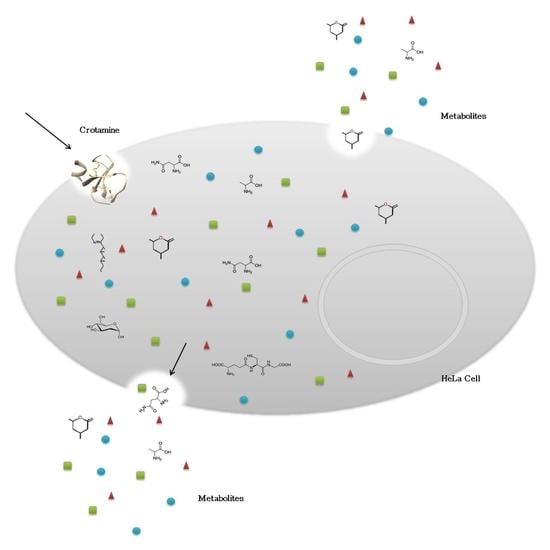
The Secreted Metabolome of Hela Cells under Effect of Crotamine, a Cell-Penetrating Peptide from a Rattlesnake Using NMR-Based Metabolomics Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line
2.2. MTT Assay
2.3. Crotamine Treatment and Metabolite Extraction
2.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Metabolite Identification
2.7. Pathway Analysis
3. Results
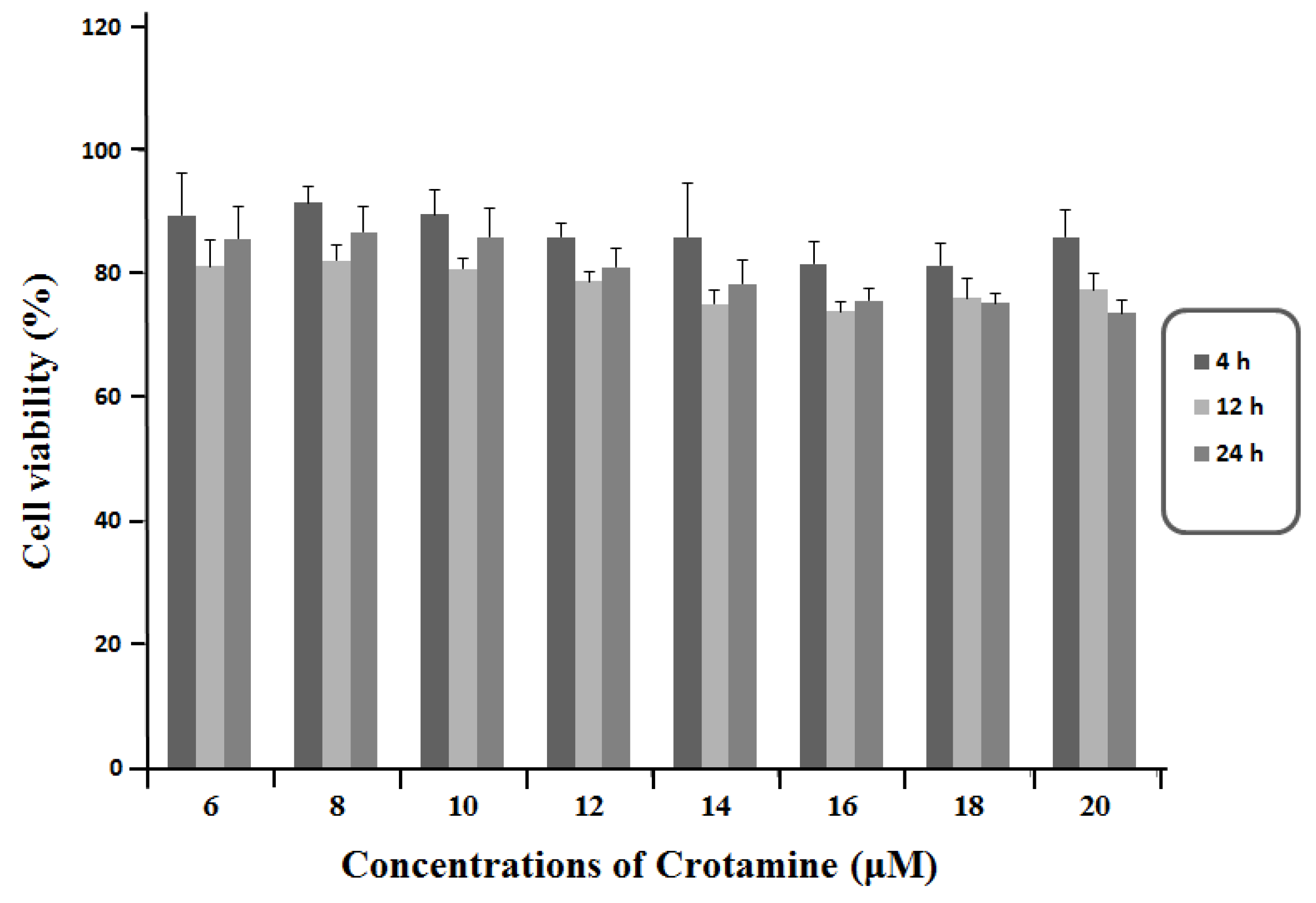
3.1. Viability of HeLa Cells in Response to the Exposure of Crotamine
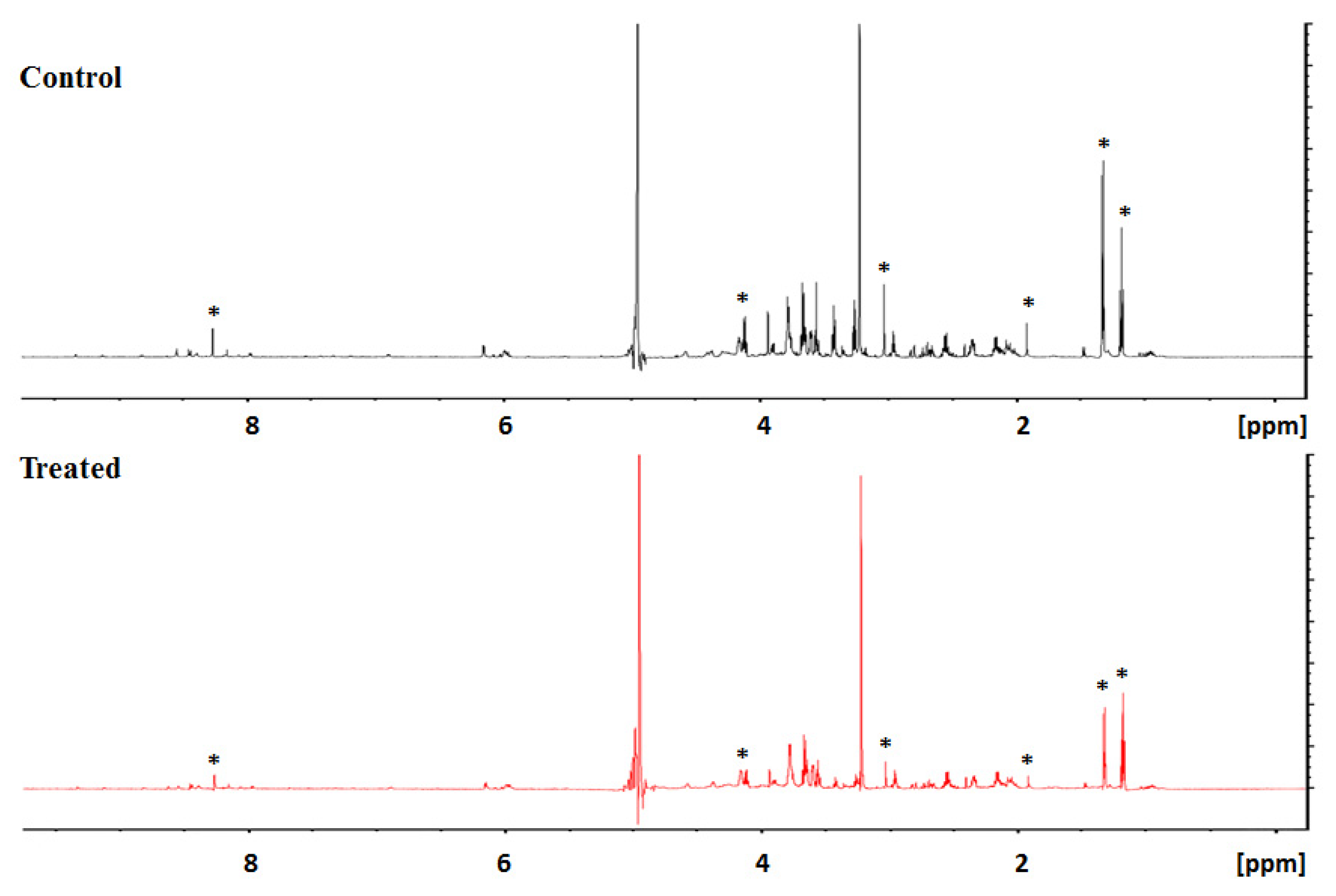
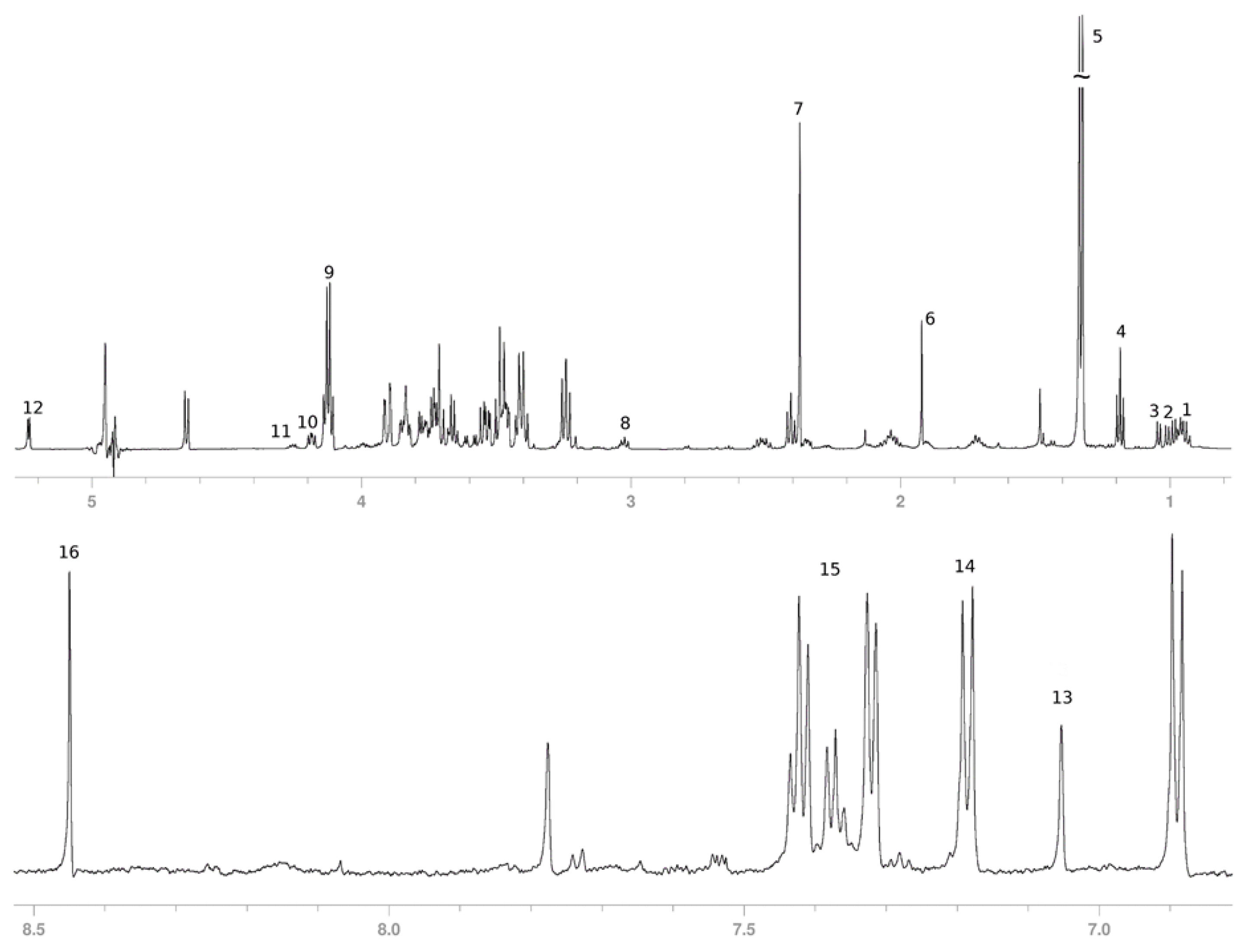
3.2. Secreted Metabolic Profile of HeLa Cells
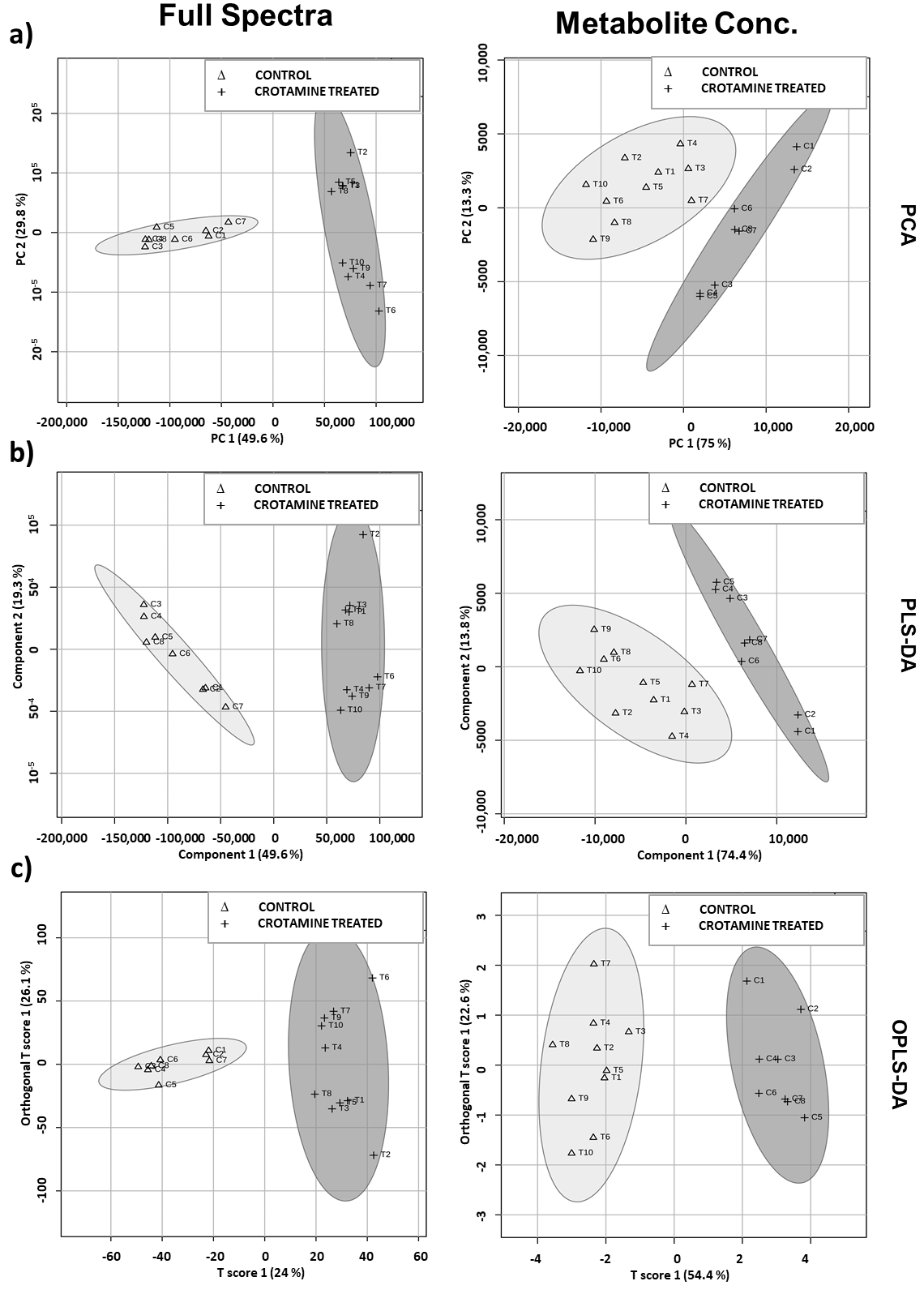
3.3. Crotamine Induced Metabolic Variation in HeLa Cells (Multivariate Data Analysis)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassanpour, S.H.; Dehghani, M. Review of cancer from perspective of molecular. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017, 4, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, A.T.; Syrjänen, K.J.; Longatto-Filho, A. Human papillomavirus (HPV) screening and cervical cancer burden. A Brazilian perspective. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syrjänen, K.; Syrjänenm, S. Papillomavirus Infections in Human Pathology, 1st ed.; John Wiley& Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, F.R.G.F.; Fregnani, J.; Zeferino, J.H.T.G.; Villa, L.C.; Federico, L.L.; Novaes, M.H.; Costa, P.E.R.S. Câncer do Colo do Útero; Tecmedd: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Ferlay, J.; Mery, L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Re-search on Cancer. Cancer Today. 2015. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INCA. Coordenação de Prevenção e Vigilância Brasil. Rio de Janeiro: Ministério da Saúde; Instituto Nacional de Câncer–Es-timativa. 2018. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/tipos-de-cancer/cancer-do-colo-do-utero (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Cushman, D.W.; Ondetti, M.A. History of the design of captopril and related inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme. Hypertension 1991, 17, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyas, V.K.; Brahmbhatta, K.; Bhatta, H.; Parmarb, U.; Patidar, R. Therapeutic potential of snake venom in cancer therapy: Current perspectives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanbhag, V.K.L. Applications of snake venoms in treatment of cancer. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicastro, G.; Franzoni, L.; de Chiara, C.; Mancin, A.C.; Giglio, J.R.; Spisni, A. Solution structure of crotamine, a Na+ channel affecting toxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 270, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, V.; Bettendorff, P.; Herrmann, T.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr.; Oliveira, E.B.; Yamane, T.; Wüthrich, K. Automated NMR structure determination and disulfide bond identification of the myotoxin crotamine from Crotalus durissus terrificus. Toxicon 2005, 46, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, M.A.; Gabdulkhakov, A.; Georgieva, D.; Sankaran, B.; Murakami, M.T.; Arni, R.K.; Betzel, C. Structure of the polypeptide crotamine from the Brazilian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fawell, S.; Seery, J.; Daikh, Y.; Moore, C.; Chen, L.L.; Pepinsky, B.; Barsoum, J. Tat-mediated delivery of heterologous proteins into cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vivès, E.; Brodin, P.; Lebleu, B. A Truncated HIV-1 Tat Protein Basic Domain Rapidly Translocates through the Plasma Membrane and Accumulates in the Cell Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16010–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarze, S.R.; Ho, A.; Vocero-Akbani, A.; Dowdy, S.F. In Vivo Protein Transduction: Delivery of a Biologically Active Protein into the Mouse. Science 1999, 285, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, E.S.; Bizerra, F.C.; Oliveira, E.B.; Moreira, J.T.; Rajabi, M.; Nunes, G.L.; de Souza, A.O.; da Silva, I.D.; Yamane, T.; Karpel, R.L.; et al. Unraveling the antifungal activity of a South American rattlesnake toxin crotamine. Biochimie 2013, 95, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerkis, I.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Prieto da Silva, A.R.B.; Pereira, A.; De Sá Júnior, P.L.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Kerkis, A.; Yamane, T. State of the Art in the Studies on Crotamine, a Cell Penetrating Peptide from South American Rattlesnake. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 675985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerkis, A.; Kerkis, I.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Oliveira, E.B.; Vianna-Morgante, A.M.; Pereira, L.V.; Yamane, T. Crotamine is a novel cell-penetrating protein from the venom of rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, A.; Kerkis, A.; Hayashi, M.A.; Pereira, A.S.; Silva, F.S.; Oliveira, E.B.; Prieto da Silva, A.R.B.; Yamane, T.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Kerkis, I. Crotamine toxicity and efficacy in mouse models of melanoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkis, A.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Yamane, T.; Kerkis, I. Properties of cell penetrating peptides (CPPs). IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, N.J.; Torrente, Y.; Camirand, G.; Bujold, M.; Chapdelaine, P.; Leriche, K.; Bresolin, N.; Tremblay, J.P. Intracellular Delivery of a Tat-eGFP Fusion Protein into Muscle Cells. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. Trojan peptides: The penetratin system for intracellular delivery. Trends Cell Biol. 1998, 8, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.D.; Hayashi, M.A.F.; Kerkis, A.; Oliveira, V.; Oliveira, E.B.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Nader, H.B.; Yamane, T.; dos Santos Tersariol, I.L.; Kerkis, I. Crotamine Mediates Gene Delivery into Cells through the Binding to Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 21349–21360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harada, H.; Kizaka-Kondoh, S.; Hiraoka, M. Antitumor protein therapy; Application of the protein transduction domain to the development of a protein drug for cancer treatment. Breast Cancer 2006, 13, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeiro, J.D.; Marinovic, M.P.; Carapeto, F.C.; Mas, C.D.; Monte, G.G.; Porta, L.C.; Nering, M.B.; Oliveira, E.B.; Hayashi, M.A.F. Oral treatment with a rattlesnake native polypeptide crotamine efficiently inhibits the tumor growth with no potential toxicity for the host animal and with suggestive positive effects on animal metabolic profile. Amino Acids 2017, 50, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.D.; Sancey, L.; Pereira, A.; Rome, C.; Oliveira, V.; Oliveira, E.B.; Nader, H.B.; Yamane, T.; Kerkis, I.; Tersariol, I.L.S.; et al. The Natural Cell-Penetrating Peptide Crotamine Targets Tumor Tissue in Vivo and Triggers a Lethal Calcium-Dependent Pathway in Cultured Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, J.; Hao, F.; Chen, C.; Bhakoo, K.; Tang, H. NMR-based metabonomics analyses of the effects of ultra-small super paramagnetic particles of iron oxide (USPIO) on macrophage metabolism. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2049–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z. Metabolic responses of HeLa cells to silica nanoparticles by NMR-based metabolomic analyses. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.B.B.; De Moraes, F.R.; Candido, N.M.; Sampaio, I.; Paula, A.S.; De Vasconcellos, A.; Silva, T.C.; Miller, A.H.; Rahal, P.; Nery, J.G.; et al. Metabolic Effects of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles on Cervical Carcinoma Cells and Nontumorigenic Keratinocytes. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4337–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst 3.0—Making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Nielsen, J. Systems medicine and metabolic modelling. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 271, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Asplund, A.; Shoaie, S.; Kampf, C.; Uhlen, M.; Nielsen, J. Identifying anti-growth factors for human cancer cell lines through genome-scale metabolic modeling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 08183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottret, L.; Wildridge, D.; Vinson, F.; Barrett, M.; Charles, H.; Sagot, M.-F.; Jourdan, F. MetExplore: A web server to link metabolomic experiments and genome-scale metabolic networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W132–W137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouatra, S.; Aziat, F.; Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Knox, C.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Saleem, F.; Liu, P.; et al. The Human Urine Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The Human Serum Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Lewis, M.J.; Morrissey, J.A.; Flegel, M.D.; Jeroncic, K.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, D.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; Tzur, D.; et al. The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selegato, D.M.; Pilon, A.C.; Neto, F.C. Plant Metabolomics Using NMR Spectroscopy. Methods Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 2037, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuperlović-Culf, M.; Barnett, D.A.; Culf, A.S.; Chute, I. Cell culture metabolomics: Applications and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-S.; Li, L.-Y.; Guan, Y.-D.; Yang, J.-M.; Cheng, Y. Anticancer strategies based on the metabolic profile of tumor cells: Therapeutic targeting of the Warburg effect. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, R.; McFarland, G.A. Inhibition of the growth of transformed and neoplastic cells by the dipeptide carnosine. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 73, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marinovic, M.P.; Campeiro, J.D.; Lima, S.C.; Rocha, A.L.; Nering, M.B.; Oliveira, E.B.; Mori, M.A.; Hayashi, M.A.F. Crotamine induces browning of adipose tissue and increases energy expenditure in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schug, Z.T.; Peck, B.; Jones, D.T.; Zhang, Q.; Grosskurth, S.; Alam, I.S.; Goodwin, L.M.; Smethurst, E.; Mason, S.; Blyth, K.; et al. Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 2 Promotes Acetate Utilization and Maintains Cancer Cell Growth under Metabolic Stress. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adekola, K.; Rosen, S.T.; Shanmugam, M. Glucose transporters in cancer metabolism. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, P.; Krześlak, A.; Bryś, M.; Lipińska, A. Glucose-dependent glucose transporter 1 expression and its impact on viability of thyroid cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 33, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labak, C.M.; Wang, P.Y.; Arora, R.; Guda, M.; Asuthkar, S.; Tsung, A.J.; Velpula, K.K. Glucose transport: Meeting the meta-bolic demands of cancer, and applications in glioblastoma treatment. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Torres, A.; Henry, R.A.; Trefely, S.; Wallace, M.; Lee, J.V.; Carrer, A.; Sengupta, A.; Campbell, S.L.; Kuo, Y.-M.; et al. ATP-Citrate Lyase Controls a Glucose-to-Acetate Metabolic Switch. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakhter, A.J.; Hamilton, J.; Konger, R.L.; Brustovetsky, N.; Broxmeyer, H.E.; Naidu, S.R. Glucose-independent Acetate Metabolism Promotes Melanoma Cell Survival and Tumor Growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21869–21879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comerford, S.A.; Huang, Z.; Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Walters, H.; Tantawy, M.N.; Fu, A.; Manning, H.C.; et al. Acetate Dependence of Tumors. Cell 2014, 159, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshii, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Yoshii, H.; Mori, T.; Kiyono, Y.; Waki, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Kudo, T.; Okazawa, H.; et al. Cytosolic acetyl-CoA synthetase affected tumor cell survival under hypoxia: The possible function in tumor acetyl-CoA/acetate metabolism. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, Y.; Waki, A.; Furukawa, T.; Kiyono, Y.; Mori, T.; Yoshii, H.; Kudo, T.; Okazawa, H.; Welch, M.J.; Fujibayashi, Y. Tumor uptake of radiolabeled acetate reflects the expression of cytosolic acetyl-CoA synthetase: Implications for the mechanism of acetate PET. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mashimo, T.; Pichumani, K.; Vemireddy, V.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Singh, D.K.; Sirasanagandla, S.; Nannepaga, S.; Piccirillo, S.G.M.; Kovacs, Z.; Foong, C.; et al. Acetate Is a Bioenergetic Substrate for Human Glioblastoma and Brain Metastases. Cell 2014, 159, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Ko, B.; Hensley, C.T.; Jiang, L.; Wasti, A.T.; Kim, J.; Sudderth, J.; Calvaruso, M.A.; Lumata, L.; Mitsche, M.; et al. Glutamine Oxidation Maintains the TCA Cycle and Cell Survival during Impaired Mitochondrial Pyruvate Transport. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghaffari, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Nielsen, J. Cancer Metabolism: A Modeling Perspective. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epstein, T.; Gatenby, R.A.; Brown, J.S. The Warburg effect as an adaptation of cancer cells to rapid fluctuations in energy demand. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-Y. Cancer Energy Metabolism: Shutting Power off Cancer Factory. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amelio, I.; Cutruzzolá, F.; Antonov, A.; Agostini, M.; Melino, G. Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaka, A.; Ajiboye, B.; Ojo, O.; Adewale, O.; Olayide, I.; Emuowhochere, R. Biology of glucose metabolization in cancer cells. J. Oncol. Sci. 2017, 3, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Wind, F.; Negelein, E. The metabolism of tumors in the body. J. Gen. Physiol. 1927, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.-M.; Yu, Z.-X.; Lin, H.; Fu, X.; Meadows, G.G. Selective amino acid restriction differentially affects the motility and directionality of DU145 and PC3 prostate cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulcsár, G.; Gaál, D.; Kulcsár, P.I.; Schulcz, Á.; Czompoly, T. A mixture of amino acids and other small molecules present in the serum suppresses the growth of murine and human tumors in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 132, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Flati, V.; Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Eleuteri, A.M. Essential amino acid mixtures drive cancer cells to apoptosis through proteasome inhibition and autophagy activation. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.-M.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Fang, W.; Meadows, G.G. Cell death of prostate cancer cells by specific amino acid restriction depends on alterations of glucose metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyh-Chang, N.; Locasale, J.W.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Zheng, Y.; Teo, R.Y.; Ratanasirintrawoot, S.; Zhang, J.; Onder, T.; Unternaehrer, J.J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Influence of Threonine Metabolism on Sadenosylmethionine and Histone Methylation. Science 2013, 339, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krall, A.S.; Xu, S.; Graeber, T.G.; Braas, D.; Christofk, H.R. Asparagine promotes cancer cell proliferation through use as an amino acid exchange factor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomback, B. Methods in Enzymology; Hirs, C., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 11, pp. 389–411. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.D.; Goetze, A.M.; Bass, R.B.; Flynn, G.C. N-terminal Glutamate to Pyroglutamate Conversion in Vivo for Human IgG2 Antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11211–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rink, R.; Arkema-Meter, A.; Baudoin, I.; Post, E.; Kuipers, A.; Nelemans, S.; Akanbi, M.H.J.; Moll, G. To protect peptide pharmaceuticals against peptidases. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2010, 61, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, N.; Ricciarelli, R.; Nitti, M.; Marengo, B.; Furfaro, A.L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Marinari, U.M.; Domenicotti, C. Role of Glutathione in Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.P.; Hofseth, L.J.; Harris, C.C. Radical causes of cancer. Nat. Cancer 2003, 3, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. The role of glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7369–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katagiri, R.; Goto, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Nishiumi, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Hidaka, A.; Budhathoki, S.; Yamaji, T.; Sawada, N.; Shimazu, T.; et al. Increased Levels of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Associated with Increased Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Prospective Case-Control Study of a Large Cohort. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1474–1482.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neinast, M.; Murashige, D.; Arany, Z. Branched Chain Amino Acids. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananieva, E.A.; Wilkinson, A.C. Branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selwan, E.M.; Edinger, A.L. Branched chain amino acid metabolism and cancer: The importance of keeping things in context. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6, S578–S584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xu, W.; Jiang, W.; Yu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yao, J.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Regulation of Cellular Metabolism by Protein Lysine Acetylation. Science 2010, 327, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeza, J.; Smallegan, M.J.; Denu, J.M. Mechanisms and Dynamics of Protein Acetylation in Mitochondria. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budczies, J.; Brockmöller, S.F.; Müller, B.M.; Barupal, D.K.; Richter-Ehrenstein, C.; Kleine-Tebbe, A.; Griffin, J.L.; Orešič, M.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C.; et al. Comparative metabolomics of estrogen receptor positive and estrogen receptor negative breast cancer: Alterations in glutamine and beta-alanine metabolism. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.E.; Brosnan, J.T. Formate: The Neglected Member of One-Carbon Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, P.; Chen, J.; Zhou, B.; Hu, J.; Zou, J.; Lu, W.; Xiang, P.; et al. 1H NMR-based metabolic profiling of human rectal cancer tissue. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holeček, M. Histidine in Health and Disease: Metabolism, Physiological Importance, and Use as a Supplement. Nutrients 2020, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Deng, P.; Bu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Li, M.; Lu, W.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; et al. 1H-NMR based metabonomic profiling of human esophageal cancer tissue. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oizel, K.; Tait-Mulder, J.; Fernandez-De-Cossio-Diaz, J.; Pietzke, M.; Brunton, H.; Lilla, S.; Dhayade, S.; Athineos, D.; Blanco, G.R.; Sumpton, D.; et al. Formate induces a metabolic switch in nucleotide and energy metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiser, J.; Schuster, A.; Pietzke, M.; Voorde, J.V.; Athineos, D.; Oizel, K.; Burgos-Barragan, G.; Wit, N.; Dhayade, S.; Morton, J.; et al. Increased formate overflow is a hallmark of oxidative cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


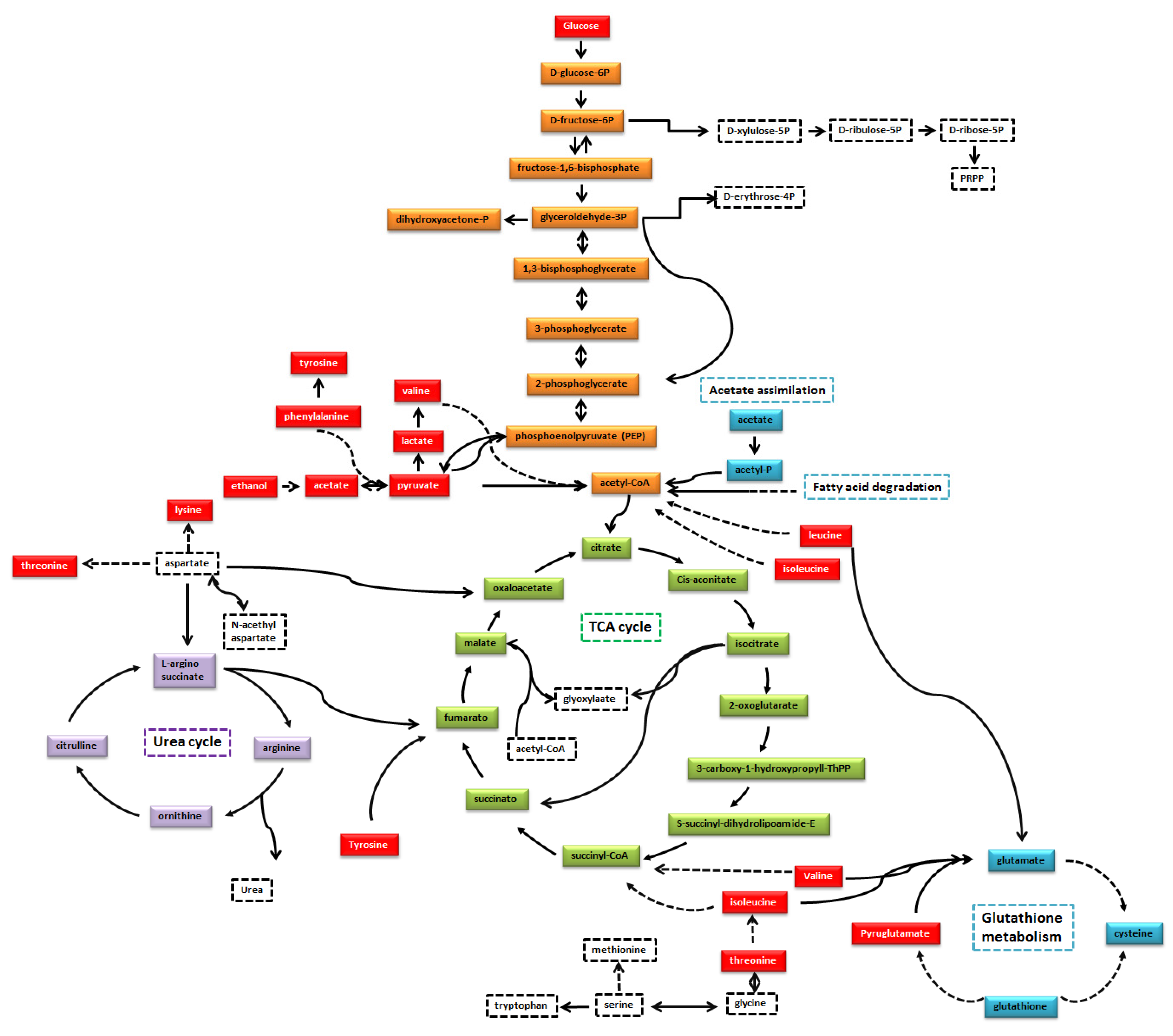
| Pathway | Coverage | Metabolites Matched | Right Tailed Fisher-Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transport of extracellular metabolites | 2.13 | 13 | 7.76 × 10−11 |
| Protein degradation | 12.73 | 7 | 1.04 × 10−10 |
| Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 11.11 | 7 | 2.81 × 10−10 |
| Artificial reactions | 8.97 | 7 | 1.31 × 10−9 |
| Transport to mitochondria | 3.56 | 9 | 9.39 × 10−9 |
| Transport lysosomal | 5.26 | 7 | 5.71 × 10−8 |
| Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis | 7.81 | 5 | 1.01 × 10−6 |
| Transport peroxisomal | 3.88 | 4 | 2.38 × 10−4 |
| Pyruvate metabolism | 6.12 | 3 | 4.35 × 10−4 |
| Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine metabolism | 4.76 | 3 | 9.13 × 10−4 |
| Glutathione metabolism | 5.56 | 2 | 5.58 × 10−3 |
| Tyrosine metabolism | 5.56 | 2 | 5.58 × 10−3 |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 2.5 | 3 | 5.80 × 10−3 |
| Transport Golgi apparatus | 3.64 | 2 | 1.27 × 10−2 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 3.03 | 2 | 1.80 × 10−2 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 2.3 | 2 | 3.02 × 10−2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coronado, M.A.; de Moraes, F.R.; Stuqui, B.; Calmon, M.F.; Eberle, R.J.; Rahal, P.; Arni, R.K. The Secreted Metabolome of Hela Cells under Effect of Crotamine, a Cell-Penetrating Peptide from a Rattlesnake Using NMR-Based Metabolomics Analyses. BioMed 2022, 2, 238-254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed2020020
Coronado MA, de Moraes FR, Stuqui B, Calmon MF, Eberle RJ, Rahal P, Arni RK. The Secreted Metabolome of Hela Cells under Effect of Crotamine, a Cell-Penetrating Peptide from a Rattlesnake Using NMR-Based Metabolomics Analyses. BioMed. 2022; 2(2):238-254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoronado, Mônika Aparecida, Fábio Rogério de Moraes, Bruna Stuqui, Marília Freitas Calmon, Raphael Josef Eberle, Paula Rahal, and Raghuvir Krishnaswamy Arni. 2022. "The Secreted Metabolome of Hela Cells under Effect of Crotamine, a Cell-Penetrating Peptide from a Rattlesnake Using NMR-Based Metabolomics Analyses" BioMed 2, no. 2: 238-254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed2020020
APA StyleCoronado, M. A., de Moraes, F. R., Stuqui, B., Calmon, M. F., Eberle, R. J., Rahal, P., & Arni, R. K. (2022). The Secreted Metabolome of Hela Cells under Effect of Crotamine, a Cell-Penetrating Peptide from a Rattlesnake Using NMR-Based Metabolomics Analyses. BioMed, 2(2), 238-254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed2020020