Abstract
Chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu) has emerged with growing evidence linking it to environmental exposures. This case–control study aimed to evaluate serum and urine trace elements (TEs) in CKDu patients, comparing them with those from control groups from endemic and non-endemic regions. TEs were analyzed in 406 participants (CKDu = 75, endemic CKD (ECKD) = 82, non-endemic CKD (NECKD) = 85, endemic control (EC) = 79, non-endemic control (NEC) = 85 using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Means ± standard deviations were compared via the t-test and categorical variables by the chi-square test. Compared to non-endemic groups, Al, Mn, Ni, Cu, Cd, and Ba in serum and urine were significantly higher in endemic areas. CKDu patients showed elevated serum V, Cr, Zn, As, and U and urinary Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Rb compared to ECKD. Compared to NEC, CKDu patients had higher serum Zn, As, and Ba and urinary Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu. Significant increases in serum V, Zn, As, Cd, Ba, and U and urinary V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Rb, and Sr were noted in CKDu vs. NECKD. Elevated serum Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, etc., and urinary Be, V, Zn, Se, etc., were observed in EC vs. CKDu. Urinary TEs positively correlated with eGFR, suggesting tubular dysfunction or prolonged exposure. Serum Se, a known reno-protective TE, was low in CKDu and ECKD. This study highlights that TE levels were high not only due to exposure but also depending on kidney health. Identified group-specific TEs may be causative in CKDu, having adverse health outcomes in some groups while potentially being protective in healthy groups.
1. Introduction
Among various non-communicable diseases, chronic kidney disease (CKD), often caused by diabetes and hypertension, is one of the most common health problems worldwide [1]. The prevalence of CKD has increased by 29.3% since the 1990s, affecting 9.1% of the global population [2]. In addition, an increase in the prevalence of CKD without known risk factors, known as chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu), has been reported over the past three decades in several tropical and subtropical countries, including El Salvador, Egypt, India, Central America, Nicaragua and Sri Lanka [3].
Interestingly, this environmental interstitial nephropathy was initially reported as a confined health problem in poor farming communities [4]. In Sri Lanka, the highest prevalence of CKDu has been reported in rural dry areas where extensive agriculture is practiced. Behavioral and environmental risk factors such as dehydration, agrochemicals, unsafe water consumption and infections were among the suspected causative agents of this enigmatic disease [5,6]. Among environmental exposures, drinking water quality has received greater attention due to the characteristic mosaic spatial distribution of the disease [7,8]. Most affected populations in these rural areas consume groundwater without pretreatment [7,9]. Therefore, in CKDu-endemic areas, there is a high probability of exposure to environmental contaminants.
There is growing evidence supporting the association between the environmental exposure to trace elements (TEs) and metalloids through drinking water or food and CKDu in Sri Lanka [10,11,12]. Although TEs are essential nutrients for the homeostasis of the human body, both their deficiency and excess can have adverse consequences [13]. Notably the inadvertent exposure to heavy metals has been reported as a possible risk factor, even for Mesoamerican nephropathy [14]. In Sri Lanka, several studies proposed the role of trace and heavy metals in drinking water in the occurrence of CKDu [15,16,17,18] with contradictory results [7,9].
Higher levels in biological samples are the most reliable way to confirm and to identify the consequences of increased exposure to TEs. Thus, the results of various studies analyzing various tissues such as hair, urine, serum and forensic kidney autopsies [19,20,21,22] are not conclusive. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the serum and urine TE levels of CKDu and compare the results with multiple controls from endemic and non-endemic regions of the disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Recruitment of Study Subjects
This case–control study was approved by the IRBS: Ethical Review Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, the University of Peradeniya (2016/EC/28). It was carried out in accordance with the institutional ethical guidelines and the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki from 2016 to 2018. All study participants were enrolled after being informed; written consent was obtained. The patient group included 75 participants with a definite CKDu diagnosis (biopsy proven) [22] attending the renal clinic Girandurukotte and Wilgamuwa, Sri Lanka. About 82 and 85 CKD participants with known CKD causes were from endemic CKD (ECKD) and non-endemic CKD (NECKD) areas, respectively. About 79 and 85 dipstick-negative, otherwise healthy individuals with normal blood pressure, blood glucose and creatinine levels were enrolled from the endemic (EC) and non-endemic (NEC) areas, respectively.
2.2. Sample Collection, Processing and Laboratory Analysis
Blood samples (10 mL) were collected from peripheral veins in plain tubes. The serum was separated immediately after clotting by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min. Spot urine samples were collected from all recruited cases into empty, sterile polypropylene urine containers.
Prepared serum and urine samples for TE analysis were transported in liquid N2 to the National Hospital, Kandy. The samples were stored at −80 °C until the analyses were carried out. Other parameters, including biochemical tests, were carried out on the same day as the sample collection. All samples were digested according to the standard operating procedures (Supplementary Data S1). Subsequently, the dissolved concentrations of TEs were analyzed using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICapQ, Thermo Fisher, Bremen, Germany) under standard operating conditions. All experiments were duplicated, and average values were used for calculations.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
All statistical calculations were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 23. Continuous variables were presented as means ± standard deviations and compared using a t-test. Categorical variables were expressed as counts and proportions and compared using the chi-square test. R software version 2024.12.0+467 was used to analyze area under the curve (AUC) in Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. A two-tailed p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analyses.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Study Participants
The study had 406 participants from different categories (CKDu, EC, NEC, ECKD and NECKD). Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of all the study participants in various groups.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of all the study individuals.
The endemic control group was slightly younger than the other groups. In the non-endemic control group, one individual had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
3.2. Descriptive Statistics of the Study Participants
In the initial step of our step-by-step approach, TEs were measured in the subjects of the control groups and compared with reported reference values. Table 2 illustrates the TE levels in serum and urine in the study groups compared to the available reference ranges. Additional details including the median and interquartile ranges are described in Supplementary Data S2.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics; mean (±SD) of TEs in serum and urine.
The TE levels were higher than the reference ranges, and the TE levels in serum and urine varied between the studied groups. The differences between groups are likely due to exposure status and kidney health. With this understanding, in the next step, we attempted to elucidate TE levels in the defined categories according to living environment and kidney health.
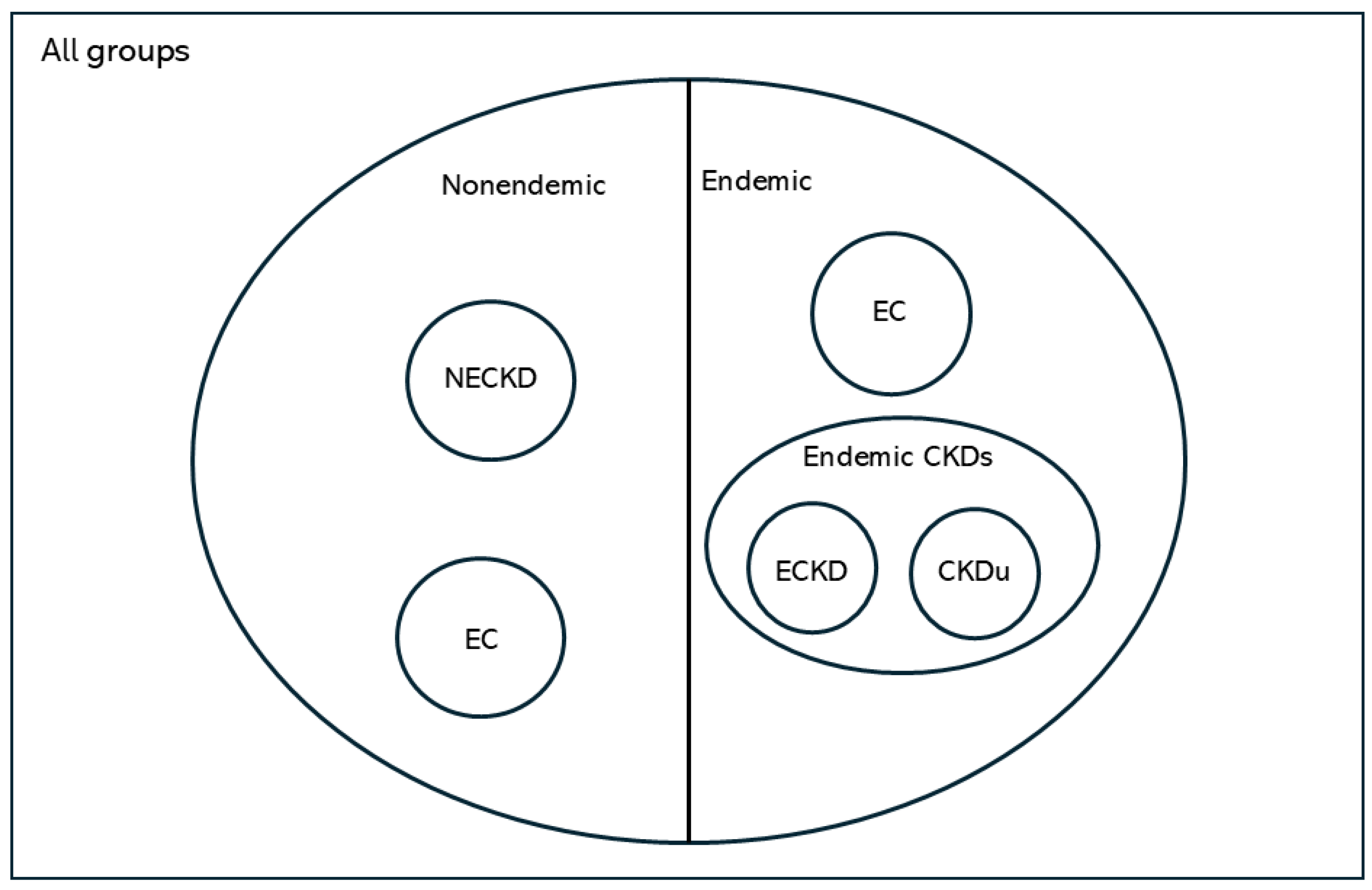
Figure 1 shows an illustration of the study groups based on living environment and kidney health.
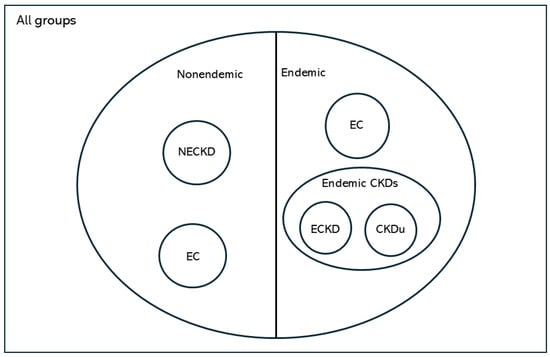
Figure 1.
Illustration of study groups based on living environment and kidney health. CKDu, chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology; EC, endemic control; NEC, non-endemic control; ECKD, endemic chronic kidney disease; NECKD, non-endemic chronic kidney disease.
3.3. Significant Changes in TE Levels in Serum and Urine
According to these study groups, TEs are analyzed and interpreted, as shown in Table 3. Table 3 shows the significantly increased/decreased mean TE levels in serum and urine in relation to the defined categories. Notably, V, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn, As, Rb, Sr, Cd, Ba, and U in serum and urinary Mn, Ni, and Cu were significantly increased in all endemic groups compared to the non-endemic groups, which reflects adverse exposures in endemic areas for CKDu. Interestingly, serum Al and urine Al, Mn, Ni, Cu, Cd, and Ba were significantly increased in the endemic group (CKDu + ECKD) compared to EC. In CKDu, serum V, Cr, Zn, As, and U and urinary Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Rb were significantly increased compared to ECKD. Additionally, serum Zn, As, and Ba and urinary Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu were increased compared to NEC. Upon comparing CKDu and NECKD, V, Zn, As, Cd, Ba, and U were significantly increased in serum, while V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Rb and Sr were significantly increased in urine. In EC vs. CKDu, Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, V, Zn, Se, Rb, Sr, U and Pb were significantly increased in EC serum, while Be, V, Zn, Se, Rb, Sr, U, Cd, and Ba were increased in EC urine.

Table 3.
Comparison of higher-than-reference-range serum and urinary TE levels between groups.
3.4. Relationship Between TEs and eGFR
Variations in TE levels in the CKD groups may be due to either their accumulation due to impaired renal function, intermittent toxic exposure, or a combination of both factors. In the subsequent step, we examined the relationship between TEs and eGFR to investigate this possibility (Table 4).

Table 4.
Significant correlations of serum and urine TEs with eGFR in chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu), endemic chronic kidney disease (ECKD), non-endemic chronic kidney disease (NECKD) groups.
None of the TEs were negatively correlated with eGFR in the CKDu group, suggesting that impaired clearance was not solely responsible for TE accumulation and higher TE levels. However, in the endemic CKD group, serum Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, As, Ba, and Pb were negatively correlated with eGFR, suggesting the importance of impaired clearance for higher values. Curiously, urinary levels of most TEs were positively correlated with eGFR, indicating that tubular dysfunction as CKDu progresses or prolonged exposure is the cause of higher levels. Notably, urine levels of a known reno-protective TE, Se, were positively correlated with eGFR in CKDu and ECKD, and the serum levels were low.
3.5. TE Levels in Heat Maps
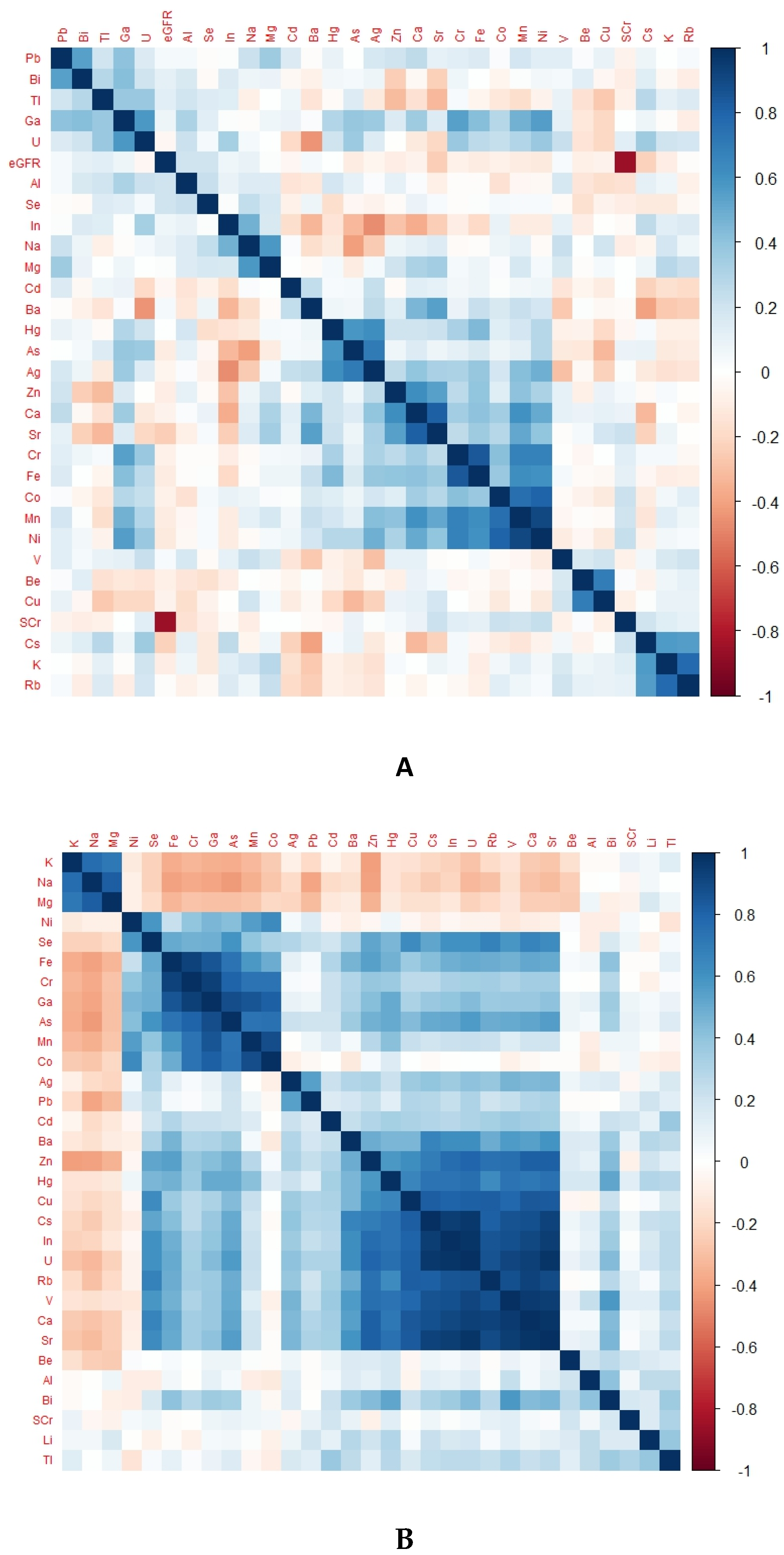
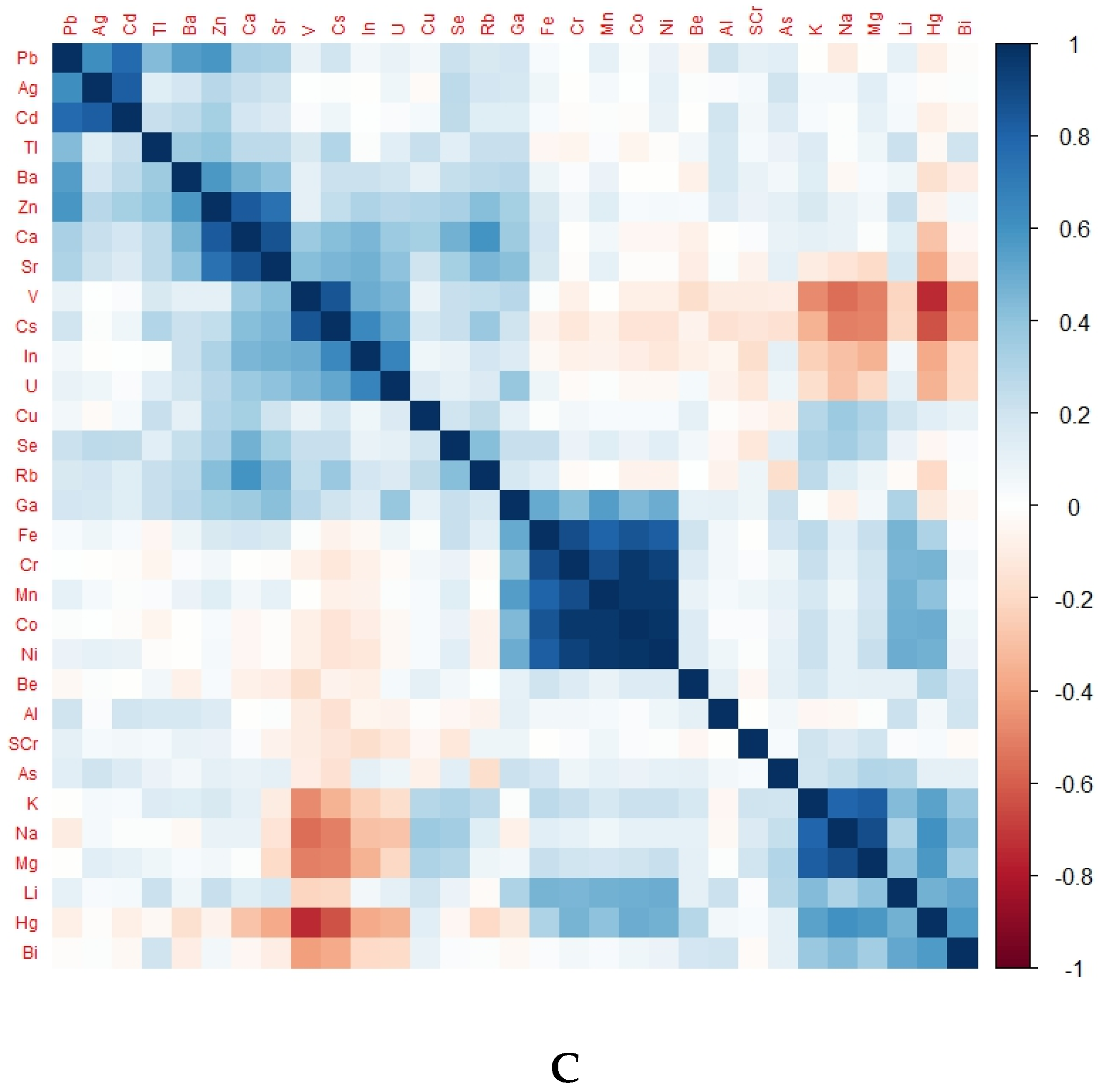
There was a differentiable pattern in the heat map of each group representing TE levels according to kidney health and exposure status (Figure 2).
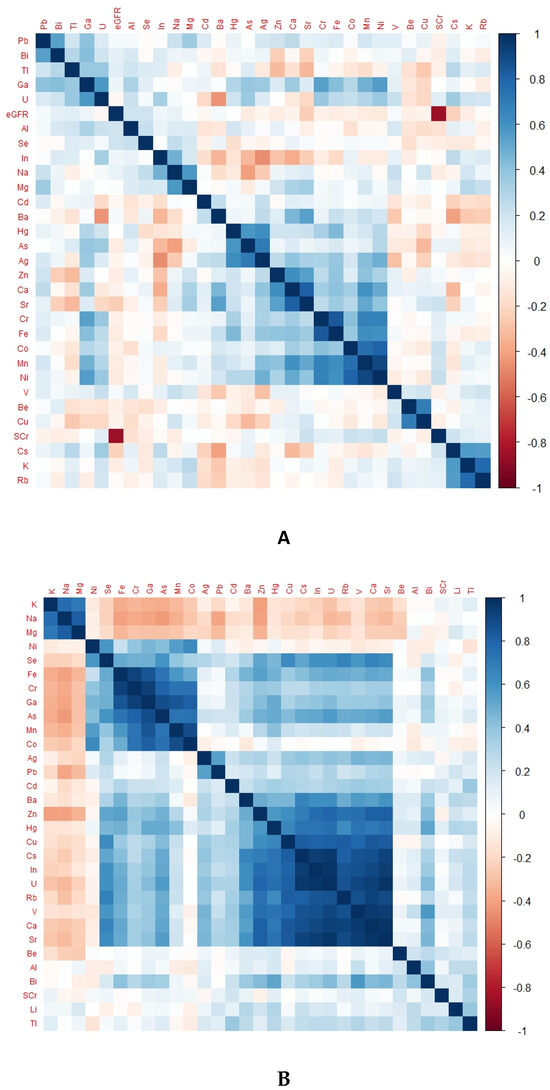
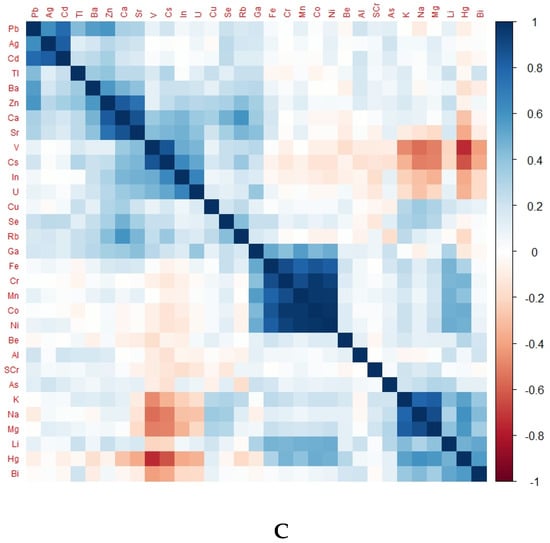
Figure 2.
Heat map of different groups representing TE levels according to kidney health and exposure status. (A) Heat map of CKDu group, (B) heat map of EC group, (C) heat map of NEC group; eGFR, glomerular filtration rate; SCr, serum creatinine.
Notably, Ni, Cr, Fe, Co, and Mn were in positively correlated clusters in almost all groups. The obvious difference between the endemic control group and CKDu was that Se, Ba, Cu, Rb, V and U were positively correlated in EC but negatively correlated in CKDu. This finding may hint towards the protective role of Se and some other TEs against the occurrence of CKDu. Positively correlated TEs in non-endemic groups and endemic CKDs with known causes were the same.
3.6. Significance of TEs to Differentiate Within Defined Categories
Ultimately, in ROC analysis, we examined the AUC of TEs with categorical significance to determine their ability to differentiate within defined categories (Table 5, Supplementary Data S3). According to these results, serum As and urine U are well suited to distinguish endemic groups from non-endemic groups. Serum V, Cr, M, Fe, Cu, Zn, Se, Rb, Cd, Sr, Pb and U are excellent for distinguishing endemic healthy controls from endemic kidney disease (CKD + CKDu). V, As, and U are excellent markers for distinguishing CKDu from CKD in the endemic area. V is a superb TE in serum and urine for differentiating non-endemic CKD from healthy controls.

Table 5.
Significant ROC data for TEs in serum and urine in different groups.
4. Discussion
4.1. TEs and Renal Involvement
The TE content in biological samples of a healthy person solely depends on the exposure level of the element in question. Nevertheless, in the presence of impaired renal function, the levels are decided by both kidney functions and the degree of exposure. The current evidence proposes that the degree of TE contamination differs between individuals living in CKDu-endemic environments and those residing in non-endemic environments [11]. In addition, the TE levels in serum and urine show differences between healthy people and people with impaired kidney function. By analyzing these differences, we aim to elucidate the possible role of TEs in the development of CKDu.
All groups generally had higher concentrations of TEs in serum and urine compared to the reference ranges. In addition, there were significantly increased TE levels in all endemic groups compared to non-endemic groups, which may reflect an increased risk of exposure in these areas. Interestingly, several TEs had higher levels in the kidney-impaired group, including CKD and CKDu, than in healthy individuals living in the same location. Some of these elements negatively correlated with the eGFR, suggesting that the accumulation is more likely due to renal dysfunction. Previous studies on CKDu in Sri Lanka have suggested the possibility that water resources are the main source of toxic elements contributing to the development of this disease [40,41]. Farmers in CKDu-endemic areas generally belong to a low-income group with limited access to clean water and do not live in an ideal living condition. According to several investigators, fertilizers used in agriculture contain significant amounts of heavy metals such as Cu, As, Co, Cr, Mo, Sr, Ti, V, Mn, Fe, Ni, Zn, Cd, Pb, Hg, Ba and Sr [13,42,43]. In addition, they described that the long-term irrigation of land and the use of inorganic fertilizers and animal manure in agriculture tend to increase the availability of trace metals and metalloids in the environment, which are toxic to humans and plants [42]. Chandrajith et al. (2005) revealed that the primary cause of the initial contamination of Sri Lankan rice soils by agricultural practices is the overuse of fertilizers [44]. In addition, some studies have found that environmental exposure to the potentially toxic elements As, Cd, and Pb is among the suggested etiological factors for CKDu [18,45]. A recent study has found that acute or long-term exposure to nephrotoxic substances or risk factors such agrochemicals, zoonotic illnesses, contaminated foods or water, alcohol consumption, smoking, and betel chewing may result in CKDu [15].
TEs can affect human health in various ways. Some TEs are toxic, so the absence or deficiency of certain TEs can pose health risks. Well-known examples are Cd nephropathy, Pb nephropathy and Li nephropathy. The results of a study of CKDu patients in Padavi-Siripura, Sri Lanka found that 48% of CKDu patients and 17.4% of controls fulfil the criteria for diagnosing chronic arsenic toxicity [40]. In the current study, mean serum As or urine As levels in CKDu were not significantly different from those of their healthy counterpart, the endemic control group. Another study on CKDu patients showed that the average urinary As level was 39.5 µg/L, ranging from 2.7 to 313 µg/L [6,10]. This is consistent with our study results. Furthermore, urinary As levels were 10 times lower in CKDu patients than in non-endemic controls, consistent with the current study results [10]. In the current study, the serum As level was significantly increased in the CKDu group compared to the NEC, ECKD and NECKD groups without significant differences in urine As levels. In a study performed by Atlani et al. (2024) in India, the authors found an increased blood As level in the CKDu group compared to the CKD group, while urine As was significantly decreased in CKDu and CKD compared to the healthy controls, which is consistent with the results of the current study [46].
The kidney is the main target organ for Cd toxicity, and Cd has been linked to kidney damage [47,48]. Itai-Itai disease in Japan has been shown to result from exposure to Cd through mining tailing runoffs in rice fields and the subsequent ingestion of contaminated rice by humans [49]. The serum Cd levels of CKDu patients were significantly higher than those of CKD patients in endemic and non-endemic areas and also showed an increased urinary Cd level (0.94 µg/L). However, the control groups had higher serum Cd values than the diseased groups. Pb accumulation has been reported in patients with renal failure [50]. For example, Staessen et al. (1992) found that blood Pb levels were inversely correlated with creatinine clearance [51]. Although the Pb levels were within reference ranges, there was a positive correlation between serum Pb levels and eGFR in our CKD groups, suggesting Pb accumulation in renal insufficiency. Similar trends have been reported for Al, Cr, V and Sr, particularly in the background of advanced renal failure or in dialysis populations [25,52]. Notably, serum Al levels were high in the CKDu-endemic group and positively correlated with eGFR.
Cu, zinc and Se are essential TEs that play various roles in the human body. Cu is important for hemoglobin synthesis, connective tissue metabolism, bone development and the antioxidant defense system [53,54]. Zn deficiency is associated with reduced immunity, leading to increased susceptibility to infections, often in uremic patients [55]. A deficiency of Se contributes to the development of cardiovascular disease, cardiomyopathy, Keshan disease, impaired immune function, anemia, and increased cancer and CKD [56]. Se deficiency is associated with reduced glutathione reductase activity and susceptibility to toxins. The results of the current study are consistent with those of previous ones. Selenium also plays a role in synthesizing thyroid hormones and antioxidant mechanisms [53]. Although the serum levels of these three important TEs were within normal limits in all groups, significantly higher values were reported in the endemic control groups. The serum Se levels were in the lower range in CKDu, with low urinary Se levels indicating a lower intake. Certain TEs, including V, Ba and Rb, were found in positively correlated clusters in endemic controls. All these findings may suggest a protective effect of some TEs in unaffected individuals in the CKDu-endemic area.
The endemic control group had the most striking TE abnormalities. Their renal functions remained normal despite elevated levels of potentially nephrotoxic elements such as Cd, As, and Ni. In contrast, individuals with CKDu had comparatively lower levels. Still, they developed the disease, and their levels were higher than the levels of the non-endemic CKDu group and the control group. In addition, this group had higher levels of protective TEs such as Se, Zn and Cu than CKDu patients. These findings strongly propose the need for future studies to analyze the role of potentially nephrotoxic TEs in the absence of protective TEs and in genetically vulnerable groups. Furthermore, epigenetic modifications due to environmental exposures have been suggested in the urine mRNA analysis of CKDu and endemic controls [57].
4.2. Significance of the Study
Our results confirm higher levels of TEs in endemic populations, more likely due to environmental exposures. Meanwhile, in the absence of the protective effects of TEs themselves or secondary to epigenetic modifications, nephrotoxic TEs could lead to nephrotoxicity, and hence, CKDu. This is the first study that has included four controls (endemic CKD, endemic healthy, non-endemic CKD and non-endemic healthy) and compared TEs in patients with CKDu.
4.3. Challenges and Future Studies
In the current study, we assume that TE levels are likely to fluctuate in acute exposures and also with hydration status. Prospective, larger cohort studies need to be conducted to avoid these limitations. The small sample size is also a limitation. The cross-sectional design precludes causal relationships, and further prospective studies need to be undertaken. This is a preliminary study, and these specific patterns of selected TEs identified in the current study need to be validated in a larger group.
5. Conclusions
Diverse adverse health exposures have been documented in populations endemic to CKDu compared to healthy populations. We have identified varying levels of TEs, likely due to environmental exposure, between these communities. Additionally, our findings suggest potential beneficial effects of TEs in healthy controls living in endemic areas for CKDu. Overall, in the absence of protective roles, nephrotoxic agents, including nephrotoxic TEs, may contribute to the development of CKDu.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/kidneydial5010011/s1, Supplementary Data S1: Digestion Procedure for Serum and urine samples, Table S1: Microwave digestion program for human serum, Table S2: Significant ROC data (AUC) for TEs in serum and urine in different groups, Table S3: Descriptive statistics; Median (IQR) of TEs in serum and urine, Figure S1: Mars-6 microwave digester.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.N.T.F., N.N. and R.C.; data curation, B.N.T.F. and H.T.K.A.; formal analysis, B.N.T.F., N.N., R.C., D.H. and H.T.K.A.; funding acquisition, R.C.; investigation, B.N.T.F., N.N. and R.C.; methodology, B.N.T.F., N.N., R.C., D.H. and H.T.K.A.; project administration, N.N. and R.C.; resources, N.N. and R.C.; software, B.N.T.F., D.H. and H.T.K.A.; supervision, N.N. and R.C.; writing—original draft, B.N.T.F.; writing—review and editing, B.N.T.F., N.N., R.C., D.H. and H.T.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Health and National Research Council (Grant No. TO 14-05), Sri Lanka.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethic Review Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, the University of Peradeniya (2016/EC/28).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All the data needed to support the results of the paper are present in the paper or Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Lishantha Gunarathna and the staff of the Renal Center at Girandurukotte, Sri Lanka, and the staff of the Renal Unit, National Hospital Kandy, Sri Lanka. We also thank the President’s Task Force for their contribution in facilitating this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Webster, J.D.; Goldoff, B.A.; Flesch, R.N.; Nadeau, P.A.; Silbert, Z.W. Hydroxyl, Cl, and F partitioning between high-silica rhyolitic melts-apatite-fluid(s) at 50–200 MPa and 700–1000 °C. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.-N. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Yang, C.-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Jayasumana, C.; Schreurs, G.; Roels, F.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; Samaee, V.; Rodrigo, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; et al. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities is a toxin-induced proximal tubular nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pett, J.; Mohamed, F.; Knight, J.; Linhart, C.; Osborne, N.J.; Taylor, R. Two decades of chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu) research: Existing evidence and persistent gaps from epidemiological studies in Sri Lanka. Nephrology 2022, 27, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, S.; Abeysekara, T.; Chandrajith, R.; Ratnatunga, N.; Gunaratne, E.D.L.; Yan, J.; Hitomi, T.; Muso, E.; Komiya, T.; et al. An Integrative Study of the Genetic, Social and Environmental Determinants of Chronic Kidney Disease Characterized by tubulointerstitial damages in the North Central Region of Srilanka. J. Occup. Health 2014, 56, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, S.; Diyabalanage, S.; Yatigammana, S.K.; Ileperuma, O.A.; Chandrajith, R. Major and trace elements in rice paddy soils in Sri Lanka with special emphasis on regions with endemic chronic kidney disease of undetermined origin. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, D.; Diyabalanage, S.; Dunuweera, S.; Rajapakse, S.; Rajapakse, R.; Chandrajith, R. Significance of Mg-hardness and fluoride in drinking water on chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Monaragala, Sri Lanka. Environ. Res. 2021, 203, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramarathna, S.; Balasooriya, S.; Diyabalanage, S.; Chandrajith, R. Tracing environmental aetiological factors of chronic kidney diseases in the dry zone of Sri Lanka—A hydrogeochemical and isotope approach. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Jeuland, M.; Manthrithilake, H.; McCornick, P. Nephrotoxic contaminants in drinking water and urine, and Chronic Kidney Disease in rural Sri Lanka. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 518–519, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, L.; Harada, K.H.; Chandrajith, R.; Hitomi, T.; Abeysekera, T.; Muso, E.; Watanabe, T.; Koizumi, A. Systematic evaluation of exposure to trace elements and minerals in patients with chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 54, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.M.; Wijewardena, H.V.; Bandara, A.; Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Rajapaksha, H. Pollution of River Mahaweli and farmlands under irrigation by Cd from agricultural inputs leading to a chronic renal failure epidemic among farmers in NCP, Sri Lanka. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Dissanayake, C. Phosphate Mineral Fertilizers, trace metals and human health. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2009, 37, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.; Hernandez, G.T. Environmental exposures, socioeconomics, disparities, and the kidneys. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015, 22, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathne, S.; Chandrajith, R.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gamage, C.D.; Ratnatunga, N.; Wijetunge, S.; Badurdeen, Z.; Guruge, S.; Elladeniya, N.; Madushan, K.P.S.; et al. Could Consumption of Trace Element–Contaminated Rice Be a Risk Factor for Acute Interstitial Nephritis with Uncertain Etiology in the Dry Zone of Sri Lanka? Biol. Trace Element Res. 2022, 200, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalal, T.B.A.; Bandara, T.W.M.A.J.; Mahawithanage, S.T.C.; Wansapala, M.A.J.; Galappaththi, S.P.L. A quantitative analysis of chronic exposure of selected heavy metals in a model diet in a CKD hotspot in Sri Lanka. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, K.E.; Redmon, J.H.; Elledge, M.F.; Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Smith, K.; Munoz, B.; Waduge, V.A.; Periris-John, R.J.; Sathiakumar, N.; Harrington, J.M.; et al. Quest to identify geochemical risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in an endemic region of Sri Lanka—A multimedia laboratory analysis of biological, food, and environmental samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatilake, N.; Mendis, S.; Maheepala, P.; Mehta, F.R. Chronic Kidney Disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.; Kawakami, T.; Nagasawa, S.; Serikawa, Y.; Motoyama, A.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; Weragoda, S.K.; Yatigammana, S.K.; Amarasooriya, A.A.G.D. Arsenic, cadmium, lead, and chromium in well water, rice, and human urine in Sri Lanka in relation to chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, S.A.; Gunawardana, J.W.; Chandrajith, R.; Thoradeniya, T.; Jayasinghe, S. Renal bioaccumulation of trace elements in urban and rural Sri Lankan populations: A preliminary study based on post mortem tissue analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, S.; Navarathna, T.; Abeysundara, H.T.K.; Rajapakse, S.; Chandrajith, R. Trace elements in native and improved paddy rice from different climatic regions of Sri Lanka: Implications for public health. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickrama, E.S.; Gunawardena, N.; Jayasinghe, S.; Herath, C. CKD of Unknown Etiology (CKDu) in SriLanka: A Multiple Clinical Case Definition for Surveillance and Epidemiological Studies. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, C.H.; Fournier, M.; Brousseau, P.; Sauvé, S. Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry as a routine method for the quantification of beryllium in blood and serum. BMC Chem. 2008, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labcorp. Available online: https://www.labcorp.com/tests/808540/beryllium-urine (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Długaszek, M.; Szopa, M.; Rzeszotarski, J.; Karbowiak, P. Magnesium, calcium and trace elements distribution in serum, erythrocytes, and hair of patients with chronic renal failure. Magnes. Res. 2008, 21, 109–117. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18705539/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Schonwald, S. Medical Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Dart, R.C., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1470–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Rockhold, W.T.; Talvitie, N.A. Vanadium Concentration of Urine: Rapid Colorimetric Method for Its Estimation. Clin. Chem. 1956, 2, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, S.; Green, S.R.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Kadavanu, T.M.; Ramachandrappa, A.; Tiwari, S.R.; Rajkumar, A.L.; Go-vindasamy, E. Trace elements in chronic haemodialysis patients and healthy individuals-a comparative study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lybra+e. Available online: https://www.lybrate.com/lab-test/chromium (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.R.; Shalahuddin Qusar, M.M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M.H.; Mustafizur Rahman, G.K.M.; Islam, M.S.; Hasnat, A. Alterations of serum macro-minerals and trace elements are associated with major depressive disorder: A case-control study. BMC Psychiatry 2008, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.; Sabbioni, E. Trace element reference values in tissues from inhabitants of the European Union. X. A study of 13 elements in blood and urine of a United Kingdom population. Sci. Total. Environ. 1998, 216, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, V.; Woittiez, J. Trace elements in human clinical specimens: Evaluation of literature data to identify reference values. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodushkin, I.; Ödman, F. Assessment of the contamination from devices used for sampling and storage of whole blood and serum for element analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2001, 15, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A. Biochemistry of Tellurium. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 5, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.S.B.; Unrine, J.M.; Vangala, C.; Sanderson, W.T.; Mandayam, S.; Murray, K.O. Evidence of nickel and other trace elements and their relationship to clinical findings in acute Mesoamerican Nephropathy: A case-control analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filler, G.; Felder, S. Trace elements in dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Ravn-Haren, G. Acute human toxicity and mortality after selenium ingestion: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 2020, 58, 126435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, W. Lithium. In Trace Elements in Humun and Animal Nutrition, 5th ed.; Mertz, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Caroli, S.; Alimonti, A.; Coni, E.; Petrucci, F.; Senofonte, O.; Violante, N. The assessment of reference values for elements in human biological tissues and fluids: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1994, 24, 363–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, M.A.C.S.; Paranagama, P.A.; Amarasinghe, M.D.; Wijewardane, K.M.R.C.; Dahanayake, K.S.; Fonseka, S.I.; Rajakaruna, K.D.I.M.P.; Mahamithawa, A.M.P.; Samarasinghe, U.D.; Senanayake, V.K. Possible link of chronic arsenic toxicity to chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Wickremasinghe, R. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Aetiology in Sri Lanka: Is Cadmium a Likely Cause? BMC Nephrol. 2011, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Gunathilake, S.; Senanayake, P. Glyphosate, hard water and nephrotoxic metals: Are they the culprits behind the epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2125–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Seneviratna, S.; Wickramaarachchi, K.; Attanayake, T.; Aturaliya, T.N.C.; Dissanayake, C.B. Natural radio-nuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: Study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Dissanayake, C.B.; Tobschall, H.J. The abundances of rarer trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.M.R.S.; Senevirathna, D.M.A.N.; Dasanayake, D.M.R.S.B.; Herath, V.; Abeysekara, T.; Rajapaksha, K.H. Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlani, M.; Kumar, A.; Ahirwar, R.; Meenu, M.N.; Goel, S.K.; Kumari, R.; Anirudhan, A.; Vallamshetla, S.; Reddy, G.S.T. Heavy metal association with chronic kidney disease of unknown cause in central India-results from a case-control study. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current Status of Cadmium as an Environmental Health Problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, G.F. Historical Perspectives on Cadmium Toxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, H.A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, G.; Roach, E.; Yasin, A.; Sharma, A.P.; Blake, P.G.; Yang, L. High prevalence of elevated lead levels in pediatric dialysis patients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.; Bernard, A.; Buchet, J.P.; Claeys, F.; Dekempeneer, L.; Ducoffre, G.; Fagard, R.; Lauwerys, R.; Lijnen, P.; Roels, H. Effects of cadmium exposure on the cardiovascular system and on calcium metabolism: Results of a cross-sectional population study. IARC Sci. Pub. 1992, 118, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Bourget, P.; Lesne-Hulin, A.; Quinquis-Desmaris, V. Study of the bioequivalence of two controlled-release formulations of morphine. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 33, 588–594. [Google Scholar]
- Brody, T. Nutritional Biochemistry; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, M.C.; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 797S–811S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Murakami, M.; Fukada, T.; Nishida, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Suzuki, T. Roles of zinc and zinc signaling in immunity: Zinc as an intracellular signaling molecule. Adv. Immunol. 2008, 97, 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, B.K.; Alfulaij, N.; Seale, L.A. The Impact of Selenium Deficiency on Cardiovascular Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Edirithilake, T.; Nanayakkara, N.; Lin, X.X.; Biggs, P.J.; Chandrajith, R.; Lokugalappatti, S.; Wickramasinghe, S. Urinary MicroRNA Analysis Indicates an Epigenetic Regulation of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka. MicroRNA 2023, 12, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).