Abstract
Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of dialysis therapy worldwide. The number of diabetes patients on dialysis in clinical settings has been increasing in Japan. In 2013, the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy (JSDT) published the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012”. While glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is used mainly as a glycemic control index for dialysis patients overseas, Japan is the first country in the world to use glycated albumin (GA) for assessment. According to a survey conducted by the JSDT in 2018, the number of facilities measuring only HbA1c has decreased compared with 2013, while the number of facilities measuring GA or both has significantly increased. Ten years have passed since the publication of the first edition of the guidelines, and several clinical studies regarding the GA value and mortality of dialysis patients have been reported. In addition, novel antidiabetic agents have appeared, and continuous glucose monitoring of dialysis patients has been adopted. On the other hand, Japanese dialysis patients are rapidly aging, and the proportion of patients with malnutrition is increasing. Therefore, there is great variation among diabetes patients on dialysis with respect to their backgrounds and characteristics. This review covers the indices and targets of glycemic control, the treatment of hyperglycemia, and diet recommendations for dialysis patients with diabetes.
1. Introduction
Diabetes is, globally, the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) for patients on dialysis. In Japan, diabetic nephropathy has been the most common cause of ESKD since 1998, accounting for 42.3% of the incidence of dialysis patients in 2018 [1]. Furthermore, the rate of diabetic nephropathy was 39.0% in all dialysis patients in 2018 [1]. Although many dialysis patients have diabetes, there are no guidelines for the management of diabetes patients on dialysis. Therefore, the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy (JSDT) published the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” [2]. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is commonly used worldwide as an index of glycemic control for dialysis patients. However, it has been demonstrated that it does not provide accurate glycemic control in patients on hemodialysis (HD) [3,4,5]. In addition to the shortened red-blood-cell lifespan (approximately 60 days), patients experience blood loss and hemorrhage due to HD therapy, and the administration of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) for the treatment of renal anemia increases the proportion of immature erythrocytes. Therefore, in HD patients, the HbA1c levels tend to be lower. On the other hand, it was reported that glycated albumin (GA) is a useful control index instead of HbA1c because it is not affected by the lifespan of red blood cells or ESA treatment [3,4,5]. Therefore, the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” of JSDT first recommended GA as an indicator of glycemic control for HD patients with diabetes. The guidelines describe the management required for diabetes HD patients: (1) indices of glycemic control and its frequency of measurement; (2) glucose concentrations in dialysate; (3) approach of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia during HD; (4) treatment by oral antidiabetic agents and insulin; (5) diet therapy; and (6) management of complications such as diabetic retinopathy, orthostatic hypotension, arteriosclerosis, and bone diseases [2]. However, in the ten years that have passed since the publication of the first edition, the background of diabetes patients on dialysis has changed and novel treatments have emerged; hence, revision is required. This review covers the indices and targets of glycemic control, the treatment of hyperglycemia, and diet recommendations for dialysis patients with diabetes.
2. Which Glycemic Index, GA or HbA1c, Demonstrates Better Performance in Dialysis Patients?
In HD patients, GA is a better indicator of glycemic control than HbA1c, which is known to underestimate and not accurately reflect mean blood-glucose levels [3,4,5]. HbA1c in HD patients is influenced by various factors, such as shortened erythrocyte lifespan, ESA for the treatment of renal anemia, the administration of iron preparations, uremia, and blood transfusion, thus potentially resulting in inaccurate measurements. ESA administration or iron supplementation can rapidly reduce HbA1c levels without improving glycemic control. The stimulation of erythropoiesis increases the proportion of young erythrocytes compared to old erythrocytes and leads to a decrease in HbA1c levels. GA is more strongly correlated with plasma glucose levels than HbA1c and is unaffected by red-blood-cell lifespan or ESA administration, making it a more reliable indicator of glycemic control in HD patients [6].
3. Target GA Levels in Hemodialysis Patients from Observational Studies and Meta-analyses
An association between GA levels and outcomes in HD patients with diabetes has been reported in multiple observational studies conducted in Japan. It has been reported that the incidence of cardiovascular complications is higher in HD patients with diabetes with GA levels ≥23% [7], and poor glycemic control in patients with GA levels ≥29% at the time of dialysis initiation is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and shortened survival [8]. It was reported that the prognosis appeared better in a group of patients with GA <20% without a history of cardiovascular events upon the start of the observation compared with higher GA groups (20.0–24.5% and >24.5%) [9]. There are also some studies from the United States that report associations between GA level, the onset of cardiovascular events [10], prognosis [10,11], admission rate [11], and duration of hospitalization in dialysis patients with diabetes [12]. Based on these results, the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” recommends GA levels <20.0% as the tentative target values for glycemic control in HD patients with diabetes. However, in patients with cardiovascular disease or who have a tendency toward hypoglycemia, GA levels < 24.0% are recommended [2]. More recently, it was reported in Taiwan that higher GA levels might be predictors of mortality not only for patients with diabetes on HD but also those without diabetes [13].
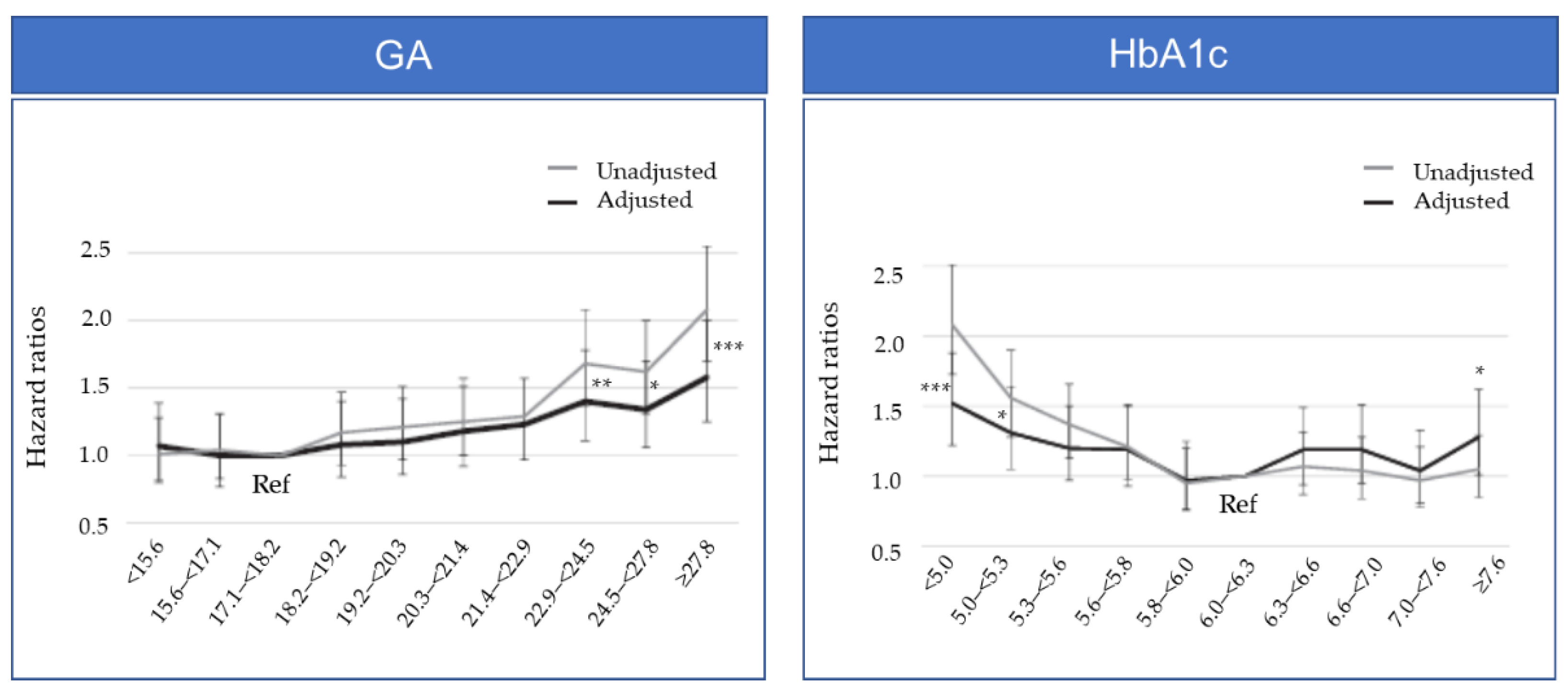
In 2018, the JSDT Renal Data Registry Committee (JRDR) reported an association between a glycemic control indicator and prognosis based on an investigation on 22,441 HD patients with diabetes [14]. The patients were stratified by deciles of the baseline GA level and HbA1c level and analyzed for the potential association with one-year mortality, a prognostic indicator for HD patients with diabetes. As a result, the groups with GA levels ≥22.9% had significantly higher adjusted hazard ratio (HR) values than the reference, with GA levels of 17.1 to <18.2% (Figure 1). Meanwhile, the groups with HbA1c of <5.3% and ≥7.6% had a significantly higher adjusted HR than the reference, with HbA1c levels of 6.0% to <6.3%, demonstrating a U-shaped trend for the HR (Figure 1) [14]. The JRDR also reported the association between three-year mortality and GA levels in 40,417 HD patients with diabetes [15]. In that report, three-year mortality showed a linear association with GA levels ≥ 18%, whereas this association was not observed between lower GA levels and three-year mortality. In malnourished patients treated with oral antidiabetic agents, increased mortality was associated with GA levels ≥ 24%. These results suggest a need to set the target GA value for glycemic control based on consideration of such factors as the use of antidiabetic agents, nutritional status, and patient background, such as cancer development status.
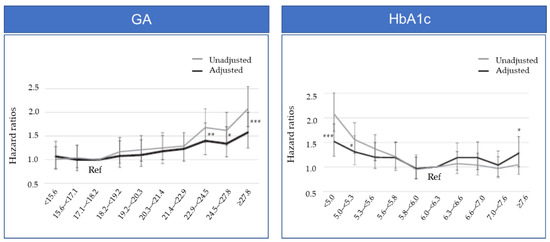
Figure 1.
Hazard ratios of all-cause mortality divided by deciles of GA levels and HbA1c levels in 22,441 hemodialysis patients. Adjusted variables include age, sex, vintage, modality, body mass index, smoking, type of diabetes, antihypertensive agents use, type of hypoglycemic agent use, hemoglobin, albumin, C-reactive protein, parathyroid hormone, calcium, phosphate, high-density lipoprotein, Kt/V, normalized protein catabolic rate, history of cardiovascular disease, and type of dialysis center. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. Ref. (Adjusted).
Furthermore, based on the multicenter prospective observational study of 841 chronic dialysis patients with diabetes for a mean study period of 3.1 years, GA levels could be a prognostic factor in predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD)-related mortality [16]. Overall, it was suggested that GA might be a more suitable parameter than HbA1c for accurately predicting the prognosis of dialysis patients with diabetes.
In 2018, the results of a meta-analysis were reported. The relationship between average blood glucose levels and HbA1c and GA levels was investigated [17]. The meta-analysis included 24 studies with 3928 patients, and it was concluded that GA was superior to HbA1c in assessing glycemic status in diabetes patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD), including CKD stages 4 and 5 and dialysis. Furthermore, the results of another meta-analysis, including 12 studies with 25,932 dialysis patients, demonstrated that GA can be an effective indicator for predicting the prognosis of dialysis patients with diabetes [18].
4. Current Glycemic Status in Diabetes Patients on Dialysis
Although JSDT presented the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” in Japan in 2013, the annual dialysis data report for 2013 by JRDR found that 53.5% of dialysis patients with diabetes had been assessed based on GA measurement, whereas 46.5% of the patients had been assessed solely on the basis of HbA1c at the end of 2013 [19]. The 2013 survey examined HbA1c and GA levels, while the 2018 survey also examined casual plasma glucose levels in addition to HbA1c and GA. The proportion of patients who were assessed according to GA was 75.9%, whereas the proportion for HbA1c only was 24.1%. Thus, the popularity of GA measurements has increased in Japan [20]. In addition, glycemic indices were investigated in two treatment groups, which were the hemodialysis, including HD and HDF patients, and the peritoneal dialysis (PD) groups.
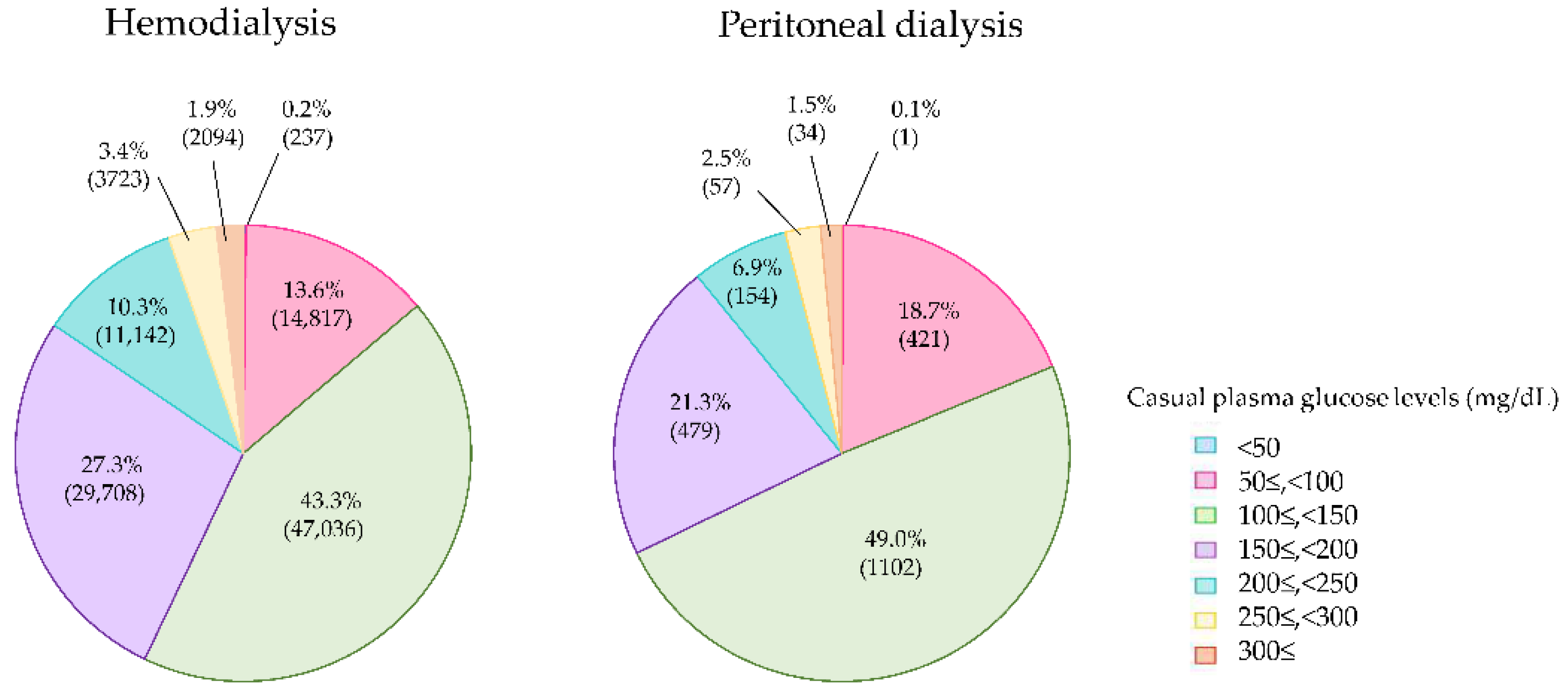
Casual plasma glucose levels were measured in 111,005 patients of 160,021 diabetes patients on dialysis. The casual plasma glucose levels in the HD and HDF groups were 151.5 ± 56.1 and 150.8 ± 55.4 mg/dL, respectively, while those in the PD group were 140.3 ± 53.4 mg/dL, lower than those in HD and HDF patients. The mean casual plasma glucose levels were equivalent between the HD and HDF patients. In total, 84.4% of the diabetes patients on HD and HDF achieved the target casual plasma glucose levels of below 200 mg/dL (Figure 2). On the other hand, 89.1% of the PD patients achieved casual plasma glucose levels of <200 mg/dL, and this rate was higher than that of the hemodialysis patients. Casual plasma glucose levels < 50 mg/dL, a finding suggestive of severe hypoglycemia, was observed in 237 hemodialysis patients (0.2%), but only 1 PD patient.
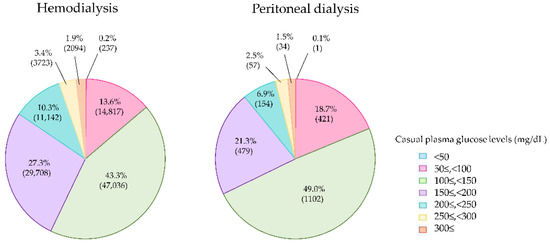
Figure 2.
Casual plasma glucose levels of diabetes patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in 2018.
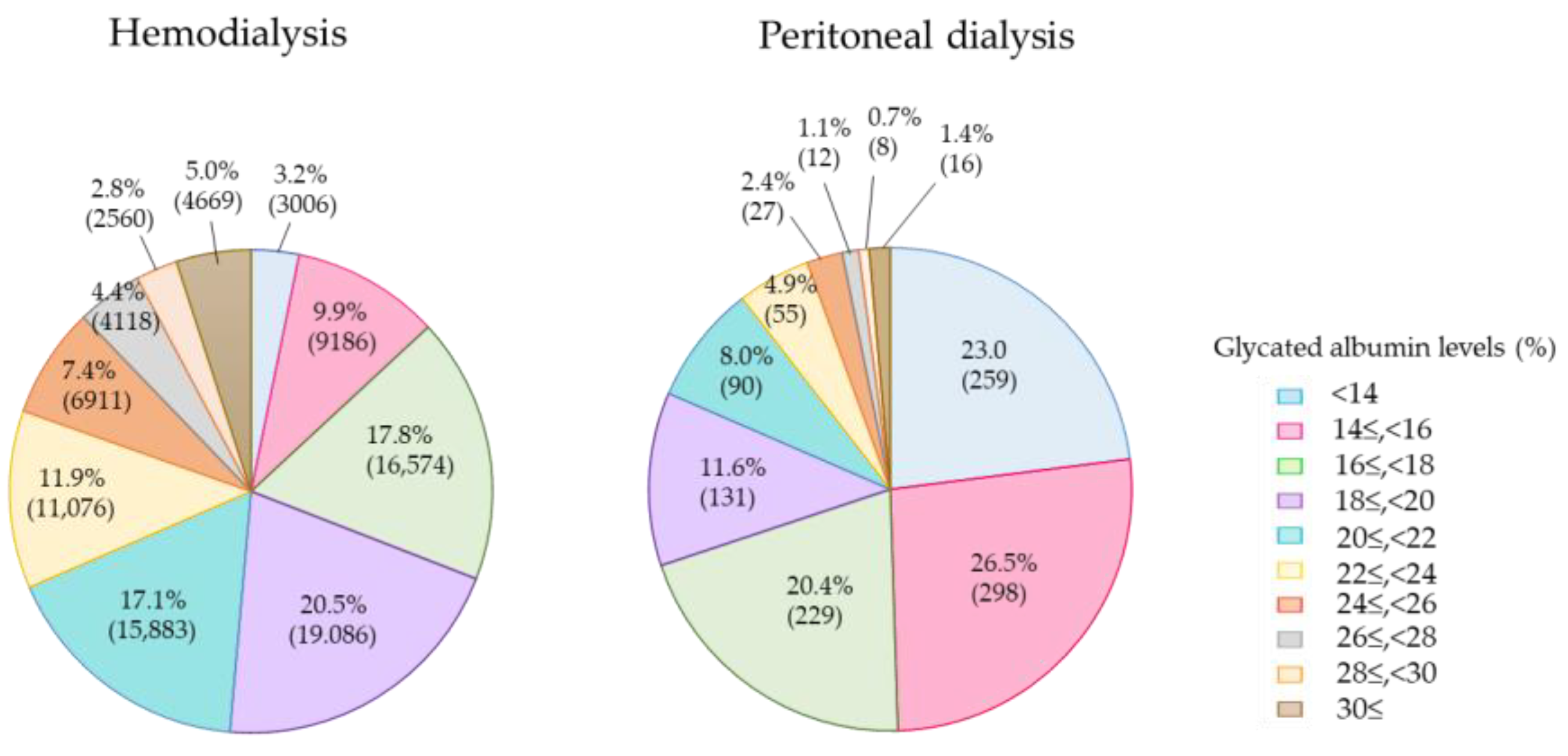
The GA levels were 16.9% ± 4.4% for the PD group and 20.9% ± 5.1% for the HD group. The levels were clearly lowered in the PD group irrespective of whether the plasma glucose levels were equivalent between the two groups (Figure 3). This finding suggests that the half-life of serum albumin is shortened in PD patients due to the loss of albumin into PD fluid. The target GA level of less than 20.0%, which is recommended in the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012”, was achieved in 51.4% in 2018, which is more than the 46.6% in the 2013 survey. In total, 80.4% of the patients achieved the target GA level of <24.0%, which is the target for patients with a history of cardiovascular diseases or who are prone to hypoglycemia.
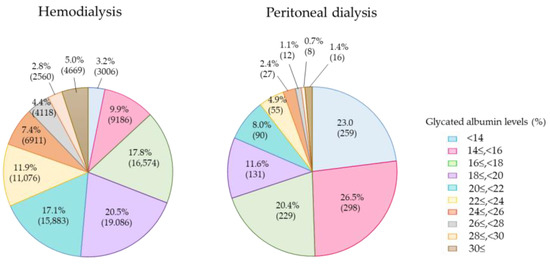
Figure 3.
Glycated albumin (GA) levels of diabetes patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in 2018.
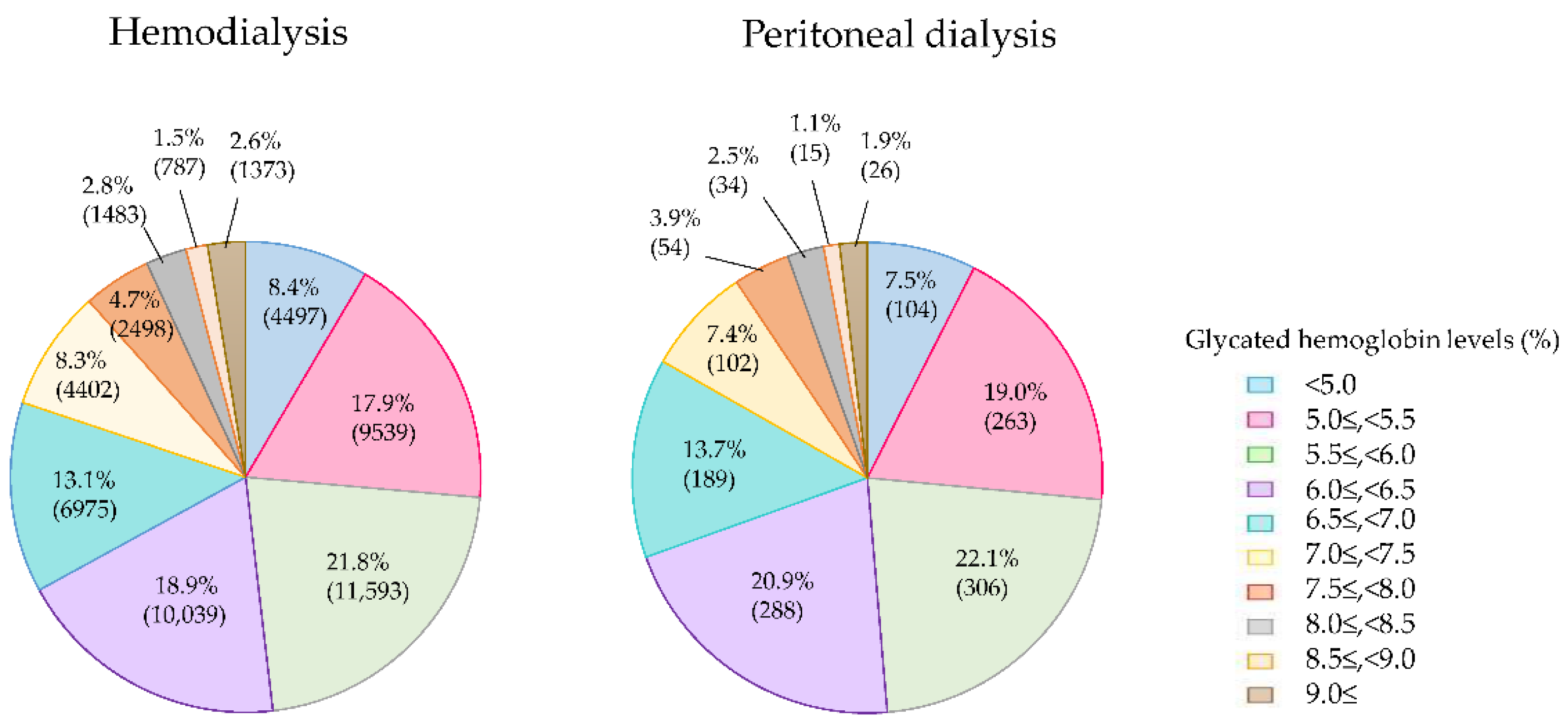
According to the 2018 survey, the average HbA1c values were almost equivalent between the three groups of PD, HD, and HDF, at 6.14% ± 1.11%, 6.17% ± 1.16%, and 6.23% ± 1.19%, respectively. These values are similar to the value of 6.19% ± 1.16% in the 2013 survey. As shown in Figure 4, when the patients were divided into groups according to HbA1c levels and the distribution ratios compared, there was no difference in the ratios between the two groups. This finding suggests that the HbA1c levels were apparently lowered in all of the dialysis patients because both the HD and the PD patients had renal anemia and were treated with ESAs.
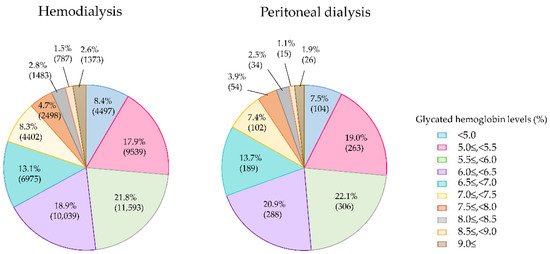
Figure 4.
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels of diabetes patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in 2018.
5. Association between GA Levels and Mortality in PD Patients
There are few reports examining the relationship between GA values and mortality in PD patients. It was reported that the GA levels are 4.5% lower in PD than in HD patients [21]. Nevertheless, there are reports that, compared with HbA1c, GA more accurately reflects glycemic control in PD patients and is associated with prognosis. In addition, JRDR reported the results of analysis of the relationship between HbA1c and GA as indicators of glycemic control and 2-year mortality in PD patients [22]. Although no association was found between HbA1c and mortality, the hazard ratio of death significantly increased when the GA value was 20.0% or higher. However, there are few studies that have examined the relationship between GA levels and mortality in PD patients. Therefore, further evidence is needed to substantiate this relationship.
6. Limitations of GA
GA levels are affected not only by plasma glucose levels but also by albumin metabolism. In patients with a prolonged albumin half-life, such as those with liver cirrhosis or untreated hypothyroidism, GA levels are increased [23,24]. Decreased GA levels may be found in patients with untreated hyperthyroidism or nephrotic syndrome [23,25]. Patients with proteinuria are known to have lower GA levels due to a shortened albumin half-life. In particular, proteinuria with nephrotic range, i.e., over 3.5 g/day, has been reported to decrease GA levels regardless of glycemic status [25]. Furthermore, GA can be falsely lowered in PD patients because the lifespan of albumin is shortened due to albumin loss into PD fluid [25,26].
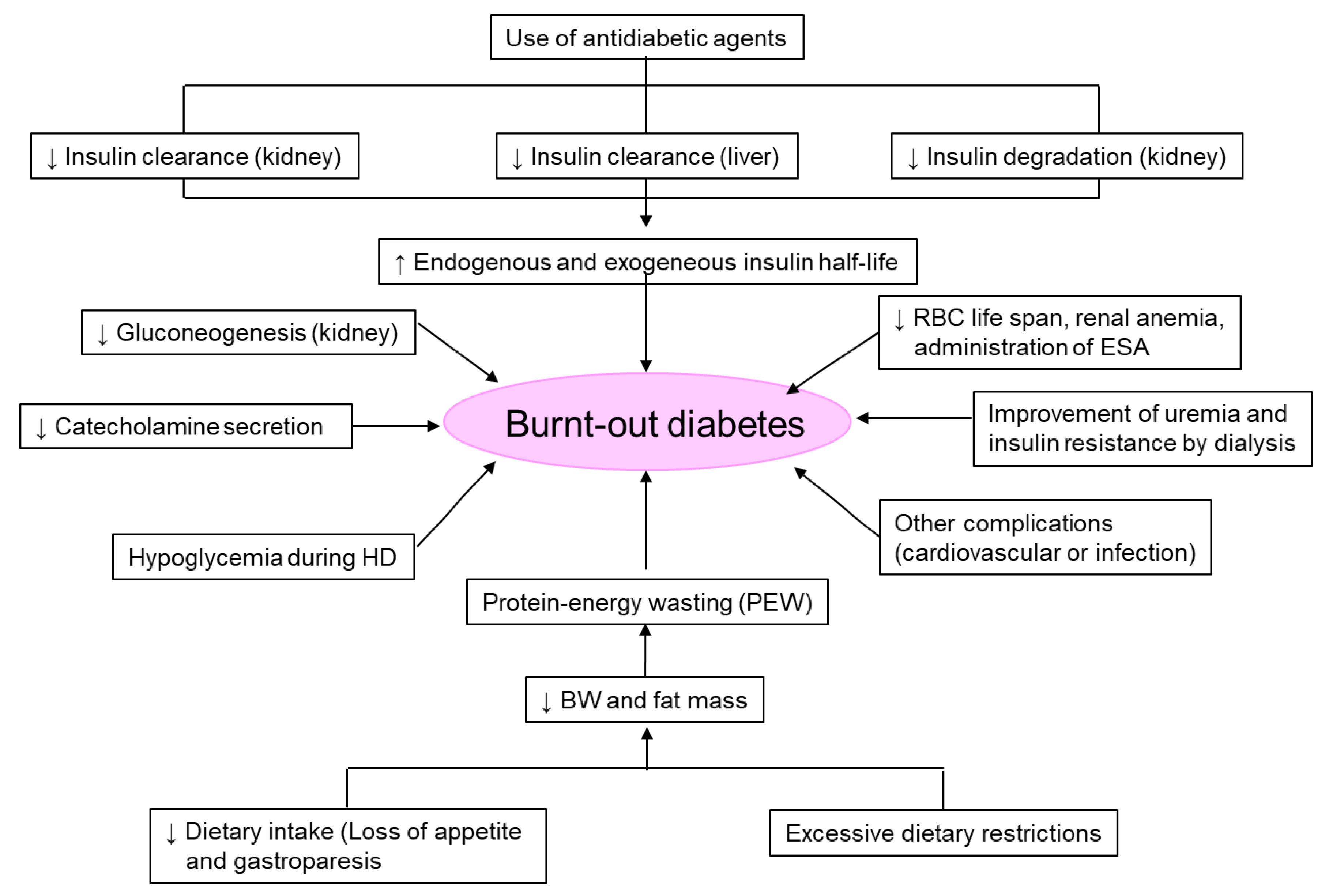
7. ‘Burnt-Out Diabetes’ Phenomenon in Patients on Dialysis
Diabetes patients undergoing dialysis due to diabetic nephropathy experience naturally improved glycemic control and normal-to-low HbA1c levels with the worsening of kidney function and decline in residual kidney function after starting renal replacement therapy, with or without antidiabetic agents. This phenomenon is called ‘burnt-out diabetes’ [27,28,29].
In a 2-year cohort study of 23,618 diabetes patients on HD in the United States, 33% of the patients had HbA1c < 6.0% [30]. When the HbA1c level of 5.0–5.9% was used as a reference, the survival rate was significantly lower both for the group with HbA1c of 7.0% or higher and with HbA1c < 5.0%. In a 6-year cohort study of 54,757 diabetes patients on dialysis in the United States, 40% of the patients had HbA1c of <6.0% [31]. When HbA1c levels of 7.0–7.9% were used as a reference, the hazard ratio (HR) for all-cause mortality increased with increasing HbA1c levels: 8.0–8.9% (HR 1.11), 9.0–9.9% (HR 1.36), and 10% or more (HR 1.59). Furthermore, the HR for all-cause mortality increased with decreasing HbA1c levels; 6.0–6.9% (1.05), 5.0–5.9% (HR 1.08), and <5.0% (HR 1.35). In the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS), the survival was significantly lower in the HbA1c of ≥9.0%, <5.0%, 5–5.9%, and 6–6.9% groups when the HbA1c 7–7.9% group was used as a reference [32]. However, when analyzed according to the presence or absence of malnutrition, which was defined as BMI < 19 kg/m2, serum albumin concentrations < 3.0 g/dL, or cachexia, the survival was significantly worse in patients with HbA1c < 5% and malnutrition. Therefore, it was suggested that the patients with lower HbA1c levels due to malnutrition might have poorer prognoses among patients with ‘burnt-out diabetes’. As shown in Figure 5, there are several factors that induce ‘burnt-out diabetes’.
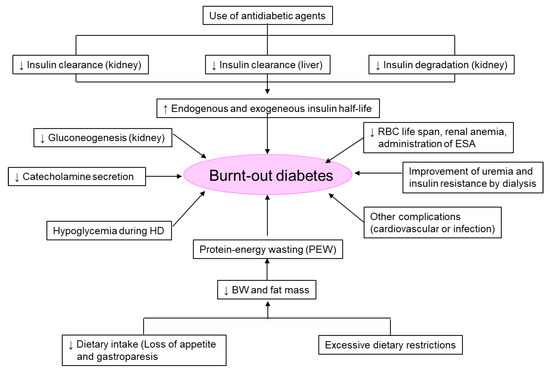
Figure 5.
Leading factors of ‘burnt-out diabetes’. BW, body weight; ESA, erythropoiesis stimulating agent; HD, hemodialysis; RBC, red blood cell.
In dialysis patients who have renal anemia and are treated with ESAs, HbA1c levels can be falsely lowered and, therefore, hyperglycemia overlooked. The two abovementioned cohort studies conducted in the United States measured only the HbA1c levels; GA and the use or non-use of antidiabetic agents were not investigated. Therefore, we conducted an investigation in order to confirm the ‘true burnt-out diabetes’ based on HbA1c, GA levels, and the use or non-use of antidiabetic agents according to the JRDR in 2013 [33]. When ‘burnt-out diabetes’ was defined as those who had HbA1c < 6.0% and were not treated with antidiabetic agents, it was found in 20.7% of HD patients. However, if we defined ‘burnt-out diabetes’ as HbA1c < 6.0%, GA < 16.0% (which was the normal value), and without antidiabetic medications, it was diagnosed in 5.4% of the patients. Therefore, the prognosis for patients with ‘true burnt-out diabetes’ must be confirmed in the future.
8. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients on Dialysis
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) measures interstitial fluid glucose-levels, indirectly estimates plasma glucose concentrations, and provides estimates of average sensor glucose values, glucose excursions, and time in range [34,35,36,37,38]. Previous studies have suggested that high mean glucose levels and glycemic abnormalities such as glucose fluctuation and hypoglycemia accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes [39,40]. GA or HbA1c indicate only average plasma glucose levels and not fluctuations in plasma glucose levels or hypoglycemia, both of which may play an important role in the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, CGM provides a subtle picture of daily blood-glucose fluctuations over 24 h. Therefore, evaluating various aspects of glycemic status may help identify patients with a high probability of developing CVD, and may lead to improving patients’ outcomes. CGM is now frequently used to monitor glycemic control and contributes to improvements in glycemic control in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who are not on dialysis [41,42,43].
Not all CGM devices are approved for use in dialysis patients, because their efficacy in dialysis patients has not yet been investigated (Table 1) [44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. However, many studies have reported that CGM is adaptable for glucose monitoring in patients on dialysis [51,52,53]. Nevertheless, whether the glycemic control of patients on dialysis can be improved by the use of CGM remains to be determined. Two reports suggested that CGM is useful for dialysis patients. The use of CGM to adjust the insulin dose significantly decreased sensor glucose levels at the 3-month follow-up [54]. Furthermore, a comparative study of blood-glucose monitoring by finger prick and CGM was performed on dialysis patients. Antidiabetic treatment was adjusted by the results of the blood-glucose monitoring by finger prick and CGM. The adjustment of diabetes medications together with use of CGM was associated with improvements in glycemic control but not in blood-glucose monitoring by finger prick [55]. It has been reported that plasma glucose concentrations in dialysis patients tend to be underestimated when inferred from HbA1c levels rather than CGM, GA, or fructosamine [56,57,58]. Furthermore, the results of the meta-analysis revealed that there was a significant correlation between CGM and the self-monitoring of blood-glucose levels [59]. Furthermore, CGM had similar correlations with HbA1c and GA values [59]. Although the question of whether CGM variables can predict late-onset diabetic complications remains to be established, CGM could play a useful role in modifying glycemic control in dialysis populations. The efficiency of CGM, which can optimize glucose levels by detecting and preventing hypoglycemia, is also worth investigating for patients on dialysis.

Table 1.
Overview of CGM models.
An international consensus report in 2019 provided the targets of ‘time in range’ for the general diabetes populations, such as those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and for high-risk populations, including the elderly [34]. Dialysis patients are included in this high-risk population. The guidelines recommend that dialysis patients should be within the target range (70–180 mg/dL) at least 50% of the time and below the range (<70 mg/dL) less than 1% of the time. However, this has not yet been fully evaluated in dialysis patients. The CGM goals for the high-risk group are focused on reducing the time spent below the target range even though they spend less time within the target range. Therefore, the average plasma glucose level is allowed to rise, and this guideline emphasizes the avoidance of hypoglycemia. However, it is unclear whether CGM can provide adequate glycemic control to prevent late-onset diabetic complications in dialysis patients. KDIGO highlights the unreliability of HbA1c in the dialysis population and recommends the use of CGM, especially for those treated with antidiabetic agents who are at high risk of hypoglycemia [60].
CGM may be an effective tool for detecting hypoglycemia, lowering overall blood glucose levels, and reducing daily fluctuation even in patients on dialysis. However, the effects of long-term CGM use in dialysis patients have not been fully evaluated, and further evaluations are required.
9. Peculiarities of Glycemic Control in Dialysis Patients
The disruption of blood glucose homeostasis occurs due to decreased renal function in dialysis patients. Dialysis patients have increased insulin resistance due to uremia, renal anemia, metabolic acidosis, and secondary hyperparathyroidism, and plasma glucose levels tend to increase. On the other hand, the kidney produces a large amount of gluconeogenesis secondary to the liver. Additionally, it also plays a role as an insulin clearance organ as well as the liver. Therefore, hypoglycemia is likely to occur due to reduced gluconeogenesis and insulin clearance in patients with impaired kidney function. Therefore, while dialysis patients have impaired glucose tolerance, they are simultaneously susceptible to hypoglycemia [61].
In addition, HD itself has a significant effect on plasma glucose levels. HD therapy often starts when plasma glucose levels rise after a meal. In Japan, many facilities use dialysate with a glucose concentration of 100 mg/dL, and plasma glucose is removed by diffusion via a dialyzer after the start of HD. In particular, a rapid drop in plasma glucose levels occurs in patients with higher plasma glucose levels before the start of HD. Therefore, when plasma glucose levels exceed 100 mg/dL during a HD session, plasma glucose is diffused from the plasma to the dialysate following the concentration gradient. Contrary to theory, the countercurrent transit of plasma through the dialyzer reduces glucose levels to less than 100 mg/dL at the post-dialyzer site in many patients [62]. This mechanism assumes that the plasma glucose is diffused into erythrocytes. Plasma glucose may be consumed within erythrocytes as a result of accelerated anaerobic metabolism, because the erythrocyte cytosolic pH changes during HD [63]. This phenomenon is thus called ‘hemodialysis-induced hypoglycemia’.
On the other hand, insulin is adsorbed and removed by the dialyzer; therefore, the concentration of plasma insulin is decreased after HD [63,64,65,66]. A rapid drop in plasma glucose levels due to HD leads to stimulated secretion of counterregulatory hormones, such as glucagon, growth hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone. These factors lead to increased plasma glucose levels after HD. This phenomenon is called ‘hemodialysis-associated hyperglycemia’ [61,67,68,69]. It is difficult to estimate the changes in plasma glucose levels in HD patients, as the effect of factors vary depending on the individual case.
10. Medications for Glycemic Control in Diabetes Patients on Dialysis
Antidiabetic agents exert their pharmacological action and then disappear as they are metabolized and excreted. However, the metabolism and excretion of antidiabetic agents is impaired by deteriorated kidney function. In particular, agents whose active metabolites are excreted by the kidney have a significant effect, requiring dose reduction, careful administration, or are contraindicated. The “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” states that sulfonylureas (SU), biguanides, and thiazolidinediones are contraindicated in patients on dialysis [2]. The oral antidiabetic agents that can be administered to dialysis patients are α-glucosidase inhibitors (α-GI), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, mitiglinide, and repaglinide (rapid-acting insulin secretagogues) [2,70]. The dose recommendations for antidiabetic agents other than insulin are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Dose recommendation in diabetes patients on dialysis.
10.1. SUs
It is not possible to remove all SUs by HD because of their high protein-binding rate. Although the key metabolic pathway is the liver, SU readily induces hypoglycemia, because active metabolites have hypoglycemic effects and accumulate in dialysis patients. Therefore, they are contraindicated in patients on dialysis in Japan. However, gliclazide is metabolized in the liver, and more than 99% of its metabolites are excreted via the kidneys and feces, approximately 70% and 20%, respectively. Furthermore, their metabolites have very low activity. Therefore, the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) guidelines state that gliclazide can be used even in patients on dialysis [71]. In addition, glipizide and gliquidone, which are not marketed in Japan, can be administered at regular doses to patients on dialysis, according to the European Best Practice Guidelines (ERBP) [72].
10.2. Biguanide
Biguanides are not metabolized and are primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys, and they accumulate in patients with renal impairment. It is well known that the administration of biguanide to patients with renal dysfunction is likely to induce lactic acidosis. Therefore, biguanides are contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment as well as dialysis patients [70,73].
10.3. Fast-Acting Insulin Secretagogues
Fast-acting insulin secretagogues stimulate insulin secretion via a mechanism similar to that for SUs. However, those effects have a faster onset of action than SUs, resulting in a rapid increase in plasma insulin levels and a shorter duration of hypoglycemic effects. The risk of hypoglycemia with fast-acting insulin secretagogues is less than that with SUs. Although there are three types of fast-acting insulin secretagogues, nateglinide, mitiglinide, and repaglinide, only nateglinide cannot be used for patients on dialysis. Because its metabolites have the effect of lowering plasma glucose levels and are excreted by the kidneys, the use of nateglinide in dialysis patients increases the risk of hypoglycemia [70]. Repaglinide is characterized by an excretion route via bile, and its metabolites have no effect on lowering plasma glucose levels. Therefore, repaglinide can be safely used even in patients on dialysis, but it is recommended that it be initiated at a low dose.
10.4. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors (α-GIs)
The use of α-GIs is rarely associated with hypoglycemia, and these agents are carefully administered to dialysis patients without dose adjustment in Japan [2,73]. However, the plasma concentrations of acarbose and miglitol may rise in patients with kidney dysfunction, and the accumulation of these agents may lead to liver failure. Therefore, the KDOQI guidelines recommend the avoidance of acarbose and miglitol in dialysis patients [71]. Moreover, caution is required with αGI administration because gastrointestinal symptoms such as flatulence, abdominal bloating, constipation, and diarrhea may occur.
10.5. Thiazolidinedione
In Japan, thiazolidinedione is contraindicated in diabetes patients with a history of cardiac failure and severe renal impairment [2,73]. Thiazolidinedione has an adverse effect on fluid retention and may induce edema, anemia, and cardiac failure. Therefore, it is also contraindicated in patients on dialysis in Japan. By contrast, thiazolidinediones are completely metabolized by the liver, and no dose adjustments are needed for patients on dialysis in other countries [71,72].
10.6. DPP-4 Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors have a lower risk of hypoglycemia when administered alone, and because they are oral agents, the prescription rate has risen rapidly and had a great impact on diabetic treatment in recent years. Many investigations have reported on the efficacy and safety of DPP-4 inhibitors in patients on dialysis [73,74,75]. All currently marketed DPP-4 inhibitors are available for dialysis patients. However, dose adjustments must be made for the use of sitagliptin, saxagliptin, alogliptin, and anagliptin according to kidney function. On the other hand, linagliptin and teneligliptin can be administered without dose adjustment, even in patients on dialysis. Furthermore, the once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitors, omarigliptin and trelagliptin, are also available with dose adjustment for patients on dialysis [76,77]. However, further studies are needed to clarify the efficacy and safety of these agents, since few reports have investigated the efficacy and safety of once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitors for dialysis patients.
10.7. SGLT2 Inhibitors
Several large-scale clinical trials have demonstrated not only the hypoglycemic effect of SGLT2 inhibitors but also their effect in suppressing the progression of CKD and heart failure [78,79,80,81,82,83]. Therefore, it is now possible to administer them to CKD and heart-failure patients. However, they cannot be administered to dialysis patients because they cannot exert their hypoglycemic effect.
10.8. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are the same class as incretin-related drugs such as DPP-4 inhibitors but stronger hypoglycemic effects in addition to extra-pancreatic effects. The once-weekly agents, duraglutide and semaglutide, can be administered at their regular dose to dialysis patients [84,85]. On the other hand, liraglutide and lixisenatide can be used with careful administration [86,87,88]. Exenatide is contraindicated in patients on dialysis. The injection of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists at a dialysis facility by medical staff is one of the therapeutic options.
10.9. Insulin Therapy
Although intensive insulin therapy helps achieve target glycemic control, it increases the risk of severe hypoglycemia in diabetes patients with normal kidney function. The dose of insulin is reduced as the kidney function declines [59,87,88,89]. The dose of insulin can be reduced by 25% relative to normal kidney function when GFR decreases to <50 mL/min/1.73 m2. Furthermore, when GFR falls to <10 mL/min/1.73 m2, the dose is reduced by 50% relative to normal kidney function [61,89,90,91]. The initiation of dialysis may improve peripheral insulin resistance, further reducing insulin requirements. Basal-supported oral therapy, which involves long-acting insulin with oral antidiabetic agents, may also be possible. Long-acting insulin can also be administered by medical staff on the day of HD for patients who have difficulty injecting themselves with insulin [92].
The advantage of insulin therapy is that it has no adverse effects, other than hypoglycemia, compared with oral antidiabetic agents, similar to those with normal kidney function. Furthermore, the incidence of prolonged hypoglycemia is also low. On the other hand, the disadvantage is that it is limited to patients who can self-manage and who can obtain the cooperation of family members to watch over and administer the injections on their behalf.
11. Dietary Recommendations
The nutritional management for diabetes patients on dialysis considers energy, protein, potassium, phosphate, salt, and vitamins [93,94], and there are few dietary guidelines specific to diabetes dialysis patients. Similar to the general diabetes population, the energy-intake requirements for dialysis patients vary by gender, age, and physical activity [95,96]. We must consider the ideal body mass index (BMI) of each patient. Considering the better outcomes observed for HD patients with a higher BMI, a BMI of at least >23.0 kg/m2 should be maintained [93,94,97]. It was reported that the maintenance of BMI above the upper 50th percentile might be associated with a higher survival rate for patients on maintenance HD [98]. However, Japanese dialysis patients are aging, and the proportion of patients with protein energy wasting (PEW) and frailty is increasing. Although the mechanisms of PEW are complex and not fully understood, several studies reported that PEW is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in dialysis patients, and the prevalence of PEW was higher in diabetes patients than in non-diabetes patients on dialysis. Non-diabetes patients on dialysis [99,100,101]. The possible risk factors for PEW include increased nutrient loss, nutritional deficiencies, increased catabolism, and metabolic acidosis, which are shared by HD patients with and without diabetes. In dialysis patients with diabetes, increased muscle protein breakdown, increased complications, increased prevalence of gastroparesis, increased inflammatory cytokines, and impaired taste are additional risk factors that may be associated with the increased prevalence of PEW [102,103,104,105,106].
Some guidelines recommend a protein intake of at least 1.1 g/kg of ideal body weight (IBW) for HD patients [93,94,95,96]. In Japan, the “Best Practice for Diabetic Patients on Hemodialysis 2012” recommends a protein intake per reference body weight in the range of 0.9–1.2 g/kg/day. This target does not differentiate between diabetes and non-diabetes patients. In addition, it is recommended not to exceed 60 g/day for men and 50 g/day for women [2]. Fat intake in the range of 20–25% of total energy intake is recommended, and recommended intakes for salt, water, potassium, and phosphorus were the same as those for non-diabetes HD patients and were not differentiated [2]. The KDOQI guidelines recommend that the composition of the total energy intake should comprise 50–60% from carbohydrates, less than 30% from fat, and at least 15% from protein [94]. Therefore, protein intake in dialysis patients should correspond to 1.1 g protein/kg IBW and at least 15% of the total energy intake. However, it was suggested that the average protein intake in Japanese dialysis patients is below 0.9 g/kg/day [107]. Therefore, the assessment tool for nutritional status should be incorporated into daily clinical practice.
Previous studies did not evaluate which nutrients and nutritional products can improve plasma glucose levels and prognosis in diabetes patients on dialysis. In addition, the question of whether nutritional interventions can increase or maintain muscle mass in dialysis patients with diabetes was not investigated. Therefore, further studies are required to elucidate these points.
12. Conclusions
Levels of GA might be a better indicator of glycemic control than levels of HbA1c in patients on HD. Although a U-shaped relationship is observed between the HbA1c levels and mortality, GA is linearly associated with mortality in dialysis patients and may predict mortality in this population. Therefore, JSDT recommends GA as an alternative indicator of glycemic control to HbA1c for diabetes patients on HD. Because there have been no randomized controlled trials on dialysis patients, however, further studies are needed to clarify the target GA levels. Moreover, additional studies are warranted to clarify the superiority of periodic CGM to standard care in order to improve glycemic control, and CGMs can help to reduce hypoglycemic episodes and other diabetic complications in the dialysis population. Once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitors and some GLP-1 receptor agonists have been added as new treatment options. Additional research is required to clarify the efficacy and safety of these agents for diabetes patients on dialysis.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nitta, K.; Goto, S.; Masakane, I.; Hanafusa, N.; Taniguchi, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakai, S.; Wada, A.; Hamano, T.; Hoshino, J.; et al. Annual dialysis data report for 2018, JSDT Renal Data Registry: Survey methods, facility data, incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2020, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, T.; Inaba, M.; Abe, M.; Kaizu, K.; Shima, K.; Babazono, T.; Tomo, T.; Hirakata, H.; Akizawa, T.; Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Best practice for diabetic patients on hemodialysis 2012. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2015, 19 (Suppl. S1), 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Okuno, S.; Kumeda, Y.; Yamada, S.; Imanishi, Y.; Tabata, T.; Okamura, M.; Okada, S.; Yamakawa, T.; Ishimura, E.; et al. Glycated albumin is a better glycemic indicator than glycated hemoglobin values in hemodialysis patients with diabetes: Effect of anemia and erythropoietin injection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Matsumoto, K. Glycated hemoglobin or glycated albumin for assessment of glycemic control in hemodialysis patients with diabetes? Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2008, 4, 482–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, T.P.; Shihabi, Z.K.; Bleyer, A.J.; Dolbare, E.L.; Byers, J.R.; Knovich, M.A.; Calles-Escandon, J.; Russell, G.B.; Freedman, B.I. Comparison of glycated albumin and hemoglobin A(1c) levels in diabetic subjects on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohzuma, T.; Tao, X.; Koga, M. Glycated albumin as biomarker: Evidence and its outcomes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, T.; Nakao, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Shino, T.; Nagaoka, Y.; Tomaru, R.; Wada, T. Association between markers of glycemic control, cardiovascular complications and survival in type 2 diabetic patients with end-stage renal disease. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, K.; Nakao, K.; Morimoto, H.; Nakao, A.; Takatori, Y.; Arimoto, K.; Taki, M.; Wada, J.; Makino, H. Glycated albumin levels predict long-term survival in diabetic patients undergoing haemodialysis. Nephrology 2008, 13, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Maekawa, K.; Okuno, S.; Imanishi, Y.; Hayashino, Y.; Emoto, M.; Shoji, T.; Ishimura, E.; Yamakawa, T.; Nishizawa, Y. Impact of atherosclerosis on the relationship of glycemic control and mortality in diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 2012, 78, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, T.; Sozio, S.M.; Plantinga, L.C.; Jaar, B.G.; Kim, E.T.; Parekh, R.S.; Steffes, M.W.; Powe, N.R.; Coresh, J.; Selvin, E. Serum fructosamine and glycated albumin and risk of mortality and clinical outcomes in hemodialysis patients. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.I.; Andries, L.; Shihabi, Z.K.; Rocco, M.V.; Byers, J.R.; Cardona, C.Y.; Pickard, M.A.; Henderson, D.L.; Sadler, M.V.; Courchene, L.M.; et al. Glycated albumin and risk of death and hospitalizations in diabetic dialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murea, M.; Moran, T.; Russell, G.B.; Shihabi, Z.K.; Byers, J.R.; Andries, L.; Bleyer, A.J.; Freedman, B.I. Glycated albumin, not hemoglobin A1c, predicts cardiovascular hospitalization and length of stay in diabetic patients on dialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.L.; Ma, W.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Shyu, J.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Wu, C.C.; Lu, K.C. Glycated Albumin Predicts Long-term Survival in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoshino, J.; Hamano, T.; Abe, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Wada, A.; Ubara, Y.; Takaichi, K.; Inaba, M.; Nakai, S.; Masakane, I.; et al. Glycated albumin versus hemoglobin A1c and mortality in diabetic hemodialysis patients: A cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, J.; Abe, M.; Hamano, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Wada, A.; Ubara, Y.; Takaichi, K.; Nakai, S.; Masakane, I.; Nitta, K. Glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c levels and cause-specific mortality by patients’ conditions among hemodialysis patients with diabetes: A 3-year nationwide cohort study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, K.; Akamatsu, M.; Fujimori, A.; Higashi, H.; Horie, Y.; Itaya, Y.; Ito, M.; Kanamaru, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kikuchi, K.; et al. Usefulness of glycated albumin as a predictor of mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients with diabetes: A multi-center, prospective cohort study. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Glycated Albumin Versus HbA1c in the Evaluation of Glycemic Control in Patients With Diabetes and CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 3, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, S.; Siriopol, D.; Afsar, B.; Comert, M.C.; Uzunkopru, G.; Sag, A.A.; Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; van Raalte, D.H.; Cherney, D.Z.; et al. Serum glycated albumin predicts all-cause mortality in dialysis patients with diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis and systematic review of a predictive biomarker. Acta. Diabetol. 2021, 58, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masakane, I.; Nakai, S.; Ogata, S.; Kimata, N.; Hanafusa, N.; Hamano, T.; Wakai, K.; Wada, A.; Nitta, K. An Overview of Regular Dialysis Treatment in Japan (As of 31 December 2013). Ther. Apher. Dial. 2015, 19, 540–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, K.; Abe, M.; Masakane, I.; Hanafusa, N.; Taniguchi, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakai, S.; Wada, A.; Hamano, T.; Hoshino, J.; et al. Annual dialysis data report 2018, JSDT Renal Data Registry: Dialysis fluid quality, hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration, peritoneal dialysis, and diabetes. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2020, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, M.; Kurajoh, M.; Mori, K.; Okuno, S.; Okada, S.; Emoto, M.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Inaba, M. Superiority of glycated albumin over glycated haemoglobin as indicator of glycaemic control and predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving peritoneal dialysis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 56, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Hamano, T.; Hoshino, J.; Wada, A.; Nakai, S.; Masakane, I. Glycemic control and survival in peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetes: A 2-year nationwide cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, M.; Murai, J.; Saito, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Kasayama, S. Effects of thyroid hormone on serum glycated albumin levels: Study on non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 84, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.; Kasayama, S.; Kanehara, H.; Bando, Y. CLD (chronic liver disease)-HbA1c as a suitable indicator for estimation of mean plasma glucose in patients with chronic liver diseases. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 81, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, T.; Nakao, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Nagaoka, Y.; Tomaru, R.; Iwasawa, H.; Wada, T. Influence of proteinuria on glycated albumin values in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.I.; Shenoy, R.N.; Planer, J.A.; Clay, K.D.; Shihabi, Z.K.; Burkart, J.M.; Cardona, C.Y.; Andries, L.; Peacock, T.P.; Sabio, H.; et al. Comparison of glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c concentrations in diabetic subjects on peritoneal and hemodialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2010, 30, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Derose, S.F.; Nicholas, S.; Benner, D.; Sharma, K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Burnt-out diabetes: Impact of chronic kidney disease progression on the natural course of diabetes mellitus. J. Ren. Nutr. 2009, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Park, J.C.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Glycemic control and burnt-out diabetes in ESRD. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lertdumrongluk, P.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Glycemic control in diabetic dialysis patients and the burnt-out diabetes phenomenon. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2012, 12, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D.; Regidor, D.L.; Jing, J.; Shinaberger, C.S.; Aronovitz, J.; McAllister, C.J.; Whellan, D.; Sharma, K. A1C and survival in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.M.; Leung, A.M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Lynch, K.E.; Brent, G.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Updates on the management of diabetes in dialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2014, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, S.P.; McCullough, K.P.; Thumma, J.R.; Nelson, R.G.; Morgenstern, H.; Gillespie, B.W.; Inaba, M.; Jacobson, S.H.; Vanholder, R.; Pisoni, R.L.; et al. Hemoglobin A(1c) levels and mortality in the diabetic hemodialysis population: Findings from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Hamano, T.; Hoshino, J.; Wada, A.; Inaba, M.; Nakai, S.; Masakane, I. Is there a “burnt-out diabetes” phenomenon in patients on hemodialysis? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 130, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freckmann, G.; Pleus, S.; Grady, M.; Setford, S.; Levy, B. Measures of Accuracy for Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices. J. Diabetes. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbalshy, M.; Haszard, J.; Smith, H.; Kuroko, S.; Galland, B.; Oliver, N.; Shah, V.; de Bock, M.I.; Wheeler, B.J. Effect of divergent continuous glucose monitoring technologies on glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabet. Med. 2022, 39, e14854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, I.; Rutherford, C.; Makarounas-Kirchmann, K.; Kirchmann, M. Meta-analysis of average change in laboratory-measured HbA1c among people with type 1 diabetes mellitus using the 14 day flash glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 164, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.; Aragona, M.; Rodia, C.; Baronti, W.; de Gennaro, G.; Bertolotto, A.; Del Prato, S. Freestyle Libre trend arrows for the management of adults with insulin-treated diabetes: A practical approach. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbaud, E.; Darier, R.; Montaudon, M.; Beauvieux, M.C.; Coffin-Boutreux, C.; Coste, P.; Douard, H.; Ouattara, A.; Catargi, B. Glycemic variability is a powerful independent predictive factor of midterm major adverse cardiac events in patients with diabetes with acute coronary syndrome. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Mi, S.H.; Tao, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.X.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, L. Impact of admission glycemic variability, glucose, and glycosylated hemoglobin on major adverse cardiac events after acute myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleppo, G.; Ruedy, K.J.; Riddlesworth, T.D.; Kruger, D.F.; Peters, A.L.; Hirsch, I.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Toschi, E.; Ahmann, A.J.; Shah, V.N.; et al. REPLACE-BG: A Randomized Trial Comparing Continuous Glucose Monitoring With and Without Routine Blood Glucose Monitoring in Adults With Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, T.; Beck, R.W.; Bailey, R.; Ruedy, K.J.; Calhoun, P.; Peters, A.L.; Pop-Busui, R.; Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Bao, S.; Umpierrez, G.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Basal Insulin: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karter, A.J.; Parker, M.M.; Moffet, H.H.; Gilliam, L.K.; Dlott, R. Association of Real-time Continuous Glucose Monitoring With Glycemic Control and Acute Metabolic Events Among Patients With Insulin-Treated Diabetes. JAMA 2021, 325, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eversense, X.L. User Guide [Internet]. Available online: https://global.eversensediabetes.com/sites/default/files/2021-11/LBL-1402-31-001_Rev_E_Eversense_User_Guide_mgdL_UK-ENG.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Dexcom. Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. User Guide [Internet]. Available online: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/dexcompdf/G6-CGM-Users-Guide.pdf#page=21 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Dexcom. Dexcom G6 Pro Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. User Guide [Internet]. Available online: https://www.dexcom.com/faq/what-dexcom-g6-pro-continuous-glucose-monitoring-cgm-system (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Abbott. FreeStyle Libre 14 Day System. Available online: https://www.freestyleprovider.abbott/us-en/freestyle-libre-14-day-system.html (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Abbott. FreeStyle Libre Pro Flash Glucose Monitoring System [Internet]. Available online: https://www.freestyle.abbott/in-en/products/freestyle-libre-pro.html (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Abbott. FreeStyle Libre 2 System IN-SERVICE GUIDE [Internet]. Available online: https://provider.myfreestyle.com/pdf/In-Service-FreeStyle-Libre-2-HCP-Sales.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Medtronic. Guardian Connect System. User Guide [Internet]. Available online: https://www.medtronicdiabetes.com/download-library/guardian-connect (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Mambelli, E.; Cristino, S.; Mosconi, G.; Göbl, C.; Tura, A. Flash Glucose Monitoring to Assess Glycemic Control and Variability in Hemodialysis Patients: The GIOTTO Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 617891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, M.; Murata, T.; Saito, N.; Kimura, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ishida, N.; Kitamura, M.; Hida, M.; Hayashi, A.; Moriguchi, I.; et al. Assessment of the accuracy of an intermittent-scanning continuous glucose monitoring device in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis (AIDT2H) study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 25, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasaki, Y.; Park, E.; You, A.S.; Daza, A.; Peralta, R.A.; Guerrero, Y.; Novoa, A.; Amin, A.N.; Nguyen, D.V.; Price, D.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring in an end-stage renal disease patient with diabetes receiving hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 2021, 34, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Képénékian, L.; Smagala, A.; Meyer, L.; Imhoff, O.; Alenabi, F.; Serb, L.; Fleury, D.; Dorey, F.; Krummel, T.; Le Floch, J.P.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring in hemodialyzedpatients with type 2 diabetes: A multicenter pilot study. Clin. Nephrol. 2014, 82, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, M.; Fourmy, C.; Henri, P.; Ficheux, M.; Lobbedez, T.; Reznik, Y. Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in dialysis patients with diabetes: The DIALYDIAB pilot study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 107, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomholt, T.; Kofod, D.; Nørgaard, K.; Rossing, P.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Hornum, M. Can the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Improve Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Receiving Dialysis? Nephron 2022, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Takano, K.; Masaki, T.; Yoshino, S.; Ogawa, A.; Shichiri, M. Distinct biomarker roles for HbA1c and glycated albumin in patients with type 2 diabetes on hemodialysis. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomholt, T.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Butt, R.; Borg, R.; Sarwary, M.H.; Elung-Jensen, T.; Almdal, T.; Knop, F.K.; Nørgaard, K.; Ranjan, A.G.; et al. Hemoglobin A1c and Fructosamine Evaluated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis Using Long-Term Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Nephron 2022, 146, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Lyu, X.L.; Sun, X.M.; Duan, B.H. Continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis: A meta-analysis. Minerva Endocrinol. 2022, 47, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Haemodialysis-induced hypoglycaemia and glycaemic disarrays. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kaizu, K.; Matsumoto, K. Plasma insulin is removed by hemodialysis: Evaluation of the relation between plasma insulin and glucose by using a dialysate with or without glucose. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2007, 11, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Kubota, T.; Shibahara, N.; Terasaki, J.; Kagitani, M.; Ueda, H.; Inoue, T.; Katsuoka, Y. The mechanism of hypoglycemia caused by hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 2004, 62, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kikuchi, F.; Kaizu, K.; Matsumoto, K. The influence of hemodialysis membranes on the plasma insulin level of diabetic patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 2008, 69, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Okada, K.; Matsumoto, K. Plasma insulin and C-peptide concentrations in diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis: Comparison with five types of high-flux dialyzer membranes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 82, e17–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Okada, K.; Ikeda, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Soma, M.; Matsumoto, K. Characterization of insulin adsorption behavior of dialyzer membranes used in hemodialysis. Artif. Organs. 2011, 35, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kaizu, K.; Matsumoto, K. Evaluation of the hemodialysis-induced changes in plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in diabetic patients: Comparison between the hemodialysis and non-hemodialysis days. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2007, 11, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Shimizu, N.; Suzuki, A.; Matoba, K.; Momozono, A.; Masaki, T.; Ogawa, A.; Moriguchi, I.; Takano, K.; Kobayashi, N.; et al. Hemodialysis-Related Glycemic Disarray Proven by Continuous Glucose Monitoring; Glycemic Markers and Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Emoto, M.; Abe, M.; Inaba, M. Visualization of Blood Glucose Fluctuations Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. J. Diabetes. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Okada, K.; Soma, M. Antidiabetic agents in patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease on dialysis: Metabolism and clinical practice. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI). KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, S62–S73. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline Development Group. Clinical Practice Guideline on management of patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease stage 3b or higher (eGFR < 45 mL/min). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S2), ii1–ii142. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, N.; Abe, M. Targets and Therapeutics for Glycemic Control in Diabetes Patients on Hemodialysis. Contrib. Nephrol. 2018, 196, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, M.; Okada, K. DPP-4 Inhibitors in Diabetic Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis in Clinical Practice. Contrib. Nephrol. 2015, 185, 98–115. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Han, E.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kim, B.S.; Cha, B.S.; Kim, C.S.; Kang, E.S. Efficacy of different dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing dialysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacra, A.; Gantz, I.; Mendizabal, G.; Durlach, L.; O’Neill, E.A.; Zimmer, Z.; Suryawanshi, S.; Engel, S.S.; Lai, E. A randomised, double-blind, trial of the safety and efficacy of omarigliptin (a once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitor) in subjects with type 2 diabetes and renal impairment. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 71, e12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, K.; Ishida, K.; Shimizu, K.; Achira, M.; Umeda, Y. Efficacy and safety of trelagliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease: Results from a randomized, phase 3 study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Anand, I.; Doehner, W.; Haass, M.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on the Clinical Stability of Patients With Heart Failure and a Reduced Ejection Fraction: The EMPEROR-Reduced Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granhall, C.; Søndergaard, F.L.; Thomsen, M.; Anderson, T.W. Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Oral Semaglutide in Subjects with Renal Impairment. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, T.; Yajima, K.; Hayashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Yasuda, K. Improved glycemic control with once-weekly dulaglutide in addition to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on hemodialysis evaluated by continuous glucose monitoring. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomholt, T.; Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Ranjan, A.G.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Borg, R.; Persson, F.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; et al. The Glycemic Effect of Liraglutide Evaluated by Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Dialysis. Nephron 2021, 145, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Jensen, T.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Christensen, K.B.; Holst, J.J.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B. Safety and Efficacy of Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and End-Stage Renal Disease: An Investigator-Initiated, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.A.; Alvarado-Ruiz, R.; Raccah, D.; Boka, G.; Miossec, P.; Gerich, J.E.; EFC6018 GetGoal-Mono Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of the once-daily GLP-1 receptor agonist lixisenatide in monotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes (GetGoal-Mono). Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, R.W.; Berns, J.S. Use of insulin and oral hypoglycemic medications in patients with diabetes mellitus and advanced kidney disease. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, G.; Riveline, J.P.; Varroud-Vial, M. Management of drugs affecting blood glucose in diabetic patients with renal failure. Diabetes. Metab. 2000, 26, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reilly, J.B.; Berns, J.S. Selection and dosing of medications for management of diabetes in patients with advanced kidney disease. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, T.; Emoto, M.; Mori, K.; Morioka, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Takahashi, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Nishizawa, Y.; Inaba, M. Thrice-weekly insulin injection with nurse’s support for diabetic hemodialysis patients having difficulty with self injection. Osaka City Med. J. 2012, 58, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fouque, D.; Vennegoor, M.; ter Wee, P.; Wanner, C.; Basci, A.; Canaud, B.; Haage, P.; Konner, K.; Kooman, J.; Martin-Malo, A.; et al. European Best Practice Guideline on nutrition. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22 (Suppl. S2), ii45–ii87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. Clinical practice guidelines for nutrition in chronic renal failure. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2000, 35, S17–S104. [Google Scholar]
- UK Renal Association. Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2009–2010. Available online: https://ukkidney.org/sites/renal.org/files/nutrition-in-ckd-5th-edition-1.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Naylor, H.L.; Jackson, H.; Walker, G.H.; Macafee, S.; Magee, K.; Hooper, L.; Stewart, L.; MacLaughlin, H.L.; Renal Nutrition Group of the British Dietetic Association; British Dietetic Association. British Dietetic Association Renal Nutrition Group Evidence Based Dietetic Guidelines Protein Requirements Of Adults On Haemodialysis And Peritoneal Dialysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavey, S.F.; McCullough, K.; Hecking, E.; Goodkin, D.; Port, F.K.; Young, E.W. Body mass index and mortality in ‘healthier’ as compared with ‘sicker’ haemodialysis patients: Results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissell, R.B.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Gillespie, B.W.; Goodkin, D.A.; Bommer, J.; Saito, A.; Akiba, T.; Port, F.K.; Young, E.W. International variations in vitamin prescription and association with mortality in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2004, 44, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Block, G.; McAllister, C.J.; Humphreys, M.H.; Kopple, J.D. Appetite and inflammation, nutrition, anemia, and clinical outcome in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupim, L.B.; Heimburger, O.; Qureshi, A.R. Accelerated lean body mass loss in incident chronic dialysis patients with diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2638–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, N.J.; Roth, H.; Aparicio, M.; Azar, R.; Canaud, B.; Chauveau, P.; Combe, C.; Fouque, D.; Laville, M.; Leverve, X.M.; et al. Malnutrition in haemodialysis diabetic patients:evaluation and prognostic influence. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupim, L.B.; Flakoll, P.J.; Majchrzak, K.M.; Aftab Guy, D.L.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A. Increased muscle protein breakdown in chronic haemodialysis patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, N.; Kopple, J.D. Effect of diabetes mellitus on protein-energy wasting and protein wasting in end-stage renal disease. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopple, J.D. Pathophysiology of protein-energy wasting in chronic renal failure. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 2475–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, S.; Nakamoto, M.; Nishihara, G.; Yasunaga, C.; Yanagida, T.; Matsuo, K.; Sakemi, T. Impaired taste acuity in patients with diabetes on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2003, 94, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masakane, I.; Taniguchi, M.; Nakai, S.; Tsuchida, K.; Goto, S.; Wada, A.; Ogata, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Hamano, T.; Hanafusa, N.; et al. Annual Dialysis Data Report 2015, JSDT Renal Data Registry. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2018, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).