Assessing Lymph Node Involvement in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Proposal of a Predictive Model Using Clinical Variables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
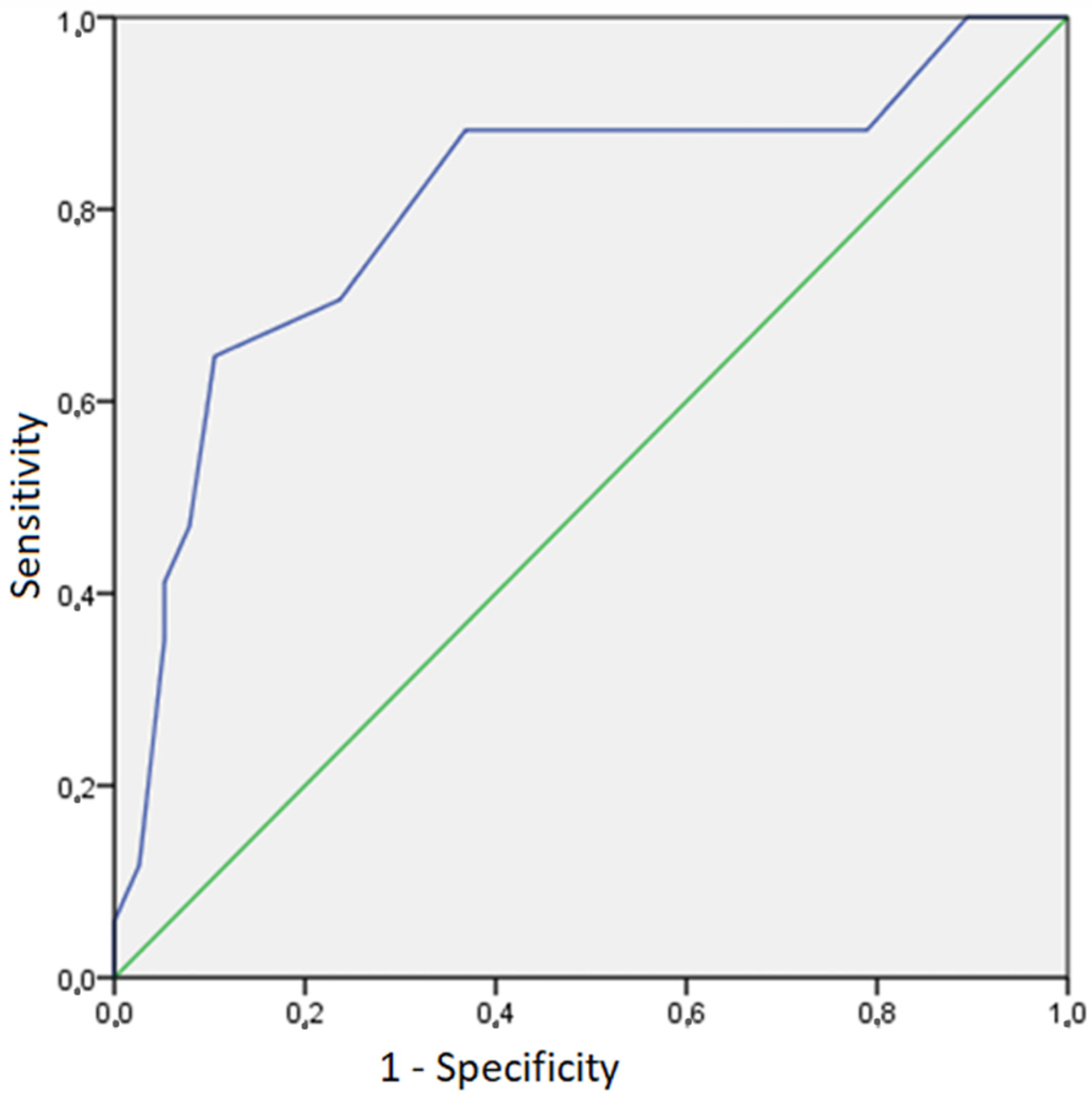
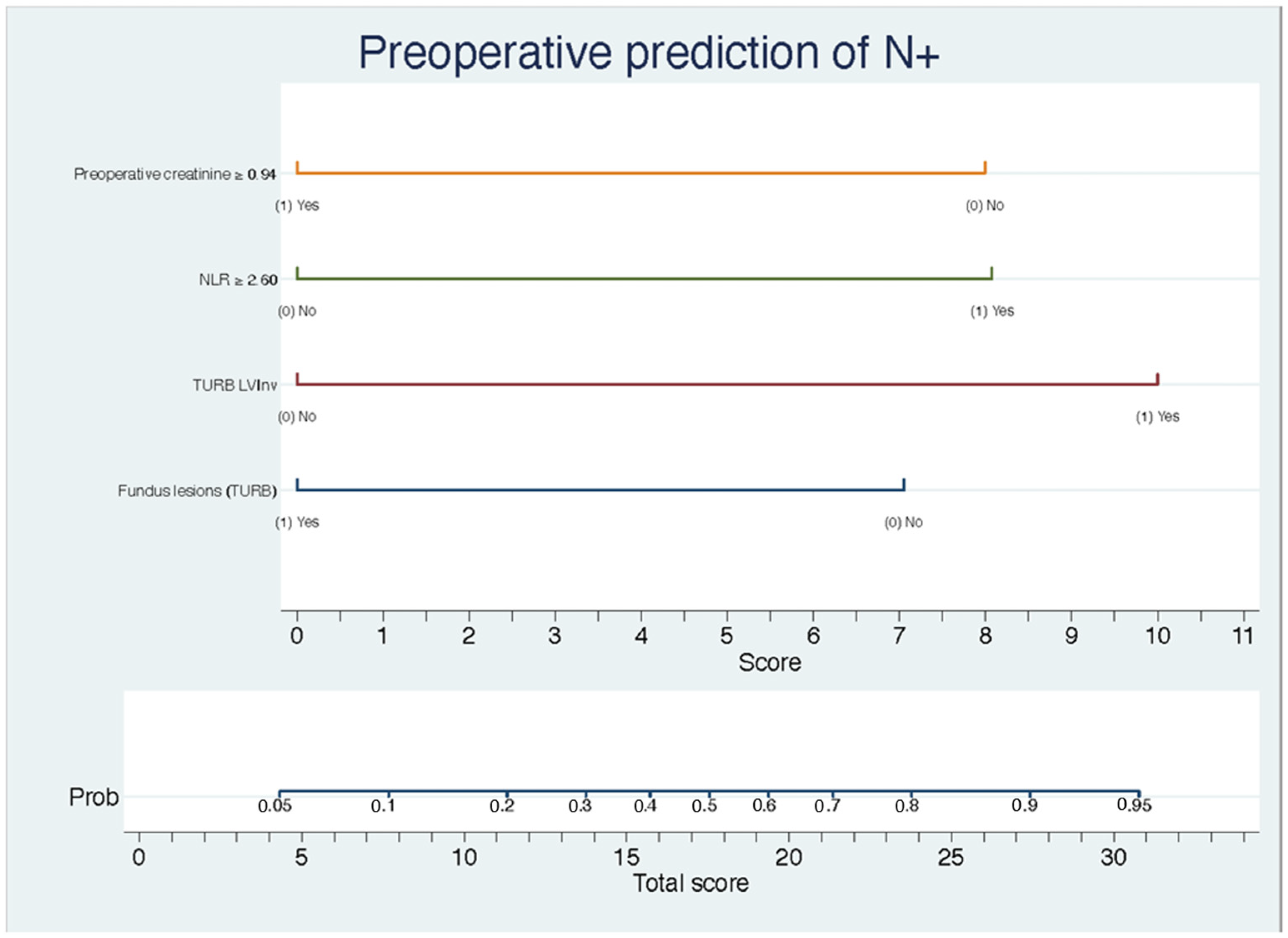
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuk, H.D.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Ku, J.H. Lymphovascular invasion have a similar prognostic value as lymph node involvement in patients undergoing radical cystectomy with urothelial carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Aprikian, A.G.; Chin, J.L.; Fradet, Y.; Izawa, J.; Estey, E.; Fairey, A.; Rendon, R.; Cagiannos, I.; Lacombe, L.; et al. Impact of concomitant carcinoma in situ on upstaging and outcome following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Zha, Z.; Qu, W.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, J. Clinicopathological factors in bladder cancer for cancer-specific survival outcomes following radical cystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, E.K.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Sukhu, R.; Yee, A.M.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Bochner, B.H. Poor prognosis of bladder cancer patients with occult lymph node metastases treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.A.; Rink, M.; Hansen, J.; Cha, E.K.; Robinson, B.; Tian, Z.; Chun, F.K.; Tagawa, S.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Fisch, M.; et al. Accurate preoperative prediction of non-organ-confined bladder urothelial carcinoma at cystectomy. BJU Int. 2012, 111, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, R.; Lam, L.L.; Erho, N.; Takhar, M.; Mitra, A.P.; Buerki, C.; Davicioni, E.; Skinner, E.C.; Daneshmand, S.; Black, P.C. Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Bladder Cancer Using Whole Transcriptome Gene Expression Signatures. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, M.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Thalmann, G.N. EAU Guidelines on: Muscle-Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer; European Association of Urology: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.S.; Bochner, B.H.; Chou, R.; Dreicer, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Holzbeierlein, J.M. Tratamiento del Cáncer de Vejiga Músculo Invasivo y No Metastásico: Guía de AUA/ASCO/ASTRO/SUO; Spanish Version; American Urological Association Education and Research: Linthicum, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Madersbacher, S.; Hochreiter, W.; Burkhard, F.; Thalmann, G.N.; Danuser, H.; Markwalder, R.; Studer, U.E. Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer today—A homogeneous series without neoadjuvant therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakiewicz, P.I.; Shariat, S.F.; Palapattu, G.S.; Perrotte, P.; Lotan, Y.; Rogers, C.G.; Amiel, G.E.; Vazina, A.; Gupta, A.; Bastian, P.J.; et al. Precystectomy Nomogram for Prediction of Advanced Bladder Cancer Stage. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartolomei, M.D.; Porav-Hodade, D.; Ferro, M.; Mathieu, R.; Abufaraj, M.; Foerster, B.; Kimura, S.; Shariat, S.F. Prognostic Role of Pretreatment Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) in Patients With Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2018, 36, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, T.; Takano, M.; Miyamoto, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kato, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Takasaki, K.; Matsuura, H.; Soyama, H.; Hirata, J.; et al. Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Was a Predictor of Lymph Node Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer Patients. Oncology 2019, 96, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluth, L.A.; Black, P.C.; Bochner, B.H.; Catto, J.; Lerner, S.P.; Stenzl, A.; Sylvester, R.; Vickers, A.J.; Xylinas, E.; Shariat, S.F. Prognostic and Prediction Tools in Bladder Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | N° (%) Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Mean (Median) | 65 (66) |
| Range | 33–83 | |
| Gender | Male | 58 (93.50) |
| Female | 4 (6.50) | |
| Presurgical creatinine | Mean (Median) | 1.04 (0.94) |
| Range | 0.46–2.31 | |
| TURB T stage | Tx | 1 (1.60) |
| Tis | 0 (0) | |
| Ta | 0 (0) | |
| T1 | 5 (8.20) | |
| T2 | 55 (90.20) | |
| CIS presence after TURB | 17 (27.40) | |
| LVInv presence after TURB | 8 (12.90) | |
| cT stage | Tx | 5 (8.50) |
| T0-T1-T2 | 27 (45.70) | |
| T3 | 20 (33.90) | |
| T4 | 7 (11.90) | |
| cN stage | N0 | 46 (79.30) |
| N1 | 6 (10.30) | |
| N2 | 3 (5.20) | |
| N3 | 3 (5.20) | |
| Presurgical NLR | Mean (Median) | 2.94 (2.25) |
| Range | 0.59–13.50 | |
| Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy | 5 (8.10) | |
| Lymph nodes obtained | Mean (Median) | 19.84 (19) |
| pT stage | Tis | 8 (12.90) |
| T0 | 5 (8.10) | |
| T1 | 8 (12.90) | |
| T2 | 7 (11.30) | |
| T3 | 21 (33.90) | |
| T4 | 13 (21) | |
| pN stage | N0 | 44 (71) |
| N1 | 6 (9.70) | |
| N2 | 12 (19.40) | |
| N3 | 0 (0) | |
| pT3 ≥ stage | ||||
| No | Yes | Total | ||
| cT3 ≥ stage | No | 18 | 14 | 32 |
| Yes | 8 | 20 | 28 | |
| Total | 26 | 34 | 60 | |
| pN+ | ||||
| No | Yes | Total | ||
| cN+ | No | 33 | 14 | 47 |
| Yes | 9 | 4 | 13 | |
| Total | 42 | 18 | 60 | |
| Variables | OR | I.C. 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative creatinine | 0.17 | 0.03–0.80 | 0.02 |
| NLR | 6.03 | 1.29–28.30 | 0.02 |
| LVInv (TURB) | 9.26 | 1.11–77.30 | 0.04 |
| Fundus lesion (RTU) | 0.21 | 0.05–0.93 | 0.04 |
| Model Calibration | X2 = 16.84 | p = 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barragán Flores, W.A.; Carrillo George, C.; Sandoval, J.M.; Cívico Sánchez, C.; Flores, C.; Muñoz, V.; Fernández Aparicio, T. Assessing Lymph Node Involvement in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Proposal of a Predictive Model Using Clinical Variables. BioMed 2024, 4, 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030017
Barragán Flores WA, Carrillo George C, Sandoval JM, Cívico Sánchez C, Flores C, Muñoz V, Fernández Aparicio T. Assessing Lymph Node Involvement in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Proposal of a Predictive Model Using Clinical Variables. BioMed. 2024; 4(3):213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarragán Flores, William A., Carlos Carrillo George, José María Sandoval, Claudia Cívico Sánchez, Cristina Flores, Victoria Muñoz, and Tomás Fernández Aparicio. 2024. "Assessing Lymph Node Involvement in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Proposal of a Predictive Model Using Clinical Variables" BioMed 4, no. 3: 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030017
APA StyleBarragán Flores, W. A., Carrillo George, C., Sandoval, J. M., Cívico Sánchez, C., Flores, C., Muñoz, V., & Fernández Aparicio, T. (2024). Assessing Lymph Node Involvement in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Proposal of a Predictive Model Using Clinical Variables. BioMed, 4(3), 213-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed4030017






