relativistic Systems. In Proceedings of the RAGtime: Workshops on Black Holes and Netron Stars, Opava, Czech Republic, 6–10 September 2021; p. E1. [Google Scholar]
- Krolik, J.H. Active Galactic Nuclei: From the Central Black Hole to the Galactic Environment; Princeton, N.J., Ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Netzer, H. The Physics and Evolution of Active Galactic Nuclei; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, T.; Netzer, H. Bloated stars as AGN broad-line clouds: The emission-line profiles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 284, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T. Bloated stars as AGN broad-line clouds: The emission-line response to continuum variations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 285, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Czerny, B.; Modzelewska, J.; Petrogalli, F.; Pych, W.; Adhikari, T.P.; Życki, P.T.; Hryniewicz, K.; Krupa, M.; Świeţoń, A.; Nikołajuk, M. The dust origin of the Broad Line Region and the model consequences for AGN unification scheme. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, B.; Du, P.; Wang, J.M.; Karas, V. A Test of the Formation Mechanism of the Broad Line Region in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2016, 832, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravity Collaboration; Sturm, E.; Dexter, J.; Pfuhl, O.; Stock, M.R.; Davies, R.I.; Lutz, D.; Clénet, Y.; Eckart, A.; Eisenhauer, F.; et al. Spatially resolved rotation of the broad-line region of a quasar at sub-parsec scale. Nature 2018, 563, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravity Collaboration; Amorim, A.; Bauböck, M.; Brandner, W.; Clénet, Y.; Davies, R.; de Zeeuw, P.T.; Dexter, J.; Eckart, A.; Eisenhauer, F.; et al. The spatially resolved broad line region of IRAS 09149-6206. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 643, A154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravity Collaboration; Amorim, A.; Bauböck, M.; Brandner, W.; Bolzer, M.; Clénet, Y.; Davies, R.; de Zeeuw, P.T.; Dexter, J.; Drescher, A.; et al. The central parsec of NGC 3783: A rotating broad emission line region, asymmetric hot dust structure, and compact coronal line region. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 648, A117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin-Souffrin, S.; Dyson, J.E.; McDowell, J.C.; Perry, J.J. The environment of active galactic nuclei. I - A two-component broad emission line model. MNRAS 1988, 232, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspi, S.; Brandt, W.N.; Maoz, D.; Netzer, H.; Schneider, D.P.; Shemmer, O.; Grier, C.J. Taking a Long Look: A Two-decade Reverberation Mapping Study of High-luminosity Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2021, 915, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskell, C.M. What broad emission lines tell us about how active galactic nuclei work. New Astron. Rev. 2009, 53, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulentic, J.W.; del Olmo, A.; Marziani, P.; Martínez-Carballo, M.A.; D’Onofrio, M.; Dultzin, D.; Perea, J.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; Negrete, C.A.; Stirpe, G.M.; et al. What does CIVλ1549 tell us about the physical driver of the Eigenvector quasar sequence? Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.; Chiang, J.; Grossman, S.A.; Voit, G.M. Accretion Disk Winds from Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 1995, 451, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Restrepo, J.E.; Lira, P.; Netzer, H.; Trakhtenbrot, B.; Capellupo, D.M. The effect of nuclear gas distribution on the mass determination of supermassive black holes. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proga, D.; Kallman, T.R. Dynamics of Line-driven Disk Winds in Active Galactic Nuclei. II. Effects of Disk Radiation. Astrophys. J. 2004, 616, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.A.; Proga, D.; Miller, L.; Long, K.S.; Turner, T.J. Multidimensional modelling of X-ray spectra for AGN accretion disc outflows—III. Application to a hydrodynamical simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M.H.; Czerny, B. Radiation pressure on dust explains the Low Ionized Broad Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.14963. [Google Scholar]
- Naddaf, M.H.; Czerny, B.; Szczerba, R. BLR size in Realistic FRADO Model. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2020, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, M.J.; Silk, J.I.; Werner, M.W.; Wickramasinghe, N.C. Infrared Radiation from Dust in Seyfert Galaxies. Nature 1969, 223, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, H.; Dai, H.; Zhang, K. Broad-line Balmer decrements in blue active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 383, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röllig, M.; Szczerba, R.; Ossenkopf, V.; Glück, C. Full SED fitting with the KOSMA-τ PDR code. I. Dust modelling. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 549, A85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risaliti, G.; Elvis, M. A non-hydrodynamical model for acceleration of line-driven winds in active galactic nuclei. A&A 2010, 516, A89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.L.; Naddaf, M.H.; Zajaček, M.; Czerny, B.; Araudo, A.; Karas, V. Nonthermal Emission from Fall-back Clouds in the Broad-line Region of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2022, 931, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Czerny, B.; Lasota, J.P.; Szuszkiewicz, E. Slim Accretion Disks. Astrophys. J. 1988, 332, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.K.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Lu, K.X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Du, P.; Li, Y.R.; Bai, J.M.; et al. Reverberation Mapping of the Narrow-line Seyfert 1 Galaxy I Zwicky 1: Black Hole Mass. Astrophys. J. 2019, 876, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvis, M. A Structure for Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouche, D.; Pozo Nuñez, F.; Kaspi, S. Direct evidence of non-disk optical continuum emission around an active black hole. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönig, S.F. Redefining the Torus: A Unifying View of AGNs in the Infrared and Submillimeter. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Ohsuga, K.; Wada, K.; Susa, H.; Misawa, T. Modeling Line-Driven Disk Wind for Broad Absorption Lines of Quasars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 65, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proga, D.; Stone, J.M.; Kallman, T.R. Dynamics of Line-driven Disk Winds in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2000, 543, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbottom, N.; Proga, D.; Knigge, C.; Long, K.S.; Matthews, J.H.; Sim, S.A. Line-driven Disk Winds in Active Galactic Nuclei: The Critical Importance of Ionization and Radiative Transfer. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Ohsuga, K.; Done, C. Line-driven disc wind in near-Eddington active galactic nuclei: Decrease of mass accretion rate due to powerful outflow. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 3616–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M.H.; Czerny, B. Mass loss rate of accretion disk in FRADO. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.08082. [Google Scholar]
- Borguet, B.C.J.; Arav, N.; Edmonds, D.; Chamberlain, C.; Benn, C. Major Contributor to AGN Feedback: VLT X-shooter Observations of S IV BALQSO Outflows. Astrophys. J. 2013, 762, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, C.; Arav, N.; Benn, C. Strong candidate for AGN feedback: VLT/X-shooter observations of BALQSO SDSS J0831+0354. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Leighly, K.M.; Terndrup, D.M.; Gallagher, S.C.; Richards, G.T. Discovery of a Remarkably Powerful Broad Absorption-line Quasar Outflow in SDSS J135246.37+423923.5. Astrophys. J. 2020, 891, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, F.; Ferland, G. The Age and Chemical Evolution of High-Redshift QSOs. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 391, L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, C.; Hamann, F.; Shields, J.C.; Constantin, A.; Foltz, C.B.; Chaffee, F.H. The Metallicity of the Redshift 4.16 Quasar BR 2248-1242. Astrophys. J. 2002, 567, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shangguan, J.; Ho, L.C.; Xie, Y. On the Gas Content and Efficiency of AGN Feedback in Low-redshift Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, A.; Laor, A. Dust inflated accretion disc as the origin of the broad line region in active galactic nuclei. MNRAS 2018, 474, 1970–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śniegowska, M.; Marziani, P.; Czerny, B.; Panda, S.; Martínez-Aldama, M.L.; del Olmo, A.; D’Onofrio, M. High metal content of highly accreting quasars. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicone, C.; Maiolino, R.; Sturm, E.; Graciá-Carpio, J.; Feruglio, C.; Neri, R.; Aalto, S.; Davies, R.; Fiore, F.; Fischer, J.; et al. Massive molecular outflows and evidence for AGN feedback from CO observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 562, A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, F. Molecular gas dynamics around nuclei of galaxies. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.06106. [Google Scholar]
- Combes, F.; García-Burillo, S.; Casasola, V.; Hunt, L.; Krips, M.; Baker, A.J.; Boone, F.; Eckart, A.; Marquez, I.; Neri, R.; et al. ALMA observations of feeding and feedback in nearby Seyfert galaxies: An AGN-driven outflow in NGC 1433. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braito, V.; Reeves, J.N.; Matzeu, G.; Severgnini, P.; Ballo, L.; Cicone, C.; Ceca, R.D.; Giustini, M.; Sirressi, M. Dramatic Changes in the Observed Velocity of the Accretion Disk Wind in MCG-03-58-007 Are Revealed by XMM-Newton and NuSTAR. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naddaf, M.-H.; Czerny, B.; Zajaček, M. The Wind Dynamics of Super-Eddington Sources in FRADO. Dynamics 2022, 2, 295-305. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2030015
Naddaf M-H, Czerny B, Zajaček M. The Wind Dynamics of Super-Eddington Sources in FRADO. Dynamics. 2022; 2(3):295-305. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2030015
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaddaf, Mohammad-Hassan, Bożena Czerny, and Michal Zajaček. 2022. "The Wind Dynamics of Super-Eddington Sources in FRADO" Dynamics 2, no. 3: 295-305. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2030015
APA StyleNaddaf, M.-H., Czerny, B., & Zajaček, M. (2022). The Wind Dynamics of Super-Eddington Sources in FRADO. Dynamics, 2(3), 295-305. https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2030015







