Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Current Perspectives and Management Strategies
Definition
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology: An Overview
2.1. Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Newborn: Preterm Infants Versus Full-Term Neonates
2.2. Neuroimaging in Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage
2.3. The Consequences of Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Post-Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus
3. Review of Conventional Management Approaches
4. The Role of the Pediatric Neurosurgeon
4.1. Neurosurgical Temporizing Measures: A Summary of Options
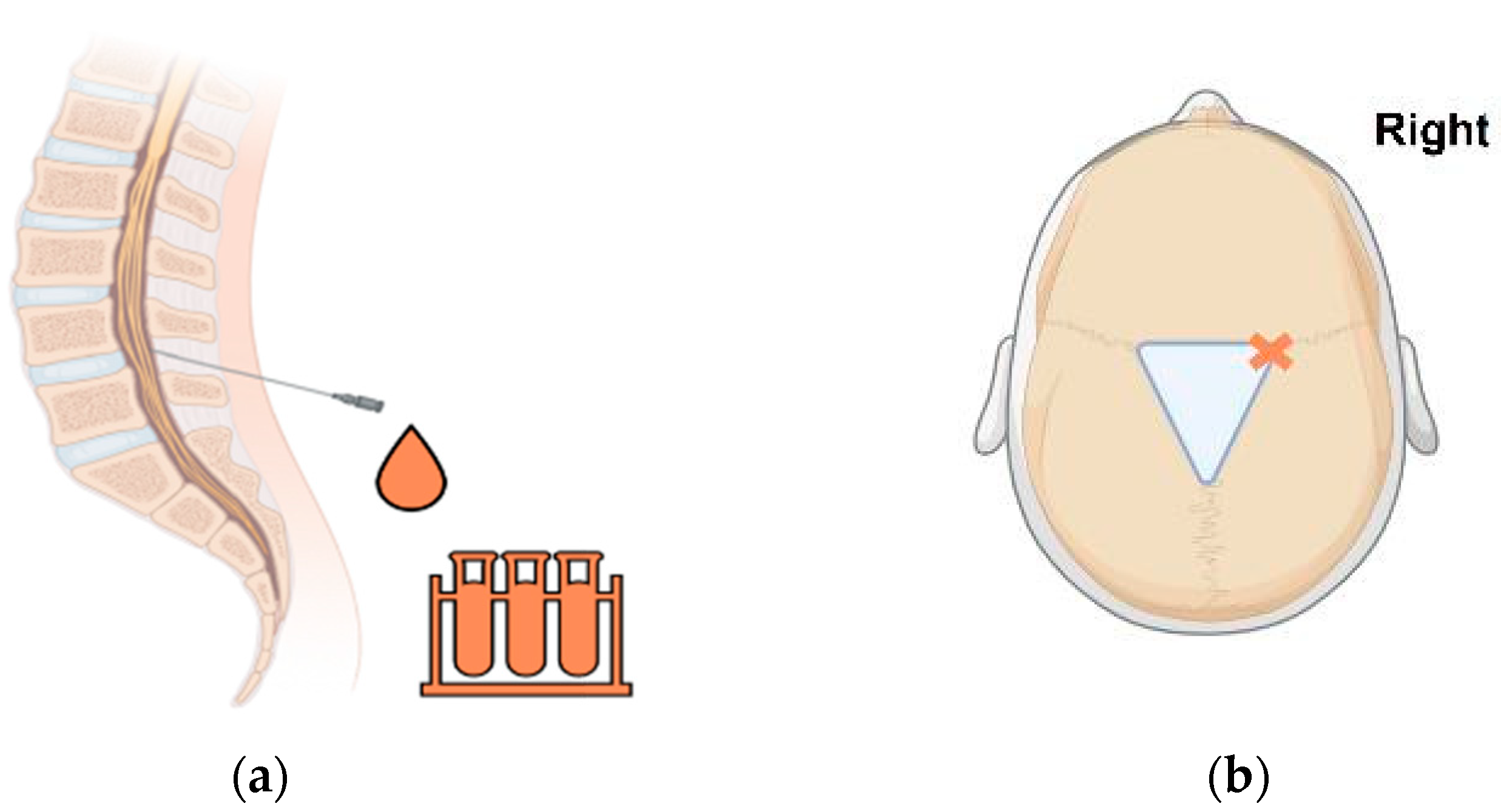
4.1.1. External Ventricular Drain (EVD)
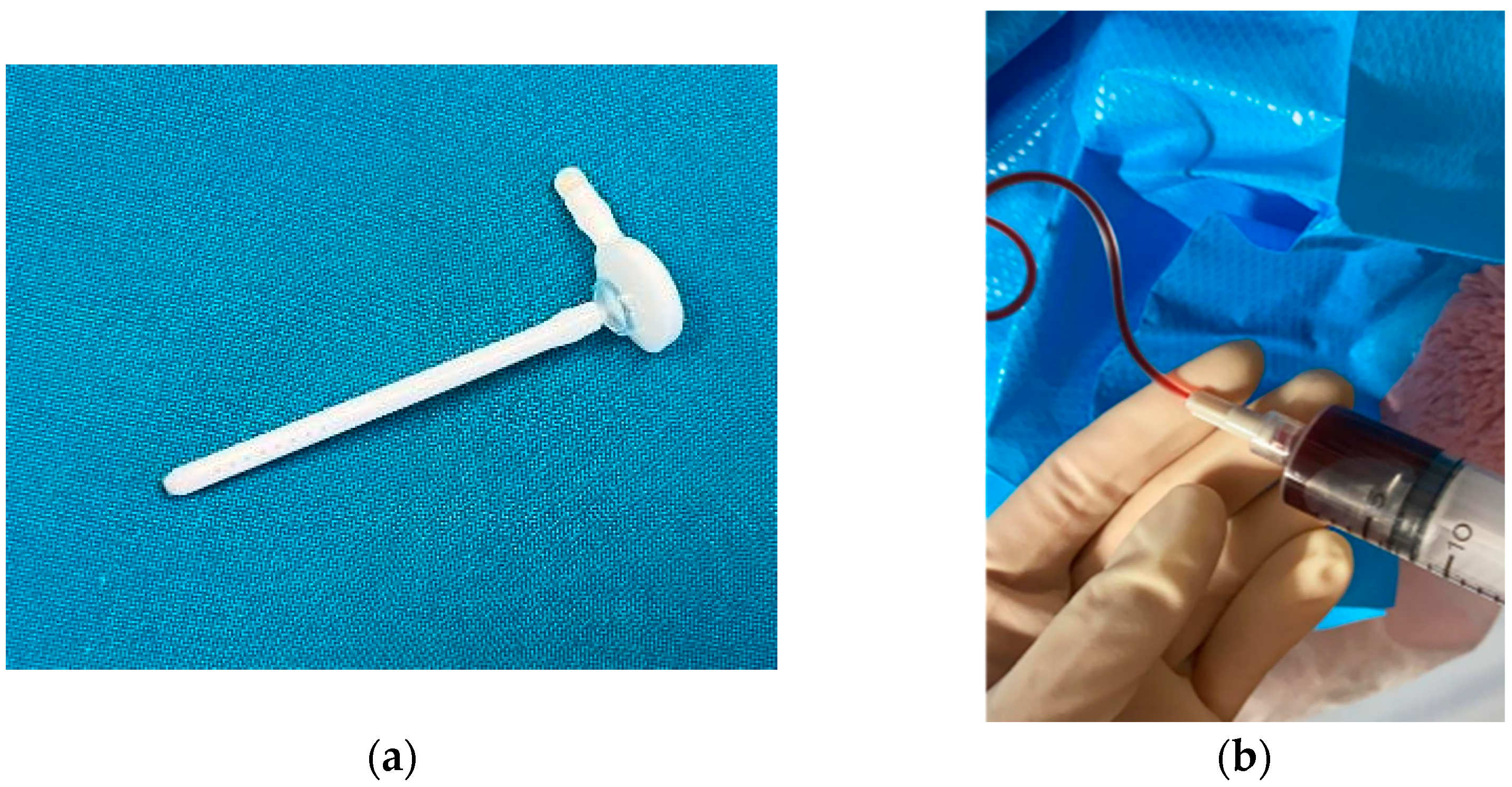
4.1.2. Ventricular Access Device (VAD)
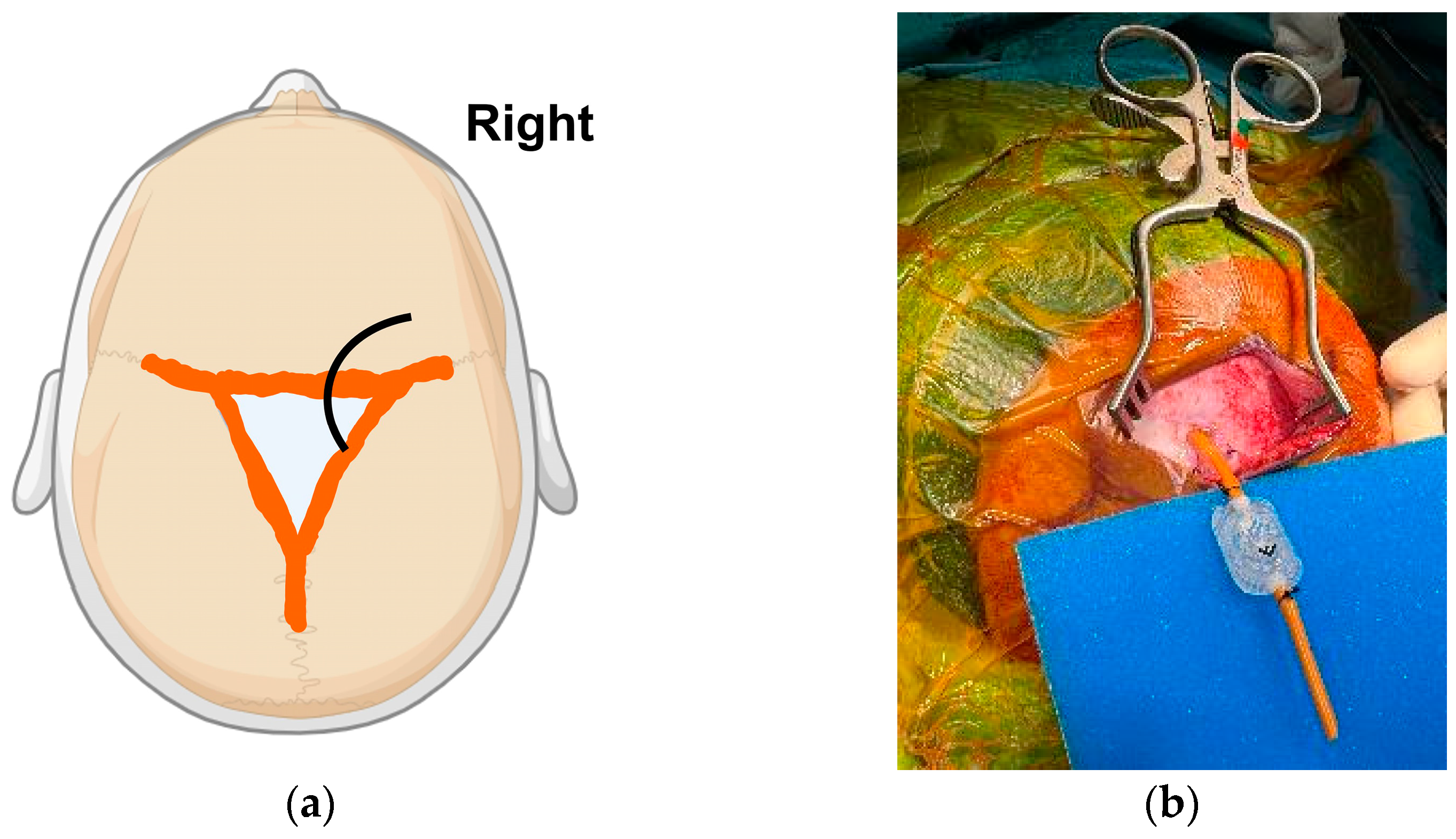
4.1.3. Ventriculo-Subgaleal Shunt (VSGS)
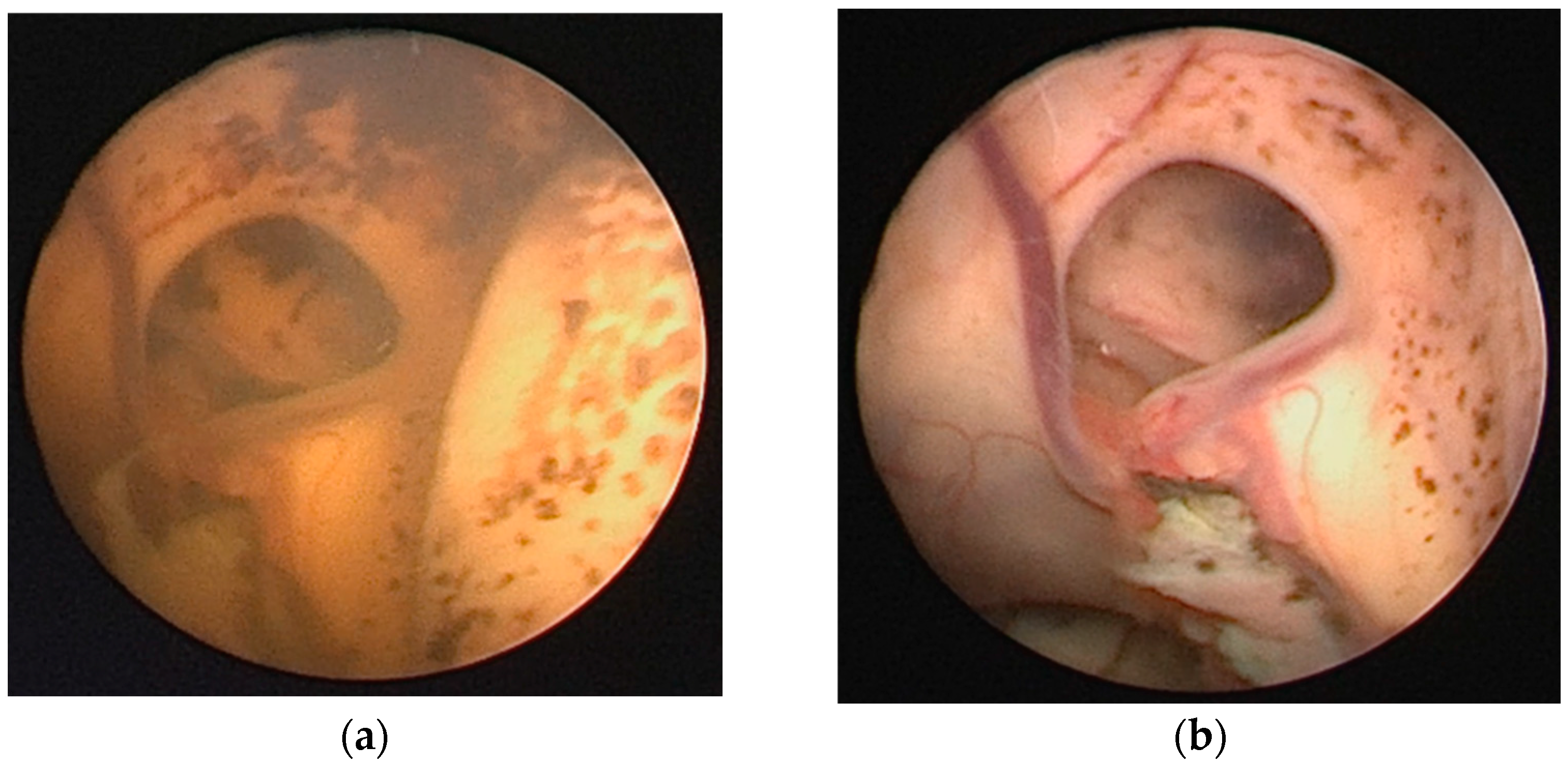
4.2. Neuroendoscopic Lavage (NEL): Background and Current Applications
4.3. The Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt (VPS) Is Imperfect but Still Relevant
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanba, E.; Eda, I.; Takashima, S.; Ohta, S.; Ohtani, K.; Takeshita, K. Intracranial hemorrhage in the full-term neonate and young infant: Correlation of the location and outcome. Brain Dev. 1984, 6, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trounce, J.Q.; Fagan, D.; Levene, M.I. Intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leucomalacia: Ultrasound and autopsy correlation. Arch. Dis. Child. 1986, 61, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsharkhas, L.; Khalessi, N.; Karimi Panah, M. Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Term Neonates: Sources, Severity and Outcome. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2015, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pande, G.S.; Vagha, J.D. A Review of the Occurrence of Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Preterm Newborns and its Future Neurodevelopmental Consequences. Cureus 2023, 15, e48968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduray, T.; Mamdoo, F.; Masekela, R. A retrospective study on the prevalence, severity and outcomes of intraventricular haemorrhage in infants with a low birth weight in a quarternary hospital in a low- to middle-income country. S. Afr. J. Child Health 2019, 13, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffel, C.; Kistler, K.D.; Sarda, S.P. Global incidence of intraventricular hemorrhage among extremely preterm infants: A systematic literature review. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 49, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.Y.M.; Naiduvaje, K.; Wong, Y.; Bhatia, A.; Ereno, I.L.; Ho, S.K.Y.; Yeo, C.L.; Rajadurai, V.S. Trends in neonatal mortality and morbidity in very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants over a decade: Singapore national cohort study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorini, B.; Keh, R.; Elllenbogen, J.; Williams, D.; Zebian, B. Intraventricular haemorrhage in prematurity. Infant 2014, 10, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- du Plessis, A.J. The role of systemic hemodynamic disturbances in prematurity-related brain injury. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.; O’Tuama, L. Cerebral intraventricular hemorrhages in infants: A widening age spectrum. Pediatrics 1980, 65, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, A.J.; van Stam, C.; Uniken Venema, M.; Koopman, C.; Groenendaal, F.; de Vries, L.S. Cognitive and Neurological Outcome at the Age of 5–8 Years of Preterm Infants with Post-Hemorrhagic Ventricular Dilatation Requiring Neurosurgical Intervention. Neonatology 2011, 101, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabh, P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: Mechanism of disease. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabh, P. Pathogenesis and prevention of intraventricular hemorrhage. Clin. Perinatol. 2014, 41, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.Y.Y.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Walker, M.L.; Seow, W.T. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt malfunctions: A reflective review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egesa, W.I.; Odoch, S.; Odong, R.J.; Nakalema, G.; Asiimwe, D.; Ekuk, E.; Twesigemukama, S.; Turyasiima, M.; Lokengama, R.K.; Waibi, W.M.; et al. Germinal Matrix-Intraventricular Hemorrhage: A Tale of Preterm Infants. Int. J. Pediatr. 2021, 2021, 6622598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.K. Neuroimaging of Germinal Matrix and Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Premature Infants. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2023, 66, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özek, E.; Kersin, S.G. Intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm babies. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 55, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, N.; Sharma, H.; Manganas, L.N.; Kirschen, G.W. Chapter 23—Development and pathology of the germinal matrix. In Factors Affecting Neurodevelopment; Martin, C.R., Preedy, V.R., Rajendram, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, S.; Mito, T.; Ando, Y. Pathogenesis of periventricular white matter hemorrhages in preterm infants. Brain Dev. 1986, 8, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, S. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the term infant. Neonatal Netw. 2000, 19, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Bender, S.; Sefkow, S.; Klingmüller, V.; Künzel, W.; Jensen, A. Peri/intraventricular haemorrhage: A cranial ultrasound study on 5286 neonates. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1997, 75, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, A.J.; Groenendaal, F.; Koopman, C.; Nievelstein, R.-J.A.; Han, S.K.; de Vries, L.S. Intracranial hemorrhage in full-term newborns: A hospital-based cohort study. Neuroradiology 2010, 52, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looney, C.B.; Smith, J.K.; Merck, L.H.; Wolfe, H.M.; Chescheir, N.C.; Hamer, R.M.; Gilmore, J.H. Intracranial hemorrhage in asymptomatic neonates: Prevalence on MR images and relationship to obstetric and neonatal risk factors. Radiology 2007, 242, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, C.J.; Beslow, L.A.; Witmer, C.M.; Vossough, A.; Jordan, L.C.; Zelonis, S.; Licht, D.J.; Ichord, R.N.; Smith, S.E. Haemorrhagic stroke in term and late preterm neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014, 99, F48–F53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhawar, B.S.; Ranger, A.; Steven, D.; Del Maestro, R.F. Risk Factors for Intracranial Hemorrhage among Full-term Infants: A Case-Control Study. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahriarian, S.; Akbari, P.; Amini, E.; Dalili, H.; Esmaeilnia Shrivany, T.; Niknafs, N.; Shariat, M.; Ghorban Sabagh, V. Intraventricular Hemorrhage in a Term Neonate: Manifestation of Protein S Deficiency—A Case Report. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 531–534. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, B.M.; Zaazoue, M.A.; Xu, G.; Ducis, K.A. Intraventricular hemorrhage in term infants: A single institutional experience between 2016 and 2020. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, M.D.; Gupta, S.L.; Brusky, R.M. The incidence and outcome of intracranial haemorrhage in newborns with haemophilia: Analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database. Haemophilia 2007, 13, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, G.H.; Ganesh, V.S.; Felie, J.M.; Gleason, D.; Hill, R.S.; Clapham, K.R.; Rakiec, D.; Tan, W.H.; Akawi, N.; Al-Saffar, M.; et al. A homozygous mutation in the tight-junction protein JAM3 causes hemorrhagic destruction of the brain, subependymal calcification, and congenital cataracts. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, M.E.; Halley, D.J.; Smit, L.S.; Lequin, M.H.; Cobben, J.M.; de Coo, R.; van Harssel, J.; Sallevelt, S.; Woldringh, G.; van der Knaap, M.S.; et al. The expanding phenotype of COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations: Clinical data on 13 newly identified families and a review of the literature. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, M.; Chau, V.; Lemyre, B. Routine imaging of the preterm neonatal brain. Paediatr. Child Health 2020, 25, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Domínguez, P.; Lecacheux, C.; Hernandez-Herrera, C.; Llorens-Salvador, R. Cranial ultrasound for beginners. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 1117–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpecht, D.; Frydryszak, D.; Miszczyk, N.; Szymankiewicz, M.; Gadzinowski, J. The incidence of severe intraventricular hemorrhage based on retrospective analysis of 35939 full-term newborns-report of two cases and review of literature. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoš, M.; Judaš, M.; Kostović, I. In vitro MRI of brain development. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 57, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, M.; Sebastianski, M.; Lemyre, B. Comparative performance of head ultrasound and MRI in detecting preterm brain injury and predicting outcomes: A systematic review. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papile, L.A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: A study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant--current concepts. Part II. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 25, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawlani, V.; Patel, M.D.; Davies, N.; Flintham, R.; Wesolowski, R.; Ughratdar, I.; Pohl, U.; Nagaraju, S.; Petrik, V.; Kay, A.; et al. Multiparametric MRI: Practical approach and pictorial review of a useful tool in the evaluation of brain tumours and tumour-like lesions. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollebrandse, N.L.; Spittle, A.J.; Burnett, A.C.; Anderson, P.J.; Roberts, G.; Doyle, L.W.; Cheong, J.L.Y. School-age outcomes following intraventricular haemorrhage in infants born extremely preterm. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021, 106, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.; Malik, P.; Desai, R.; Shelar, V.; Bekina-Sreenivasan, D.; Satnarine, T.A.; Lavado, L.K.; Singla, R.; Chavda, D.; Kaul, S.; et al. Post-Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus and Outcomes Amongst Neonates With Intraventricular Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Cureus 2021, 13, e18877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, R.A.; Burton, V.J.; Allen, M.C.; Robinson, S.; Soares, B.P. Preterm neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcome: A focus on intraventricular hemorrhage, post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus, and associated brain injury. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongena, P.; Ederies, A.; Azzopardi, D.V.; Edwards, A.D. Confidence in the prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome by cranial ultrasound and MRI in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 95, F388–F390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rees, P.; Callan, C.; Chadda, K.R.; Vaal, M.; Diviney, J.; Sabti, S.; Harnden, F.; Gardiner, J.; Battersby, C.; Gale, C.; et al. Preterm Brain Injury and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, K.; Wilson-Costello, D.; Taylor, H.G.; Mercuri-Minich, N.; Hack, M. Grades I-II intraventricular hemorrhage in extremely low birth weight infants: Effects on neurodevelopment. J. Pediatr. 2006, 149, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolisetty, S.; Dhawan, A.; Abdel-Latif, M.; Bajuk, B.; Stack, J.; Lui, K. Intraventricular hemorrhage and neurodevelopmental outcomes in extreme preterm infants. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, P.; de Vries, L.S. White matter injury in infants with intraventricular haemorrhage: Mechanisms and therapies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.; Whitelaw, A.; Thoresen, M.; Love, S. The pathogenesis of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, J.P., 2nd. Pathophysiology of congenital and neonatal hydrocephalus. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, A.; Jary, S.; Kmita, G.; Wroblewska, J.; Musialik-Swietlinska, E.; Mandera, M.; Hunt, L.; Carter, M.; Pople, I. Randomized trial of drainage, irrigation and fibrinolytic therapy for premature infants with posthemorrhagic ventricular dilatation: Developmental outcome at 2 years. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e852–e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, A.; Evans, D.; Carter, M.; Thoresen, M.; Wroblewska, J.; Mandera, M.; Swietlinski, J.; Simpson, J.; Hajivassiliou, C.; Hunt, L.P.; et al. Randomized clinical trial of prevention of hydrocephalus after intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infants: Brain-washing versus tapping fluid. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e1071–e1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.R.; Ayers, S.; Campbell, M.J.; Elbourne, D.; Hope, P.; Johnson, A. Randomized, controlled trial of acetazolamide and furosemide in posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation in infancy: Follow-up at 1 year. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassan, H.; Eshel, R.; Golan, I.; Kohelet, D.; Ben Sira, L.; Mandel, D.; Levi, L.; Constantini, S.; Beni-Adani, L. Timing of external ventricular drainage and neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, P.; Tietze, A.; Walch, E.; Bittigau, P.; Bührer, C.; Schulz, M.; Aigner, A.; Thomale, U.W. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years after neuroendoscopic lavage in neonates with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 26, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhiwala, J.H.; Hong, C.J.; Nassiri, F.; Hong, B.Y.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Kulkarni, A.V. Treatment of posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation in preterm infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes and complications. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2015, 16, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, D.I.; McComb, J.G.; Krieger, M.D. Craniotomy for fenestration of multiloculated hydrocephalus in pediatric patients. Oper. Neurosurg. 2005, 57, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnakota, A.; Wright, J.M.; Tomei, K.L. A Precursor to Multiloculated Hydrocephalus: Case Report and Review of Literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinchon, M.; Rekate, H.; Kulkarni, A.V. Pediatric hydrocephalus outcomes: A review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hislop, J.E.; Dubowitz, L.M.; Kaiser, A.M.; Singh, M.P.; Whitelaw, A.G. Outcome of infants shunted for post-haemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1988, 30, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedetti, L.; Lugli, L.; Marrozzini, L.; Baraldi, A.; Leone, F.; Baroni, L.; Lucaccioni, L.; Rossi, C.; Roversi, M.F.; D’Amico, R.; et al. Safety and Success of Lumbar Puncture in Young Infants: A Prospective Observational Study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 692652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooman, D.; Portess, H.; Sparrow, O. A review of the current treatment methods for posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus of infants. Cerebrospinal Fluid. Res. 2009, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Shim, K.W. Temporary Surgical Management of Intraventricular Hemorrhage in Premature Infants. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2023, 66, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreusser, K.L.; Tarby, T.J.; Kovnar, E.; Taylor, D.A.; Hill, A.; Volpe, J.J. Serial lumbar punctures for at least temporary amelioration of neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Pediatrics 1985, 75, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelaw, A.; Lee-Kelland, R. Repeated lumbar or ventricular punctures in newborns with intraventricular haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 4, Cd000216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvalishvili, A.; Khinikadze, M.; Gegia, G.; Khutsishvili, L. Neuroendoscopic lavage versus traditional surgical methods for the early management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.-F. Surgical management of intraventricular hemorrhage and posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in premature infants. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomale, U.W.; Cinalli, G.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Al-Hakim, S.; Roth, J.; Schaumann, A.; Bührer, C.; Cavalheiro, S.; Sgouros, S.; Constantini, S.; et al. TROPHY registry study design: A prospective, international multicenter study for the surgical treatment of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in neonates. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellons, J.C., 3rd; Shannon, C.N.; Holubkov, R.; Riva-Cambrin, J.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Limbrick, D.D., Jr.; Whitehead, W.; Browd, S.; Rozzelle, C.; Simon, T.D.; et al. Shunting outcomes in posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus: Results of a Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network prospective cohort study. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Iwanaga, J.; Oskouian, R.J.; Loukas, M.; Jerry Oakes, W.; Shane Tubbs, R. Ventriculosubgaleal shunting—A comprehensive review and over two-decade surgical experience. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, G.E.; Graf, C.J. Subgaleal shunt for temporary ventricle decompression and subdural drainage. J. Neurosurg. 1977, 47, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassanito, P.; Serrao, F.; Gallini, F.; Bianchi, F.; Massimi, L.; Vento, G.; Tamburrini, G. Ventriculosubgaleal shunt and neuroendoscopic lavage: Refining the treatment algorithm of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansasuta, A.; Boongird, A. Ventriculo-subgaleal shunt: Step-by-step technical note. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2007, 90, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, J.G.; Ramos, A.D.; Platzker, A.C.; Henderson, D.J.; Segall, H.D. Management of hydrocephalus secondary to intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm infant with a subcutaneous ventricular catheter reservoir. Neurosurgery 1983, 13, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulmer, B.B.; Grabb, P.A.; Oakes, W.J.; Mapstone, T.B. Neonatal ventriculosubgaleal shunts. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 80–83, discussion 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fountain, D.M.; Chari, A.; Allen, D.; James, G. Comparison of the use of ventricular access devices and ventriculosubgaleal shunts in posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Köksal, V.; Öktem, S. Ventriculosubgaleal shunt procedure and its long-term outcomes in premature infants with post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubbs, R.S.; Smyth, M.D.; Wellons, J.C., 3rd; Blount, J.; Grabb, P.A.; Oakes, W.J. Life expectancy of ventriculosubgaleal shunt revisions. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2003, 38, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.K.; Kumar, C.R.; Wylen, E.L.; Nanda, A. Ventriculosubgaleal shunts for posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in premature infants. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2005, 41, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, F.; Adegbite, A.; Shapiro, K.; Miller, K. Ventriculosubgaleal shunts: Management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in premature infants. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1992, 18, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, H.; Mawla, A.A.; Kazah, J. The incidence, timing, and predisposing factors of germinal matrix and intraventricular hemorrhage (GMH/IVH) in preterm neonates. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, C.A.; Choudhri, A.F.; Auguste, K.I.; Limbrick, D.D.; Rogido, M.; Mitchell, L.; Flannery, A.M. Pediatric hydrocephalus: Systematic literature review and evidence-based guidelines. Part 2: Management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in premature infants. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. PED 2014, 14, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.F.; Baird, L.C.; Klimo, P.; Mazzola, C.A.; Nikas, D.C.; Tamber, M.S.; Flannery, A.M. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Treatment of Pediatric Hydrocephalus: Update of the 2014 Guidelines. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeyman, S.I.; Boukas, A.; Jayamohan, J.; Magdum, S. Neuroendoscopic lavage for the management of neonatal post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus: A retrospective series. Child’s Nerv. Syst. ChNS Off. J. Int. Soc. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2022, 38, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etus, V.; Kahilogullari, G.; Karabagli, H.; Unlu, A. Early Endoscopic Ventricular Irrigation for the Treatment of Neonatal Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus: A Feasible Treatment Option or Not? A Multicenter Study. Turk. Neurosurg. 2018, 28, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Arcangues, C.; Schulz, M.; Bührer, C.; Thome, U.; Krause, M.; Thomale, U.W. Extended Experience with Neuroendoscopic Lavage for Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Neonates. World Neurosurg. 2018, 116, e217–e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Bührer, C.; Pohl-Schickinger, A.; Haberl, H.; Thomale, U.W. Neuroendoscopic lavage for the treatment of intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in neonates. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 13, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A standardised protocol for neuro-endoscopic lavage for post-haemorrhagic ventricular dilatation: A Delphi consensus approach. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2022, 38, 2181–2187. [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Caballero, J.; Rivero-Garvia, M.; Arteaga-Romero, F.; Herreria-Franco, J.; Lozano-Gonzalez, Á.; Marquez-Rivas, J. Neuroendoscopic lavage for the management of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in preterm infants: Safety, effectivity, and lessons learned. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 26, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.P.; Ajmera, S.; Thomas, F.; Dave, P.; Lillard, J.C.; Wallace, D.; Broussard, A.; Motiwala, M.; Norrdahl, S.P.; Venable, G.T.; et al. Shunt Failure-The First 30 Days. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.X.; Han, H.P.; Foo, Y.W.; Chan, Y.H.; Ng, L.P.; Low, D.C.Y.; Seow, W.T.; Low, S.Y.Y. Paediatric ventriculoperitoneal shunt failures: 12-year experience from a Singapore children’s hospital. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 3445–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S. Neonatal posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus from prematurity: Pathophysiology and current treatment concepts. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2012, 9, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A. Permanent Surgical Treatment for Posthemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Preterm Infants. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2023, 66, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, D.H.; Vachhrajani, S.; Bohnstedt, B.N.; Patel, N.B.; Patel, A.J.; Fox, B.D.; Jea, A.; Boaz, J.C. Analysis of the risk of shunt failure or infection related to cerebrospinal fluid cell count, protein level, and glucose levels in low-birth-weight premature infants with posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2011, 7, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelaw, A.; Aquilina, K. Management of posthaemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012, 97, F229–F233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez Sandoval, P.; Hernández Rosales, P.; Quiñones Hernández, D.G.; Chavana Naranjo, E.A.; García Navarro, V. Intraventricular hemorrhage and posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus in preterm infants: Diagnosis, classification, and treatment options. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmesallamy, W.A.E.A.; Abofaid, A.M.A.; Mohamed, M.S.; Taha, M.M. Pediatric ventriculoperitoneal shunt: A comparative study between anterior fontanel ultrasound-guided versus conventional cranial end insertion. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluski, J.; Zajciw, P.; Hariharan, P.; Morgan, A.; Morales, D.M.; Jea, A.; Whitehead, W.; Marupudi, N.; Ham, S.; Sood, S.; et al. Characterization of a multicenter pediatric-hydrocephalus shunt biobank. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limwattananon, P.; Kitkhuandee, A. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt failure in pediatric patients: An analysis of a national hospitalization database in Thailand. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 28, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydon, H.L.; Hayward, R.; Harkness, W.; Bayston, R. Physical properties of cerebrospinal fluid of relevance to shunt function. 2: The effect of protein upon CSF surface tension and contact angle. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 9, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, S.; Sani, R.; Graf, K.; Uhl, E.; Godau, J.; Deinsberger, W. CSF shunt valve occlusion-does CSF protein and cell count matter? Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, K.L. The Evolution of Cerebrospinal Fluid Shunts: Advances in Technology and Technique. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2017, 52, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, M.L.; Ng, L.P.; Low, D.C.Y.; Seow, W.T.; Low, S.Y.Y. Programmable Shunt Valves for Pediatric Hydrocephalus: 22-Year Experience from a Singapore Children’s Hospital. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade | Papile Criteria (Based on CT Scans) | Volpe Criteria (Based on CUS Imaging) | Representative Illustration (Brain Section in Coronal View) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Hemorrhage limited to the sub-ependymal matrix | Hemorrhage without intraventricular extension or with hemorrhage occupying <10% of ventricular area | 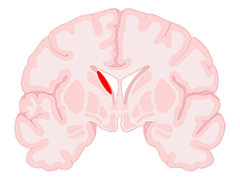 |
| II | Hemorrhage extending into the ventricular system (<50%), without acute ventriculomegaly | Hemorrhage occupying 10–50% of ventricular area |  |
| III | Hemorrhage extending into the ventricular system ≥50% or ≥1 lateral ventricles OR Hemorrhage extending into a dilated ventricle | Hemorrhage occupying >50% of ventricular area | 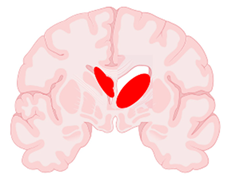 |
| IV | Hemorrhage grade I, II or III with extension into brain tissue | Periventricular echodensity (periventricular venous hemorrhagic infarction) |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chua, F.H.Z.; Ng, L.P.; Low, S.Y.Y. Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Current Perspectives and Management Strategies. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1948-1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040127
Chua FHZ, Ng LP, Low SYY. Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Current Perspectives and Management Strategies. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(4):1948-1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040127
Chicago/Turabian StyleChua, Felicia H. Z., Lee Ping Ng, and Sharon Y. Y. Low. 2024. "Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Current Perspectives and Management Strategies" Encyclopedia 4, no. 4: 1948-1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040127
APA StyleChua, F. H. Z., Ng, L. P., & Low, S. Y. Y. (2024). Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Current Perspectives and Management Strategies. Encyclopedia, 4(4), 1948-1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4040127






