Novel Association of rs17111557(T) in PCSK9 with Higher Diastolic Blood Pressure in Northern Ghanaian Adults: Candidate Gene Analysis from an AWI-Gen Sub-Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design and Sample Size Justification
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Demographic, Blood Pressure, and Anthropometric Data
2.3.2. Genotyping and Imputation of Candidate Genes
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Determination of Minor Allele Frequencies of Associated Variants in Other Populations and Functional Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Anthropometric Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. Association of Gene Variants with Blood Pressure Indices
3.3. Minor Allele Frequencies of rs17111557 in PCSK9 in Other Populations
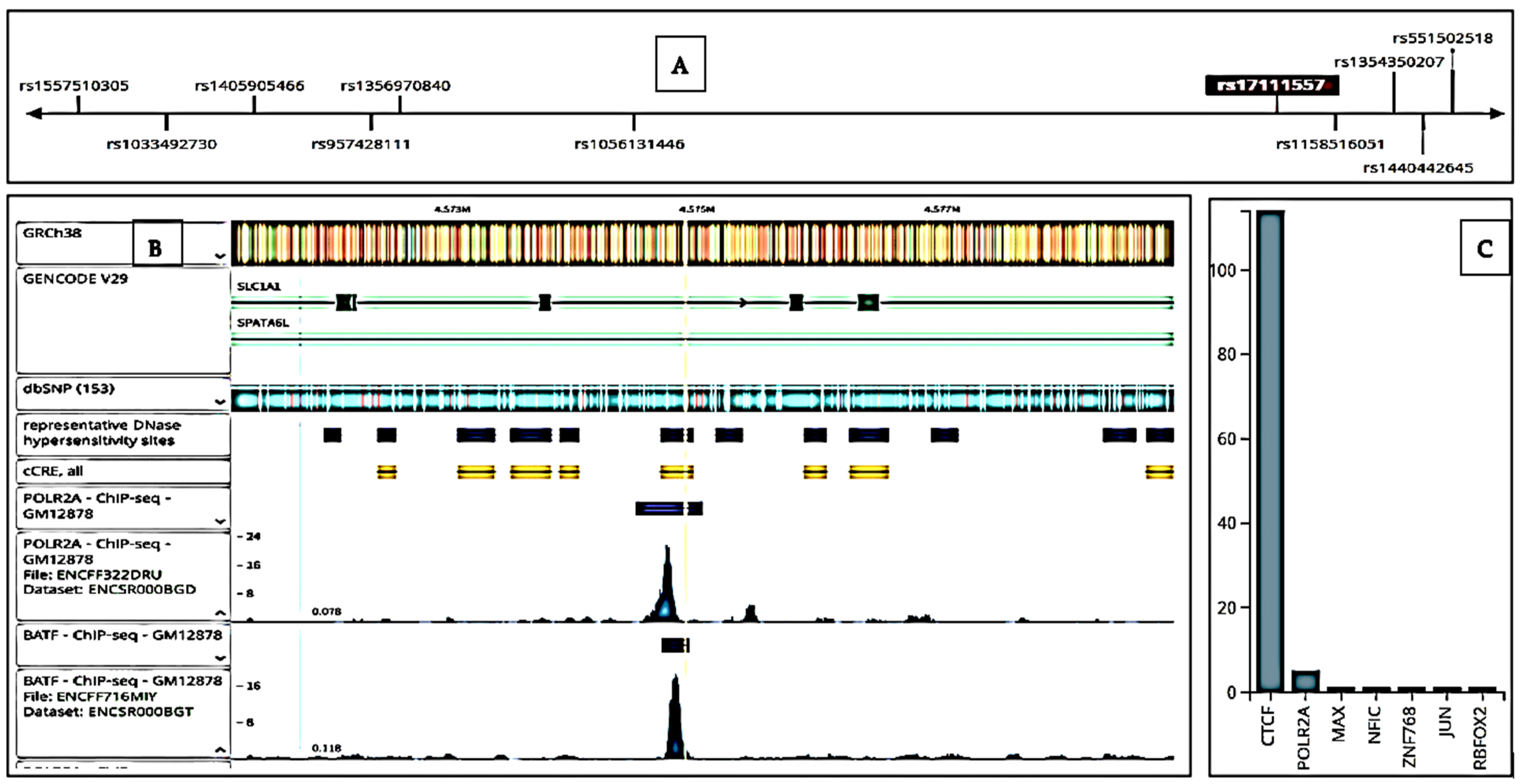
3.4. Functional Analysis of rs17111557 in PCSK9
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Song, L.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Tian, Y. Ideal cardiovascular health metric and its change with lifetime risk of cardiovascular diseases: A prospective cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanni, A.; Enrico, A.; Aime, B.; Michael, B.; Marianne, B.; Jonathan, C.; Josef, C.; Michael, C.; Nicole, D.; Sophia, E.B.; et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erem, C.; Hacihasanoglu, A.; Kocak, M.; Deger, O.; Topbas, M. Prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension and associated risk factors among Turkish adults: Trabzon hypertension study. J. Public Health 2009, 31, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Aslibekyan, S.; Tiwari, H.K.; Zhi, D.; Sung, Y.J.; Hunt, S.C.; Rao, D.C.; Broeckel, U.; Judd, S.E.; Muntner, P.; et al. PCSK9 variation and association with blood pressure in African Americans: Preliminary findings from the HyperGEN and REGARDS studies. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Choudhury, A.; Hazelhurst, S.; Crowther, N.J.; Boua, P.R.; Sorgho, H.; Agongo, G.; Nonterah, E.A.; Micklesfield, L.K.; Norris, S.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis of blood pressure traits and hypertension in sub-Saharan African populations: An AWI-Gen study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgut Cosan, D.; Colak, E.; Saydam, F.; Yazıcı, H.U.; Degirmenci, I.; Birdane, A.; Colak, E.; Gunes, H.V. Association of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene polymorphisms and concentration with essential hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2016, 38, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colima-Fausto, A.G.; Sánchez-Corona, J.; Ramírez-López, G.; García-Zapien, A.G.; Magaña-Torres, M.T. Association of the -629C>A (rs1800775) CETP polymorphism with the development of essential hypertension in the Mexican population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2020, 24, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yako, Y.Y.; Balti, E.V.; Matsha, T.E.; Dzudie, A.; Kruger, D.; Sobngwi, E.; Agyemang, C.; Kengne, A.P. Genetic factors contributing to hypertension in African-based populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yamada, Y.; Kato, K.; Yoshida, T.; Yokoi, K.; Matsuo, H.; Watanabe, S.; Ichihara, S.; Metoki, N.; Yoshida, H.; Satoh, K.; et al. Association of polymorphisms of ABCA1 and ROS1 with hypertension in Japanese individuals. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ali, S.A.; Soo, C.; Agongo, G.; Alberts, M.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Boua, R.P.; Choudhury, A.; Crowther, N.J.; Depuur, C.; Gómez-Olivé, F.X.; et al. Genomic and environmental risk factors for cardiometabolic diseases in Africa: Methods used for phase 1 of the AWI-Gen population cross-sectional study. Glob. Health Action 2018, 11 (Suppl. S2), 1507133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, M.; Crowther, N.; Tambo, E.; Agongo, G.; Baloyi, V.; Dikotope, S.; Gómez-Olivé, X.; Jaff, N.; Sorgho, H.; Wagner, R.; et al. The AWI-Gen Collaborative Centre: Understanding the interplay between genomic and environmental risk factors for cardiometabolic diseases in sub-Saharan Africa. Glob. Health Epidemiol. Genom. 2016, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduro, A.R.; Wak, G.; Azongo, D.; Debpuur, C.; Wontuo, P.; Kondayire, F.; Welaga, P.; Bawah, A.; Nazzar, A.; Williams, J.; et al. Profile of the Navrongo Health and Demographic Surveillance System. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Wen, X.; Yang, W. Association of the lipoprotein lipase gene Ser447Ter polymorphism with hypertension and blood pressure variation: Evidence from an updated meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2017, 39, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J. Sample size requirements for association studies of gene-gene interaction. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, M.M.; Schildcrout, J.; Baldwin, S.; Edwards, T.; Lipworth, L.; Robinson-Cohen, C. Genetic variants association with systolic blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e027993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Cortes, D.; Griffiths, L.R. Methods for extracting genomic DNA from whole blood samples: Current perspectives. J. Biorepos. Sci. Appl. Med. 2014, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensemble Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, R.C.C.; Bortolin, R.H.; Borges, J.B.; de Oliveira, V.F.; Dagli-Hernandez, C.; Marçal, E.D.S.R.; Bastos, G.M.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Faludi, A.A.; Silbiger, V.N.; et al. LDLR and PCSK9 3’ UTR variants and their putative effects on micro RNA molecular interactions in familial hypercholesterolemia: A computational approach. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 9165–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.F.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Patel, R.S.; Fairhurst-Hunter, Z.; Lyall, D.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Horta, B.L.; Hyppönen, E.; Power, C.; et al. PCSK9 genetic variants and risk of type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Men | Women | Total | * p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex/n (%) | 846 (46%) | 993 (54%) | 1839 (100%) | 0.001 |
| Smoking status/n (%) | ||||
| No | 298 (35.3) | 960 (96.7) | 1258 (68.4) | p < 0.001 |
| Yes | 548 (64.8) | 33 (3.2) | 581 (31.6) | |
| Age/years | 51 ± 5.8 | 52 ± 5.8 | 51 ± 5.8 | <0.001 |
| BMI/kg/m2 | 20.9 ± 3.2 | 22.3 ± 3.9 | 21.6 ± 3.6 | <0.001 |
| WC/cm | 7.3 ± 0.8 | 7.7 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| DBP/mmHg | 77.0 ± 12.9 | 77.2 ± 12.6 | 77.1 ± 12.7 | 0.760 |
| SBP/mmHg | 125.0 ± 20.4 | 123.3 ± 22.6 | 124.1 ± 21.6 | 0.094 |
| PP/mmHg | 47.9 ± 10.9 | 46.1 ± 13.1 | 46.9 ± 12.2 | 0.001 |
| MAP/mmHg | 93.0 ± 14.9 | 92.6 ± 15.4 | 92.8 ± 15.2 | 0.533 |
| SNP | Genotype | Minor Allele | # MAF | pHWE | Without Covariate Adjustment | * With Covariate Adjustment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β Value | S.E | p Value | β Value | S.E | p Value | |||||
| rs17111557 | TC | T | 0.113 | 0.402 | 6.240 | 1.479 | 0.003 | 5.984 | 1.476 | 0.006 |
| 1:55522141 | GA | G | 0.192 | 0.310 | 0.311 | 1.091 | 0.153 | 0.246 | 1.090 | 0.164 |
| rs625619 | AG | A | 0.225 | 0.791 | 3.035 | 1.096 | 0.672 | 2.976 | 1.093 | 0.771 |
| Population | MAF |
|---|---|
| * Kassena-Nankana population | 0.113 |
| # KGP Sub-Saharan Africans | 0.136 |
| KGP Europeans | 0.007 |
| KGP African Americans | 0.066 |
| KGP Asians | 0.009 |
| Functionality Item | Value |
| Localization | 3′UTR |
| CADD Score | 0.171 |
| RDB Score | 0.55436 |
| VEP | Benign |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aweeya, J.A.; Gowans, L.J.J.; Nonterah, E.A.; Asoala, V.; Ansah, P.; Ramsay, M.; Agongo, G. Novel Association of rs17111557(T) in PCSK9 with Higher Diastolic Blood Pressure in Northern Ghanaian Adults: Candidate Gene Analysis from an AWI-Gen Sub-Study. BioMed 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5030015
Aweeya JA, Gowans LJJ, Nonterah EA, Asoala V, Ansah P, Ramsay M, Agongo G. Novel Association of rs17111557(T) in PCSK9 with Higher Diastolic Blood Pressure in Northern Ghanaian Adults: Candidate Gene Analysis from an AWI-Gen Sub-Study. BioMed. 2025; 5(3):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5030015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAweeya, Joseph A., Lord J. J. Gowans, Engelbert A. Nonterah, Victor Asoala, Patrick Ansah, Michele Ramsay, and Godfred Agongo. 2025. "Novel Association of rs17111557(T) in PCSK9 with Higher Diastolic Blood Pressure in Northern Ghanaian Adults: Candidate Gene Analysis from an AWI-Gen Sub-Study" BioMed 5, no. 3: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5030015
APA StyleAweeya, J. A., Gowans, L. J. J., Nonterah, E. A., Asoala, V., Ansah, P., Ramsay, M., & Agongo, G. (2025). Novel Association of rs17111557(T) in PCSK9 with Higher Diastolic Blood Pressure in Northern Ghanaian Adults: Candidate Gene Analysis from an AWI-Gen Sub-Study. BioMed, 5(3), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5030015







