Biomechanical Behavior of Female Breast—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
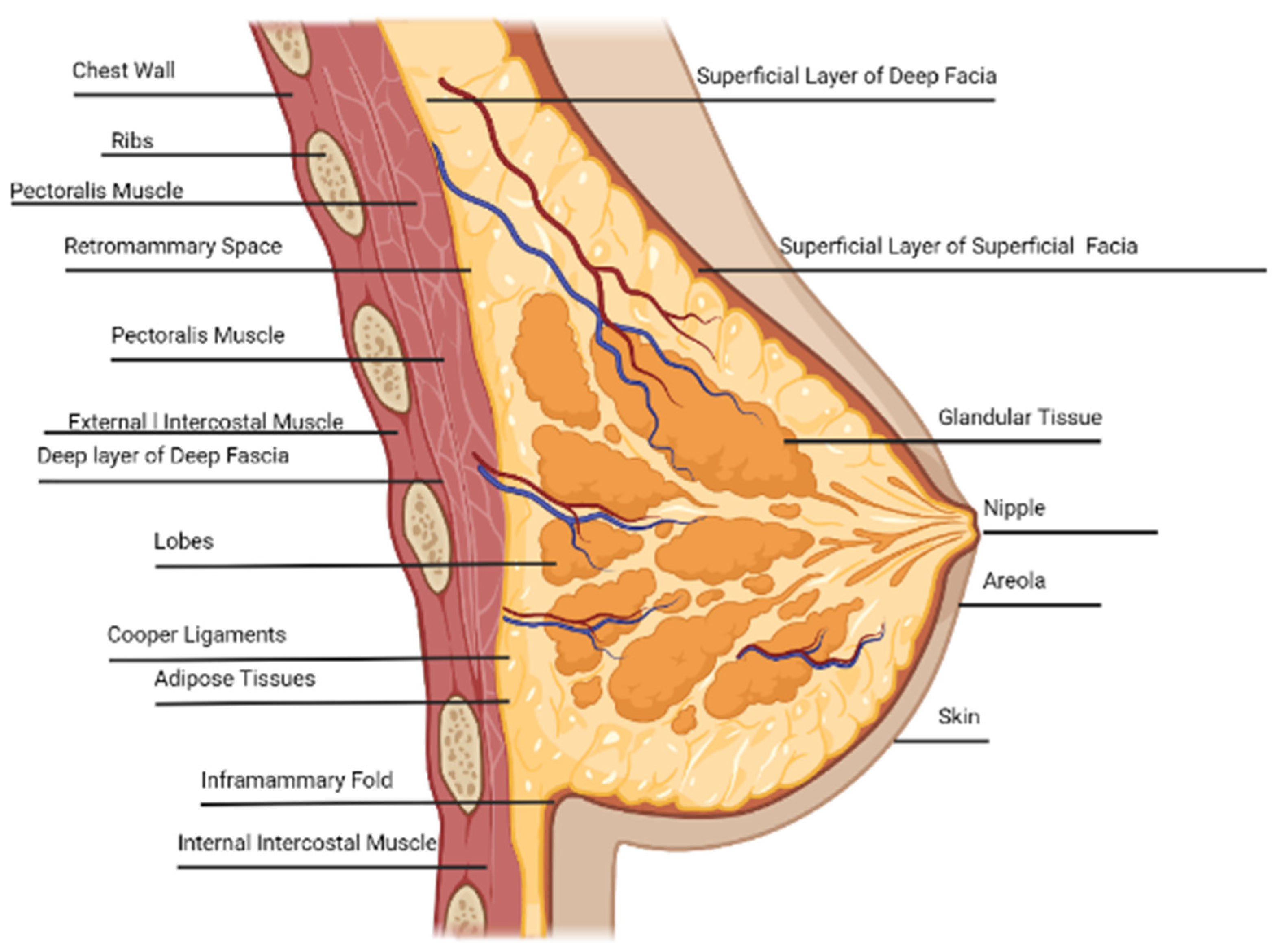
3. Anatomy of Breast
3.1. Rib Cage
3.2. Pectoralis and Intercostal Muscle
3.3. Intercostal Space
3.4. Fibroglandular Tissue
3.5. Lobes, Nipple, Areola, and Ducts
3.6. Glandular Tissue
3.7. Adipose Tissue
3.8. Inframammary Fold
3.9. Cooper’s Ligament
4. Effects of Age and Stages of Breast Development
4.1. Tanner Staging Breast Development
4.2. Effects of Hormones and Age
5. Breast Skin

5.1. Stratum Corneum, Epidermis, Dermis, and Hypodermis
5.2. Breast Skin Characterization
6. Breast Tissue Mechanics
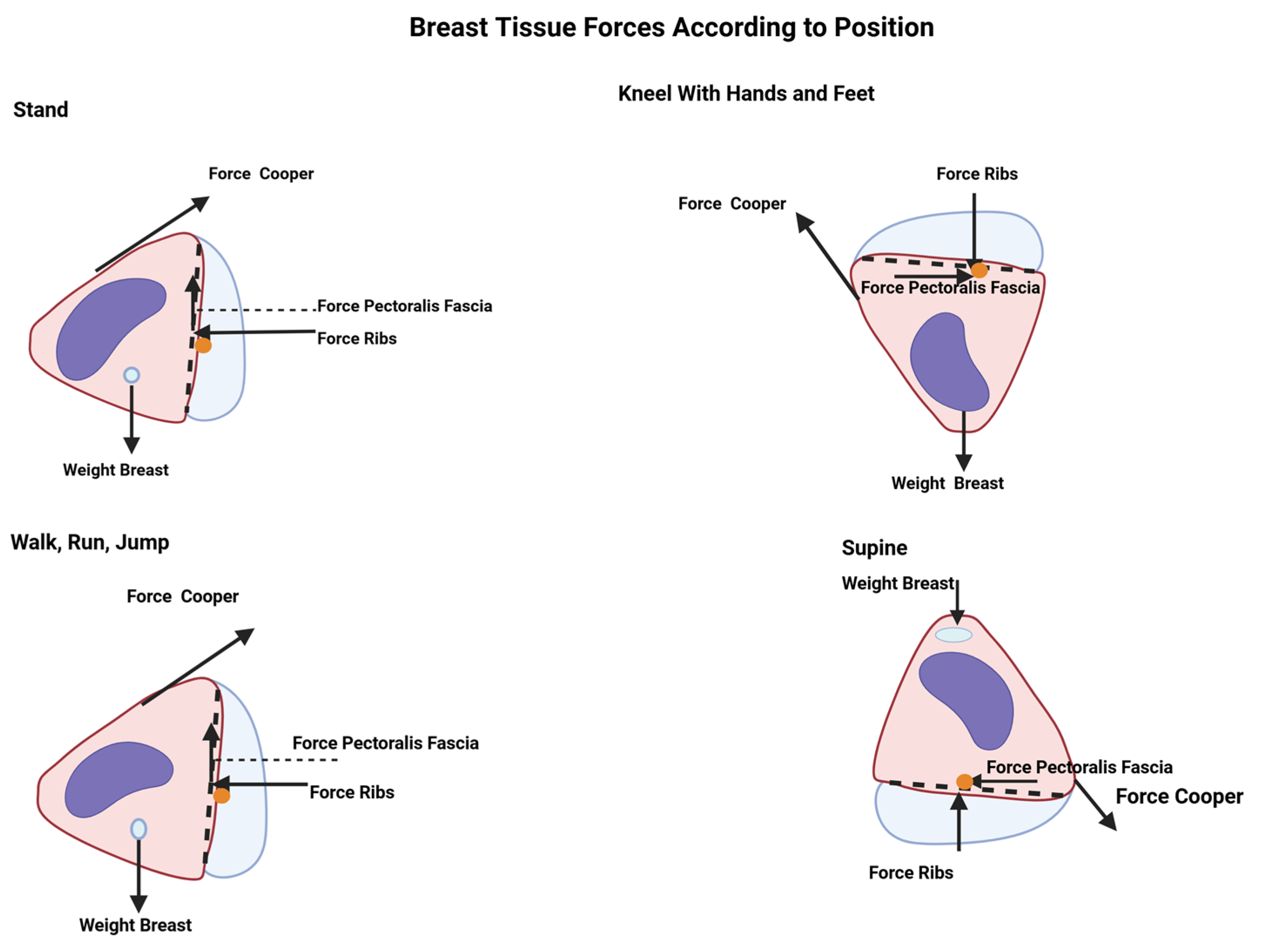
6.1. Breast Force in Newton’s Second Law
6.2. Tissue Expanders
6.3. Breast Compression
6.4. Viscoelasticity
6.5. Creep
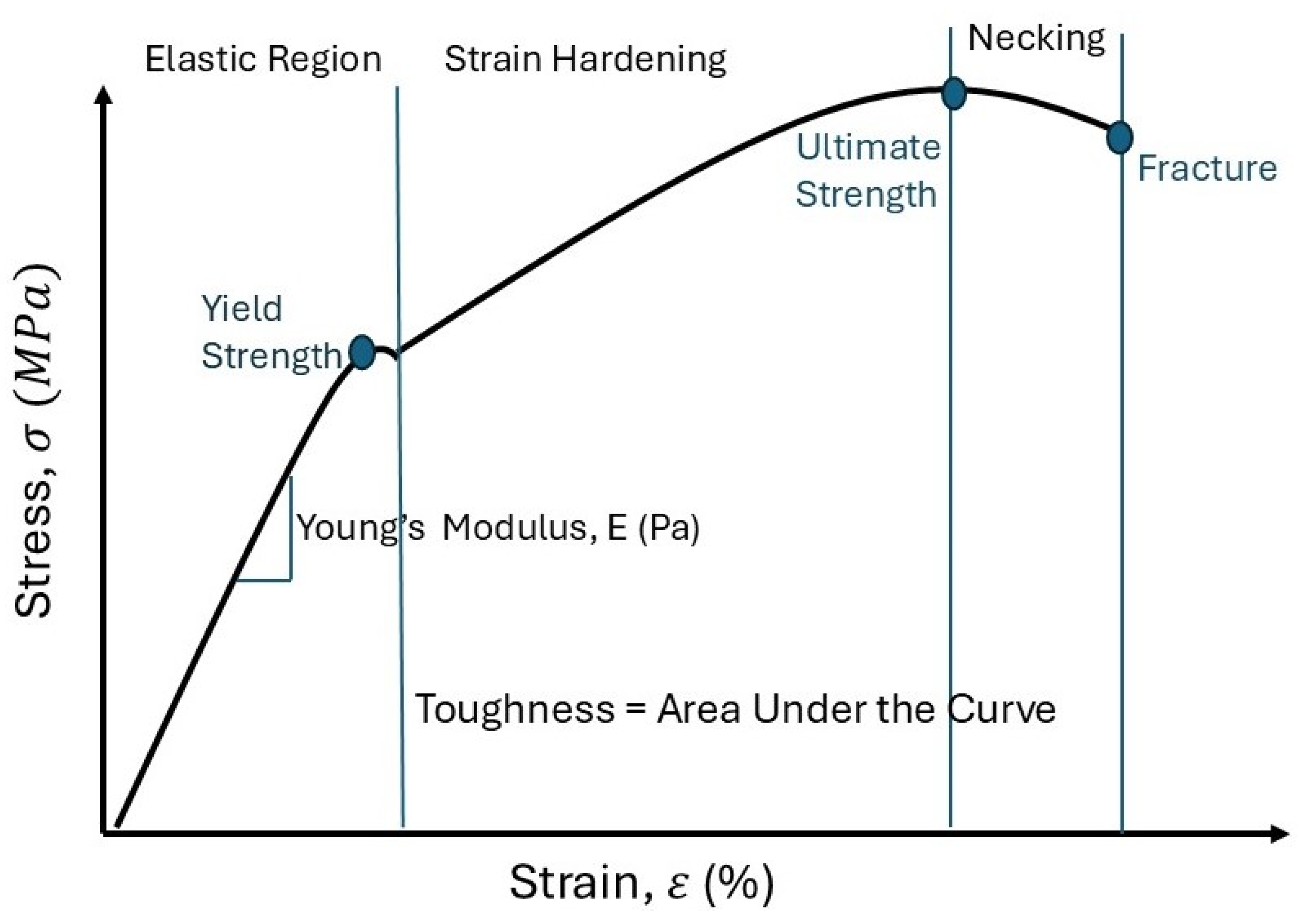
6.6. Young’s Modulus of Breast Tissue
6.7. Stiffness
6.7.1. Boyd’s Radial Stiffness
6.7.2. Linear Stiffness
6.7.3. Density
6.7.4. Increment of Strain Energy Density
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onyebeke, L.C.; Papazaharias, D.M.; Freund, A.; Dropkin, J.; McCann, M.; Sanchez, S.H.; Hashim, D.; Meyer, J.D.; Lucchini, R.G.; Zuckerman, N.C. Access to Properly Fitting Personal Protective Equipment for Female Construction Workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2016, 59, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamandi, F.; Pooler, T.; Runser, A.; Asman, C.; Bailey, R.; Robinson, N.; Goswami, T. Bioenergetics Analysis of Bra-Breast Interface. Appl. Mech. 2022, 3, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.; Cameron, M.; Fitzgerald, K. Breast size, bra fit and thoracic pain in young women: A correlational study. Chiropr. Osteopat. 2008, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltman, C.E.; Steele, J.R.; McGhee, D.E. Breast volume is affected by body mass index but not age. Ergonomics 2017, 60, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramardika, D.D.; Kasaluhe, M.D.; Barokah, S. Bra Usage Duration and Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. J. Bidan Cerdas 2023, 5, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltman, C.E.; Steele, J.R.; McGhee, D.E. Does breast size affect how women participate in physical activity? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhee, D.E.; Steele, J.R. Breast Biomechanics: What Do We Really Know? Physiology 2020, 35, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.H.; Ringrose, C.; Hyland, R.; Cole, A.; Brotherston, T. A method of assessing female breast morphometry and its clinical application. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1999, 52, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczyk, M.; Kasielska-Trojan, A.; Antoszewski, B. A New Tool for Breast Anthropometric Measurements: Presentation and Validation for Women and Men. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gefen, A.; Dilmoney, B. Mechanics of the normal woman’s breast. Technol. Health Care 2007, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garamone, J. Groups Work to Eliminate, Diminish Barriers to Women’s Military Service. U.S. Department of Defense. 23 January 2022. Available online: https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/Article/2908233/groups-work-to-eliminate-diminish-barriers-to-womens-military-service/ (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Le, Q.H.; Nguyen, H.C. Breast Anthropometry: Values and Application in Breast Surgery for Vietnamese Women. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateina, C.; Mandalidis, D. Effects of Artificially Induced Breast Augmentation on the Electromyographic Activity of Neck and Trunk Muscles during Common Daily Movements. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.M.; Martins, P. A review of bioengineering techniques applied to breast tissue: Mechanical properties, tissue engineering and finite element analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1161815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, K. Skin thickness of Korean adults. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2002, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskar, S.; Kehm, R.; Terry, M.B. Breast Tissue Composition—Why It Matters and How Can We Measure It More Accurately in Epidemiology Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, W.; Parakkal, P.F. An Introduction to Skin. In Function of Skin, 3rd ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, M.; Kumaraswamy, N.; Reece, G.P.; Hanson, S.E.; Fingeret, M.C.; Markey, M.K.; Ravi-Chandar, K. Characterization of human female breast and abdominal skin elasticity using a bulge test. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 103, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matousek, S.A. Discussion: The Attachments of the Breast to the Chest Wall: A Dissection Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 23e–26e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yip, J.; Yick, K.-L. Construction of multi-component finite element model to predict biomechanical behaviour of breasts during running and quantification of the stiffness impact of internal structure. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2024, 23, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute SEER Training Modules. Breast Anatomy. National Cancer Institute. Available online: https://training.seer.cancer.gov/breast/anatomy.html (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information STATPEARLS [Internet]. Physiology, Menstrual Cycle. National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information STATPEARLS [Internet]. 24 October 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500020/ (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Rendina, E.A.; Ciccone, A.M. The Intercostal Space. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2007, 17, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mîra, A.; Carton, A.-K.; Muller, S.; Payan, Y. A biomechanical breast model evaluated with respect to MRI data collected in three different positions. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 60, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briot, N.; Chagnon, G.; Burlet, L.; Gil, H.; Girard, E.; Payan, Y. Experimental characterization and modelling of breast Cooper’s ligaments. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2022, 21, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, F.; Hughes, T.; Barrios, P.; Borgstrom, M. Clinical location of the fourth and fifth intercostal spaces as a percent of the length of the sternum. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, H. The ribs and intercostal spaces. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care Med. 2008, 9, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazira, P.J.; Ellis, H.; Mahadevan, V. Anatomy and physiology of the breast. Surgery 2022, 40, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelar, J.d.M.; Aliverti, A.; Rattes, C.; Ximenes, M.E.; Campos, S.L.; Brandão, D.C.; Fregonezi, G.; de Andrade, A.D. The Expansion of the Pulmonary Rib Cage during Breath Stacking Is Influenced by Age in Obese Women. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rivard, A.B.; Galarza-Paez, L.; Peterson, D.C. Anatomy, Thorax, Breast. NIH National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information. 17 July 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519575/ (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- AlHarbi, Y. Anatomical Variations in the Pectoralis Minor Muscle Origin and Insertion: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e46329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, A.; Reiner, M.M.; Warneke, K.; Keiner, M.; Nakamura, M.; Tilp, M. Relationship between pectoralis major stiffness and shoulder extension range of motion. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1349426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettering Health ketteringhealth.org/Breasthealth. Breast Health Why a Mammogram; Kettering Health: Kettering, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe, M.J.; Byng, J.W.; Boyd, N.F. 21—Quantitative Image Analysis for Estimation of Breast Cancer Risk. In Handbook of Medical Imaging Biomedical Engineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krouskop, T.A.; Wheeler, T.M.; Kallel, F.; Garra, B.S.; Hall, T. Elastic Moduli of Breast and Prostate Tissues under Compression. Ultrason. Imaging 1998, 20, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.; Park, J.H. Breast Geometry Characterization of Young American Females Using 3D Image Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, D.; Burford, K.; Dench, P.; Dean, N.; Griffin, P. Measurement of breast volume using body scan technology (computer-aided anthropometry). Work 2012, 41, 4038–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, C.; Diorio, C.; Durocher, F. The Importance of Breast Adipose Tissue in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 57600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koscinski, K. Breast firmness is of greater importance for women’s attractiveness than breast size. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2019, 31, e23287–e23299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.M.; Al Youha, S.M.; Joukhadar, N.; Konder, R.B.; Stecco, C.; Wheelock, M.E. Anatomy of the Breast Fascial System: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 149, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramião, N.G.; Martins, P.S.; Rynkevic, R.; Fernandes, A.A.; Barroso, M.; Santos, D.C. Biomechanical properties of breast tissue, a state-of-the-art review. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2016, 15, 1307–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Openstax. University Physics Volume 1 12.3 Stress, Strain, and Elastic Modulus. Rice University. 1999–2024. ISBN 10: 1938168275. Available online: https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-1/pages/12-3-stress-strain-and-elastic-modulus (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Goodbrake, C.; Li, D.S.; Aghakhani, H.; Contreras, A.; Reece, G.P.; Markey, M.K.; Sacks, M.S. On the three-dimensional mechanical behavior of human breast tissue. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 50, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuel, M.; Bokor, B.R. Tanner Stages. StatPearls [Internet]. Bookshelf ID: NBK470280. 11 December 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470280/ (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Lteif, A.; Javed, A. Development of the Human Breast. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2013, 27, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman-Verhoeff, M.E.; Gredvig-Ardito, C.; Barker, D.H.; Saletin, J.M.; Carskadon, M.A. Classifying Pubertal Development Using Child and Parent Report: Comparing the Pubertal Development Scales to Tanner Staging. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 66, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Kumari, B.; Kalyan, G.; Kaur, B.; Devi, K.; Preeti; Saranjna; Singh, G. Anthropometric Breast Measurements and Brasserie Wearing Practices of North Indian Women. Indian J. Surg. 2022, 84, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV Infection in Infants and Children: Towards Universal Acess Recommendiations for Public Health Approach 2010 Revision; Annex H Sexual Maturity Rating (Tanner Staging) in Adolescents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK138588/ (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Krishna, K.B.; Witchel, S.F. Normal and Abnormal Puberty. Endotext. 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279024/ (accessed on 18 August 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Asokan, G.; Onnela, J.-P.; Baird, D.D.; Jukic, A.M.Z.; Wilcox, A.J.; Curry, C.L.; Fischer-Colbrie, T.; Williams, M.A.; Hauser, R.; et al. Menarche and Time to Cycle Regularity Among Individuals Born Between 1950 and 2005 in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2412854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Editors of Encylopedia. Middle Ages. Britannica. 15 September 2024. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/event/Middle-Ages (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Adkins, E.N.; Anderson, S.; McKoy, T.; Maduka, N.; Goswami, T. Etiology of Breast Development and Asymmetry. Adv. Gen. Pract. Med. 2022, 4, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govrin-Yehudain, J.; Dvir, H.; Preise, D.; Govrin-Yehudain, O.; Govreen-Segal, D. Lightweight Breast Implants: A Novel Solution for Breast Augmentation and Reconstruction Mammaplasty. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2015, 35, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, S. Skin 1: The structure and functions of the skin. Nurs. Times 2019, 115, 30–33. Available online: https://cdn.ps.emap.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2019/11/191127-Skin-1-the-structure-and-functions-of-the-skin.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Sutradhar, A.; Miller, M.J. In vivo measurement of breast skin elasticity and breast skin thickness. Ski. Res. Technol. 2012, 19, e191–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmi, B.J.; Blackwell, S.J.; Mancoll, J.S.; Phillips, L.G. Creep vs. Stretch: A review of the Viscoelastic Properties of Skin. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1998, 41, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm Beach State Collage. Chapter 06 Lecture Outline Anatomy Physiology The Unity of Form and Function Seventh Edition. Available online: https://www.palmbeachstate.edu/slc/Documents/AandP1ch06Lecture.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Huang, S.; Boone, J.M.; Yang, K.; Kwan, A.L.C.; Packard, N.J. The effect of skin thickness determined using breast CT on mammographic dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, T.P.B.; Rajagopal, V.; Nielsen, P.M.; Nash, M.P. Patient-Specific Modeling of Breast Biomechanics with Applications to Breast Cancer Detection and Treatment. Patient-Specif. Model. Tomorrow’s Med. 2011, 9, 379–412. [Google Scholar]
- Zherebtsov, E.; Dremin, V.; Popov, A.; Doronin, A.; Kurakina, D.; Kirillin, M.; Meglinski, I.; Bykov, A. Hyperspectral imaging of human skin aided by artificial neural networks. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 3545–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rosso, J.Q.; Levin, J. The Clinical Relevance of Maintaining the Functional Integrity of the Stratum Corneum in both Healthy and Disease-affected Skin. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2011, 4, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Filon, F.L. Skin Morphology. In Adverse Effects of Engineered Nanomaterials; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 357–380. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, N.F.; Li, Q.; Melnichouk, O.; Huszti, E.; Martin, L.J.; Gunasekara, A.; Mawdsley, G.; Yaffe, M.J.; Minkin, S. Evidence that Breast Tissue Stiffness is Associated with Risk of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Cohen, P.R.; Bahl, D.; Levine, E.M.; Khaliq, W. Race and Ethnic Categories: A Brief Review of Global Terms and Nomenclature. Cureus 2023, 15, e41253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, S.A.; Semler, M.R.; Rameau, S. The sum of all parts: A multi-level exploration of racial and ethnic identity formation during emerging adulthood. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G. Tissue Mechanics and Fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, A.A. Physics of Open Fractures: Reconsidering Tissue Viability, Contamination Risk and Importance of Wound Debridement. J. Appl. Math. Phys. 2021, 9, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trębacz, H.; Barzycka, A. Mechanical Properties and Functions of Elastin: An Overview. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdewi, E.F. Mechanical Properties of Reinforcing Steel Rods Produced by Zliten Steel Factory. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.; Pathak, K. 17—Mechanical stability of dental materials. In Applications of Nanocomposite Material in Dentistry; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 285–305. ISBN 9780128137420. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, C.; Sanchez, A.; Scurr, J. Estimating the gravity induced three dimensional deformation of the breast. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 4134–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Openstax. University Physics Volume 1 5.3 Newton’s Second Law. Rice University. 1999–2024. ISBN 10: 1938168275. Available online: https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-1/pages/5-3-newtons-second-law (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Haug, E.G. Different Mass Definitions and Their Pluses and Minuses Related to Gravity. Foundations 2023, 3, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansraj, K.J. Breast Forces on the Spine. Surg. Technol. Int. 2016, 28, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.-J.; Farhadi, R.V.; Nash, D.W.; Kaleeny, J.; Povoski, S.P.; Chao, A.H. The current use of tissue expanders in breast reconstruction: Device design, features, and technical considerations. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2023, 21, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafali, D.; Liu, F.C.; Raman, K.; Maheta, B.; Saldana, G.M.; Heldman, L.; Cevallos, P.; Nazerali, R. The Best Under Stress: An Analysis of Breast Tissue Expander Response to External Forces. Aesthetic Surg. J. Open Forum 2023, 5, ojad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor-Del-Moral, J.A.; Pascual-Francisco, J.B.; Susarrey-Huerta, O.; Resendiz-Calderon, C.D.; Gallardo-Hernández, E.A.; Farfan-Cabrera, L.I. Characterization of Viscoelastic Poisson’s Ratio of Engineering Elastomers via DIC-Based Creep Testing. Polymers 2022, 14, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi, H.; Shariyat, M. A nanoindentation modeling of viscoelastic creep and relaxation behaviors of ligaments mechanical characteristics of biological tissues. In Proceedings of the 17th Iranian Conference of Biomedical Engineering (ICBME2010), Isfahan, Iran, 3–4 November 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoegl, N.; Knauss, W.G.; Emri, I. Poisson’s Ratio in Linear Viscoelasticity—A Critical Review. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2002, 6, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.; Maršálek, P.; Sengul, I.; Pelikán, A.; Janoutová, J.; Horyl, P.; Roman, J.; Sengul, D.; Junior, J.M.S. Evaluation of breast stiffness pathology based on breast compression during mammography: Proposal for novel breast stiffness scale classification. Clinics 2022, 77, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.K.; Pepin, K.; Brandt, K.R.; Mazza, G.L.; Pockaj, B.A.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Northfelt, D.W.; Anderson, K.; Kling, J.M.; et al. Association of breast cancer risk, density, and stiffness: Global tissue stiffness on breast MR elastography (MRE). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 194, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, A.; Plewes, D. A method to measure the hyperelastic parameters of ex vivo breast tissue samples. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 4395–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Chan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, R.-F.; Su, M.-Y. Evaluation of breast stiffness measured by ultrasound and breast density measured by MRI using a prone-supine deformation model. Biomark. Res. 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xia, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, Y.; Gu, B. Breast shape classification and discrimination driven by local features-focusing on Chinese women in their 20s. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2022, 90, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Third Love. Breast Shape Dictionary: Understanding Your Breast Shape. Third Love. 11 September 2023. Available online: https://www.thirdlove.com/blogs/learn/breast-shape-dictionary (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Great Place To Work. ThirdLove Company Overview. Great Place to Work. July 2023. Available online: https://www.greatplacetowork.com/certified-company/7010800#:~:text=ThirdLove%20is%20an%20American%20lingerie,women%20in%20San%20Francisco%2C%20CA (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Johnson, M. What Are the Most Common Breast Shapes? Healthline, 26 April 2019. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/health/breast-shapes (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Healthline. About Us. Healthline. 2024. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/about/about-us (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- El-Shazly, M.; El-Oteify, M.; Megeed, H.; Ahmed, B. Assessment of the breast volume by a new simple formula. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2006, 39, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontell, M.E.; Saad, N.; Brown, A.; Rose, M.; Ashinoff, R.; Saad, A. Single Stage Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy and Reduction Mastopexy in the Ptotic Breast. Plast. Surg. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi-Rokas, H.E.; Li, P.; Mitchell, K.B. Development of US Army Tactical Brassiere (ATB) Sizing System. Digit. Hum. Model. Appl. Optim. 2023, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, A.; Boroojeni, F.R.; Naeimipour, S.; Reustle, N.; Selegård, R.; Aili, D.; Dabrosin, C. Increased matrix stiffness enhances pro-tumorigenic traits in a physiologically relevant breast tissue-monocyte 3D model. Acta Biomater. 2024, 178, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Dense Breasts: Answers to Commonly Asked Questions. National Cancer Institute. 4 June 2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/breast-changes/dense-breasts#:~:text=The%20four%20breast%20density%20categories,be%20extremely%20dense%20(D) (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Sak, M.A.; Littrup, P.J.; Duric, N.; Mullooly, M.; E Sherman, M.; Gierach, G.L. Current and Future Methods for Measuring Breast Density: A Brief Comparative Review. Breast Cancer Manag. 2015, 4, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.Y.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, M.J.; Moon, H.J. Mammographic Density Estimation with Automated Volumetric Breast Density Measurement. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Daly, C.; Puckett, Y. New Breast Mass. National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information. 6 October 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560757/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
| Female Breast Tissue Skin Thickness | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Location | Methodology | Age | Race | Ethnicity | Bra Size | Thickness (mm) | Reference |
| Lateral | 1.38 0.24 | [7] | |||||
| Superior | 1.38 0.24 | [7] | |||||
| Medial | 1.97 0.26 | [7] | |||||
| Inferior | 1.97 0.26 | [7] | |||||
| Lateral Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 71 | White | Non-Hispanic | 2.6 | [18] | |
| Lateral Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 37 | Black | Non-Hispanic | 4.4 | [18] | |
| Medial Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 37 | Black | Non-Hispanic | 4.3 | [18] | |
| Breast—Unknown Location | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 69 | Asian | Unknown | 3.55 | [18] | |
| Breast—Unknown Location | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 55 | White | Non-Hispanic | 3.05 | [18] | |
| Breast—Unknown Location | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 41 | Other | Hispanic | 4.05 | [18] | |
| Lateral Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 66 | Black | Non-Hispanic | 2.6 | [18] | |
| Lateral Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 66 | Black | Non-Hispanic | 3.0 | [18] | |
| Medial Breast | Fresh tissue—breast and abdomen cancer patients (mastectomy and/or reconstructive)—calipers, the Bulge test, and finite element modeling | 33 | White | Non-Hispanic | 3.15 | [18] | |
| Epidermis—Chest | Fresh tissue—biopsy—measured with a microscope | 16–50 | Korean | 0.101 | [15] | ||
| Dermis—Chest | Fresh tissue—biopsy/skin operations—measured with a microscope | 16–50 | Korean | 1.3778 | [15] | ||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | 1.45 0.29 mean 1.0–2.2 range | [58] | ||||
| Epidermis | CT scan prototype | 0.07–1.4 range | [58] | ||||
| Dermis | CT scan prototype | 0.6 mm–3.0 range | [58] | ||||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | A | 1.47 0.07 | [58] | |||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | B | 1.76 0.04 | [58] | |||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | C | 1.38 0.10 | [58] | |||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | D | 1.38 | [58] | |||
| Anterior–Posterior Breast | CT scan prototype | DD | 0.95 0.07 | [58] | |||
| Epidermis | 0.07–1.4 | [58] | |||||
| Dermis | 0.6–3.0 | [58] | |||||
| Stiffness Scale vs. BI-RADS Classification of Breast Density | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stiffness Scale | BI-RADS Classification of Breast Density | |||||||||
| Class | Defin. | Palpation Response | Energy (x,y) Direction ∆U [J ∗ mm−3] | Grade | Grade | Classification | Description | Density % | Population % | References |
| I | Easily examined | Best palpation candidate. | (0.0, 1.5) | Grade 1 | A | Fatty breast tissue | Almost all fatty tissue | <25% | 10 | [33,80,93,95] |
| II | Well examined | <(1.5, 3.0) | Grade 2 | B | Scattered fibroglandular breast tissue | Predominantly fatty tissue, with some dense glandular and fibrous connective tissue | 25–50% | 40 | [33,80,93,95] | |
| III | Sufficiently examined | <(3.0, 4.5) | Grade 3 | C | Heterogeneously dense breast tissue | More glandular and fibrous connective tissue compared to fatty tissue | 51–75% | 40 | [33,80,93,95] | |
| IV | Difficult to examine | Not a candidate for palpation; use other methods (i.e., MRI, US, etc.). Requires exams more often. | <(4.5, 6.0) | Grade 4 | D | Extremely dense breast tissue | Mostly glandular and fibrous connective tissue | >75% | 10 | [33,80,93,95] |
| V | Non-exam | Not a candidate for palpation; use other methods (i.e., MRI, US, etc.). Requires exams more often. | <(6.0, 7.5) | Grade 5 | >95% | [80,96] | ||||
| Grade 6 | Malignant tissue biopsy validation | [96] | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galbreath, S.; Goswami, T. Biomechanical Behavior of Female Breast—A Review. BioMed 2025, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010005
Galbreath S, Goswami T. Biomechanical Behavior of Female Breast—A Review. BioMed. 2025; 5(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalbreath, Sheila, and Tarun Goswami. 2025. "Biomechanical Behavior of Female Breast—A Review" BioMed 5, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010005
APA StyleGalbreath, S., & Goswami, T. (2025). Biomechanical Behavior of Female Breast—A Review. BioMed, 5(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed5010005







