Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Diagnose and Predict the Outcome of Diabetic Kidney Disease—Where Do We Stand?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Available Renal MRI Techniques
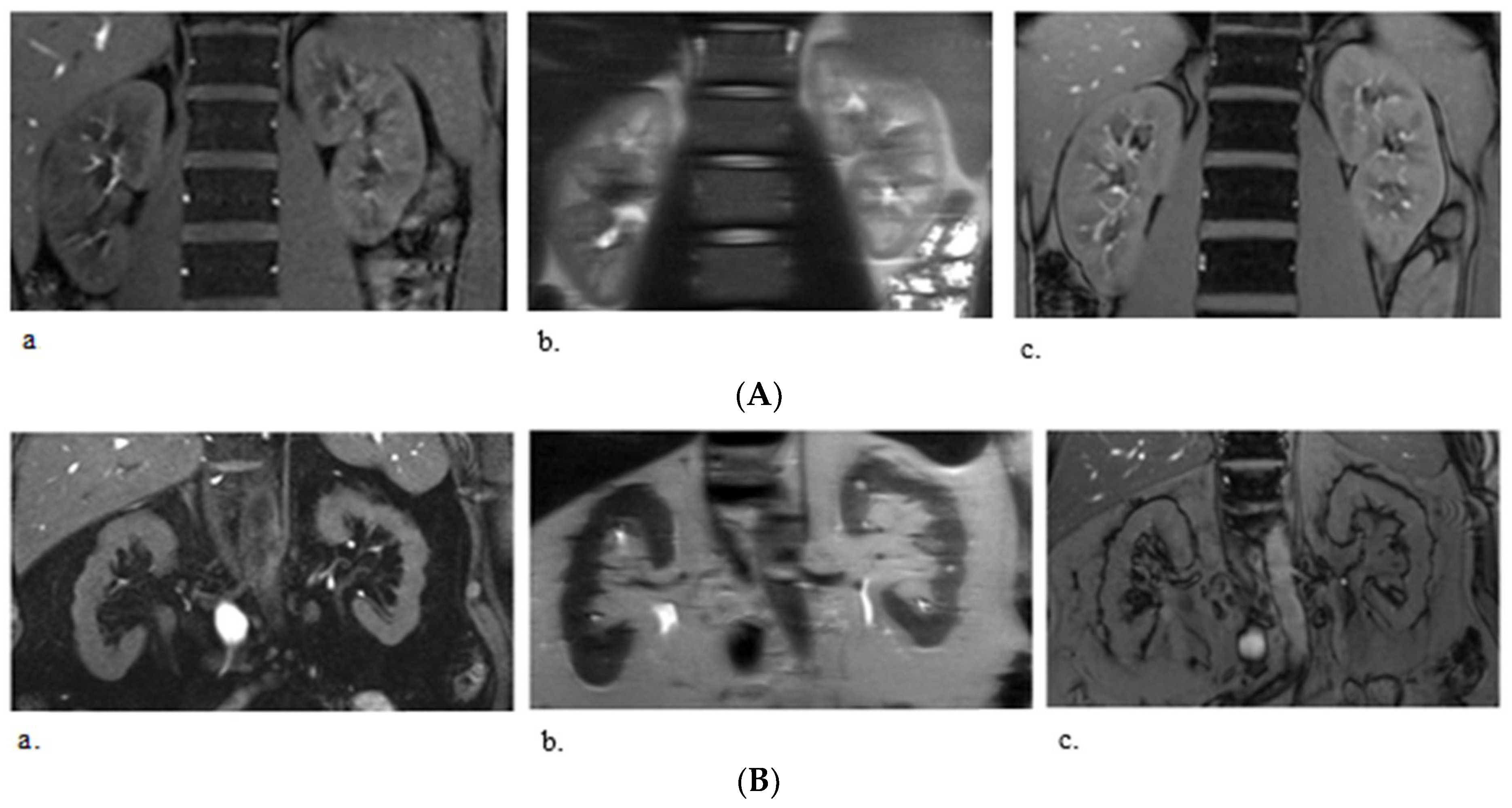
2.1. T1 and T2 Mapping
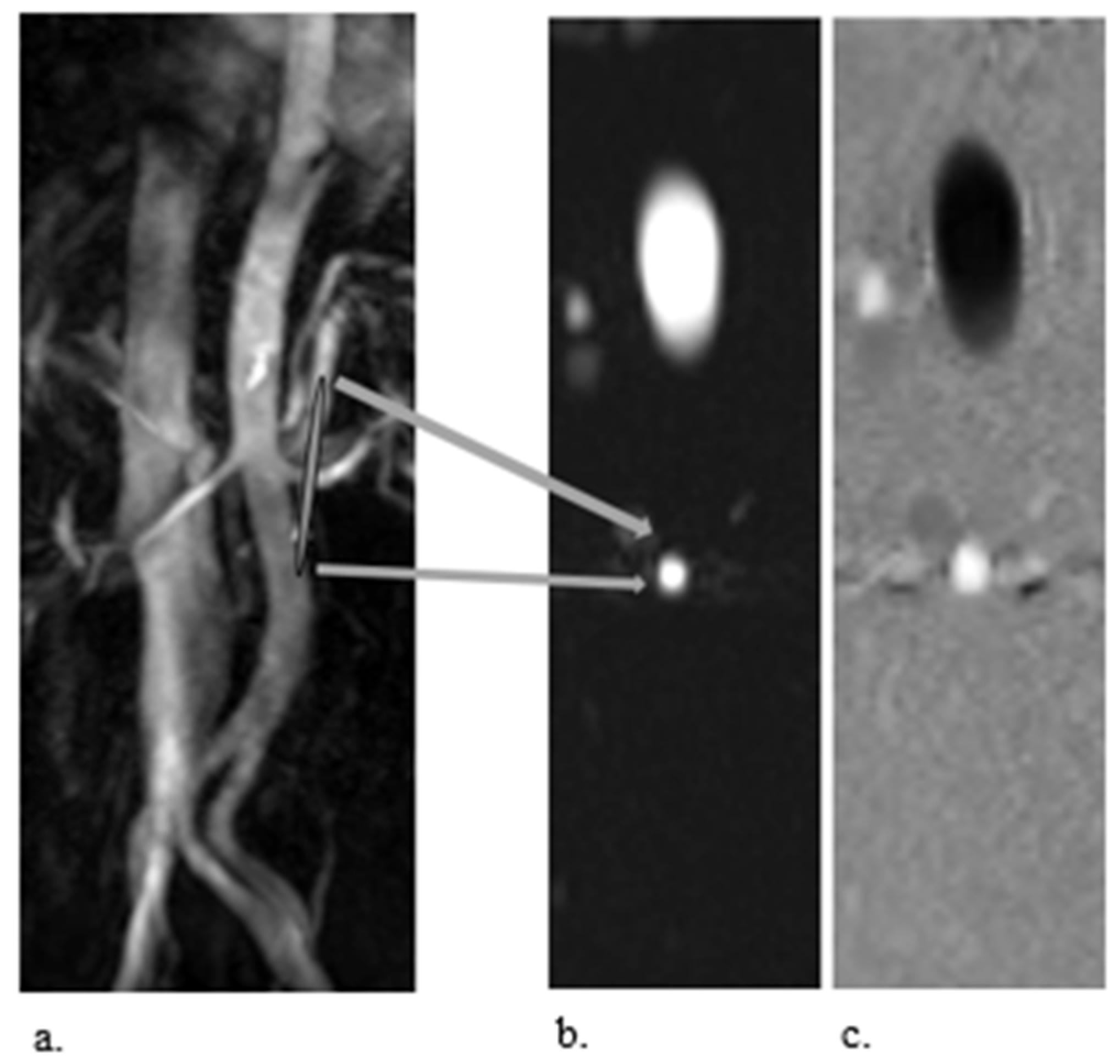
2.2. Phase–Contrast MRI
2.3. Arterial Spin Labelling
2.4. BOLD-MRI
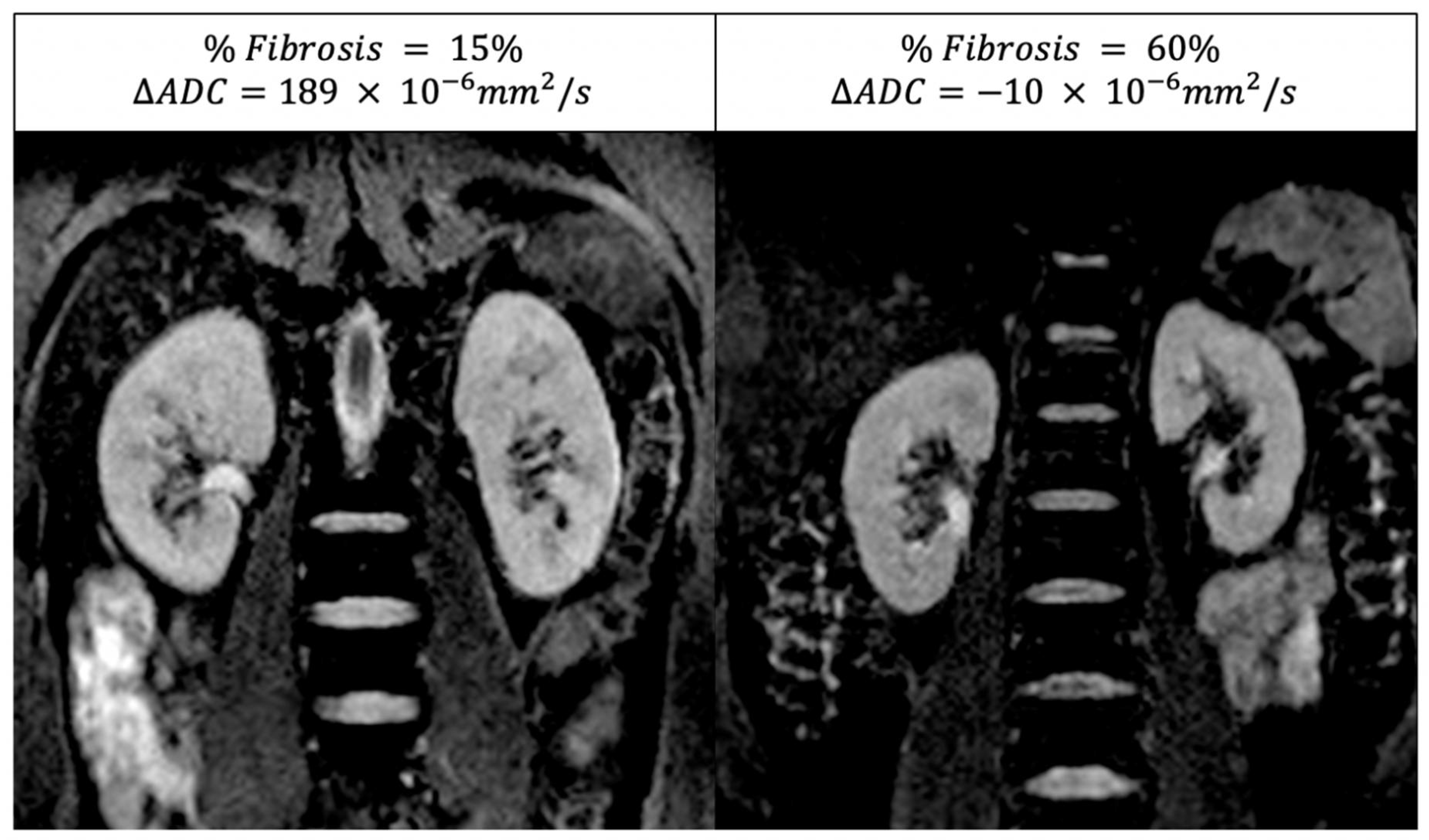
2.5. Diffusion MRI
3. Renal MRI and Diabetic Kidney Disease
3.1. T1 and T2 Mapping
3.2. PC-MRI
3.3. ASL-MRI
3.4. BOLD-MRI
3.5. DWI-MRI
4. Multiparametric MRI
5. Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 850–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reutens, A.T. Epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. Med. Clin. 2013, 97, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Pippias, M.; Noordzij, M.; Stel, V.S.; Andrusev, A.M.; Aparicio-Madre, M.I.; Arribas Monzon, F.E.; Asberg, A.; Barbullushi, M.; Beltran, P.; et al. The European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) Registry Annual Report 2016: A summary. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.S. The discovery of diabetic nephropathy: From small print to centre stage. J. Nephrol. 2006, 19 (Suppl. S10), S75–S87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.J.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Curhan, G.; Hsu, C.Y. Renal insufficiency in the absence of albuminuria and retinopathy among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2003, 289, 3273–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, H.; Rezaii, I. Diabetic kidney disease; review of the current knowledge. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 2013, 2, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.; Pruijm, M.; Burnier, M.; Selby, N.M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys: Where do we stand? The perspective of the European COST Action PARENCHIMA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, ii1–ii3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.I.; Jerums, G.; Skene, A.; Crammer, P.; Power, D.; Cheong, K.Y.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; McNeil, K.; Baker, S.T.; Fioretto, P.; et al. Renal structure in normoalbuminuric and albuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes and impaired renal function. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3620–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Kosugi, T.; Haneda, M.; Rivard, C.J.; Long, D.A. Abnormal angiogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, L.G.; Norman, J.T. Chronic hypoxia as a mechanism of progression of chronic kidney diseases: From hypothesis to novel therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, S.; Pihl, L.; Khan, N.; Gustafsson, H.; Palm, F. Pronounced kidney hypoxia precedes albuminuria in type 1 diabetic mice. Am. J. Physiology. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 310, F807–F809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljimani, A.; Caroli, A.; Laustsen, C.; Francis, S.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Bane, O.; Nery, F.; Sharma, K.; Pohlmann, A.; Dekkers, I.A.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bane, O.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Milani, B.; Dekkers, I.A.; Deux, J.F.; Eckerbom, P.; Grenier, N.; Hall, M.E.; Inoue, T.; Laustsen, C.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal BOLD MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, I.A.; de Boer, A.; Sharma, K.; Cox, E.F.; Lamb, H.J.; Buckley, D.L.; Bane, O.; Morris, D.M.; Prasad, P.V.; Semple, S.I.K.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal T1 and T2 mapping MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, F.; Buchanan, C.E.; Harteveld, A.A.; Odudu, A.; Bane, O.; Cox, E.F.; Derlin, K.; Gach, H.M.; Golay, X.; Gutberlet, M.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal ASL MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, A.; Villa, G.; Bane, O.; Bock, M.; Cox, E.F.; Dekkers, I.A.; Eckerbom, P.; Fernandez-Seara, M.A.; Francis, S.T.; Haddock, B.; et al. Consensus-Based Technical Recommendations for Clinical Translation of Renal Phase Contrast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.; Noble, R.; Prestwich, B.; Kasmi, I.; Taal, M.W.; Francis, S.; Selby, N.M. Multiparametric MRI assessment of renal structure and function in acute kidney injury and renal recovery. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Berchtold, L.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; de Perrot, T.; Vesin, C.; Martin, P.Y.; de Seigneux, S.; Vallee, J.P. New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Index for Renal Fibrosis Assessment: A Comparison between Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and T1 Mapping with Histological Validation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; de Boer, A.; Sharma, K.; Boor, P.; Leiner, T.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Moser, E.; Caroli, A.; Jerome, N.P. Magnetic resonance imaging T1- and T2-mapping to assess renal structure and function: A systematic review and statement paper. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, ii41–ii50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, G.; Ringgaard, S.; Hermann, I.; Noble, R.; Brambilla, P.; Khatir, D.S.; Zollner, F.G.; Francis, S.T.; Selby, N.M.; Remuzzi, A.; et al. Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging to assess renal perfusion: A systematic review and statement paper. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spithoven, E.M.; Meijer, E.; Borns, C.; Boertien, W.E.; Gaillard, C.A.; Kappert, P.; Greuter, M.J.; van der Jagt, E.; Vart, P.; de Jong, P.E.; et al. Feasibility of measuring renal blood flow by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Odudu, A.; Nery, F.; Harteveld, A.A.; Evans, R.G.; Pendse, D.; Buchanan, C.E.; Francis, S.T.; Fernandez-Seara, M.A. Arterial spin labelling MRI to measure renal perfusion: A systematic review and statement paper. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, ii15–ii21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artz, N.S.; Wentland, A.L.; Sadowski, E.A.; Djamali, A.; Grist, T.M.; Seo, S.; Fain, S.B. Comparing kidney perfusion using noncontrast arterial spin labeling MRI and microsphere methods in an interventional swine model. Investig. Radiol. 2011, 46, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruijm, M.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Liss, P.; Van der Niepen, P.; Textor, S.C.; Lerman, L.O.; Krediet, C.T.P.; Caroli, A.; Burnier, M.; Prasad, P.V. Renal blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging to measure renal tissue oxygenation: A statement paper and systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, ii22–ii28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.; Dissing, T.H.; Morkenborg, J.; Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H.; Hansen, L.H.; Pedersen, L.B.; Grenier, N.; Frokiaer, J. Validation of quantitative BOLD MRI measurements in kidney: Application to unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niendorf, T.; Pohlmann, A.; Arakelyan, K.; Flemming, B.; Cantow, K.; Hentschel, J.; Grosenick, D.; Ladwig, M.; Reimann, H.; Klix, S.; et al. How bold is blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) magnetic resonance imaging of the kidney? Opportunities, challenges and future directions. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, L.; Friedli, I.; Vallee, J.P.; Moll, S.; Martin, P.Y.; de Seigneux, S. Diagnosis and assessment of renal fibrosis: The state of the art. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2017, 147, w14442. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Gutierrez, J.M.; Fernandez-Seara, M.A.; Echeverria-Chasco, R.; Garcia-Fernandez, N. Perspectives on the Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Noninvasive Evaluation of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, B.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, J.; Du, G. Use of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging to detect early changes in diabetic kidneys. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 2728–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Shang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Gu, H.; Dou, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Native T1 Mapping in Assessing Kidney Fibrosis for Patients With Chronic Glomerulonephritis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 772326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, I.A.; Paiman, E.H.M.; de Vries, A.P.J.; Lamb, H.J. Reproducibility of native T1 mapping for renal tissue characterization at 3T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhummiany, B.A.; Shelley, D.; Saysell, M.; Olaru, M.A.; Kuhn, B.; Buckley, D.L.; Bailey, J.; Wroe, K.; Coupland, C.; Mansfield, M.W.; et al. Bias and Precision in Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Estimates of Renal Blood Flow: Assessment by Triangulation. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatir, D.S.; Pedersen, M.; Jespersen, B.; Buus, N.H. Evaluation of Renal Blood Flow and Oxygenation in CKD Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, J.C.; Sondergaard-Heinrich, N.; de Melo, J.M.L.; Haddock, B.; Rasmussen, I.K.B.; Safavimanesh, F.; Hansen, C.S.; Storling, J.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Groop, P.H.; et al. Acute effects of dapagliflozin on renal oxygenation and perfusion in type 1 diabetes with albuminuria: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Gutierrez, J.M.; Garcia-Fernandez, N.; Slon Roblero, M.F.; Paramo, J.A.; Escalada, F.J.; Wang, D.J.; Benito, A.; Fernandez-Seara, M.A. Arterial spin labeling MRI is able to detect early hemodynamic changes in diabetic nephropathy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Li, L.P.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Hack, B.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M. Cortical Perfusion and Tubular Function as Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlates with Annual Loss in Renal Function in Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Okada, H.; Inukai, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kikuta, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takenaka, T.; Katayama, S.; Tanaka, J.; et al. Noninvasive evaluation of kidney hypoxia and fibrosis using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Z.; Ye, Y.J.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Zhang, C.B.; Qian, L.; Lu, X.H.; Cai, X.R. Non-invasive assessment of early stage diabetic nephropathy by DTI and BOLD MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, S.S.; Gullaksen, S.; Vernstrom, L.; Ringgaard, S.; Laustsen, C.; Funck, K.L.; Laugesen, E.; Poulsen, P.L. Evaluation of renal oxygenation by BOLD-MRI in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes and matched controls. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilzadeh, N.; Zanchi, A.; Milani, B.; Ledoux, J.B.; Braconnier, P.; Burnier, M.; Pruijm, M. Acute hyperglycemia increases renal tissue oxygenation as measured by BOLD-MRI in healthy overweight volunteers. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 150, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Shimada, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Tanaka, J.; Okada, H. Reduced oxygenation but not fibrosis defined by functional magnetic resonance imaging predicts the long-term progression of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.P.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Hack, B.; Wang, C.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M.; Prasad, P.V. Medullary Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent MRI Index (R2*) is Associated with Annual Loss of Kidney Function in Moderate CKD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2020, 51, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruijm, M.; Milani, B.; Pivin, E.; Podhajska, A.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M. Reduced cortical oxygenation predicts a progressive decline of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Sedor, J.R.; Gulani, V.; Schelling, J.R.; O’Brien, A.; Flask, C.A.; MacRae Dell, K. Use of diffusion tensor MRI to identify early changes in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, P.; Yagci, A.B.; Dursun, B.; Herek, D.; Fenkci, S.M. Renal diffusion-weighted imaging in diabetic nephropathy: Correlation with clinical stages of disease. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 20, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrdanin, T.; Nikolic, O.; Molnar, U.; Mitrovic, M.; Till, V. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of renal function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Thacker, J.; Li, L.P.; Haque, M.; Li, W.; Koenigs, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sprague, S.M. Multi-Parametric Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease by MRI: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimori, J.Y.; Isaka, Y.; Hatanaka, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Ichimaru, N.; Fujikawa, A.; Shibata, H.; Fujimori, A.; Miyoshi, S.; Yokawa, T.; et al. Visualization of kidney fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by long diffusion tensor imaging MRI with spin-echo sequence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Hartono, S.; Hennedige, T.; Koh, T.S.; Chan, C.M.; Zhou, L.; Rumpel, H.; Martarello, L.; Khoo, J.B.; Koh, D.M.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion tensor imaging of early renal fibrosis induced in a murine model of streptozotocin induced diabetes. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 38, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, L.; Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Martinez, C.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; de Perrot, T.; Combescure, C.; Martin, P.Y.; Vallee, J.P.; et al. Validation of the corticomedullary difference in magnetic resonance imaging-derived apparent diffusion coefficient for kidney fibrosis detection: A cross-sectional study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, L.; Crowe, L.A.; Combescure, C.; Kassai, M.; Aslam, I.; Legouis, D.; Moll, S.; Martin, P.Y.; de Seigneux, S.; Vallee, J.P. Diffusion-magnetic resonance imaging predicts decline of kidney function in chronic kidney disease and in patients with a kidney allograft. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, E.F.; Buchanan, C.E.; Bradley, C.R.; Prestwich, B.; Mahmoud, H.; Taal, M.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Validation, Interventions, and Alterations in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, K.; Hockings, P.D.; Jensen, G.; Unnerstall, T.; Leonhardt, H.; Jarl, L.V.; Englund, C.; Francis, S.; Sundgren, A.K.; Hulthe, J.; et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging allows non-invasive functional and structural evaluation of diabetic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Fukaya, D.; Amano, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Tomori, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Niitsu, M.; Okada, H. Comparison of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging sequences with laboratory parameters for prognosticating renal function in chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, K.M.; Lienczewski, C.; Papale, M.; Koivuviita, N.; Maziarz, M.; Dutius Andersson, A.M.; Sharma, K.; Pontrelli, P.; Garcia Hernandez, A.; Bailey, J.; et al. Prognostic imaging biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease (iBEAt): Study protocol. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Dekkers, I.A.; Huang, L.; Tao, Q.; Paiman, E.H.M.; Bizino, M.B.; Jazet, I.M.; Lamb, H.J. Renal sinus fat volume in type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with glycated hemoglobin and metabolic risk factors. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pruijm, M.; Aslam, I.; Milani, B.; Brito, W.; Burnier, M.; Selby, N.M.; Vallée, J.-P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Diagnose and Predict the Outcome of Diabetic Kidney Disease—Where Do We Stand? Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 407-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2030036
Pruijm M, Aslam I, Milani B, Brito W, Burnier M, Selby NM, Vallée J-P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Diagnose and Predict the Outcome of Diabetic Kidney Disease—Where Do We Stand? Kidney and Dialysis. 2022; 2(3):407-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2030036
Chicago/Turabian StylePruijm, Menno, Ibtisam Aslam, Bastien Milani, Wendy Brito, Michel Burnier, Nicholas M. Selby, and Jean-Paul Vallée. 2022. "Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Diagnose and Predict the Outcome of Diabetic Kidney Disease—Where Do We Stand?" Kidney and Dialysis 2, no. 3: 407-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2030036
APA StylePruijm, M., Aslam, I., Milani, B., Brito, W., Burnier, M., Selby, N. M., & Vallée, J.-P. (2022). Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Diagnose and Predict the Outcome of Diabetic Kidney Disease—Where Do We Stand? Kidney and Dialysis, 2(3), 407-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial2030036







