Abstract
Background: Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) is a rare inflammatory lung disease typically responsive to glucocorticoids, but is prone to relapse and, in some cases, progressive deterioration. A subset of patients develops fibrosing CEP, a distinct phenotype characterized by irreversible parenchymal remodeling and declining lung function, for which no standard treatment exists. Although biologic therapies targeting interleukin-5 (IL-5) are effective in relapsing CEP, their role in fibrosing forms remains unclear. Case Presentation: We report the case of a 43-year-old man with idiopathic CEP initially treated with systemic glucocorticoids, which were discontinued due to severe adverse effects. Despite subsequent therapy with inhaled steroids and azathioprine, the disease relapsed and progressed to a fibrosing phenotype, as confirmed by radiologic and functional assessments. An off-label treatment with subcutaneous mepolizumab, 100 mg, every 4 weeks was started. After eight months of therapy, the patient achieved clinical stability, improved lung function, and the radiologic stabilization of fibrotic changes, without the need for any further treatment with a corticosteroid. Conclusions: This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first documented case of fibrosing CEP treated with an anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody, highlighting its potential role as a steroid-sparing agent and immunomodulator even in the fibrotic phase of disease. Further research is warranted to define the place of biologics in the management of CEP with a fibrosing evolution and possible combinations with antifibrotic drugs.
1. Introduction
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) is an idiopathic inflammatory lung disorder, characterized by extensive eosinophilic infiltrate in the lung parenchyma, along with subacute symptoms such as a cough, dyspnea, malaise, and fever. First-line treatments consist of systemic glucocorticoids, which usually induce a rapid clinical and radiographic improvement. However, a relapse is common when steroids are tapered or discontinued [1,2]. Consequently, many patients with CEP require long-term low-dose steroids to maintain remission [1,2]. Prolonged corticosteroid use can lead to severe side effects (e.g., osteoporosis, weight gain, and diabetes) [3], prompting the exploration of steroid-sparing treatments.
In recent years, biologic agents have emerged as promising therapies for severe eosinophilic disorders, including idiopathic CEP [4]. Among these are monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 or its receptor (IL-5Rα). Mepolizumab—a humanized anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody indicated for severe eosinophilic asthma, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, hypereosinophilic syndrome, and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps [5]—and also reslizumab (anti-IL-5) and benralizumab (anti-IL-5Rα) have demonstrated clinical benefits in relapsing or steroid-dependent CEP, based on case reports and small case series [4,6,7]. These agents can induce the remission of CEP with a reduction or discontinuation of steroids in numerous reported cases [4,6,7]. Although no randomized controlled trials have yet been conducted, accumulating real-world evidence supports the IL-5 pathway blockade as an effective steroid-sparing strategy in CEP [4].
A subset of CEP patients develops progressive lung fibrosis, sometimes termed “fibrotic CEP”. In such cases, persistent eosinophilic inflammation is believed to lead to the irreversible structural remodeling of the lung. This phenomenon, first described in the 1990s [8], is not uncommon with long-standing diseases: in a recent retrospective analysis, 23 (37%) CEP patients showed radiologic evidence of pulmonary fibrosis during a follow-up [9]. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis may develop in patients with this fibrotic presentation, whenever the patient presents at least two of the following three characteristics: functional decline (>5% FVC decline), clinical deterioration, or radiological worsening [10]. Radiological worsening may appear as an increased extension of the fibrotic areas, as well as new or worsened fibrotic features such as traction bronchiectasis or fibrotic ground-glass opacities [11]. Regarding the evolution of CEP, patients who develop fibrotic changes tend to be older and male, and fibrotic CEP is associated with worse outcomes and higher mortality [9]. Currently, no established treatment exists for fibrosing CEP beyond controlling the underlying eosinophilic inflammation [2]. The role of antifibrotic therapies—such as nintedanib, which is approved for progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) [12]—remains uncertain in this specific context, with limited clinical data available. Given the effectiveness of anti-IL-5 biologics in non-fibrotic CEP, it is of great interest whether these agents can alter the course of fibrotic CEP. We report a case of fibrotic CEP in which an anti-IL-5 therapy was employed, describing the clinical course and outcomes and comparing it with the existing literature.
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Patient History
A 43-year-old Caucasian man presented to another center in 2019 with a 3-month history of a cough, a low-grade fever (up to 38 °C), and exertional dyspnea. He was a former smoker (approximately 7 pack-years, he quit in his 20s) and worked as a graphic designer with no known occupational/environmental exposures. His past medical history was unremarkable. Blood tests at presentation showed mild circulating eosinophilia (640 cells/uL) and a total IgE of 77 KUA/L; RAST testing revealed a non-clinically relevant mild sensitization to dust mites (d1 0.20 KUA/L, d2 0.19 KUA/L), and autoimmune screening (ANA, ENA, ANCA, rheumatoid factor, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, myositis-specific autoantibodies, and myositis-associated autoantibodies) was negative. A high-resolution CT (HRCT) demonstrated multiple bilateral patchy opacities, including ground-glass infiltrates with some pseudonodular consolidations and bronchial dilatation, more prominent in the peripheral regions (Figure 1a). Bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) showed a BAL fluid with an eosinophil differential count of 40%. A transbronchial lung biopsy revealed prominent eosinophilic infiltration without evidence of vasculitis or granulomatous inflammation. Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) showed normal baseline spirometry, with a reduced diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO, 61%). A non-specific bronchial challenge with methacholine excluded the diagnosis of bronchial asthma. Additionally, there were no sino-nasal symptoms (including nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, hyposmia, facial pain, or history of chronic sinusitis) or clinical features suggestive of the eosinophil-associated involvement of other organs. Based on these findings, along with the exclusion of secondary causes of eosinophilia, a diagnosis of idiopathic chronic eosinophilic pneumonia was made.
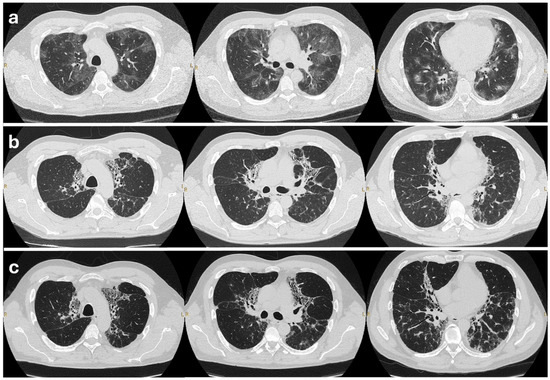
Figure 1.
High-resolution CT chest scans of the patient at three stages. (a) The inflammatory phase (2019): Baseline HRCT showing bilateral patchy ground-glass opacities and consolidations. These changes predominantly involve subpleural regions, consistent with active CEP. (b) The fibrosing phase (2021–2023): HRCT after years of relapsing disease off steroids, demonstrating an evolution towards fibrosis. Reticular opacities and traction bronchiectasis in the upper lobes can be seen. (c) Post-treatment (2025): HRCT after 8 months of mepolizumab therapy, showing stable fibrotic changes. Reticulation and bronchiectasis persist unchanged; no new inflammatory lesions are seen.
2.2. Initial Treatment and Outcome
The patient was started on high-dose oral prednisone (50 mg daily) from May 2019. His respiratory symptoms and radiographic opacities improved significantly within weeks. After 2 months, the prednisone was gradually tapered. However, the patient developed adverse effects consistent with glucocorticoids toxicity, including multiple osteoporotic fractures and avascular necrosis of the left femoral head, ultimately requiring total hip arthroplasty in 2020. Bone densitometry revealed osteoporosis of the lumbar spine and osteopenia of the right femur. Due to these complications, glucocorticoids were discontinued by mid-2020. Over the subsequent year of therapy, the patient’s respiratory condition slowly worsened. By late 2020 and early 2021, he reported recurrent dry cough and exertional dyspnea, and prednisone was reintroduced (starting from 25 mg per day) between the end of 2020 and March 2021. A HRCT performed in July 2021 revealed a progression towards fibrosis with an interstitial thickening within areas of parenchymal band-like opacities associated with traction bronchiectasis, along with residual patchy ground-glass opacities and consolidations (Figure 1b). These findings were consistent with an evolution to fibrotic CEP. PFTs at that time showed a mild restrictive defect [total lung capacity (TLC) 4.99 L, 79% predicted] with a reduced DLCO of 56% predicted (Figure 2). Another course of prednisone was started at a dose of 15 mg daily, with concomitant treatment for bone protection, including a bisphosphonate and calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
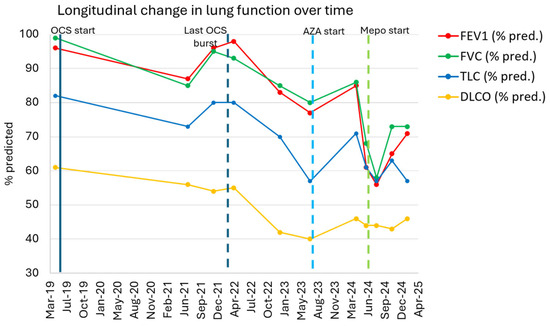
Figure 2.
The longitudinal change in lung function. The patient’s FEV1 (% predicted), FVC (% pred.) TLC (% pred.), and DLCO (% pred.) are plotted over time. Key treatment interventions are highlighted. The patient had no relapses on mepolizumab, allowing for the avoidance of further systemic steroids. OCSs: oral corticosteroids.
2.3. Further Management
After the diagnosis of fibrotic CEP, the patient was referred to our center at the end of 2021. We gradually tapered prednisone to discontinuation by March 2022 and introduced beclomethasone/formoterol 200/6 mcg. Given his relapsing disease and the side effects of glucocorticoids, azathioprine (AZA) 150 mg/day was initiated as a steroid-sparing immunosuppressant after excluding a thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) deficiency. However, the patient himself deferred the initiation of AZA until July 2023. At that time, he still reported moderate dyspnea (mMRC grade 2) and crackles on chest auscultation. Over the next months, the patient’s symptoms persisted and progressed despite AZA treatment. In early 2024, he experienced worsening cough, and AZA was discontinued due to lack of benefit and development of neutropenia. By April 2024, his symptoms had worsened significantly, with severe dry cough (often resulting in gagging/vomiting) and exertional breathlessness on mild exertion. Sputum was minimal, consisting of thick clear mucus. Blood eosinophil count in April 2024 was 420 cells/µL. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) was 36 ppb (normal value < 25 ppb).
In June 2024—five years following the initial diagnosis—the patient’s CEP was in a fibrotic phase with clinical, functional, and radiologic progression despite AZA, inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs), and previous prolonged therapy with prednisone. Spirometry on June 2024 showed a forced expiratory volume in first second (FEV1) of 2.13 L (61% pred.), forced vital capacity (FVC) of 2.95 L (68% pred.), TLC 4.04 L (61% pred.), and DLCO 44% pred., confirming a restrictive pattern with significant decline (Figure 2). HRCT at that time showed similar features as compared to 2023 with a fibrosing pattern characterized by extensive fibrotic changes with diffuse reticulations and traction bronchiectasis, especially in the upper lobes, and no evidence of new consolidations. Given the lack of response to AZA and the patient’s progressive clinical and functional decline, after discussing the case among multidisciplinary team, we decided to initiate off-label biologic therapy targeting IL-5, with the aim of attenuating eosinophilic inflammation, potentially stabilizing the fibrotic CEP. Following discussion with the patient and informed consent, subcutaneous mepolizumab 100 mg was started in June 2024 and continued every 4 weeks thereafter.
2.4. Outcome on Mepolizumab
Over the first 2–3 months of mepolizumab therapy, the patient experienced no immediate symptomatic relief. He continued to report daily dry cough and moderate exertional dyspnea (mMRC 2). However, he remained clinically stable without any acute relapses or requirement for rescue systemic steroids. By the August 2024 follow-up, his clinical condition remained stable. Pulmonary function in August 2024 was slightly worse compared to the prior one (Figure 2), possibly reflecting a delayed response to treatment. By November 2024 (after approximately 5 months of mepolizumab), initial signs of objective improvement were noted. Spirometry showed an FEV1 of 2.35 L (65% pred.), FVC of 3.26 L (73% pred.), and TLC of 4.27 L (63% pred.) (Figure 2). DLCO was 43% of the predicted value in November 2024, essentially unchanged (Figure 2). Blood eosinophil count had dropped to <50 cells/μL. He also noted a subjective improvement in dyspnea and a slight reduction in cough frequency, though cough persisted. On a 6 min walking test in November 2024, the patient walked 390 m with minimal desaturation (nadir SpO2 94% on room air from a baseline of 98%), indicating fair exercise tolerance.
After 8 months of continuous mepolizumab therapy, at the February 2025 visit, the patient’s condition was stable and improved relative to the pre-biologic baseline. FEV1 had risen to 2.54 L (71% pred.), and FVC was 3.22 L (73% pred.), with TLC 3.90 L (57% pred.). DLCO was 46% pred. (Figure 2). Meanwhile, he had not experienced any CEP relapses or acute worsening. Follow-up imaging demonstrated stability of the fibrosing changes: the HRCT performed in January 2025 showed an unchanged extent of reticular fibrosis and traction bronchiectasis compared to mid-2024, with no new consolidations or ground-glass opacities (Figure 1c). Radiological exams were reviewed by independent radiologist and also by an expert thoracic radiologist in the multidisciplinary team. Owing to the clinical and radiologic stabilization, mepolizumab was continued. Introduction of antifibrotic therapy (such as nintedanib) was considered but ultimately deferred, since the criteria for progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) were not met (the patient had stable lung function and no radiologic progression while on mepolizumab). The patient continues mepolizumab with regular follow-up visits.
3. Discussion
This case illustrates a fibrotic variant of CEP successfully managed with an anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody. The patient initially presented in 2019 with non-fibrotic CEP that responded adequately to glucocorticoids. However, multiple relapses upon steroid tapering, coupled with serious steroid-related complications, ultimately led to progressive pulmonary fibrosis. His clinical course highlights the challenge of long-term CEP management: while high-dose steroids are effective in the acute phase, their prolonged use is limited by toxicity, and disease remission may not be maintained after steroid withdrawal [1,2]. In our patient, steroid-sparing immunosuppression with azathioprine failed to achieve disease control. However, we acknowledge that pulmonary function values showed a modest and transient improvement during the early months of the azathioprine treatment, despite persistent symptoms. The mepolizumab therapy, by contrast, led to a clear disease stabilization: no further clinical relapses occurred, the lung function decline was arrested and partially reversed, and no new radiographic infiltrates appeared. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported use of an anti-IL-5 biologic in fibrotic CEP. The positive outcome suggests that targeting eosinophils can benefit even the fibrotic phase of the disease, possibly by controlling ongoing inflammation.
Our patient’s experience aligns with a growing body of evidence supporting IL-5 blockade in refractory CEP. Numerous case reports and small series over the last decade have demonstrated that mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab can induce remission in relapsing CEP and allow the reduction or discontinuation of glucocorticoids [4,6,7,13]. Tashiro et al. reported four patients with frequently relapsing CEP who were treated with anti-IL-5 or anti-IL-5R agents, all of whom achieved clinical remission and steroid discontinuation [7]. Likewise, in a retrospective study of 10 CEP patients, a mepolizumab treatment reduced the annual relapse rate to zero and enabled prednisone tapering in all cases [6]. Importantly, that study noted the complete or near-complete resolution of lung infiltrates on follow-up imaging in the majority of patients [6], suggesting the absence of fibrotic CEP among the study population and that biologic therapy in early phases of the disease might prevent the progression to fibrosis. A recent scoping review identified over 60 CEP patients treated with monoclonal antibodies; among those receiving anti-IL-5 therapies, virtually all showed clinical improvements with no further relapses and significant reductions in maintenance steroid doses [4]. Thus, our patient’s remission on mepolizumab is consistent with the effectiveness observed in prior reports. He was also able to remain off systemic steroids, avoiding further corticosteroid exposure and its associated risks.
A key novelty of this case lies in the presence of established pulmonary fibrosis. In “pure” CEP (without fibrosis), successful biologic therapy often yields the rapid radiographic clearing of eosinophilic pneumonia lesions [6]. In our patient, fibrotic CEP is characterized by an irreversible architectural distortion—reticulation and traction bronchiectasis—that persists despite treatment [8]. In our patient, even after mepolizumab, the HRCT showed residual reticular changes and traction bronchiectasis consistent with fibrosis. These fibrotic changes had accumulated during the years of inadequately controlled inflammation. The goal of therapy in fibrotic CEP is primarily to halt further eosinophil-driven damage, rather than the regression of fibrosis. Mepolizumab appeared to achieve this goal: the fibrotic pattern remained stable on serial imaging, with no extension or new fibrotic lesions. The lung function (FEV1, FVC, DLCO) actually improved slightly with the therapy, likely reflecting the resolution of active inflammation and possibly some recovery of reversible components (e.g., ventilation in areas of the lung that were inflamed but not yet fibrotic).
The effectiveness of the anti-IL-5 therapy in fibrosing CEP may be explained by the persistence of low-grade eosinophilic inflammation, even in the fibrotic phase. Eosinophils contribute not only to acute inflammation but also to tissue remodeling and fibrogenesis through the release of profibrotic mediators, such as TGF-β1, IL-13, and cytotoxic granule proteins like major basic protein (MBP) and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) [14,15,16,17]. These mediators promote fibroblast activation, myofibroblast differentiation, and extracellular matrix deposition. IL-5 plays a central role in supporting eosinophil recruitment and survival, thus sustaining this profibrotic microenvironment. By depleting eosinophils, the IL-5 blockade may interrupt this process, reducing further parenchymal injury and limiting the fibrotic progression. This mechanistic rationale aligns with our patient’s clinical course, in which the eosinophil suppression with mepolizumab was associated with the stabilization of the lung function and radiologic findings. The effectiveness of the anti-IL-5 therapy in fibrosing CEP may be explained by the persistence of low-grade eosinophilic inflammation, even in the fibrotic phase. Eosinophils are known to contribute not only to acute inflammation but also to tissue remodeling and fibrogenesis. Through the release of cytotoxic granule proteins, profibrotic cytokines (e.g., TGF-β), and matrix-modifying enzymes, eosinophils can sustain fibroblast activation and promote extracellular matrix deposition. Therefore, in fibrosing CEP, where inflammation and fibrosis coexist, ongoing eosinophilic activity may continue to drive the progression. By depleting eosinophils, the IL-5 blockade could attenuate this process, halt further parenchymal injury, and prevent additional fibrotic remodeling. This mechanistic rationale aligns with our patient’s clinical trajectory, in which the eosinophil suppression with mepolizumab was associated with functional and radiologic stabilization. Fibrotic CEP is an emerging phenotype that warrants attention. Historically, CEP was thought to rarely progress to fibrosis, but recent data indicate this is a relatively frequent complication with long-term diseases. In the largest published cohort (62 CEP patients followed at the Mayo Clinic), 37% developed radiologic evidence of pulmonary fibrosis during follow-up [9]. Fibrosis tended to develop within 2 years of the CEP diagnosis. Risk factors included a male sex, an older age, and a lack of coexisting asthma [9]. Interestingly, coexistent asthma was associated with a lower risk of fibrosis in that study [9], possibly because asthmatic CEP patients receive more aggressive anti-inflammatory inhaled therapy early on. This is also the reason why, in the context of adverse events related to systemic glucocorticoids, our patient was treated with ICSs despite the absence of a diagnosis of asthma and the absence of clear indications. Whether an earlier intervention (e.g., ICS or biologics) could have prevented the fibrotic remodeling in this case is speculative. Once fibrotic CEP is established, management is challenging, as the efficacy of antifibrotic drugs approved for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) is unproven in this context [12,18]. There has been discussion on the use of antifibrotic therapy in progressive fibrotic CEP on a case-by-case basis; for instance, nintedanib could be considered if there is documented disease progression despite optimal anti-inflammatory treatment, given its efficacy in other progressive fibrosing ILDs [12]. In our case, the multidisciplinary team considered initiating nintedanib if further radiologic progression occurred. However, as the lung function stabilized and imaging remained unchanged on mepolizumab, the criteria for PPF were not met [10], and the antifibrotic therapy was deferred. Other options discussed in the event of further clinical deterioration during treatment with mepolizumab included increasing the mepolizumab dose to 300 mg every four weeks. However, unlike in other conditions such as HES and EGPA, a dose escalation has not shown a significant benefit in CEP [4]. Switching to benralizumab was also considered, given its potentially greater effectiveness in reducing tissue eosinophilia due to its distinct mechanism of action; however, this remains speculative, as head-to-head comparisons in CEP are lacking [4]. The decision to initiate mepolizumab rather than benralizumab was primarily based on published experience in CEP and was not influenced by regulatory or ethical constraints regarding off-label use. No institutional or ethical barriers limited the choice of one anti-IL-5/IL-5R agent over another. This case suggests that controlling eosinophilic inflammation with an IL-5 inhibitor may slow or limit the progression of the fibrotic process, at least in the short to medium term, potentially obviating the need for antifibrotics. A longer-term follow-up will be needed to see if fibrotic CEP remains stable on the anti-IL-5 monotherapy or if the fibrotic progression eventually resumes. Ultimately, our case contributes novel evidence suggesting that IL-5 targeted therapy may provide a clinical benefit not only in eosinophilic lung disorders driven by pure inflammation but also in those with a mixed inflammatory–fibrotic component.
From a patient management perspective, the use of mepolizumab in this case had several advantages. The drug was well-tolerated with no observed or reported side effects during the follow-up period. It allowed the discontinuation of AZA (which apart from being ineffective in this case, carries risks of infection and liver toxicity) and avoided any further corticosteroid exposure. The patient’s symptoms and quality of life improved as his disease stabilized. One key barrier to the broader use of IL-5-targeted therapy in CEP remains the access and cost, particularly given its off-label status in non-asthmatic patients. In our case, off-label use was initiated given the lack of options and the patient’s severe disease course. As more evidence accumulates, it is to be hoped that anti-IL-5 therapy may become a recognized indication for refractory CEP.
This case also underscores the importance of multidisciplinary care in fibrotic lung diseases. The diagnosis and treatment plan were formulated with input from radiologists and both the team of pulmonologist experts in ILD management and the team of pulmonologists subspecializing in asthma and eosinophilic lung diseases. A collaborative approach ensured the patient received comprehensive management addressing both inflammatory and fibrotic components of his illness. This report has some limitations. First, as a single-patient case report, its findings are inherently anecdotal and lack generalizability to broader patient populations. Second, the follow-up duration was limited to 8 months, which may not be sufficient to fully assess long-term clinical and radiologic outcomes. Third, the symptom improvement was primarily self-reported. Future studies with a longer follow-up and objective outcome measures are needed to better define the role of the anti-IL-5 therapy in fibrotic CEP.
4. Conclusions
We report a challenging case of fibrotic CEP that was effectively managed with the IL-5 inhibiting monoclonal antibody, mepolizumab. This case suggests that even in CEP patients who have developed pulmonary fibrosis, targeting the eosinophilic pathway may contribute to disease stability and provide a steroid-sparing benefit. The mepolizumab therapy led to the suppression of eosinophilic inflammation and was associated with the stabilization of the lung function and no radiologic evidence of further fibrotic progression during the follow-up period. These findings reinforce the emerging role of biologic agents as effective options in relapsing or refractory CEP [4]. Clinicians should recognize fibrosing CEP as a potential evolution of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, particularly in cases of prolonged, uncontrolled inflammation. The early introduction of steroid-sparing therapies, including biologics targeting the IL-5 axis, may help mitigate this progression. Notably, our case suggests that fibrotic CEP may not inevitably worsen once eosinophilic inflammation is adequately controlled. Further research is needed to establish the optimal management of fibrotic CEP, including the role of anti-IL-5/IL-5R biologics and whether a combination with an antifibrotic therapy could confer additional benefits. This case adds to the growing rationale for prospective investigations and registry-based analyses exploring biologic therapies in eosinophilic lung diseases with a fibrotic overlap.
Author Contributions
U.S. and D.P. clinically managed the patient, conceived the report, and drafted the original manuscript. G.C. and E.R. contributed to the collection and organization of the clinical and functional data. E.C., M.T. and R.P. critically reviewed the manuscript and contributed to the clinical interpretation. E.B. and S.B. critically reviewed the manuscript. P.S. supervised the clinical management and reviewed the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The IRB approval is exempt according to the Italian laws on privacy (Art. 20–21, Legislative Decree No. 196/2003; Official Journal No. 190, 14 August 2004). Ethical review and approval are not required for single-patient case reports based exclusively on existing and anonymized clinical data.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy concerns.
Conflicts of Interest
U.S. has received honoraria for lectures or consultancy from AstraZeneca, Chiesi Farmaceutici, GlaxoSmithKline, Insmed, MSD, Menarini, Sanofi, and Sanofi Suisse. U.S. also acknowledges the financial support from Chiesi Farmaceutici for a second-degree master program. E.C. has received honoraria for lectures or consultancy from Boehringer Ingelheim. R.P. has received honoraria for lectures or consultancy from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, and CSL Vifor. P.S. has received consulting fees from Chiesi Farmaceutici, Novartis, and PPM Services; advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, CSL Behring, GlycoCore Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Structure Therapeutics, and Trevi; speaker fees from Boehringer-Ingelheim; and institutional grants from Chiesi, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and PPM Services. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANAs | Antinuclear Antibodies |
| ANCAs | Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies |
| AZA | Azathioprine |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar Lavage |
| CEP | Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia |
| DLCO | Diffusing Capacity of the Lung for Carbon Monoxide |
| ENA | Extractable Nuclear Antigens |
| FeNO | Fractional exhaled Nitric Oxide |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second |
| FVC | Forced Vital Capacity |
| HRCT | High-Resolution Computed Tomography |
| ICSs | Inhaled Corticosteroids |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| IL-5 | Interleukin-5 |
| IL-5Rα | Interleukin-5 Receptor Alpha |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| mMRC | Modified Medical Research Council Dyspnea Scale |
| PFTs | Pulmonary Function Tests |
| PPF | Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| RAST | RadioAllergoSorbent Test |
| SpO2 | Peripheral Oxygen Saturation |
| TLC | Total Lung Capacity |
| TPMT | Thiopurine Methyltransferase |
References
- Marchand, E.; Cordier, J.-F. Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2006, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, M.; Robinson, D.; Sagar, M.; Chen, L.; Ghamande, S. Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia: Clinical Perspectives. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volmer, T.; Effenberger, T.; Trautner, C.; Buhl, R. Consequences of Long-Term Oral Corticosteroid Therapy and Its Side-Effects in Severe Asthma in Adults: A Focused Review of the Impact Data in the Literature. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo, A.D.; Castrillon, A.I.; Serrano, C.D.; Fernandez-Trujillo, L. Monoclonal Antibodies in Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia: A Scoping Review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Nucala 100 mg solution for injection–Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/nucala-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Brenard, E.; Pilette, C.; Dahlqvist, C.; Colinet, B.; Schleich, F.; Roufosse, F.; Froidure, A. Real-Life Study of Mepolizumab in Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Lung 2020, 198, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, H.; Takahashi, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Sadamatsu, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kimura, S.; Sueoka-Aragane, N. Anti-IL-5 Agents for the Treatment of Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia: A Case Series. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Shijubo, N.; Koba, H.; Mori, Y.; Satoh, M.; Morikawa, T.; Abe, S. Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia Progressing to Lung Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baqir, M.; Peikert, T.; Johnson, T.; Tandon, Y.; Yi, E.; Schroeder, D.; Ryu, J. Idiopathic Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia Evolving to Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Analysis: Eosinophilic Pneumonia and Fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2022, 39, e2022020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratella, E.; Borghesi, A.; Calandriello, L.; Cortese, G.; Della Casa, G.; Giraudo, C.; Grassedonio, E.; Larici, A.R.; Palmucci, S.; Romei, C.; et al. Quantification of Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis by Visual Scoring of HRCT Images: Recommendations from Italian Chest Radiology Experts. Radiol. Med. 2025, 130, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-E.; Lee, W.-J.; Son, E.-J.; Kim, T.-H.; Jeon, D.-S.; Kim, Y.-S. The Experience of Reslizumab Treatment for Frequent Relapsing Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia Accompanying Asthma: A Case Series. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, PA4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoine, F.; Lacy, P. Eosinophil Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors: Emerging Roles in Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, C.L.; Ackerman, S.J.; Zheng, T.; Elias, J.A. Eosinophil-Fibroblast Interactions. Granule Major Basic Protein Interacts with IL-1 and Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in the Stimulation of Lung Fibroblast IL-6-Type Cytokine Production. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4449–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi-Schaffer, F.; Garbuzenko, E.; Rubin, A.; Reich, R.; Pickholz, D.; Gillery, P.; Emonard, H.; Nagler, A.; Maquart, F.A.X. Human Eosinophils Regulate Human Lung- and Skin-Derived Fibroblast Properties in Vitro: A Role for Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9660–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagai, U.; Dadfar, E.; Lundahl, J.; Venge, P.; Sköld, C.M. Eosinophil Cationic Protein Stimulates TGF-Β1 Release by Human Lung Fibroblasts In Vitro. Inflammation 2007, 30, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Bois, R.M.; du Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).