Abstract
Shotgun metagenomics (SMg) usefulness for brain abscess diagnosis is not known. We describe a case of brain abscess diagnosed with SMg and provide a review of the literature. A 70-year-old woman was diagnosed with multiple brain abscesses. Standard culture techniques and 16S rRNA gene sequencing of abscess samples remained negative. SMg finally revealed the presence of sequences from Streptococcus anginosus and Fusobacterium nucleatum, leading to antimicrobial treatment adaptation and corticosteroids initiation. The patient finally recovered. A literature review retrieved fifteen other cases of brain abscesses diagnosed with SMg. SMg results led to changes in patient management in most cases. The existing literature about the performances of SMg, its advantages, future evolutions, and limitations is then discussed. SMg place in routine should be evaluated and defined through prospective studies.
1. Introduction
A brain abscess is a focal infection causing cerebritis that develops into a collection of pus surrounded by a well-vascularized collagenous capsule [1]. Community-acquired brain abscess remains rare (reported incidence of 0.4 to 0.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants worldwide) but can be life-threatening for patients. The mortality rate is 10–15%. Only 70% of patients have a good outcome with minor or no neurologic sequelae [1,2]. Imaging should include MRI with diffusion sequences, especially to rule out tumors. Microbiological documentation of brain abscesses is challenging with routine microbiological techniques as cultures remain negative in one-third of cases [1]. Empirical antimicrobial therapy can be suboptimal, contributing to increased morbidity and mortality. Rapid identification of pathogens is essential to guide antimicrobial management. Shotgun metagenomics (SMg) allows untargeted sequencing of all DNA and RNA present in a biological sample. The detection and identification of all present microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites) is possible without any a priori microbiological hypothesis. The SMg approach is revolutionizing some infectious diseases research fields with the discovery of new pathogens and the analysis of microbiomes; however, its place in clinical routine is still not well characterized.
We report the case of a patient diagnosed with brain abscesses, microbiologically documented using SMg. Then, we review the literature about the microbiological documentation of brain abscess with SMg, and we discuss the technique’s performances and limits.
2. Detailed Case Description
A 70-year-old woman with a medical history of high blood pressure was admitted to our hospital for walking disorders. She developed a fever (38.5 °C) and left hemiplegia. A cerebral Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan was performed and revealed seven intra-axial, bilateral, sustentorial tissular lesions up to 35 mm in diameter, suspected of metastases or abscesses (Figure 1). Empirical antibiotic therapy with high doses of ceftriaxone (75 mg/kg/d) and metronidazole (500 mg/t.i.d.) was initiated. Looking for a primitive malignancy lesion, a chest-abdomen-pelvis CT scan revealed a pulmonary necrotizing mass measuring 93 × 43 × 40 mm. Anatomopathological analysis of a bronchial aspiration and a transbronchial puncture showed nonspecific inflammation. Bacterial and mycobacterial cultures remained negative, as well as blood cultures. Transthoracic echocardiography showed no signs of endocarditis. A second MRI revealed no sign of improvement after 12 days of antibiotic therapy. The hypothesis of malignant lesions was withheld, and antibiotic therapy was interrupted.
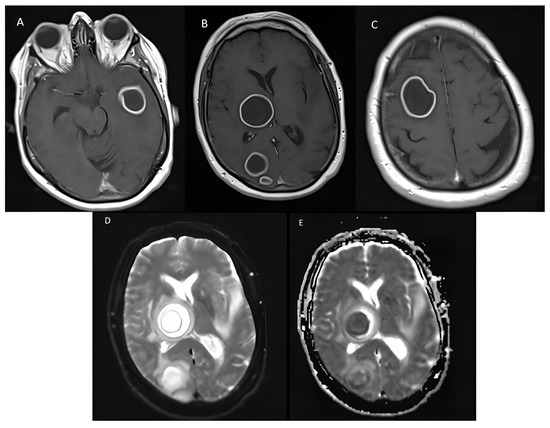
Figure 1.
Axial T1-weighted brain MRI shows masses with a necrotic center surrounded by a capsule in (A) the left temporal lobe, (B) the right occipital lobe and basal ganglia, and (C) the right frontal lobe. A high signal in axial diffusion (D) and the ADC map with a low signal (E) from the lesion of the right occipital lobe represent restricted diffusion.
Three days later, the patient experienced reduced consciousness, leading to respiratory distress. She was transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and put on mechanical ventilation. Meropenem and anti-tuberculosis drug therapy were initiated. A stereotactic surgery with a cerebral biopsy and aspiration of a temporal lesion was performed. The anatomopathological examination of the cerebral biopsy showed acute, nonspecific inflammation, as in pulmonary samples. Standard bacterial (aerobic and anaerobic)/mycobacterial/mycological direct examination and culture of the cerebral biopsy remained negative, as well as Sanger sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, Nocardia spp., and Toxoplasma gondii PCR. A SMg analysis consisting of an unbiased in-house pan-microorganism DNA- and RNA-based method (MetaMIC® software, V2.2.1) was performed [3] and revealed the presence of Streptococcus anginosus and Fusobacterium nucleatum. These results led to the initiation of corticosteroid therapy against cerebral oedema, the discontinuation of meropenem and anti-mycobacterial therapies, and the introduction of ceftriaxone and metronidazole. The patient regained consciousness under therapy and was discharged from the ICU eight days after admission.
A dental consultation with panoramic radiography revealed an infectious source on tooth 44, which was suspected to be the etiology of the hematogenous brain abscesses. The patient received appropriate dental care. A cerebral MRI performed after six weeks of antibiotic therapy showed a significant reduction in the abscesses’ size. Antibiotic therapy was extended by 12 weeks. The patient’s condition continued to improve. She benefited from neuromuscular rehabilitation and regained the ability to walk with assistance.
3. Discussion
In the present case, conventional microbiology methods and Sanger sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene failed to identify the causative pathogens when SMg succeeded. The antibiotic spectrum was narrowed, and anti-mycobacterial therapy was discontinued, thus limiting broad-spectrum molecule exposure and preventing potential side effects. As the causative pathogens were from the oral microbiota, a dental origin was investigated. Reassurance of both patients and clinicians on appropriate antimicrobial coverage led to the initiation of corticosteroids to treat cerebral oedema, which resulted in rapid clinical improvement.
Pathogen identification is crucial and has led to many decisions in the management of patients. As a result, the opportunity for de-escalation once microbiological results are available is still a controversy. However, microbiological documentation of brain abscesses is challenging. Bacterial documentation is mostly obtained from abscess aspiration samples, as blood cultures are often sterile and lumbar punctures can result in clinical degradation. Access to abscess samples has become easier with the increased use of stereotactic surgery and progress in imaging. Diffusion weight imaging (DWI) MRI has indeed high sensitivity (95%) and specificity (94%) for the differentiation of brain abscess from other intracranial cystic mass lesions, such as glioblastoma [4]. Restricted diffusion, consisting of a high DWI and a low ADC signal, is usually found in brain abscesses. This reflects the high cellularity and viscosity of the pus. In contrast, cystic tumors show low DWI and a high ADC signal. Stereotactic surgery is a micro-invasive technique that can be used for any brain abscess whose size is greater than 1 cm in order to aspirate the pus with excellent clinical safety [2]. Brain abscess aspiration samples are cultured using non-selective media with a long incubation time after Gram staining. However, culture remains negative in one-third of cases and often fails to identify all involved pathogens [1]. This lack of sensitivity can be explained by the use of empirical antibiotic therapy prior to the sampling, as in our case. As a delay in the initiation of antimicrobial therapy can result in a poor outcome and abscess sampling cannot always be performed immediately, antibiotic therapy is frequently initiated before sampling. Another explanation of negative cultures is the involvement of slow-growing, difficult-to-cultivate, or “uncultivable” bacteria that require specific growth conditions, such as strict anaerobic organisms [2]. Moreover, conventional culture is challenged in cases of polymicrobial infection. To overcome these limits, molecular approaches can be used in addition to culture. The most commonly used technique is Sanger sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene (bacterial universal gene rrs) [5]. This technique is also unsuitable in cases of polymicrobial infection and targets only bacteria.
New molecular techniques such as SMg are freeing themselves from these limits. SMg involves several steps: pre-extraction (use of mechanical, enzymatic, and chemical procedures), extraction, library preparation, and sequencing (mostly using the Illumina sequencing platform). An environmental (molecular-grade water) and a positive (microbial community) control can be included in each run and processed through the entire protocol. In our case, sequencing data were analyzed by means of in-house and patented MetaMIC® software (V2.2.1), composed of a mosaic of modules [6].
Previous studies have provided evidence of SMg significant input for pathogen identification of several infectious diseases [7,8], such as meningitis/encephalitis [9], necrotizing soft-tissue infections [3], pneumonia [10], bloodstream infections [11], or prosthetic joint infections [12]. Gu et al. demonstrated that SMg sensitivity and specificity of detection were 79% and 91% for bacteria and 91 and 89% for fungi, based on 182 various body fluids. Their work also compared two sequencing platforms: Illumina (San Diego, USA), used in our case and in most cases in the literature, and Nanopore (Oxford, UK). Both showed the same performances, yet the sequencing running time was much shorter for Nanopore (50 min versus 24 h) [8]. Compared to conventional culture and sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene, SMg appeared to be more informative for bacterial documentation [3,6,8,9,13,14]. For instance, in a study by Zhao et al., SMg identified a pathogen in all 82 abscess samples from patients with osteoarticular infections, compared with 48% by culture [13]. With a different aim, Miao et al. investigated SMg performances for diagnosing infectious disease on 511 specimens, mostly from respiratory sites, retrospectively classified as infectious and non-infectious [14]. Sensitivity and specificity were 51% and 86%, respectively; in cases with antimicrobial exposure, sensitivity was 53% versus 34% for culture. Furthermore, in a series of 58 cases of encephalitis or meningitis, diagnosis was made solely by SMg in 13 cases (22%) [9]. These data show that SMg increases the sensitivity to detect pathogens and improves the diagnosis of infectious diseases as a last resort test. Finally, SMg enables the detection of the resistance gene that can overcome the absence of conventional antibiograms.
Empirical anti-tuberculosis treatment is often started in the case of undocumented lesions of the central nervous system, even without risk factors. The sensitivity of both culture and PCR approaches is low. To our knowledge, no case of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis brain abscess diagnosed with SMg has been published. Zhou et al. compared SMg with mycobacteriological culture and PCR (GenXpert) in 105 direct clinical samples, including 49 cerebrospinal fluids (CSFs). Sensitivity was 71%, well above culture (43%) and PCR (29%). Combined sensitivity (PCR and SMg) was 86% [15]. This highlights the fact that diagnosing central nervous system tuberculosis is difficult. SMg can help clinicians make alternative diagnoses, as in our case, and improve tuberculosis diagnosis sensitivity.
A literature review on SMg use for brain abscesses microbiological documentation retrieved only fifteen other cases published as case reports or short series [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Most sampling was conducted after the start of the antibiotics, which affected conventional culture. SMg was performed, mostly because of negative culture, on the abscess sample in six cases, on the CSF in eight cases, on the serum in two cases, and on the abscess localization in one case (Table 1). CSF analysis showed aseptic meningitis, yet with positive SMg for pathogen DNA. This can make microbiological documentation possible without the need for invasive procedures. Pathogen identifications included various pathogens, such as anaerobic bacteria, Nocardia sp., but also bacterial species from the oral microbiota, as in the present case (Table 1). Nocardia sp. was identified in five cases, two of which had no previous risk factors. These species are resistant to the antibiotic therapy proposed for immunocompetent patients. Culture was positive in 3/5 cases; species identification by SMg was faster than conventional methods, although Ziehl–Nielsen staining was suggestive in one case.

Table 1.
Reported cases of brain abscess diagnosed with shotgun metagenomics (SMg).
In these fifteen published cases, SMg results led to changes in patient management in most cases (12/15). However, only cases with positive results have been published, which highlights the need for prospective studies to evaluate the diagnostic performance of brain abscesses. SMg was also able to identify nonbacterial causes of brain abscess, such as fungi [26]. SMg allowed detection of amoebae [29], fungi [30], and viruses, even previously unknown [31], in other central nervous system infections such as encephalitis. This shows one of SMgs greatest advantages, which is its non-targeted approach.
SMg has some limitations. First, this new technique is still expensive (several hundred euros per sample) and has a long turnaround time [6]. Access to routine clinical practice is therefore difficult [3]. However, improvements to the technique continue to make sequencing faster and less expensive. Second, SMg does not allow testing for exhaustive antimicrobial drug susceptibility and needs to be used in addition to conventional methods. The detection of resistance genes can be used as a surrogate. Third, sensitivity can decrease in cases with a high human DNA background. Depletion and enrichment methods need to be improved. Fourth, contaminating DNA from the environment can lead to false positive identification, and the clinical context remains fundamental for interpretation. Finally, the implementation of the SMg approach in clinical laboratories requires specialized skills in bioinformatics and the biological and clinical interpretation of sequencing results.
4. Conclusions
Bacterial identification of brain abscesses is challenging but decisive in guiding the patient’s management. SMg is a promising new molecular identification method of particular interest in this disease considering its characteristics: high morbidity, polymicrobial and/or anaerobic-caused infection, frequent use of antibiotics prior to sampling. SMg is better suited to be used in addition to conventional identification methods, considering its limitations and challenges in result interpretation. As physicians begin to include SMg in clinical practice, this approach needs to be more accessible at reasonable cost and delay. Prospective studies are required to assess SMg clinical impact and cost-effectiveness.
Author Contributions
W.L., C.L., J.P., C.R., C.B., L.Q., G.H.-A., S.A. and A.C. contributed to this study’s conception and design. Data collection and analysis were performed by W.L., C.L., J.P. and A.C. The first draft of this manuscript was written by W.L., C.L., J.P. and A.C., and all authors commented on previous versions of this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and according to the reference methodology MR-003 of the Commission Nationale Informatique et Libertés. Ethical review and approval were waived for this study according to French law regarding MR-003 non-interventional studies.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brouwer, M.C.; Coutinho, J.M.; van de Beek, D. Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneville, R.; Ruimy, R.; Benzonana, N.; Riffaud, L.; Carsin, A.; Tadié, J.M.; Piau, C.; Revest, M.; Tattevin, P.; The ESCMID Study Group for Infectious Diseases of the Brain (ESGIB). An update on bacterial brain abscess in immunocompetent patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.; Jary, A.; Hua, C.; Woerther, P.-L.; Bosc, R.; Desroches, M.; Sitterlé, E.; Gricourt, G.; De Prost, N.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; et al. Pathogen identification by shotgun metagenomics of patients with necrotizing soft-tissue infections. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.X.; Li, B.; Yang, H.F.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Zheng, H.J.; Gong, Q.Y. Can diffusion-weighted imaging be used to differentiate brain abscess from other ring-enhancing brain lesions? A meta-analysis. Clin Radiol. 2014, 69, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Masalma, M.; Lonjon, M.; Richet, H.; Dufour, H.; Roche, P.-H.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.-E. Metagenomic analysis of brain abscesses identifies specific bacterial associations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoureux, C.; Surgers, L.; Fihman, V.; Gricourt, G.; Demontant, V.; Trawinski, E.; N’debi, M.; Gomart, C.; Royer, G.; Launay, N.; et al. Prospective comparison between shotgun metagenomics and Sanger sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene for the etiological diagnosis of infections. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 761873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkins, L.M.; Bryson, A.L.; Miller, S.A.; Mitchell, S.L. Navigating clinical utilization of direct-from-specimen metagenomic pathogen detection: Clinical applications, limitations, and testing recommendations. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Deng, X.; Lee, M.; Sucu, Y.D.; Arevalo, S.; Stryke, D.; Federman, S.; Gopez, A.; Reyes, K.; Zorn, K.; et al. Rapid pathogen detection by metagenomic next-generation sequencing of infected body fluids. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Arevalo, S.; Yu, G.; Neuhaus, J.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Briggs, B.; Langelier, C.; et al. Clinical metagenomic sequencing for diagnosis of meningitis and encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Larkin, P.M.; Zhao, D.; Ma, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Clinical impact of metagenomic next-generation sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage in the diagnosis and management of pneumonia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumaz, S.; Stevens, P.; Grumaz, C.; Decker, S.O.; Weigand, M.A.; Hofer, S.; Brenner, T.; von Haeseler, A.; Sohn, K. Next-generation sequencing diagnostics of bacteremia in septic patients. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoendel, M.J.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Yao, J.Z.; Chia, N.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Patel, R. Identification of prosthetic joint infection pathogens using a shotgun metagenomics approach. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhou, W.; Fan, J.; Yan, G.; Qin, S.; Pang, Y. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing improves diagnosis of osteoarticular infections from abscess specimens: A multicenter retrospective study. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Yao, Y.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Microbiological diagnostic performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied to clinical practice. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67 (Suppl. S2), S231–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Ruan, Q.; Jiang, N.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Ying, Y.; Qian, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Diagnosis Efficacy of Active Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Infection via Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing of Direct Clinical Samples. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.L.; Guo, L.Y.; Wu, H.L.; Feng, W.Y.; Chen, T.M.; Liu, G. Evaluation of next-generation sequencing for the pathogenic diagnosis of children brain abscesses. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Yan, S.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X. Case report: Metagenomics next-generation sequencing can help define the best therapeutic strategy for brain abscesses caused by oral pathogens. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 644130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura with brain abscess caused by Nocardia farcinica diagnosed using metagenomics next-generation sequencing of the cerebrospinal fluid: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishido, A.A.; Vostal, A.; Mayer, R.; Ho, C.; Baddley, J.W. Diagnosis of central nervous system invasive aspergillosis in a liver transplant recipient using microbial cell-free next generation DNA sequencing. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, R.; Qu, D.; Ye, Q.; Chen, X. Rapid and accurate diagnosis of brain abscess caused by Nocardia asiatica with a combination of Ziehl-Neelsen staining and metagenomics next-generation sequencing. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ocak, U.; Gong, Y. An unusual case report of brain abscess caused by Prevotella loescheii identified using the metagenomic next-generation sequencing. IDCases 2020, 20, e00758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.Y.; Xu, G.R.; Dai, T.J. Precision diagnosis and therapy of a case of brain abscesses associated with asymptomatic pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, S.; Li, J.; Xia, H.; Liu, X. Brain abscess caused by Nocardia farcinica and diagnosed by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 803554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, H. Case report: Multiple abscesses caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis diagnosed by metagenomic next-generation sequencing. Front Med. 2023, 9, 1089863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhuang, S.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Lyu, X. Brain Abscess Caused by Nocardia brevicatena in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 7693–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Ma, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shen, H. Brain abscess caused by Scedosporium boydii in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient: A case report and literature review. Indian. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 40, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Chen, S.; Yu, Z.; Yu, T. Multifocal brain abscesses caused by invasive Streptococcus intermedia: A case report. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 893627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Xue, X.H. Coinfection of Streptococcus suis and Nocardia asiatica in the human central nervous system: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 6283–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakata, S.; Sakiyama, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Ikeda, M.; Takahata, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Arata, H.; Yonezawa, H.; Kirishima, M.; et al. The application of shotgun metagenomics to the diagnosis of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis due to Balamuthia mandrillaris: A case report. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.H.; He, X.J.; Nie, J.M.; Guan, S.S.; Chen, Y.K.; Liu, M. Central nervous system aspergillosis misdiagnosed as Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in a patient with AIDS: A case report. AIDS Res. Ther. 2022, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Gricourt, G.; Ndebi, M.; Demontant, V.; Poiteau, L.; Burrel, S.; Boutolleau, D.; Woerther, P.L.; Calvez, V.; Stroer, S.; et al. Fatal Encephalitis Caused by Cristoli Virus, an Emerging Orthobunyavirus, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).