Plasma Renin Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
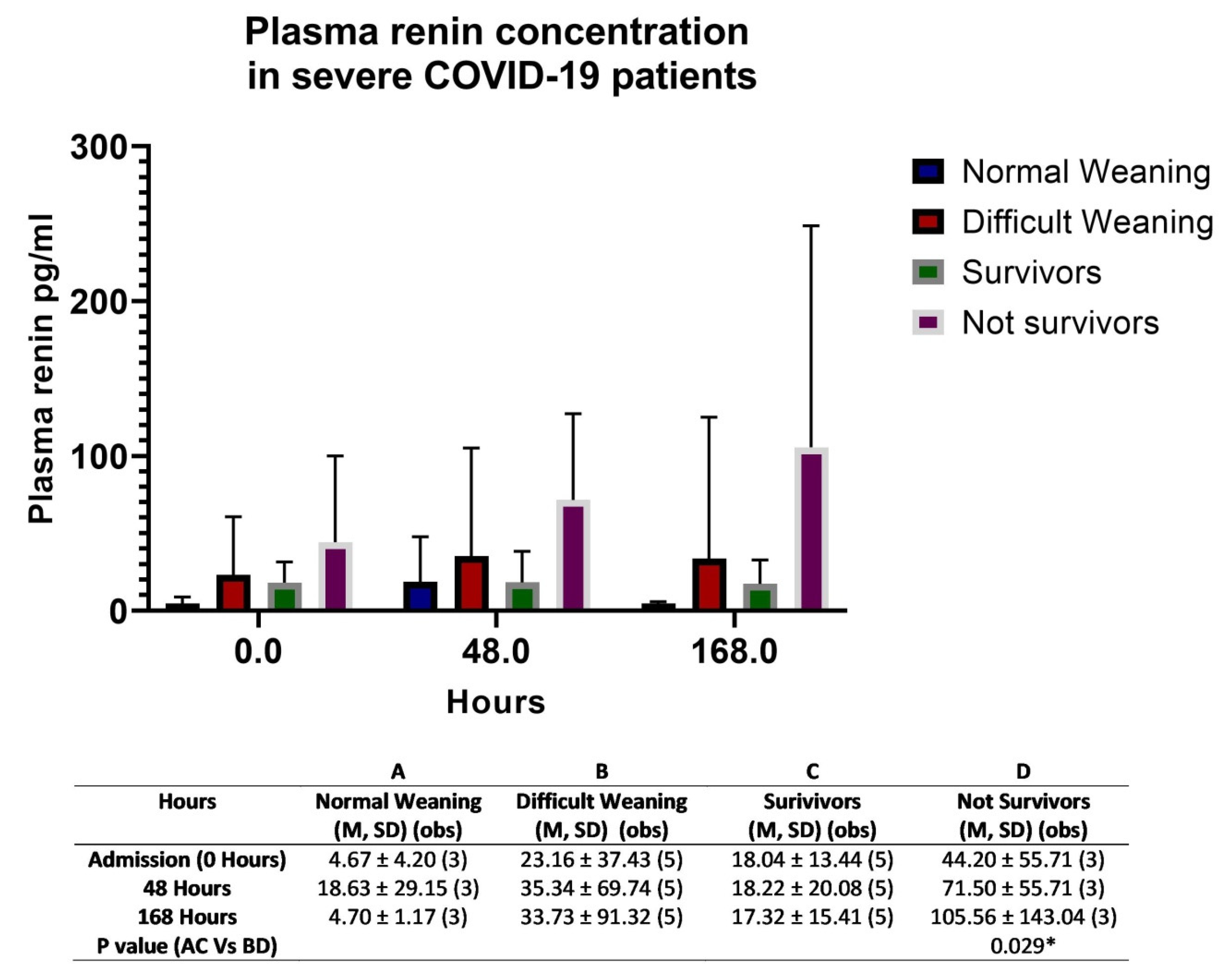
3. Discussion
Study Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleeson, P.J.; Crippa, I.A.; Mongkolpun, W.; Cavicchi, F.Z.; Van Meerhaeghe, T.; Brimioulle, S.; Taccone, F.S.; Vincent, J.-L.; Creteur, J. Renin as a Marker of Tissue-Perfusion and Prognosis in Critically Ill Patients*. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, A.; Giuliani, E.; Marchetti, G.; Ugoletti, E.; Della Volpe, S.; Albertini, G. Plasma renin concentration as a predictor of outcome in a medical intensive care setting: A retrospective pilot study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lumpuy-Castillo, J.; Lorenzo-Almorós, A.; Pello-Lázaro, A.M.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C.; Egido, J.; Tuñón, J.; Peiró, C.; Lorenzo, Ó. Cardiovascular Cardiovascular Damage in COVID-19: Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.; Critelli, R.; Lasagni, S.; Melegari, A.; Curatolo, A.; Celsa, C.; Romagnoli, D.; Melegari, G.; Pivetti, A.; Di Marco, L.; et al. Dynamic angiopoietin-2 assessment predicts survival and chronic course in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melegari, G.; Rivi, V.; Zelent, G.; Nasillo, V.; De Santis, E.; Melegari, A.; Bevilacqua, C.; Zoli, M.; Meletti, S.; Barbieri, A. Mild to Severe Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19: Cases Reports. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, A.M.; César, E.C.; Martín-Montañez, E.; Alvarez, E.S.; Lopez, P.M.; Romero-Zerbo, Y.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.; Garrido, J.L.V. Acute Lung Injury Biomarkers in the Prediction of COVID-19 Severity: Total Thiol, Ferritin and Lactate Dehydrogenase. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.; Boyle, E.; Jefferson, S.; Heslop, C.; Mohan, P.; Mohanraj, G.; Sidow, H.; Tan, R.; Hill, S.; Woolard, J. Role of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone and Kinin–Kallikrein Systems in the Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19 and Long COVID. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cure, E.; Ilcol, T.B.; Cure, M.C. Angiotensin II, III, and IV may be important in the progression of COVID-19. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2020, 21, 147032032097201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harky, A.; Chor, C.Y.T.; Nixon, H.; Jeilani, M. The controversy of using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in COVID-19 patients. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2021, 22, 1470320320987118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Viveiros, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Zhong, J.-C.; Turner, A.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient | Age (Year) | SAPS II % (Percentage) | Comorbidities | Plasma Renin pg/mL | SOFA SCORE (Points) | 90-Day Survivors | Difficult Weaning | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | ||||||
| Id 001 | 59 | 7.9% | Hypertension | 37.10 | 8.00 | 11.00 | 4 | 2 | 4 | Yes | Yes |
| Id 002 | 21 | 2.0 | Psychiatric, smoker | 9.50 | 52.30 | 6.00 | 4 | 3 | 2 | Yes | No |
| Id 003 | 63 | 7.9% | Prev. myocardial infarction (ACE receptors blocker) | 18.60 | 19.70 | 40.40 | 4 | 2 | 2 | Yes | Yes |
| Id 004 | 65 | 16.7% | Hypertension, hypothyroidism (ACE inhibitors) | 107.50 | 40.50 | 31.50 | 4 | 3 | 2 | No | Yes |
| Id 005 | 55 | 7.2% | None | 23.10 | 9.00 | 25.40 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Yes | Yes |
| Id 006 | 63 | 21.0% | None | 1.90 | 2.10 | 3.70 | 4 | 4 | 2 | Yes | No |
| Id 007 | 54 | 9.7% | Diabetes II, hypothyroidism | 2.60 | 1.50 | 4.40 | 3 | 4 | 3 | No | No |
| Id 008 | 61 | 9.7% | None | 22.5 | 172.50 | 206.70 | 3 | 4 | 3 | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melegari, G.; Veronesi, L.; Maccieri, J.; Ponzetta, F.; Osmenaj, S.; Barbieri, A. Plasma Renin Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. BioMed 2021, 1, 94-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed1020008
Melegari G, Veronesi L, Maccieri J, Ponzetta F, Osmenaj S, Barbieri A. Plasma Renin Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. BioMed. 2021; 1(2):94-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed1020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelegari, Gabriele, Lucia Veronesi, Jessica Maccieri, Francesco Ponzetta, Suela Osmenaj, and Alberto Barbieri. 2021. "Plasma Renin Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients" BioMed 1, no. 2: 94-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed1020008
APA StyleMelegari, G., Veronesi, L., Maccieri, J., Ponzetta, F., Osmenaj, S., & Barbieri, A. (2021). Plasma Renin Concentration in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. BioMed, 1(2), 94-98. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed1020008






